Microeconomics (ECON-2023 UARK) Exam 2
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Consumer Surplus (CS)
the amount a buyer is willing to pay for a good minus the amount the buyer actually pays for it
Producer Surplus (PS)
the amount a seller is paid for a good minus the seller's cost
Willingness to Pay (WTP)
the maximum amount that a buyer will pay for a good
Willingness to Sell (WTS)
Minimum price the seller would voluntarily accept for the good.
What does WTP measure?
how much a buyer values a good
The amount a buyer saves when purchasing a good is their....
consumer surplus
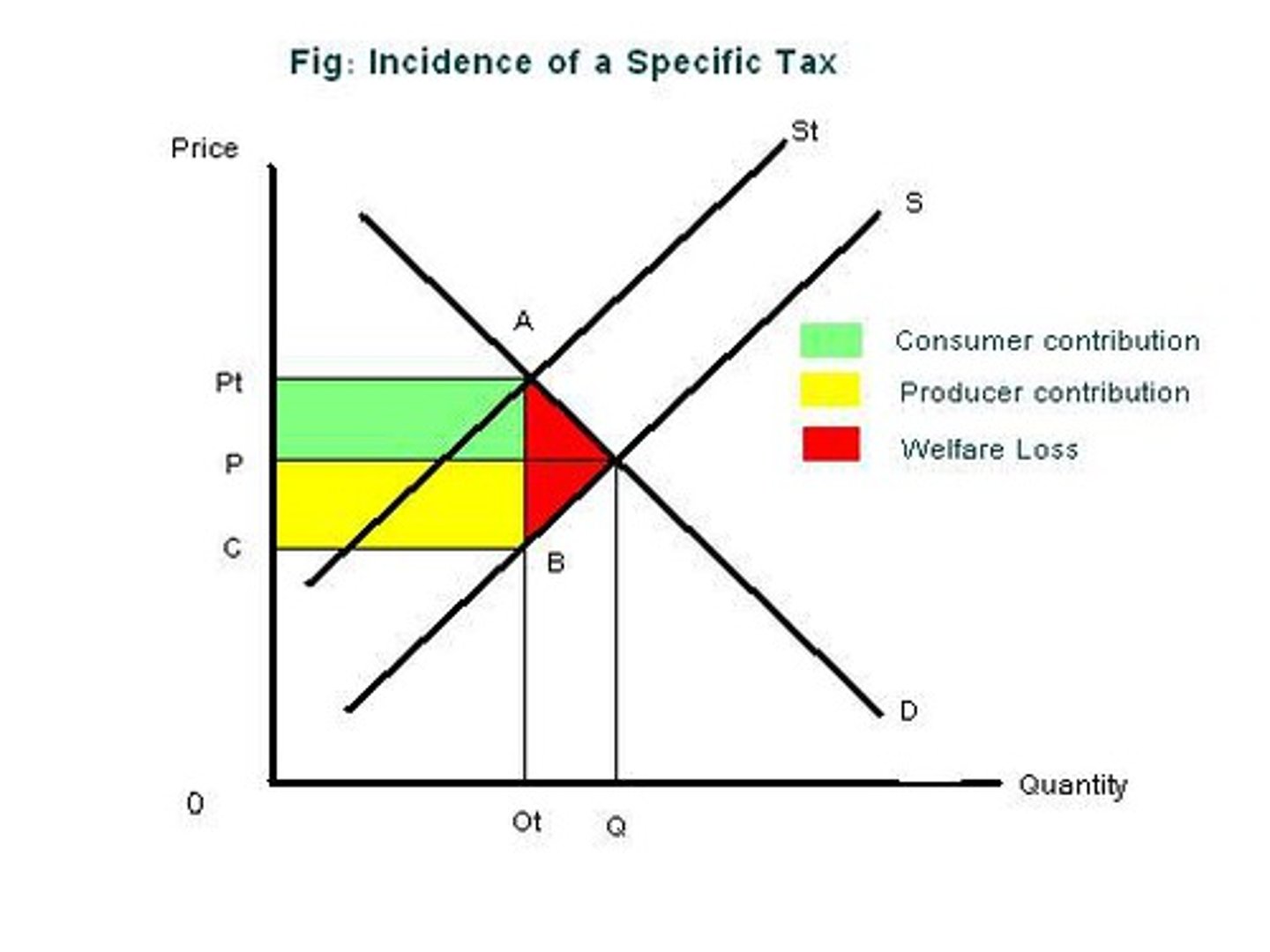
If a tax is levied on consumers...
some of the burden is passed to producers since the market price falls
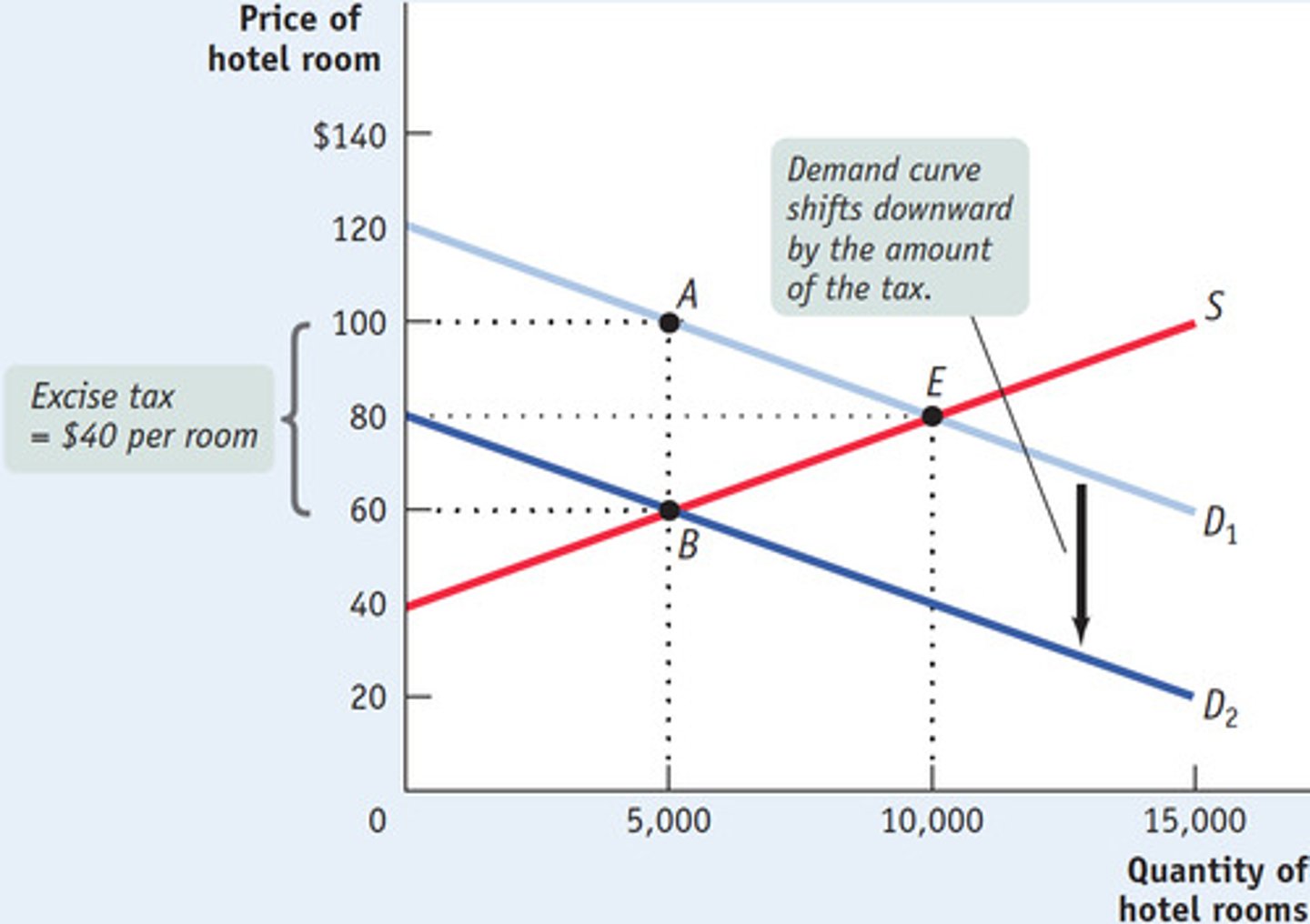
If a tax is levied on producers...
some of the burden is passed to consumers since the market price increases
Consumer surplus is measured with which curve?
demand curve
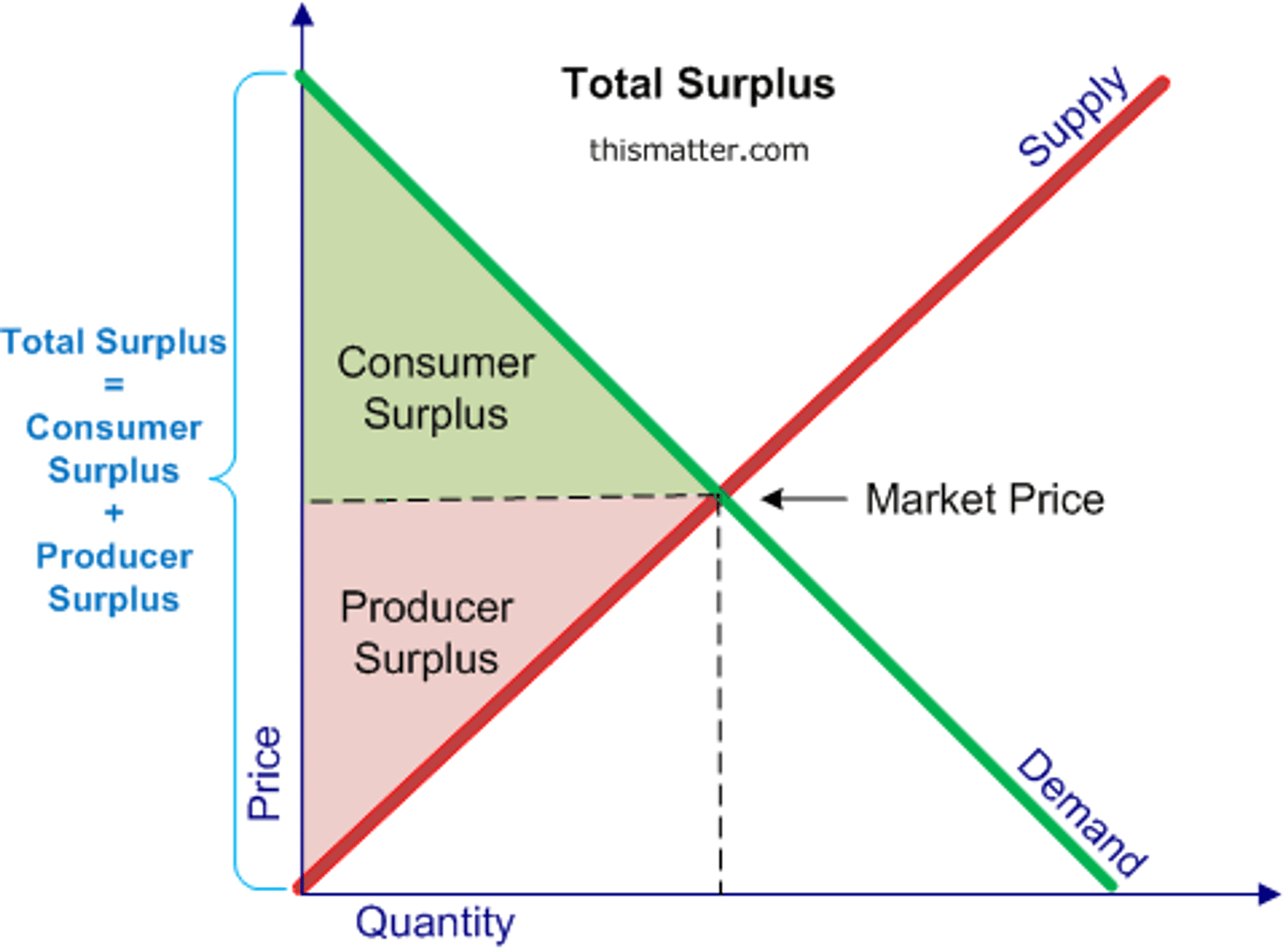
Producer surplus is measured with which curve?
supply curve
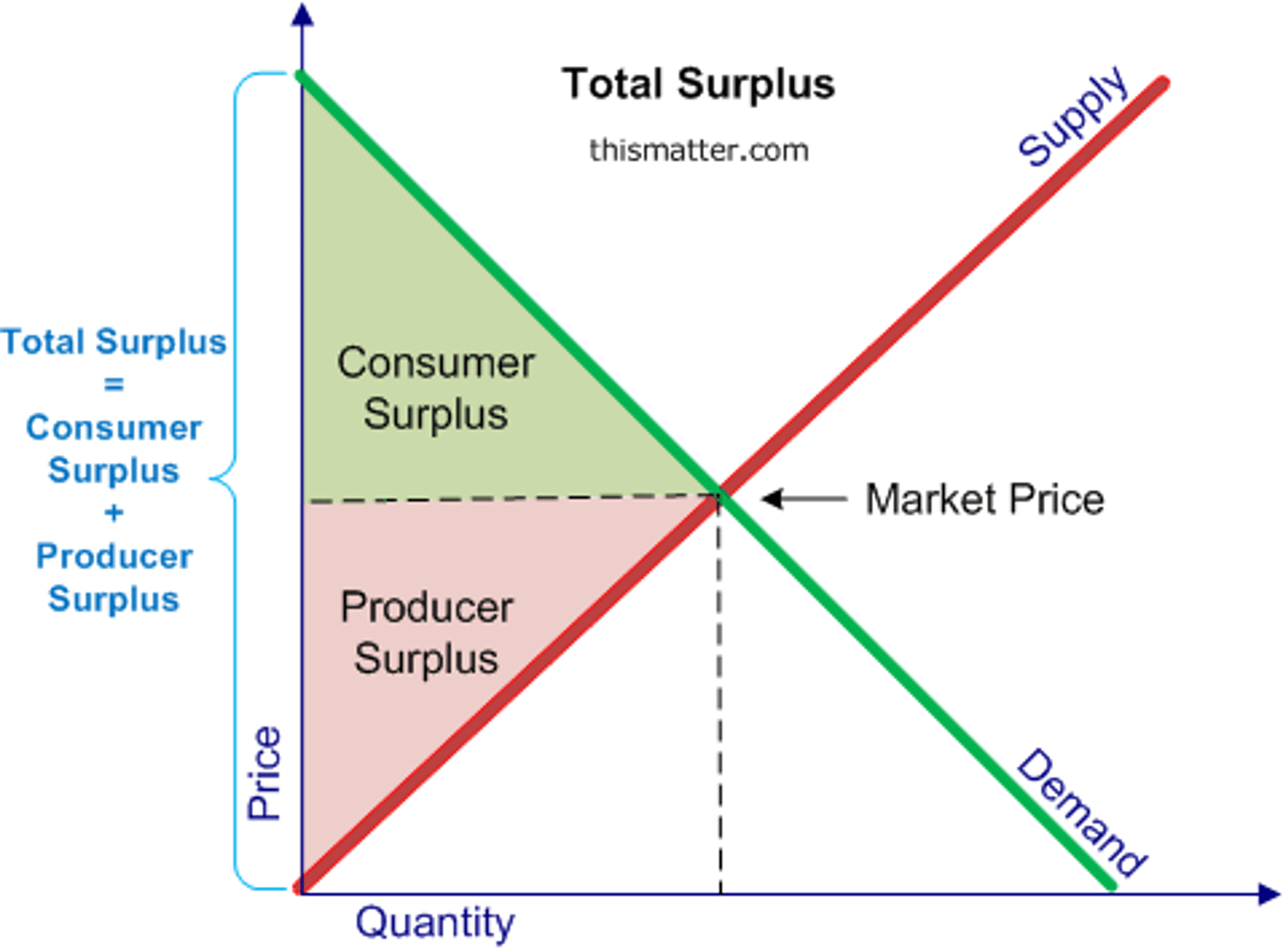
Where on the graph is consumer surplus?
The area below the demand curve and above the price measures the CS.
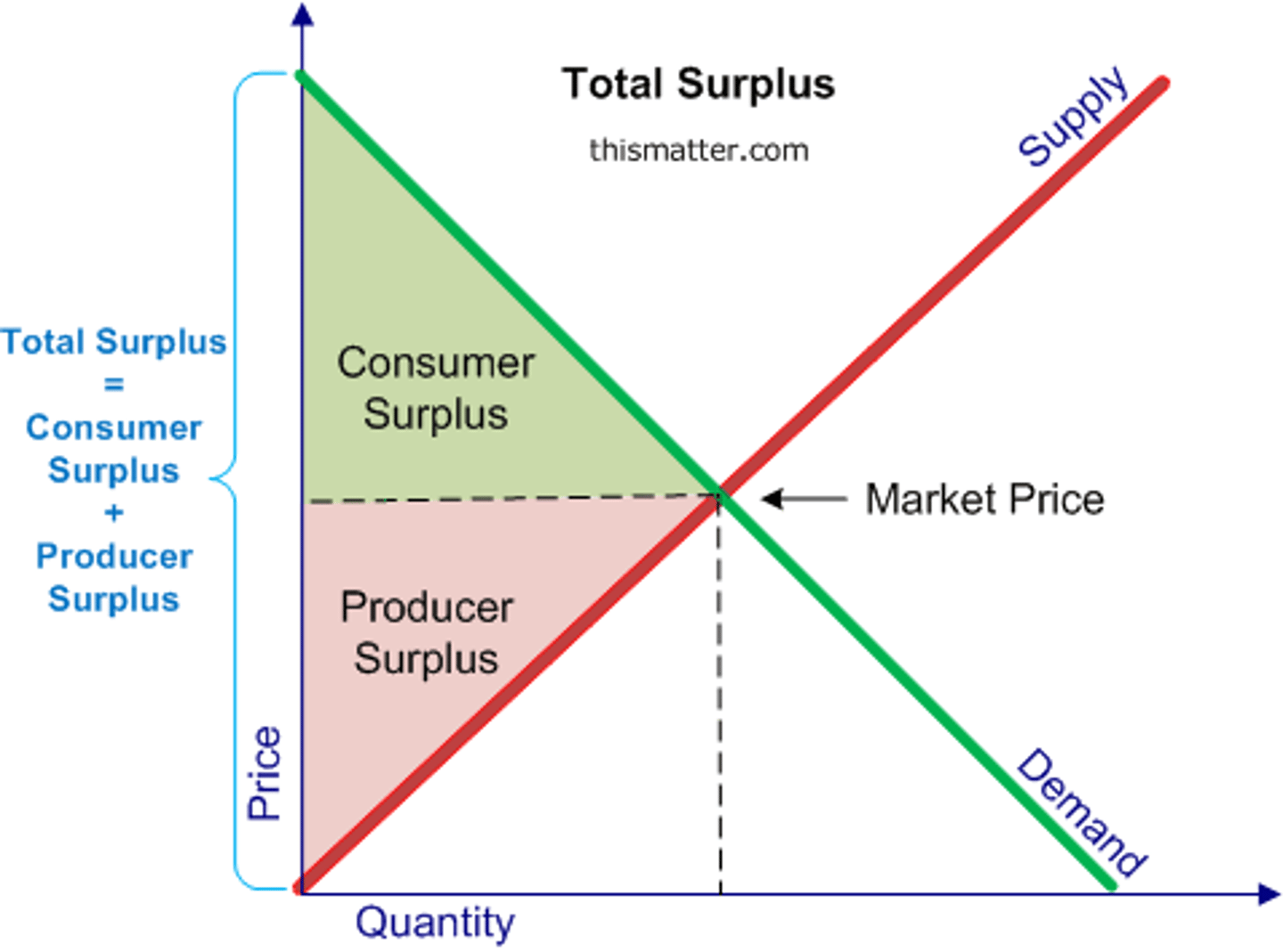
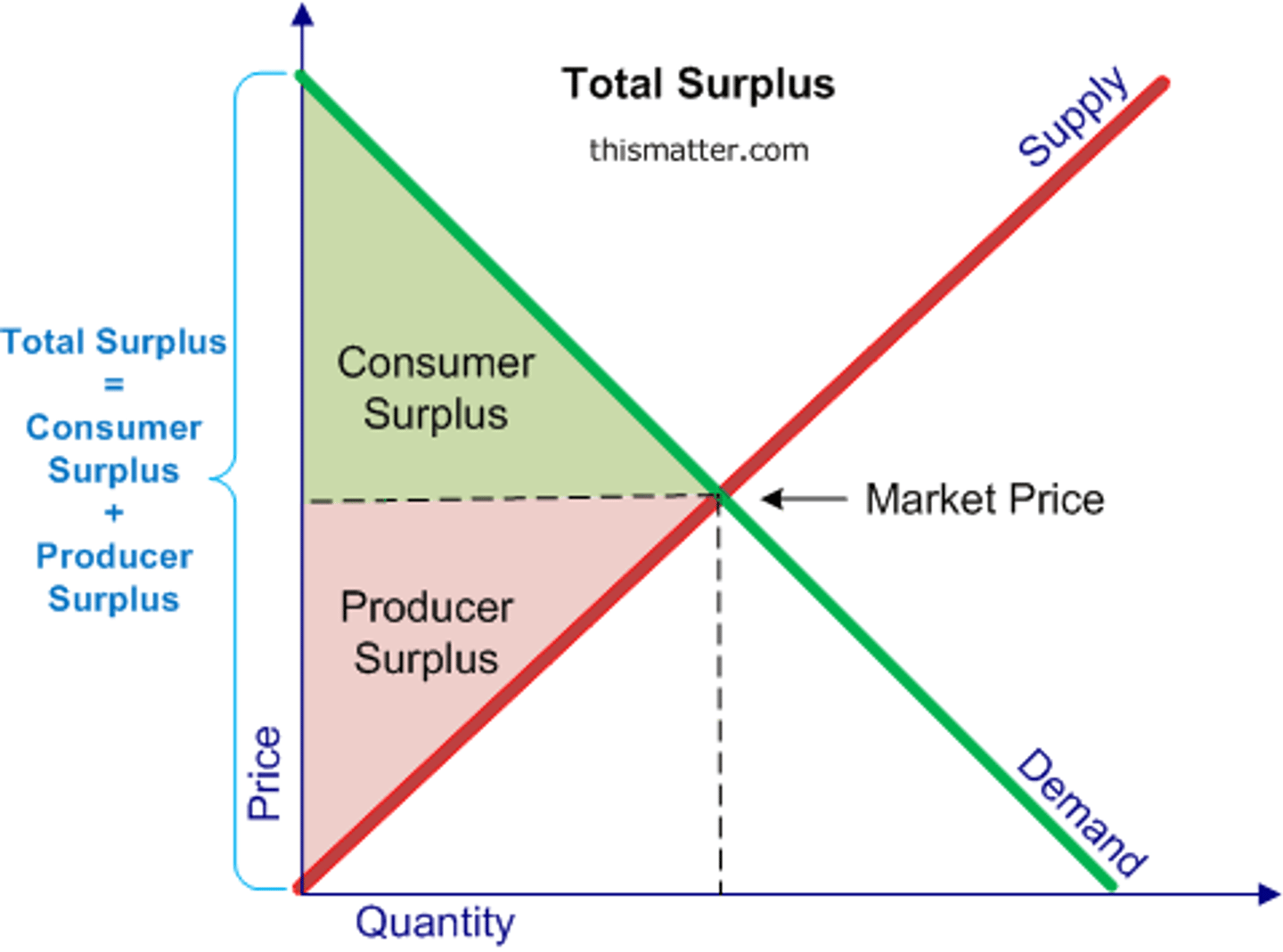
Where on the graph is producer surplus?
The area above the supply curve and below the price measures the PS.
What does consumer surplus measure?
the benefit that buyers receive from a good as the buyers themselves perceive it
What does producer surplus measure?
the benefit sellers receive from participating in a market
What is a marginal seller?
the seller who would leave the market first if the price were any lower
What is a marginal buyer?
the buyer who would leave the market first if the price were any higher
Total surplus
consumer surplus + producer surplus (or value to buyers - cost to sellers)
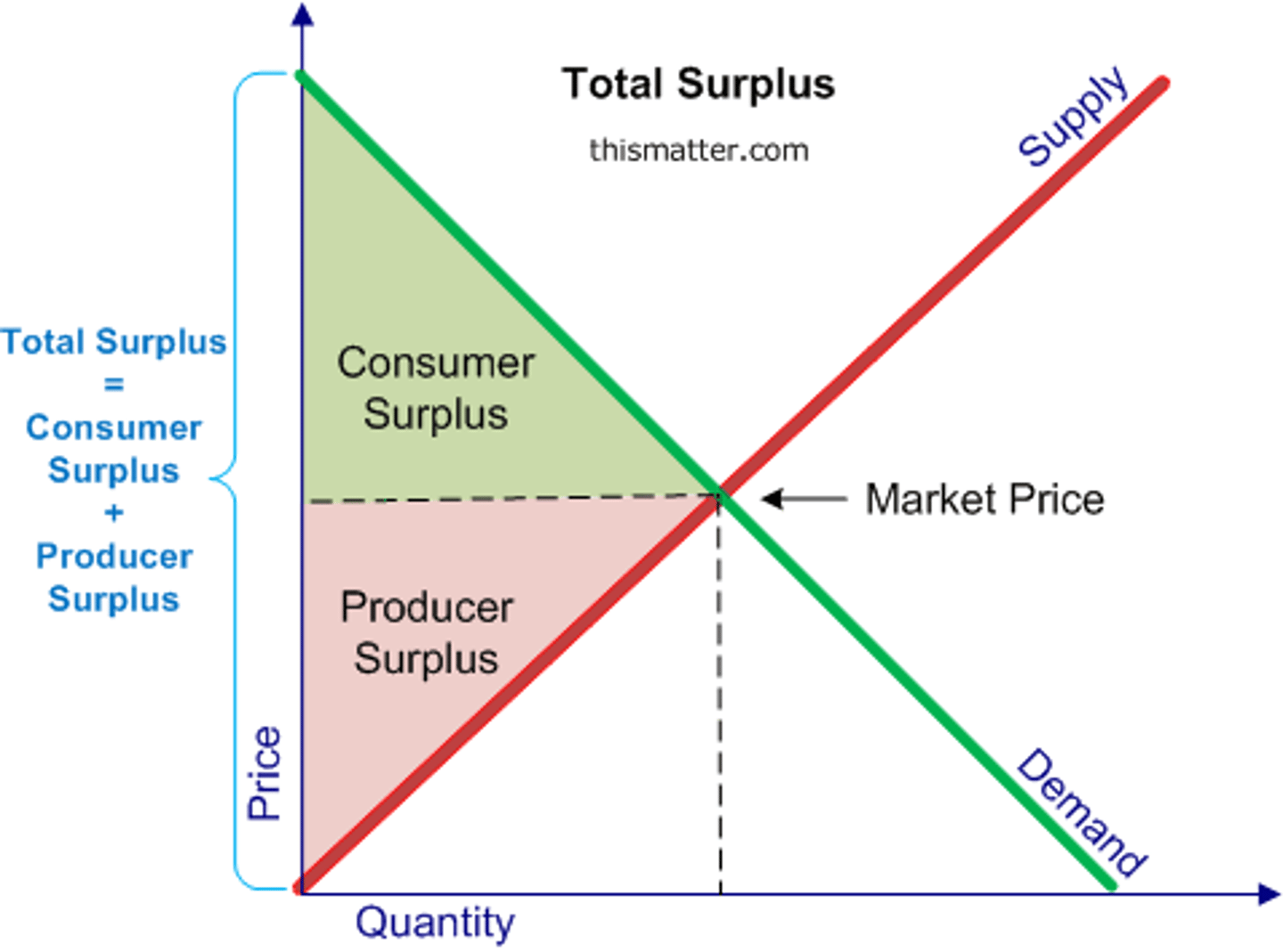
Efficiency
the property of society getting the most it can from its scarce resources
Equality
the property of distributing economic prosperity uniformly among the members of society
Free markets allocate the supply of goods to the buyers who ___________________, as measured by their willingness to pay.
value them most highly
Free markets allocate the demand for goods to the sellers who can produce them ______________.
at the lowest cost
Free markets produce the quantity of goods that ______________ the sum of consumer and producer surplus.
maximizes
Market Power
the ability of a single economic actor (or small group of actors) to have a substantial influence on market prices
Externalities
A side effect of an action that affects a third party other than the buyer or seller.
Total Revenue
the total amount of money a firm receives by selling goods or services
Total Cost
the market value of the inputs a firm uses in production
Profit
Total Revenue - Total Cost
Explicit Costs
input costs that require an outlay of money by the firm
Implicit Costs
input costs that do not require an outlay of money by the firm
Total cost is...
the sum of explicit and implicit costs.
Economic Profit
total revenue minus total cost, including both explicit and implicit costs
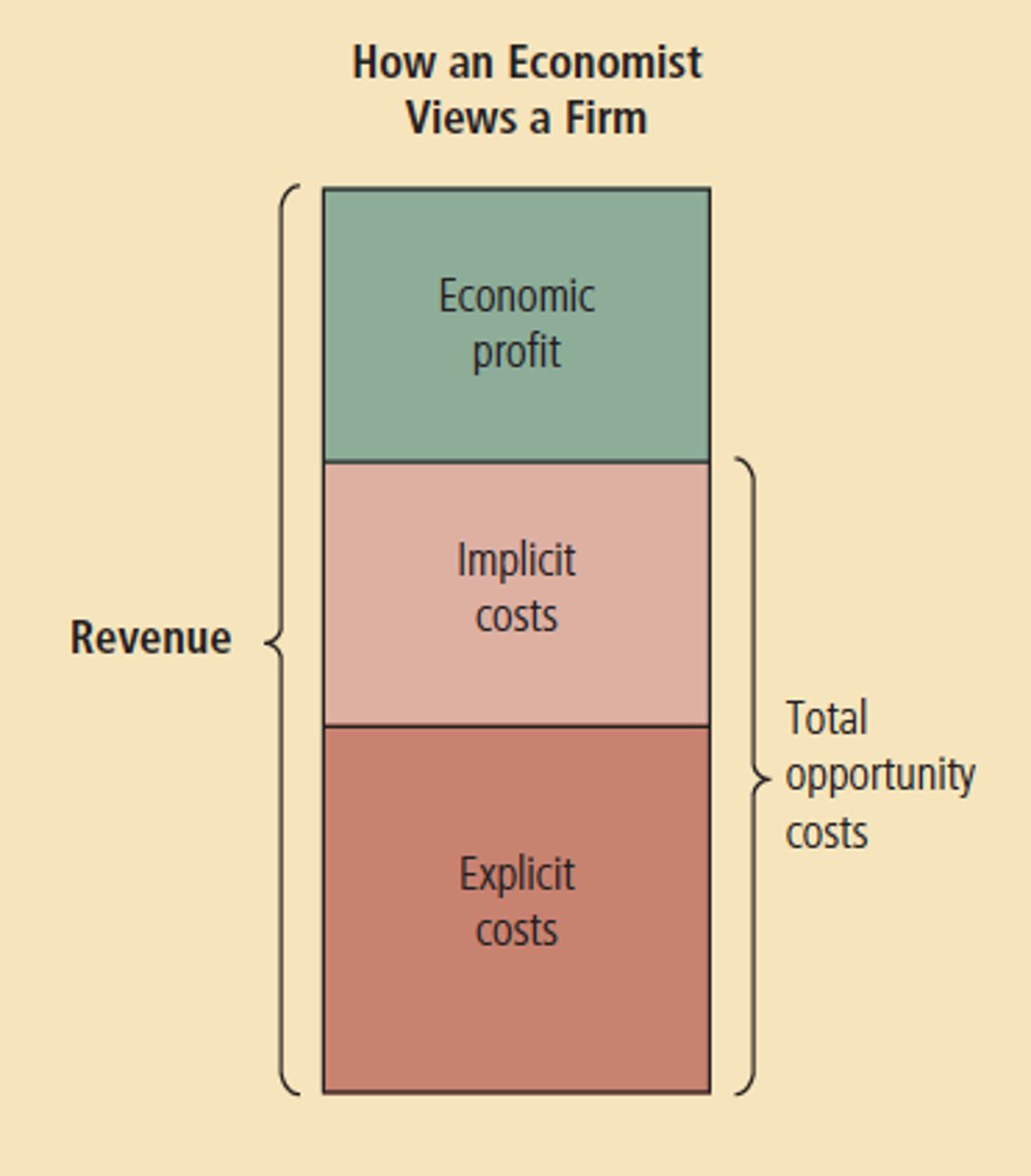
Accounting Profit
total revenue minus total explicit costs only
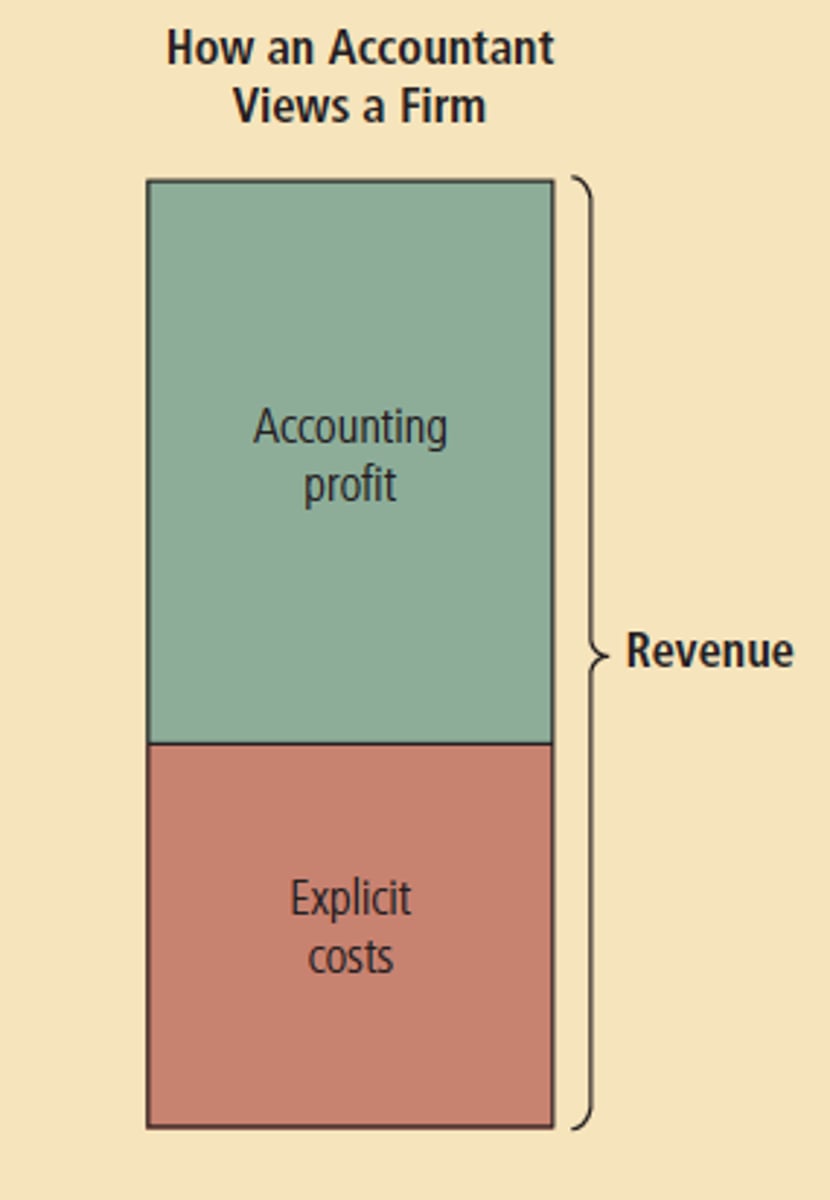
Usually accounting profit is __________ than economic profit.
larger
At the equilibrium price of a good, the good will be purchased by those buyers who...
value the good more than the price.
Corn chips and potato chips are substitutes. Good weather that sharply increases the corn harvest would __________.
increase consumer surplus in the market for corn chips and decrease producer surplus in the market for potato chips
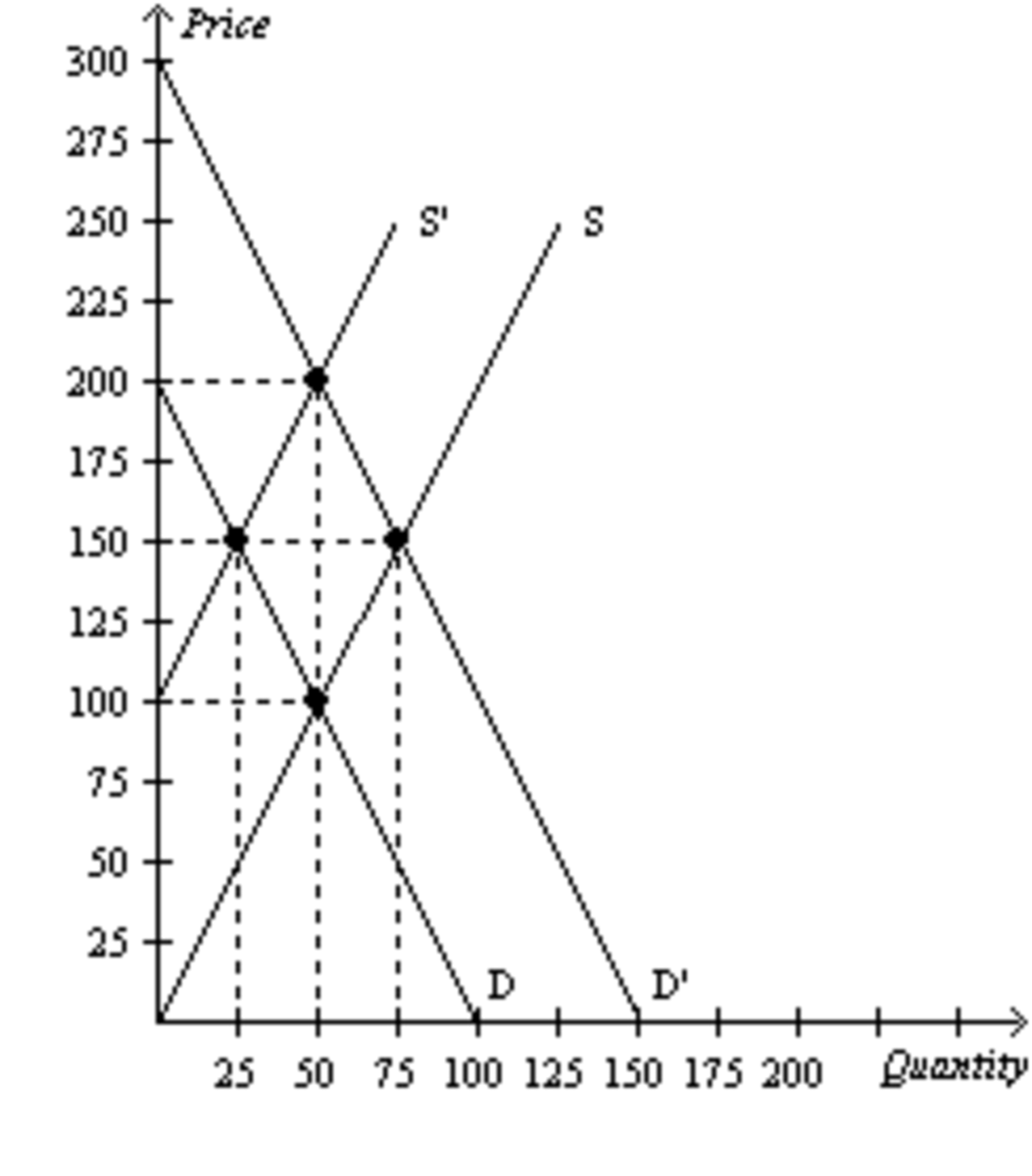
If the supply curve is S', the demand curve is D, and the equilibrium price is $150, what is the producer surplus?
$625
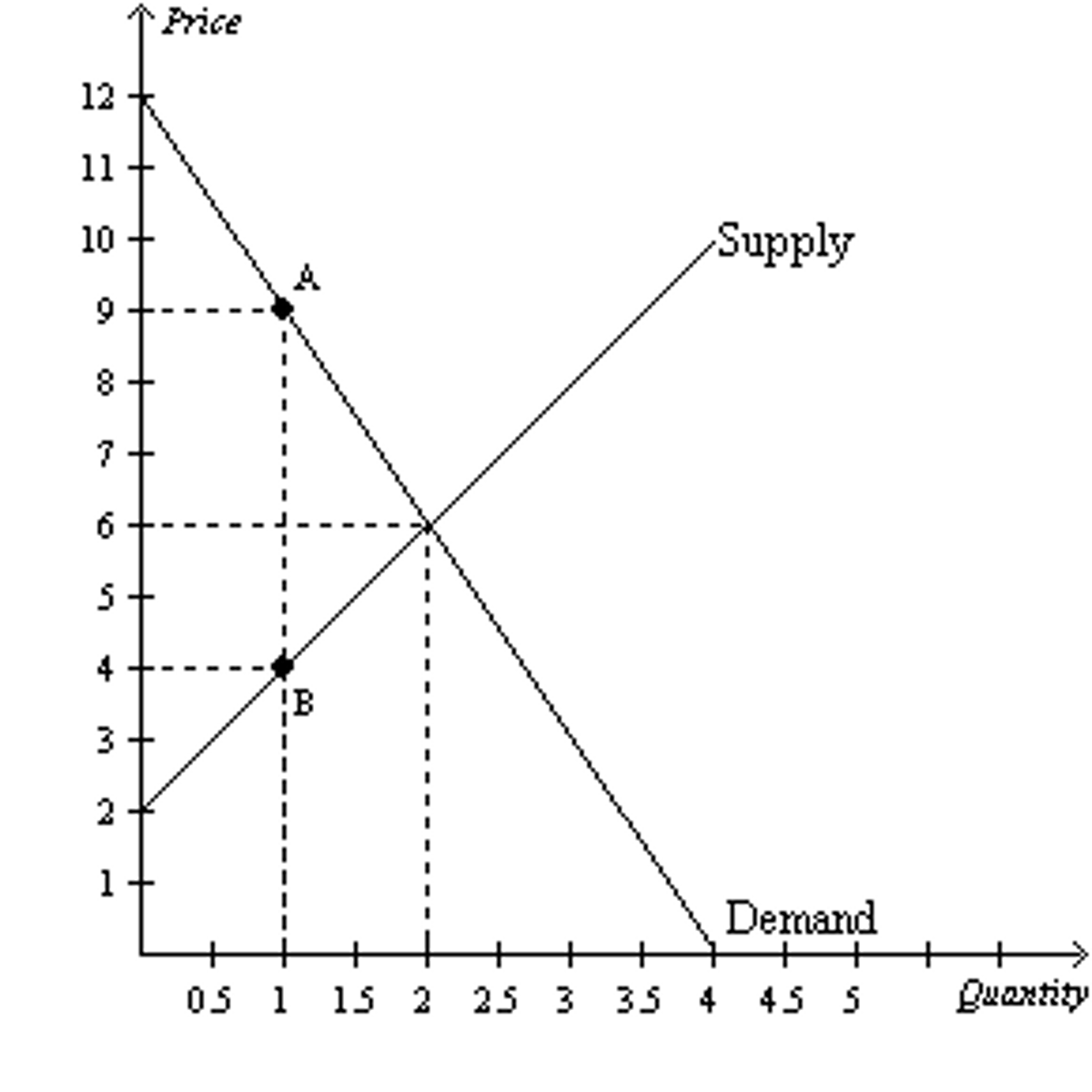
The amount of deadweight loss that results from this tax is ___________.
$2.50
When a firm's only variable input is labor, then the slope of the production function measures the _______________.
marginal product of labor.
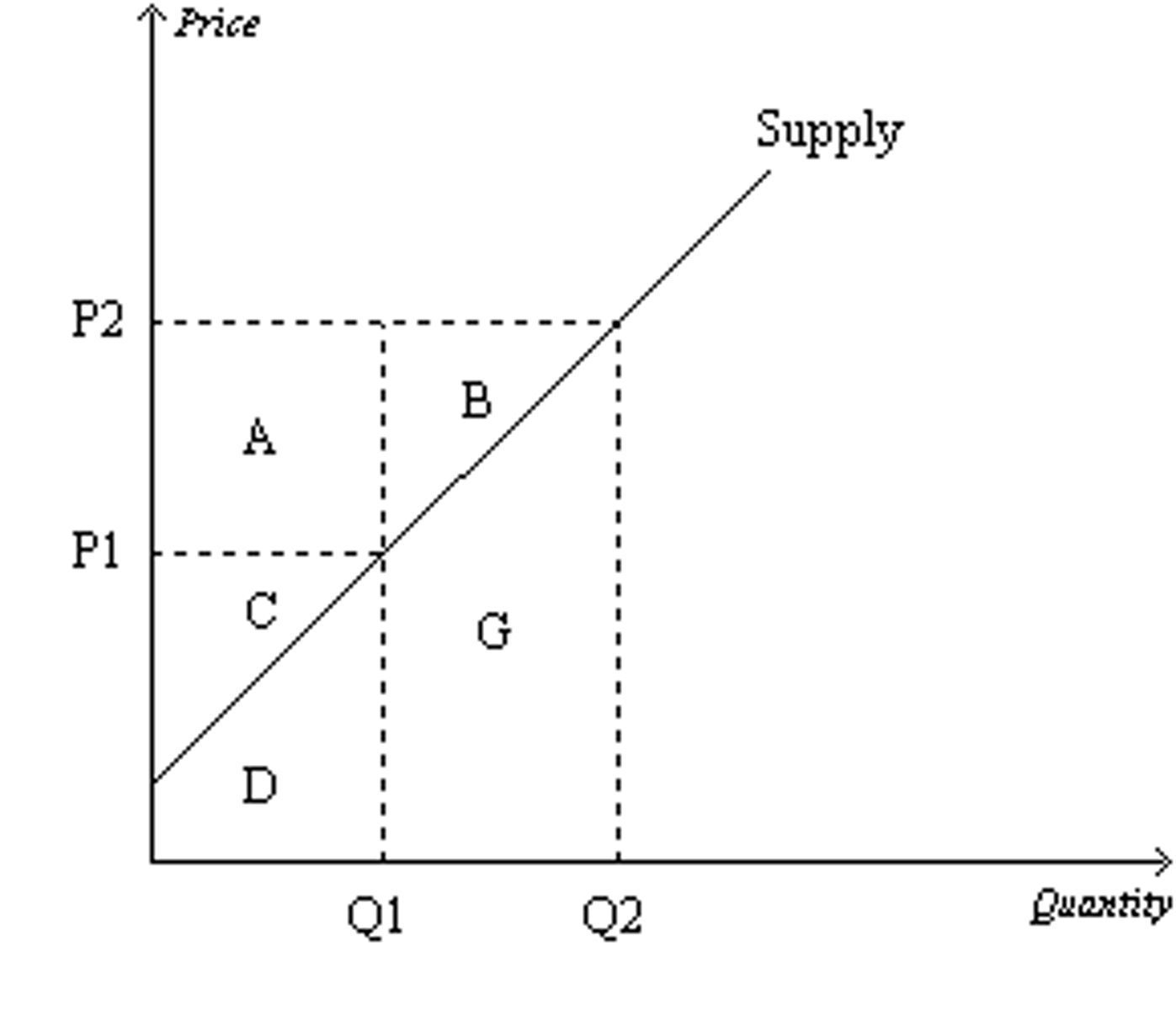
When the price rises from P1 to P2, which area represents the increase in producer surplus due to new producers entering the market?
B
Hot dogs and hot dog buns are complements. An increase in the price of flour used to make hot dogs buns will __________________.
decrease consumer surplus in the market for hot dog buns and decrease producer surplus in the market for hot dogs.
Which of the following will cause a decrease in producer surplus?
income increases and buyers consider the good to be inferior
Do binding price floors, binding price ceilings, or taxes increase total surplus?
No; imposing taxes or price ceiling/floors only decreases total surplus.
Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2. The SIZE of the tax is....
P2~P8
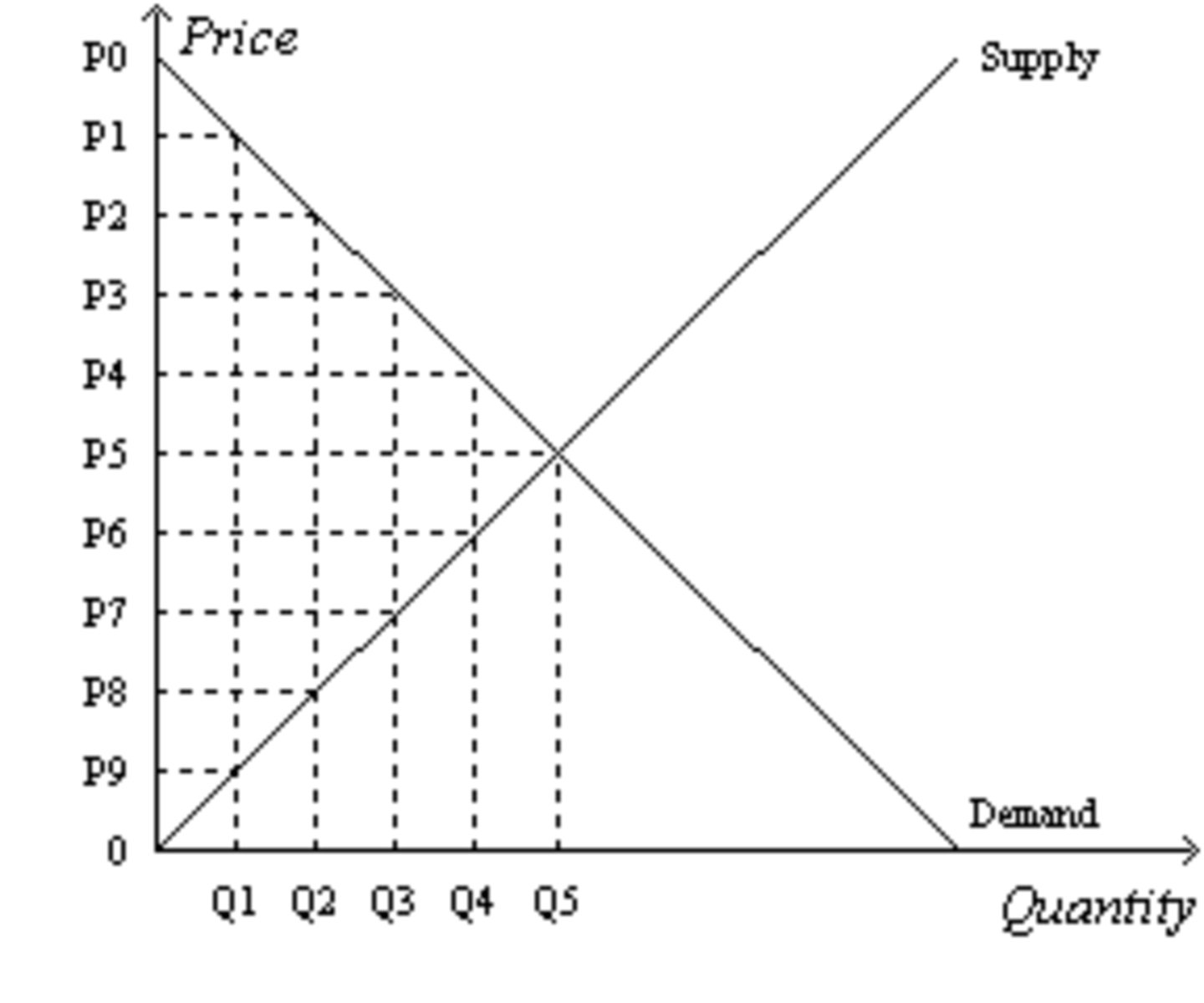
Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2. The TAX REVENUE is.....
(P2-P8) * Q2
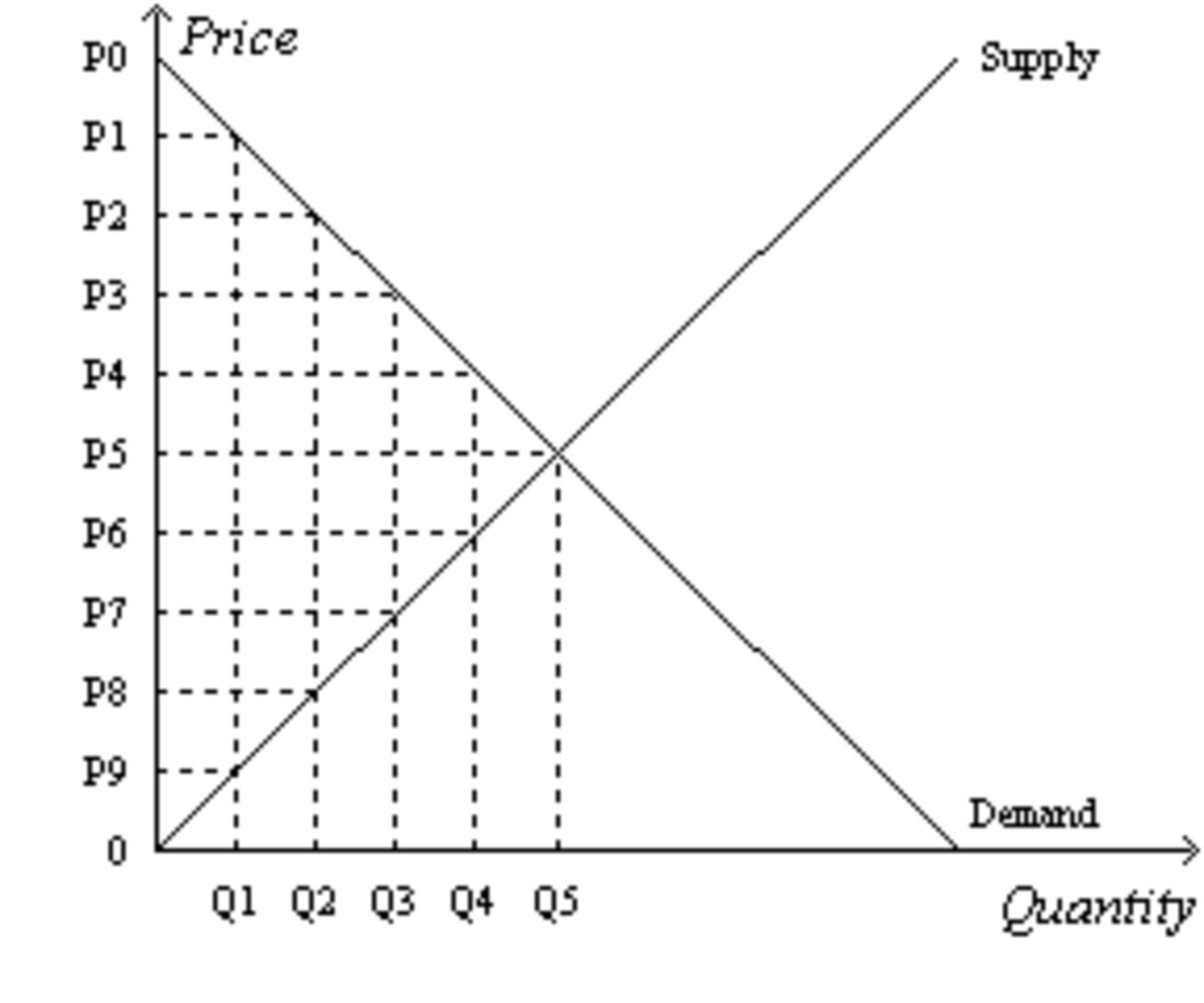
Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2. The price that SELLERS RECEIVE is....
P8
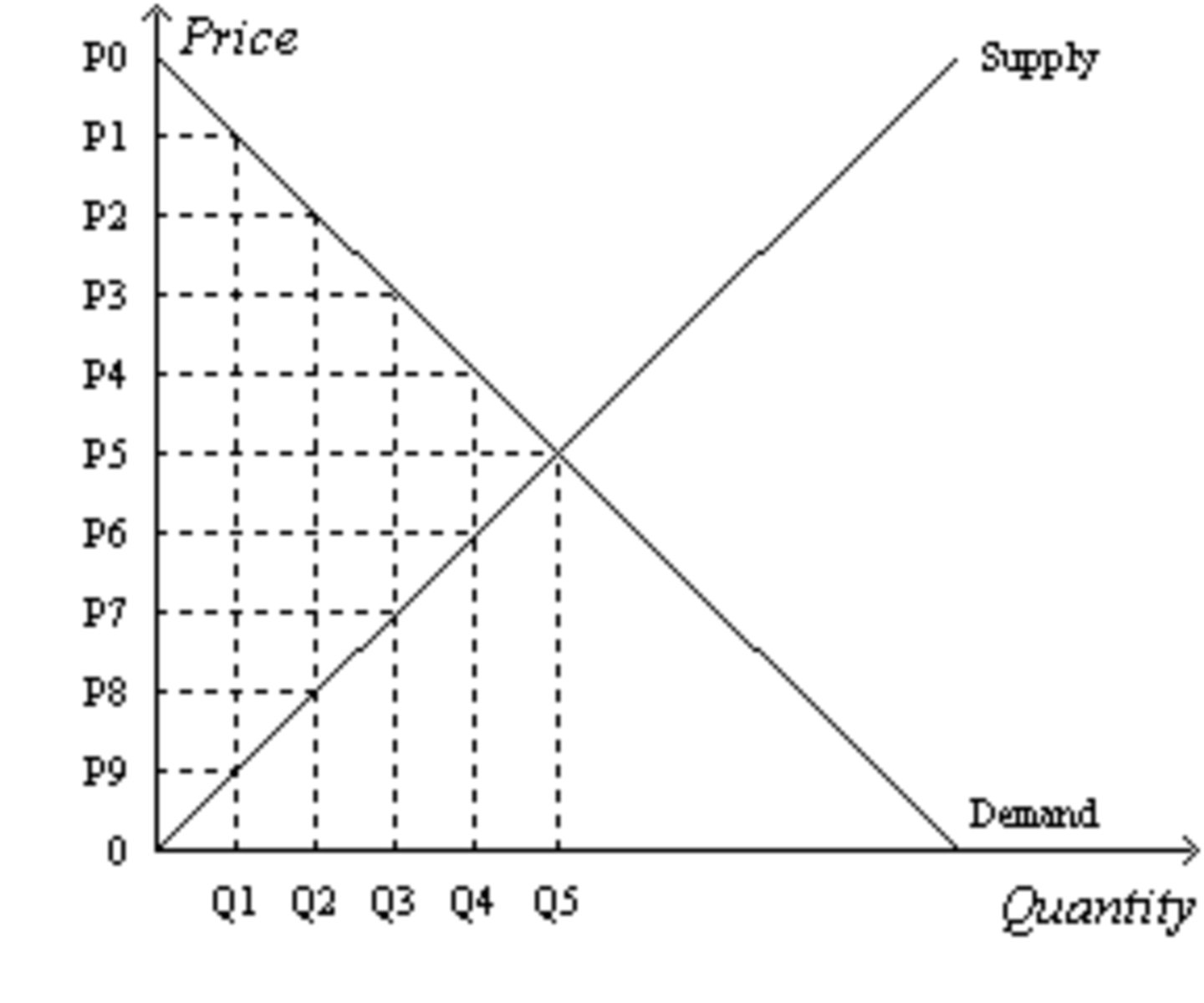
Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2. The price that BUYERS PAY is....
P2
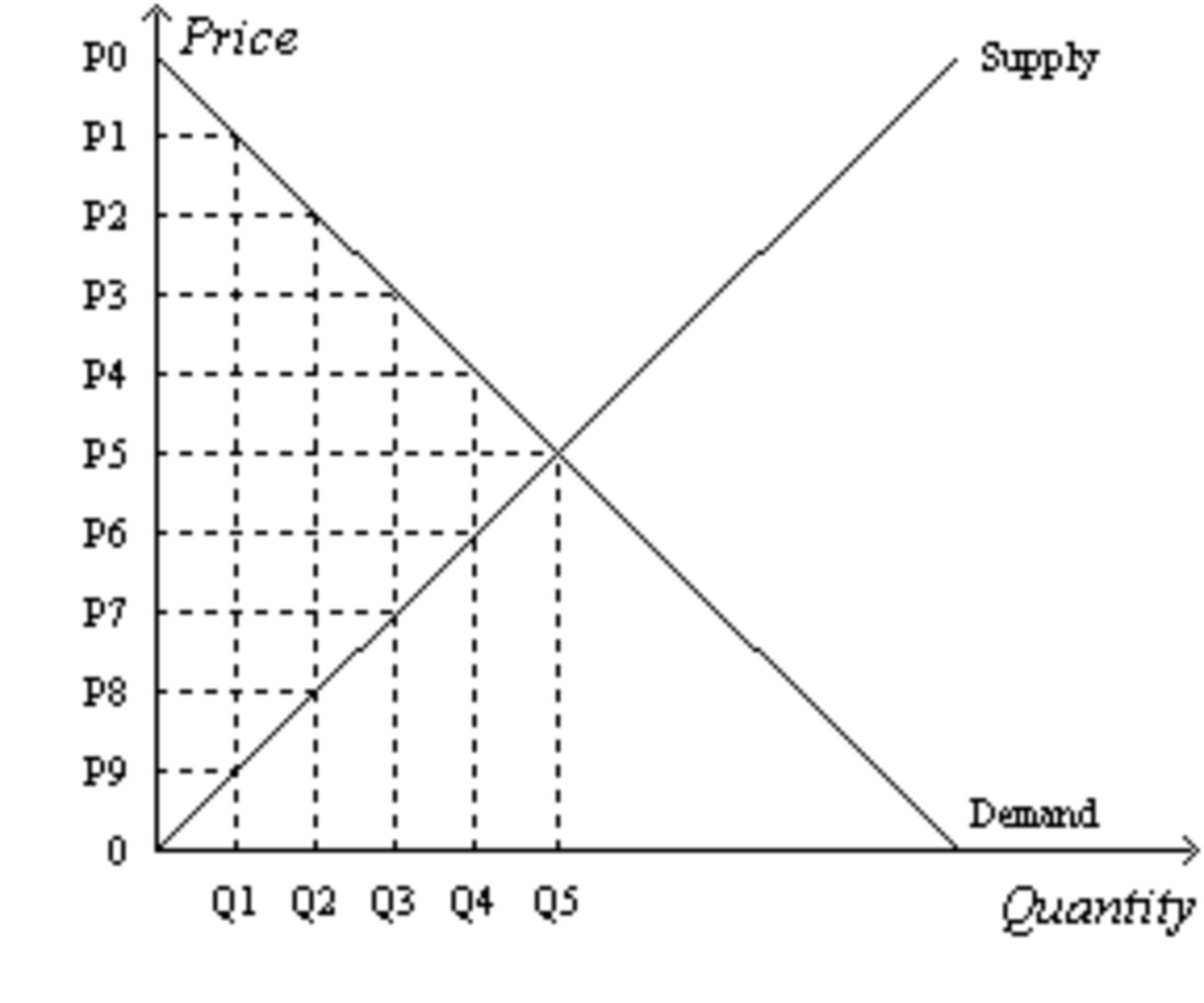
Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2. Without the tax, the TOTAL SURPLUS is...
[1/2 x (P0-P5) x Q5] + [1/2 x (P5-0) x Q5]
![<p>[1/2 x (P0-P5) x Q5] + [1/2 x (P5-0) x Q5]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6cc14d04-7de5-4f2b-8c24-89746ff75d42.jpg)
A simultaneous increase in both the demand for MP3 players and the supply of MP3 players would imply that...
Consumers value MP3s more and it costs less for producers to make them
When a firm is operating at an efficient scale...
average total cost is minimized
When a firm is making a profit-maximizing production decision, which of the following principles of economics is likely to be most important to the firm's decision?
The cost of something is what you give up to get it.
Production Function
the relationship between the quantity of inputs used to make a good and the quantity of output of that good
Marginal Product
the increase in output that arises from an additional unit of input
In the presence of a negative externality, such as pollution...
the social cost of the good exceeds the private cost. Therefore, Optimum Quantity < Market Quantity.
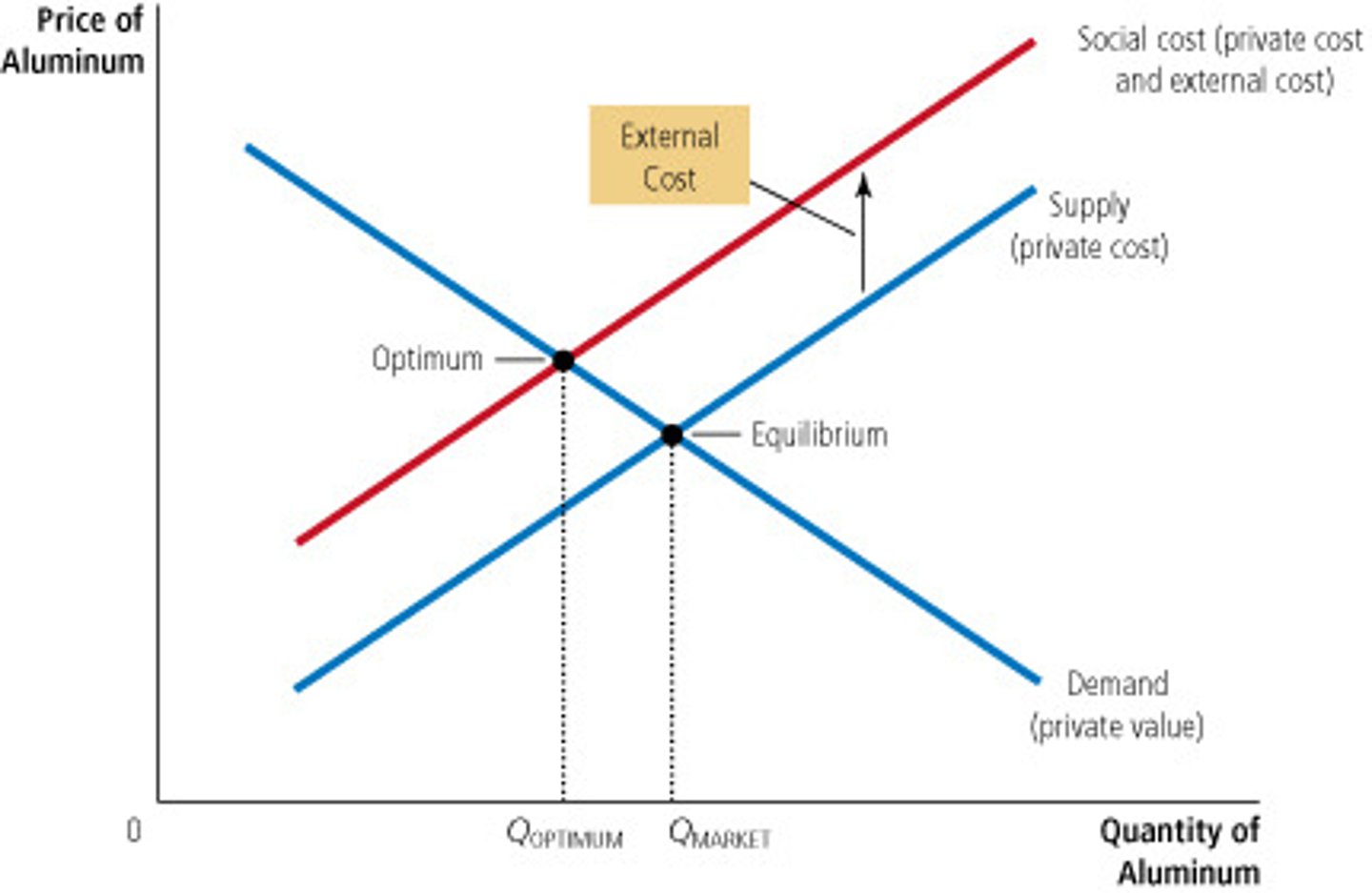
In the presence of a positive externality...
the social value of the good exceeds the private value. Therefore, Optimum Quantity > Market Quantity.
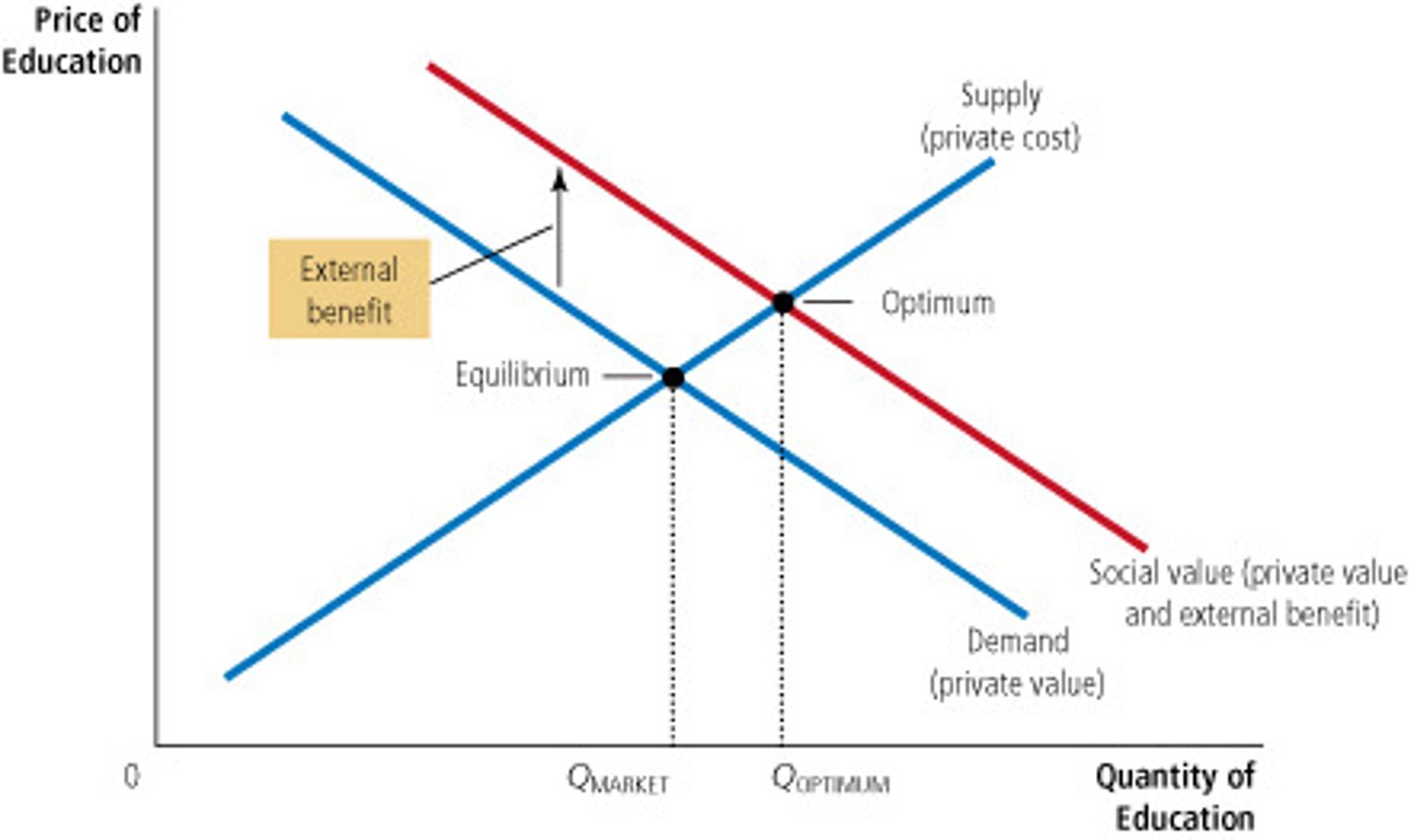
Negative externalities....
lead markets to produce a LARGER quantity than is socially desirable
Positive externalities...
lead markets to produce a SMALLER quantity than is socially desirable
How does the government control the effect of externalities?
By taxing goods that have negative externalities and subsidizing goods that have positive externalities.
Subsidy
A government payment that supports a business or market