Prelim Module 3 Test
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
The liver is a _______. It is the _________ internal organ. And it is an accessory organ of __________.
gland; largest; digestion
What are the normal measurement of the liver in
Transverse?
Anteroposterior?
Length?
transverse: 20-22.5 cm
Anteroposterior: 10-12.5 cm
Length: 13-15.5cm
What are the normal weight measurements of the liver in men and women?
1,200 g in women
1,600 g in men
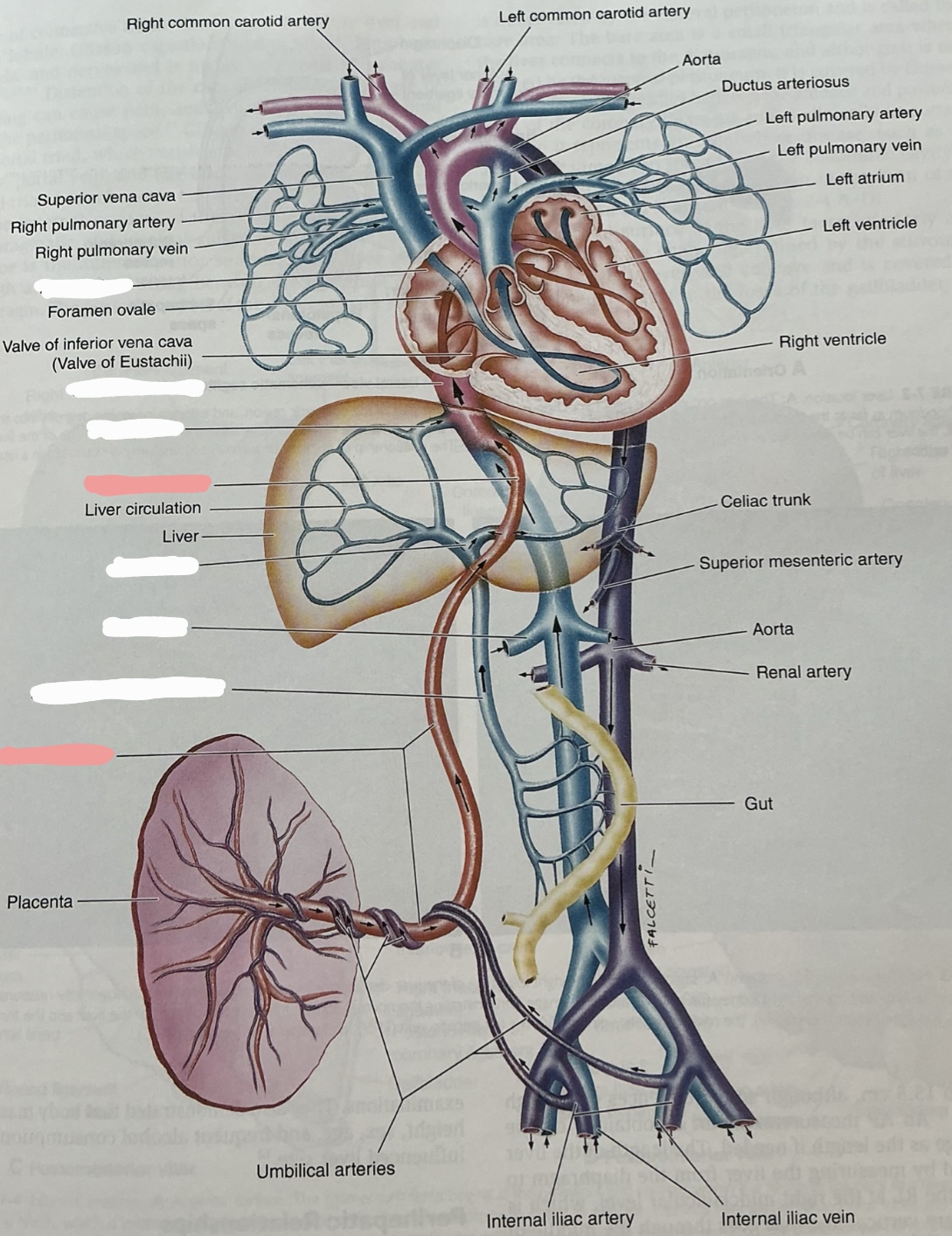
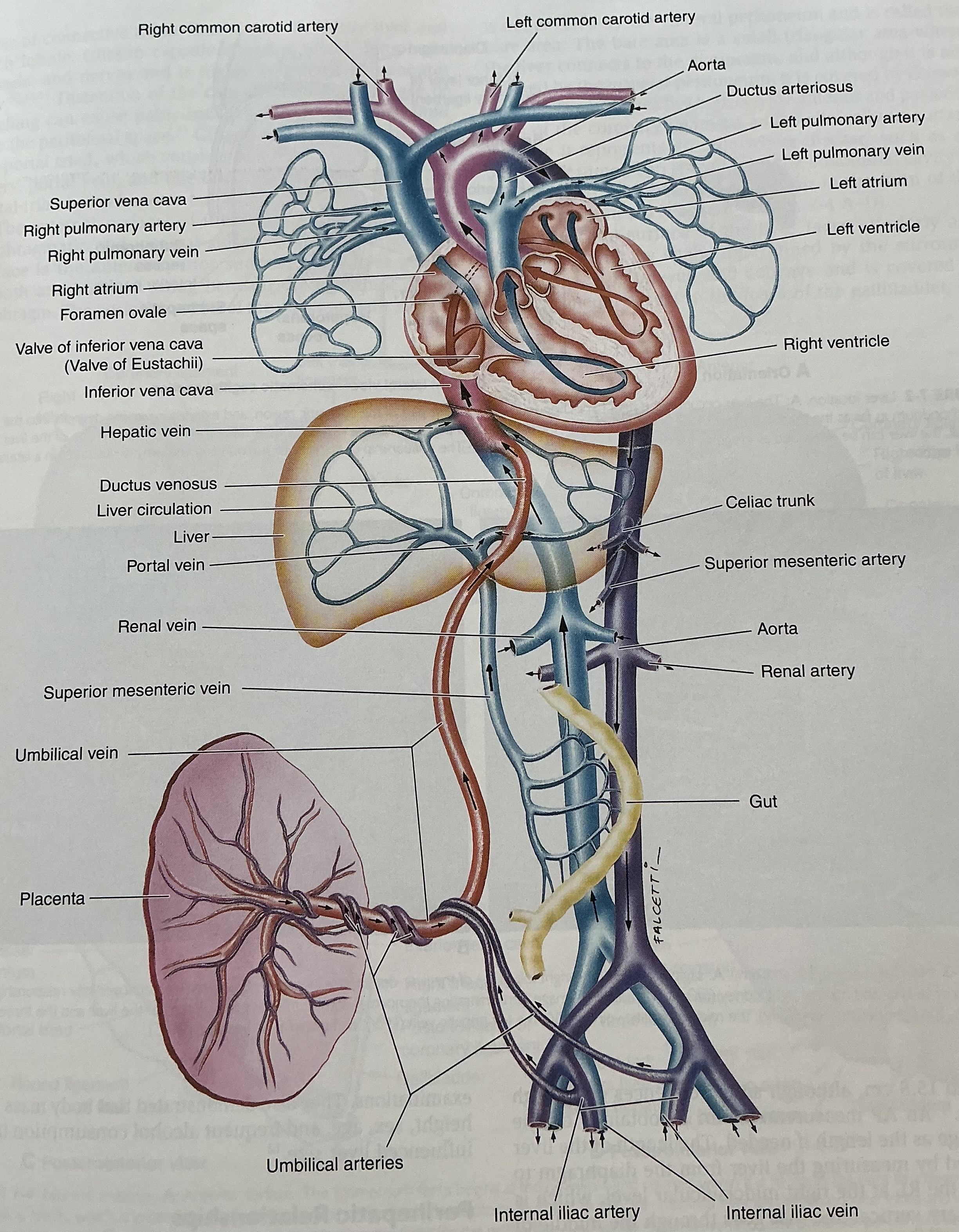
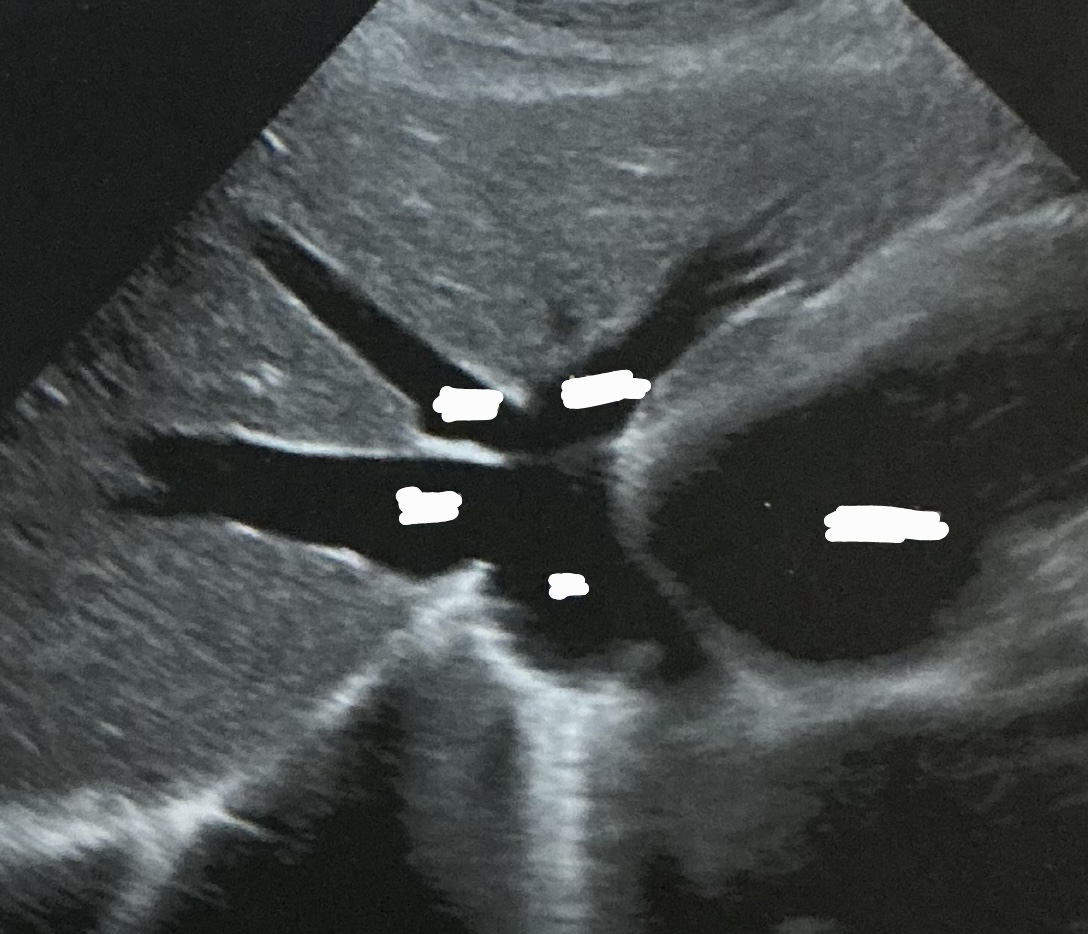
Label this image
Describe the portal triad which is found in each of the 8 segments. What are the segmental divisions based on?
1) hepatic artery: ventral and medial
2) portal vein: dorsal
3) bile duct: ventral and lateral
hepatic veins provide boundary and portal veins
The Riedel lobe appears as a finger-like projection of the right lobe of the liver. What pathology does it give the impression of? Is it more common in women or men?
hepatomegaly; women
The liver receives dual blood supply from what two vessels? What is the place iin which the blood mixes called?
hepatic artery and portal vein
liver sinusoids
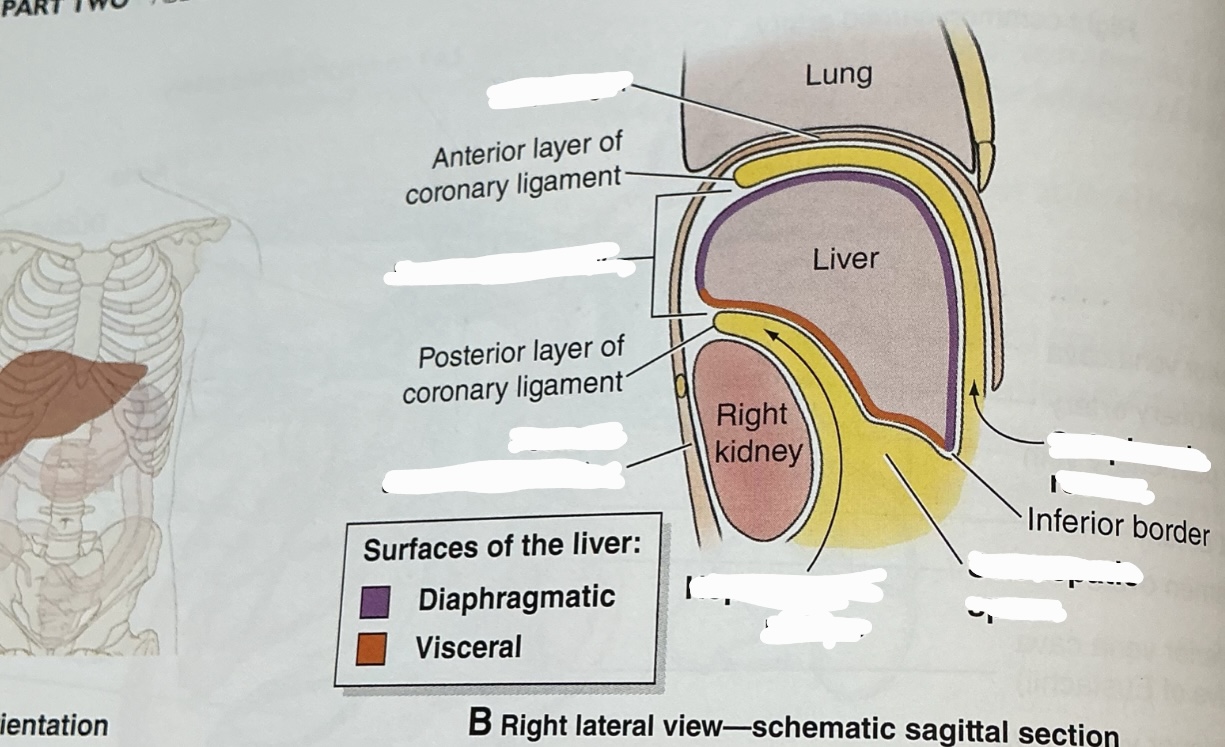
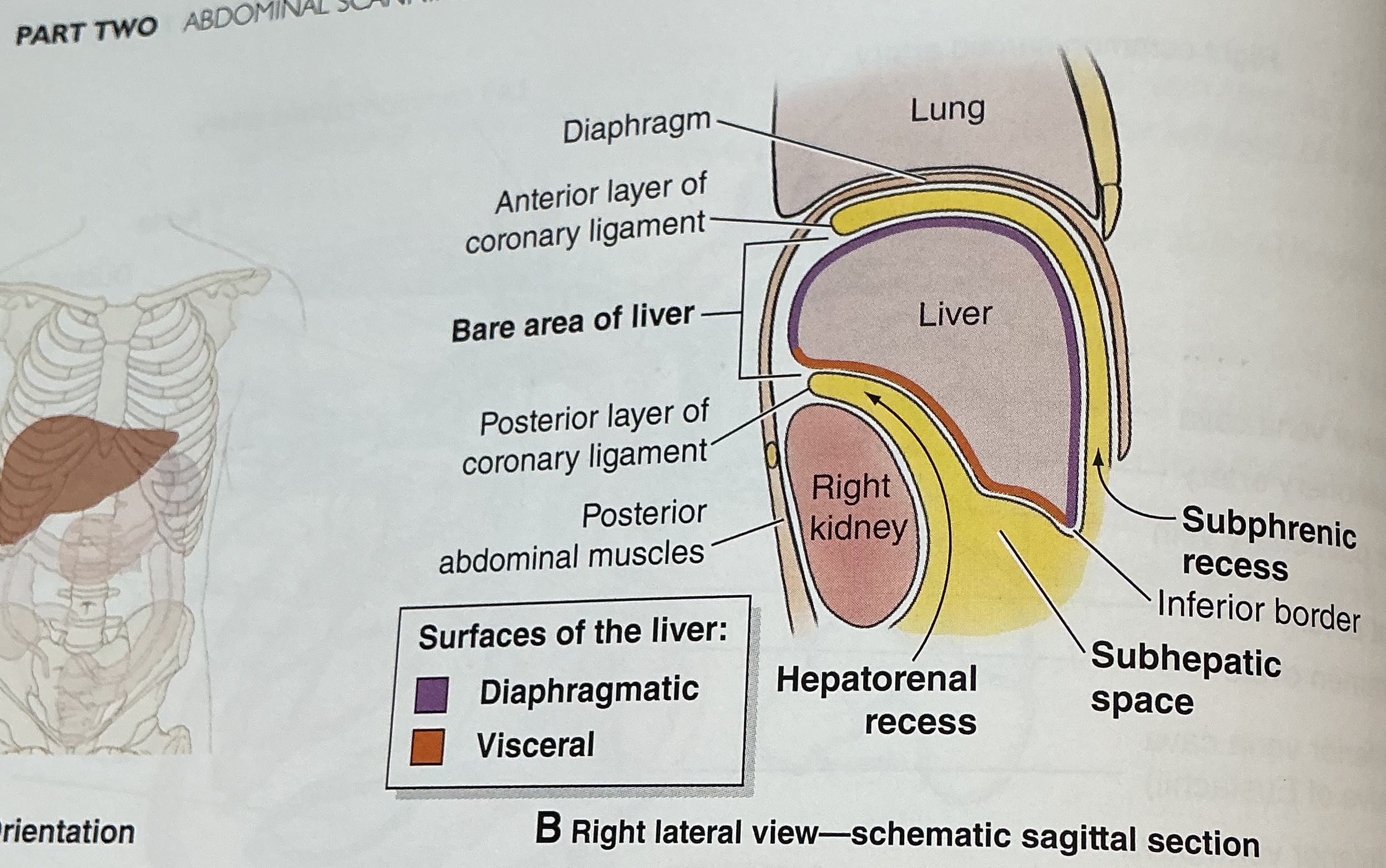
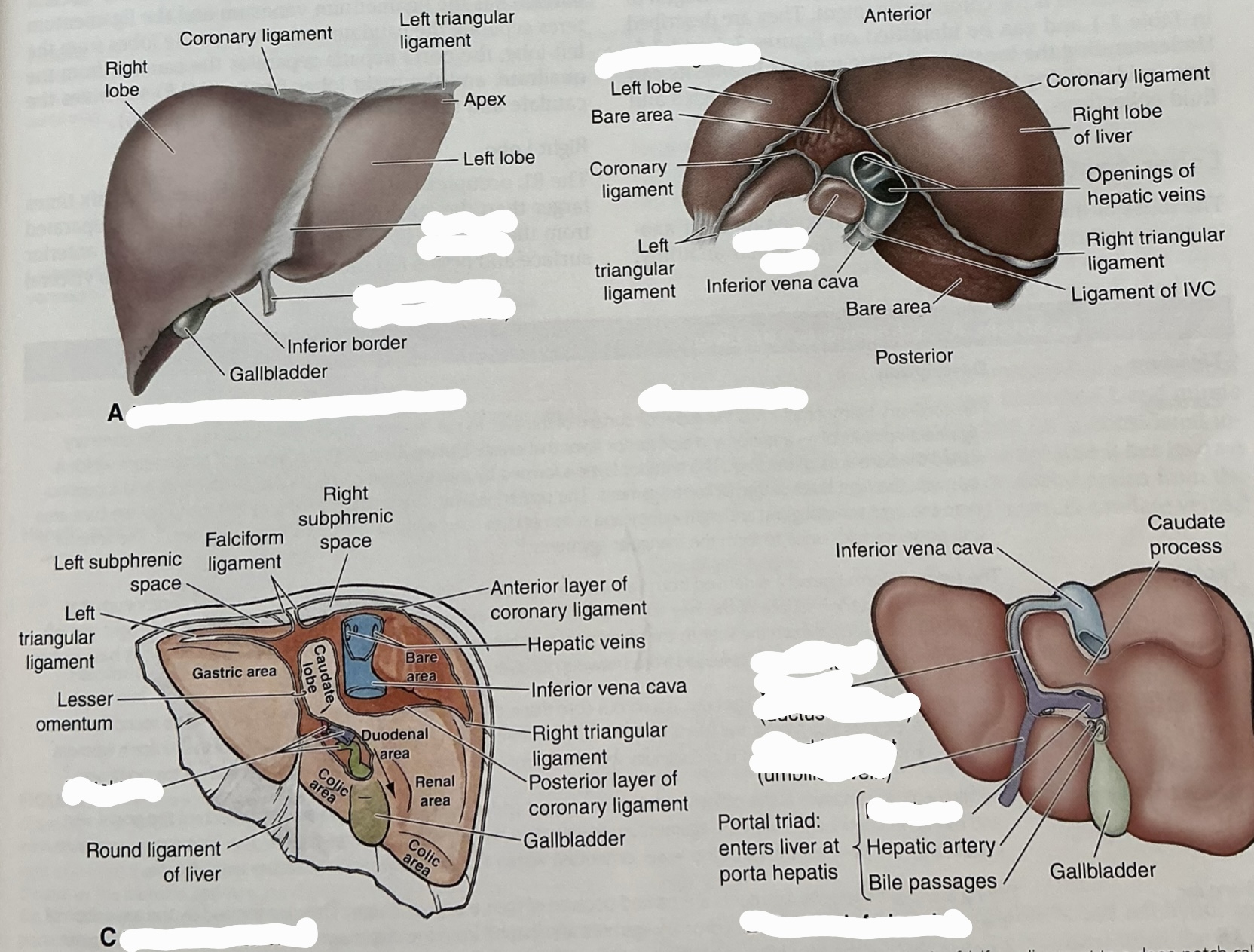
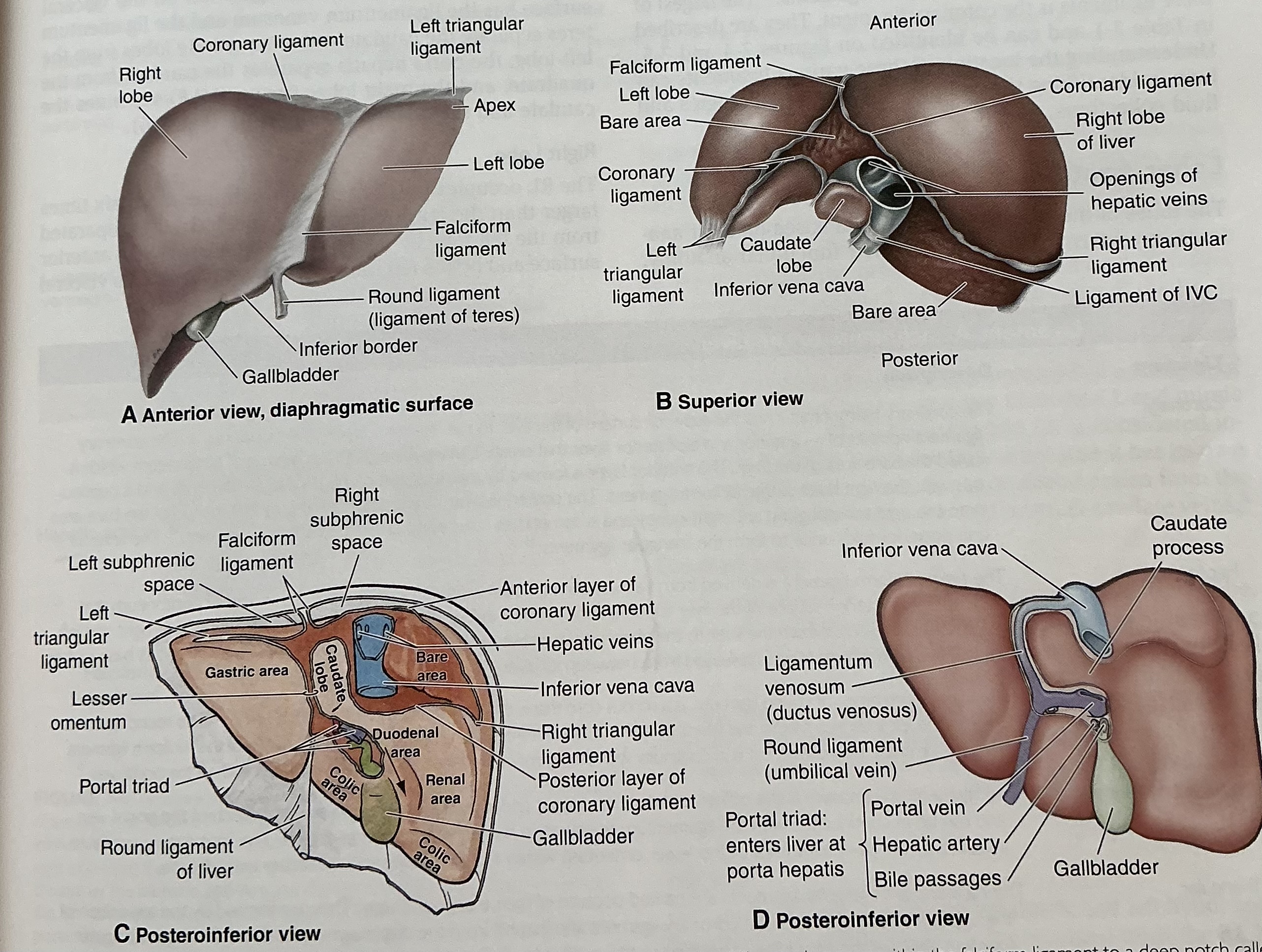
Falciform ligament
anchors anterior surface of liver to anterior abdominal wall
Separates anatomic right and left liver lobes
At its base, ligamentum teres released from between its layers
Ligamentum teres (round ligament)
remnant of left umbilical vein
Divides left lobe into medial and lateral sections
Joins the left branch of the portal vein
ligametum venosum
obliterated ductus venosus
Coronary ligament
attaches superior surface of liver to inferior surface of diaphargm
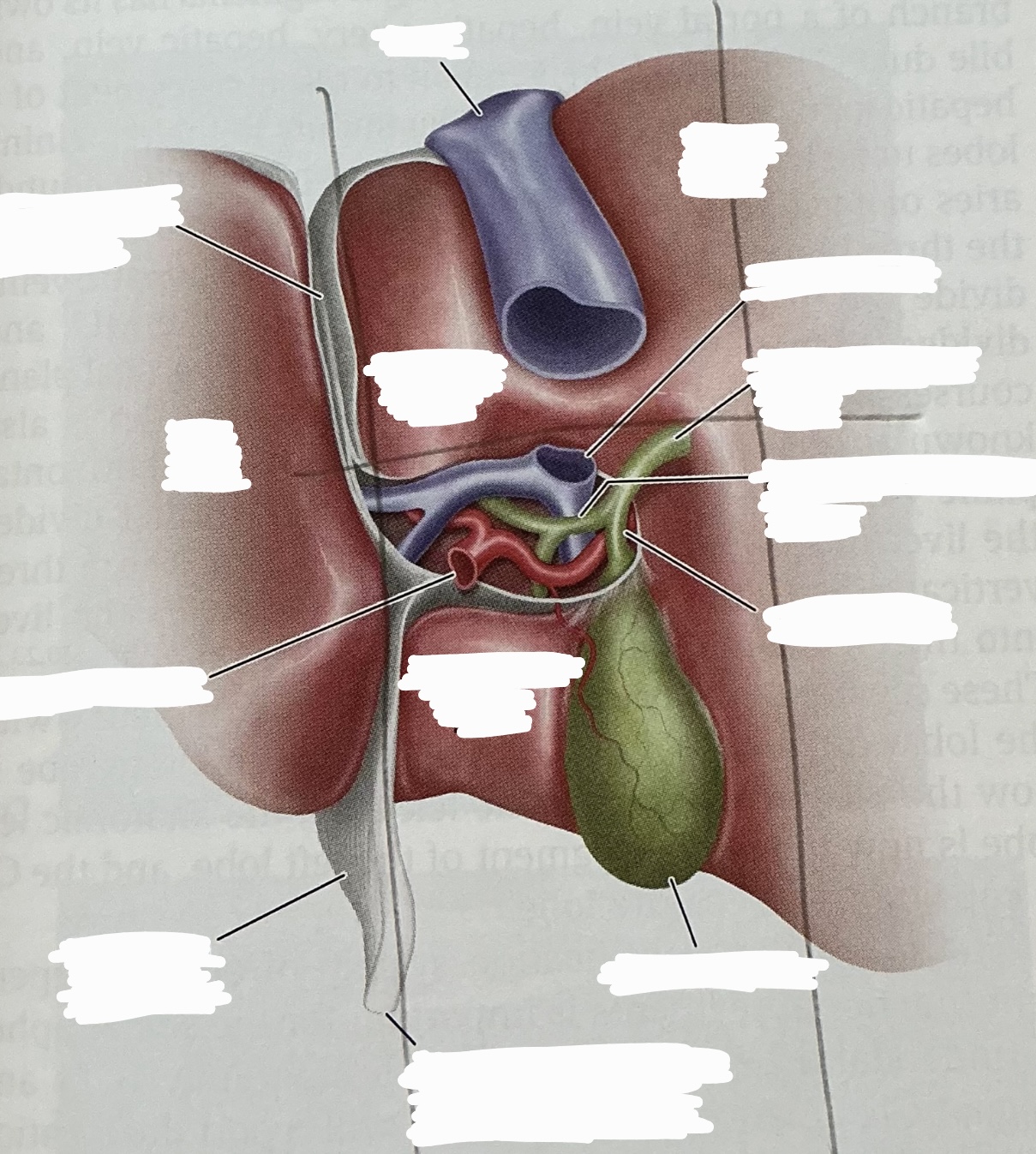
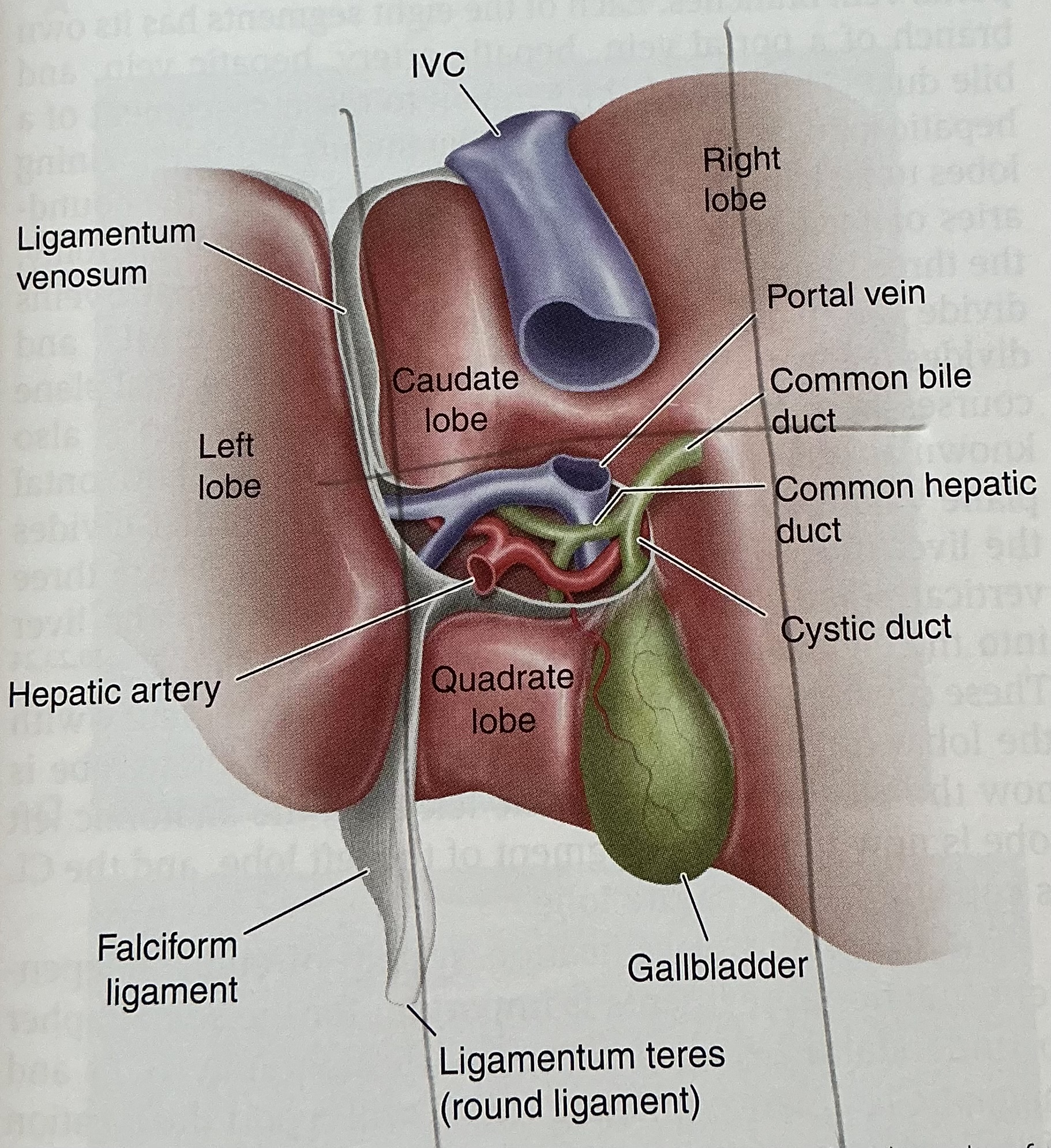
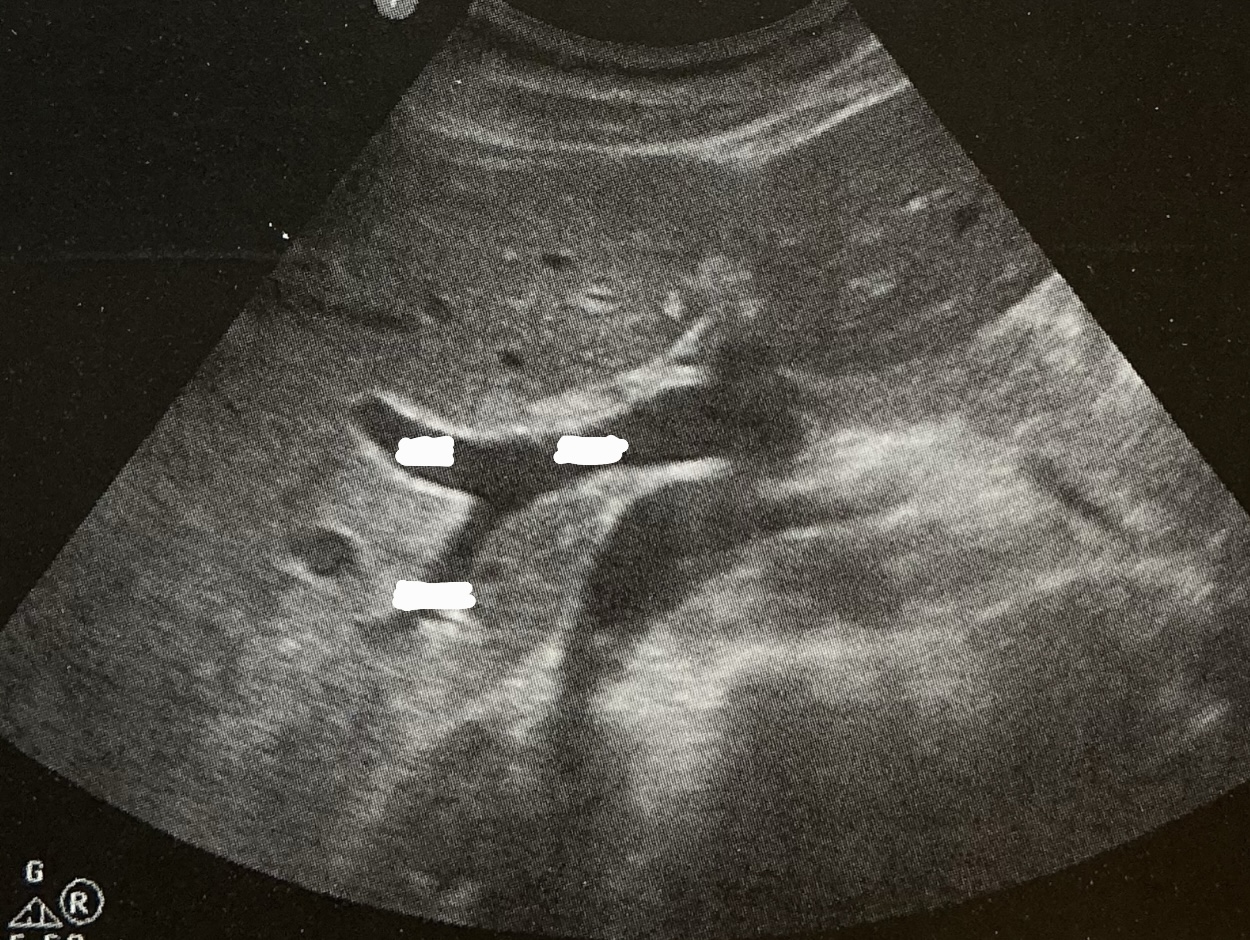
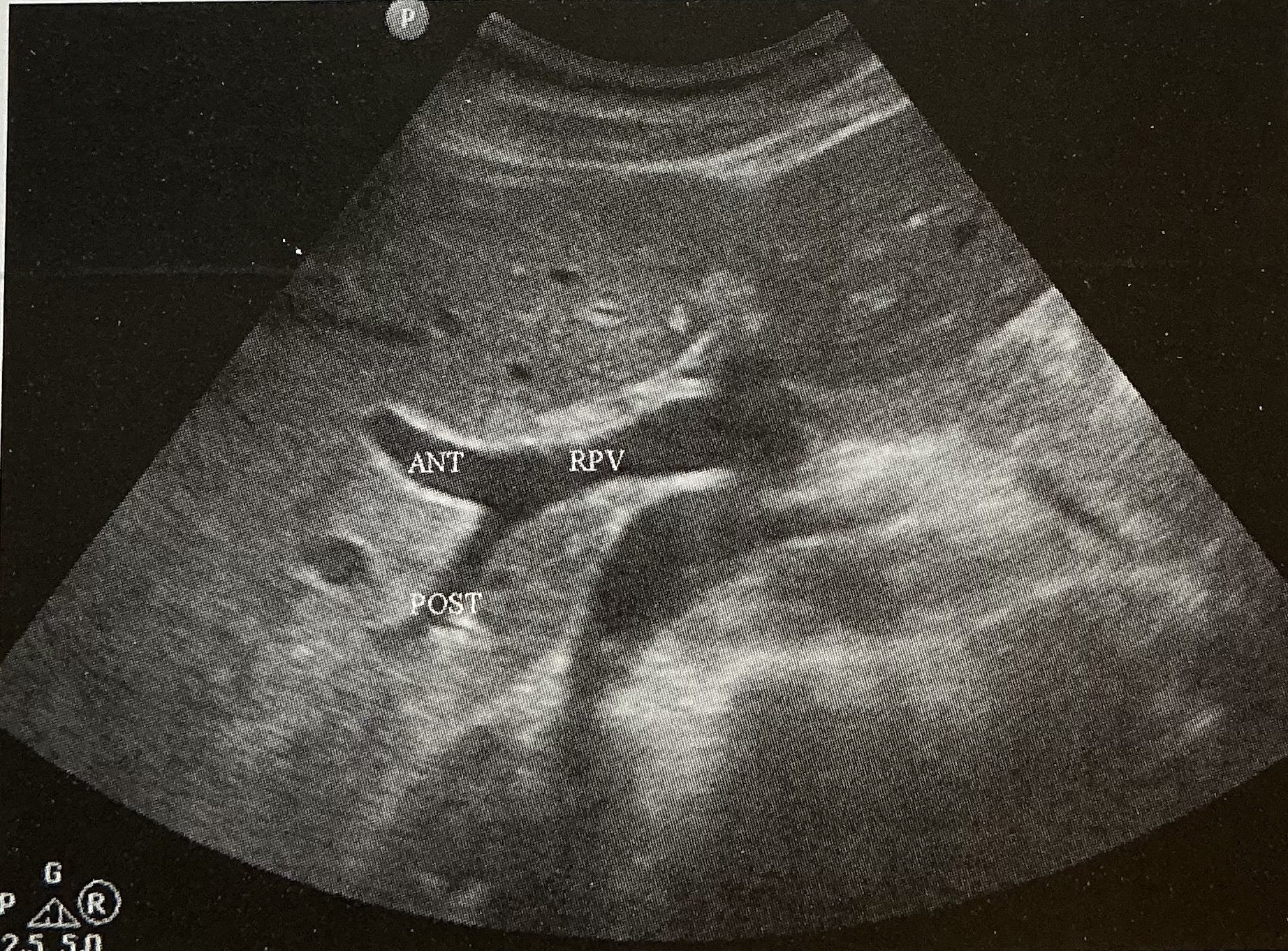
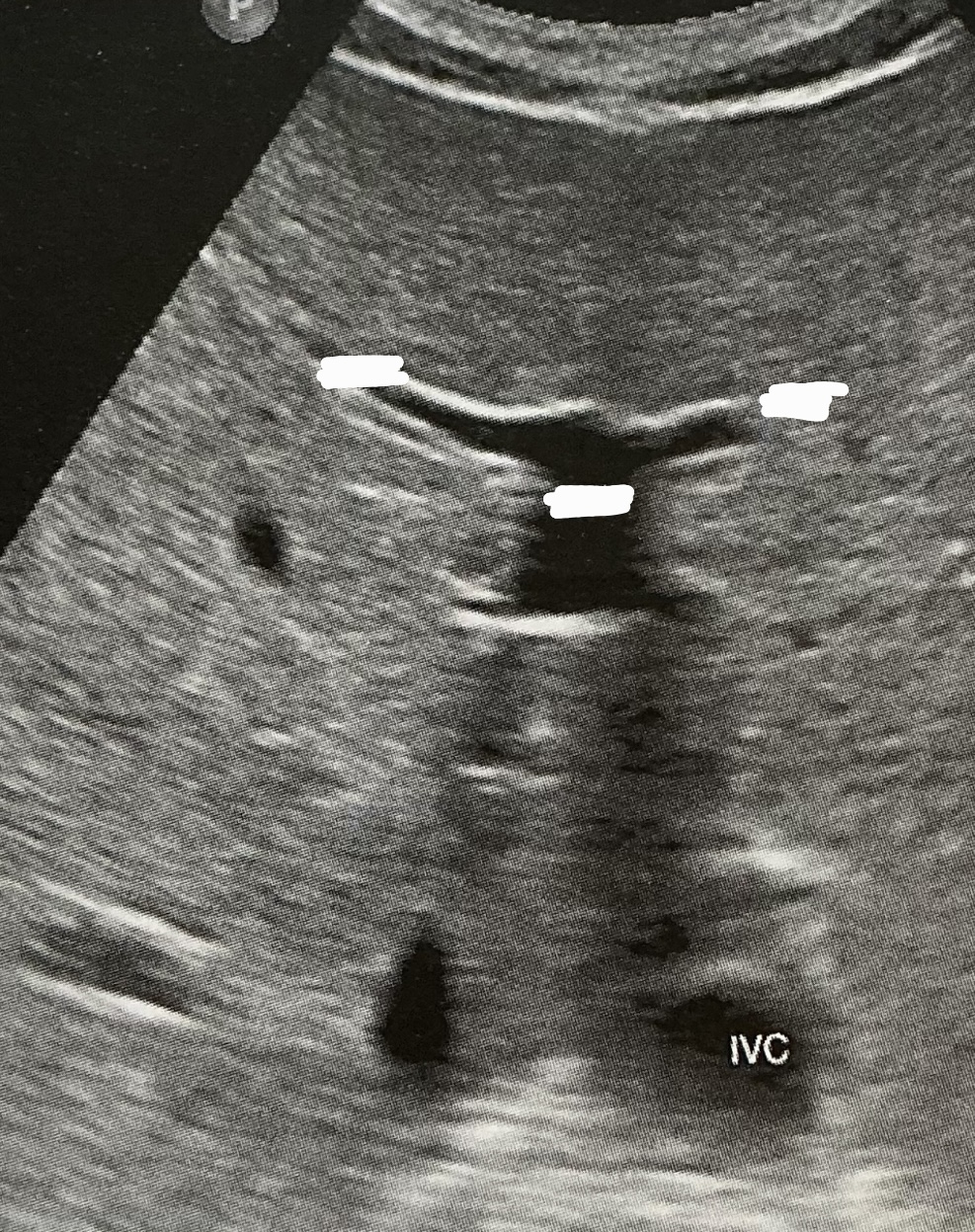
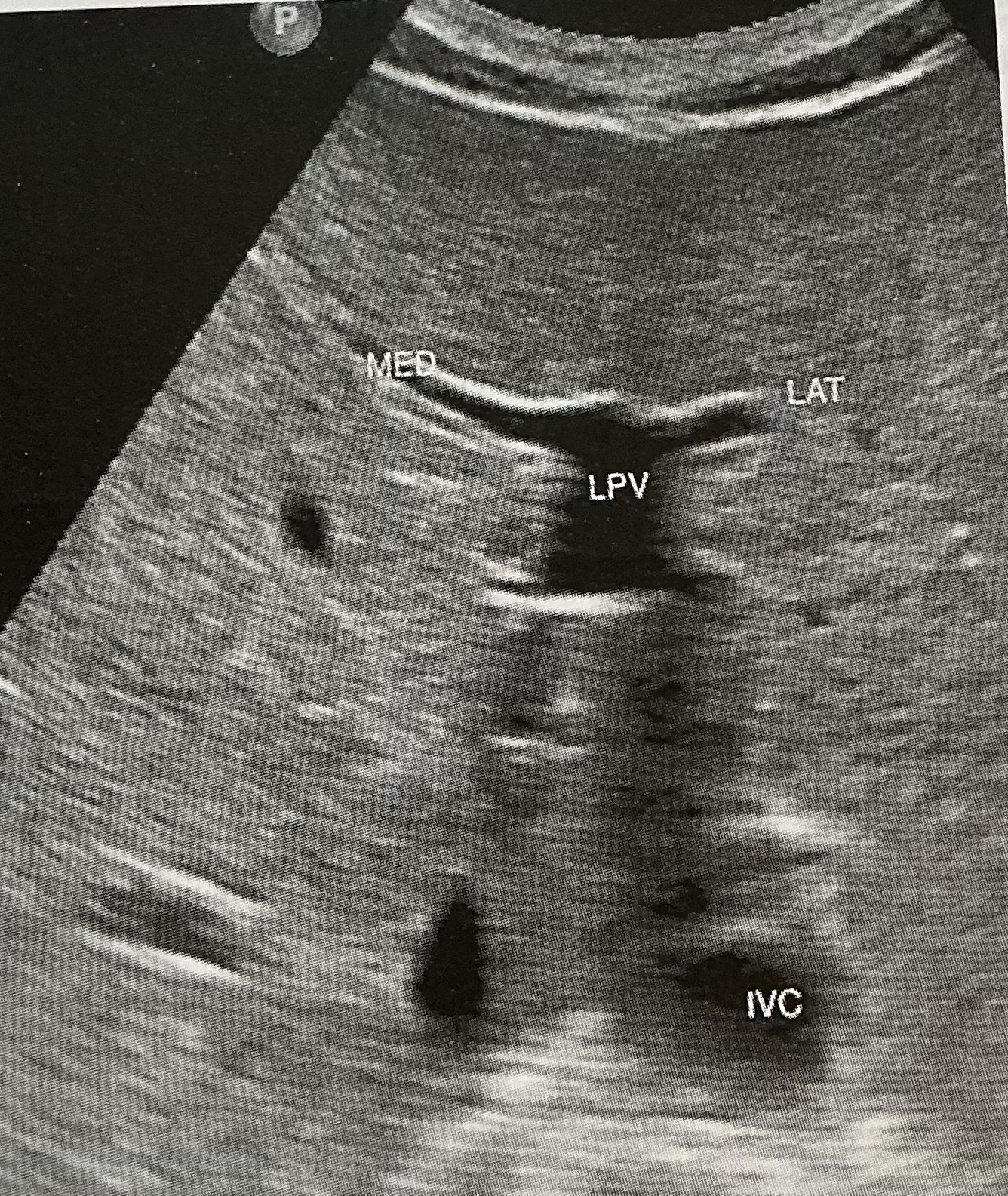
What is the sonographic criteria for differentiating the portal veins and hepatic veins?
origin and drainage; echogenic walls; branching patterns; caliber changes and Doppler signal; segmental locations
What is this photo depicting?
situs inversus
What are the sonographic signs to differentiate the bile duct and hepatic artery?
1) pulsations from arteries not veins
2) a crossing artery can indent a duct or vein but arteries are less easily deformed
3) duct can have various calibers along course, arteries are uniform in caliber
4) duct parallels vein closely, artery may do so for short distance
5) arteries may be tortuous
6) arteries produce pulsatile Doppler signals, ducts produce no signals
What happens at the porta hepatis? What happens at a fissure?
porta hepatis: vessels converge, entering the liver
Fissure: portal vein and hepatic artery enter, bile duct exicts
Mickey mouse sign
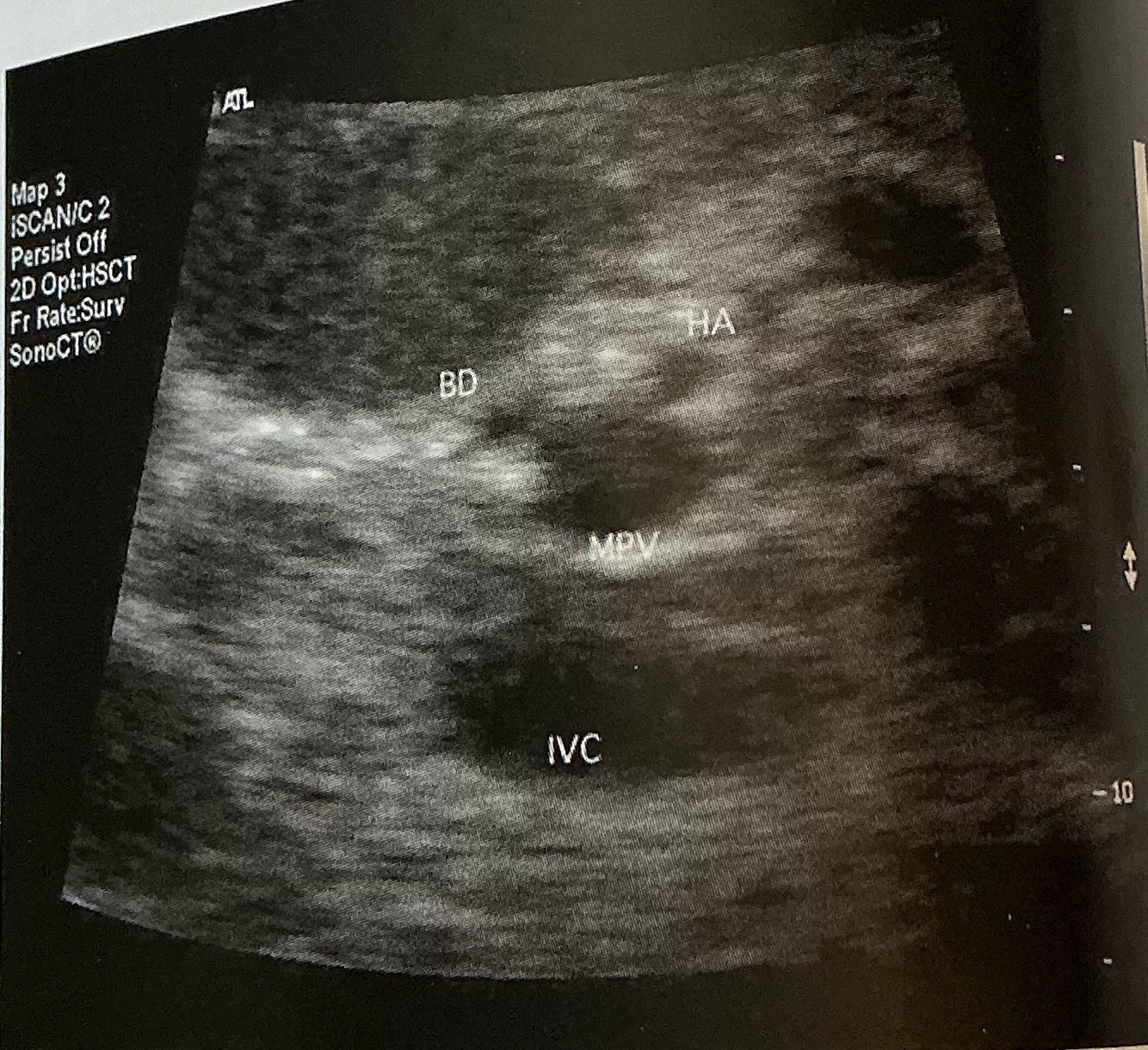
What is the normal diameter of the bile duct? What is the normal diameter of the hepatic artery?
bile duct: 4-8mm
Hepatic artery: 2-6mm
What are the functions of the liver?
****factory, warehouse, power plant, waste disposal plant*****
Bile formation and secretion; carbohydrate, fat, protein metabolism; reticuloendotheolial tissue activity; storage depot; blood reservoir; heat production; detoxification; lymph formation
What are the three cell types?
1) hepatocyte in parenchyma
2) biliary epithelial
3) Kupffer cells
What three veins converge at the portal confluence?
IMV, SMV, splenic vein
ALT
A liver enzyme most specific to hepatocellular damage
AST
an enzyme found in all tissues, but in largest amounts in the liver; an increase can indicate hepatocellular damage
ALP
an enzyme found in liver tissue that can be elevated with biliary obstruction
AFP
a tumor marker frequently elevated in cases of hepatocellular carcinoma and certain testicular cancers
What is diffuse hepatocellular disease?
hepatocyte dysfunction causes glycogen storage disease, fatty infiltration, hepatitis, and cirrhosis
What is the sonographic appearance of the phases of hepatitis?
normal at first
Acute phase: hyperechoic portal vein walls, hypoechoic parenchyma owing to swelling of the liver
Chronic phase: increased amount of fibrous tissue and inflammatory cells surrounding hepatic lobules produces coarse echo pattern
What is this sign? In what disease does this happen?
Starry star sign
acute hepatitis
What happens to the liver architecture in cirrhosis? In the chronic phase, what happens at the end?
cirrhosis destroys the normal liver lobule architecture
chronic and severe cirrhosis ends in necrosis
How does the liver appear in the different phases of cirrhosis?
early stage: hepatomegaly; liver may appear hyperechoic compared to normal renal parenchyma; diffuse parenchymal changes lead to diagnosis of hepatocellular diseaes
Progression: tissue begins to atrophy and attenuates more sound; fibrosis appears more coarse; vascular structures are not readily visualized and may present an irregular contour owing to nodular regneration
Portal hypertenion: splenomegaly and ascites may be seen
* * new vascular channels called collaterals can form, bypassing portal venous blood from the liver
In cirrhosis, what may happen to portal vein velocities and the hepatic artery?
portal vein velocities are often reduced and become hepatofugal
Hepatic artery will enlarge with elevated velocities to maintain hepatic perfusion
Normal portal venous inflow is characterized by what type of phasic flow and how much pulsatility?
continuous monophasic flow and little pulsatility
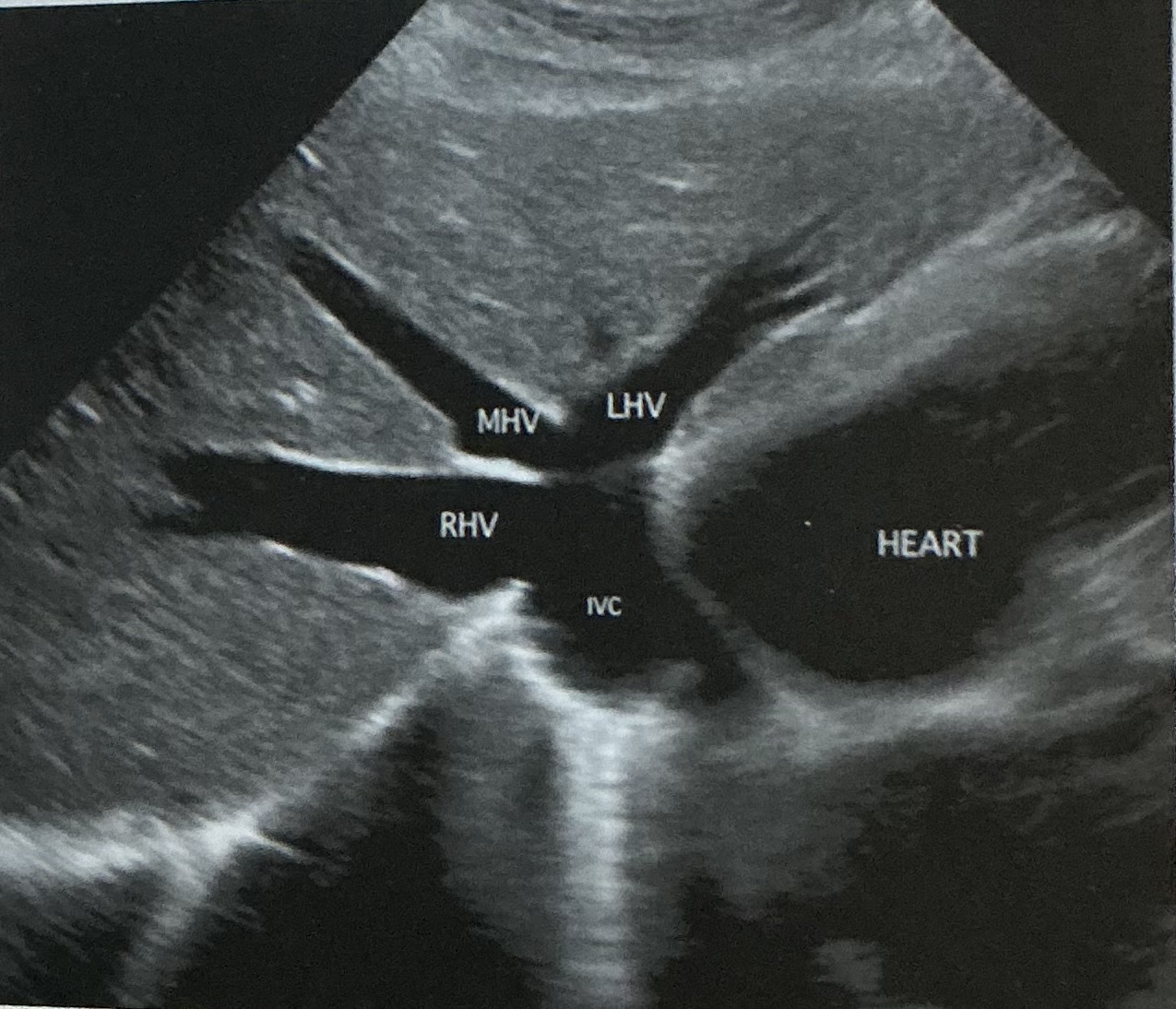
Label this picture
what sign is it depicting
Why does this happen?
What sign does the hepatic veins normally depict?
Canadian moose sign
Dilatation from right heart failure
Playboy bunny sign
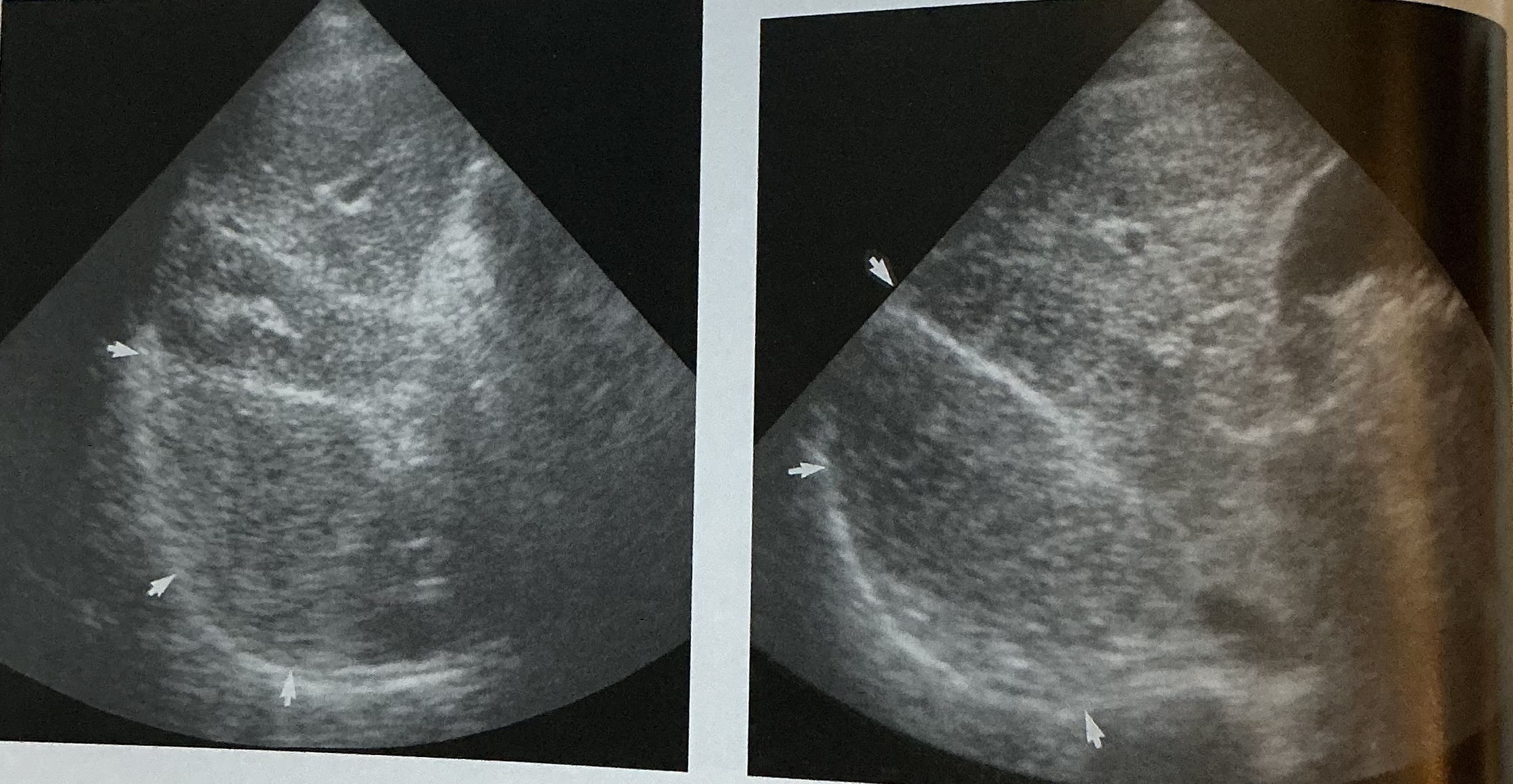
What pathology is this photo depicting? What is the sign that can be seen in this pathology? What type of infection is this?
schistosomiasis; turtleback sign; parasitic found in other parts of the world
How do hepatic abscesses occur? What cells fight off infection?
hepatic abscesses are normally caused by bacterial, amebic, or parasitic infection
kupffer cells remove bacteria so efficiently that infection rarely occurs
With congenital cysts, are solitary cysts or multiple cysts more common? Which lobe is more commonly affected? What are the categories of acquired cysts?
solitary cysts are more common; the right lobe is affected twice as often
Traumatic, parasitic, inflammatory