PLTW Biomed 1.2
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Autopsy
A systematic examination of the entire body after death. It helps the forensics team determine clues to homicides and the medical team determine a time and cause of death. These must occur when a person has died mysteriously.
Cause Of Death
The specific injury that led to the victim's death in a direct manner (Stab Wound, Gunshot, Heart Attack, Organ Failure)

Mechanism Of Death
What happened in the body physiologically that led to the death (Blood Loss, Cardiac Arrest, Asphyxia, Cerebral Contusion)
Manner Of Death
The circumstances that resulted in the death, whether it was unnatural or natural. (Natural, Accidental, Suicidal, Homicidal)

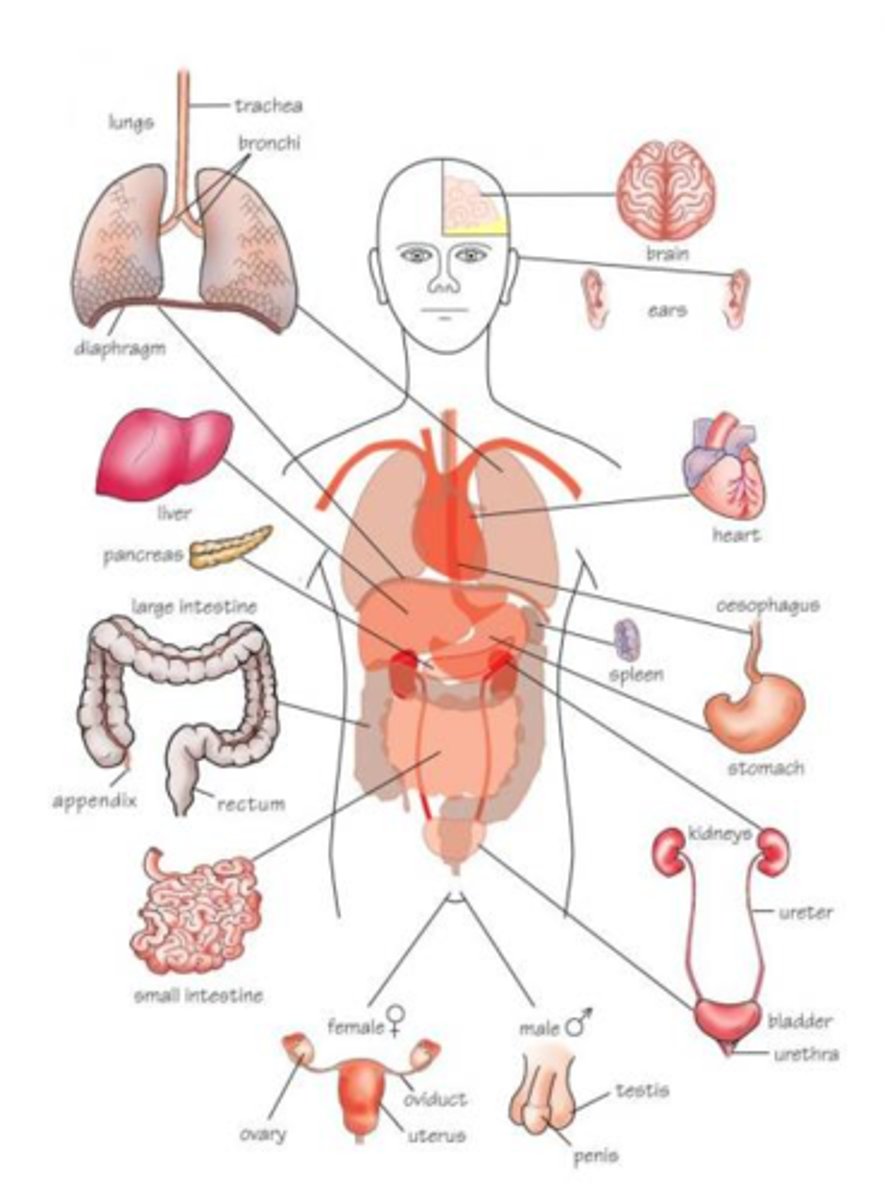
Organ System
A group of organs in a body that work together to perform a specific function.
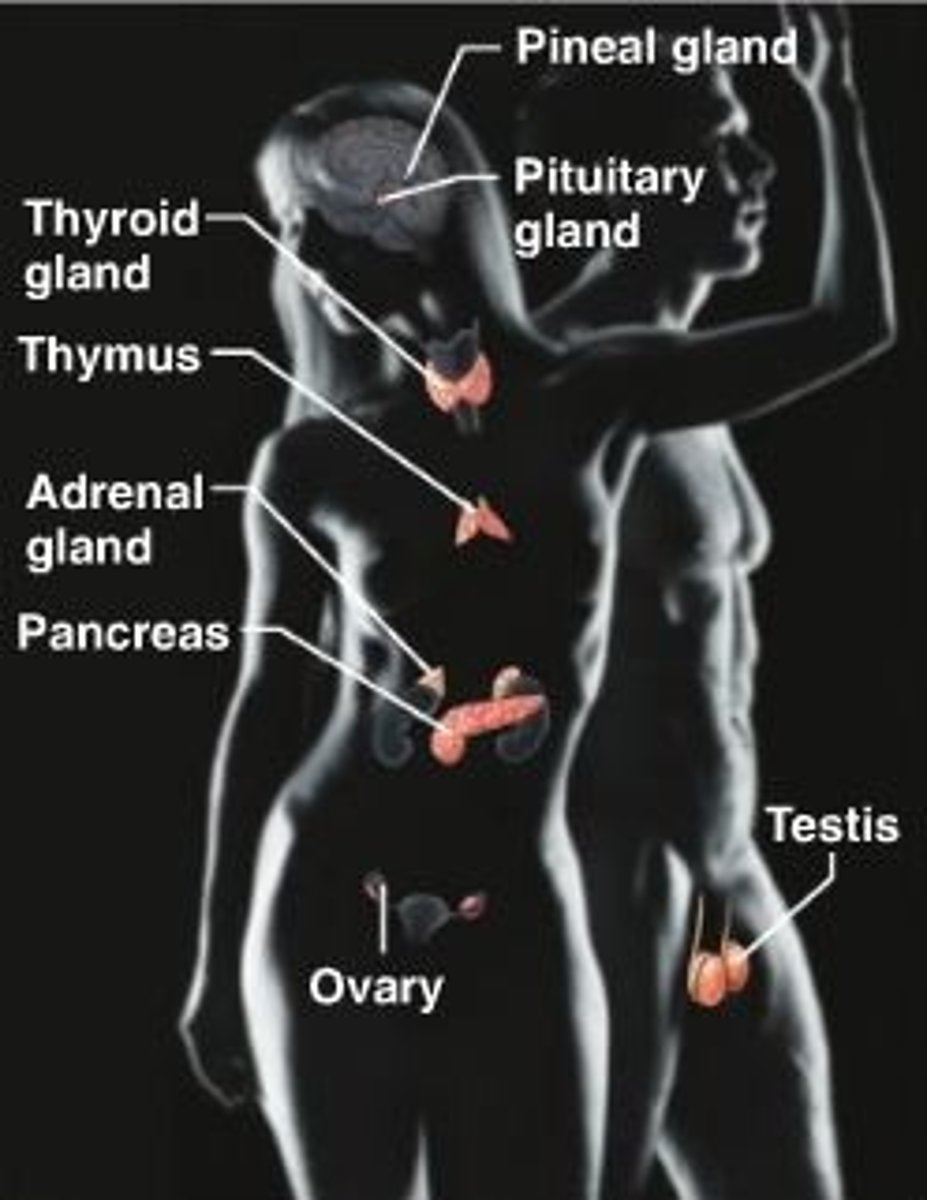
Endocrine System
The system that eliminates waste in the body and balances water amounts in the body.
Circulatory System
The system that pumps blood all around the body using veins and arteries to replenish the oxygen and distribute it among the organs.

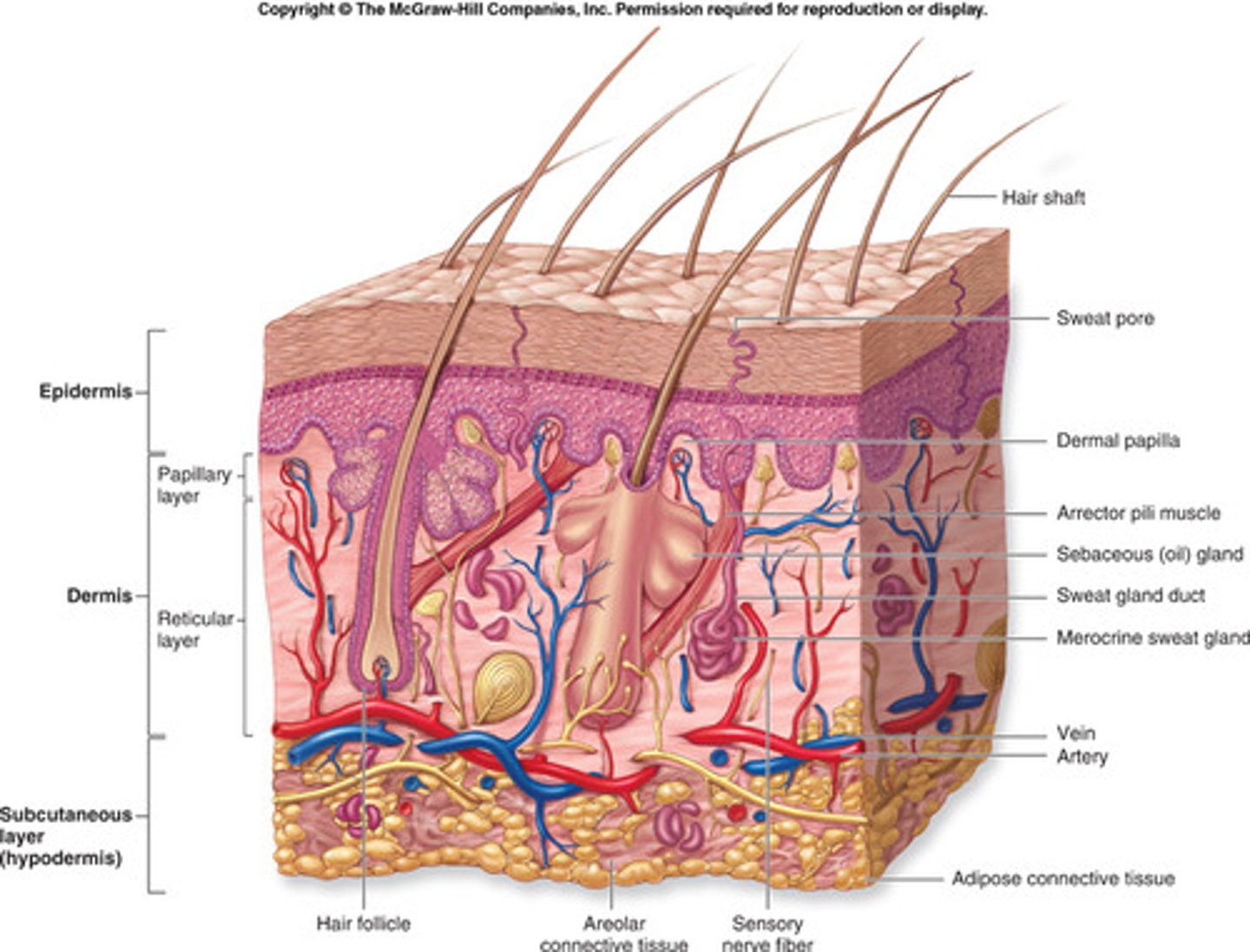
Integumentary System
This system that regulates body temperature and serves as the external covering of the body to protect. It also aids the other body systems as well.
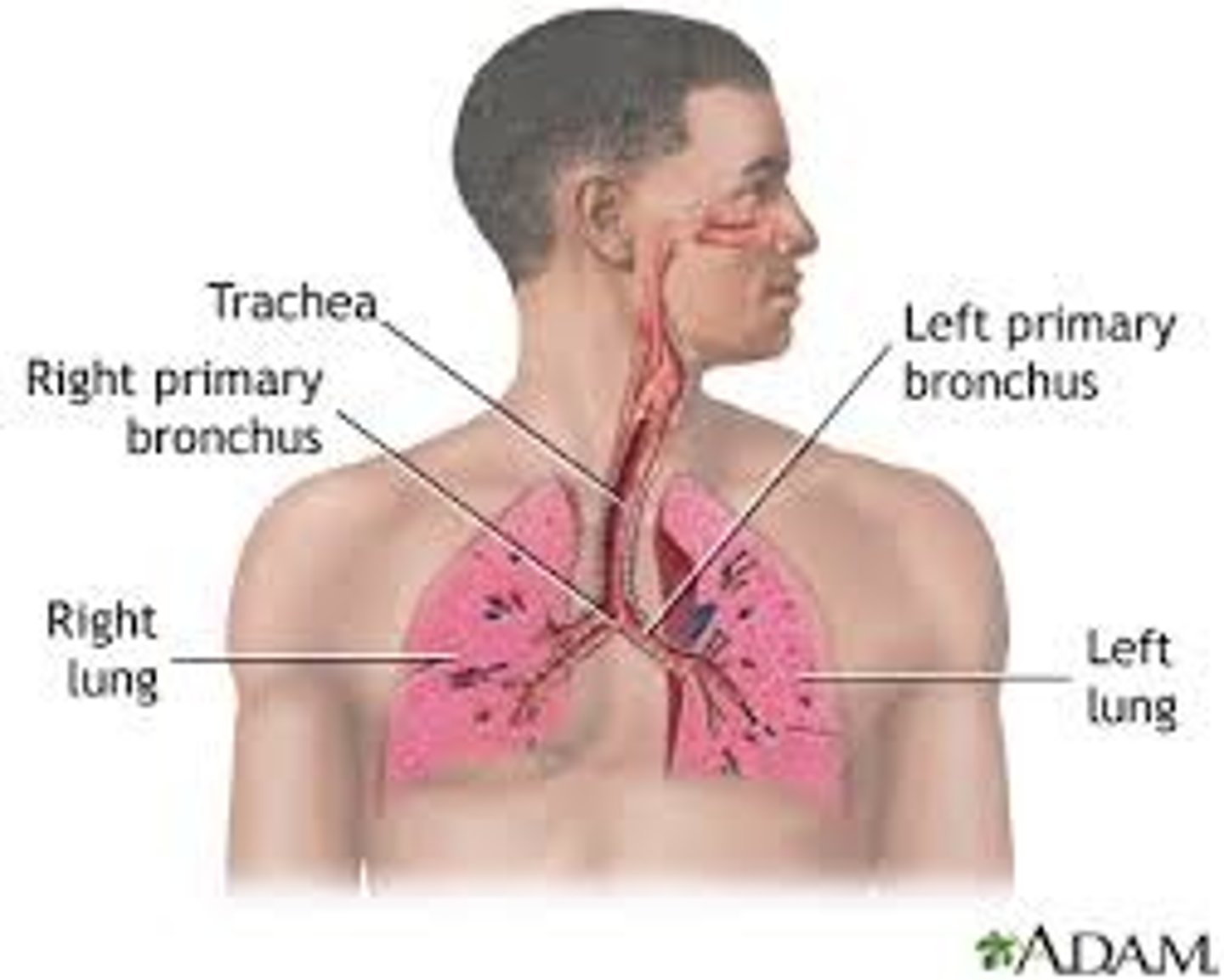
Respiratory System
The system that keeps blood supplied with oxygen from inhaling and removes carbon dioxide from exhaling.
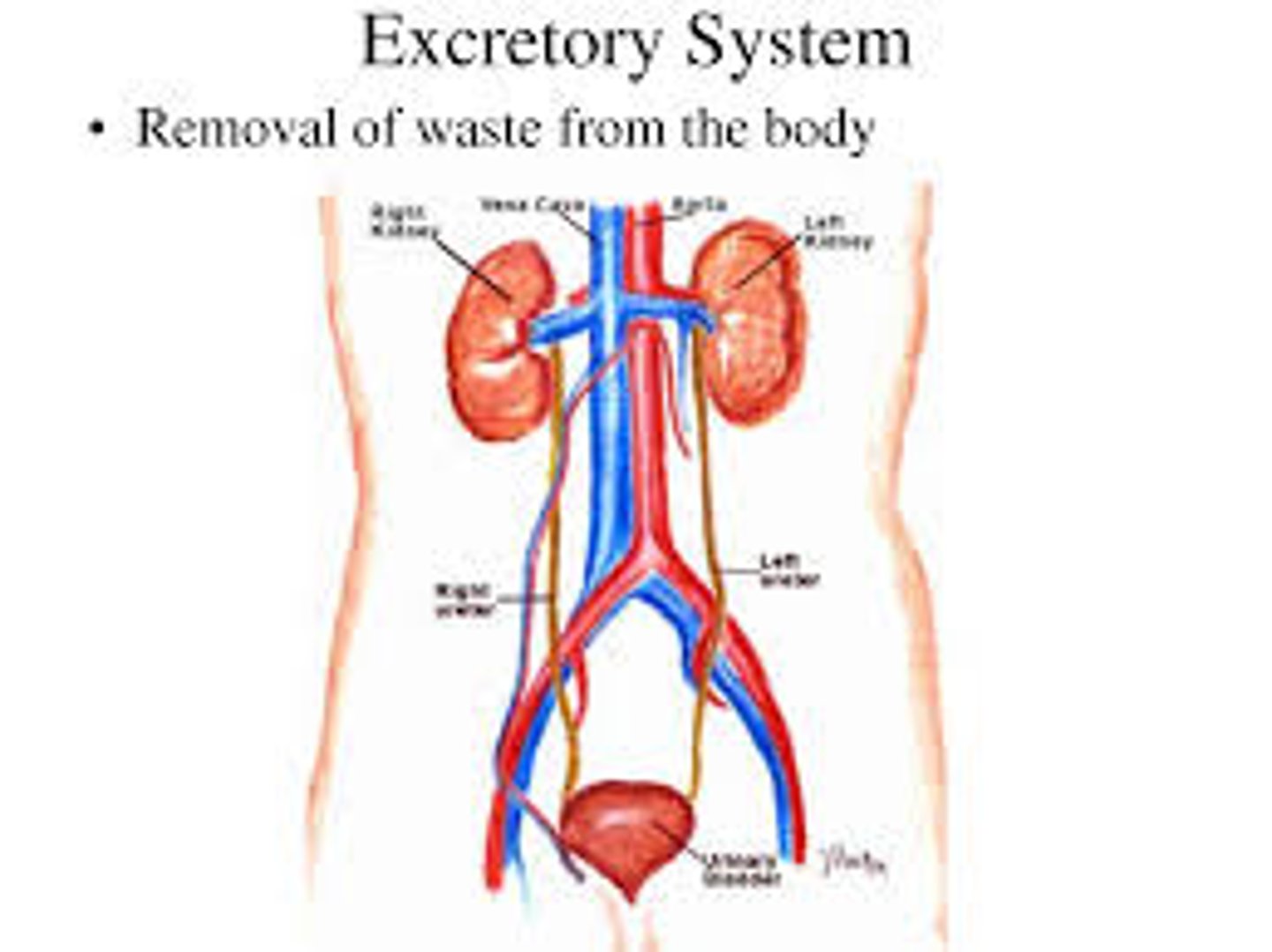
Excretory System
The system that secretes hormones to contribute to reproduction and metabolism in the cells
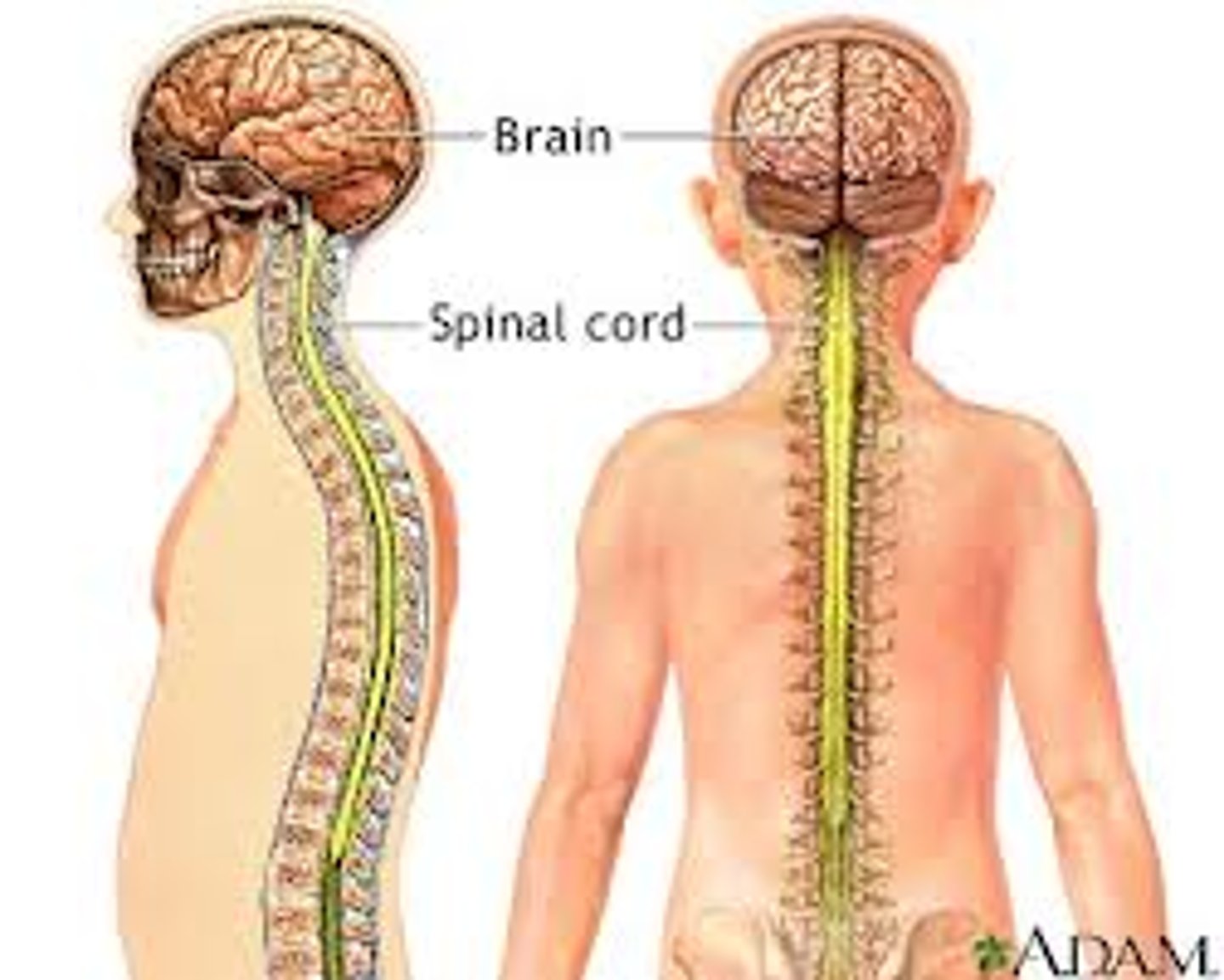
Nervous System
The system that responds to changes externally and internally and processes information
Immune System
The system that filters blood in the body and fights against foreign attacks from viruses and bacteria.
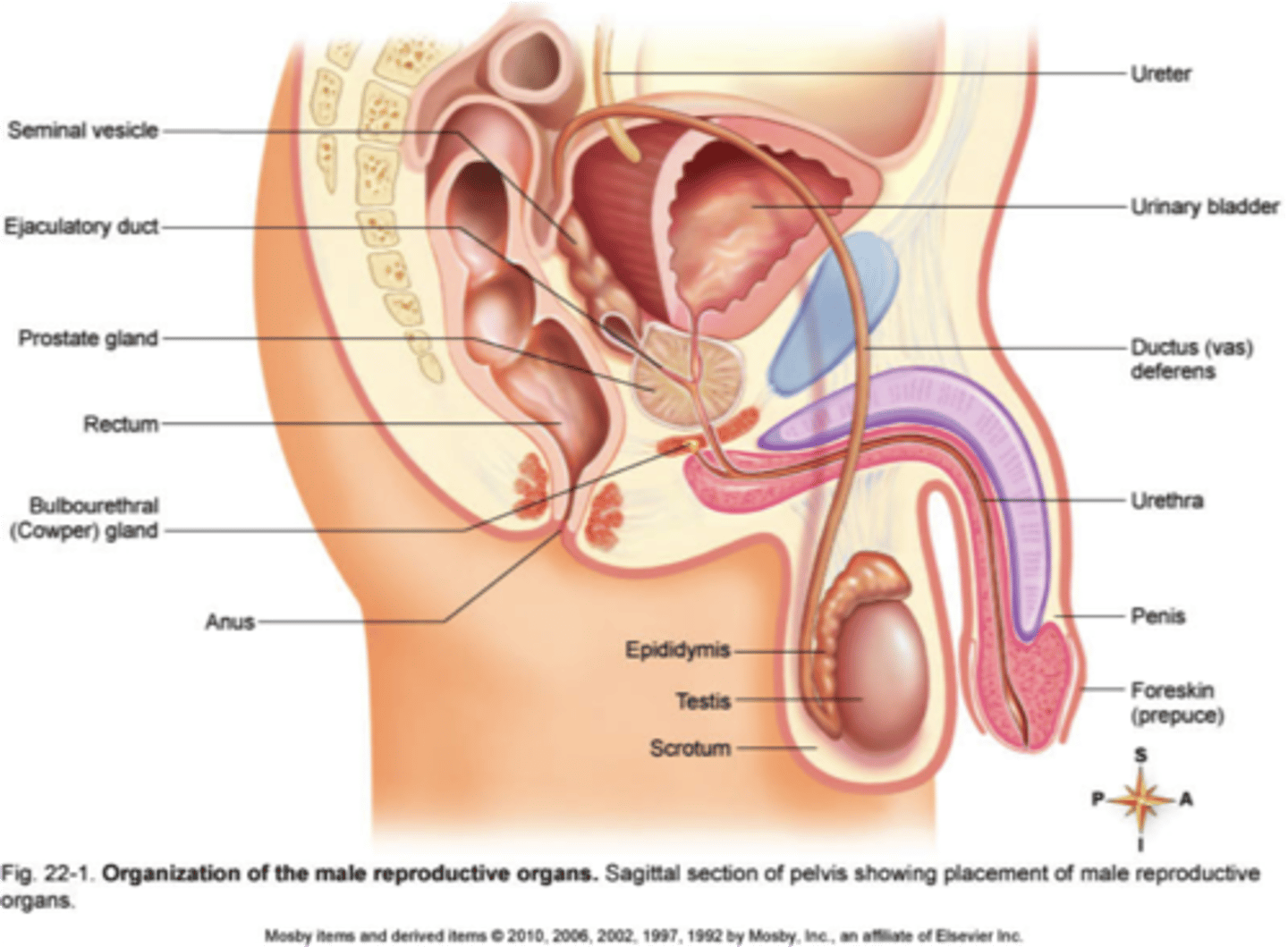
Reproductive System
The system that produces and transports semen to nurture offspring
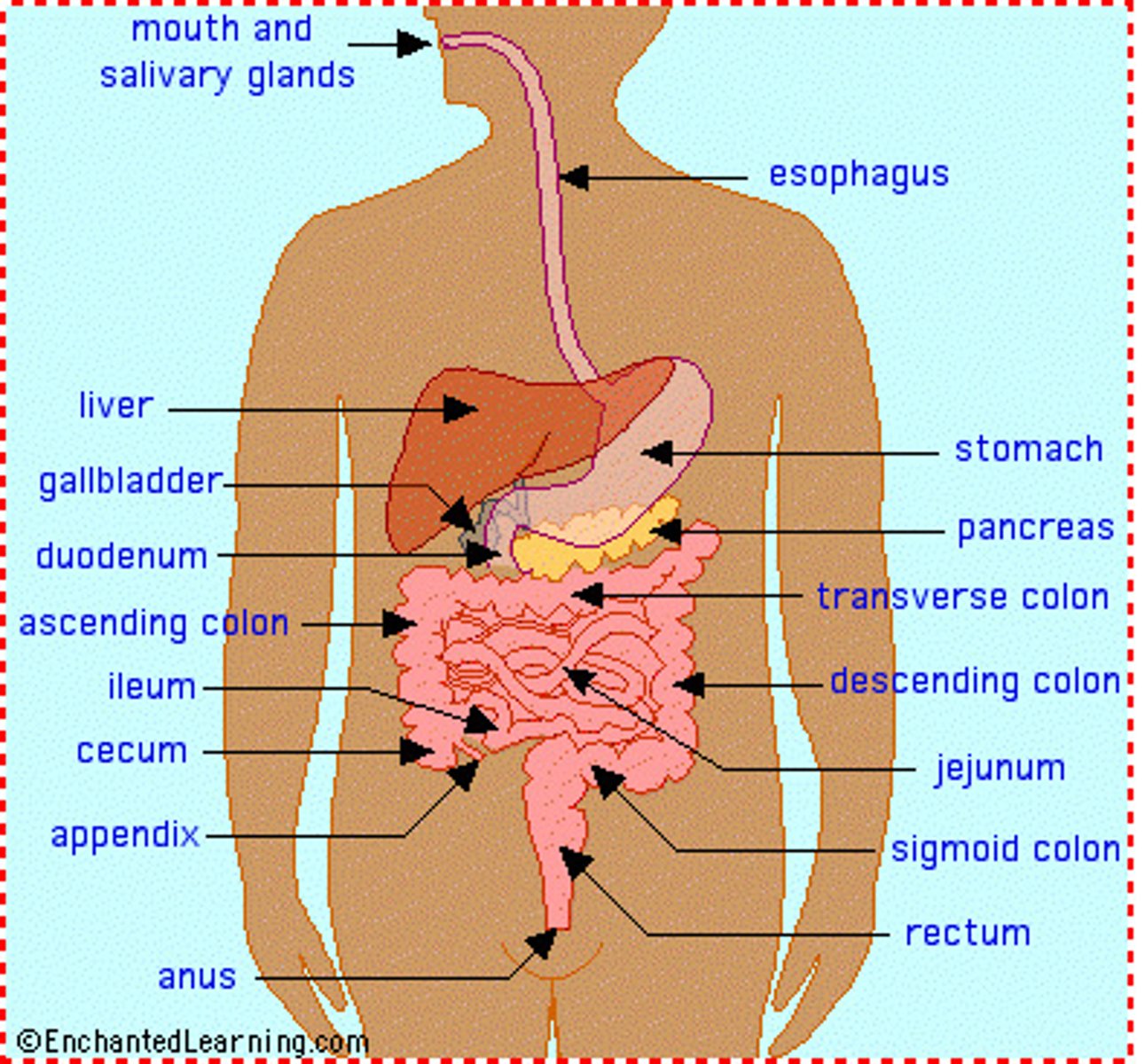
Digestive System
The system that breaks down food into nutrients and rids body of digestive waste
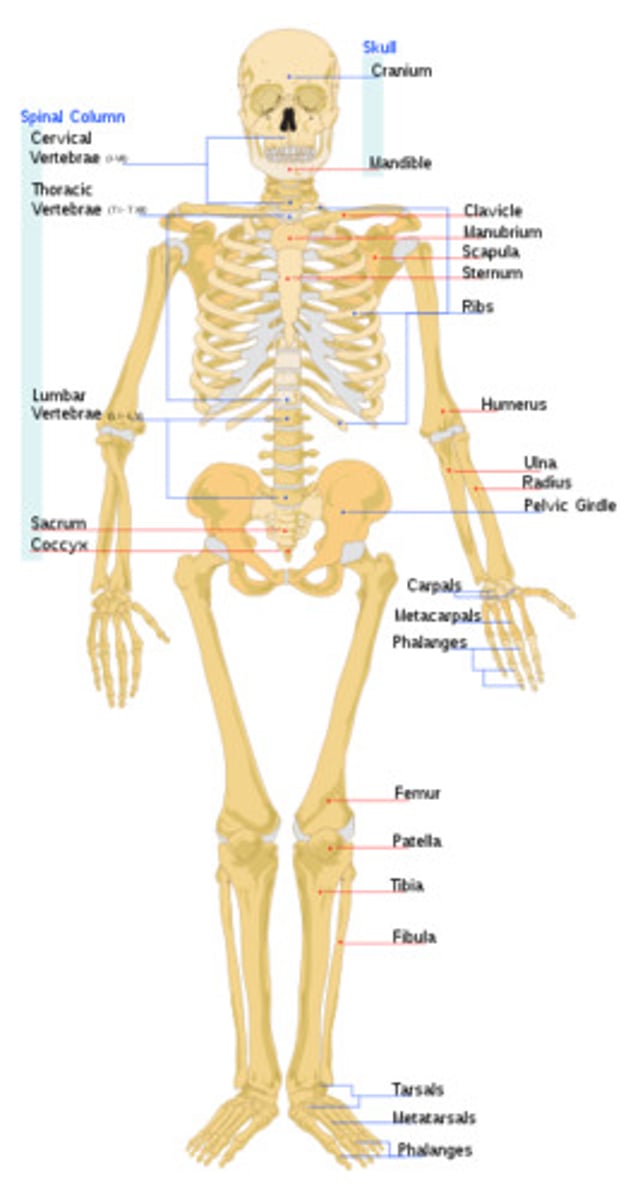
Skeletal System
The system that supports and protects the organs, stores minerals, and serve as framework for movement.
Muscular System
The system that moves the organs and body, maintains posture and produces insulation.
Physiological Time Of Death
The determined time that the decedent's organs stopped working and functioning
Estimated Time Of Death
The estimated time that the medical examiner determined based on the autopsy

Legal Time Of Death
The legal time that is recorded on the death certificate of the decedent based on the location and state of the death.

Glaister Equation
A formula used for determining the approximate time period since death based on body temperature
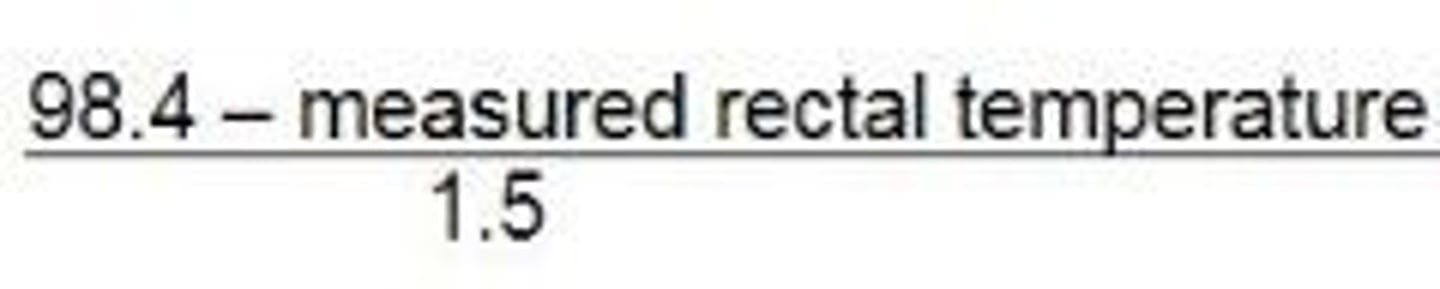
Algor Mortis
The cooling of the body after death. This happens immediately after death and ends 24 hours post mortem.
Rigor Mortis
The stiffening of the body after death. This happens 2-4 hours after death and ends around 36 hours after death.
Livor Mortis
The pooling of the blood in tissues after death resulting in a reddish color to the skin due to the force of gravity. This happens around 5 hours after death.
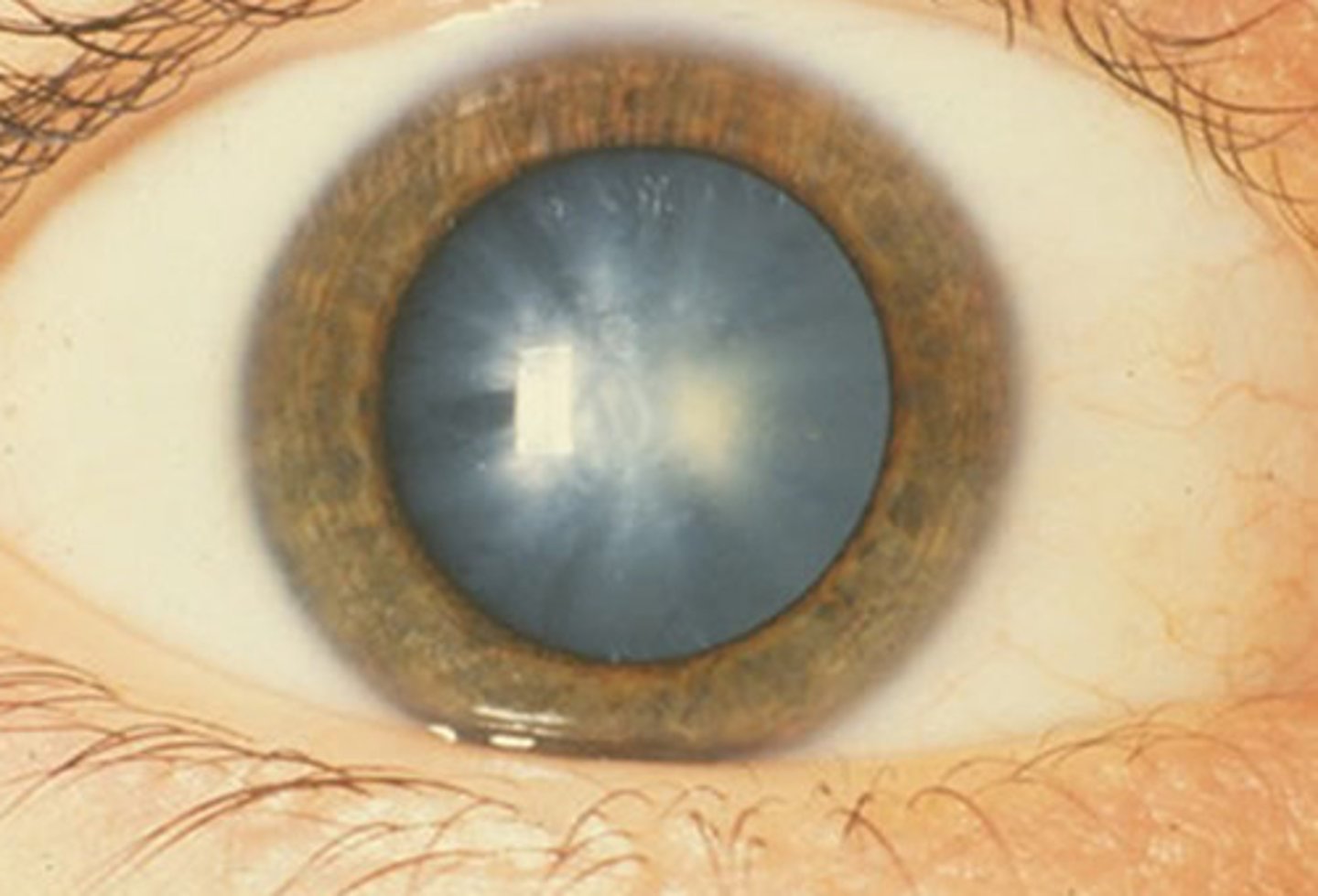
Clouding Of The Corneas
The eyes begin to cloud because the pupils no longer have reflexes to reflect light. This happens around 30 minutes after death.
Decomposition
The body begins to break down and rot, which makes it one of the longest processes post mortem. This happens 36-48 hours after the death of the person.

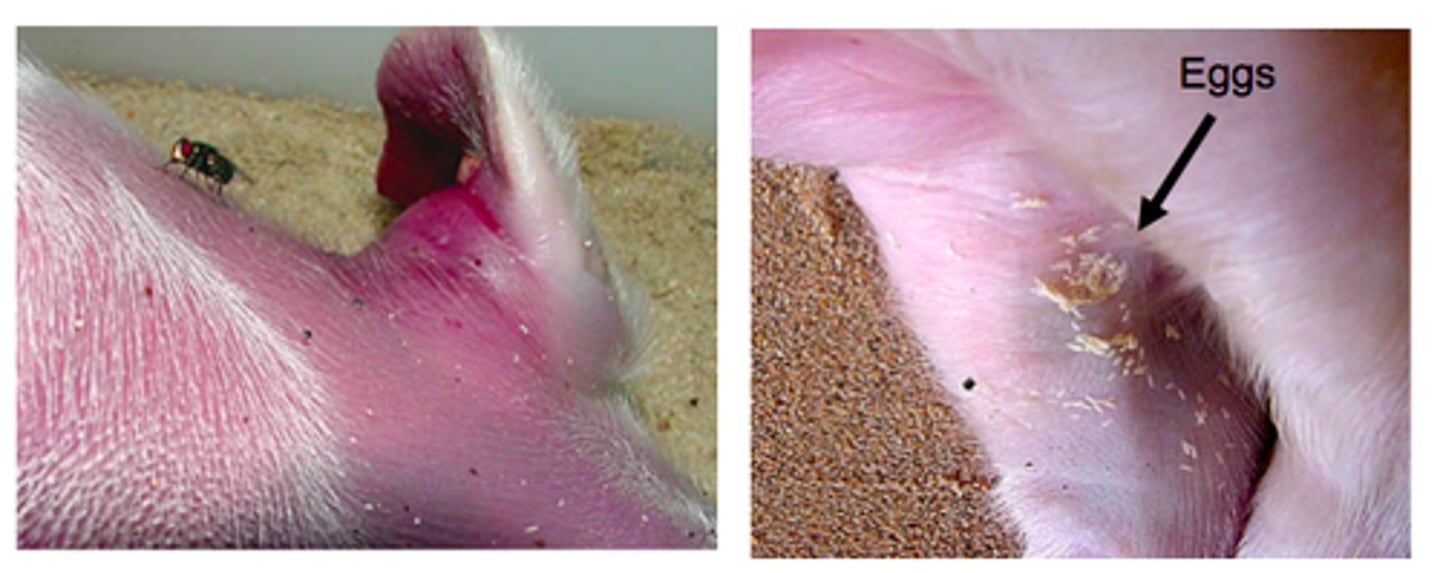
Insect Activity
Insects, including blowflies, lay eggs, which hatch into larvae and adult insects, which live on the body. This can happen really anytime post mortem, but it mostly happens during the decomposition step.
Forensic Toxicology
The examination of the digestive system of the body to identify any toxic and poisonous substances the decedent ingested prior to their death.

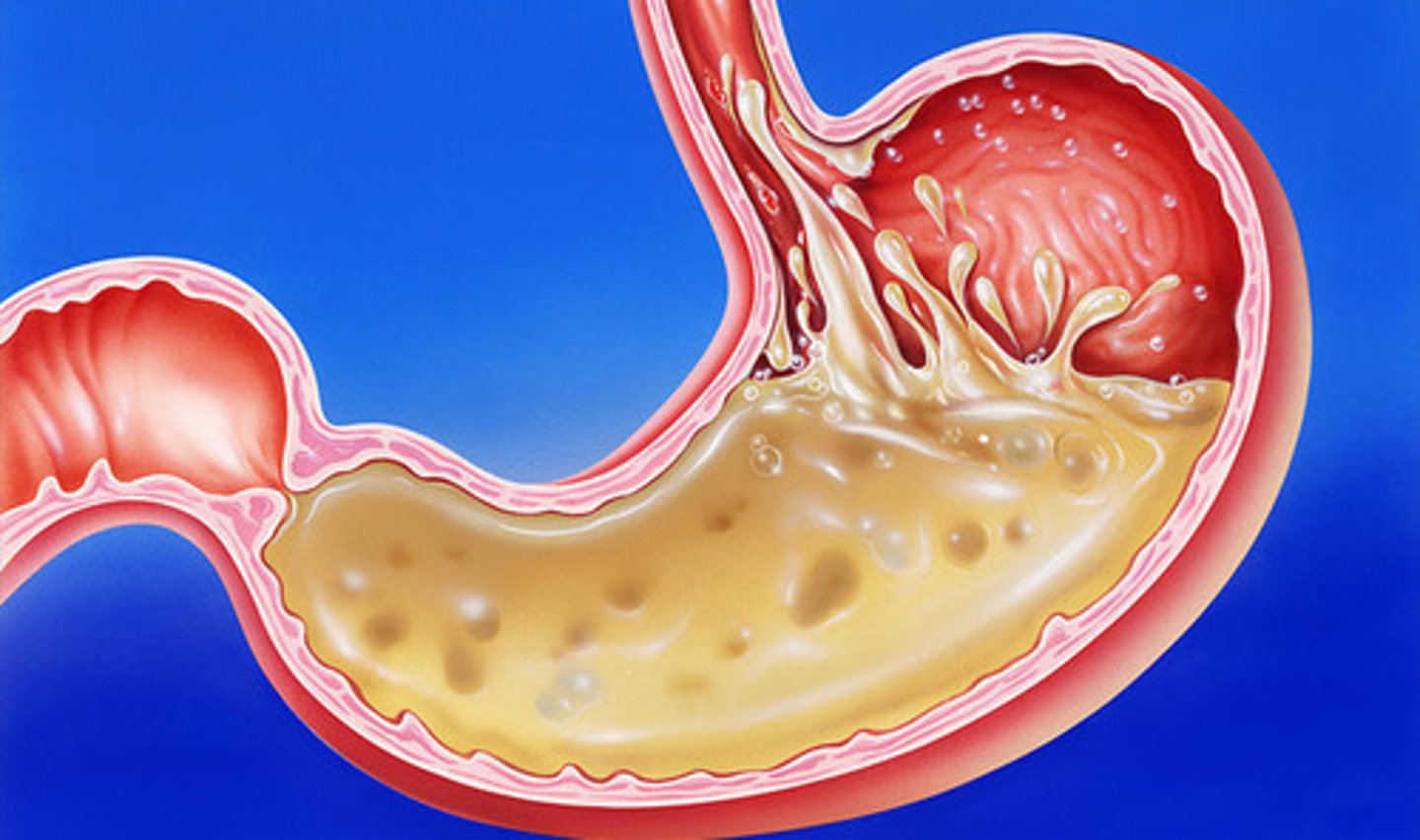
Physical Digestion
The mechanical breakdown of large food particles into smaller ones

Chemical Digestion
The body's use of acids in the small intestine and the stomach to break down the small parts of food into small molecules of nutrients to turn into energy
Metabolism
Metabolism is the process of breaking food down into very small molecules of nutrients to turn into energy, which happens in the small intestine. These small molecules of nutrients are call metabolites, which reside in the tissues and many other places in the body. Any ingested chemicals can disrupt the process of metabolism, which could be deadly.
Histology
The study of the microscopic anatomy of tissues
Central Nervous System
Processes information sent by the peripheral nervous system about the environment, makes decisions, and sends signals back to the peripheral nervous system to make changes in movement.
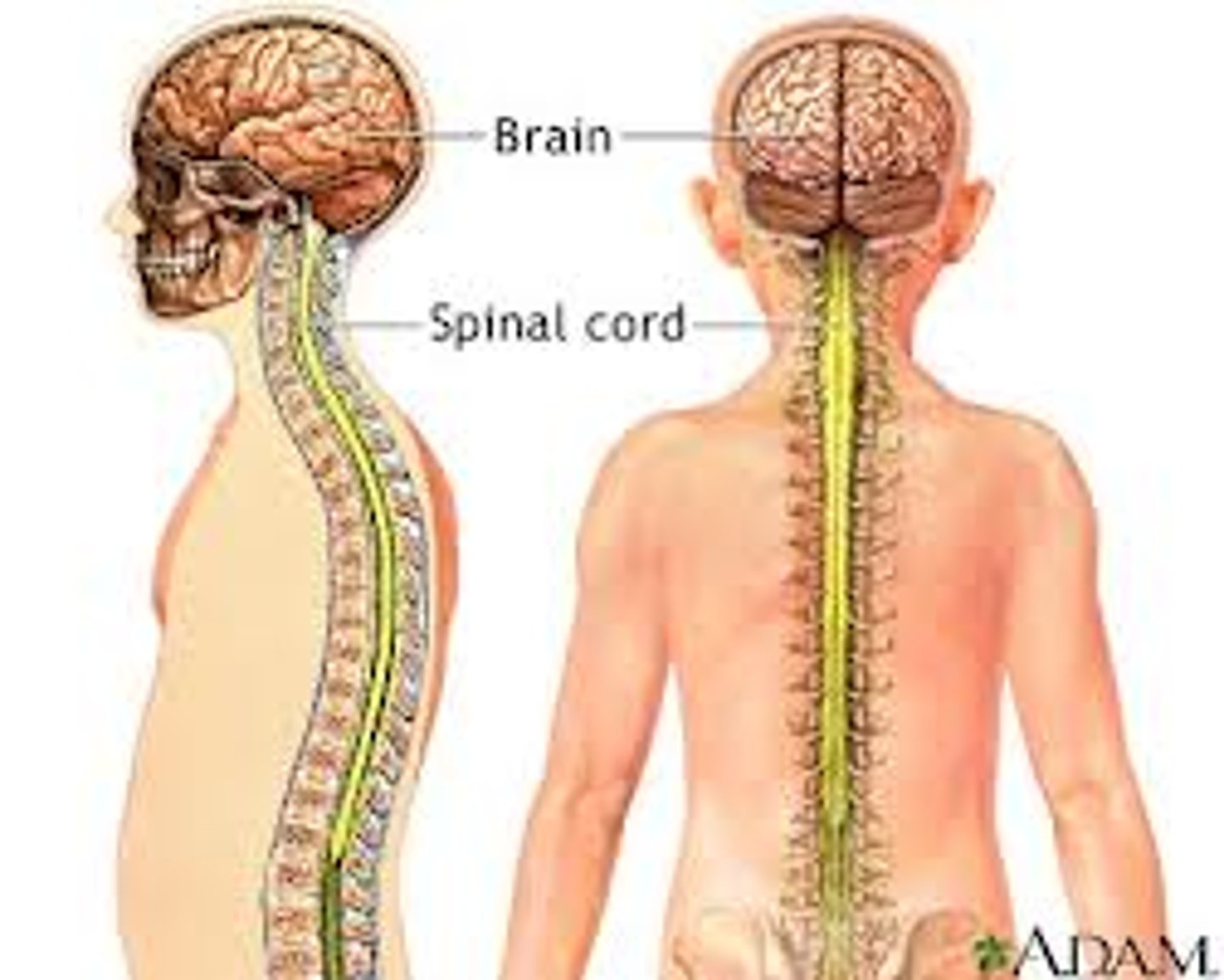
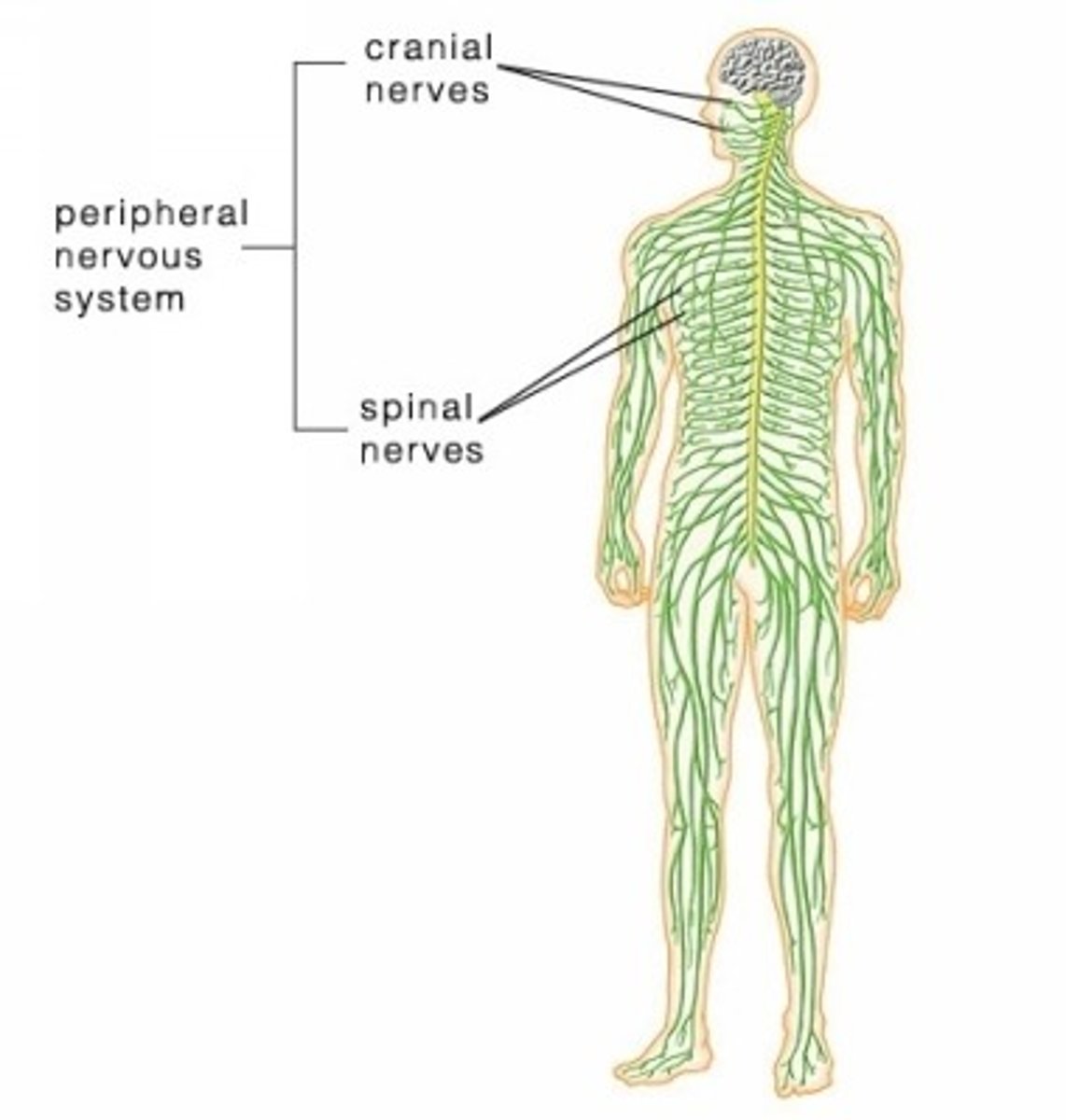
Peripheral Nervous System
Takes in information from the outside world, sends it to the central nervous system, and takes orders from signals sent from brain.
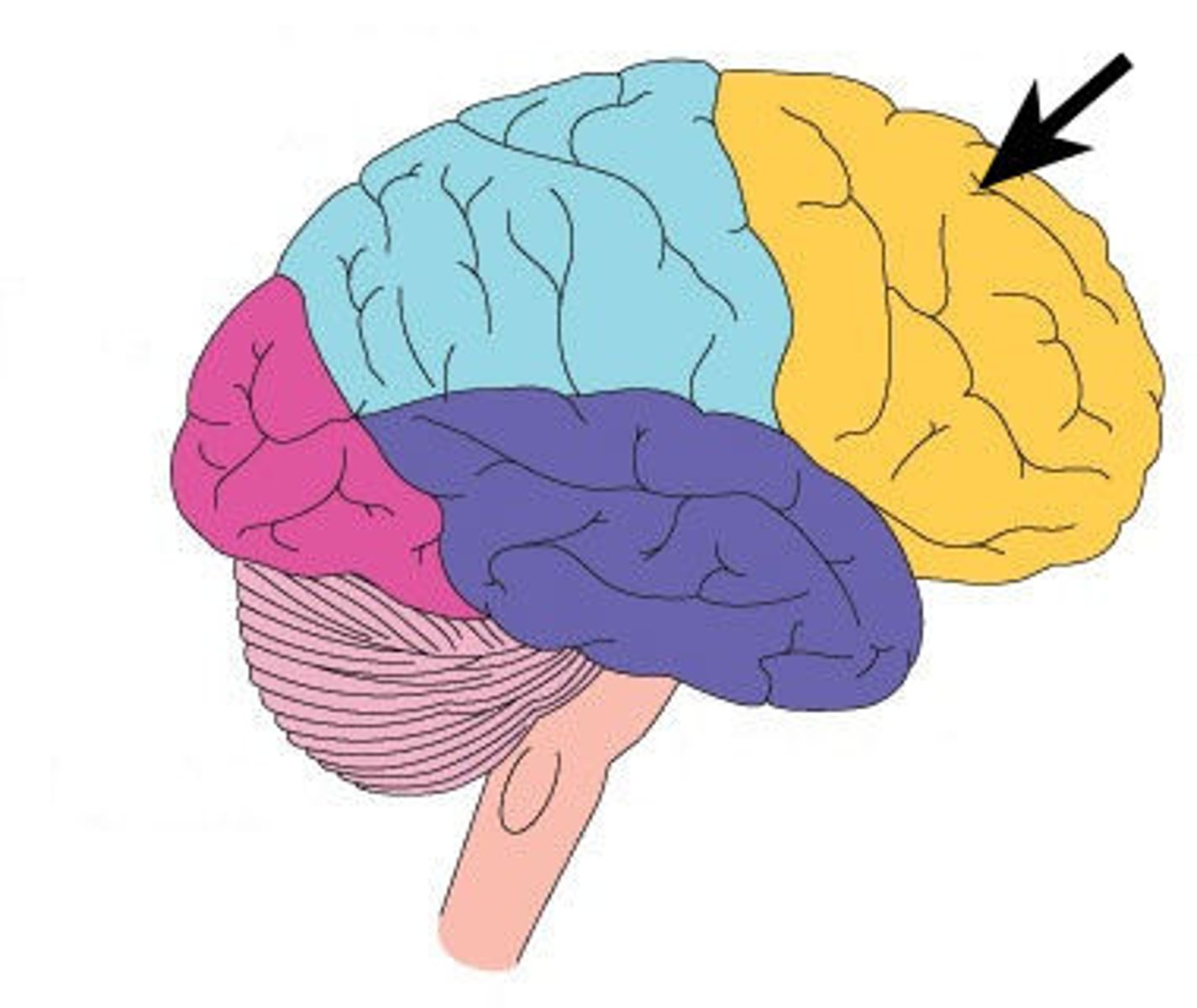
Frontal Lobe
The Frontal Lobe is responsible for planning and organizing information. It also controls behavior and emotions
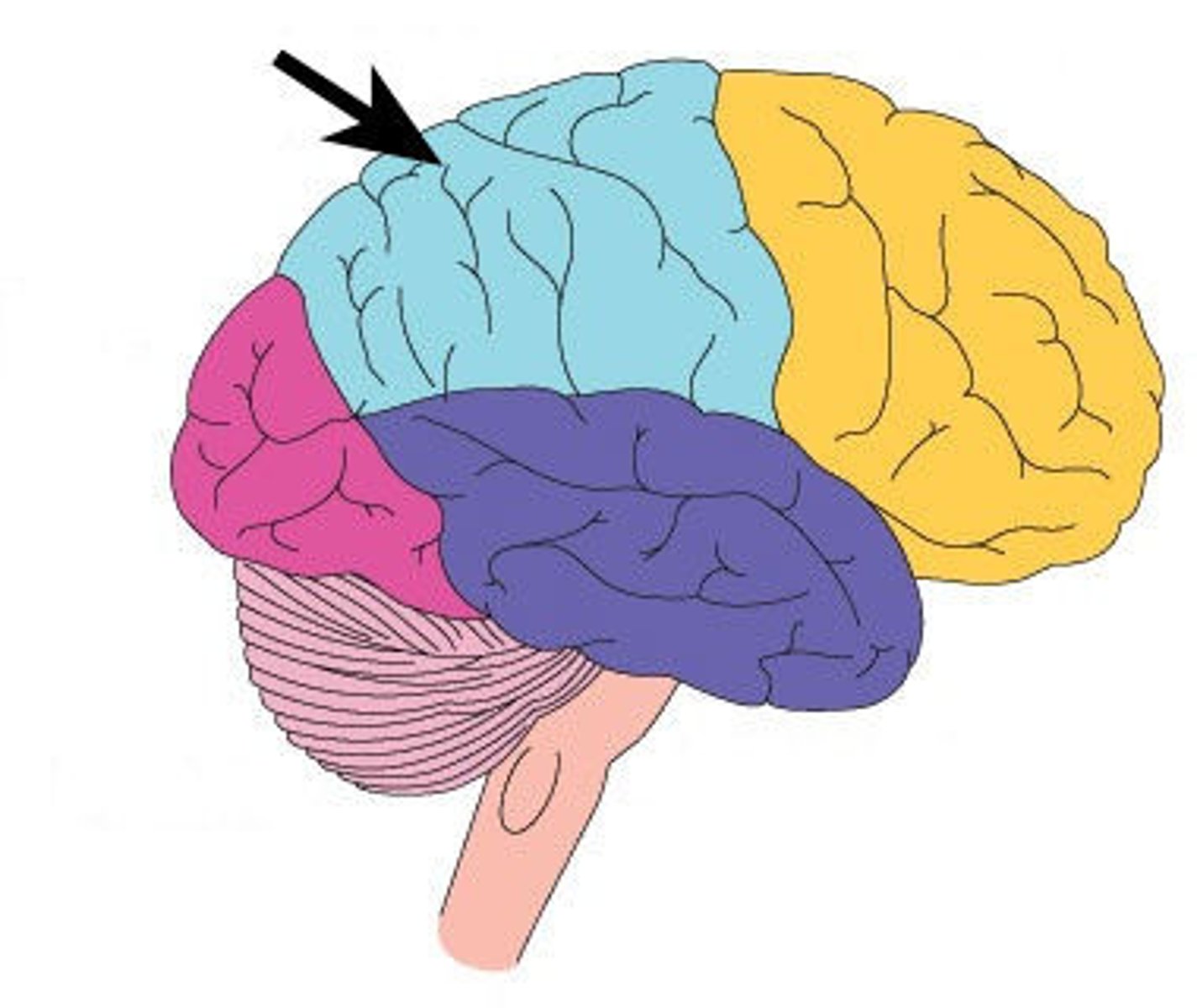
Parietal Lobe
The Parietal Lobe integrates sensory and visual details in the decisions that the brain makes.
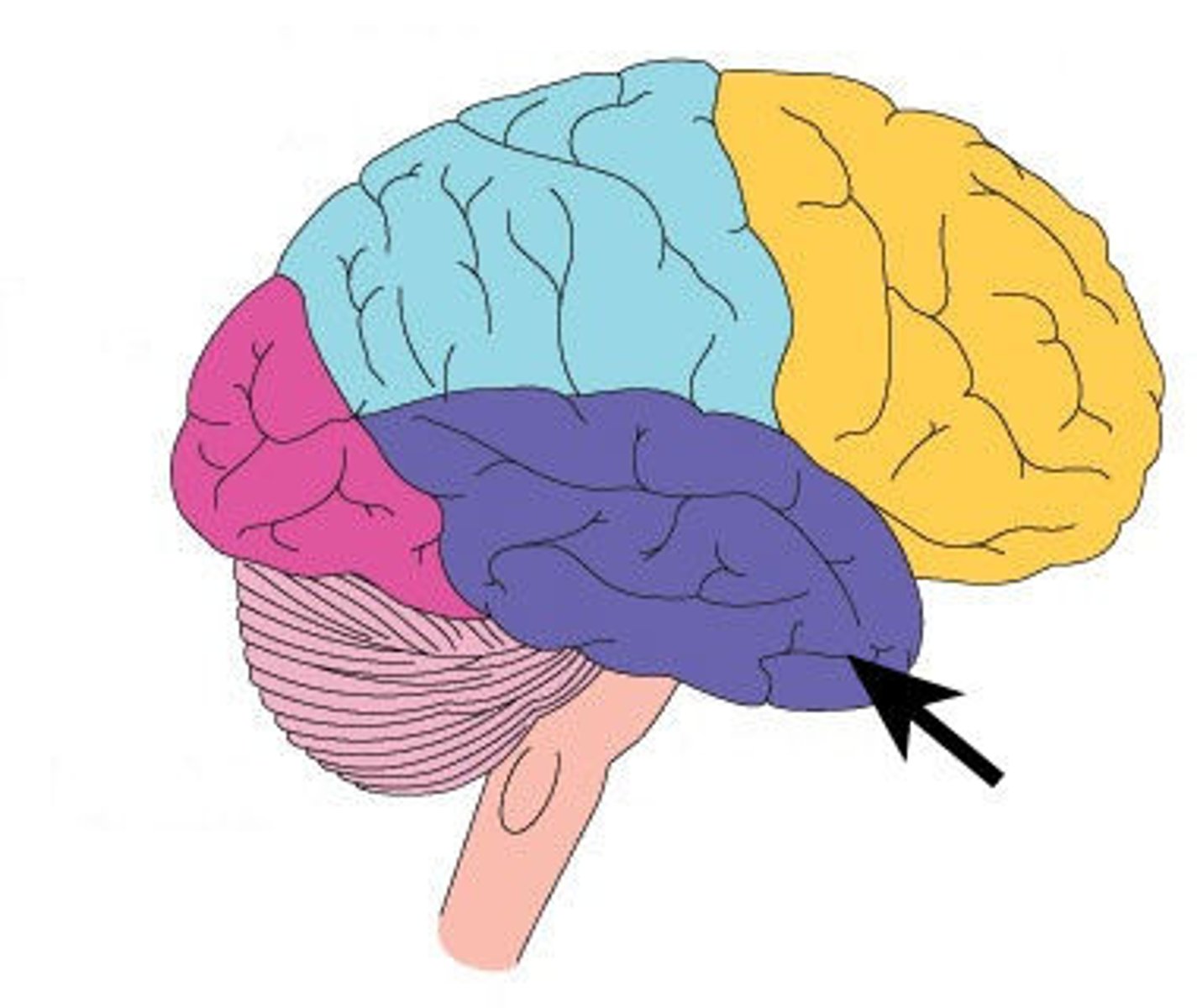
Temporal Lobe
The Temporal Lobe processes language and stores information for any long term memory
Occipital Lobe
The Occipital Lobe receives and processes sensory nerve impulses from the eyes
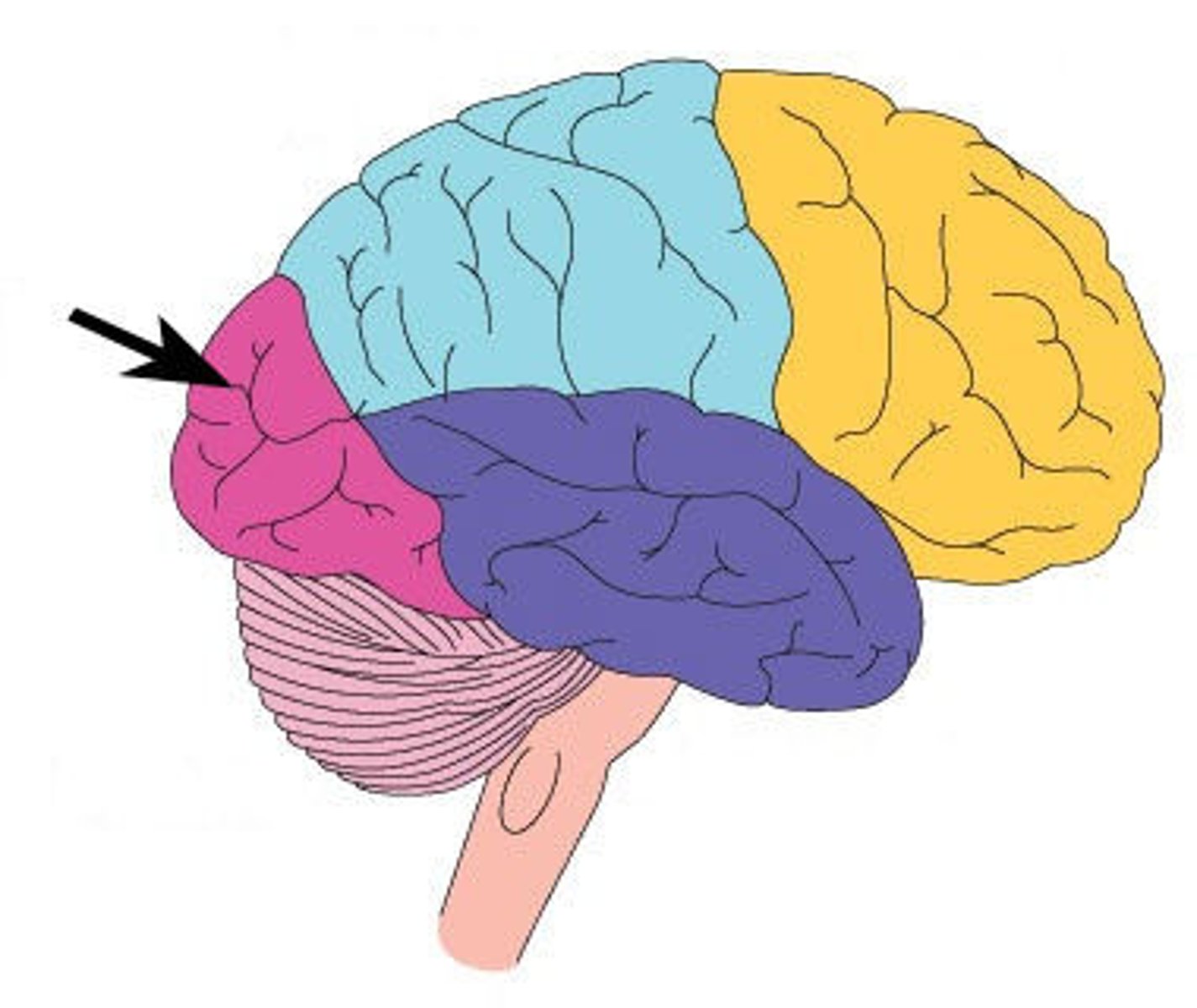
Normal Brain
No indication of chronic or traumatic brain damage
Traumatic Brain Injury
A brain dysfunction caused by an outside force to the head.
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
A progressive degeneration, and/or death, of nerve cells caused by repeated head injuries, such as repeated concussions.
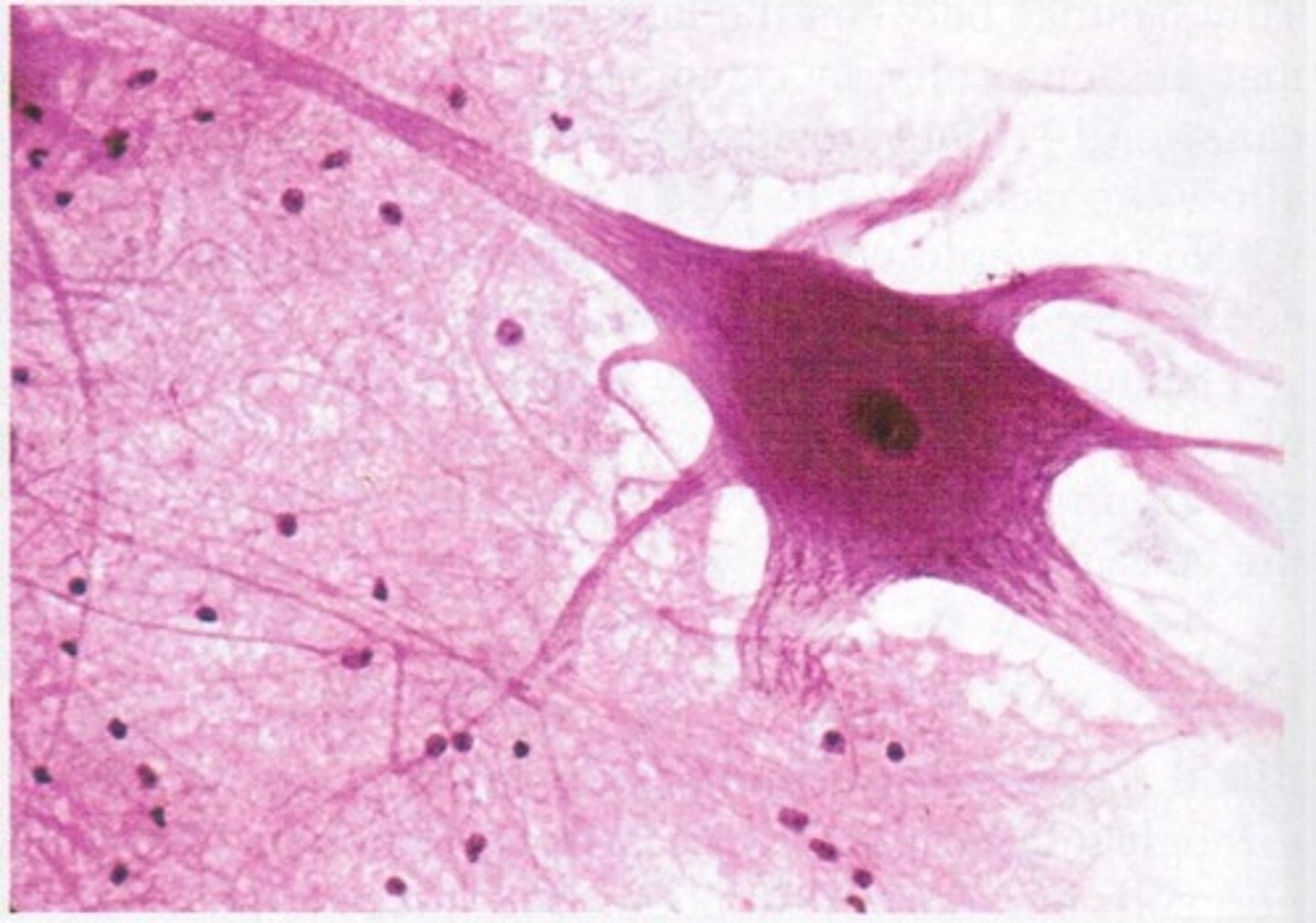
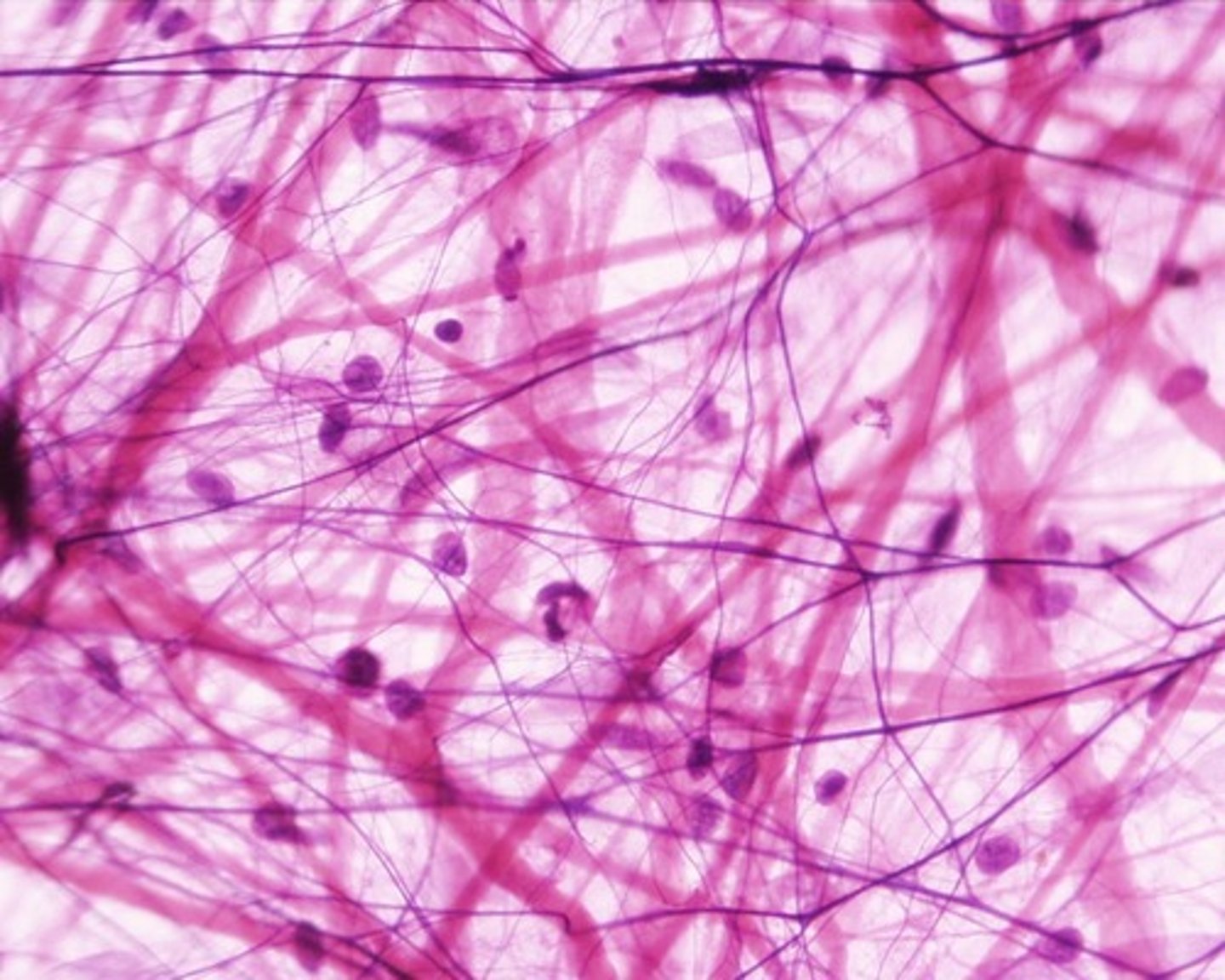
Nervous Tissue
Nerves, the spinal cord, and the brain are composed of nervous tissues. This tissue, made up of specialized cells called neurons, works to receive, interpret, and respond to signals.
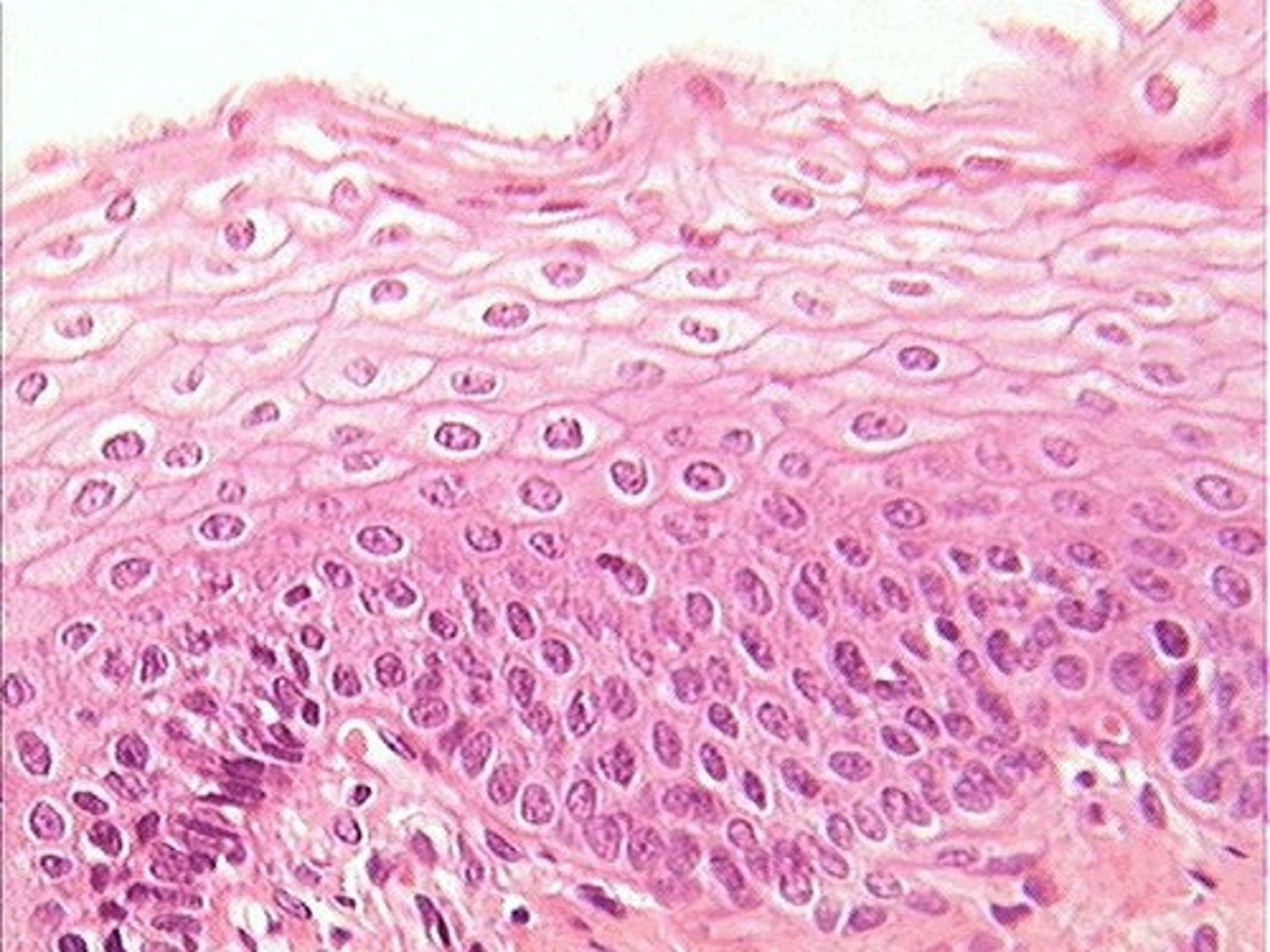
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue is composed of epithelial cells aligned in sheets and connected to one another. This tissue can be found lining the outer surfaces of all organs and blood vessels, in the mouth, and on the surfaces of humans. This tissue works to absorb, secrete, protect, and sense for us.
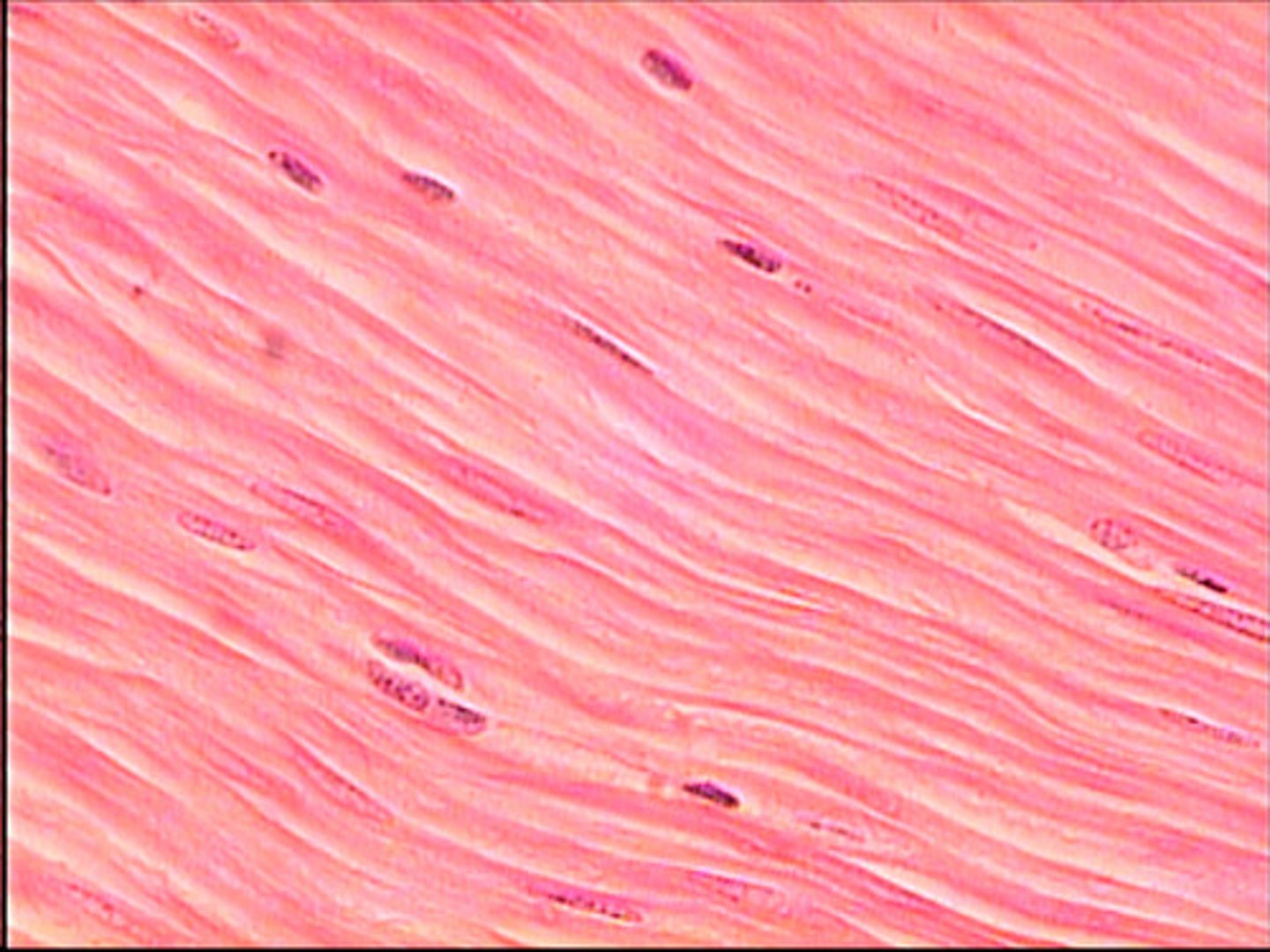
Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissue makes up the muscles found in the body. Muscle tissue can be striated, smooth, or cardiac. Striated muscle tissue, also known as skeletal muscle tissue, is attached to bones. Smooth muscle tissue is found in the walls of internal organs. Cardiac muscle tissue is found in the walls of the heart. This tissue provides the ability to contract.
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue supports and connects other tissue types in the body. Different types of connective tissue work to hold organs in place, attach muscle to bones, link bones with joints, or enable other tissues (like lungs) to stretch. It is found attached to and in between other tissues types in the body.
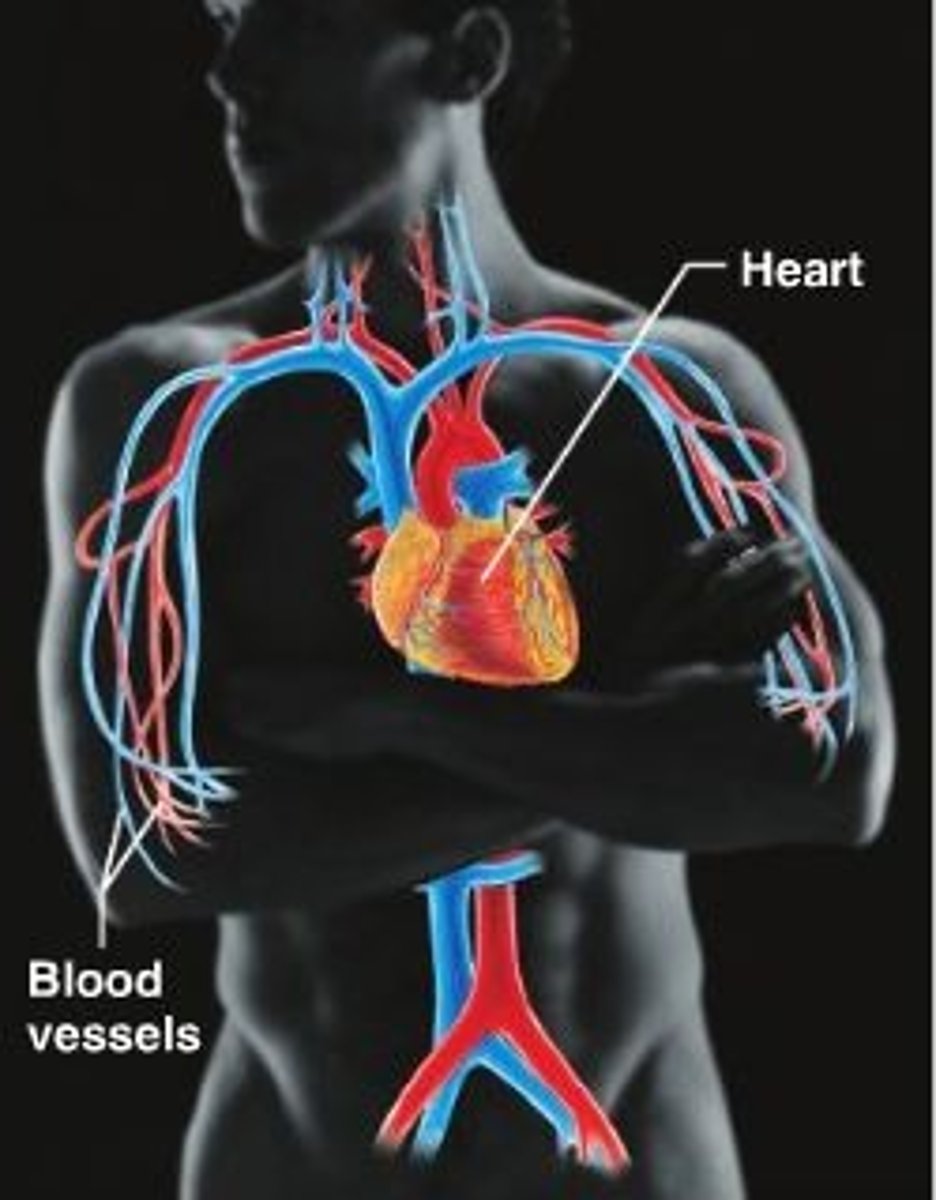
cardiovascular system
The transport system of the body responsible for carrying oxygen and nutrients to the body and carrying away carbon dioxide and other wastes; composed of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
systemic circulation
The series of vessels that bring oxygenated blood from the heart to tissues and return deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart. It includes the left atrium, left ventricle, aorta, and pulmonary veins.
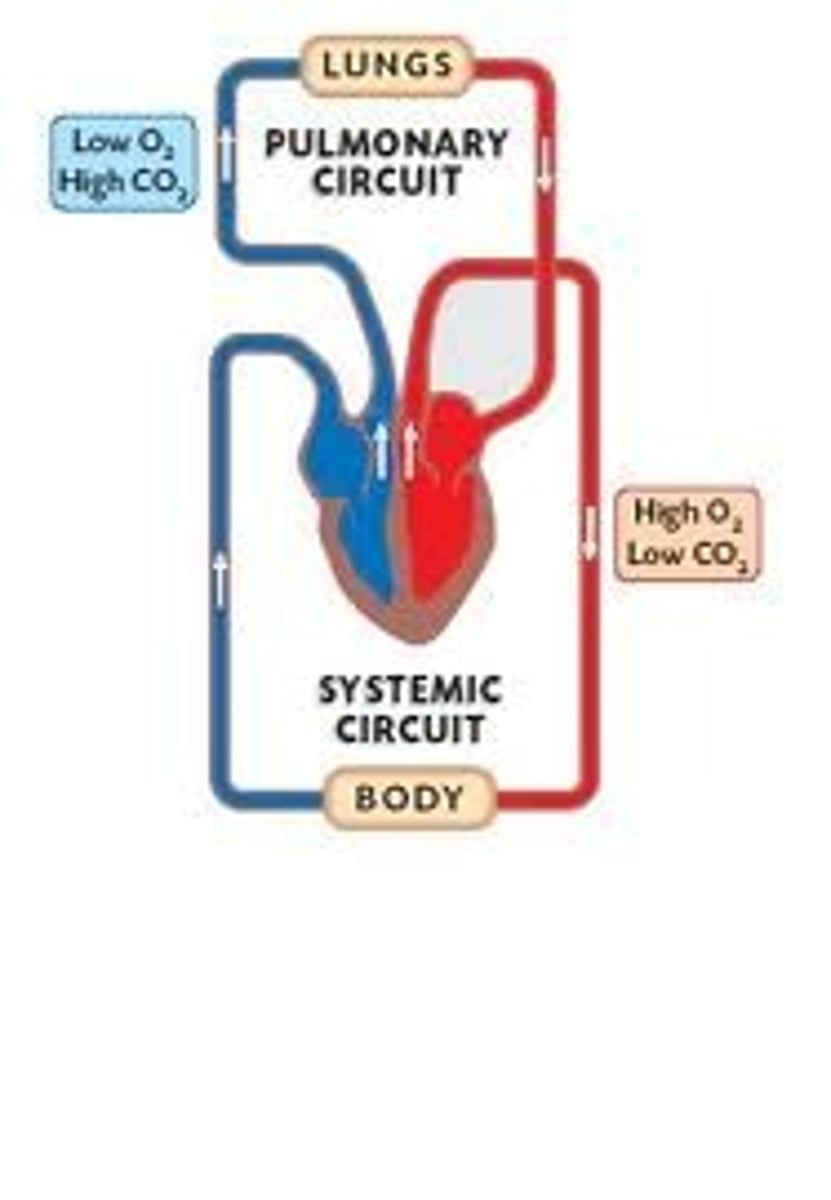
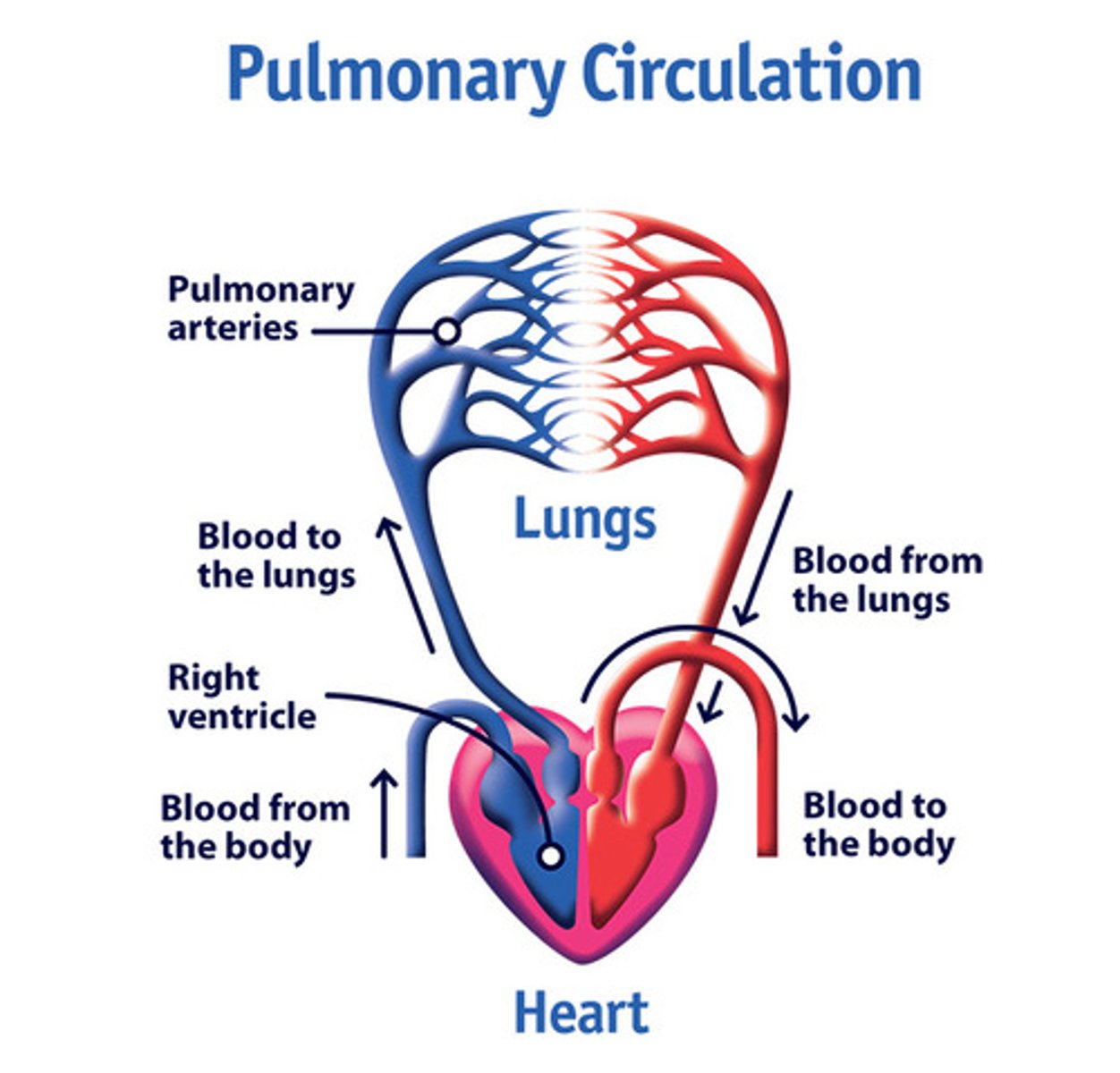
Pulmonary Circulation
Part of the circulatory system in which deoxygenated blood moves from the right atrium of the heart to the lungs (through arteries) to become oxygenated and then returns to the left side of the heart (through veins). It includes the right atrium, the right ventricle, and the pulmonary arteries.
Coronary Arteries
The blood vessels that supply oxygen to the tissues of the heart
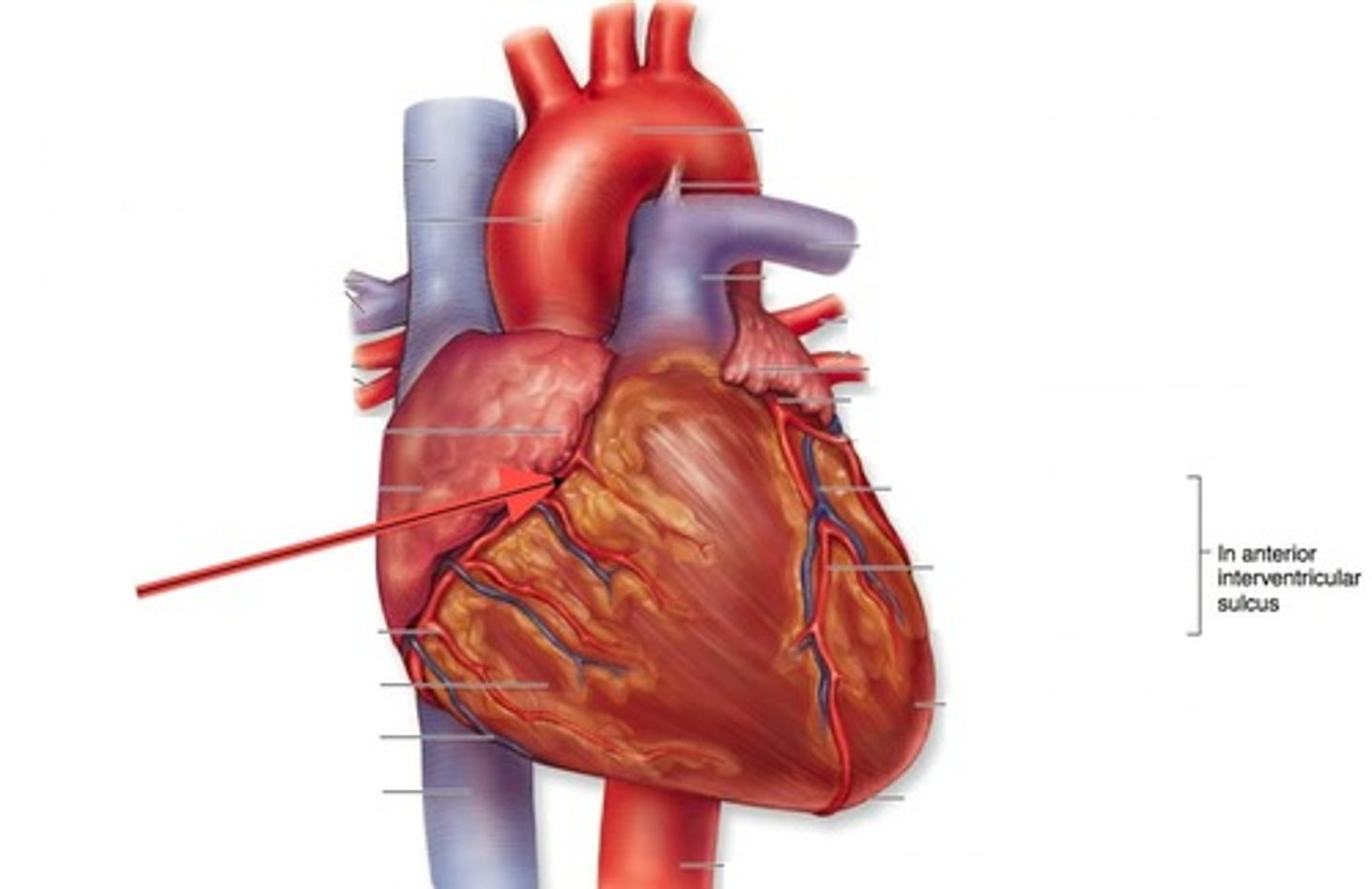
Right Ventricle
The chamber that receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the lungs.
Left Ventricle
The thickest chamber and is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood to tissues all over the body.
Apex
The lowest part of the heart that is narrower than the rest of the heart
Auricles
The ear-like extensions of the atria.
Right Atrium
Chamber that receives deoxygenated blood from the vena cava.
Left Atrium
Chamber that receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
Brachiocephalic Artery
A major artery that branches from the arch of the aorta.
Superior And Inferior Vena Cava
One of the largest veins in the human body. Returns blood to the right atrium from the upper and lower half of the body.
Aorta
The largest artery in the body. Carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the rest of the body.
Mitral Valve
The Valve that separates the left atrium from the left ventricle found in the left side of the heart.
Tricuspid Valve
The Valve that separates the right atrium from the right ventricle found in the right side of the heart
Pulmonary Veins
The veins that send oxygenated blood to the heart for distribution among the body. These veins are attached to the left atrium and ventricle.
Pulmonary Arteries
The arteries that send deoxygenated blood to the lungs to replenish the oxygen within them. These arteries are attached to the right atrium and ventricle.
Papillary Muscles
Muscles located in the ventricles that attach to the cusps of the tricuspid and mitral valves via the chordae tendineae found in both sides of the heart. These muscles tug the chordae tendineae to open and close the valves
Chordae Tendineae
Fibrous cords that attach to the tricuspid and mitral valves found in both sides of the heart. They are tugged at to open every valve in the heart simultaneously.
Aortic Valve
The Valve found in the aorta that permits blood to flow into the aorta from the left ventricle
Angina
Chest pain due to a reduced blood flow in the heart. Angina is the primary symptom of Coronary Artery Disease. Symptoms include Tightness and Heaviness
Atherosclerosis
The buildup of plaque in an artery's walls. Atherosclerosis can lead to events such as heart attacks or stroke due to the plaque damaging the inner wall or completely blocking the artery, stopping blood flow. Symptoms include High Cholesterol, Diabetes, Obesity, and Aging
Myocardial Farction
The death of a heart muscles that results from the plaque from Atherosclerosis. This can create blood clots that can clog up smaller coronary arteries in the heart. Symptoms include Nausea and Sweating
Aortic Valve Stenosis
The obstruction of blood flow within the Aorta. As one ages, the aorta begins to stiffen, causing the valves in the aorta to slow down and only partially allow blood to go through the valve. Symptoms include Fainting and Dizziness
Patent Foramen Ovale
An abnormal hole within the atria of the heart. Present at birth, it usually is harmless .Typically, PFO holes are genetic. Symptoms include Ischemic Stroke and Migraines.
Congestive Heart Failure
A cardiovascular disorder caused by multiple disorders that causes your heart to be slow to send blood throughout your body. Less blood exits the ventricle with each heart beat, making you weaker and more tired. CHF is a result of coronary artery disease and high blood pressure. Symptoms include Metabolic Syndrome and High Blood Pressure
Ventricular Septal Defect
A hole within the septum which allows oxygen rich blood to mix with the oxygen poor blood. Symptoms include having a bluish tint to your skin color and swelling
Bacterial endocarditis
An infection caused by the invasion of bacteria into the bloodstream, where it settles in the lining of a valve or vessel. Notable symptoms include chills and fever.
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
The thickening of the heart that slows down blood flow due to the thicker artery walls not allowing as much to flow into and out of the heart. Symptoms include Arrythmias and Shortness of Breath