Quiz 2 (Mitotic Phases, Organelles, & Foot/Leg Bones)
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Mitosis
The division of a single parent cell that produces two genetically identical daughter cells.
Prophase
The nuclear envelope disappears.
The spindle fibers first appear.
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes and chromosomes become visible.
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell.
The spindle fibers attach to centromeres of chromosomes.
Anaphase
Centromeres break, and daughter chromosomes begin migrating toward opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase
The nuclear envelope reappears, forming two distinct nuclei.
The chromosomes unwind into chromatin.
Cytokinesis is completed, forming two separate daughter cells.
Mitotic Spindle
A series of spindle fibers or microtubules that attach to the centromere and centrioles.
What is cytokinesis and during which mitotic phase is it completed?
The equal division of cytoplasm into two daughter cells. It is completed in the telophase.
What causes the separation of chromosomes?
Contraction and relaxation of spindle fibers (the mitotic spindle).
What cells do not undergo cellular division?
Nervous and cardiac muscle cells.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Involved in protein synthesis (folding of proteins and sending them away if misfolded).
Covered in ribosomes.
Located in the cytoplasm.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Involved in lipid synthesis.
Detoxifies drugs and toxins by processing and inactivating them.
Located in the cytoplasm.
Ribosome
Site of protein synthesis.
Free ribosomes are found in the cytoplasm for internal protein production. Membrane-bound ribosomes are found on the rough endoplasmic reticulum for export and membrane protein synthesis.
Mitochondria
Main source of energy for cells, producing energy in the form of ATP.
Located in the cytoplasm.
Lysosome
Digest the nutrients that come into the cell or old organelles.
Break down cellular waste.
Located in the cytoplasm.
Femur
Longest/largest bone in the human body, making up the thigh bone.
Greater Trochanter of Femur
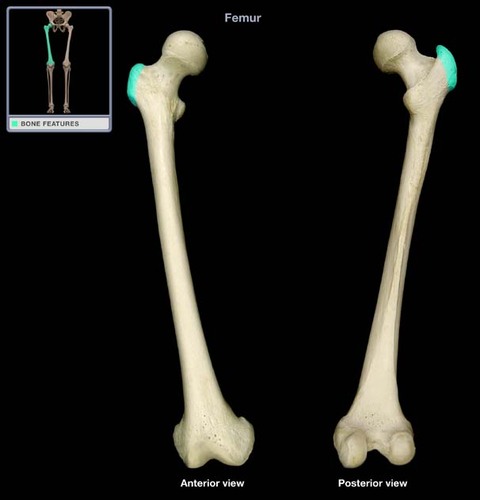
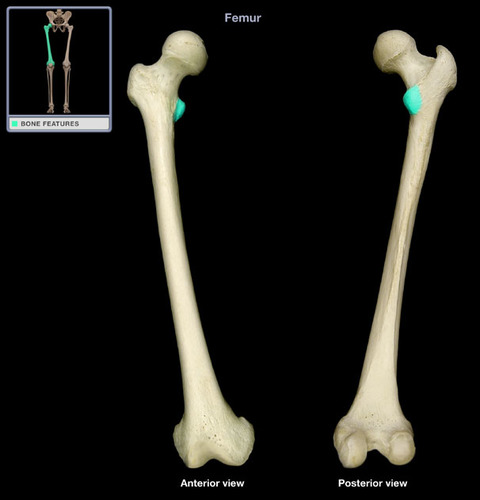
Lesser Trochanter of Femur
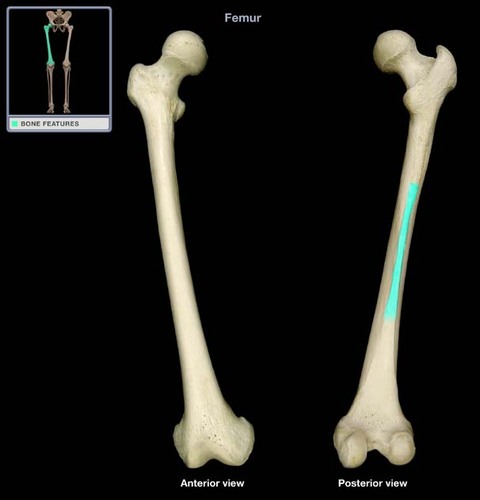
Linea Aspera
Ridge extending down the posterior surface of femoral shaft.
Medial Condyle of Femur
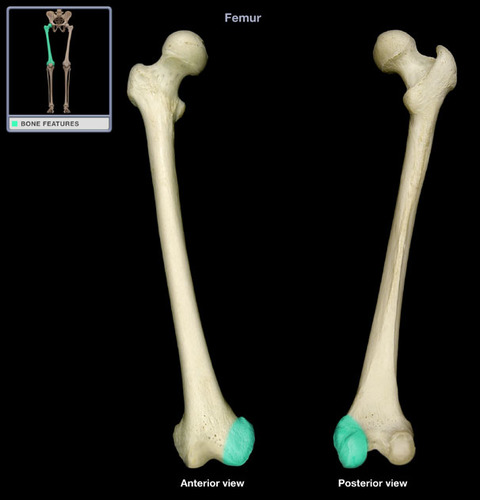
Lateral Condyle of Femur
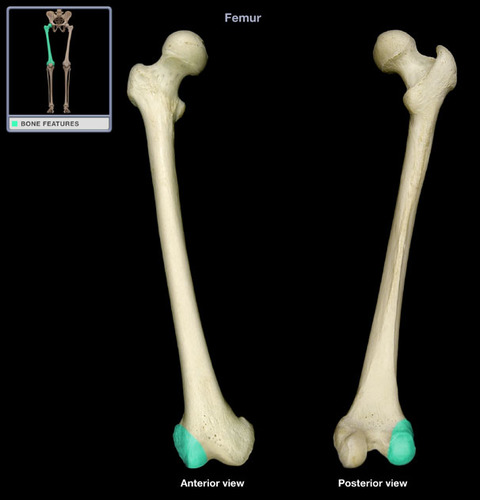
Popliteal Fossa
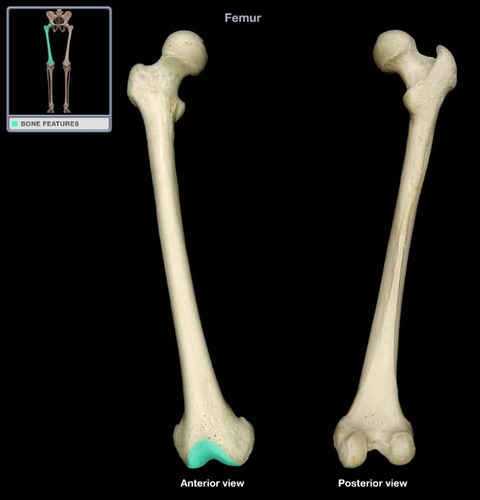
Patellar Groove
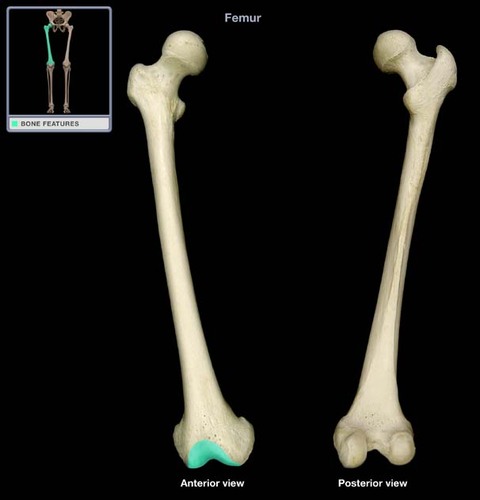
Tibia
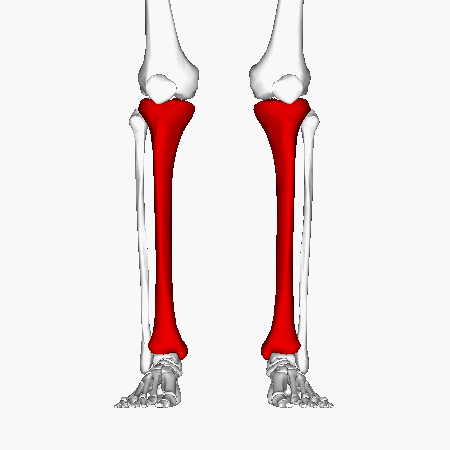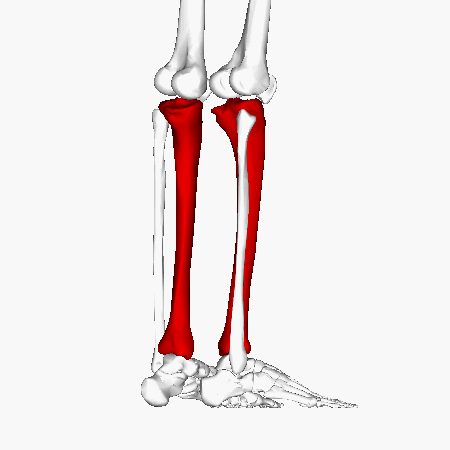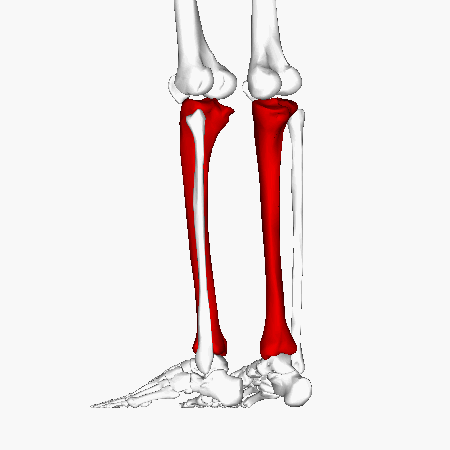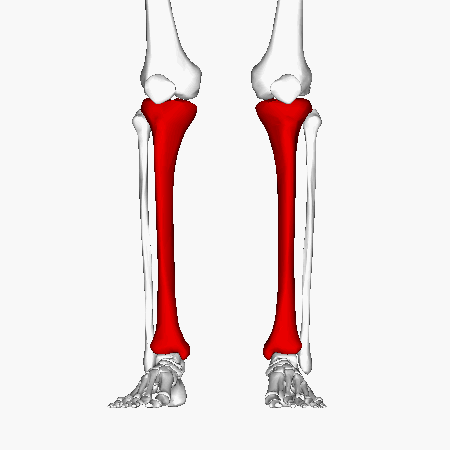
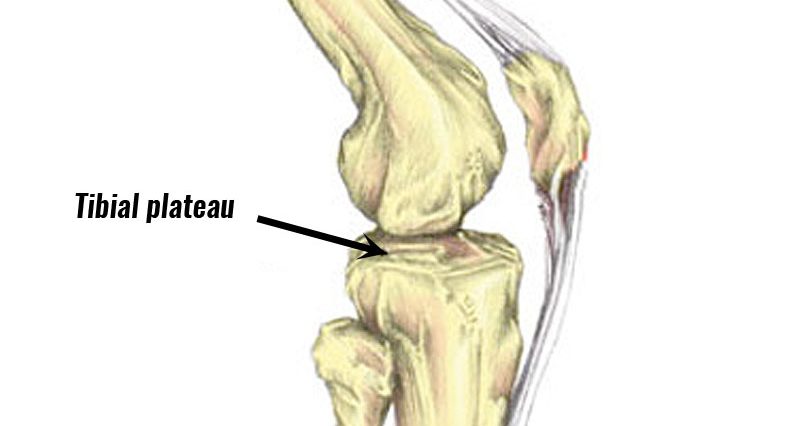
Tibial Plateau
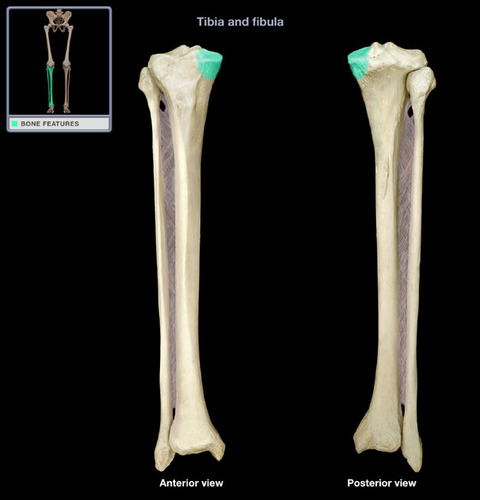
Medial Condyle of Tibia
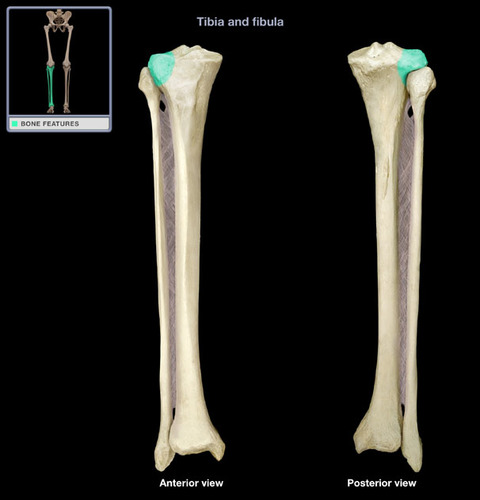
Lateral Condyle of Tibia
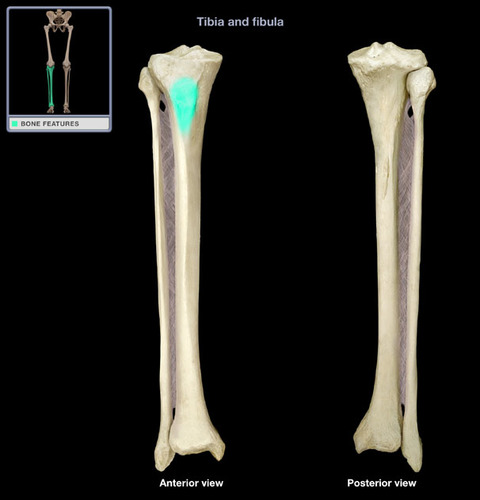
Tibial Tuberosity
Medial Malleolus
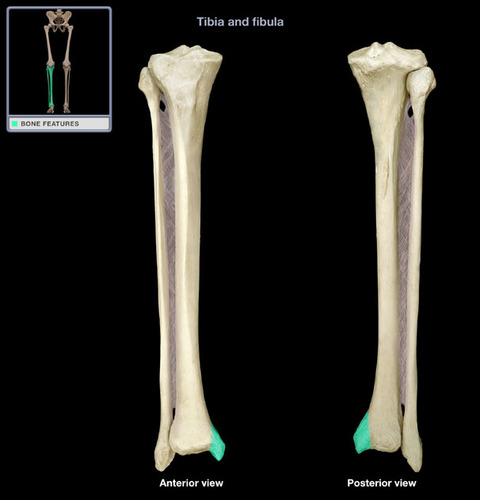
Crest of Tibia
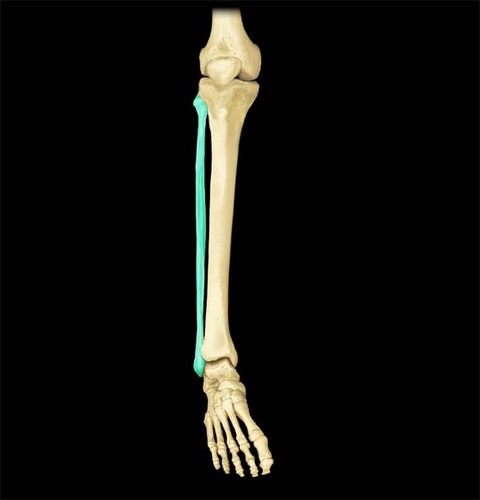
Fibula
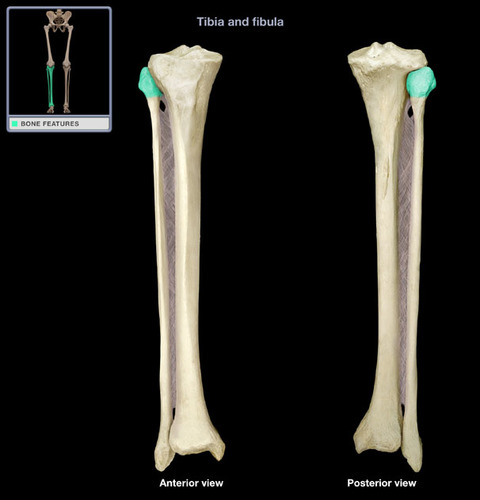
Head of Fibula
Styloid Process
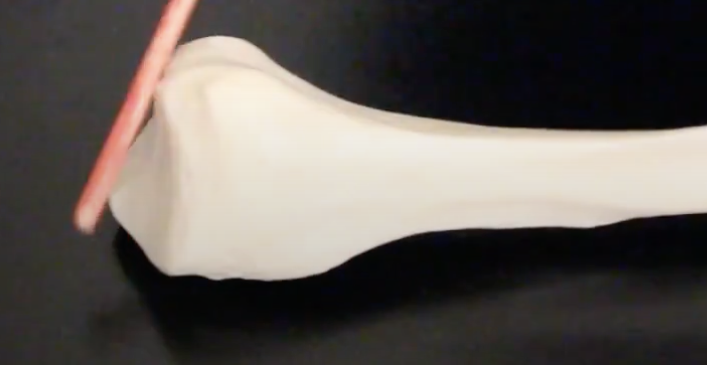
Lateral Malleolus
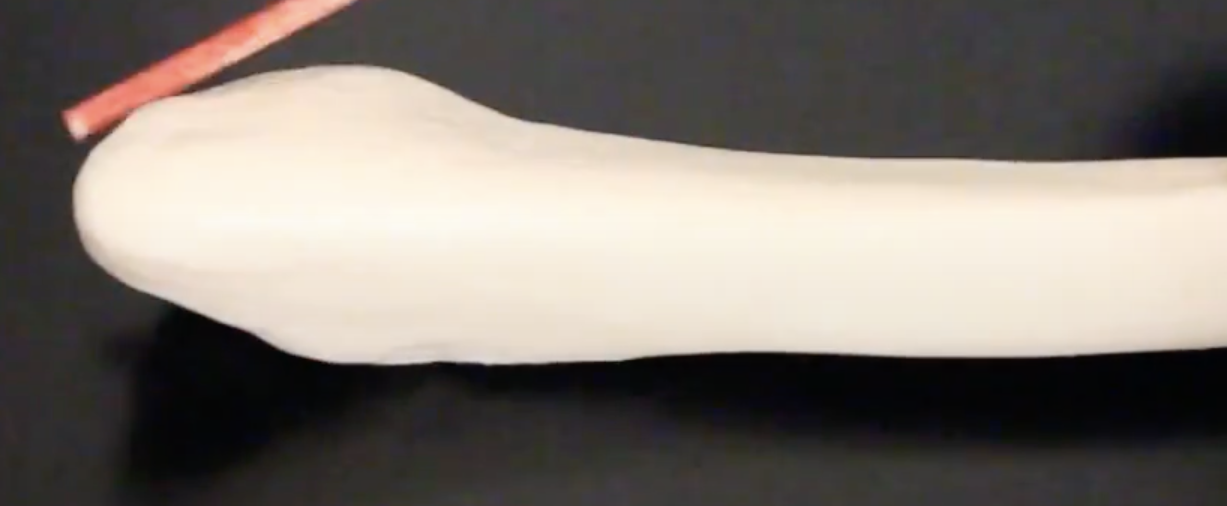
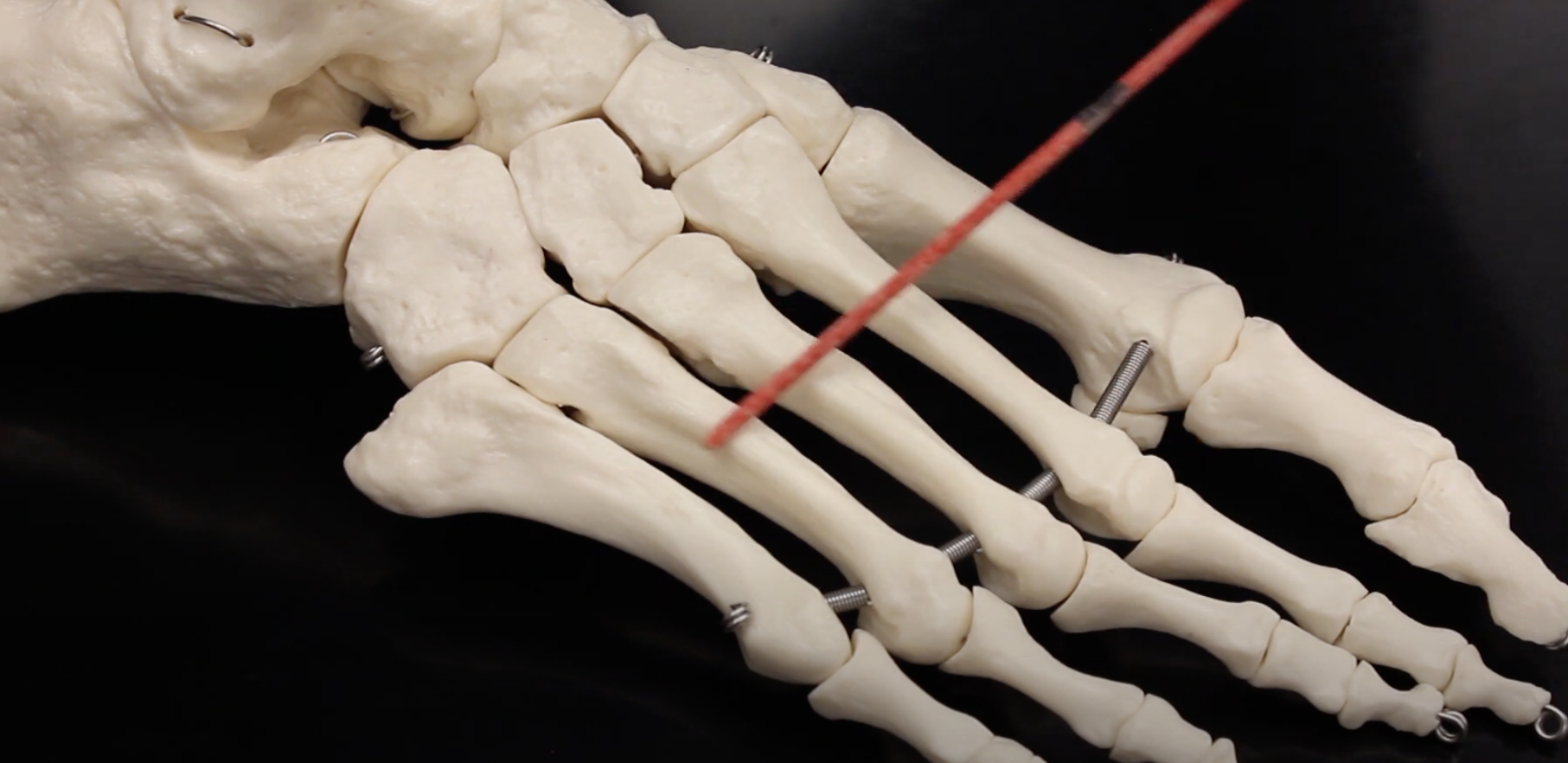
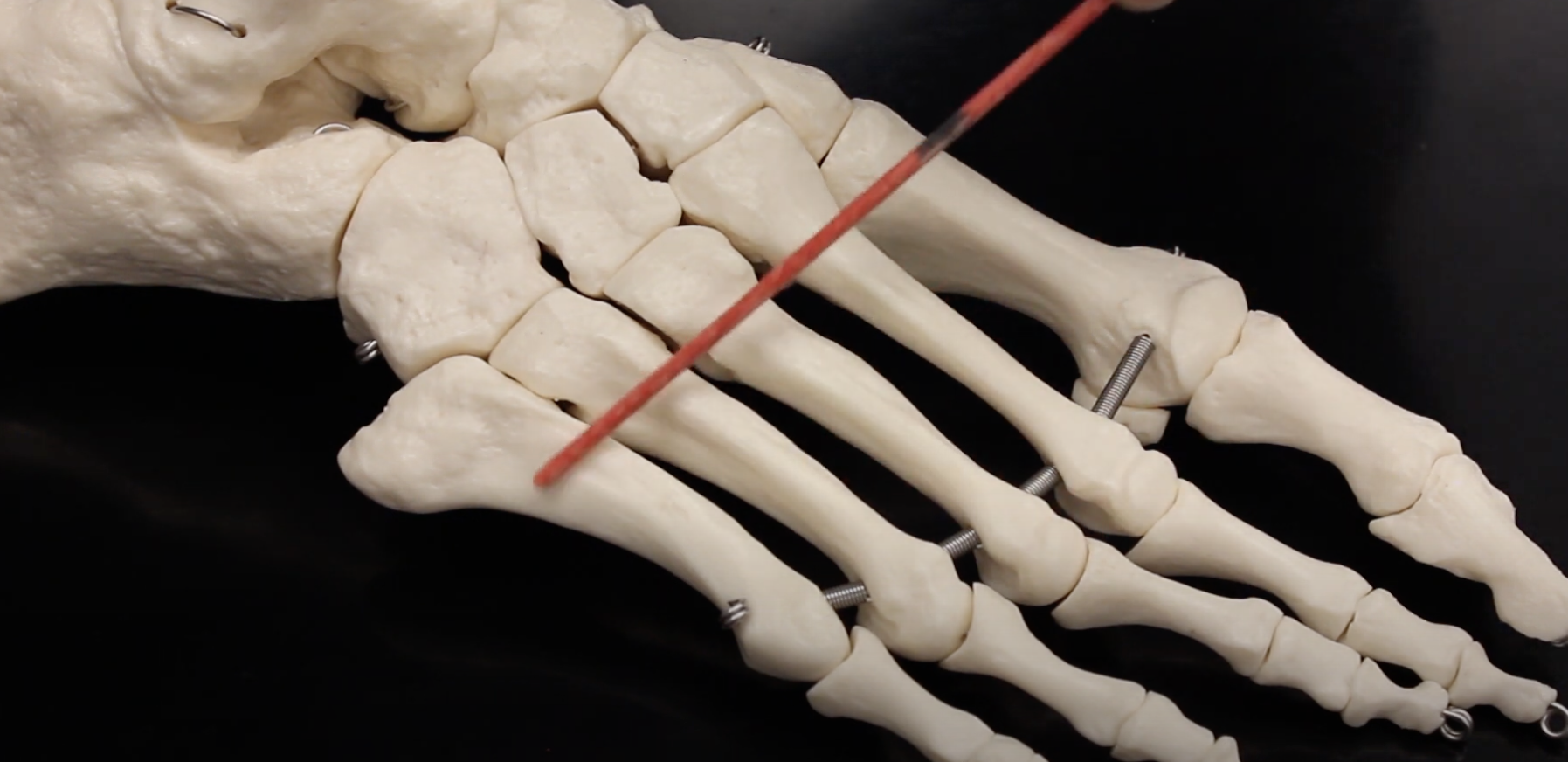
Metatarsal I
Connecting tarsals to phalanges for big toe.
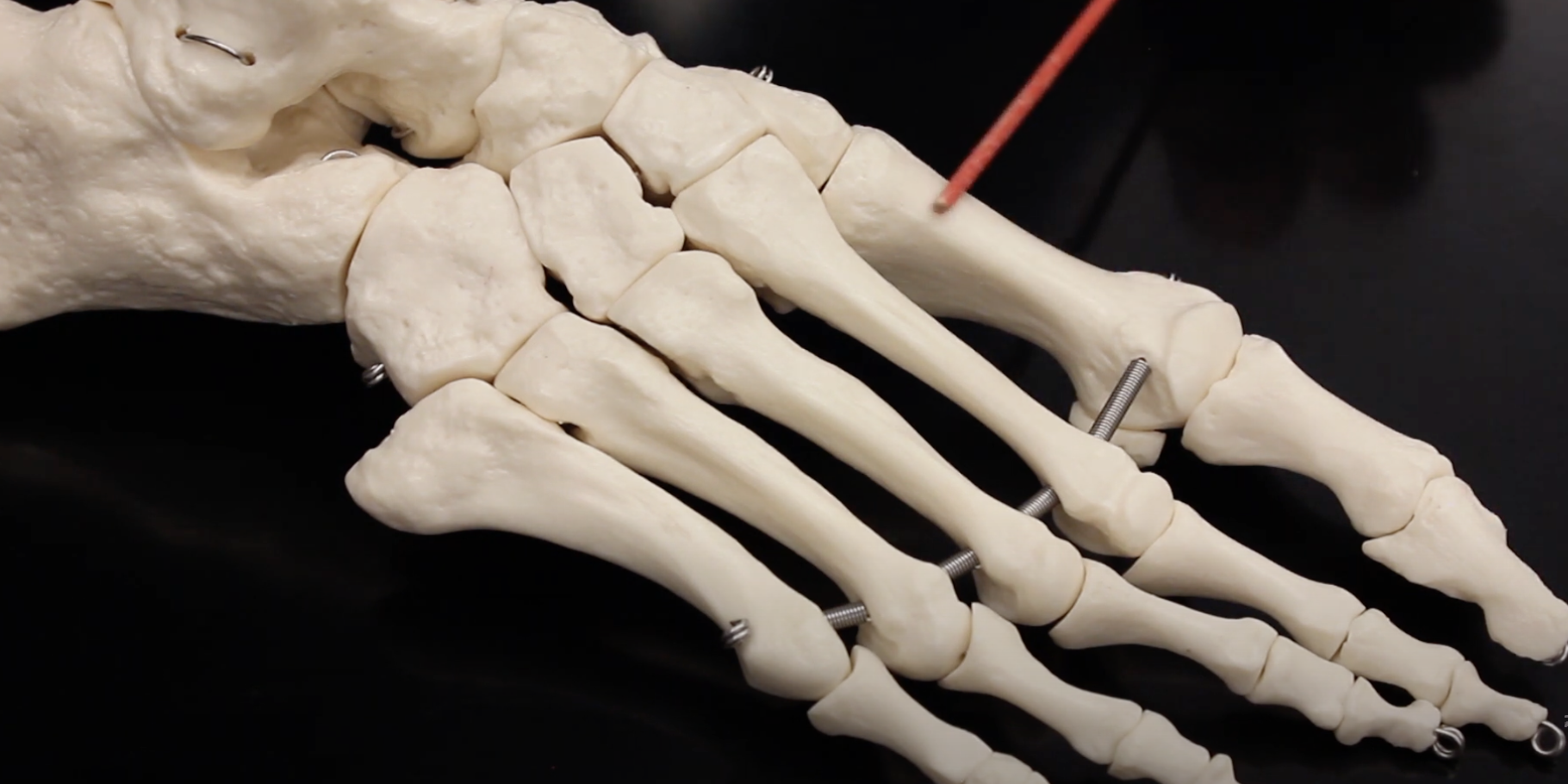
Metatarsal II
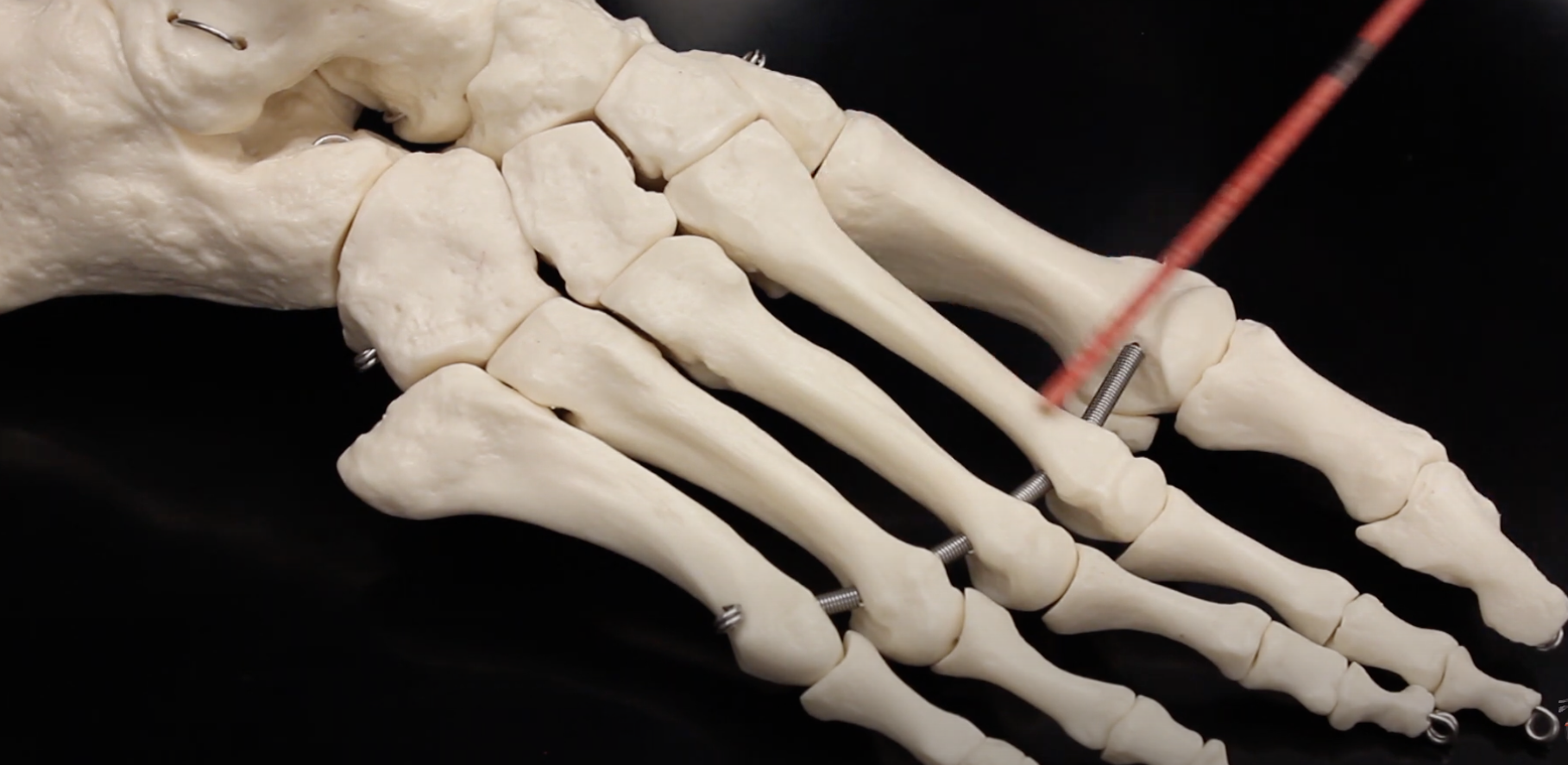
Metatarsal III
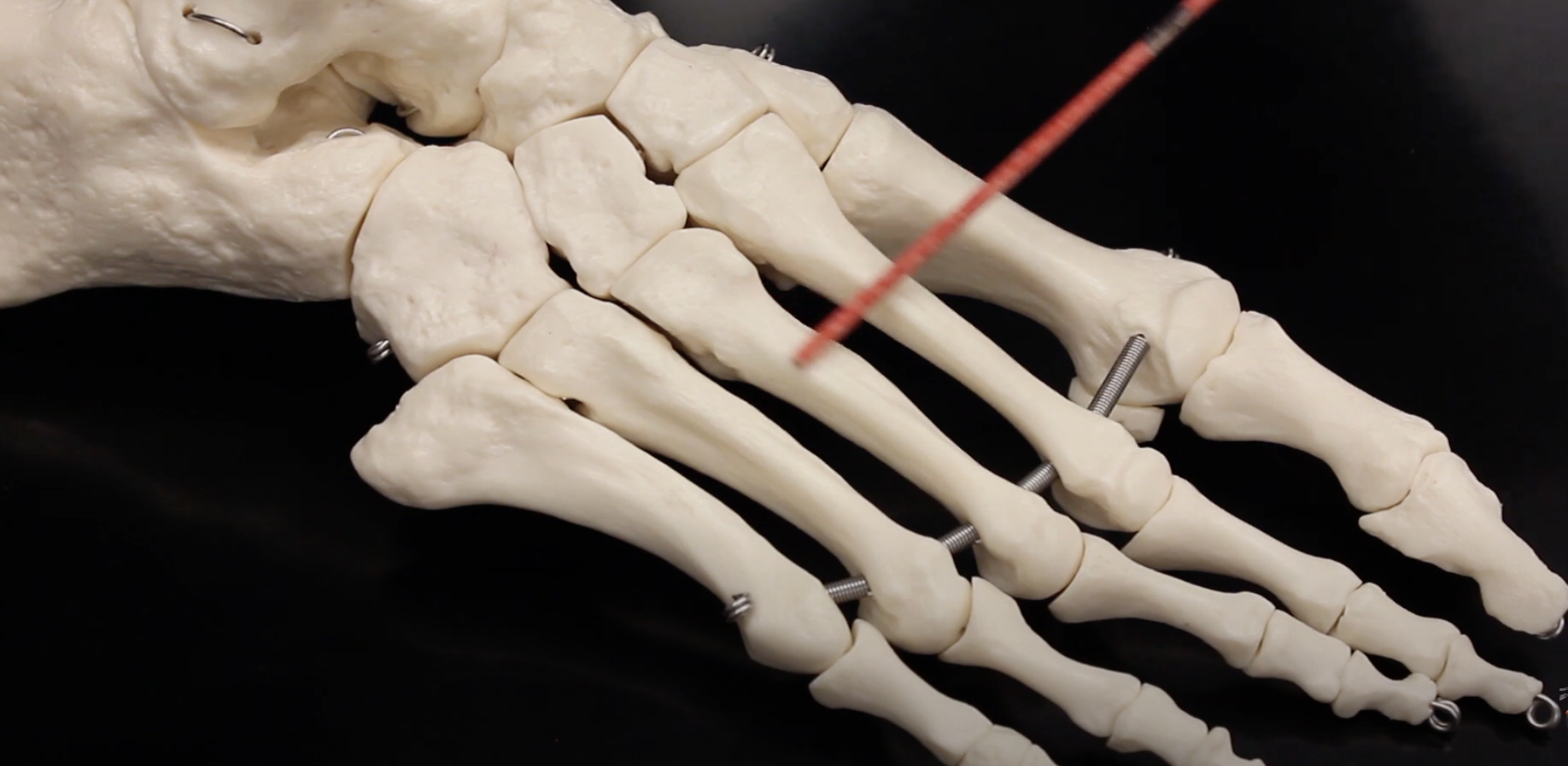
Metatarsal IV
Metatarsal V
Phalanges (Proximal)
Phalanges (Middle)
Phalanges (Distal)
Medial Cuneiform
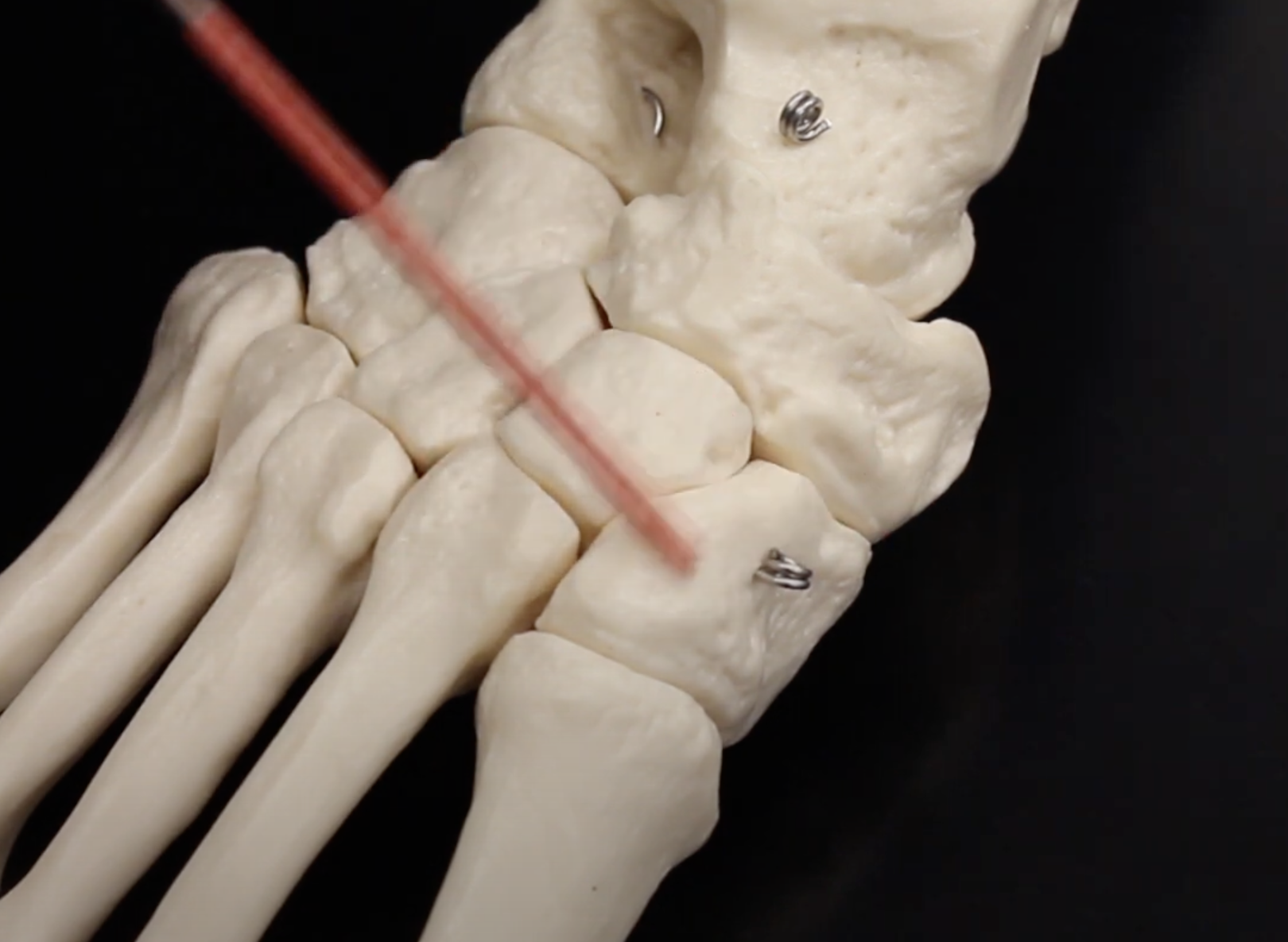
Intermediate Cuneiform
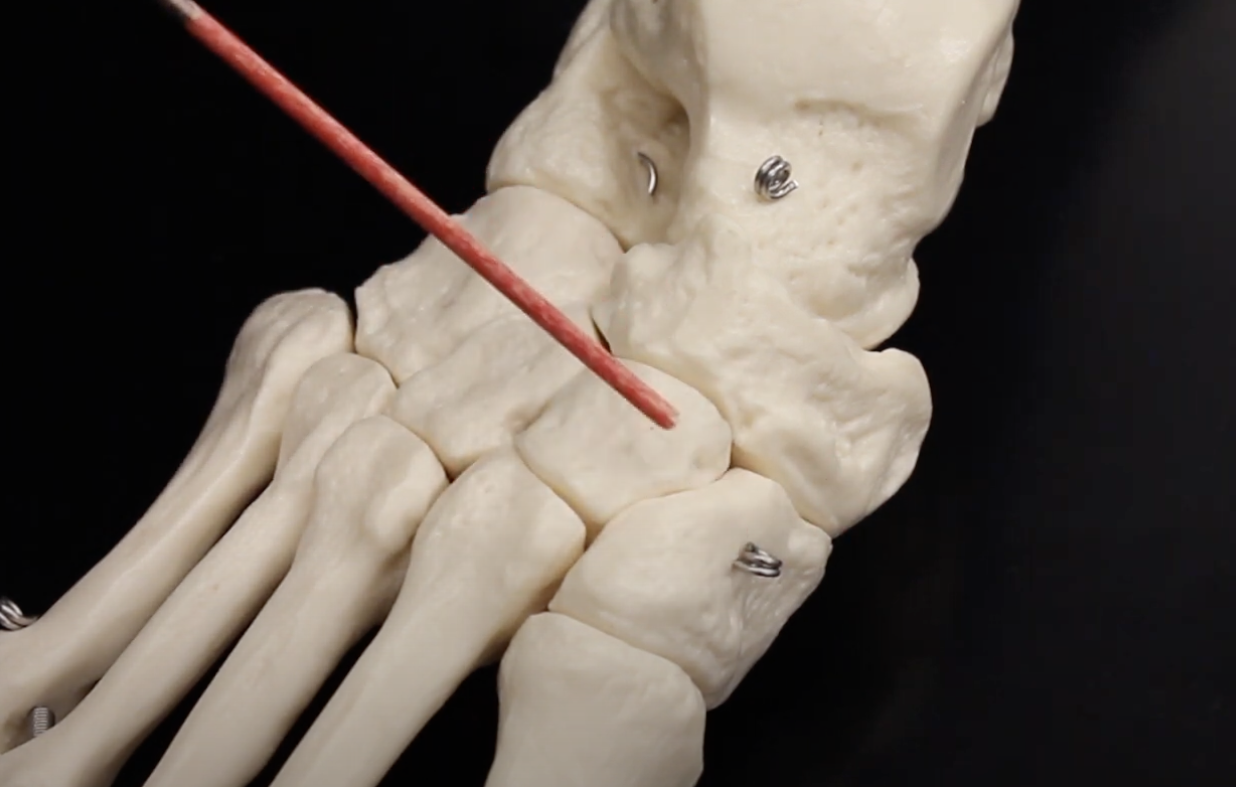
Lateral Cuneiform
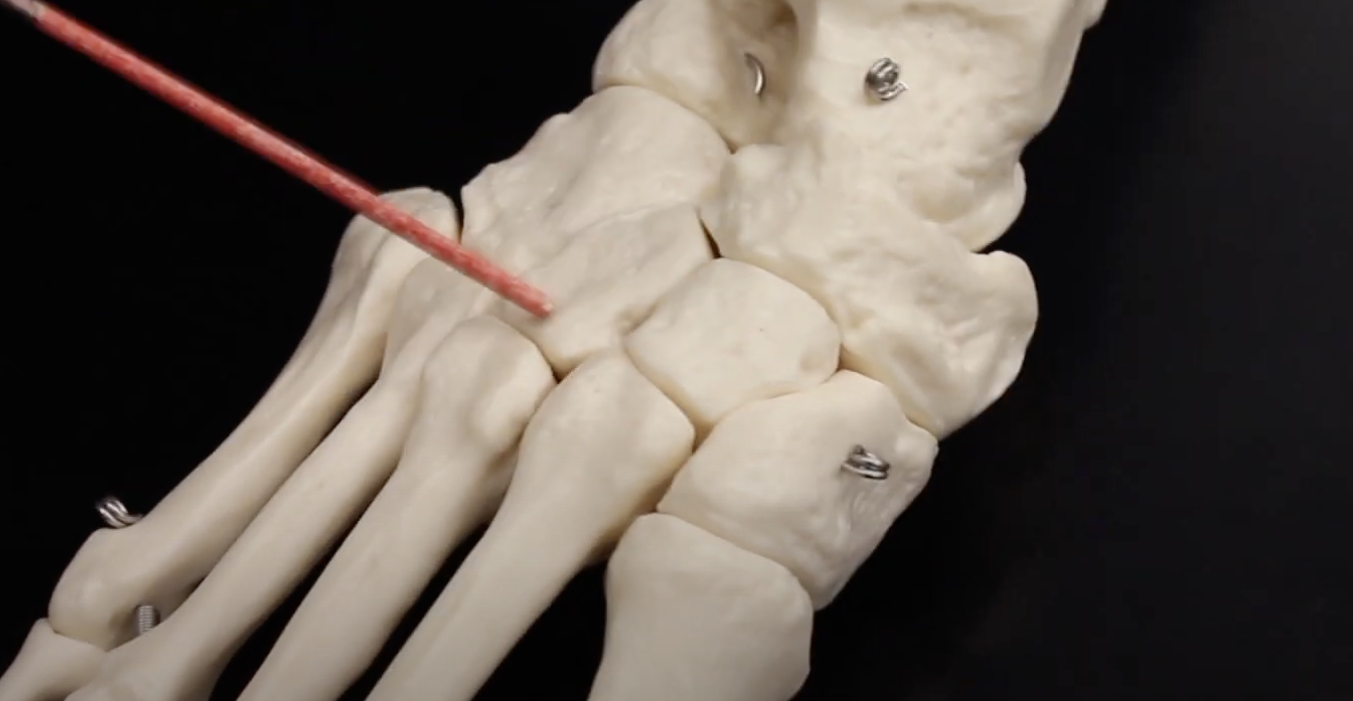
Cuboid
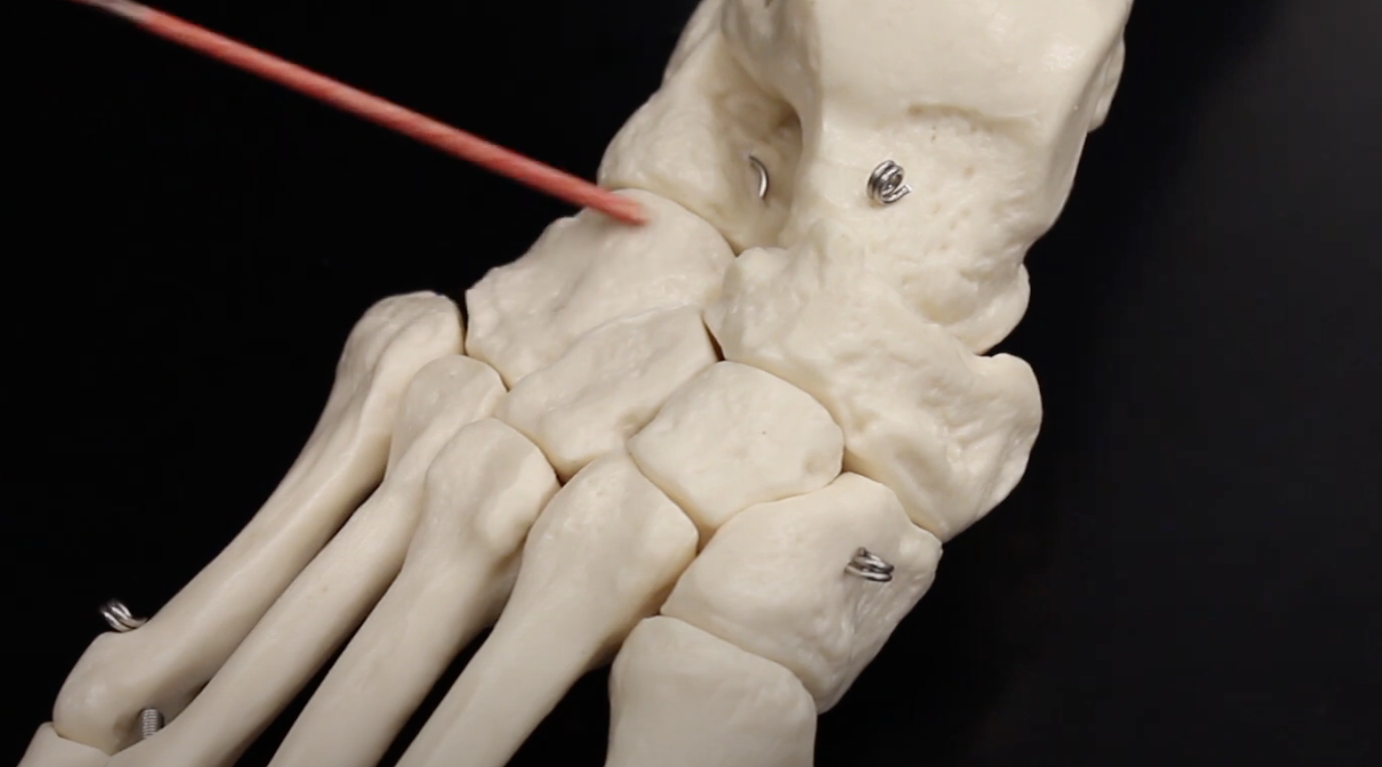
Navicular
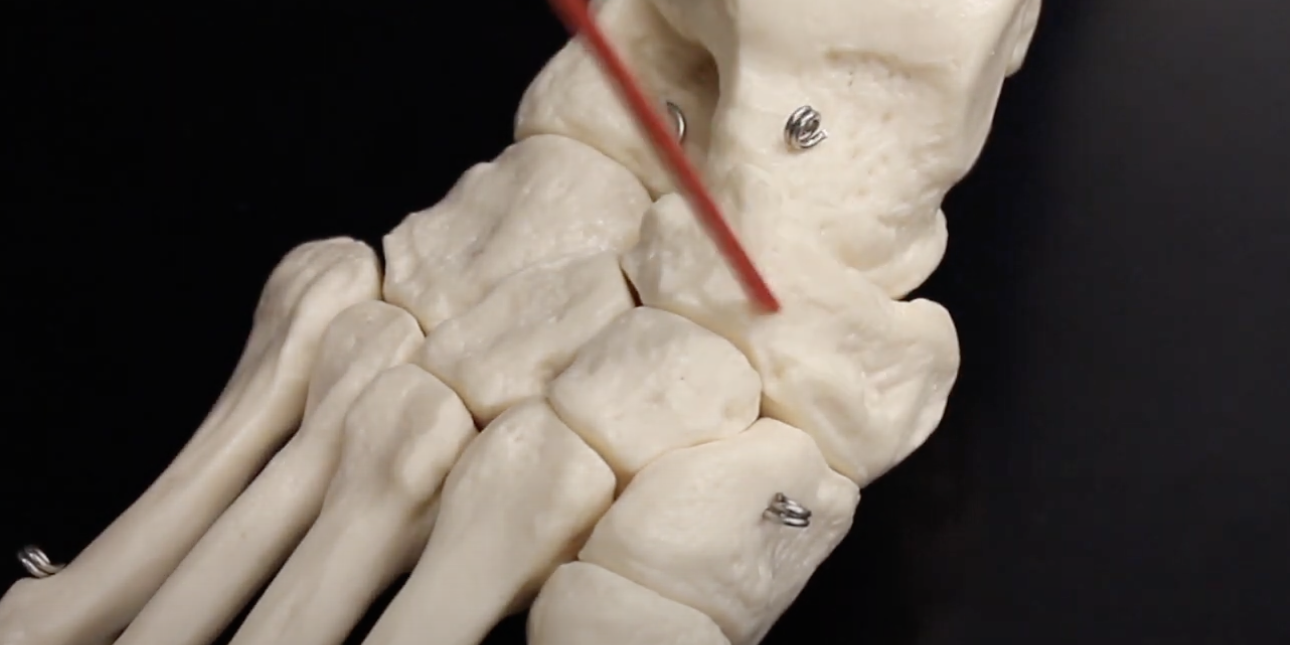
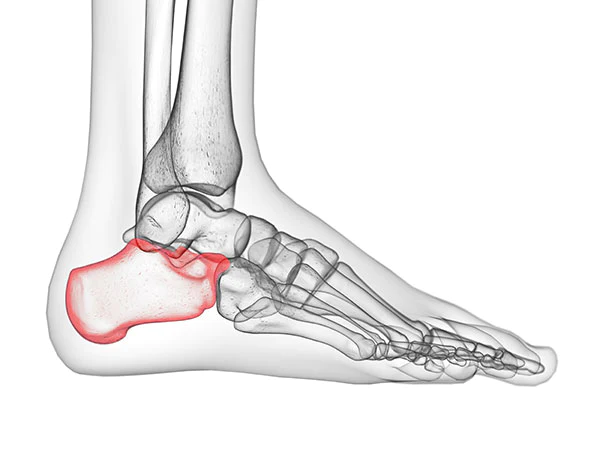
Calcaneus
Talus
