Unit 1 AP Human Geography Key Terms
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Only covers the Key Terms given to me on the sheet of paper for Unit one. IS MISSING SOME AS OF 02/14/2024 (self note: go back into AMSCO Book Unit 1 to add in more vocab)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
spatial patterns
the general arrangements of things being studied and the repeated sequences of events, or processes, that create them.
quantitative data
data measured using numerical facts
geospatial data
tools and methods used to collect, analyze, and visualize spatial data related to the Earth's surface.
qualitative resources
non-numeric information that captures the qualities, characteristics, and experiences of a subject.
scales of analysis
the level or perspective at which a problem or issue is studied or addressed.
reference map
they are aptly named because they are designed for people to refer to for general information about places.
political map
Show and label human-created boundaries and designations, such as countries, states, cities, and capitals.
physical map
show and label natural features, such as mountains, rivers, and deserts.
thematic map
Maps that show spatial aspects of information or of a phenomenon.
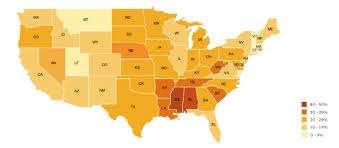
choropleth map
A type of map that uses various colors, shades of one color, or patterns to show the location and distribution of spatial data. They often show rates or other quantitative data in defined areas, such as the percentage of people who speak English.
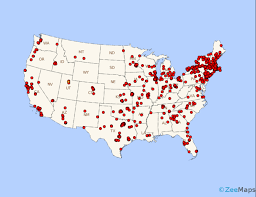
dot distribution map
A type of map used to show the specific location and distribution of something across a map. Each dot represents a specified quantity. One may stand for one building or for millions of people that own dogs.
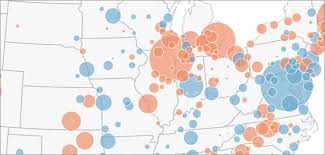
graduated symbol map (proportional symbol maps)
A type of thematic map that uses symbols of different sizes to indicate different amounts of something. Larger sizes indicate more of something, and smaller sizes indicate less. These types of maps make it easy to see where the largest and the smallest of a phenomena are by simply comparing the symbols to each other. Map key can be used to determine the exact amount.
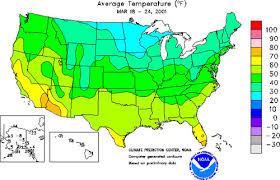
isoline map
A type of map that uses lines that connect points of equal value to depict variations in the data across space. Where lines are close together, the map depicts rapid change, and where the lines are farther apart, the phenomenon is relatively the same.
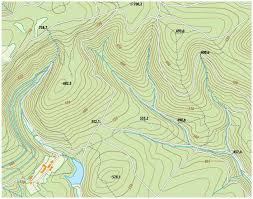
topographic map
Points of equal elevation are connected on these maps, creating contours that depict surface features. Most popular among hikers.
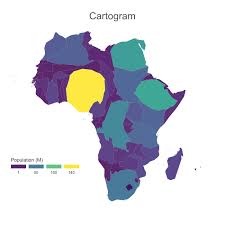
cartogram
This map shows the sizes of countries (or states, countries, or other areal units) are shown according to some specific statistics. They are useful because they allow for data to be compared, much like a graph, and distance and distribution are also visible like on a traditional map.
scale
the ratio between the size of things in the real world and the size of those same things on the map
small-scale map
show a larger amount of area with less detail. example: global scale Earth at night is an example.
large-scale map
shows a smaller amount of area with a greater amount of detail, example: North America at night is an example.
location
Identifies where specific phenomena are located either on a grid system or relative to another location.
absolute location
the precise spot where something is according to a system.
relative location
A description of where something is in relation to other things.
direction
It is used in order to describe where things are in relation to each other such as using cardinal directions (North, east, south, and west) or intermediate directions (southeast or southwest).
distance
A measurement of how far or how near things are to one another.
absolute distance
Usually measured in terms of feet, miles, meters, or kilometers. example: from your home to your school it’s 2.2 miles.
relative distance
Indicates the degree of nearness based on time or money is often dependent on the mode of travel.
example: traveling from home to school takes 10 minutes
elevation
The distance of features above sea level, usually measured in feet or meters
patterns
The general arrangement of things
clustered (agglomerated) distribution
A phenomena arranged in a group or concentrated area
dispersed distributions
phenomena are spread out over a large area
field observations
The act of physically visiting a location, place, or region and recording, firsthand, information there.
remote sensing
Gathers information from satellites that orbit the earth or other craft above the atmosphere.
Uses cameras or other sensors mounted on aircraft or satellites to collect digital images or video of the earth’s surface.
Used to determine land cover and use, monitoring environmental changes, assessing spread of spatial phenomena, and monitoring the weather
Global Positioning System (GPS)
Receivers on the earth’s surface use the locations of multiple satellites to determine and record a receivers exact location.
It’s used to precisely locate borders, navigate ships/aircraft/cars, and mapping lines
Geographic Information System (GIS)
A computer system that can store, analyze, and display information from multiple digital maps or geospatial data sets
Analyzing of crime data and transportation/travel time, monitoring the effects of pollution, and planning urban area
spatial approach
Considers the arrangement of the phenomena being studied across the surface of the earth.
also looks at elements such as the movements of people and things, changes in places overtime, and even human perceptions of space and place
space
The area between two or more phenomena or things
place
The specific human and physical characteristics of a location.
site
The characteristics at the immediate location
example: the soil type, climate, labor force, and human structures
situation
The location of a place relative to its surrounding and its connectivity to other places.
sense of place
The way humans tend to perceive the characteristics of places in different ways based on their personal beliefs.
toponyms
Places names a located is designated
time-space compression
The shrinking “time-distance,” or relative distance, between locations
flow
The patterns and movements of ideas, people, products, and other phenomena
distance decay
The concept of the inverse relationship between distance and connection
human-environmental interaction
The dual relationship between humans and the natural world.
natural resources
Includes items that occur in the natural environment that people can use.
examples: air, water, oil, fish, soil, and minerals
sustainability
Relates to trying to use resources now in way that allow their use in the future with minimizing negative impacts on the environment
land use
The study of how land is utilized, modified, and organized by people
environmental determinsism
The belief that landforms and climate are the most powerful for shaping human behavior and societal development while ignoring the influence of culture
possibilism
A view that acknowledges limits on the effects of the natural environment and focuses more on the role that human culture plays.
global scale
Shows the entire world
examples:
global earth at night image
world population density map
world regional scale
Shows multiple countries of the world
examples:
North america
South Asia
national scale
Shows one country
example:
The United States
national regional scale
Shows a portion of a country or a region(s) within a country
local scale
Shows a province, state, city, county, or a neighborhood.
examples:
Tennessee
Moscow
region
Contains boundaries, unifying characteristics, cover space, and are created by people
formal region (uniform region; homogenous region)
Region united by one or more traits such as:
political, such as Brazil in South America
physical, such as the Sahara, a vast desert in northern Africa
cultural, such as southwestern Nigeria, an area where most people speak Yoruba
economic, such as the Gold Coast of Africa (Ghana), which exports gold
functional region (nodal region)
These regions are organized around a focal point and are defined by an activity, usually political, social, or economic, that occurs across the region
Are United by networks of communication, transportation, and other interactions
perceptual region
Region that is defined by the informal sense of place that people ascribe to them.
examples:
The American East
The Middle East
Upstate New York