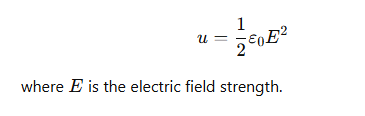15- Lenz's law and inductance
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is Lenz’s Law?
An induced current always acts to oppose the change that produced it.
How does Lenz’s Law help determine the sign of induced emf?
It ensures that the induced current flows in a direction that opposes the change in magnetic flux.
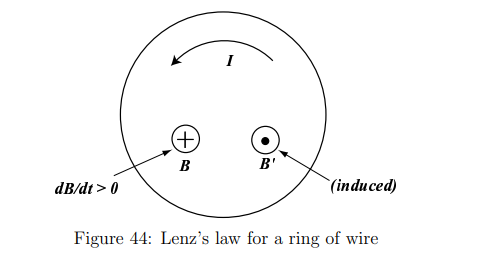
What happens when a magnetic field B(t) through a ring increases?
The induced current generates a magnetic field B’ opposite to B, reducing the change.
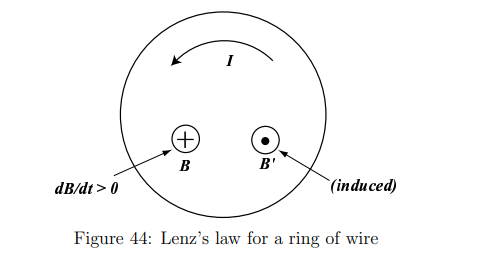
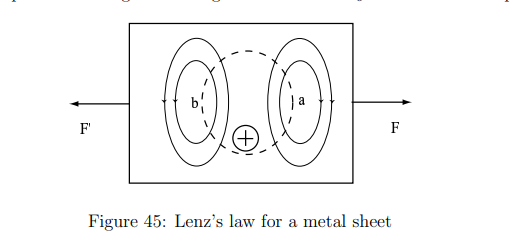
What happens when a metal plate moves through a magnetic field?
Where metal enters the field: The induced currents create a field opposite to the increasing B0.
Where metal exits the field: The induced currents create a field parallel to B0, opposing the decrease.
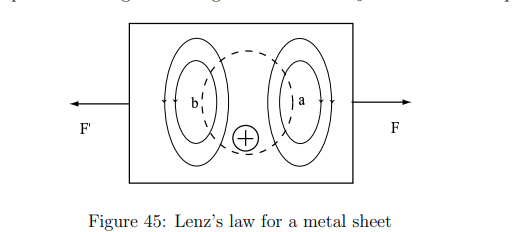
How does Lenz’s Law relate to forces on moving conductors?
The induced currents interact with the magnetic field, producing a force opposing the motion.
What is the magnetic field inside a long solenoid?
μ0 is the permeability of free space,
n is the number of turns per unit length,
I is the current.
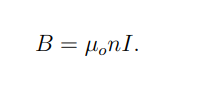
How do you calculate the magnetic flux through each turn of a solenoid?
A is the cross-sectional area.
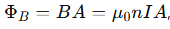
What is the back emf induced in a solenoid?
b is the solenoid length.
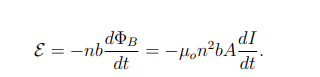
What is the definition of self-inductance?
It is the ratio of back emf to the rate of change of current:
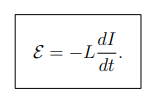
What is the formula for the inductance of a long solenoid?
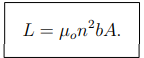
How is energy stored in an inductor similar to energy stored in a capacitor?
Just as energy is stored in the electric field of a capacitor, energy is stored in the magnetic field of an inductor.
What equation describes the conservation of energy in a circuit with an inductor and resistor?
VL is the voltage across the inductor
VR is the voltage across the resistor.
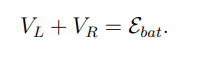
What is the total energy stored in an inductor?
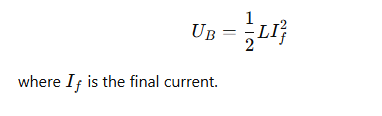
What is the energy density (energy per unit volume) of a magnetic field?
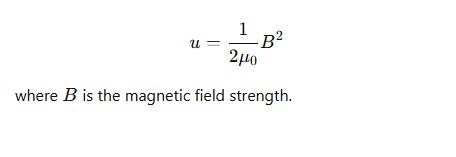
What is the analogous energy density formula for an electric field?