CS Lecture 2 Abstract Data Types
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Abstract Data Types
data type (object data + applications)
Users of the ADT don’t need to know what the implementation is (“how”)
They only need to know the functionality (“what”)
Someone has to care about the “how” – it needs to get built by someone!
We call this person the “implementer”
In this course we will deal with ADTs from both the user’s and the implementer’s perspective.
How do we represent ADTs in java
generic types “T” types

what does this do
swap any two items in an array (of any T type) with the same method

what does this do
creates a genetic method that can sort any array of comparables
“<T extends Comparable<? super T>>” means that this method (bubbleSort) can work on any type (T) that extends Comparable<T> or extends Comparable<superclass of T>.
Can you have more than one generic type
yuh
The wild card operator (?)
represents an unknown class type
Bag ADT “rules”
no rule about how many items to put, order of items, duplicate items, what type of items can go in
impossible to fumble
What is missing from BagInterface
Doesn’t mention what types of data can be stored in Bags
strings? integers? arraylists of strings?
doesn’t mention any implementation of guidance on how things should be implemented
what should each of those methods do?
how should we handle special cases
What is a benefit of Bag
we don’t care about order so it’s good for adding and removing very fast
Preconditions
specifically the assumed state of the ADT before a method is executed
Postconditions
specify the intended state of the ADT after method execution
possible abnormal bag situtations where add might return false
Bag is in an invalid state
bag is full
newentry is an invalid object
supresswarning
Code is going to do smth will cause an error with the compiler but it supress allows it to compile anyway
Look over recap for all slides
What does ‘? extends T’ describe?
Refers to the T interface
A boolean expression to see if something extends T
Refers to any class that extends the generic type T
Refers to any class that implements the generic type T
3 and 4
ArrayBag<?> vs. ArrayBag<T>
ArrayBag<?> = an arraybag that can operate on any type
ArrayBag<T> = an arraybag that operates on the generic type T
Pros of using array for bag
adding an entry to the bag is fast
removing an entry is fast
Cons of using an array for bag
may be wasteful of memory
doubling capacity requires copying each item to a new array
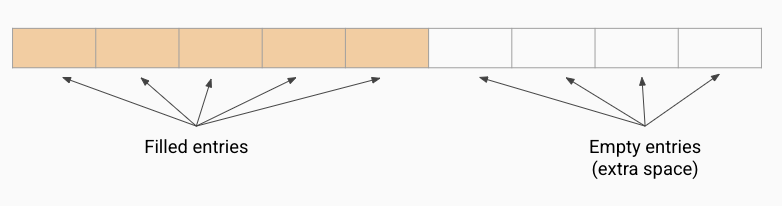
Bag Array Implementation: how could this be an issue
the white squares are extra space, if we add 4 more items to the bag they would no longer be wasted (in use). However, if we don’t add any more items, those 4 spaces can’t be used by any other program and are wasted space