Elasticity, Supply and Competition
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Competition
The rivalry between firms or producers in a market.
Elasticity
Responsiveness of quantity demanded to price changes.
Shifts in Supply
Changes in supply caused by various factors except price.
increase = shift to right
decrease = shift to left
Movements Along Supply Curve
Changes in supply due to price changes
Cost of Production
Costs for a producer to produce a good / service.
PINTS WC (Factors impacting supply / causing shift)
Productivity
Indirect taxes
Number of Firms
Technology
Subsidies
Weather and disease
Cost of production
How does technology affect supply?
Advancements in technology means increase productivity and supply.
How do taxes affect supply?
Government levies that affect production costs, and therefore incentives to supply.
How do subsidies affect supply?
Government payments to lower production costs, therefore increase incentive to supply.
How does the weather affect supply?
Environmental conditions affecting agricultural supply.
How do Prices of Other Goods affect supply?
Influence of substitute goods on production decisions and supply incentives.
How do the number of firms affect supply?
More total firms in an industry increases supply levels.
Economies of Scale
Cost advantages from increased production levels.
Efficiency
The measure of how well scarce resources are used to produce final goods / services.
Increased supply means what to sales?
Increased supply may lead to higher sales volume.
Monopoly
Market dominance by a single firm.
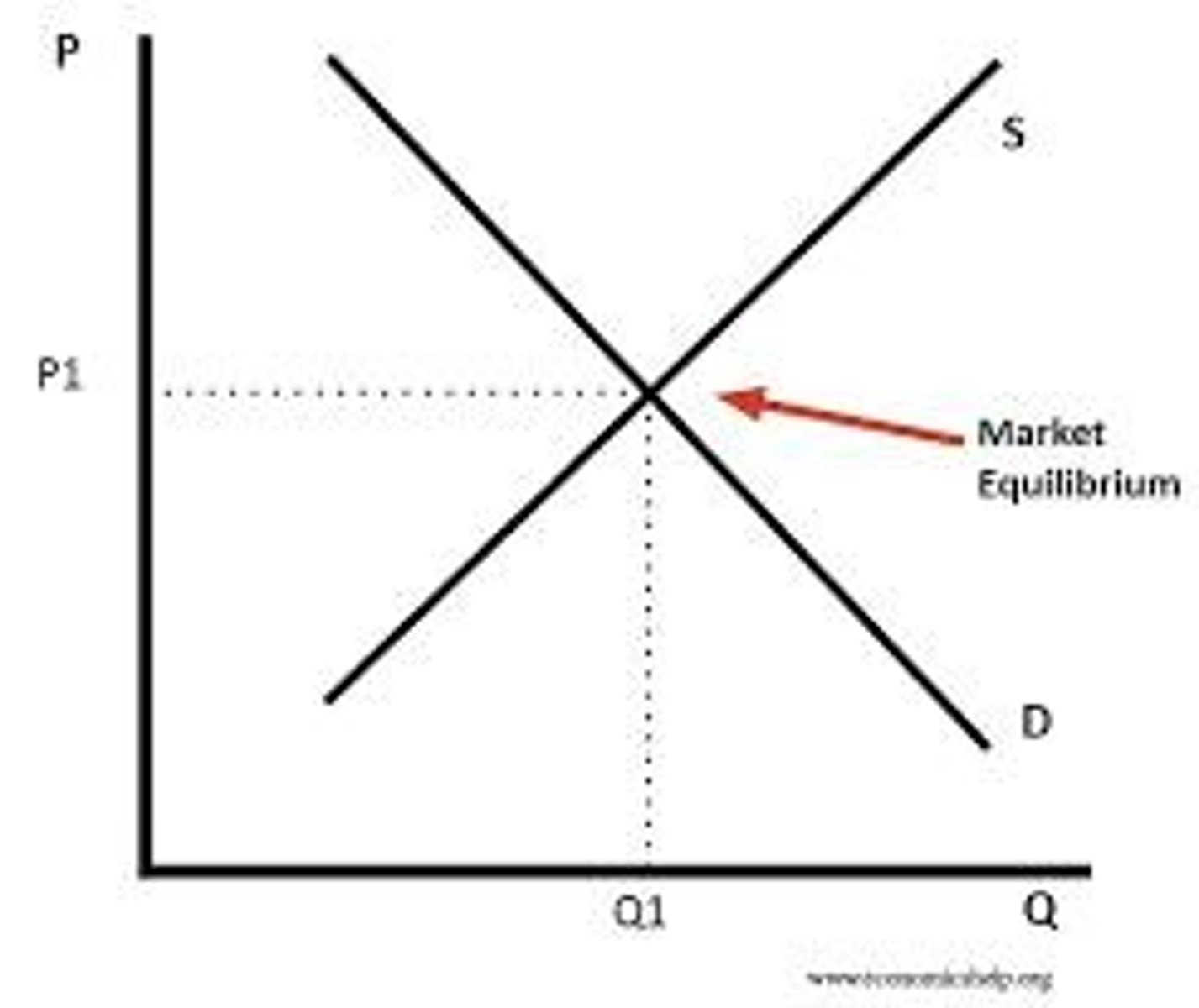
Equilibrium
State where quantity supplied equals quantity demanded.
Market Equilibrium
Planned demand equals planned supply in the market.
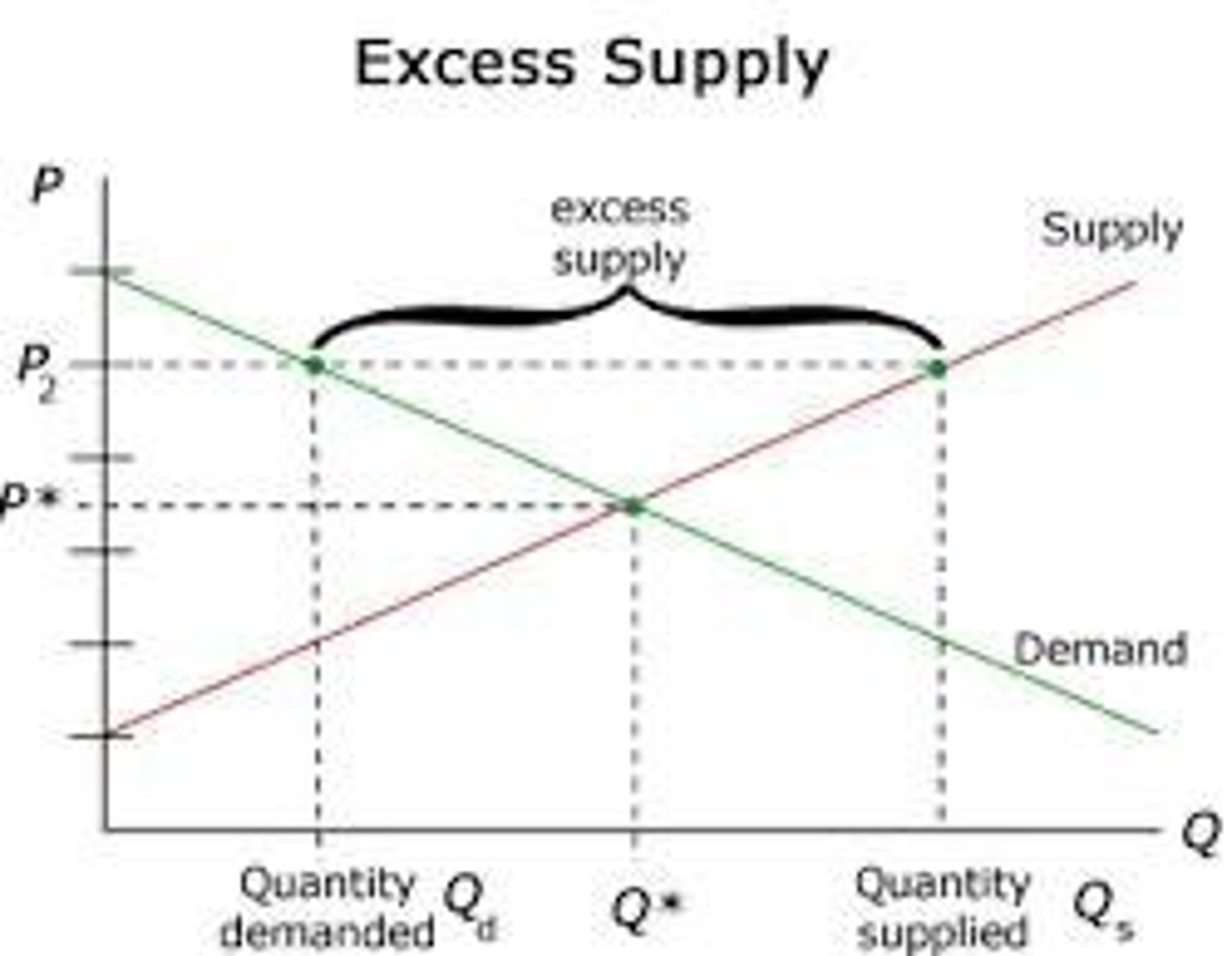
Excess Supply
When supply exceeds demand at a given price.
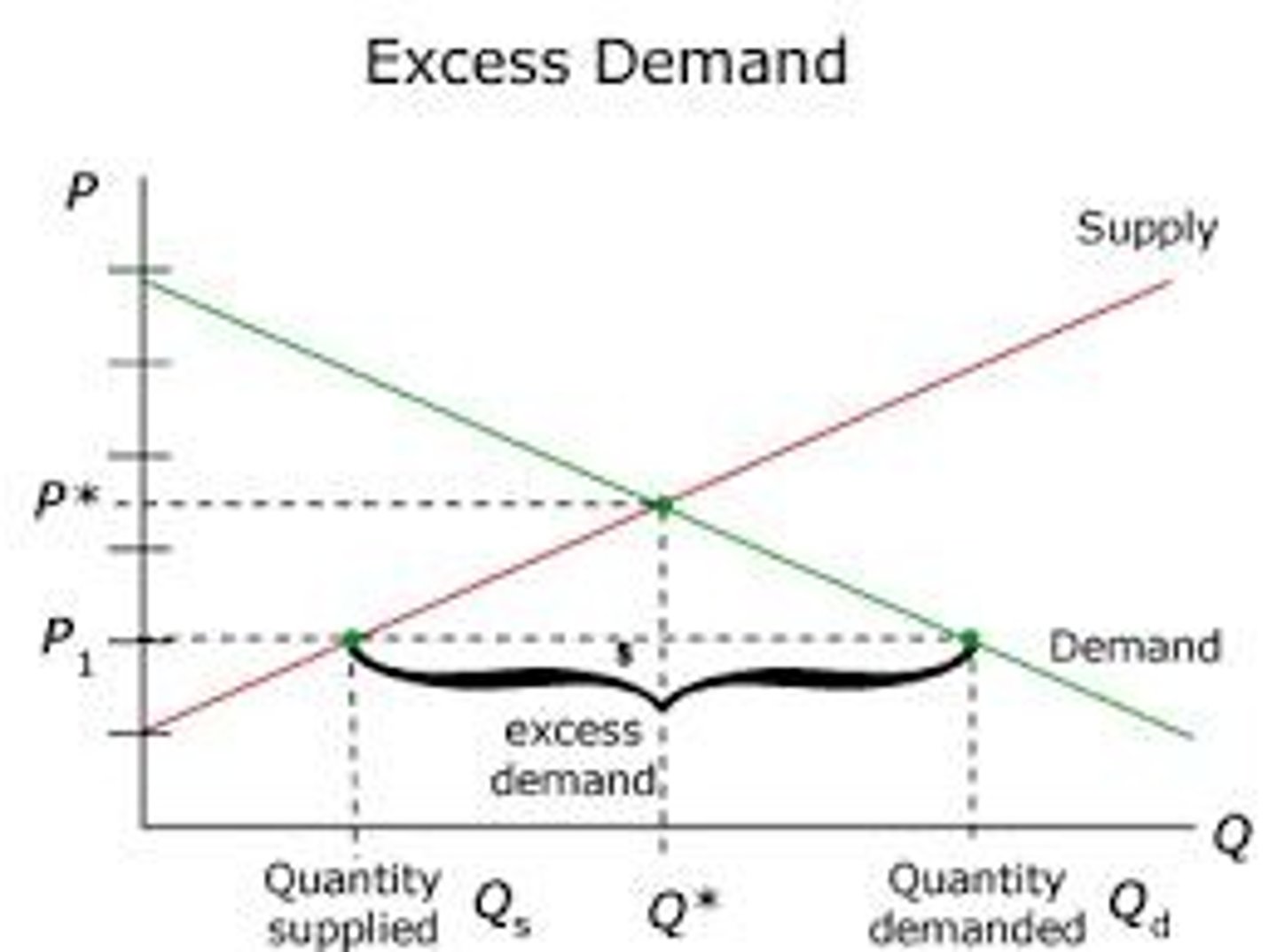
Excess Demand
When demand exceeds supply at a given price.
Firm Reaction to Excess Supply
Lower prices to sell unsold stock.
Firm Reaction to Excess Demand
Increase prices to balance supply and demand. (demand will lower)
Price Elasticity of Supply (PES)
Measure of how much supply changes with price.
What is perfect competition?
Market structure where a large number of firms sell homogeneous products and there are no obstacles to entry or exit of firms into the market.
Perfect Competition conditions:
- Large number of buyers and sellers
- Perfect market information
- Able to sell/buy as much as they wish at the ruling market price
- Unable to influence ruling market price
- Homogenous/identical products
- No barriers to entry or exit in the long run
What is monopolistic competition?
Market structure where large number of firms are competing in a market, each having enough product differentiation to achieve a degree of monopolistic power, and therefore have some power over the price they charge.
E.g. local restaurants, hair salons, local pubs.
What is an oligopoly?
Market structure where control over the supply of a product is in the hands of a small number of producers and each one can influence prices and affect competition.
E.g. O2, EE, Vodafone
What is a duopoly?
A market structure where there are only two firms in the market.
What is a monopoly?
Market structure in which there is only one producer / seller for a product, and the only business in an industry. A monopoly would have 100% market share.
What is a business monopoly?
When one business controls 25% or more of a particular market, whilst not being a complete monopoly and having other competitors.
What market structure is best for consumers and why?
Perfect competition
- lower prices
- more choice
What market structure is worse for consumers and why?
Monopolies
- high prices
- little choice
What are potential gains of competitive markets to consumers?
- prices will be lower
- lots of choice in market
- quality may be constantly improving
- incentive to innovate and produce new products as firms try to stay ahead of competition
What are the potential gains of competitive markets to firms?
- likely to be more efficient and have lower production costs
- may be easier to attract workers as there are lots of workers doing the same job
What are the potential losses of competitive markets to firms?
- prices likely to be driven much lower than in less competitive markets - may lead to reduced profit margins
- Lower profit margins may mean less funds available for re-investment
- a constant pressure to cut costs to be efficient
What are the potential gains in monopolistic markets to consumers?
- large firms may benefit from economics of scale, meaning firms may choose to pass on benefits of this to consumer in the form of lower prices
- product quality and range may be higher because (a): have profits to re-invest (b): they have incentive to do so as they want to keep their monopolistic power
What are potential gains of monopolistic markets to firms?
- prices are likely to be more price inelastic, meaning they can keep prices higher
- lack of competition means higher prices and therefore higher profit margins
- no pressure to constantly lower costs
What are potential losses of monopolistic markets to consumers?
- less competition is likely, so this means higher prices
- less choice in the market
- product quality and range/consumer service may decline - monopolies have a captured market
What are potential losses of monopolistic markets to firms?
- lack of competitive pressures may make this firm become stale and unresponsive to consumer demand