Rates of reaction
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is meant by ‘rate of reaction’?
The rate of a chemical reaction is how fast reactants are turned into products.
What equations could you use to find the rate of reaction?
rate of reaction = amount of reactant used/ time (how quickly the reactants are used up)
rate of reaction = amount of product formed/ time (how quickly products are formed)
What are the three ways to measure rate of reaction?
measure the volume of gas given off in a certain amount of time
[if a gas is one of the products like CO2, not H2] measure the decrease in mass as the gas is given off
[reactions that make the solution go cloudy] measure the amount of light they allow through, it will decrease as the reaction goes on
What is the collision theory?
It is that reactions can only take place when the particles that make up the reactants come together. The particles cannot just bump into each other, instead, they must collide with enough energy to react.
The energy needed for particles to react is the activation energy.
What is the activation energy?
It is the minimum amount of energy that colliding particles must have before they react.
What are the 2 ways that will make it more likely for a reaction to happen or for the rate of reaction to increase?
Increasing the frequency of reacting particles colliding with each other
Increasing the amount of energy they have when they collide
What are the 4 factors that affect rate of reaction?
surface area of a solid
concentration of solution or pressure of gas
temperature
use of catalyst
Describe the effect of surface area of a solid on the rate of a reaction.
Increasing the surface area of a solid reactant, increases the rate of reaction.
For example, break up the solid into smaller pieces to increase the rate of reaction. Because that increases the number of collisions between reactants per second. (increasing collision frequency, increases rate of reaction)
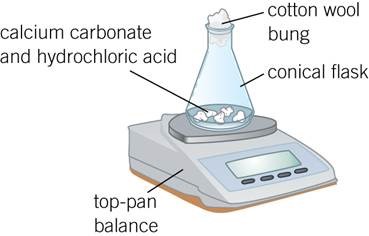
Describe the 2 experiment to show the effect of changing surface area of a solid on the rate of reaction.
Both experiments should use the comparison of large and small chips of calcium carbonate.
Measuring the loss in mass as the CO2 escapes
Measure 25 cm3 of 1.0 mol/dm3 hydrochloric acid using a 25 cm3 measuring cylinder and pour it into a 250 cm3 conical flask.
Weigh out 1.00 g of calcium carbonate using a weighing boat.
Place the conical flask on a top-pan balance, quickly add the calcium carbonate to the acid in the flask, and put a piece of cotton wool loosely in the mouth of the flask.
Immediately start the clock and record the total mass: this is the mass at t = 0.
Record the mass at 30-s intervals until there is no further change in mass.
Plot a graph of total mass in g (y-axis) against time in seconds (x-axis) and draw a best fit line through the points.
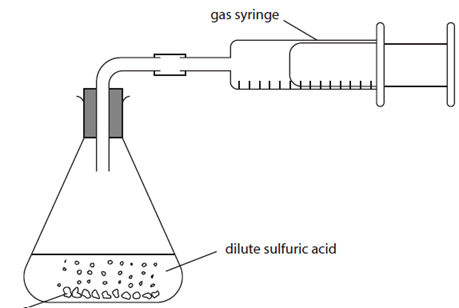
Measuring the volume of gas (CO2) produced
Measure 25 cm3 of 1.0 mol/dm3 hydrochloric acid using a 25 cm3 measuring cylinder and pour it into a 250 cm3 conical flask.
Weigh out 1.00 g of calcium carbonate using a weighing boat.
Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram.
Add the calcium carbonate to the conical flask. Immediately connect the bung and start the clock
Record the volume at 20-s intervals until there is no further change in volume.
Plot a graph of total volume in cm3 (y-axis) against time in seconds (x-axis) and draw a best fit line through the points.
Describe the effect of concentration of a solution on the rate of a reaction.
Increasing the concentration of the reactants in a solution, increases the rate of reaction
This is because increasing the conc. increases the number of particles moving around in the same volume. So the more crowded they are, the more frequently collisions occur and so the rate of reaction increases.
Describe the effect of pressure of a gas on the rate of a reaction.
Increasing the pressure of a gas increases the rate of reaction
This is because the gas molecules are pushed closer together and so they collide more frequently, increasing the rate of reaction.
Describe the effect of temperature on the rate of a reaction.
Increasing the temperature always increases the rate of reaction.
This is shown by the collision theory, where increasing the temp, the particles gain kinetic energy, so they move faster and collide more frequently.
The collisions are more energetic and so a greater percentage of collisions have energy > activation energy.
Describe the effect of a catalyst on the rate of a reaction.
A catalyst speeds up the rate of reaction
This is because the use of a catalyst makes it so that a greater proportion of collisions are successful and have more energy > activation energy.
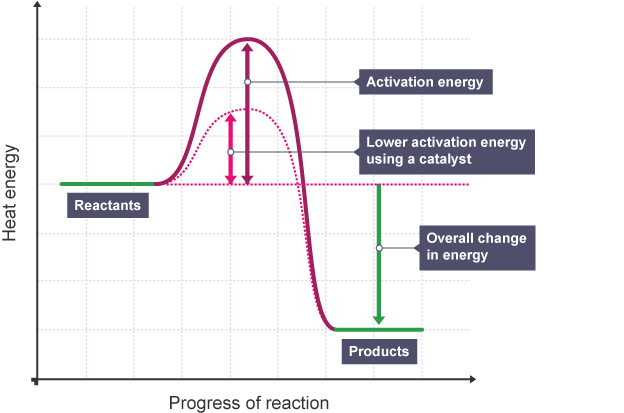
How does a catalyst work?
A catalyst works by providing a different reaction pathway with a lower activation energy so a greater proportion of collisions are successful.
Note that the catalyst itself does not take part in the reaction and so is chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction.
Describe a practical investigating the effect of different solids on the catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide solution.
Measure 25 cm3 of hydrogen peroxide using a measuring cylinder and add it to a conical flask
Add (1g) of catalyst A
Close it with a bung that has a gas syringe attached to it
Record the volume of gas produced in (30 s)
Repeat using different catalysts
The most effective catalyst produces the greatest volume of gas
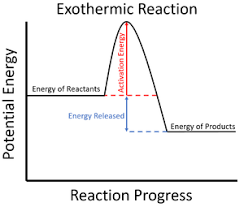
Explain a reaction profile of an exothermic reaction, showing ∆H and activation energy.
The overall energy change is negative.
Explain a reaction profile of an endothermic reaction, showing ∆H and activation energy.
The overall energy change is positive.
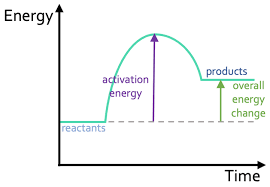
Explain a reaction profile of an exothermic reaction with a catalyst, showing ∆H and activation energy.
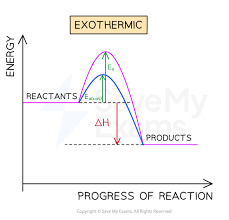
Explain a reaction profile of an endothermic reaction with a catalyst, showing ∆H and activation energy.