Week 9- DMS 211 Scrotum and Prostate
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
normal measurement of testes
3-5 x 2-4 x 3 cm
each testis is divided into ___ lobules which contain __________________
250-400, seminiferous tubules
the seminiferous tubules converge at the ________ of each lobule and anastomose to form ________________
apex, rete testis
how does the rete testis drain
into the epi head through efferent ductules
normal length of the epididymis
6 to 7 cm
the epi is divided into the...
head, body, and tail
the largest part of the epi is the ____ measuring ________
head, 6 to 15 mm in width
where is the epi located
superior to upper pole of testis
the epi contains _____ efferent ductules which converge to form the ____________
10 to 15, body and tail
the epi becomes the __________ which then continues into the ______________
vas deferens, spermatic cord
location of the epi body
posterolateral testis from upper to lower pole
location of the epi tail
posterior to lower pole of testis
appendix of the epi
small protuberance from the head
what component of the testis makes them appear as echogenic
seminiferous tubules
what is the main function of the testes
store and produce sperm
why do the testes hang away from the body
body temp is too hot for sperm to survive
what is cut in a vasectomy
vas deferens
mediastinum
where all the tubules join together at rete testes
the testis are covered by the...
tunica albuginea
mediastinum testis
posterior aspect of tunica albuginea that forms vertical septum
function of the mediastinum
support vessels and ducts coursing through testis
what lines the inner surface of the scrotum
tunica vaginalis
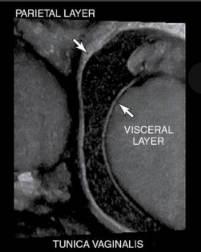
what are the layers of tunica vaginalis
parietal- creates the scrotal wall
visceral- surrounds testis and epi
where do hydroceles form
in space between parietal and visceral layers tunica vaginalis
the vas deferens is the continuation of the
ductus epididymis
verumontanum
junction of ejaculatory ducts and urethra
contents of the spermatic cord
vas deferens
testicular arteries
venous pamp plexus
lymphatics, nerves

location of spermatic cord
extends from scrotum to inguinal canal
function of spermatic cord
suspends the testes in the scrotum

blood supply to the testis
testicular arteries from abdominal aorta, cremasteric (EIA) and deferential artery (IIA)
venous pampiniform plexus
where venous drainage of the scrotum occurs
where do varicoceles happen?
at venous pampiniform plexus
the RT testicular vein drains into the ______________
IVC
the left testicular vein drain into the ___________________
left renal vein
2D imaging is important for diagnosing...
cystic and solid masses
hydrocele
undescended testis
hernia
spectral doppler is important for diagnosing...
torsion
when assessing for torsion you must get
both venous and arterial flow
__________________ flow will disappear first in torsion
venous
color doppler is important for diagnosing...
epididymitis and orchitis
if there is inflammation color will show...
hypervascularity
measuring vessels is important for diagnosing...
varicocele
what measurement is abnormal meaning there is a varicocele present?
AP over 3mm
when diagnosing ___________________ and ______________________ the valsalva movement is needed
hernia and varicocele
if a pt presents with scrotal pain what needs to be ruled out?
torsion
if a pt presents with trauma what needs to be ruled out?
hemorrhage
scrotal trauma may cause acute scrotal issues such as
hydrocele, hematocele, rupture
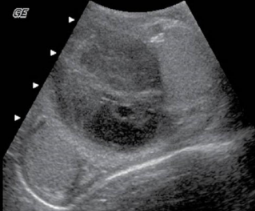
sono findings assoc with scrotal rupture
interruption of tunica albuginea, irregular contour, scrotal wall thickening, hematocele
sono appearance of acute hematocele
echogenic with numerous highly visible echos
with time hematoceles may show
low-level echoes and develop septations
sono appearance of hematoma
large, heterogenous areas within scrotum-- become more complex with time
____________________ and ____________________ are also asssoc with trauma to the testis
epididymitis and torsion
what is epididymo-orchitis
infection of epididymis and testis which usually occurs secondary to epididymitis
epididymo-orchitis is most commonly caused by...
spread of lower urinary tract infection via spermatic cord
what is the most common cause of acute scrotal pain in adults
epididymo-orchitis
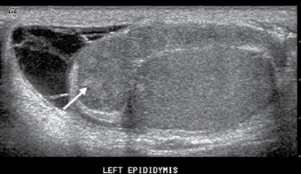
sono appearance of epididymo-orchitis
epi is enlarged and hypoechoic
hyperemic flow
secondary hemorrhage may be seen with focal hyperechoic areas
what is the buddy sign?
showing both testicles with the same color box and settings
when evaluating epididymo-orchitis the ___________________ sign is very important
buddy sign
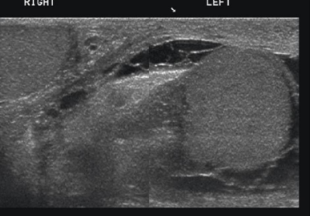
assoc findings of epididymo-orchitis
scrotal wall thickening and hydrocele (low level or anechoic echoes) in the anterolateral area of testes
pyocele
pus fills space between layers of tunica vaginalis, occurs when untreated infection or abscess ruptures associated with trauma/surgery/torsion
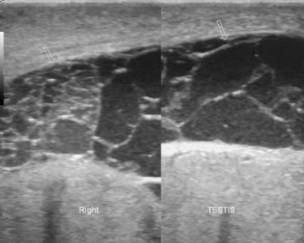
sono appearance of pyocele
internal septations, loculations, debris
when may infarction occur in the testis
with severe cases of orchitis

sono appearance of infarction
swollen testis within tunica albuginea, obstruction, decreased flow
bell clapper deformity
occurs when tunica vaginalis completely surrounds testis, epi, distal sperm cord, and twisted within scrotum
_______________ testis are 10 times more likely to be torsed
undescended
torsion of the ___________________ is a surgical emergency an d must be salvaged before _____ for 20% chance
spermatic cord, 12 hours
peak incidence of torsion is at _____
14 yo
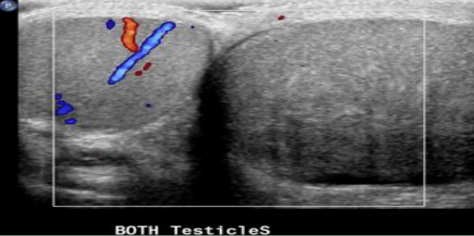
signs/symptoms of torsion
sudden onset scrotal pain with swelling, nausea, vomiting
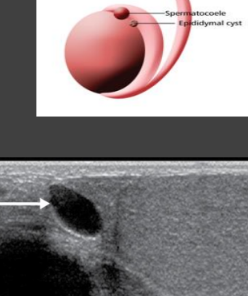
epididymal cysts
small clear cysts with serous fluid that are asymptomatic but may be palpable
most scrotal cysts are __________________
extratesticular located in the epi or tunica albuginea
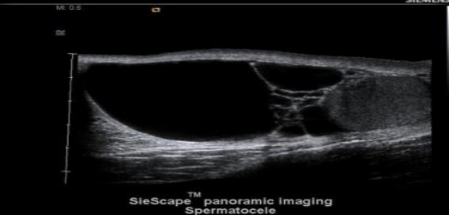
spermatocele
cystic dilation of the efferent ductules of epi and always in epi head
__________________ are seen more often following a vasectomy
spermatoceles
varicocele
abnormal dilation of veins within the pampiniform- primary caused by incompetent venous valve, secondary caused by increased pressure on sperm vein
varicoceles are more common on the _____________ side
left
causes of varicocele
renal hydronephrosis, abdominal mass, liver cirrhosis, and abdominal malignancy in lt renal vein may cause noncompressible veins
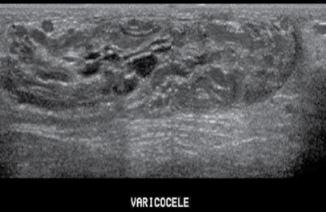
sono appearance of varicocele
less than 2 mm diameter, numerous tortuous tubes within sperm cord, tend to increase in response to Valsalva maneuver
scrotal hernia
occurs when bowel (most common), omentum, or other structures herniate into the scrotum
sono appearance of scrotal hernia
peristalsis seen in scrotum
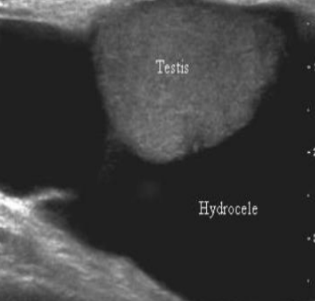
hydroceles are a collection of _____ fluid with painless swelling, and commonly associated with epididymo-orchitis and torsion
serous
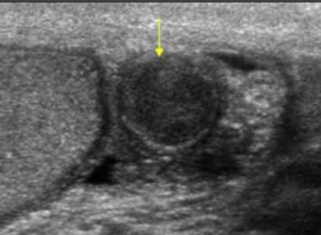
sperm granuloma
chronic inflammatory reaction to extravasation of spermatozoa anywhere within epididymis/vas deferens
____________________________ are most common in pt with a hx of vasectomy
sperm granuloma
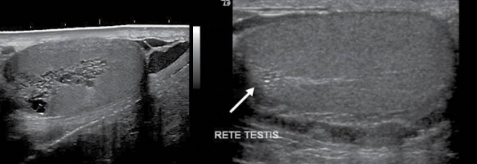
tubular ectasia of rete testis
uncommon benign condition with cystic dilation and formation of cysts within the rete testis
associated with spermatocele, epididymal, or testicular cyst
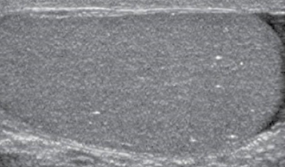
microlithiasis
development of small calculi in testis associated with testicular malignancy, cryptorchidism, Klinefelter’s syndrome, infertility, varicoceles, testicular atrophy, and male pseudohermaphroditism
microlithiasis is usually
bilateral and less than 3 mm
germ cell tumors trends
testicular cancer is uncommon
most common malignancy in 15-35yo
most curable form of cancer
undescended tests are 2.5-8 times more likely to be cancer
types of germ cell tumors of the testis
seminoma, choriocarcinoma, embryonal cell tumors
signs/symptoms of germ cell tumors of the testis
painless lump, enlarged testis, vague discomfort

sono appearance of germ cell tumors
focal hypoechoic masses with no calcs
extratesticular masses are usually _________________ while intratesticular masses are more likely to be ___________________
benign, malignant
______________________ are more aggressive than ___________
embryonal cell tumors, seminomas

embryonal cell carcinoma
heterogenous and less circumscribed
areas of increased echogenicity from calcs, hemorrhage, fibrosis
what is the most common germ cell tumor
seminoma

main indicator for choriocarcinoma
elevated hCG
most common metstasis to testis
prostate or kidneys
metastasis to testis is ___________
bilateral and rare occurring later in life

sono appearance of metastasis
solid hypoechoic mass with mutliple lesions
_______________ makes pt more susceptible to seminoma
undescended testis
cryptorchidism (undescended)
testes do not descend
where may undescended testis be located?
inguinal canal, abdomen, other locations
most common place for testicular ectopia
superficial inguinal canal
anorchia
born without testis