psych sem 2 exam
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
sensation
an automatic physical reaction to a stimulus that is the same for everyone
occurs in the cells in sense organs and neural pathways does not involve brain
stages of sensation
reception
transduction
transmission
reception
stimulus, or change to stimulus, is detected by sensory receptor cells in sense organs
cells specialised to detect and respond to a specific type & level of energy in environment
transduction
sensory receptors convert stimulus energy into electrochemical impulses
necessary as NS can only transmit and process energy in electrochemical form
transmission
electrochemically charged neural impulses leave sensory receptor site and travel along specific nerve fibres
nerve fibres connect to specific sensory areas in brain specialised to receive them
perception
psychological activity that gives meaning to the stimuli our sense organs detect
stages of perception
selection
organisation
interpretation
selection
specialised neurons (feature detectors) select specific features of electrochemical impulses travelling to brain so they can be organised into meaningful patters or wholes that can be interpreted
organisation
reassembling of features of sensory stimuli to form a whole or pattern that can be given meaning
interpretation
giving meaning to stimuli so we understand what they represent about the external world
attention
a voluntary or involuntary tendency to orient towards and focus on a particular stimulus and ignore other stimuli
can be focused externally or internally
can be automatic (little conscious awareness) or controlled process (full awareness required)
selective attention
ability to redirect our focus to a specific or limited range of stimuli while ignoring or filtering out others
controlled processing allows for selective attention
cherry’s cocktail party year
1953
cherry’s cocktail party (1953)
investigates selective attention in auditory processing → how people can focus on one convo in a noisy environment whilst filtering out others
demonstrated that we filter out unattended auditory information early in processing
divided attention
capacity to attend to and perform two or more activities at the same time
automatic processing facilitates divided attention
decreases the amount of attention being placed on only one task or idea
focused attention
attending to a particular stimulus while ignoring others → requires high level of awareness
automatic process
little amount of conscious awareness
requires little attention or mental effort
enables us to have divided attention
controlled process
full conscious awareness required
requires selective attention
must actively focus attention on task
functions of attention
orientating sensory stimuli
controlling behaviour
maintaining altertness within a stimulus
processes of memory
encoding
storage
retrieval
encoding (transduction)
an initial step in memory process in which information is put into a representation form that is able to be stored and accessed
storage
retention of information and memories overtime (patterns in connectivity of neurons used)
retrieval
recovery of information & memories from storage, usually involves recollection of material from LTM → STM
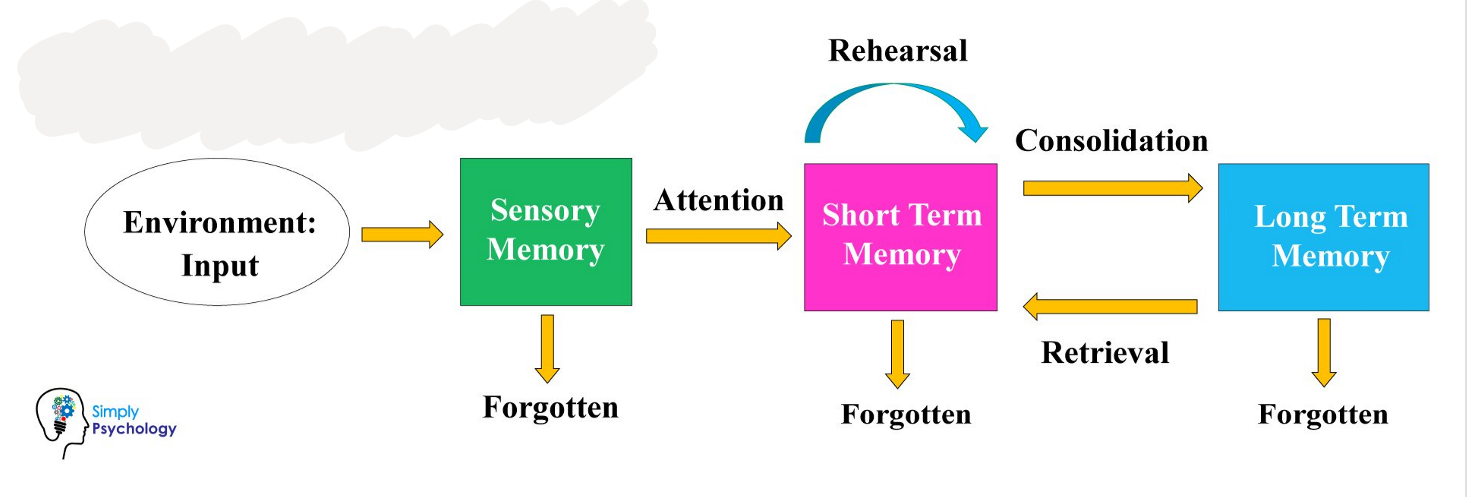
atkinson and shiffrin multi-store model of memory (1968)
multi-store model - sensory memory
1st memory store
temporary mechanism that retains and processes input from five senses
if attended to, it is transferred to STM, if not then forgotten
primarily processes iconic memory and echoic memory
duration: 0.3-0.4 secs (visual) 3-4 secs (echoic)
capacity: very high
encoding: different stores per sense
multi-store model - short term memory
capacity to hold very limited amount of information in temporary buffer for a short period of time
duration: 20 - 30 seconds
capacity: limited 7± two items ← MILLER’S LAW
encoding: mainly auditory
multi-store model - long term memory
transferred to long term after elaborative/continual rehearsal
unlimited in capacity, permanent in duration, encoded semantically
can be recalled to STM when needed
can divided into declarative (explicit) and procedural (implicit) memory
declarative memory
branch of long-term memory
conscious memories that can be brought to the mind and described as spoken
- semantic: memory for facts
- episodic: personal experiences, memories of events and facts in our daily life
procedural memory
branch of long-term memory
outside conscious awareness, memory for procedures e.g. how to ride a bicycle
extending capacity of short-term memory
chunking: recognising a familiar pattern in STM and combining the individual elements into single units → chunk
allows recognition of familiar objects, words and phrases instead of disconnected visual features and meaningless sounds
extending duration STM
maintenance rehearsal: mentally repeat information using “inner voice”.
loop connected to STM store, allows encoding
used when we want to keep information active in STM to achieve a goal
protection against forgetting - LTM
elaborative rehearsal: asking yourself questions about information you’ve received
strengthens existing memory traces and organises information in a way that assists with retrieval
retrieval: bringing relevant info from LTM to STM as part of the encoding process
Atkinson and Shiffrin (1968) strengths
gives a good understanding of the structure and process of the STM - allows researchers to expand
studies e.g. HM provide evidence to support distinction between STM and LTM
Atkinson and Shiffrin (1968) weaknesses
oversimplified, especially when suggesting short- & long-term memory operate in a single, uniform fashion
Baddeley & Hitch year
1974
baddeley & hitch (1974) working memory model
short term memory as a system with multiple components, takes into account dynamic processes involved in cognitions & ability to carry out two tasks simultaneously
mental operations can be performed on information being storeed
4 components of working memory model
central executive
visuospatial sketchpad
phonological loop
episodic buffer ← added in 2000 by Baddeley
central executive
responsible for monitoring and coordinating operations of slave systems (VSS and PL) - relates them to long term memory
decides which information is attended to and which parts of working memory to send info to be dealt with (VSS or PL)
focuses on specific parts of tasks and decides how to divide attention between different tasks
directs attention and gives priority to particular activities
phonological loop
deals with spoken and written material → auditory short-term memory
phonological store and articulatory control process
phonological store
inner ear, holds information in speech-based form for 1-2 seconds, either from outside world or recalled long-term memory (limited capacity)
articulatory control process
inner voice- rehearsing information from phonological store (extends duration)
visuospatial sketchpad
“inner eye” - visual short-term memory, processes visual and spatial information
can manipulate images in 2&3 dimensions, typically can only do one and not the other
criticism: some may have visual, no spatial or vice versa
episodic buffer (baddeley, 2000)
sub-system allowing component of WM to interact with LTM
limited capacity, temporary storage system, holds about 4 chunks of information
capable of holding info in any form - can combine auditory from PL with visual from VSS, connects these with LTM but still under control of central executive