Bio Study Guide
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/157
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
1
New cards
x-axis
independent variable
2
New cards
y-axis
dependent variable
3
New cards
Purpose of Control Group
to have a standard for comparison
4
New cards
Constant
things that don't change (kept the same)
5
New cards
independent variable
a variable that is being changed
6
New cards
dependent variable
variable being measured
7
New cards
Hypothesis
testable statement, may be supported or refuted
written as an "if-then" statement
written as an "if-then" statement
8
New cards
Qualitative Data
categorical data
ex. (warm, blue, cold)
ex. (warm, blue, cold)
9
New cards
Quantitative Data
direct measurements, numerical data
ex. (temp. time)
ex. (temp. time)
10
New cards
Inorganic Molecules
building blocks of organic compounds
11
New cards
Organic Molecules
make up living organisms
- contain carbon
- contain carbon
12
New cards
Dehydration Synthesis Reaction
when water is removed during the formation of a polymer
(taking out H2O and making a protein)
(taking out H2O and making a protein)
13
New cards
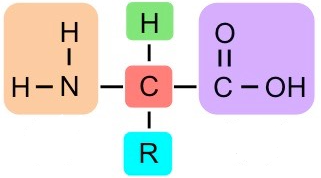
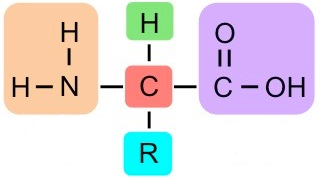
What group is in orange?
Amine Group
14
New cards
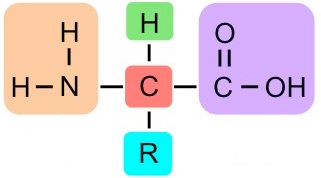
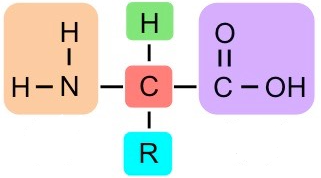
What group is in purple?
Carboxylic Acid
15
New cards
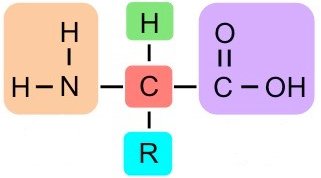
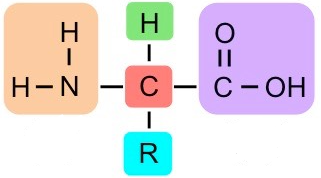
What is the "R"?
Radical
16
New cards
What 2 groups are identical in every amino acid?
Amine group and carboxylic acid group
17
New cards
What is a radical?
Why is it important?
Why is it important?
Radicals determine which amino acid is formed
They're the one part in an amino acid that's different
They're the one part in an amino acid that's different
18
New cards
What two products are produced during the formation of a peptide bond?
Protein and water
19
New cards
Polypeptide
chain of amino acids
20
New cards
Between which two parts of the amino acids are peptide bonds formed?
Between amine group and carboxylic acid group
21
New cards
Carboxylic Acid
COOH
carbon, oxygen, oxygen, hydrogen
carbon, oxygen, oxygen, hydrogen
22
New cards
Amine Group
NH2
23
New cards
Molecule
consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
24
New cards
Single Bond
a sharing of one pair of valence electrons
(single covalent bond)
(single covalent bond)
25
New cards
Double Bond
the sharing of two pairs of valence electrons
(Double Covalent Bond)
(Double Covalent Bond)
26
New cards
Miller-Urey Experiment
simulated early conditions thought to be on Earth
27
New cards
4 Macromolecules
carbohydrate
protein
lipid
nucleic acids
protein
lipid
nucleic acids
28
New cards
Nucleic Acid
(DNA & RNA)
made up of chains of nucleotides (sugar, phosphate, and nitrogen base)
made up of chains of nucleotides (sugar, phosphate, and nitrogen base)
29
New cards
Proteins
made up of chains of amino acids
30
New cards
Lipid
fatty acid chain
found in cell membrane of all living things
found in cell membrane of all living things
31
New cards
Carbohydrates
chains of sugar molecules
used as primary energy source for cells
used as primary energy source for cells
32
New cards
Polymerization
bonding smaller molecules together to make bigger molecules
33
New cards
What had to be present for life to form?
1) Simple, organic molecules such as amino acids
2) complex organic molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids
2) complex organic molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids
34
New cards
Current Theory About Origin of First Life Forms
1) chemical evolution
2) polymerization
3) microsphere formation
4) protocell and prokaryote formation
2) polymerization
3) microsphere formation
4) protocell and prokaryote formation
35
New cards
Chemical Evolution
building organic molecules from inorganic molecules
36
New cards
Microspheres
long chains of complex organic molecules eventually formed a circle around a water droplet
37
New cards
Protocells and Prokaryotes
small chains of nucleic acids became trapped in the sphere creating a protocell
this eventually developed into a prokaryote
this eventually developed into a prokaryote
38
New cards
Characteristics of 1st life
- single celled
- prokaryotic
- chemotrophic (fed of chemicals)
- anaerobic
- prokaryotic
- chemotrophic (fed of chemicals)
- anaerobic
39
New cards
Characteristics of Life
- made of cells
- reproduce
- obtain and use energy
- maintain homeostasis
- pass on traits
- respond to environment
- grow and develop
- reproduce
- obtain and use energy
- maintain homeostasis
- pass on traits
- respond to environment
- grow and develop
40
New cards
Spontaneous Generation
idea that life could come from nonliving things
41
New cards
Biogenisis
living things only come from other livings things
42
New cards
Eyepiece
10x magnification
43
New cards
Endosymbiotic theory
how eukaryote cells could have evolved from prokaryote cells
44
New cards
Prokaryotes
no nucleus
no membrane bound organelles
no membrane bound organelles
45
New cards
Eukaryotes
nucleus
membrane bound organelles
membrane bound organelles
46
New cards
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have these in common
cell membrane
cytoplasm
ribosomes
genetic material
cytoplasm
ribosomes
genetic material
47
New cards
Mutualism
a symbiosis where both organisms benefit
48
New cards
Evidence for Endosymbiotic Theory
1) Mitochondria and Chloroplast have their own DNA
2) size of mitochondria and chloroplast tend to be same size as bacteria
3) when mitochondria and chloroplast divide, they divide similarly to how bacteria divides
2) size of mitochondria and chloroplast tend to be same size as bacteria
3) when mitochondria and chloroplast divide, they divide similarly to how bacteria divides
49
New cards
Leeweunhoek
made his own microscope and discovered bacteria
50
New cards
Hooke
first to call cells cells
saw cells in a cork
saw cells in a cork
51
New cards
Shleiden
All plants are made of cells
52
New cards
Schwann
all animals are made of cells
53
New cards
Virchow
All cells come from other cells
54
New cards
Scientific Name
genus - species
55
New cards
Heterotroph
cannot produce its own food
56
New cards
Autotroph
produces its own food
57
New cards
Nucleus
aids in production of ribosomes
stores DNA
stores DNA
58
New cards
Vacuole
storage area of cell and breaks down cell waste
can take upto 90% of a cell's volume (in plant cells)
can take upto 90% of a cell's volume (in plant cells)
59
New cards
Lysosomes
filled with enzymes that digest substances
60
New cards
Cell Membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
61
New cards
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
contains enzymes that catalyze many reactions
contains enzymes that catalyze many reactions
62
New cards
Vesicles
carries proteins and lipids from golgi apparatus to other cell compartments or from outside the cell membrane into the cell
63
New cards
Cytoskeleton
moves structures within cell
helps divide during mitosis
maintains shape
acts as tracks for vesicles to move along
helps divide during mitosis
maintains shape
acts as tracks for vesicles to move along
64
New cards
Mitochondria
produces ATP
65
New cards
Free Ribosomes
produce proteins
66
New cards
Golgi Apparatus
modifies and sorts proteins and lipids that have been synthesized in the cell
67
New cards
Endoplasmic Recticulum
involved in production of lipids and proteins that will either becomes part of the cell membrane or be released from the cell
68
New cards
Cell Wall
provides support and protection outside the cell membrane
69
New cards
Chloroplast
during photosynthesis it uses the sun's energy, water and carbon dioxide to produce sugars and oxygen
70
New cards
Nucleolus
makes ribosomes
71
New cards
Not in common between animal and plant cells
plant - cell wall, chloroplast, one large vacuole
Animal - lysosomes, many small vacuoles
Animal - lysosomes, many small vacuoles
72
New cards
Modern Cell Theory
- cell is the smallest living unit in all living organisms
- all living things area made up of cells
- all cells come from preexisting cells
- all living things area made up of cells
- all cells come from preexisting cells
73
New cards
What does the cell membrane do?
- protects and supports the cell
- helps maintain homeostasis
- regulates amount of vital substances in the cell
- helps maintain homeostasis
- regulates amount of vital substances in the cell
74
New cards
Polar Heads
hydrophilic (water loving), unequal sharing of electrons among atoms
75
New cards
Nonpolar Tails
hydrophobic (water fearing), equal sharing of electrons amount atoms
76
New cards
Simple Diffusion
does not require transport protein
moves with concentration gradient (high-low)
moves with concentration gradient (high-low)
77
New cards
Facilitated Diffusion
requires transport protein
moves with concentration gradient
moves with concentration gradient
78
New cards
Selectively Permeable
allows some things to enter
79
New cards
Purpose of Proteins in Membrane
transport molecules across membrane
communicate with other cells
cell-to-cell recognition
enzymes
communicate with other cells
cell-to-cell recognition
enzymes
80
New cards
Passive Transport
movement of molecules with concentration gradient
requires no energy
requires no energy
81
New cards
Diffusion
movement of molecules from high to low concentration
82
New cards
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
83
New cards
Solute
dissolved substance
84
New cards
Solvent
dissolving substance
85
New cards
Hypertonic
higher concentration of solute outside the cell
water leaves cell
(cells will shrivel up)
water leaves cell
(cells will shrivel up)
86
New cards
Hypotonic
lower conc of solute outside cell
water moves into cell
(animal cell will lyse (burst)) (normal for plants (turgid))
water moves into cell
(animal cell will lyse (burst)) (normal for plants (turgid))
87
New cards
Isotonic
equal conc of solutes
(normal for animal cells) (plant cell wilts (flaccid))
(normal for animal cells) (plant cell wilts (flaccid))
88
New cards
Active Transport
low conc -> high conc
requires ATP
requires ATP
89
New cards
Bulk Transport
(endocystosis)
when cells ingest large particles, membrane folds inward and pinches off, material is enclosed in a vesicle, transported to lysosome for digestion
(exocytosis)
vesicles fuse with membrane, releasing contents
when cells ingest large particles, membrane folds inward and pinches off, material is enclosed in a vesicle, transported to lysosome for digestion
(exocytosis)
vesicles fuse with membrane, releasing contents
90
New cards
Pinocytosis
solutes or fluids
(endocytosis)
("drinking")
(endocytosis)
("drinking")
91
New cards
Phagocytosis
large particles, cells
(endocytosis)
("eating")
(endocytosis)
("eating")
92
New cards
Enzymes
catalyze chemical reactions that synthesize large biological molecules
93
New cards
Denature
lose their shape
can't catalyze
can't catalyze
94
New cards
Reactant
substance changed by reaction
95
New cards
Product
substance made by reaction
96
New cards
Bond Energy
amount of energy that will break a bond between two atoms
97
New cards
Chemosynthesis
deep in ocean in hydrothermal vents
produce food
use iron and other chemicals
produce food
use iron and other chemicals
98
New cards
ATP
adenosine triphosphate
99
New cards
ADP
Adenosine diphosphate
100
New cards
Photosynthesis reactants
sun energy, CO2, H2O