lecture 1: examination and diagnosis of the endocrine system
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
1. Eyes and eyebrows
2. Skin changes
3. Hands and nails
4. Hair
things to assess in general endocrine exam
-eye changes: fundoscopic eye changes, xanthoma
most significant change associated with primary hypercholesterolemia
•Hypothyroidism
•Nephrotic syndrome
•Pancreatitis
examples of secondary hyperlipidemias than present like primary hypercholesterolemia
A "xanthoma" is a general term referring to yellowish cholesterol deposits that can appear anywhere on the body, while "xanthelasma" is a specific type of xanthoma that exclusively appears on or around the eyelids, usually presenting as flat, yellowish plaque
what is the difference between xanthoma and xanthelasma?
xanthomas
yellow deposits of cholesterol in tendons and soft tissues
copper wiring
Retinal arteries develop increased light reflex w/ bright coppery luster. Become full & torturous; associated with fatty deposit, often found in conjunction with hypertension
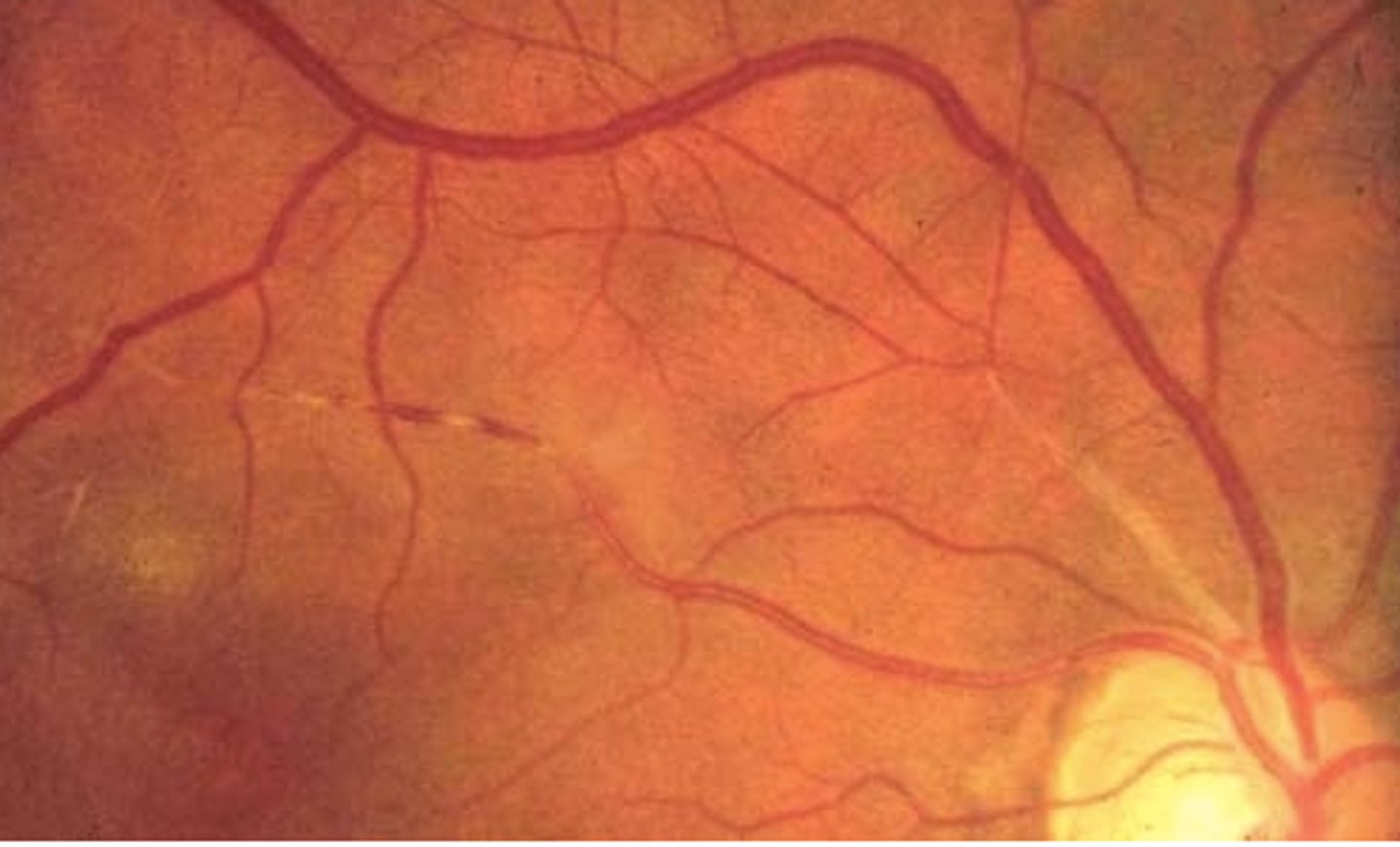
hypercholesterolemia with the infiltration of lipids into the vessel
in the elderly, copper wiring may be present with
•Hemorrhages
•Exudates
•Neovascularization
eye changes associated with type 2 DM
-Acanthosis nigricans
-candida ininfections
-diabetic dermopathy
skin changes associated with type 2 DM
•Decreased or absent light touch, temperature sensation, and proprioception
•Loss of deep tendon reflexes in ankles
neurologic changes associated with type 2 DM
•Dry
•Muscle atrophy
•Claw toes
•Ulcers
foot changes associated with type 2 DM
-mild visual changes, capillary leaks
-microaneurysms
-macular edema
-cotton wool spots
non proliferative and early fundoscopic changes associated with diabetes
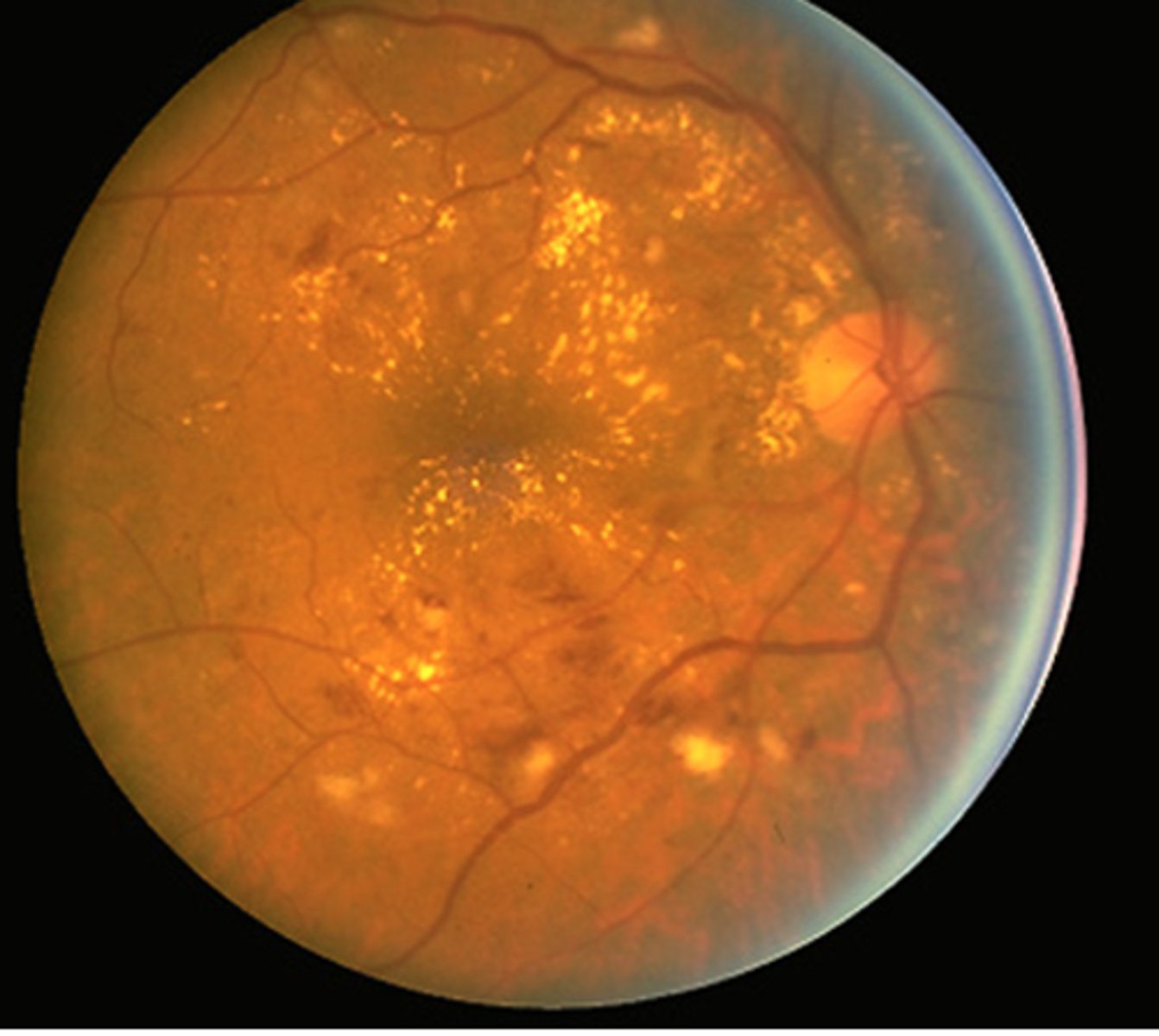
diabetic retinopathy!
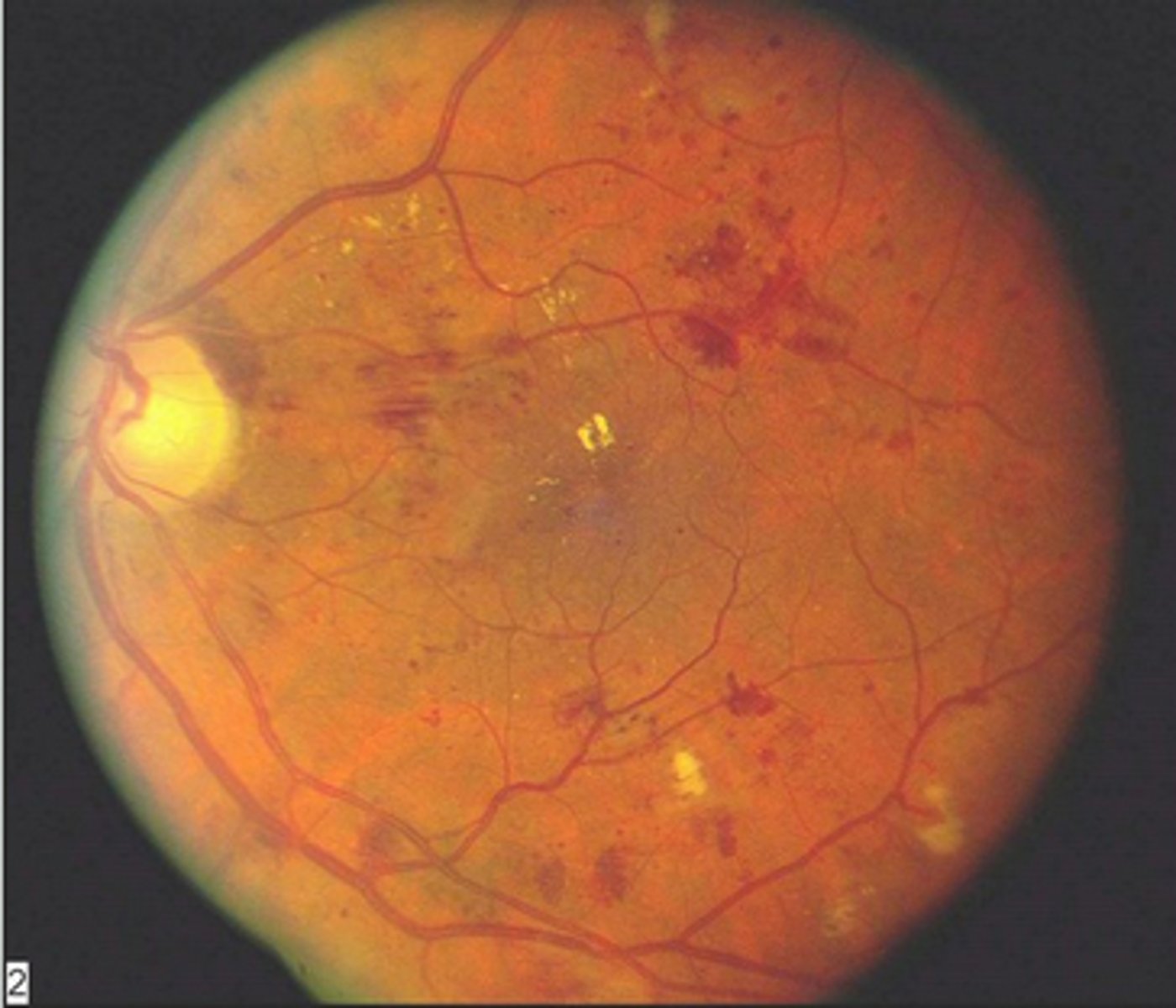
advanced disease, profound visual loss, nneovascularization, fragile vessels bleed
-retinal detachment
proliferative fundoscopic changes in diabetes
laser
treatment for the proliferative eye changes of diabetes
candida albicans
change associated with type 2 diabetes
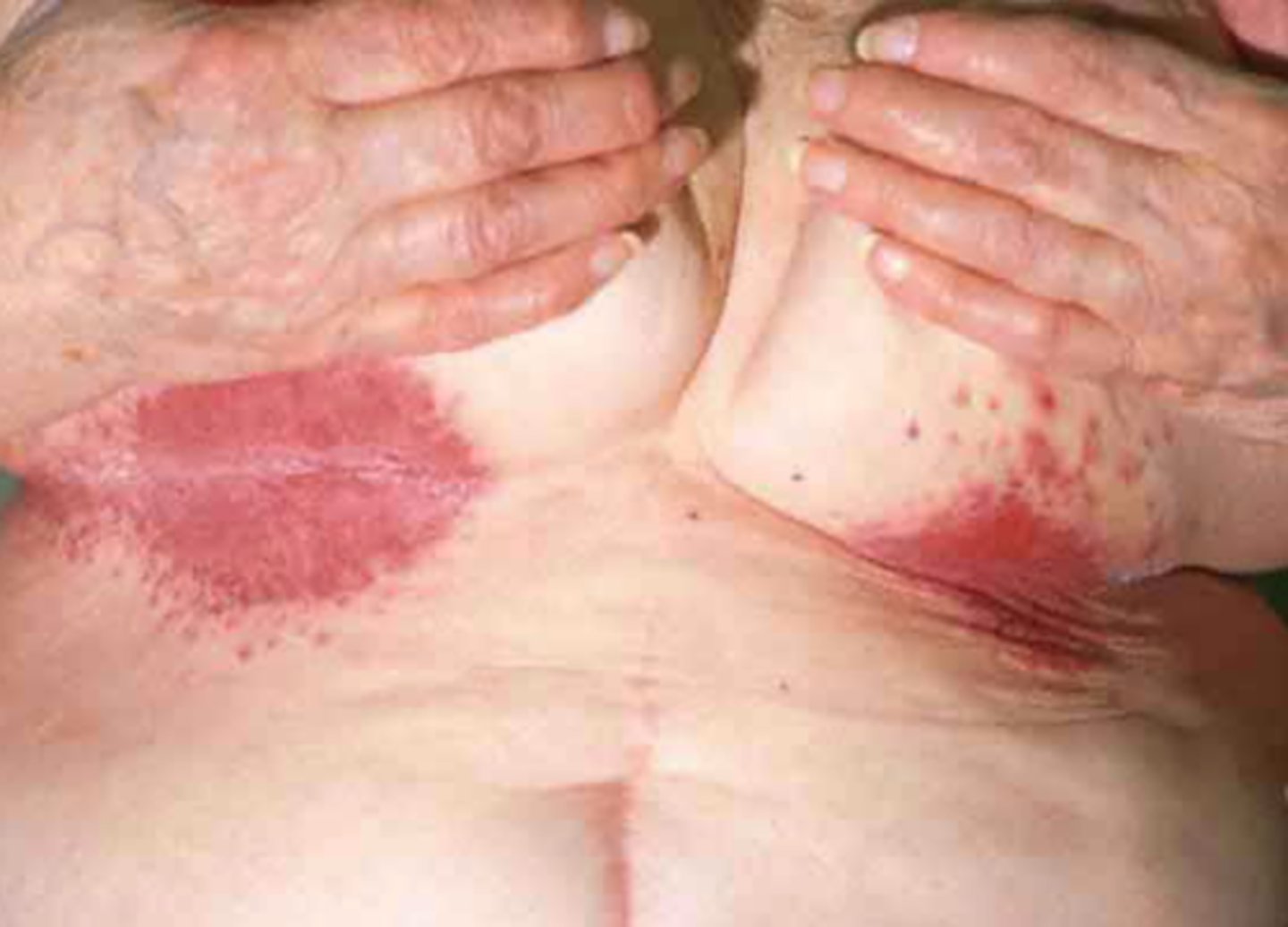
diabetic dermopathy
Most common
Red-brown, round or oval patches
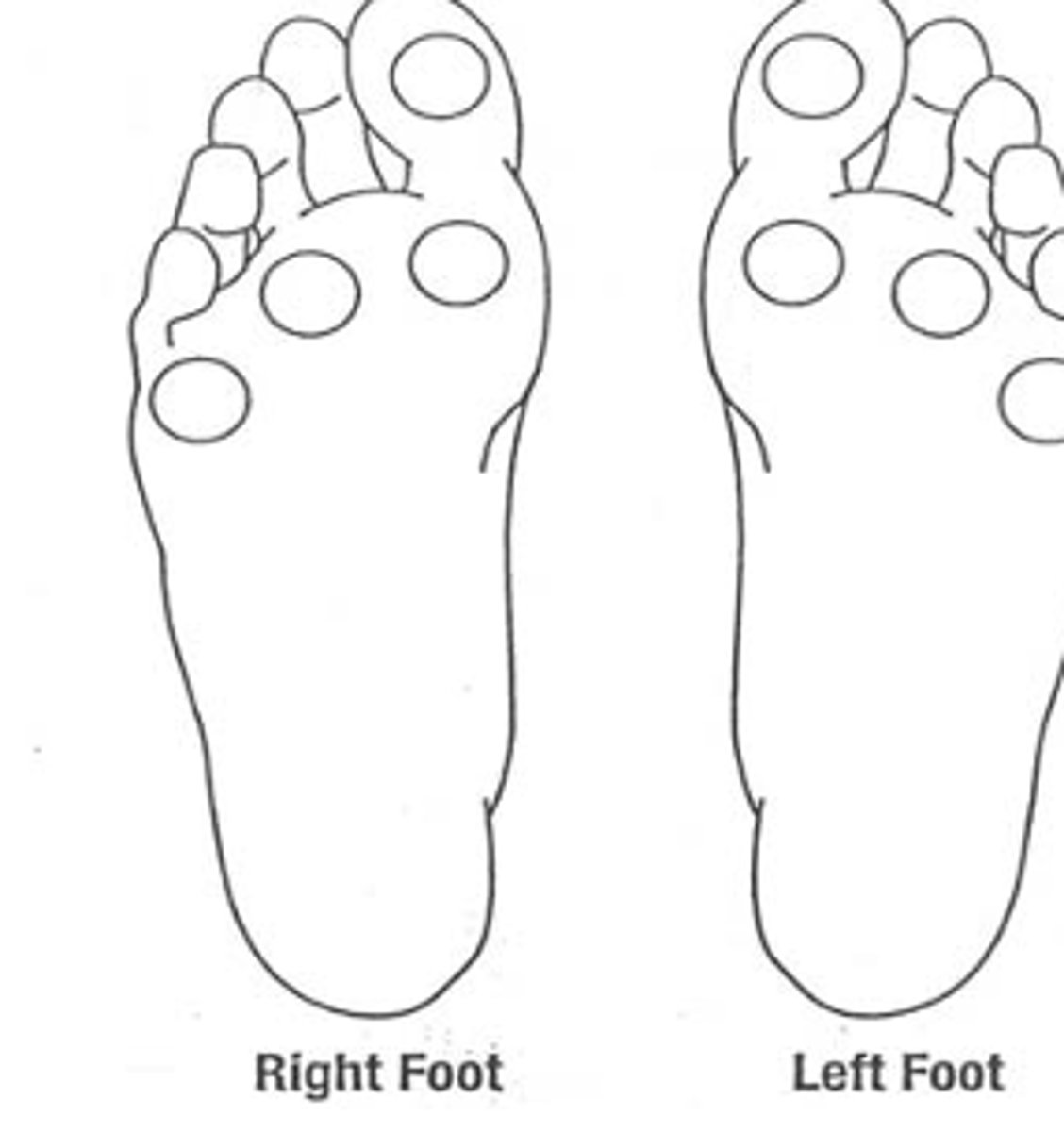
Semmes-Weinstein monofilament 5.07, apply 10 grams of force
tool to do monofilament testing
1. Have the patient close their eyes.
2. Test four sites on each foot in random sequence. Avoid scars, calluses, and ulcers.
3. Hold the 10-g MF perpendicular to the test site, and then bow it to a C-shape for one second.
4. grade pts response; total of 3 applications to each site
describe the procedure to do monofilament testing
vibratory testing
•Tuning fork more accurate in studies detecting diabetic peripheral neuropathy
•Vibratory testing picks up much earlier disease
best test for diabetic foot exam
1. Use only the 128-Hz tuning fork (TF).
2. Demonstrate the sensation of vibration and its differentiation from pressure by applying the TF either to the wrist or elbow during and after stopping vibration.
3. Ask the patient to close their eyes.
4. Test the dorsum of each hallux (first or great toe) just proximal to the nail bed. Place the index finger of the other hand beneath the patient's toe to feel the vibration and determine the accuracy of the patient's response. Apply the TF perpendicularly with a constant pressure.
5. Use an initial sham test on each foot by applying a non-vibrating TF to be sure the patient does not mistake the sensation of pressure for vibration: " Is the tuning fork vibrating?" The patient should answer, "No."
6. Use the "on-off" method to score the patient's response:
procedure of vibratory testing for diabetic foot exam
at least 5 incorrect responses
-score may be 0-8 based on testing each great toe twice for feeling beginning vibration and cessation
vibratory test finding diagnostic of peripheral neuropathy
•A normal 70-year-old detects vibration 10 seconds or more in the hallux
•15 seconds distal joint of the finger
vibratory testing findings of a normal 70 year old
•Younger patients detects vibration 15 seconds or more in hallux
•Up to 25 seconds in fingers
vibratory testing findings of a normal young patient
•Normal consistency is meaty or rubbery
normal consistency of the thyroid
sternocleidomastoid m.
thyroid lobes are covered largely by what muscle?
no-sometimes can be slightly
is the normal thyroid visible or palpable
•Normal neck position, then with neck extended, then extended while swallowing water
•The thyroid gland is fixed to the trachea and rises when swallowing
•Tangentially shine a light from the inferior border, observe trachea for deviation
steps to inspecting the thyroid
•Anterior and posterior
•Pull muscles aside when palpating laterally
•Flex neck forward to relax SCM
•Push and pull trachea to one side to palpate contralateral side
•Tilt head or rotate to the side and palpate
steps to palpating the thyroid
-thyroid enlargement can cause impingement--> bruits
-hyperthyroidism can cause systolic or continous bruit
why do we auscultate the carotids for bruits during a thyroid exam?
graves
soft thyroid indicates what pathology?
hashimoto's, malignancy
firm thyroid indicates what pathology?
Thyroiditis Types
tender thyroid indicates what pathology?
pregnancy
enlarged thyroid indicates what pathology?
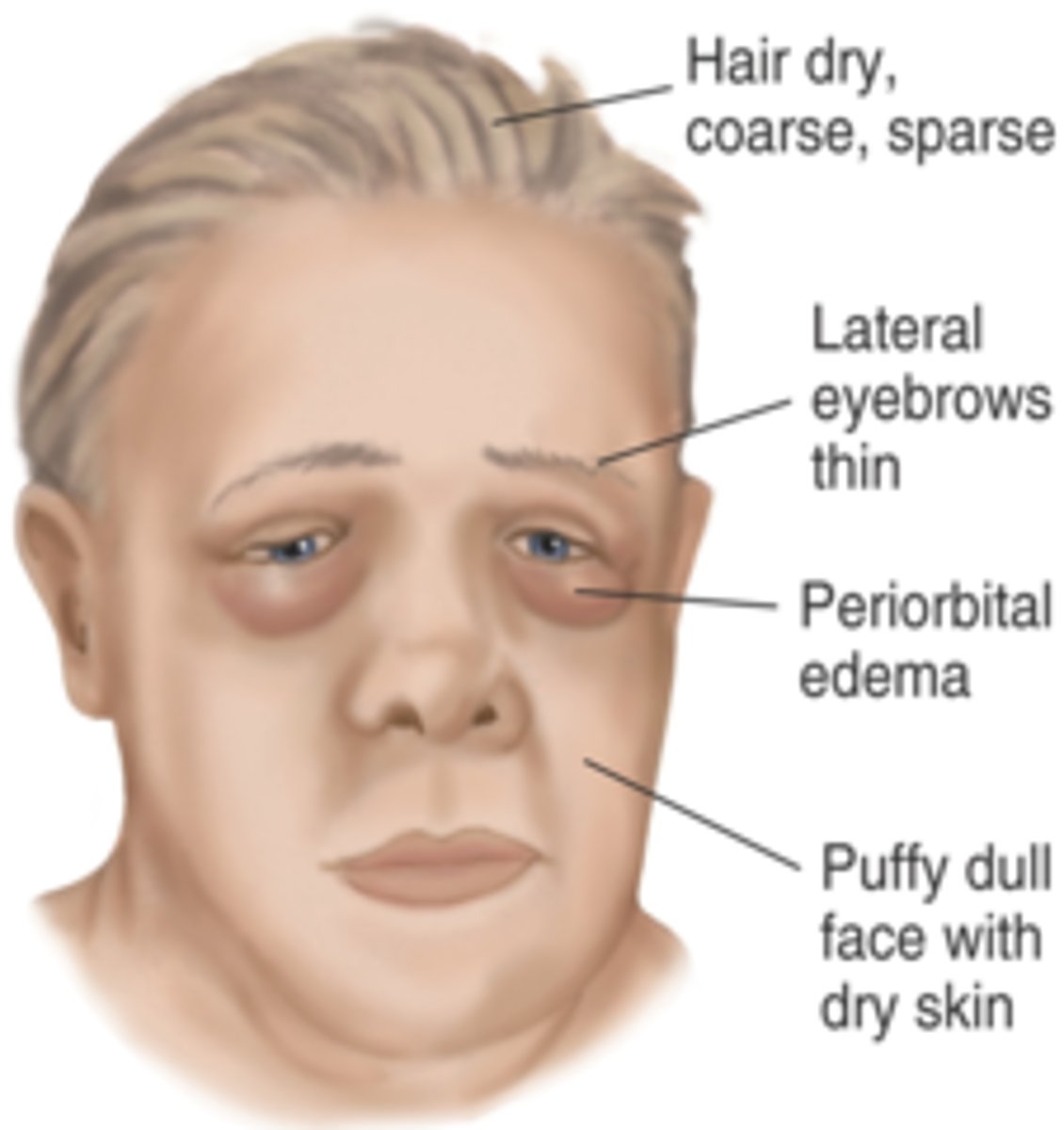
hypothyroidism
thinning hair, thick fingernails, hearing difficulty, infertility indicates
•Dry, rough, thick skin covered with fine superficial scales especially prominent over elbow, knees, and heels
•Pale, waxy, cool skin, sometimes with a yellow tinge
-brittle nails wth transverse striations
-lack of sweating
cutaneous manifestations of hypothyroidism
•Interstitial edema due to increased tissue osmotic pressure from mucopolysaccharide deposits, or from vasoconstriction, anemia, and defective conversion of β-carotene into vitamin A
-periorbital edema due to mucopolysaccharide deposition with increased osmotic effect annd fluid accumulation
pathophys of the edema associated with hypothyroidism
•Involving scalp, lateral third of eyebrows (non-specific), or generalized
•Generalized being more typical of secondary hypothyroidism but can be seen in either form
alopecia findings associated with hypothyroidism
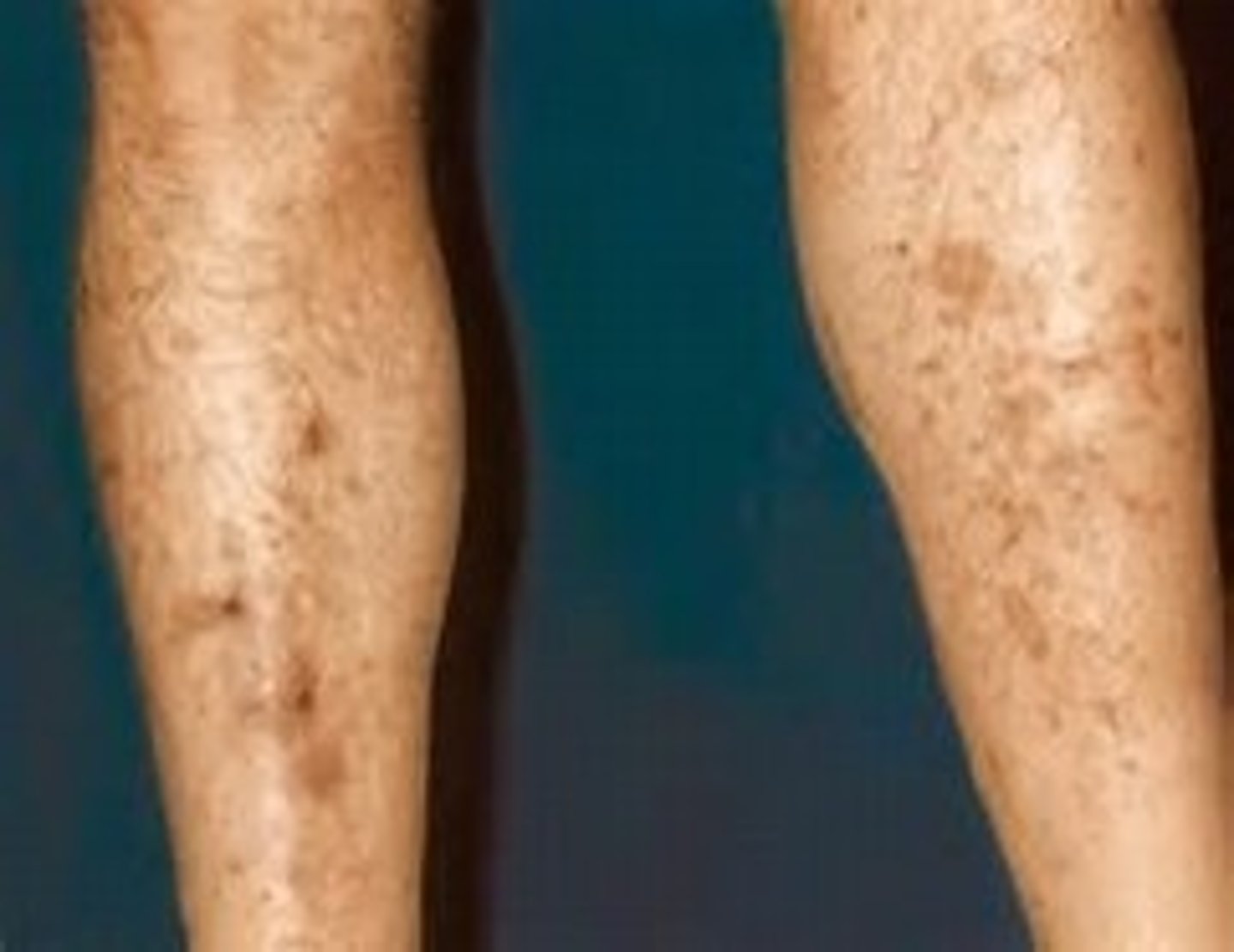
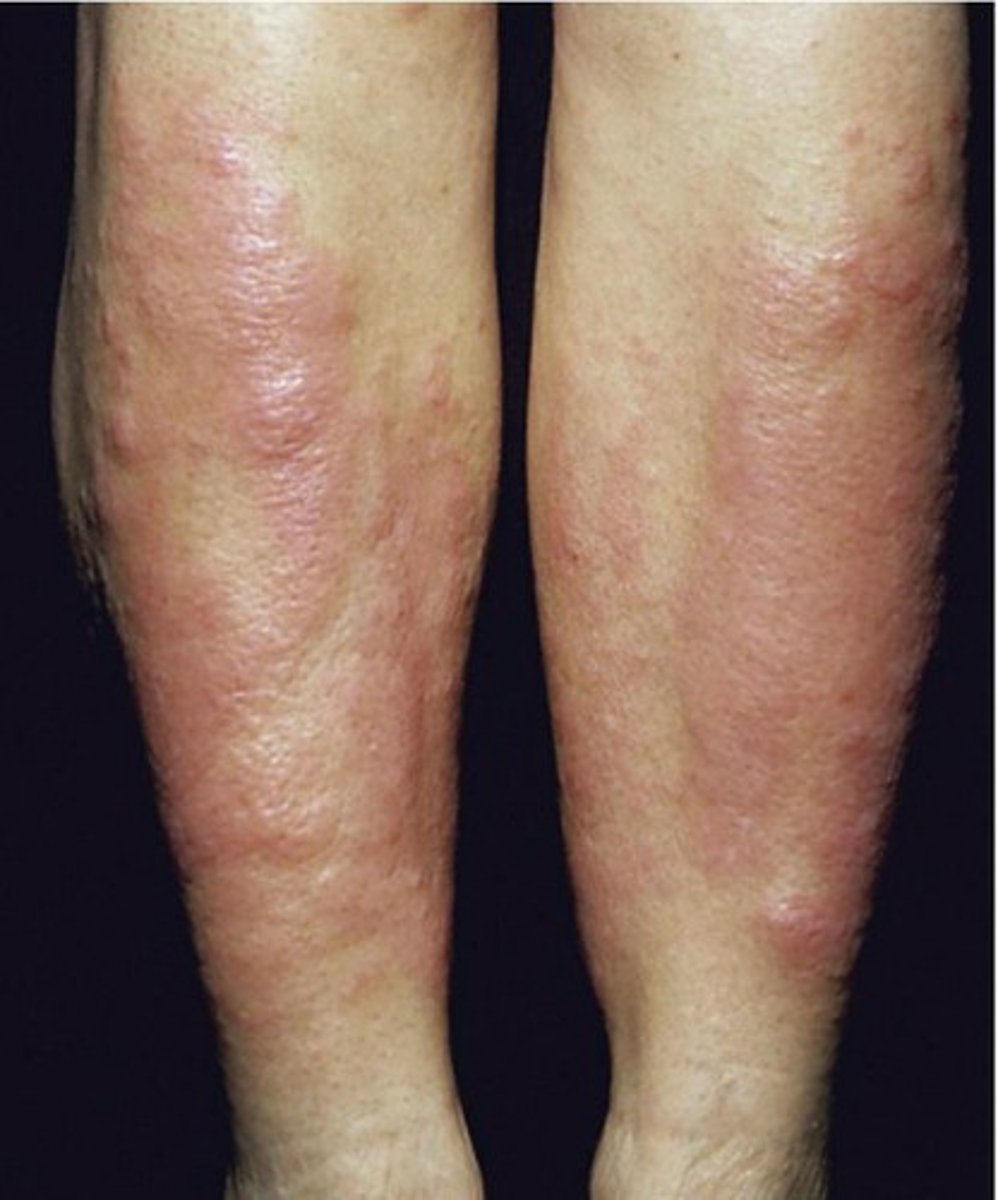
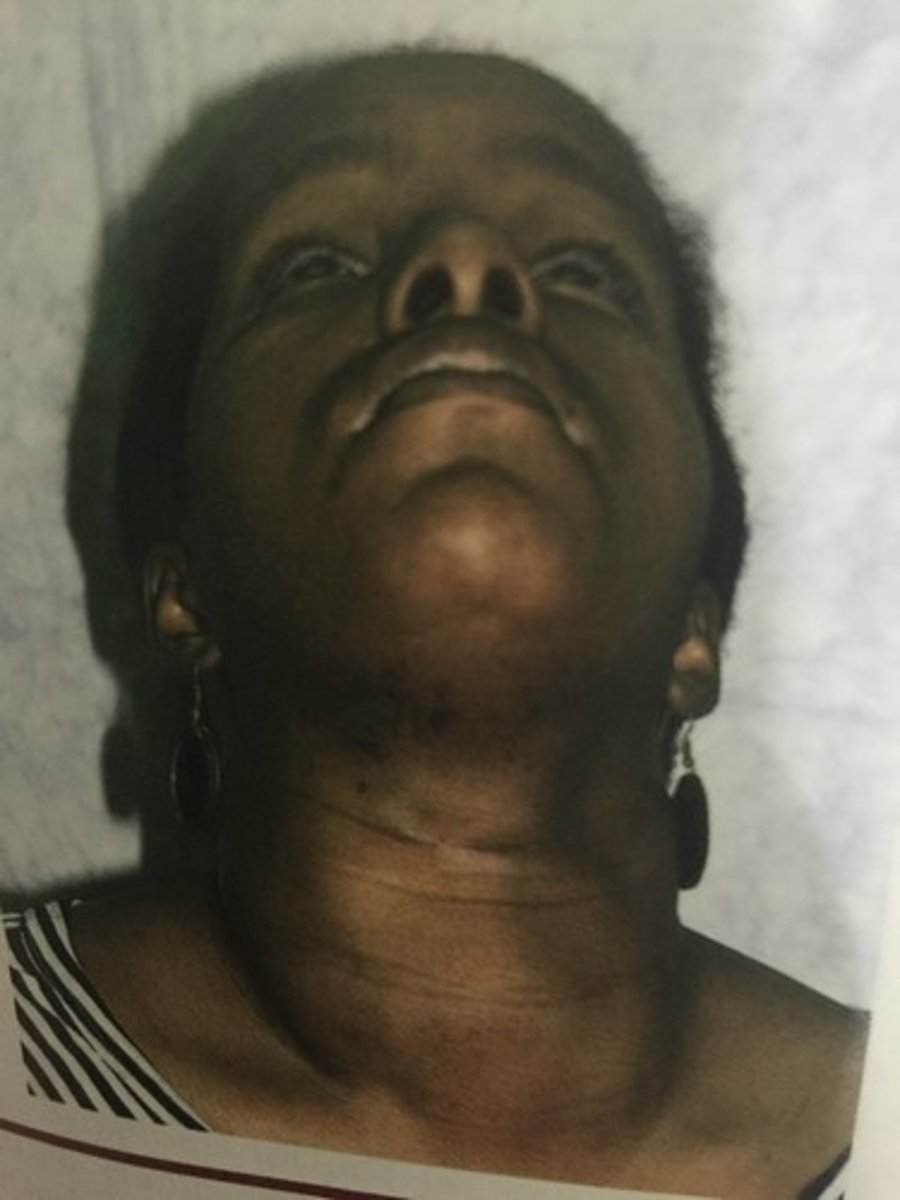
pretibial myxedema
Due to accumulations of mucopolysaccharides
Changes are reversible with thyroid hormone
hypothyroidism
Notice the bilateral ptosis, apathetic facies, and absent eyebrows indicating
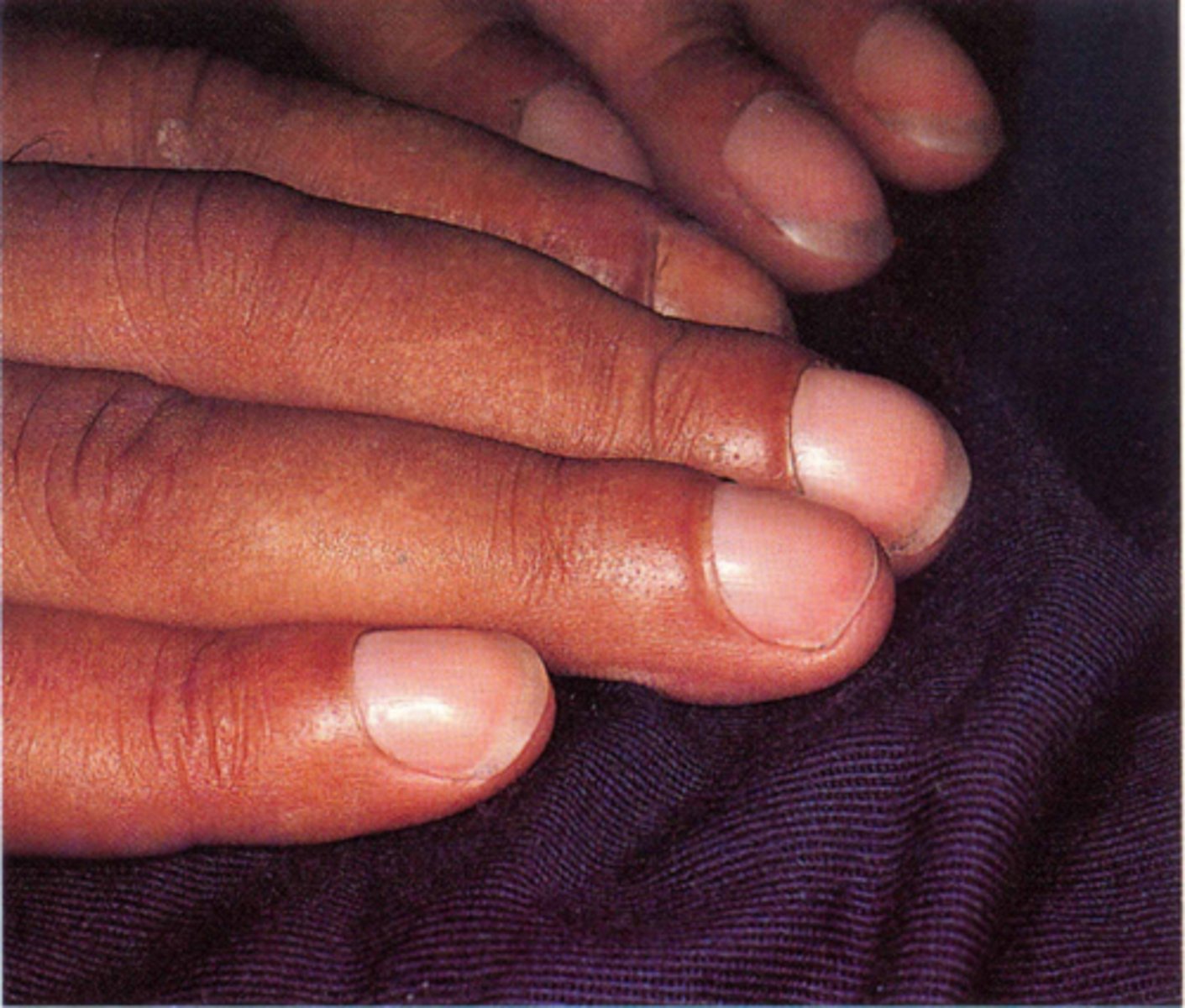
thyroid acropachy
•An uncommon condition associated with autoimmune dysfunction of the thyroid gland (as in Graves' disease) that is marked especially by swelling and clubbing of fingers and toes and periostitis of the hands and feet
periorbital edema, myxedema
clinical characteristics in both hypo and hyperthyroidism
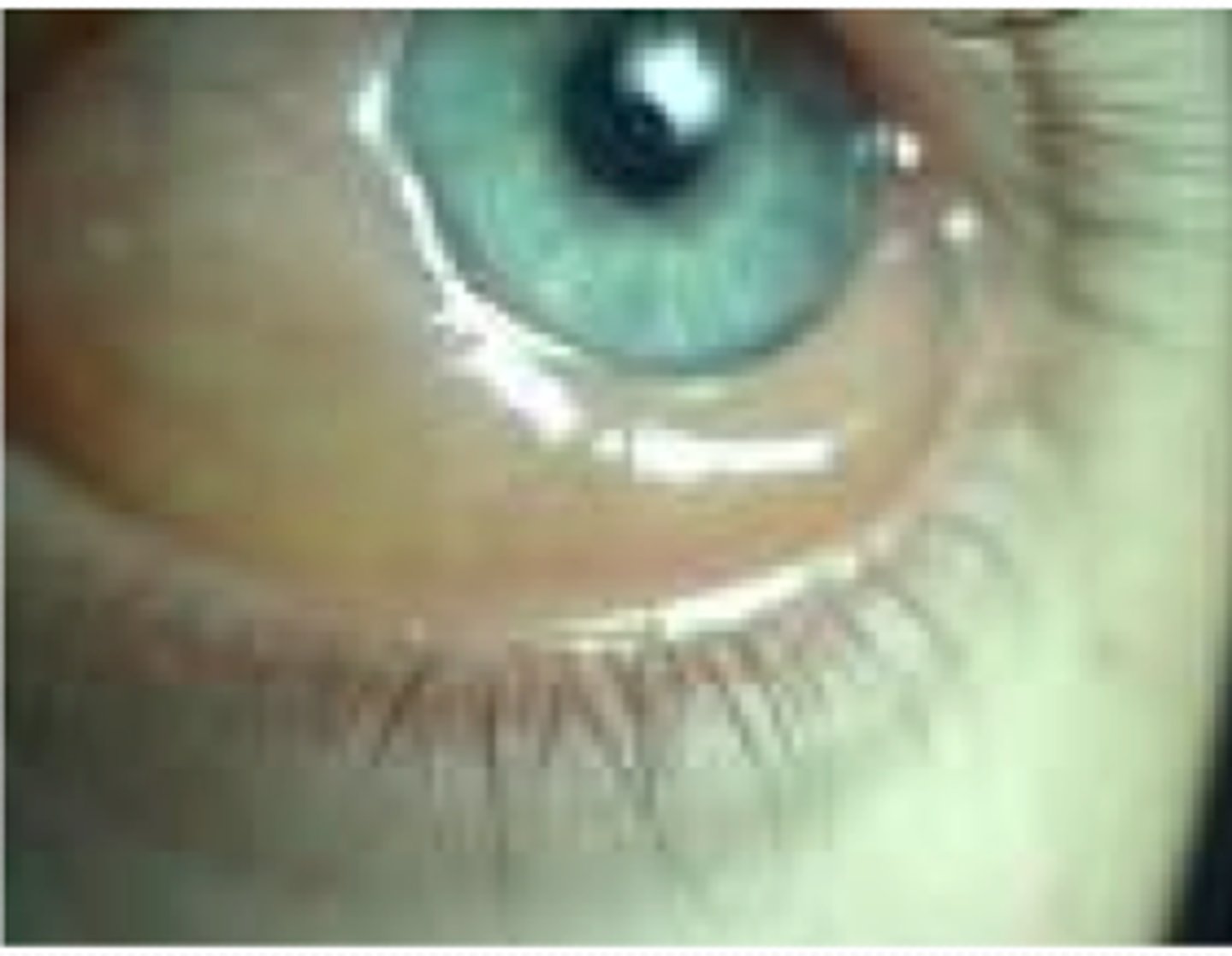
chemosis
•Swelling of the conjunctiva due to exudation from abnormally permeable capillaries; associated with hyperthyroidism
•Nonspecific sign of eye irritation
•The eyes may become difficult or impossible to fully close
•Measurement using prisms or special ruler (exophthalmometer)
OR
with sclera seen above iris
how do you measure lid retraction from proptosis
proptosis
sclera seen below iris indicates
lid retraction
lid intersects iris indicates
•Clubbing of fingers
•Painless
•Periosteal bone formation and periosteal proliferation
•Soft tissue swelling--> pigmented, hyperkeratotic
findings associated with thyroid acropachy
•Raised surface
•Thick, leathery consistency
•Nodularity (maybe)
•Sharply demarcated margins
•Prominent hair follicles
•Usually over pretibial area
•Non-tender
describe localized myxedema associated with hyperthyroidism
goiter in grave's disease
what do these thyroid findings indicate?
•Diffuse increase in thyroid gland size
•Soft to slightly firm
•Non-nodular
•Bruit and/or thrill
•Mobile
•Non-tender
•Without prominent adenopathy
multinodular goiter
nodular enlargement of the thyroid associated with hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism will have persistent problems with systolic hypertension and lid lag
-pheochromocytomas won't respond to beta blockers
what is the main clinical difference of hyperthyroidism and pheochromocytoma?
pheochromocytoma
•Spells or paroxysms of headache, severe hypertension with paradoxical responses to antihypertensives, severe unexplained orthostatic hypotension, palpitations, and diaphoresis
Conn's syndrome (primary hyperaldosteronism)
-autonomous aldosterone secretion, usually aldosteronoma
-hypernatremia with hypokalemia
-hypertensive with rare edema
-weakness, abdominal distension, ileus from hypokalemia
abnormal hair growth
define hirsutism
addison's disease
•Chronic adrenal insufficiency
•Complain of fatigue, weakness, and abdominal pain
•Severe cases, hypotension and coma
•Some have marked cravings of salt due to urinary loss
•Hyperpigmentation
•Hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, Na:K ratio <30:1
•ACTH elevated
•Diabetes mellitus
•Heart disease
•Hyperhydrosis
metabolic manifestations of acromegaly
•Bitemporal hemianopsia
•Bilateral loss of temporal vision due to pressure at optic chiasma
visual changes associated with acromegaly
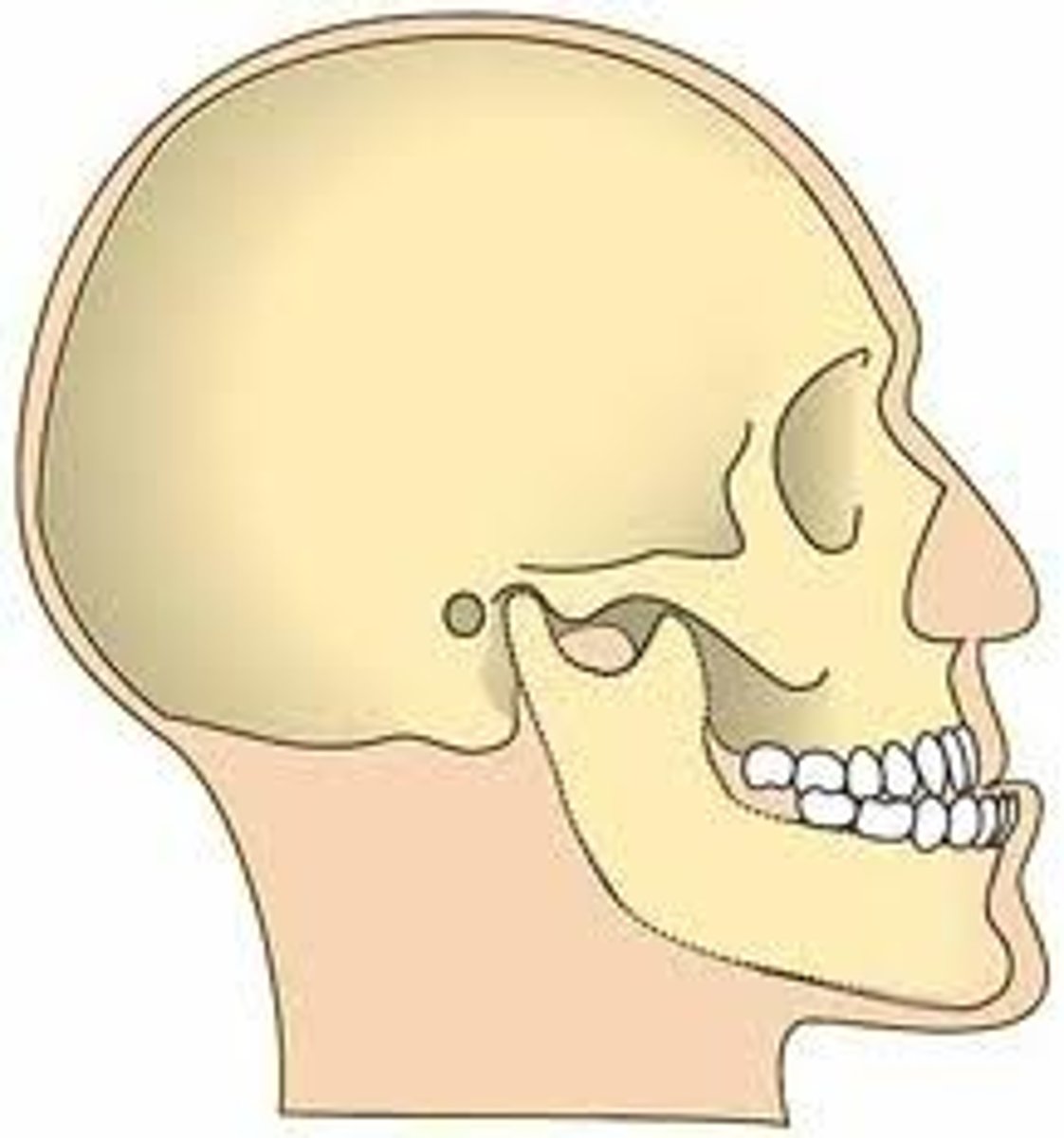
Prognathism
Projection of the jaw or jaws that may cause problems with mouth closure and alignment of the teeth. Associated with acromegaly
•Increased neuromuscular irritability
•Hyperreflexia
•Carpopedal spasm
•Hypotension and irregular heart rhythm
•Dry skin
•Ridged brittle nails
•Seizures, tetany, facial spasms, cramping, paresthesias
•Hyperactive bowel sounds, bronchospasm, laryngospasm
•Depression, slowed responses
manifestations of hypoparathyroidism
chvostek's sign
•Medical sign observed in patients with low calcium
•Increased neuromuscular irritability
•Tapping on cheek causes facial twitching
trousseau sign
carpopedal spasm induced when blood flow to the arm is occluded using a blood pressure cuff or tourniquet, causing ischemia to the distal nerves; suggestive sign for latent tetany in hypocalcemia
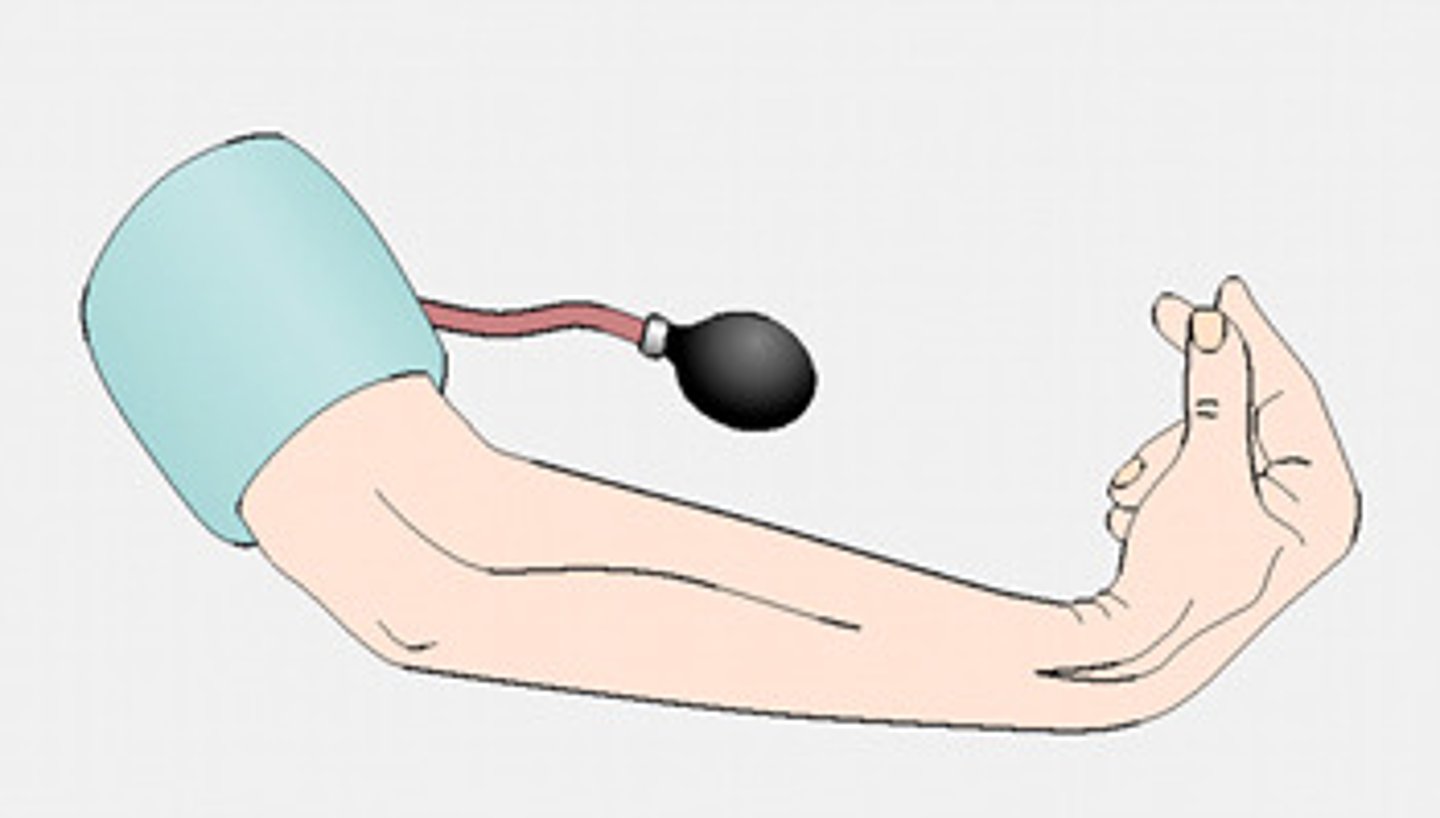
trousseau sign
•Medical sign observed in patients with low calcium
•May be positive before other manifestations of hypocalcemia such as hyperreflexia and tetany
•Believed to be more sensitive than Chvostek sign for hypocalcemia
-HTN and bradycardia
-abdominal pain
-muscle weakness: esp proximal, longstanding bony tenderness
-hyporeflexia
-tongue fasciculations
-band keratopathy
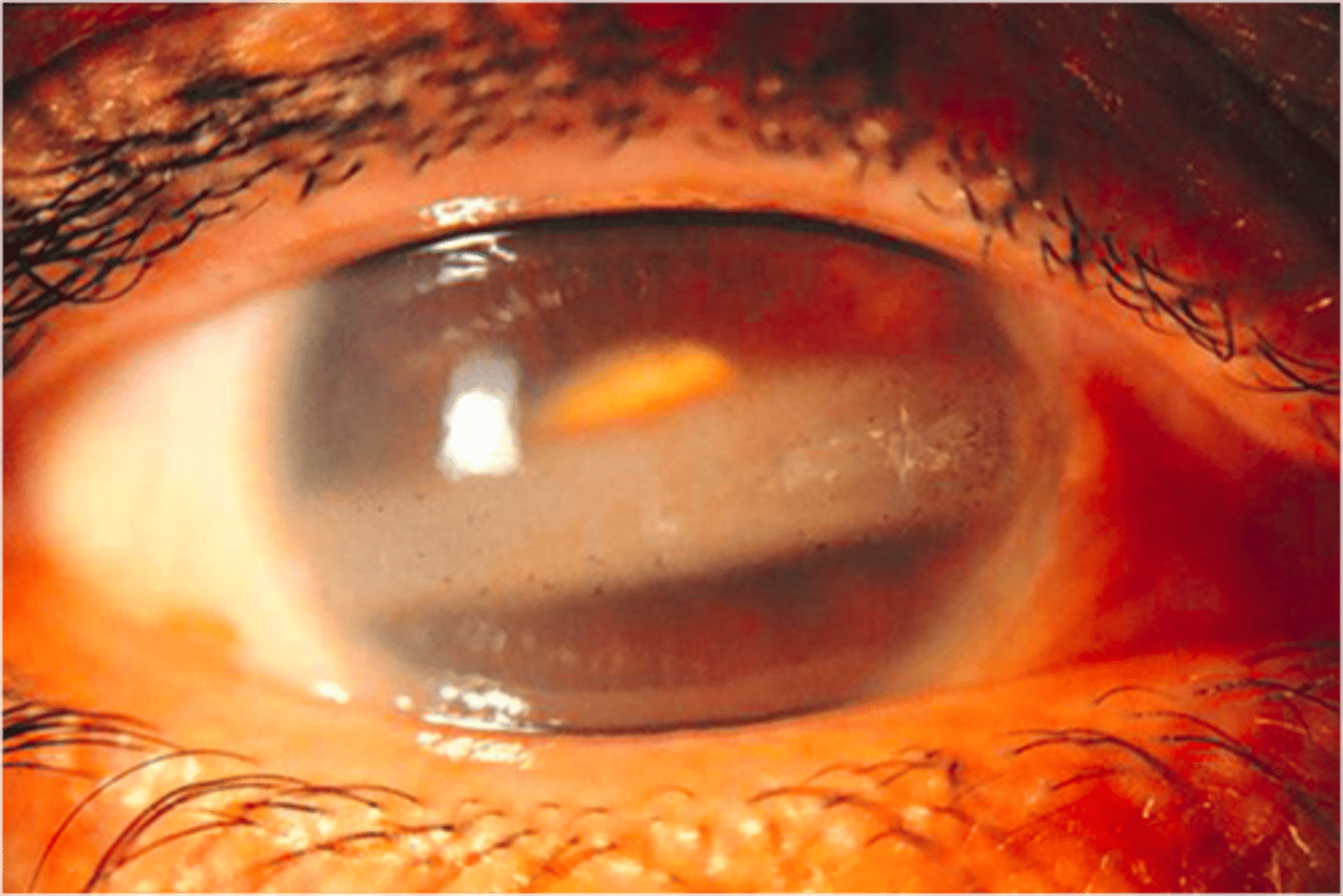
signs of hyperparathyroidism
band keratopathy
deposition of calcium in the superficial cornea, associated with hyperparathyroidism
check reflexes
neuro check associated with thyroid exam