X-Ray Interactions With Matter
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Explain Bremsstrahlung radiation (review from target interactions)
incoming electron is slowed by force field of the nucleus
electron continues in a different direction with reduced energy
loss of kinetic energy given off as an x-ray
a wide variety of x-ray energies are emitted
beam is said to be polyenergetic/heterogenous
Explain characteristic radiation (review from target interactions)
incoming electron ejects electron from k-shell (of tungsten)
outer shell electron drops into the vacancy
x-ray energy emitted is equal to the difference in binding energy of the electrons involved
a cascade is created as electrons from outer shells drop into the vacancies in the inner shells
specific x-ray energy can be calculated because the binding energy of the tungsten shells is known
Short wavelength photons have ___ energy and ___ penetrability
high energy and high penetrability
Long wavelength photons have ___ energy and ___ penetrability
low energy and low penetrability
Define attenuation
the reduction in the number of x-ray photons in the beam, and subsequent loss of energy as the beam passes through matter
X-ray photons interact with matter and lose energy in 4 different ways:
absorbed
attenuated
scattered
transmitted
___ beam creates the image
remnant (exit)
What is a latent image?
an image that is stored until you do something with it (needs to be processed)
stored in the IR
All interactions between x-rays and matter take place at the ___ level
atomic
Low energy x-rays interact at the level of ___
Moderate energy x-rays interact at the level of ___
High energy x-rays interact at the level of ___
low: whole atom
moderate: orbital electrons
high: nuclei
Interactions that produce x-rays in the diagnostic range occur in the ___ energy range and involve___
occur in the moderate energy range and involve orbital electrons
Electron binding energy is equal to ___
the force with which the electron is held in the shell
Protons have a ___ charge
Neutrons have a ___ charge
Electrons have a ___ charge
P: +
N: 0
E: -
The closer the electron is to the nucleus, the ___ (tighter/looser) it is bound in its orbital shell
tighter
The farther away from the nucleus that the electron is, the __ (greater/lesser) the total energy of the electron
greater
List the 5 basic x-ray interactions with matter
photoelectric absorption
coherent scattering
Compton scattering
pair production
photodisintegration
Which 2 interactions are part of the remnant beam?
photoelectric absorption and Compton
Photoelectric (PE) absorption/effect occurs when ___
energy of the incident photon is slightly greater than binding energy of k shell (which varies with different tissues of the body)
In PE absorption/effect, what happens with the incident photon?
it ejects an inner shell electron that becomes a photoelectron
the incident photon is then completely absorbed by the patient (delivers patient dose)
PE effect occurs at which orbital shell?
K-shell
How does PE effect end up creating characteristic radiation?
when K-shell electron is ejected, vacancy is filled by L or M shell electron (this energy gives off secondary radiation equal to the difference in binding energy of the two shells)
The probability of photoelectric interaction ___ as the energy of the incident photon increases
decreases
The probability of photoelectric interaction ___ as the atomic number of absorber/matter increases
increases
For a photoelectric interaction, the energy of the incident electron must be greater than ___
the binding energy of the inner shell electron
A photoelectric interaction is more likely to occur with electrons that have ___ binding energies (atomic #)
high
What type of interaction is primarily responsible for the subject contrast in a latent image?
photoelectric
Coherent scatter occurs with energies ___
<10 keV
In coherent scatter, a ___ photon interacts with an electron
low energy
Thompson coherent scatter causes temporary excitation on ___
a single electron
Rayleigh coherent scatter causes temporary excitation on ___
the entire atom
The secondary photon from coherent scatter travels in ___ direction with ___ energy as incident photon
different direction; same energy
Is coherent scatter significant for Dx? Explain
no; doesn’t affect the image
In Compton scatter, what happens with the incident photon?
it ejects an outer-shell electron, then continues in a different direction with less energy as scatter
In Compton scatter, what is the ejected outer shell electron called?
Compton electron or recoil electron
What direction are Compton scattered electrons ejected in?
any direction (0-180o)
The more forward the direction of the Compton scattered electron, the ___ energy it retains
more
Compton scattered electrons that travel in a forward direction are more likely to ___
reach the IR (have a serious impact on image quality)
What is the keV diagnostic range for compton scatter?
50-140 keV
Compton scatter has a ___ impact on contrast. What does it cause to our scale of contrast?
negative and reduces contrast and causes a longer scale of contrast
Do Compton interactions add any useful diagnostic information?
no
What is backscatter radiation?
scatter that is deflected back toward the source (only a small number of photons backscatter)
What is the primary source of occupational exposure?
backscatter
What energies does pair production occur at?
>1.02 MeV
Pair production occurs when a high energy photon ___
interacts with the nucleus of an atom
What type of imaging uses pair production?
PET
List and explain the electrons created in pair production
negatron
is absorbed
positron
extremely volatile
combines with negative electron
releases 2 positrons moving in opposite directions
Pair production creates ___ reactions
annihilation
What energies does photodisintegration occur at?
>10 MeV
Does photodisintegration occur during x-ray imaging?
no
What happens in photodisintegration?
high energy photon excites the nucleus, and then the nucleus emits a fragment
At 50 kVp, what is the ratio of photoelectric and Compton scatter?
At 120 kVp, what is the ratio of photoelectric and Compton scatter?
50 kVp: 50/50
120 kVp: 25% photoelectric 75% Compton
An increase in energy has a(n) ___ interaction within the patient
decreased
Photoelectric absorption occurs with ___ energies
low
Compton scatter occurs with ___ energies
high
As kV increases, the total number of transmitted photons ___, and contrast ___
transmitted photons increases
contrast decreases
PE interactions ___ contrast, while Compton interactions ___ contrast
PE: create contrast
Compton: degrade contrast
Absorption occurs with what 3 things?
low kVp
high atomic number
contrast medium
High kVp produces a ___ percentage of scatter
high
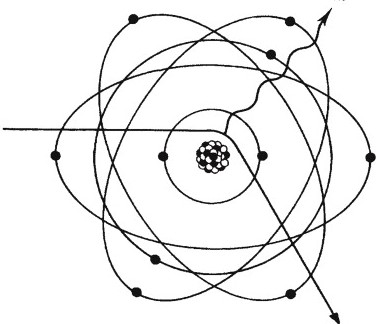
What type of interaction is shown?
Bremsstrahlung
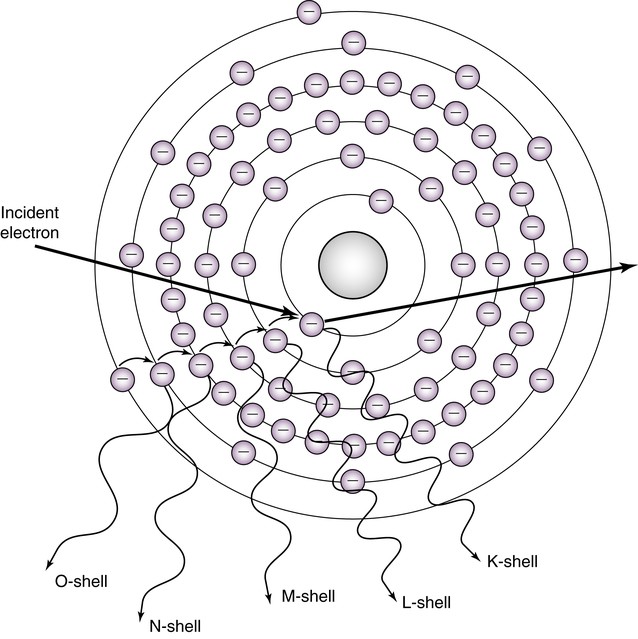
What type of interaction is shown?
characteristic
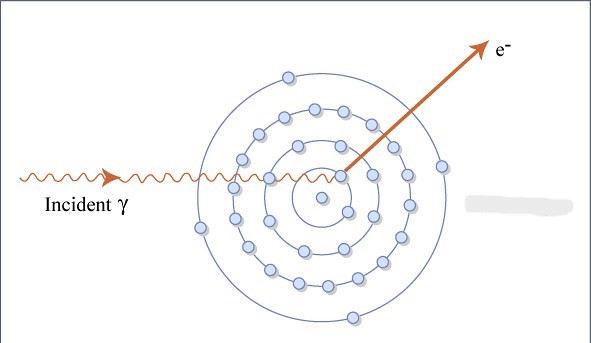
What type of interaction is shown?
photoelectric absorption
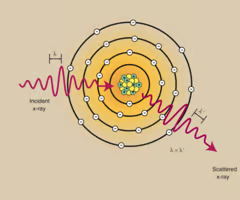
What type of interaction is shown?
coherent scatter
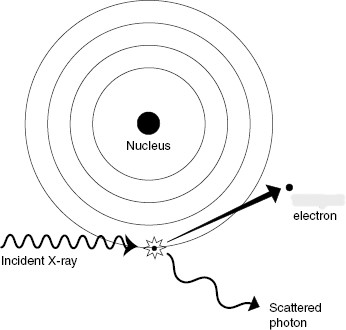
What type of interaction is shown?
Compton scatter
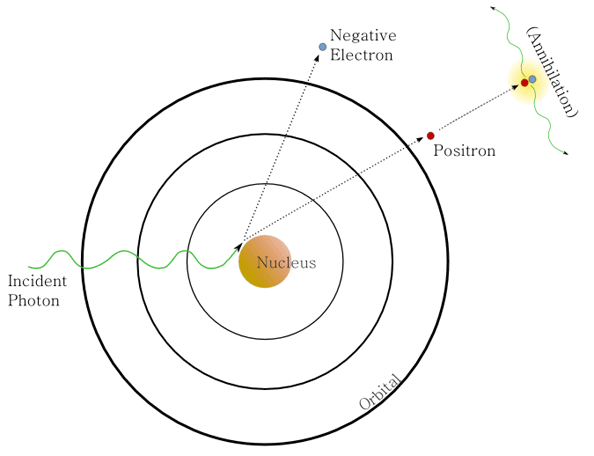
What type of interaction is shown?
pair production
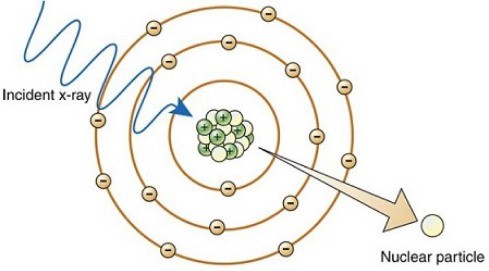
What type of interaction is shown?
photodisintegration