Chapter 7: Cellular Respiration and fermentation
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
oxidative phosphorylation, fermentation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What are the things consisted in the Oxidative Phosphorylation?
electron transport chain
chemiosmosis
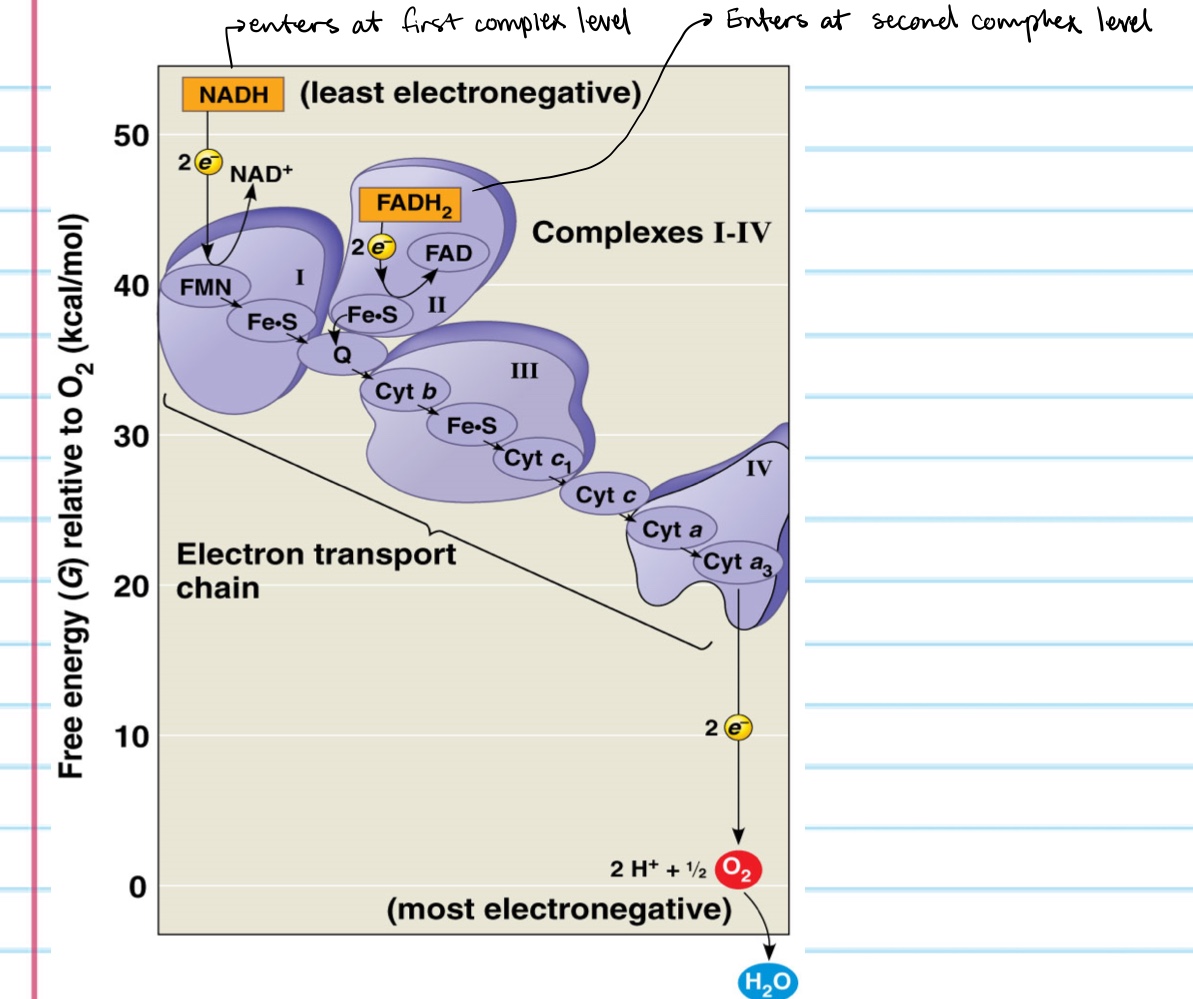
Describe the Pathway of Electron transport?
the electron transport chain is in the Cristal of the mitrochondrion
most of the chains components are proteins, which exist in multi-protein complexes
the electron transport chain generates no ATP
NADPH and FADH2 carry electrons to the electron transport chain
unlike an uncontrolled reaction, the electron transport chain passes electrons in a series of steps instead of one explosive reaction
O2 pulls electrons down the chain in an energy-yielding tumble
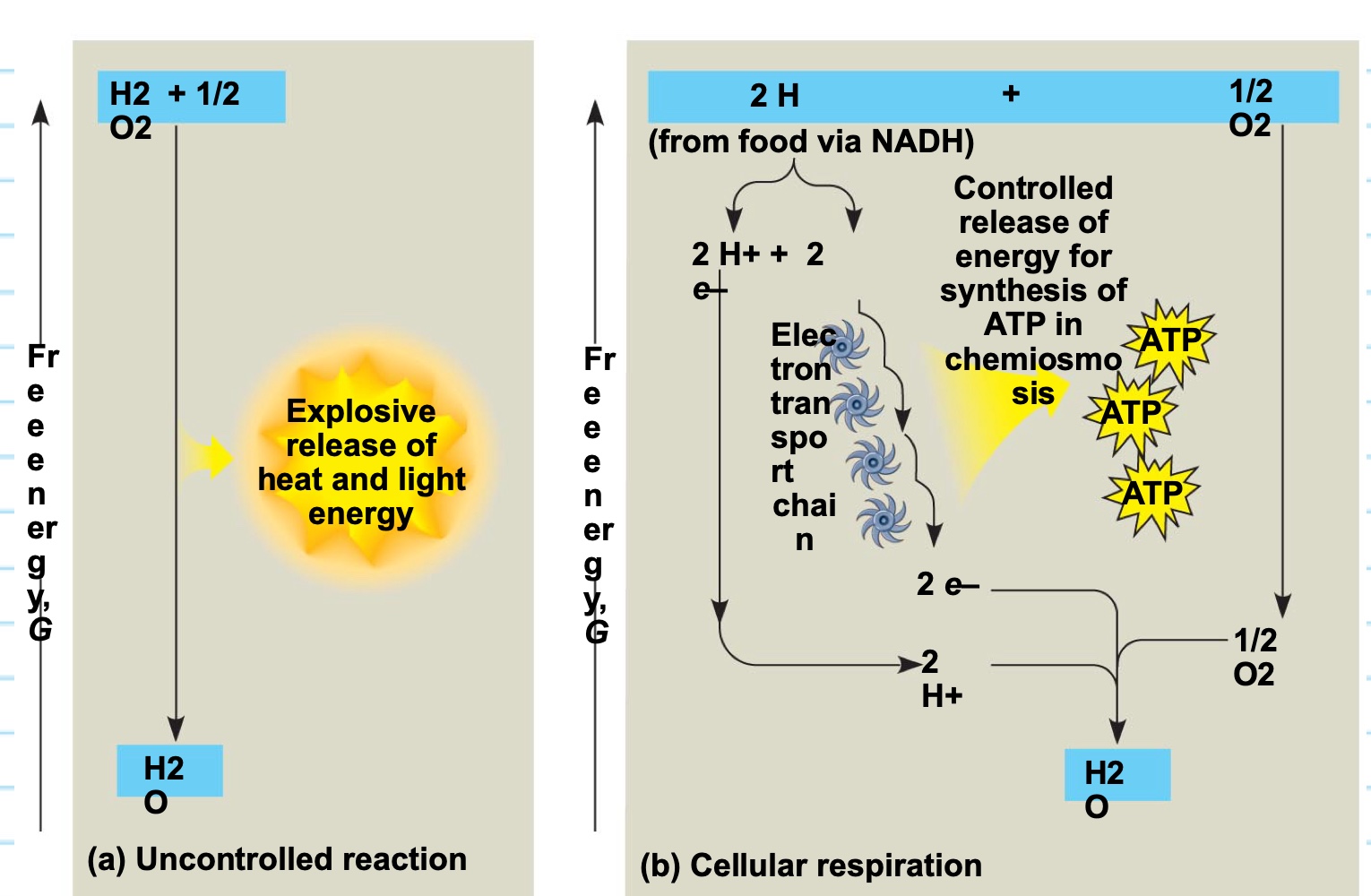
what is the difference between uncontrolled reaction and cellular respiration?
uncontrolled reaction → has an explosive release of heat and light energy
cellular respiration → has a controlled release of energy for synthesis of ATP in chemiomosis
what is the process of Chemiosmosis: the energy-coupling mechanism
H+ moves across the membrane, passing through channels in ATP synthase
this is an example of chemises, the use of energy in a H+ gradient to drive cellular work
the H+ gradient is referred to as proton-motive force, emphasizing its capacity to do work
ATP synthase produces ATP by oxidative phosphorylation
what does fermentation consist of?
glycolysis
reactions that regenerate NAD+, which can be reused by glycolysis
what are the two common types of fermentation?
alchohol fermentation
lactic acid fermentation
what happens in alcohol fermentation?
pyruvate is converted to ethanol
CO2 is released
Alcohol fermentation by yeast is used in brewing, winemaking, and baking
what happened in Lactic acid fermentation?
Pyruvate is converted to lactate
no release of CO2
lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt
human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce (ex. exercise)
Compare fermentation and Aerobic Respiration
both processes use glycolysis to oxidize glucose to pyruvate
the process have different final electron acceptors: an organic molecule [(such as pyruvate in lactic) or acetaldehyde (in ethanol)] in fermentation and O2 in cellular respiration
cellular respiration produces up to 32 ATP per glucose molecule; fermentation produces 2 ATP per glucose molecule