Cross Sectional Chapter 4
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is the purpose of the Vertebral Column?
to support the weight of the body, help maintain posture, and protect the delicate spinal cord and nerves
What curve is present with the Cervical and Lumbar sections?
Lordotic Curves
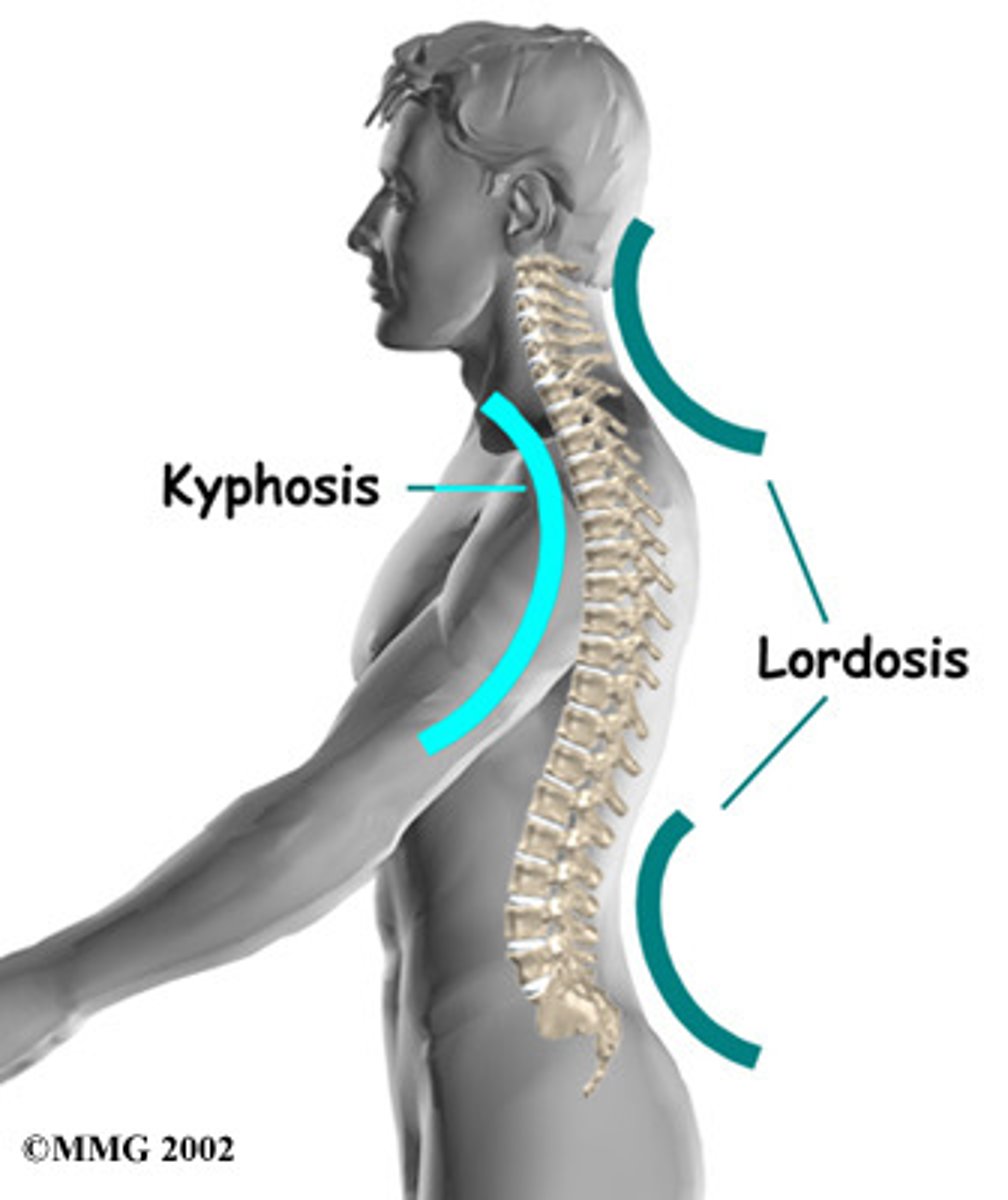
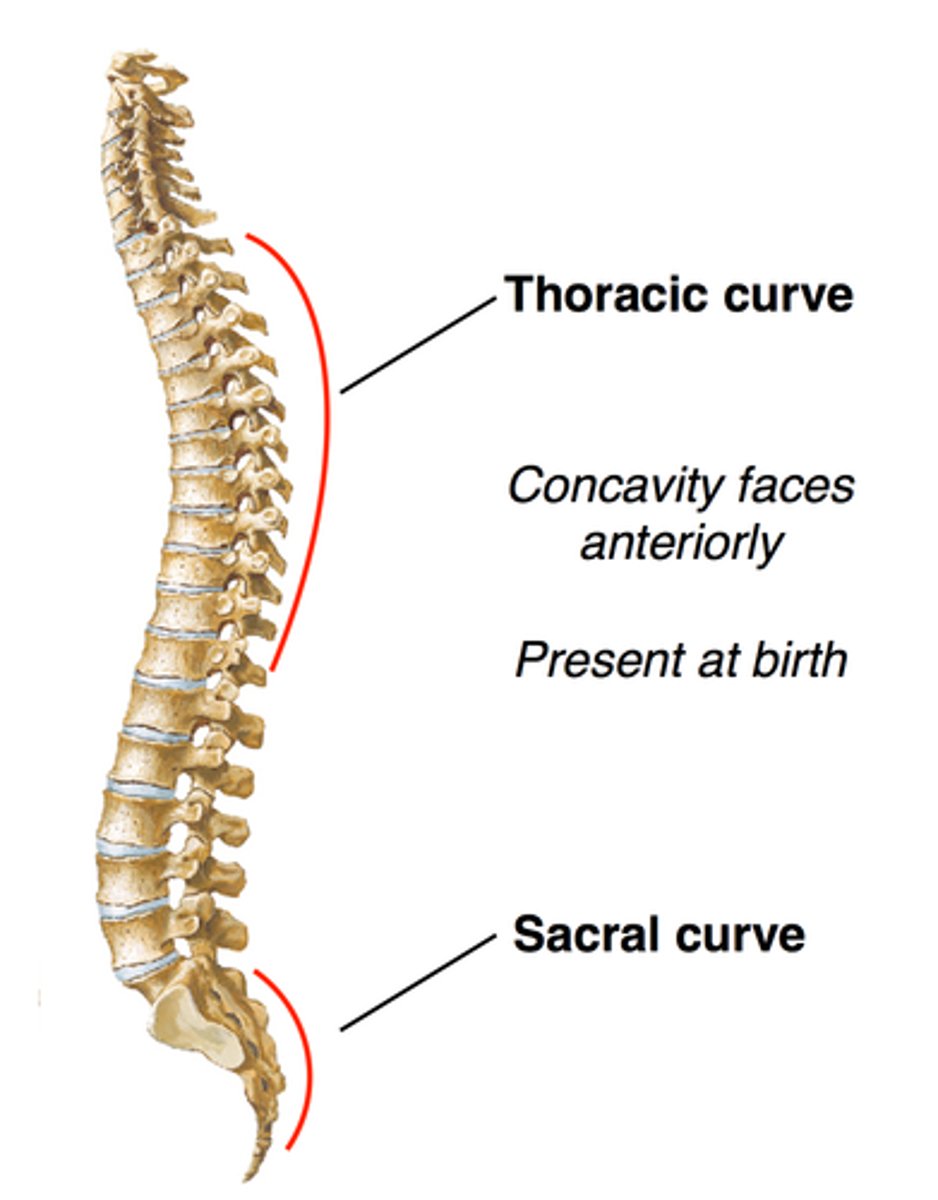
What curve is present with Thoracic and Sacral sections?
Kyphotic Curves
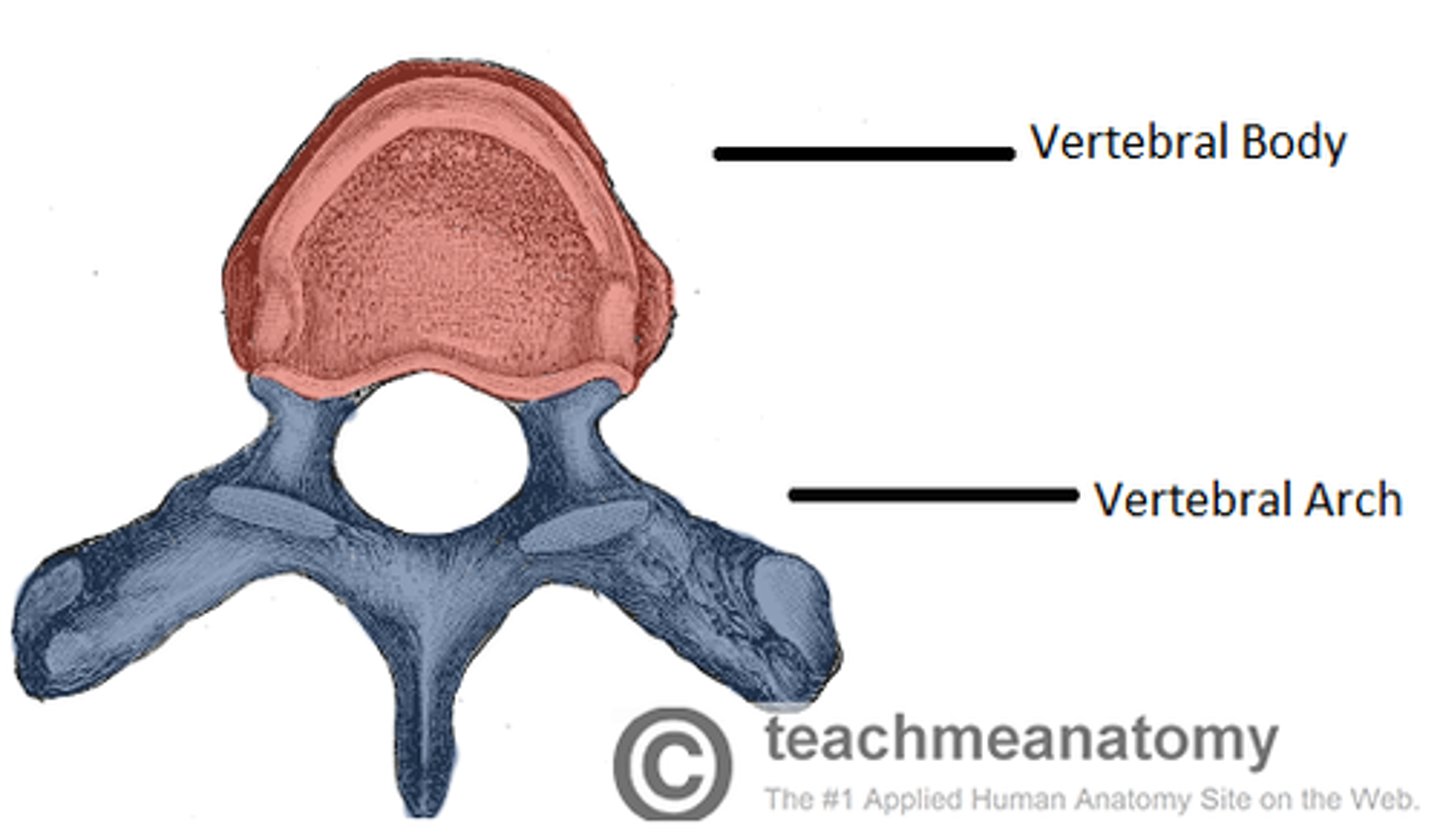
What are the two parts of a typical vertebrae?
body and vertebral arch
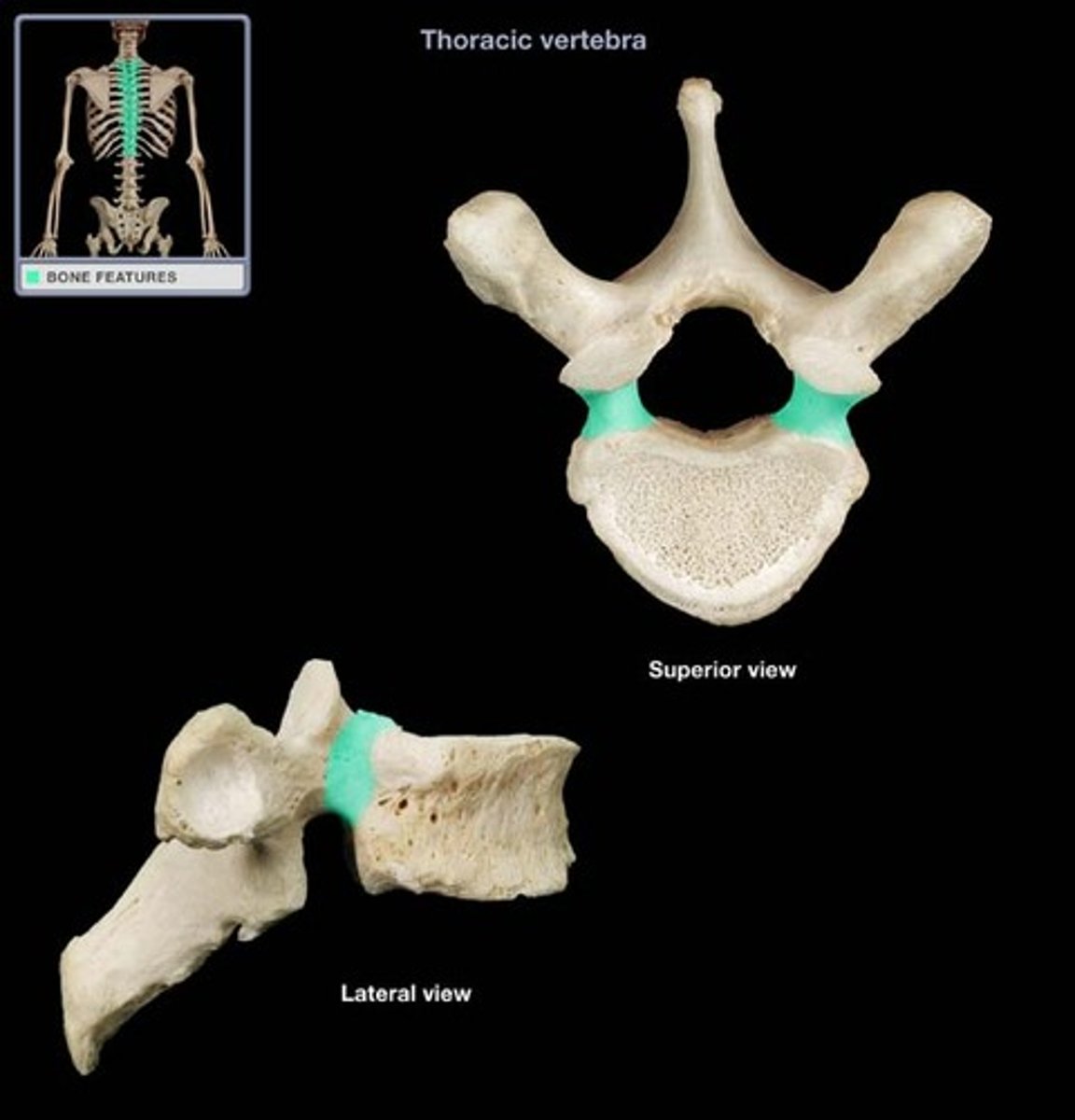
Pedicle
Projecting posteriorly from the body on the right and left
Laminae
The 2 pedicles meet up with the right and left lamina.
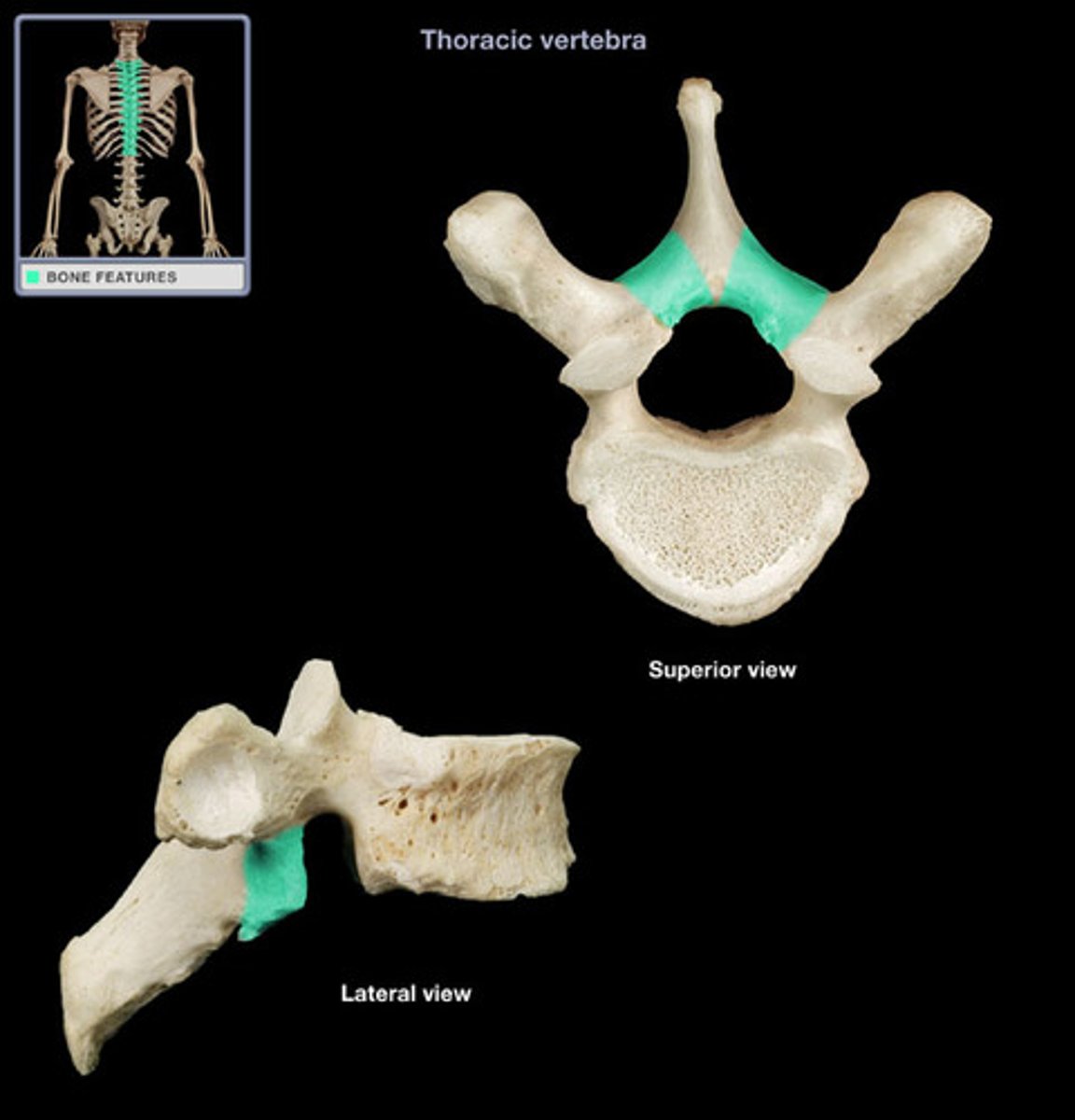
Spinous process
Each lamina joins in the middle to form the most posterior aspect of the vertebral arch, the spinous process.
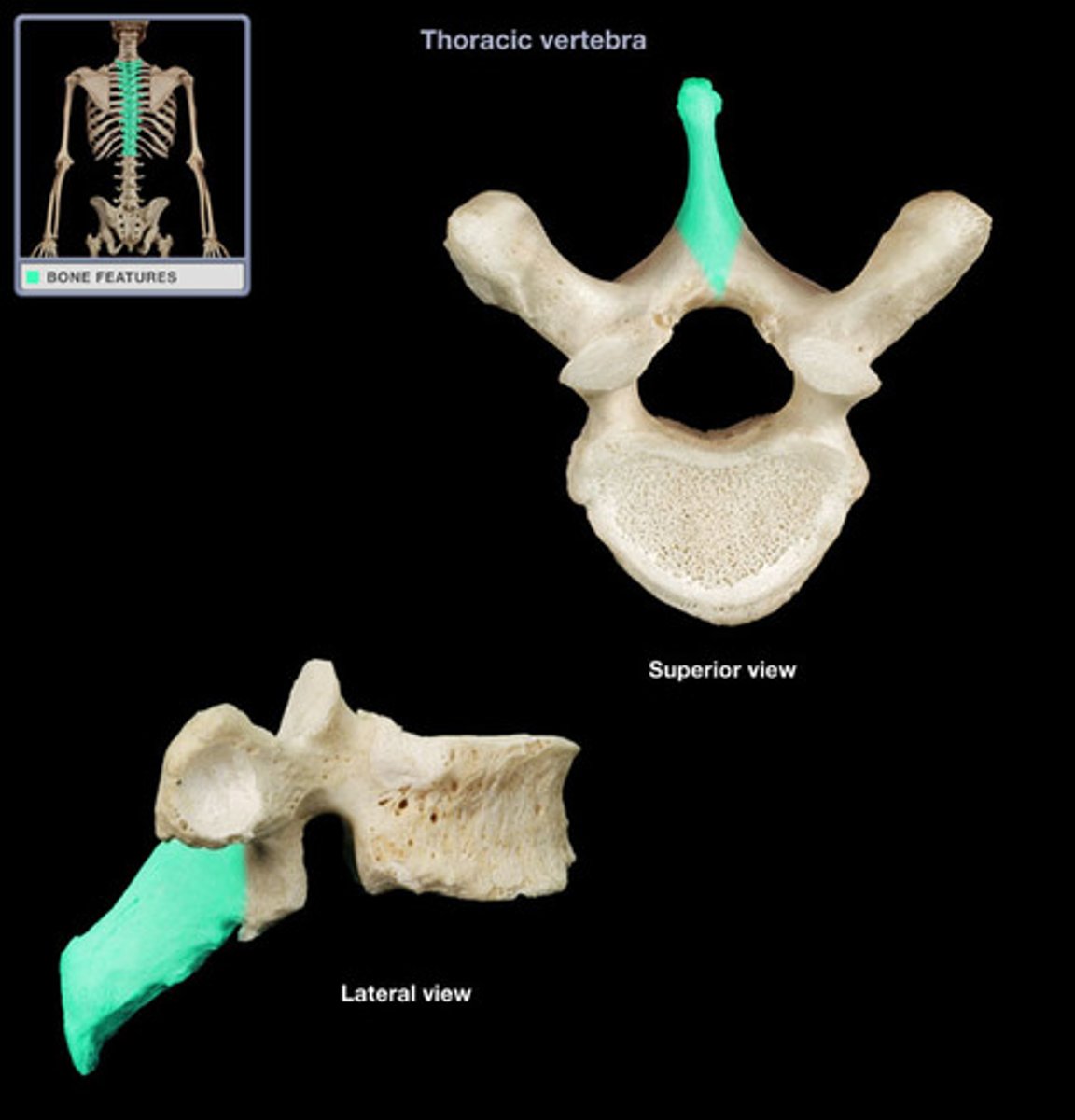
Transverse processes
The 2 transverse processes project laterally around the pedicle and lamina junction on both the right and the left side.
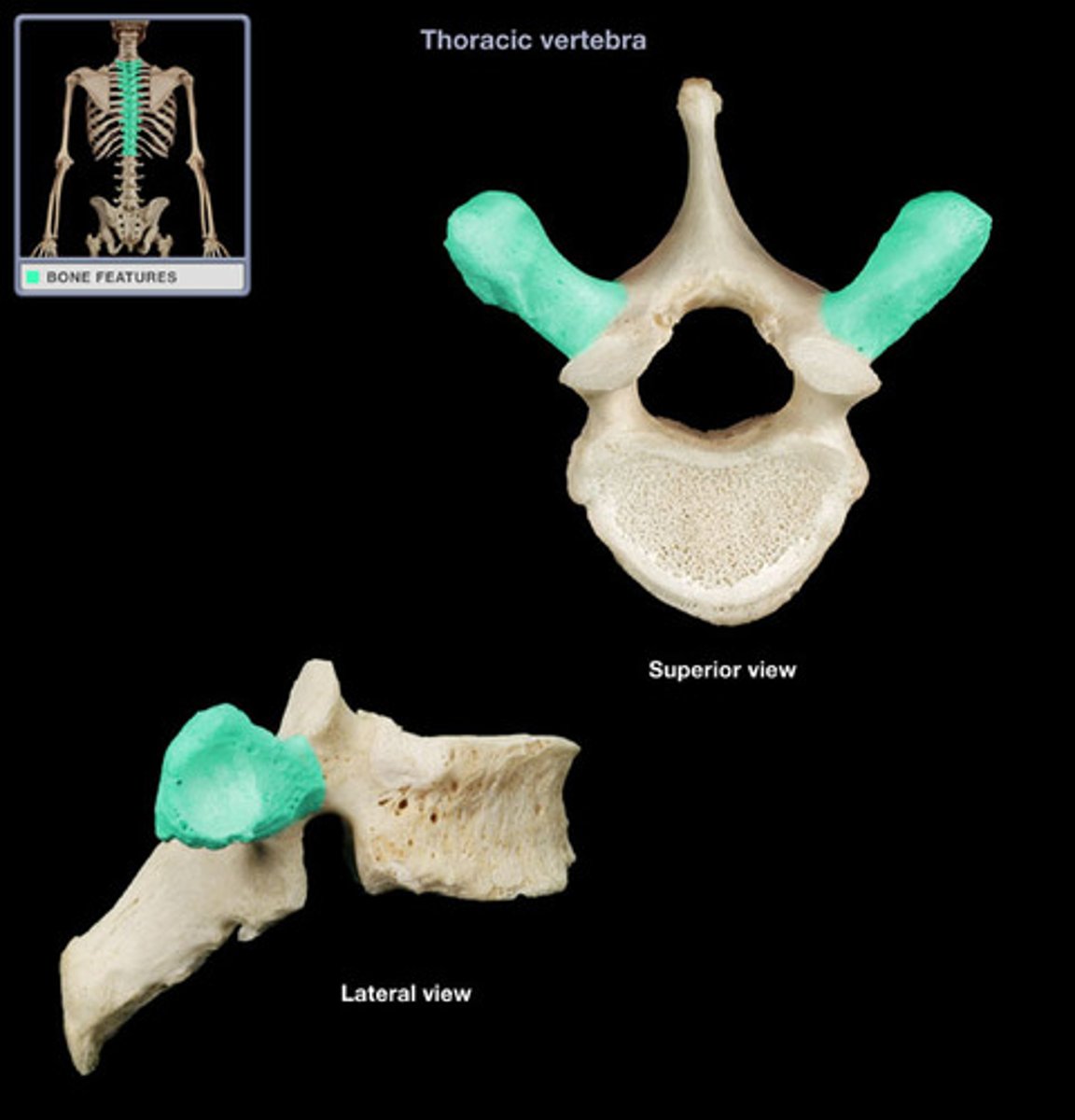
Superior articular process
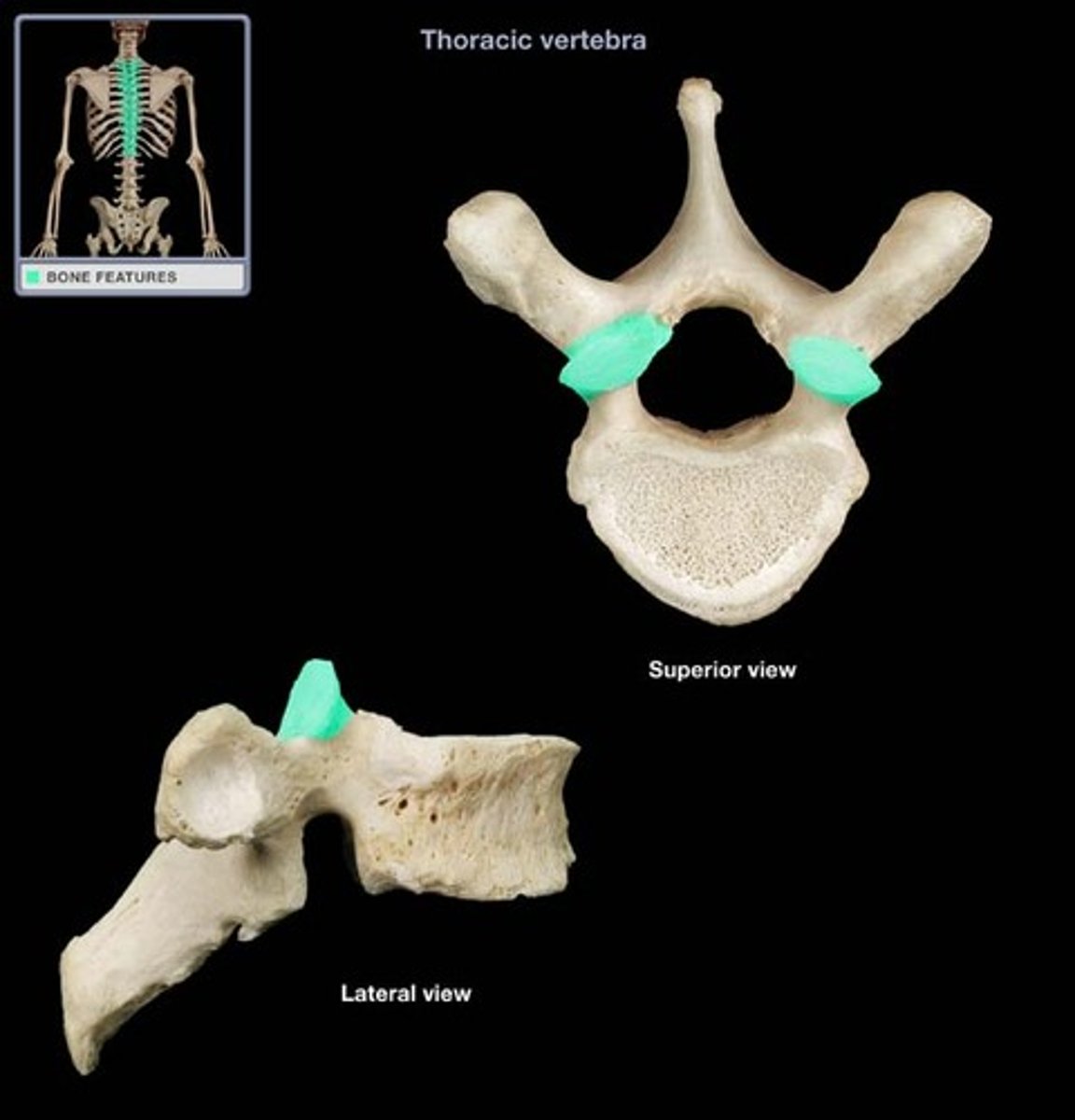
Inferior articular process
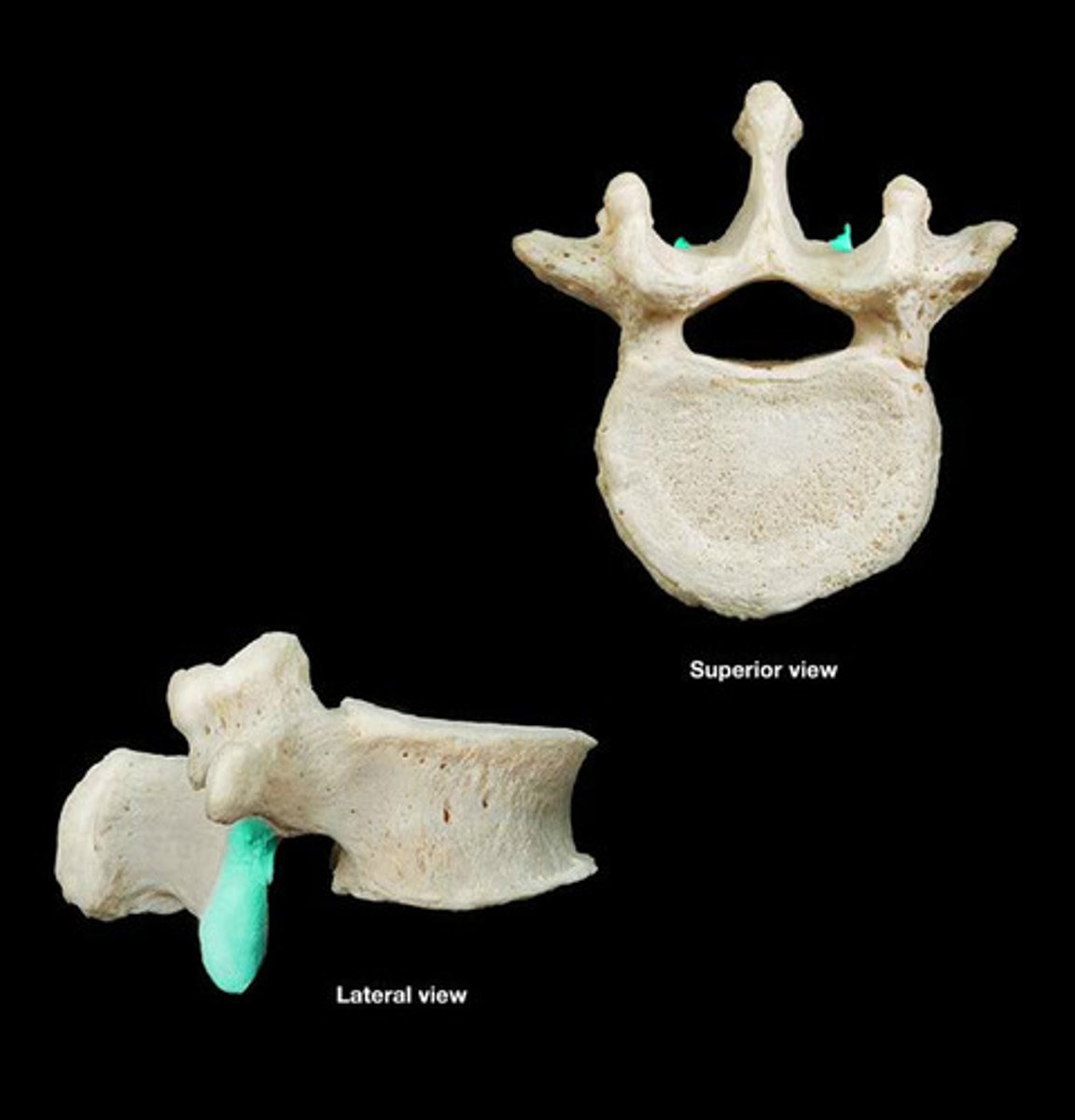
Superior costal facet
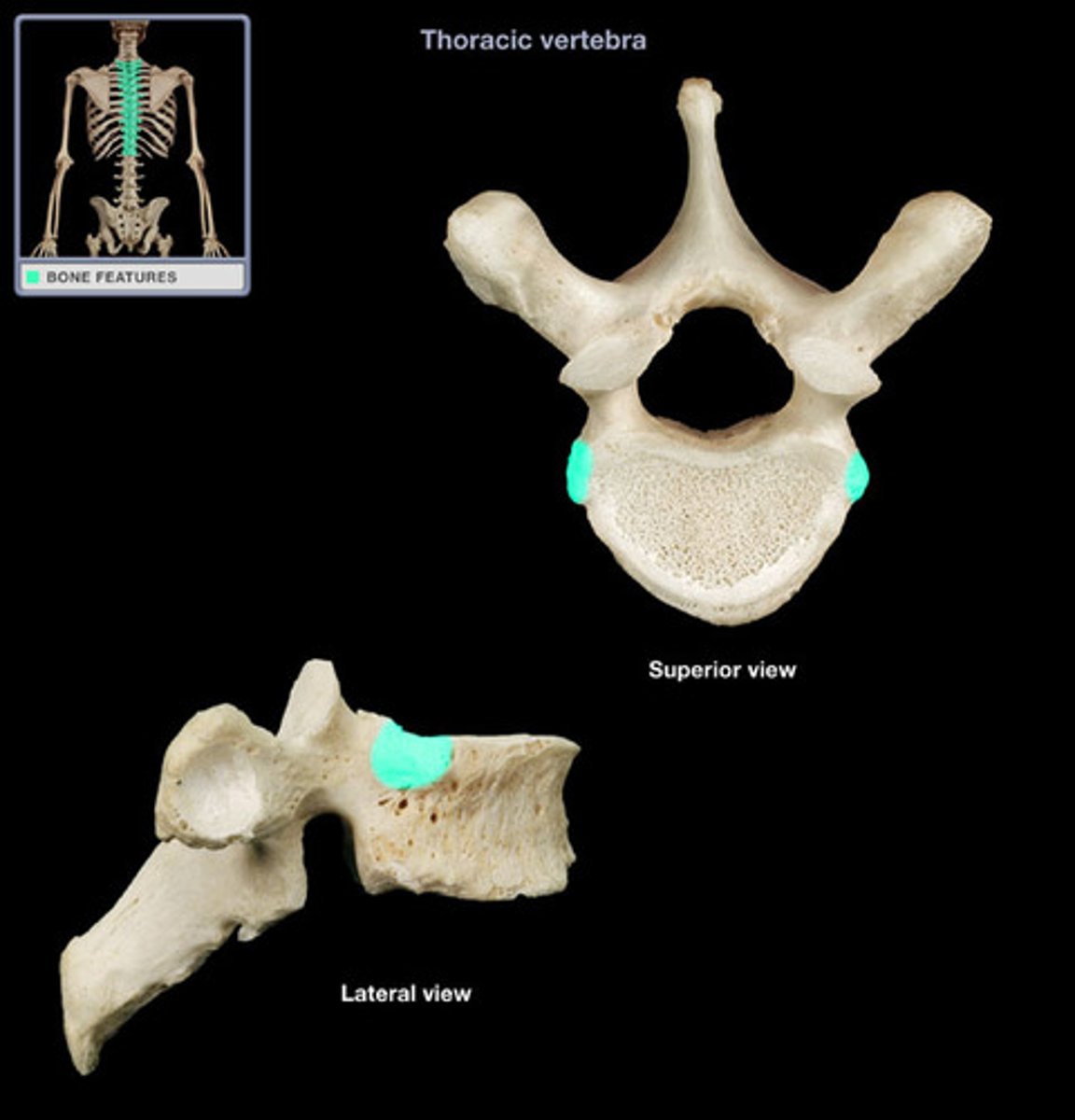
Inferior costal facet
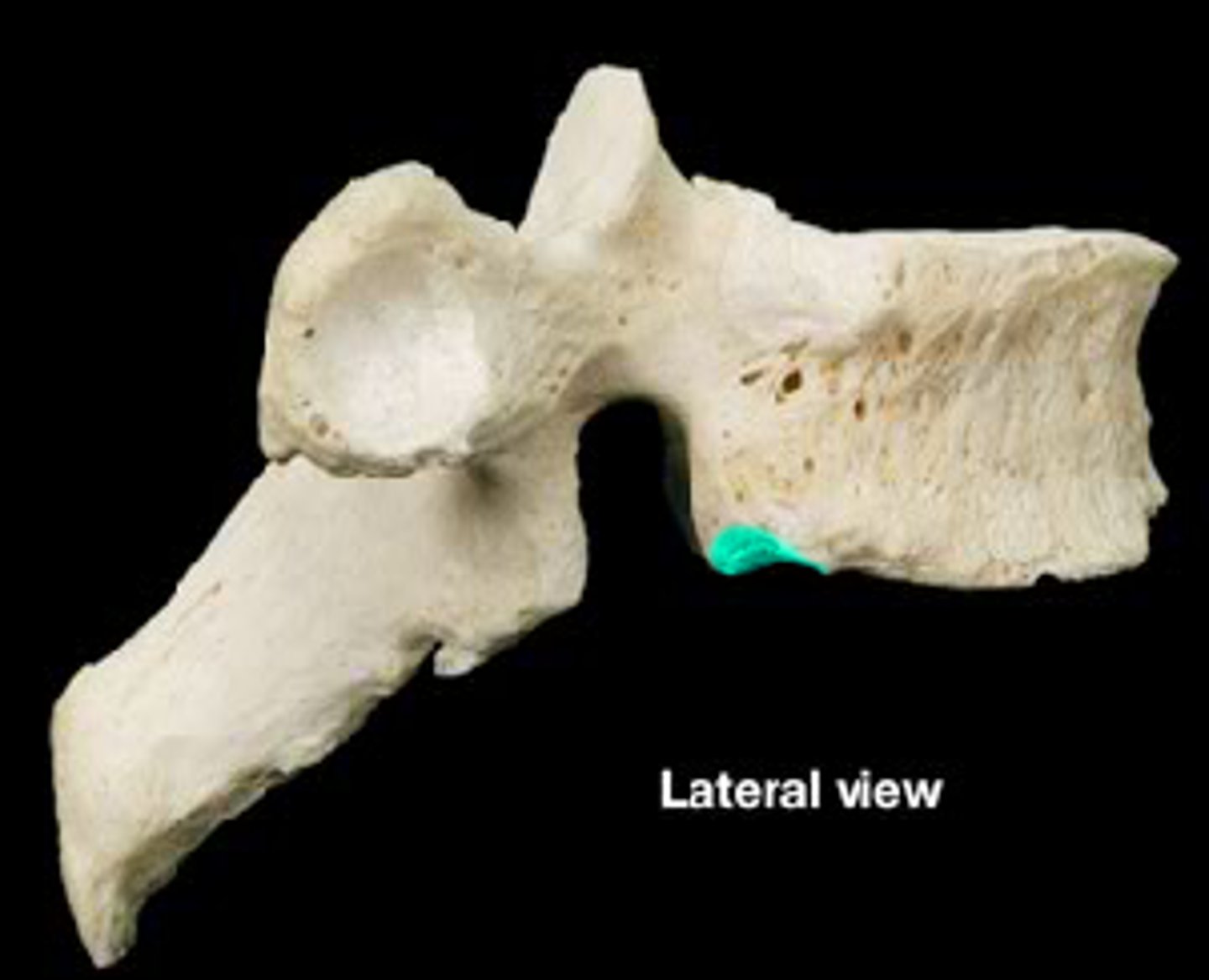
Zygopophyseal joint
bilateral between superior and inferior facets
synovial
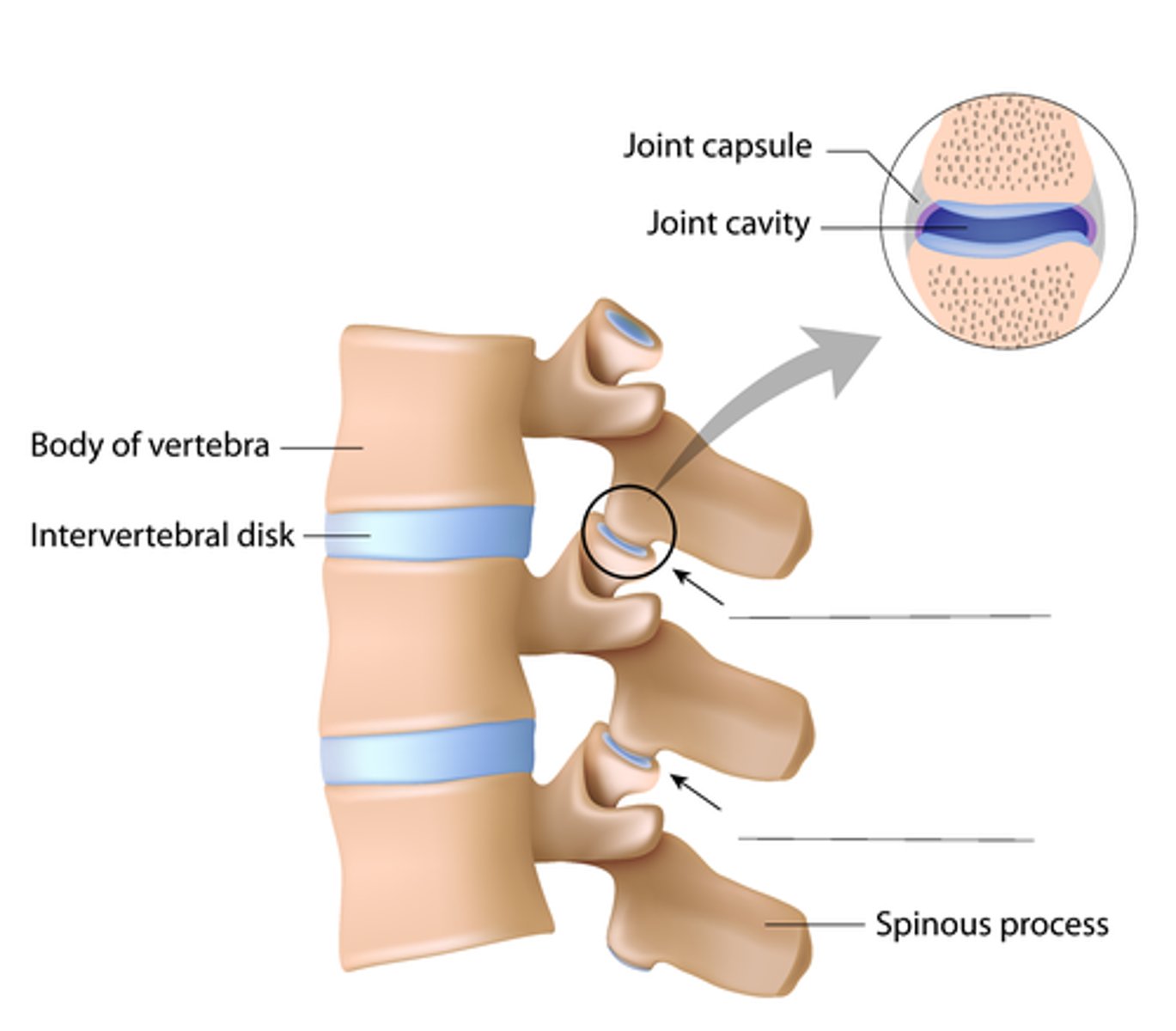
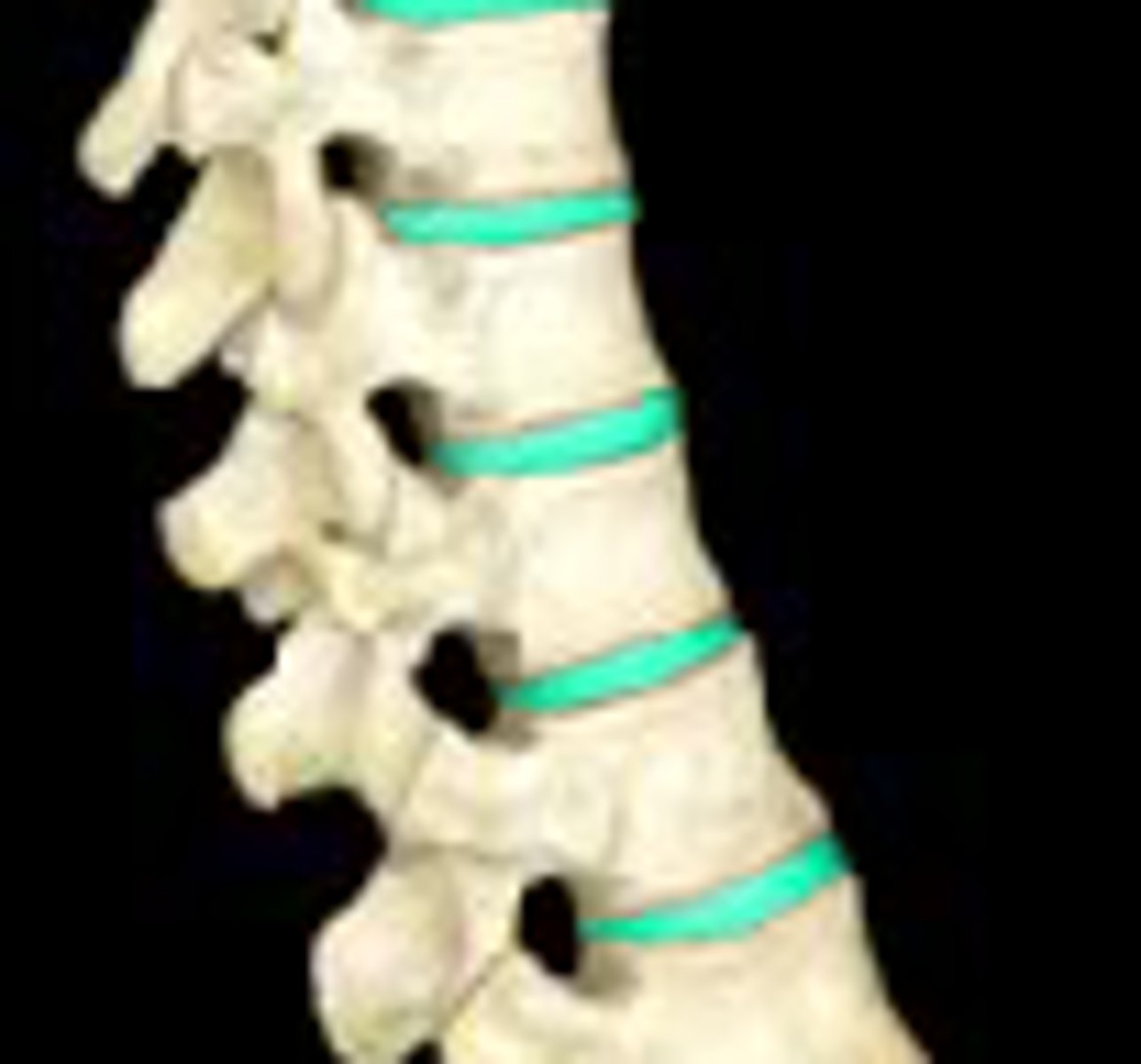
Intervertebral Dics
Fibrocartilage pads found between each vertebra that help to cushion
-filled with water
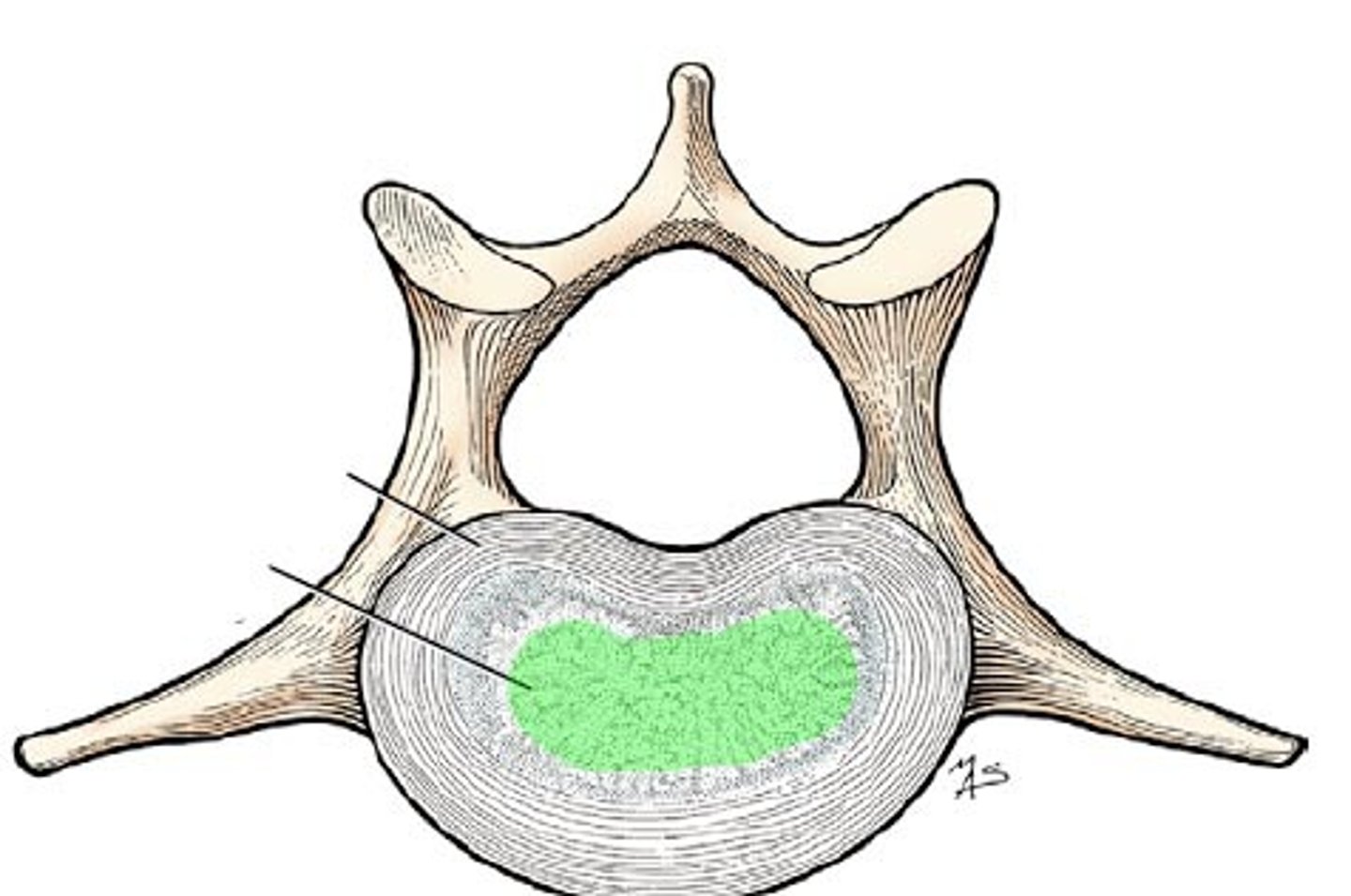
Nucleus pulposus
The soft, semi-gelatinous material in the middle of the disk
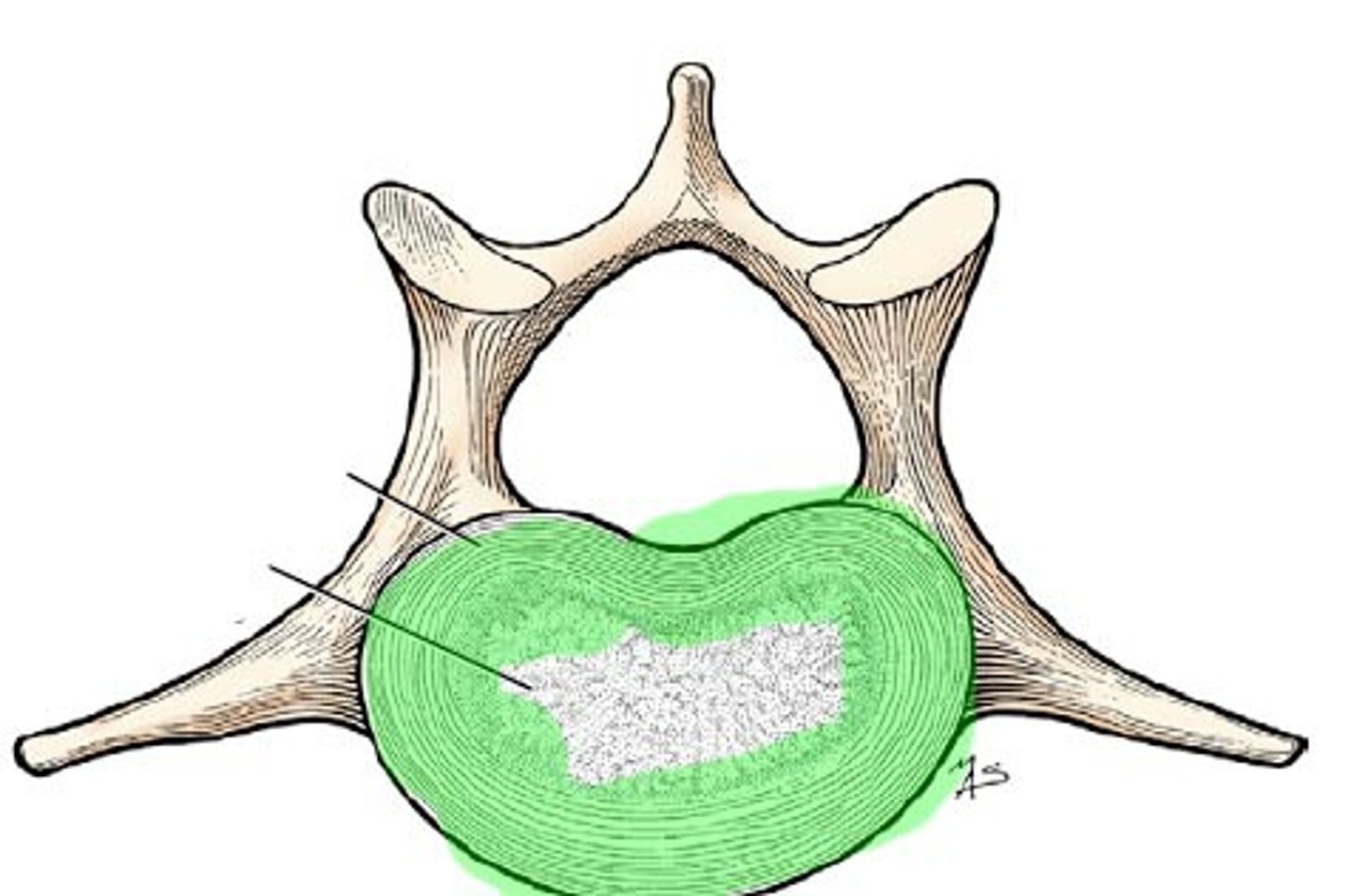
Annulus fibrosus
The firm outer portion of the disk
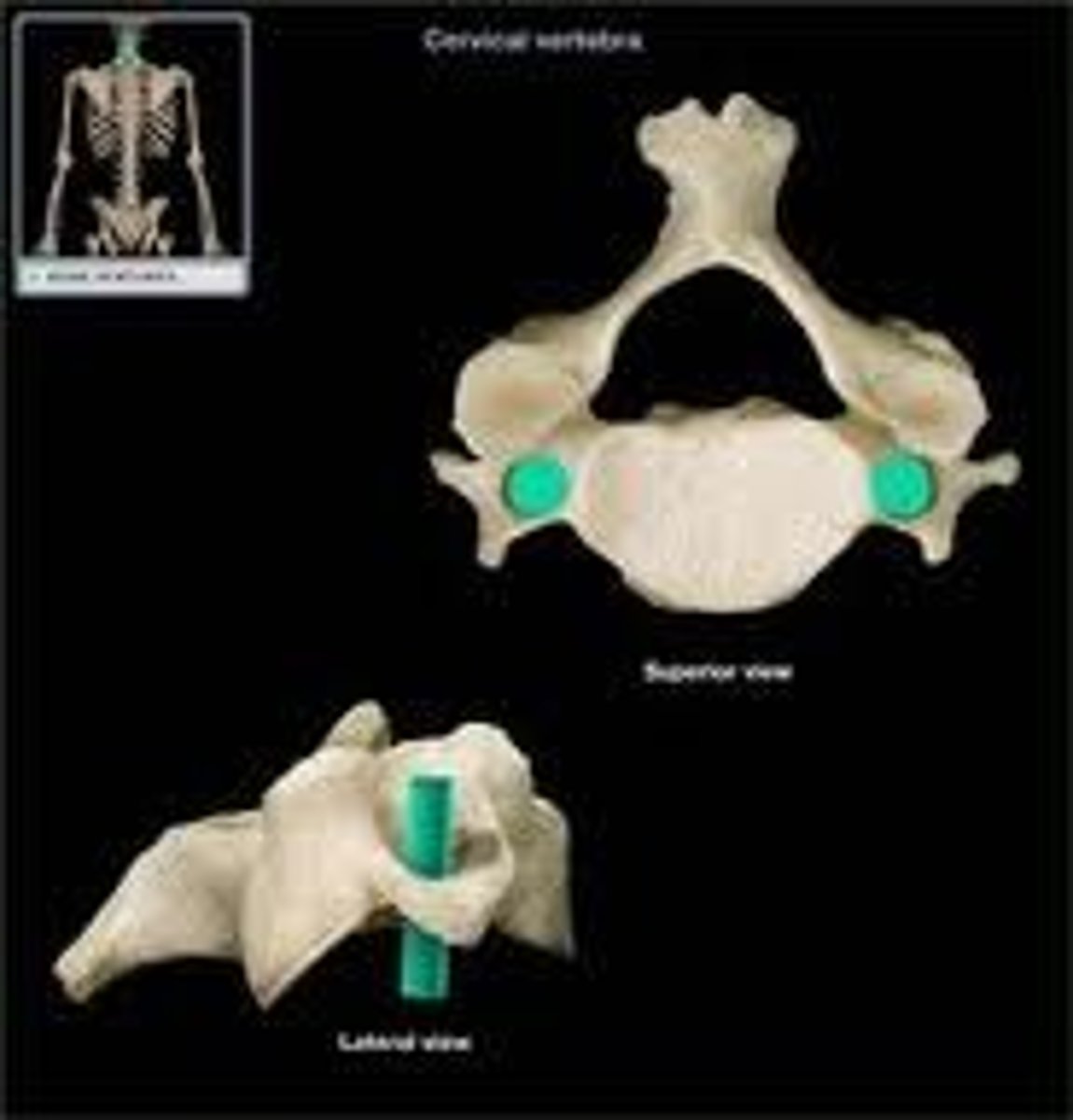
Transverse foramina
Special to C1-C7 and allow for the vertebral arteries and veins to pass through them so blood can get to our head.
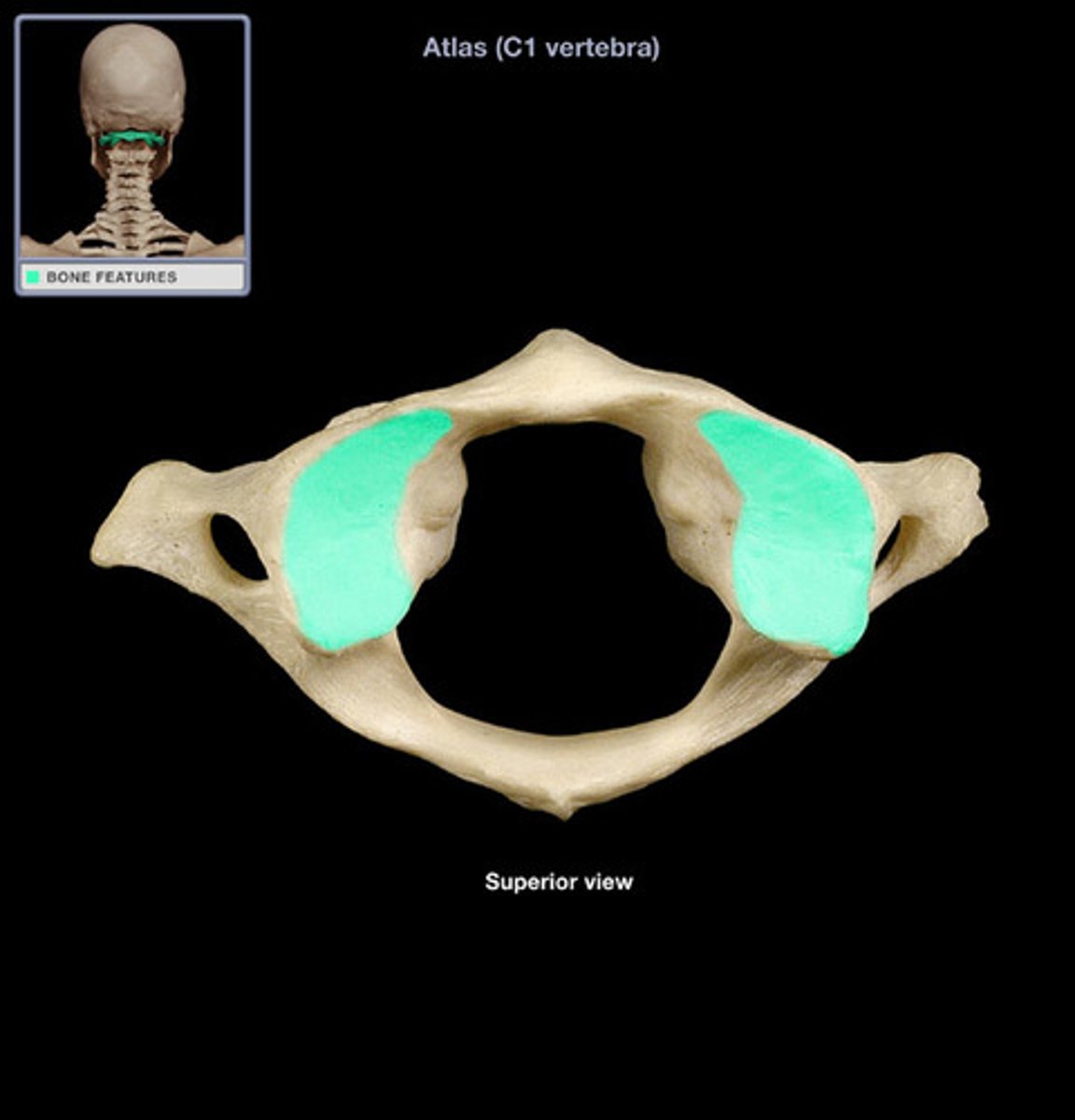
C1 Atlas
supports head, has no body or spine, the two transverse processes have superior facets which the occipital condyles articulate
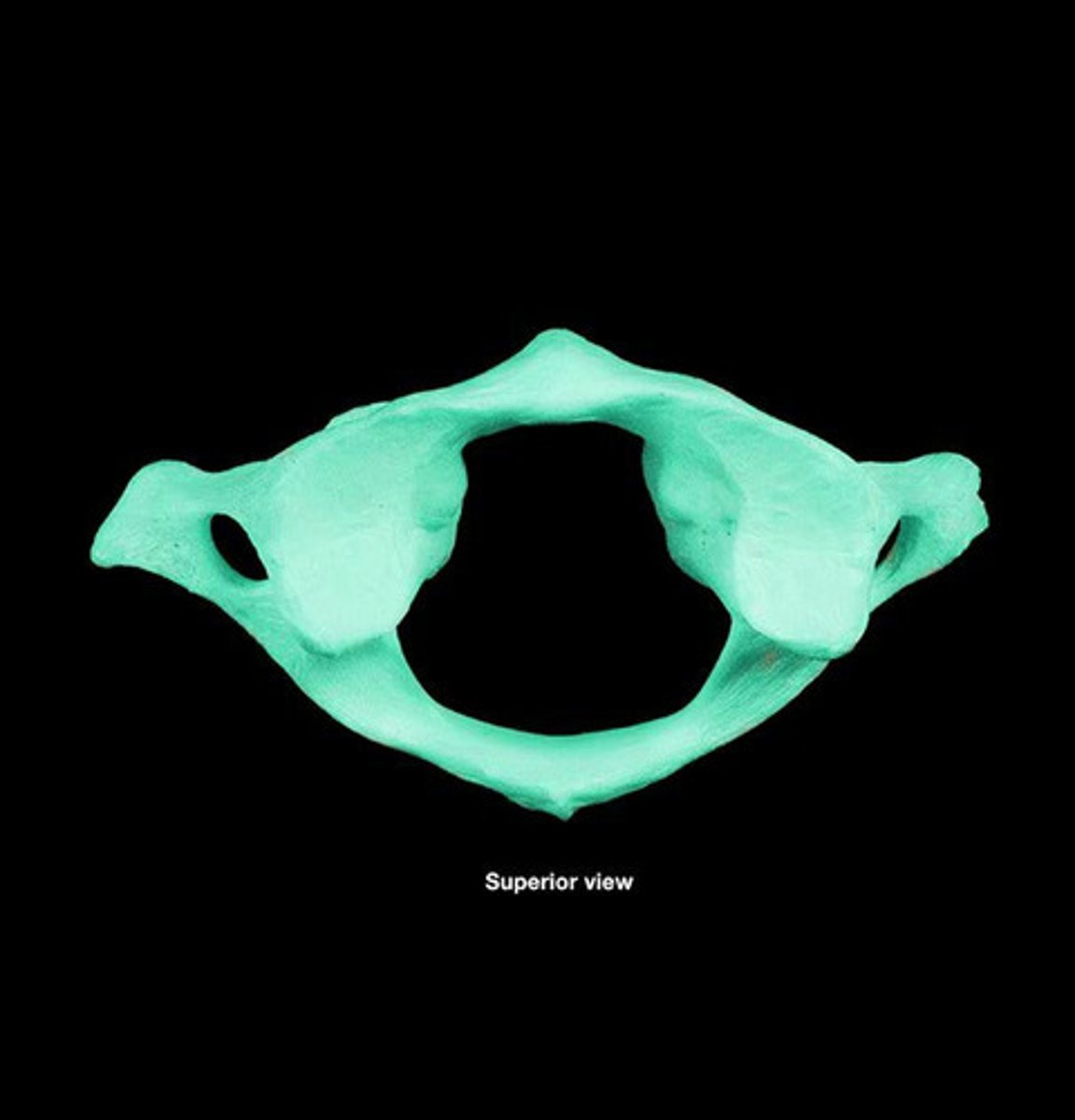
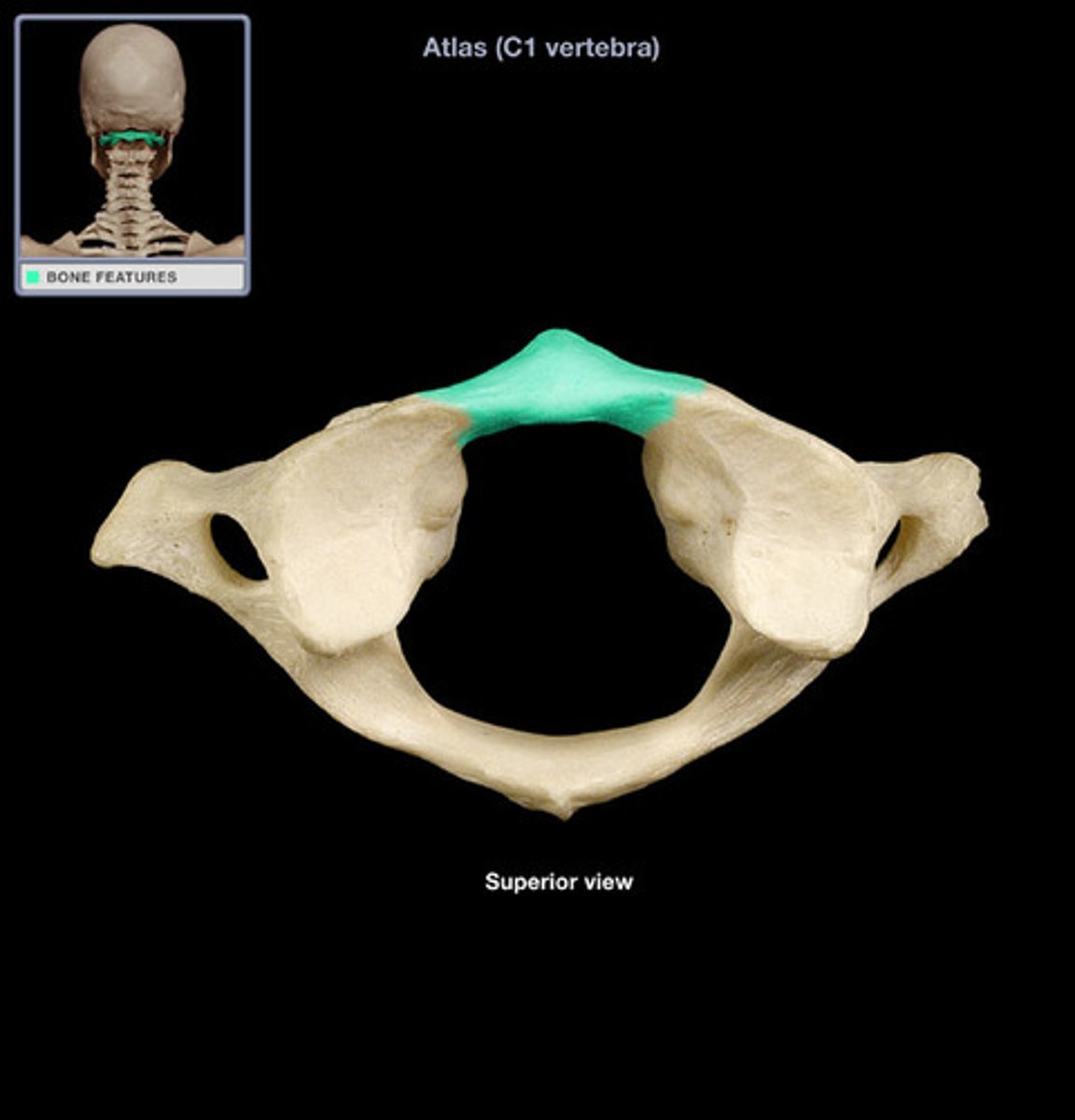
C1 anterior arch
- anterior tubercle on anterior surface
- facet for dens on posterior surface
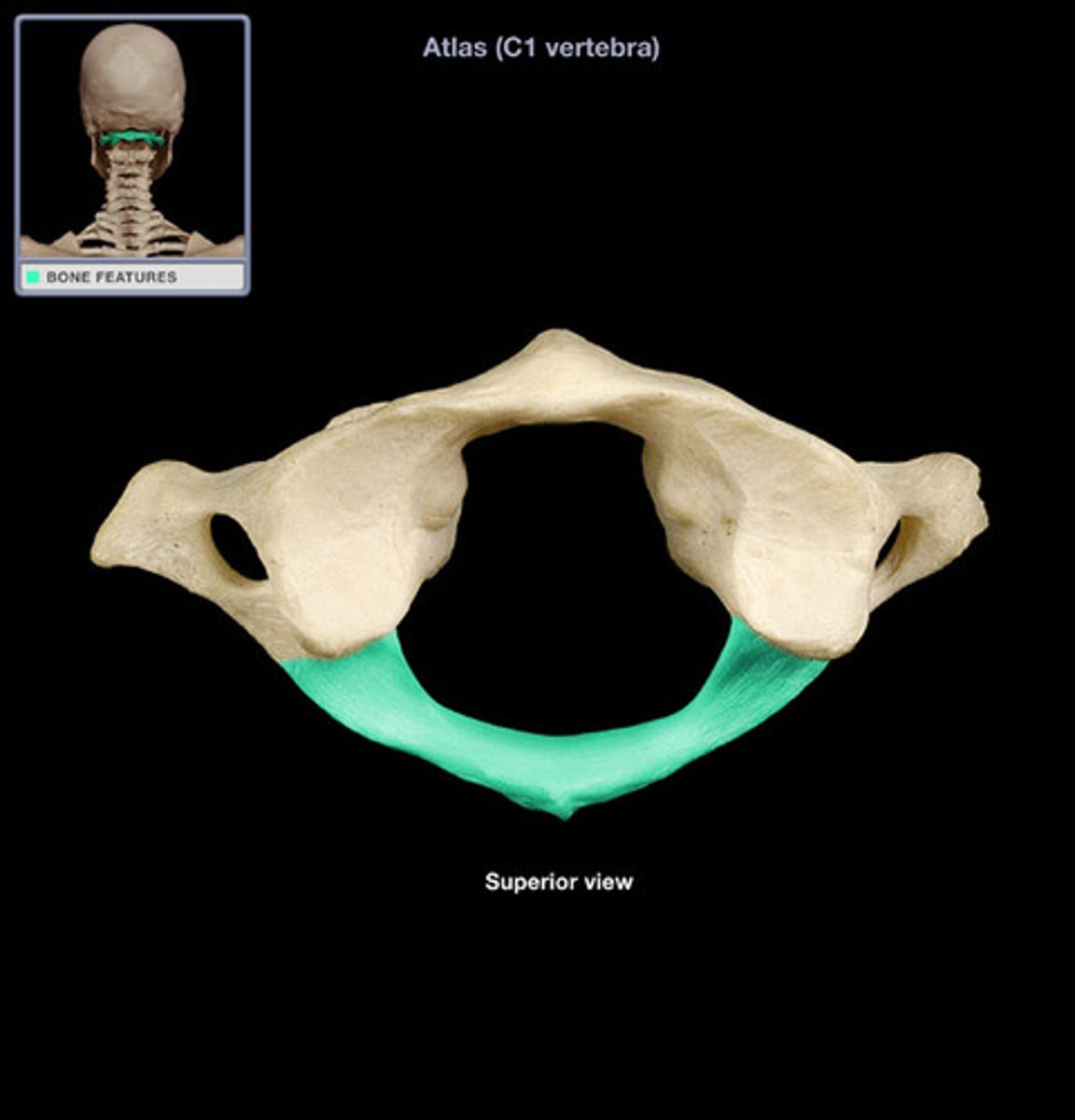
C1 Posterior arch
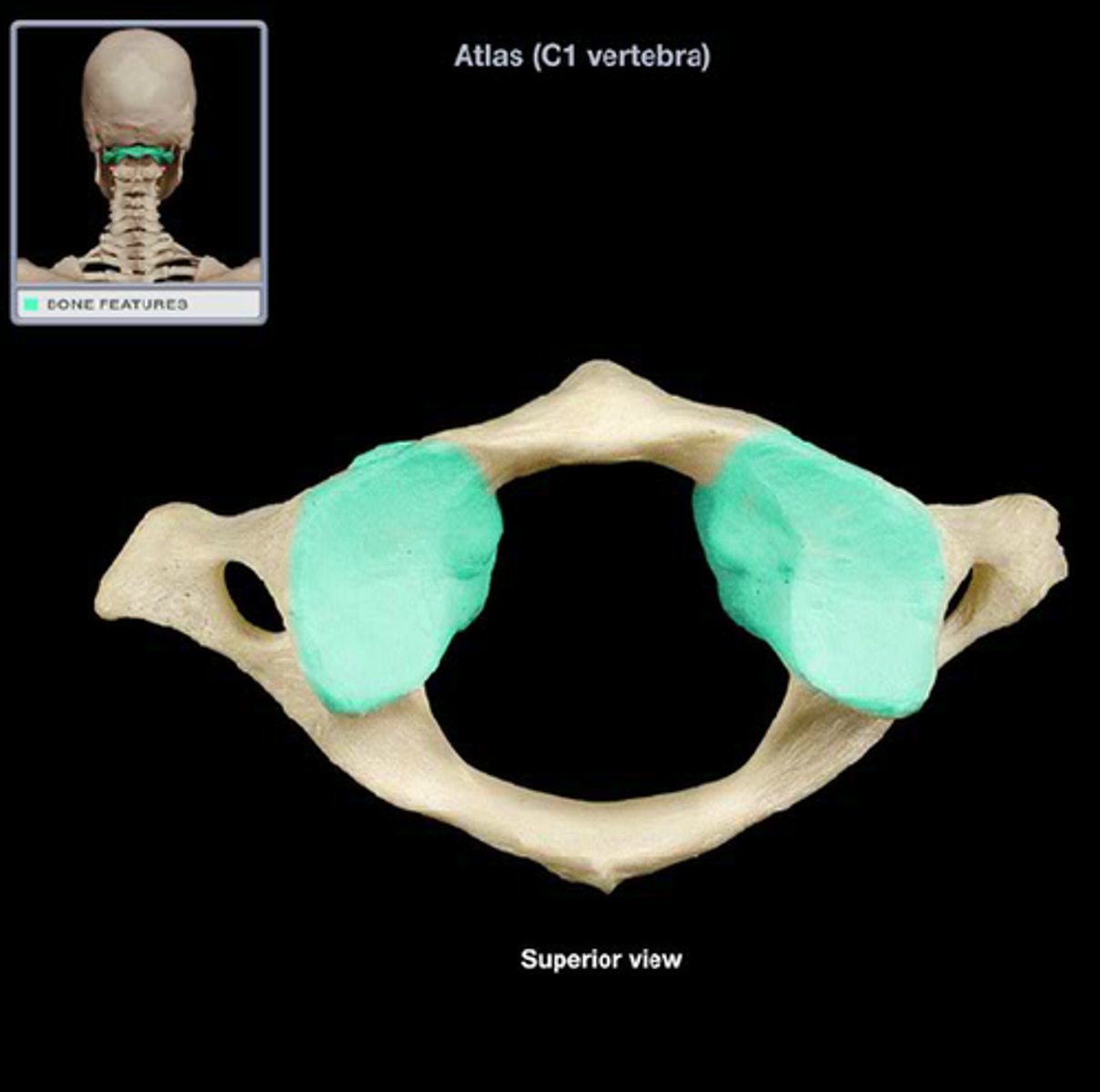
C1 lateral mass
C1 superior articular process
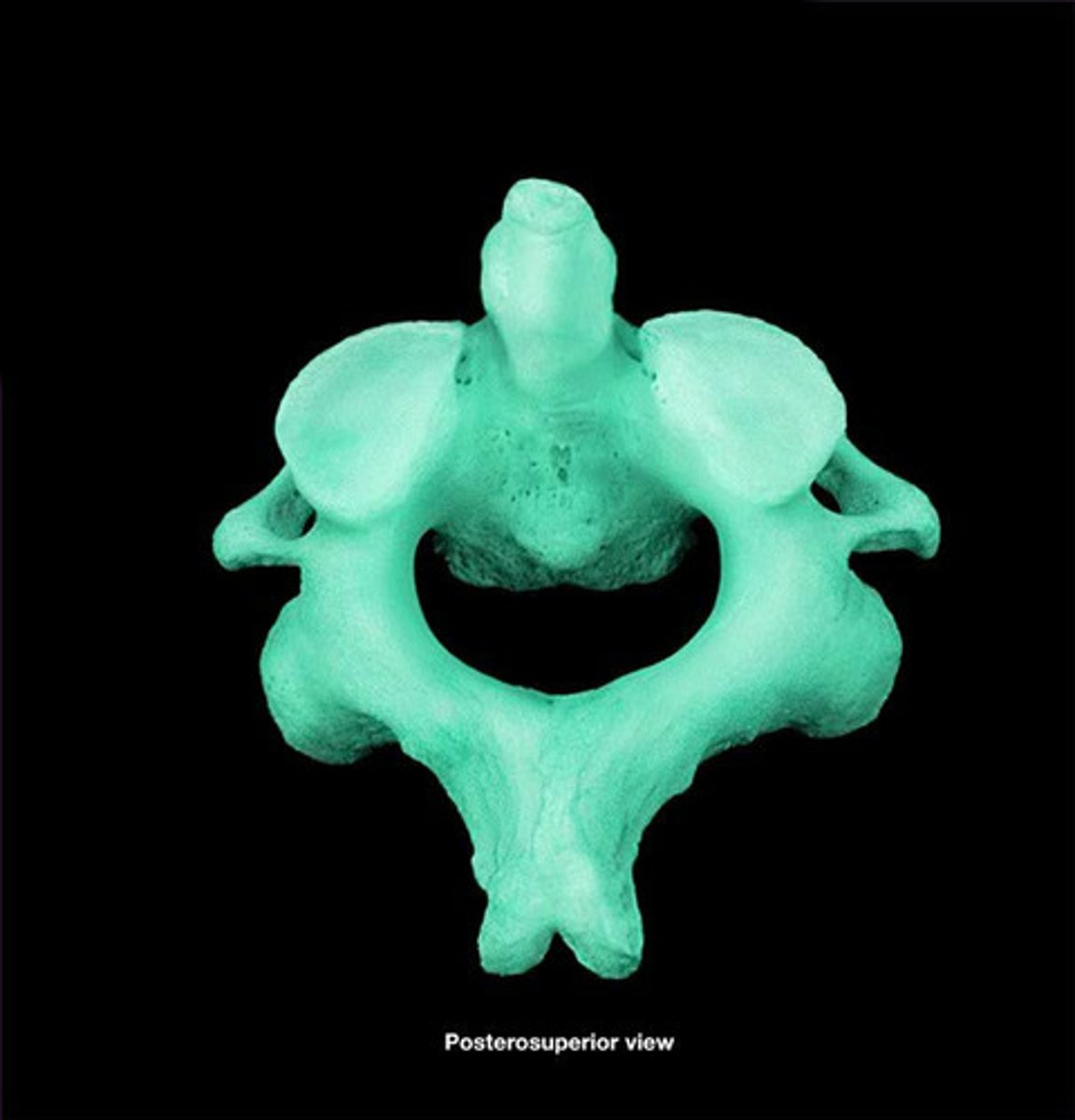
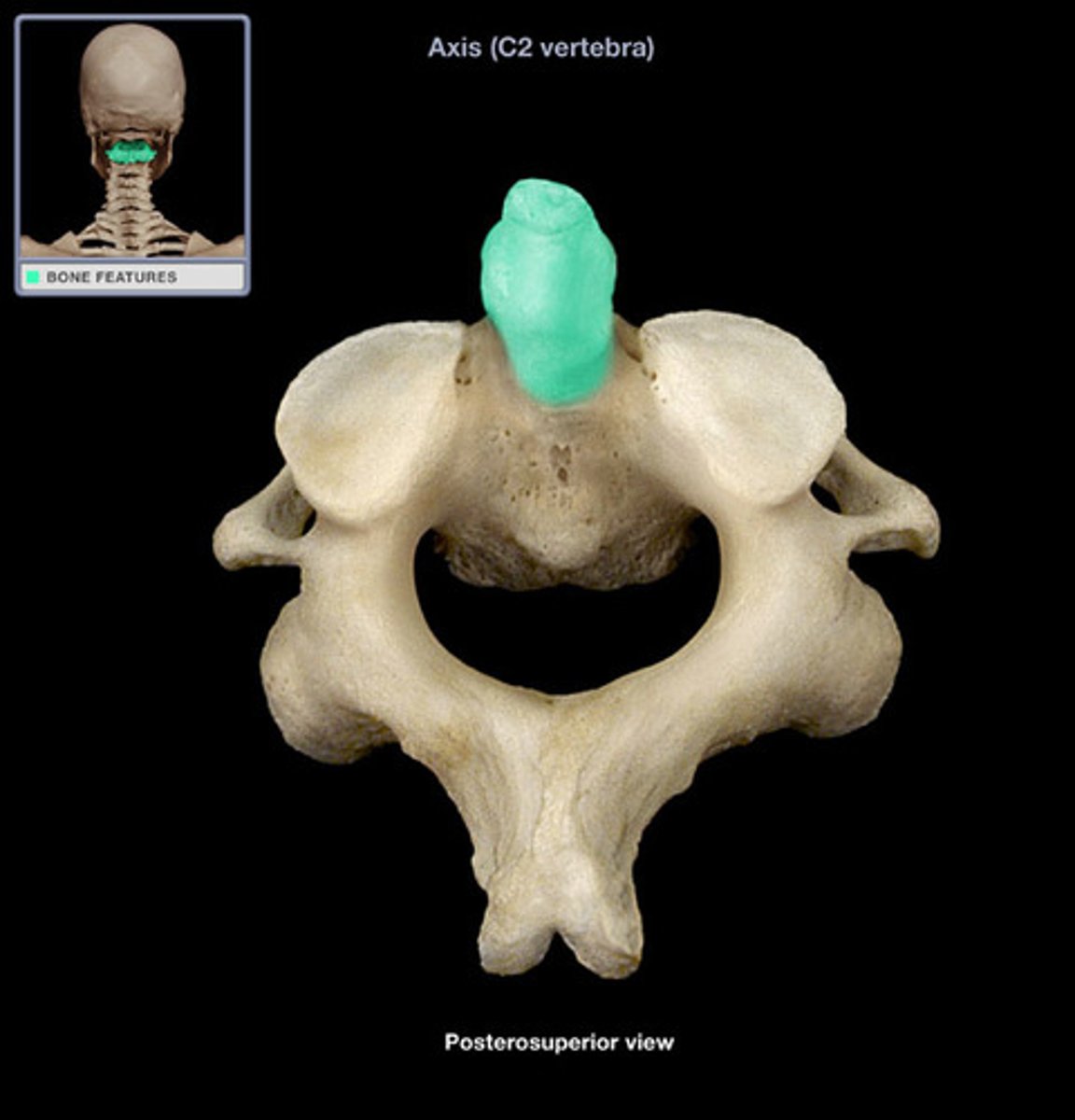
C2 Axis
Odontoid process
Also known as the dens
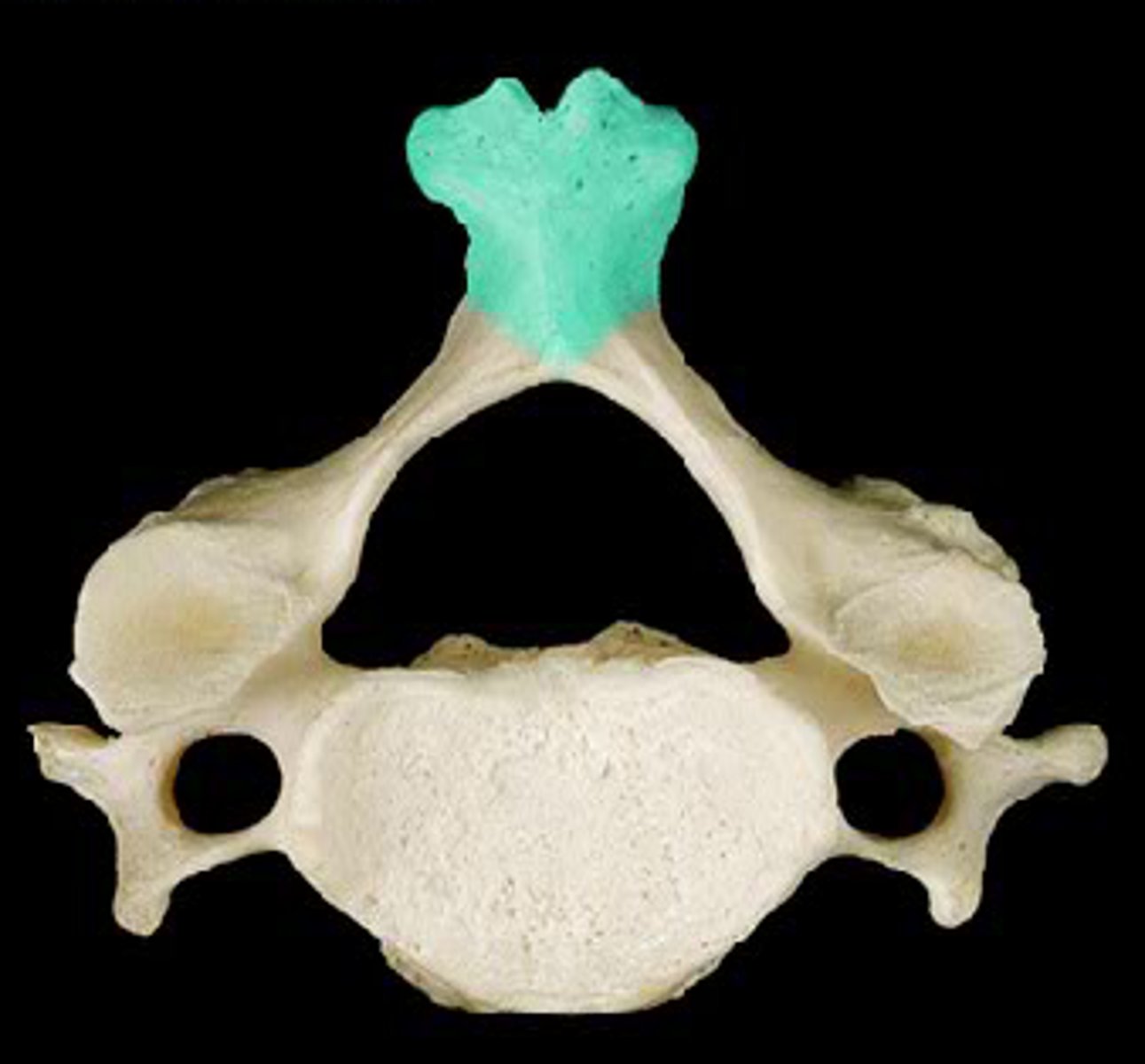
What is the special trait seen in C3-C6?
Bifid Spinous process
What is unique to C7?
it has a large single spinous process. This spinous process can be easily felt on the back of your neck due to its size.
What facet's are unique to the Thoracic vertebrae?
the costal facets that connect with ribs
Costovertebral joint
The head of the ribs will articulate to the costal facets of the vertebral body
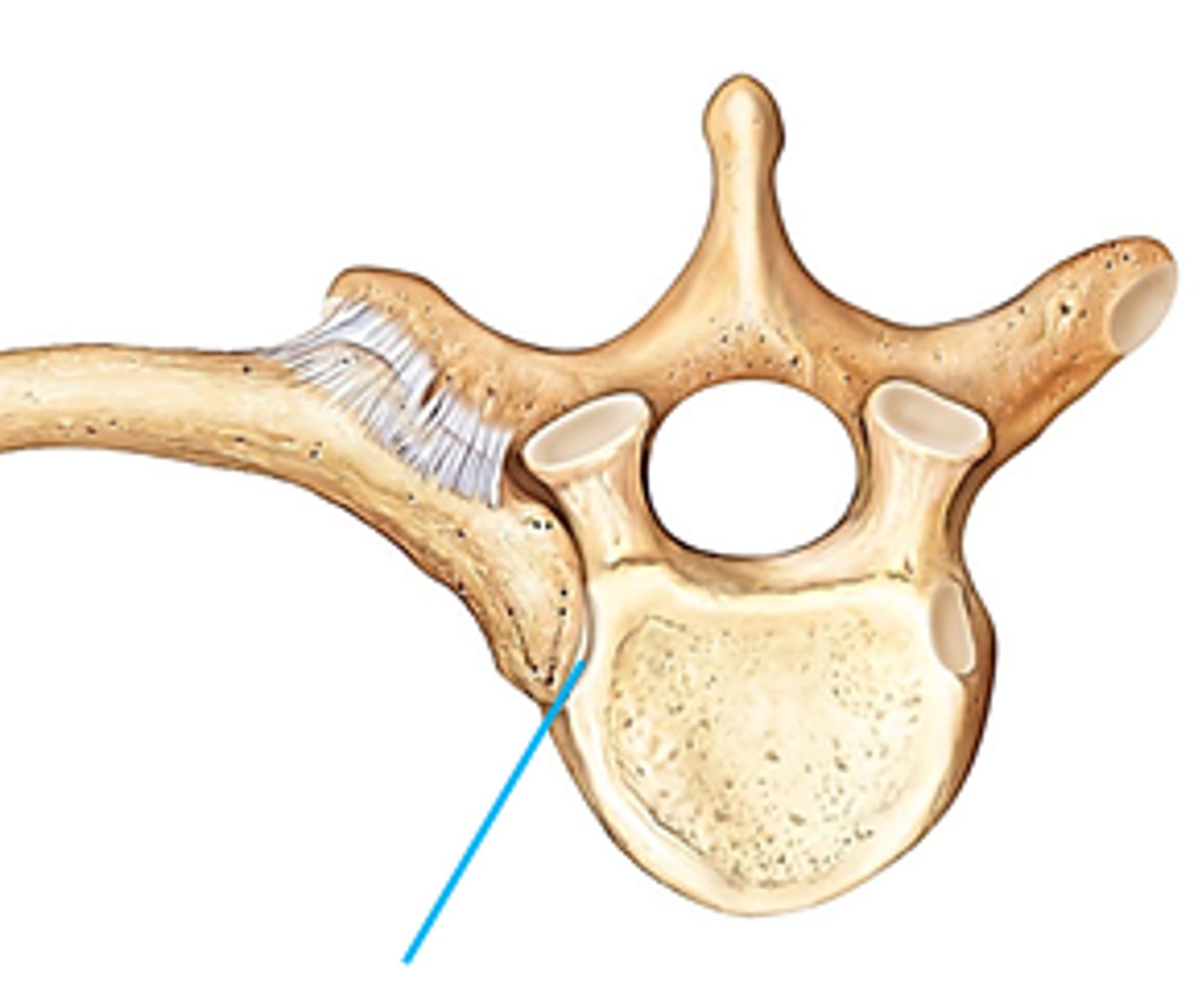
Costotransverse joint
The tubercle of the ribs will articulate to the costal facets of the transverse process
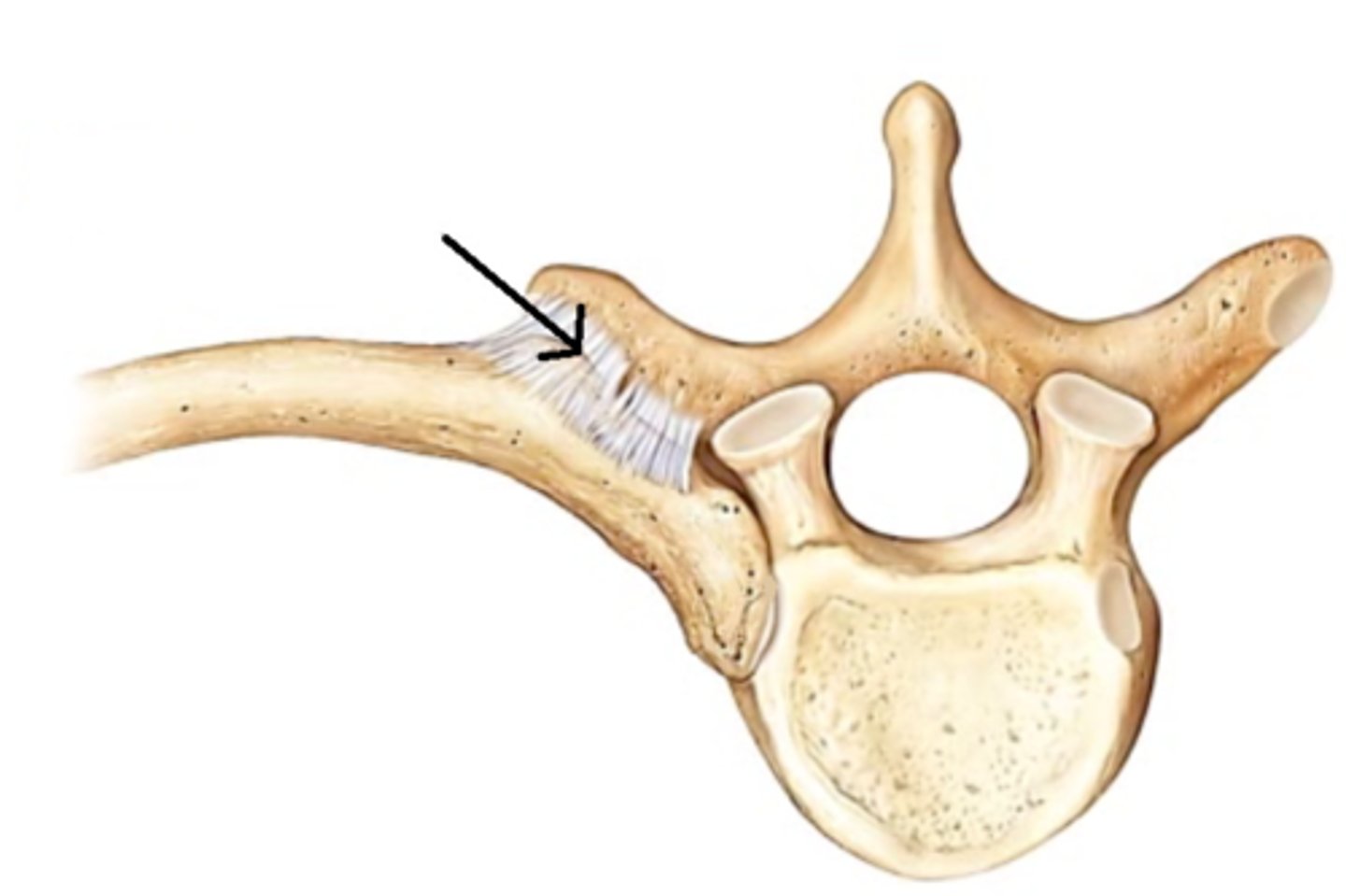
What is unique about L5?
It's the largest vertebral body and transverse process because it supports the entire weight of the body
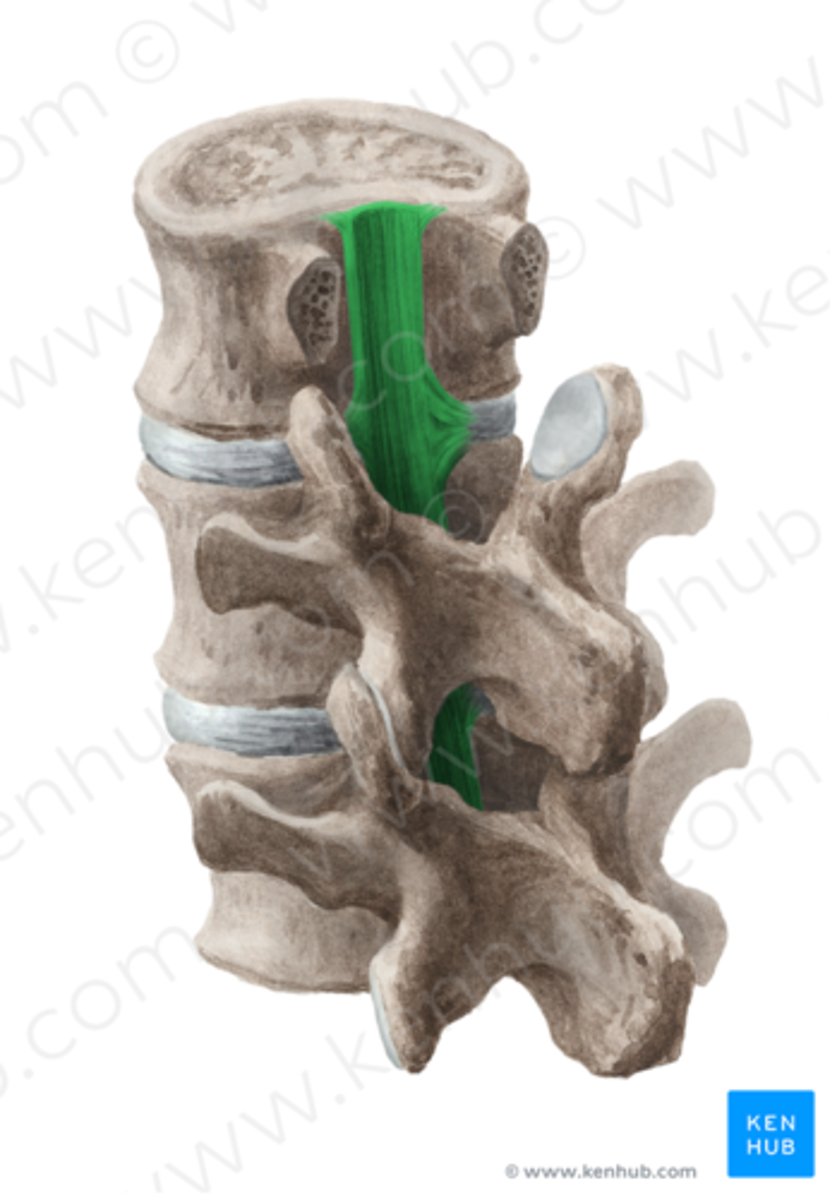
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament
Location; Anterior surface of vertebral bodies
Start/Stop; C1 to Sacrum
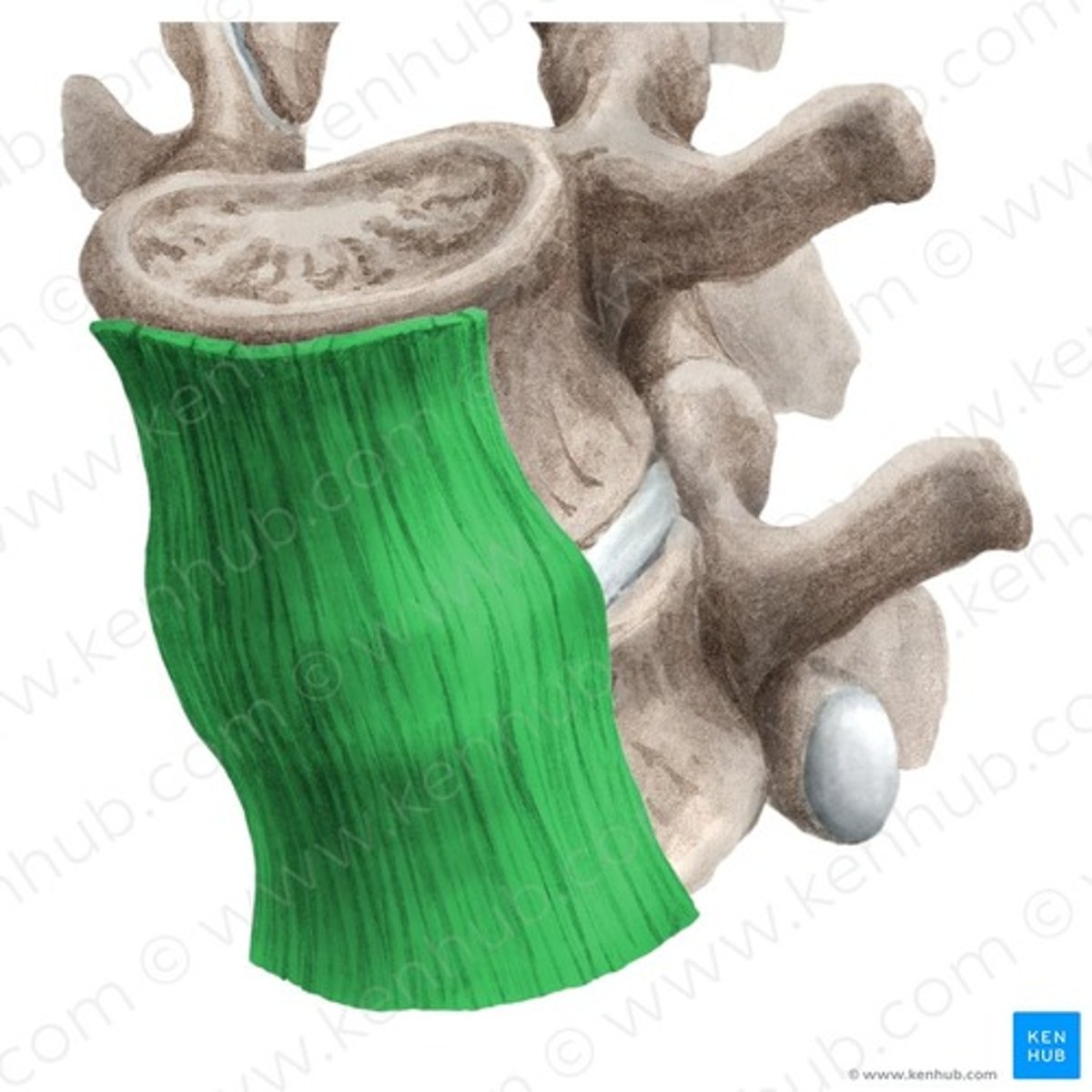
Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
Location; Posterior surface of vertebral bodies
Start/Stop; C2 to Sacrum
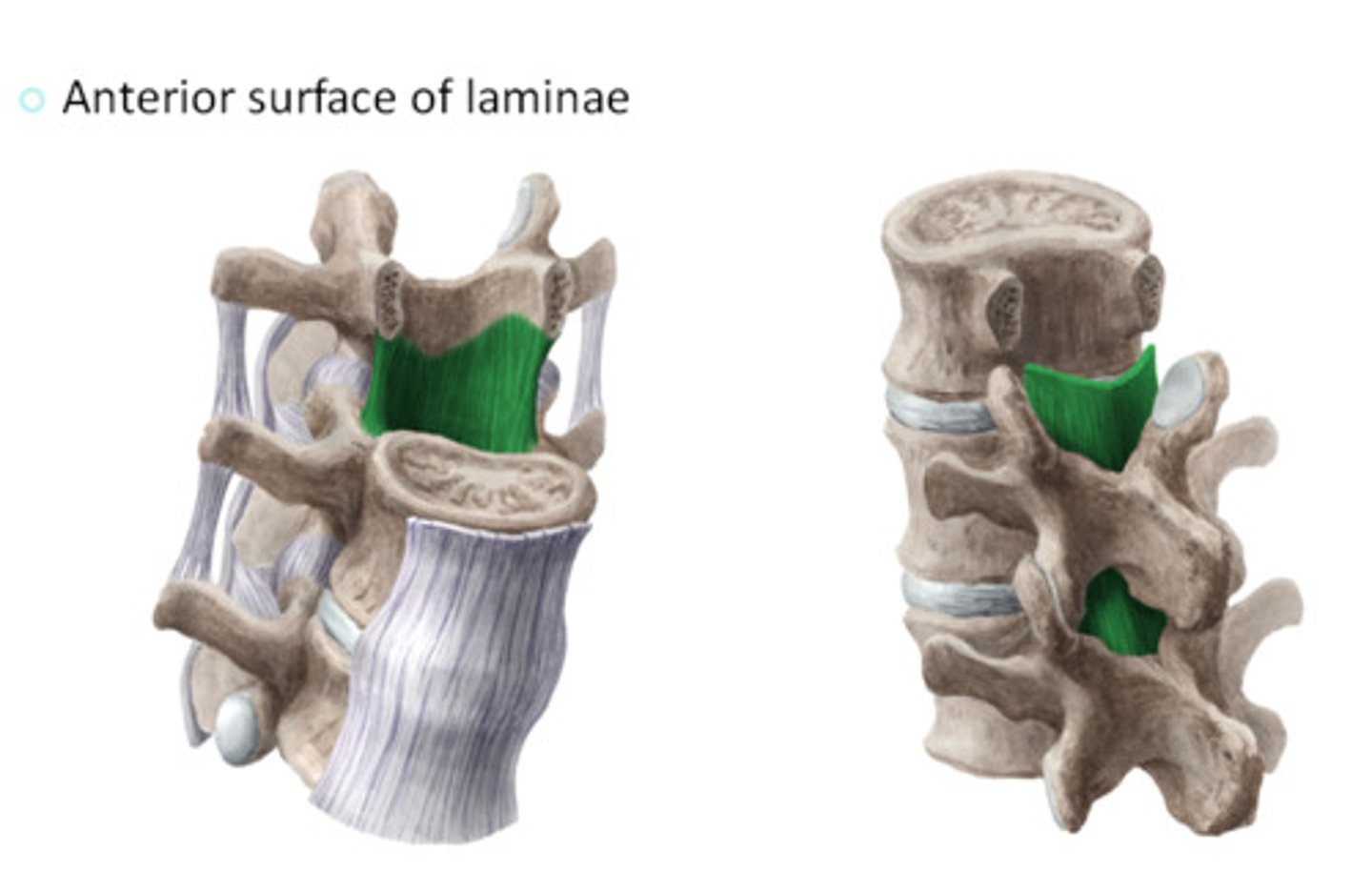
Ligamentum Flavum
Location; Along the medial aspect of the laminae of the vertebrae
Start/Stop; C2 to L5
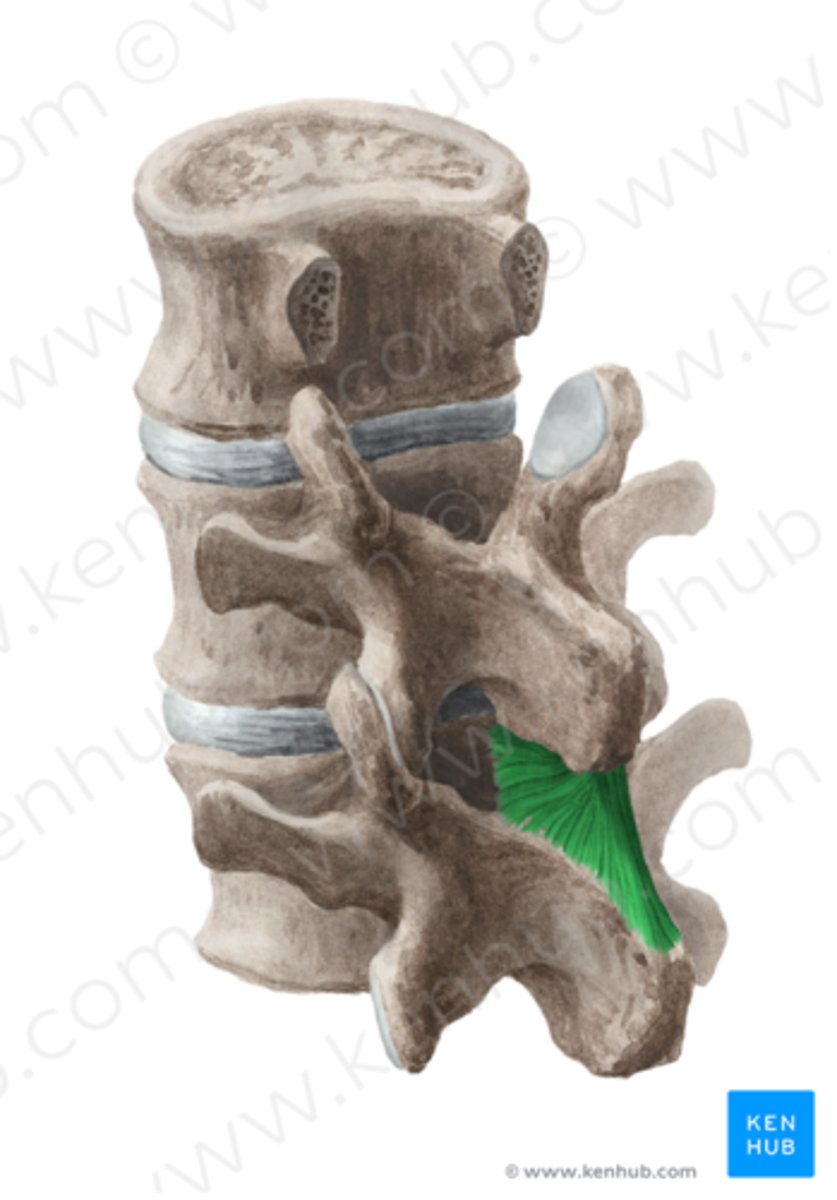
Interspinous Ligament
Location; Between adjacent spinous process
Start/Stop; Throughout spinal column
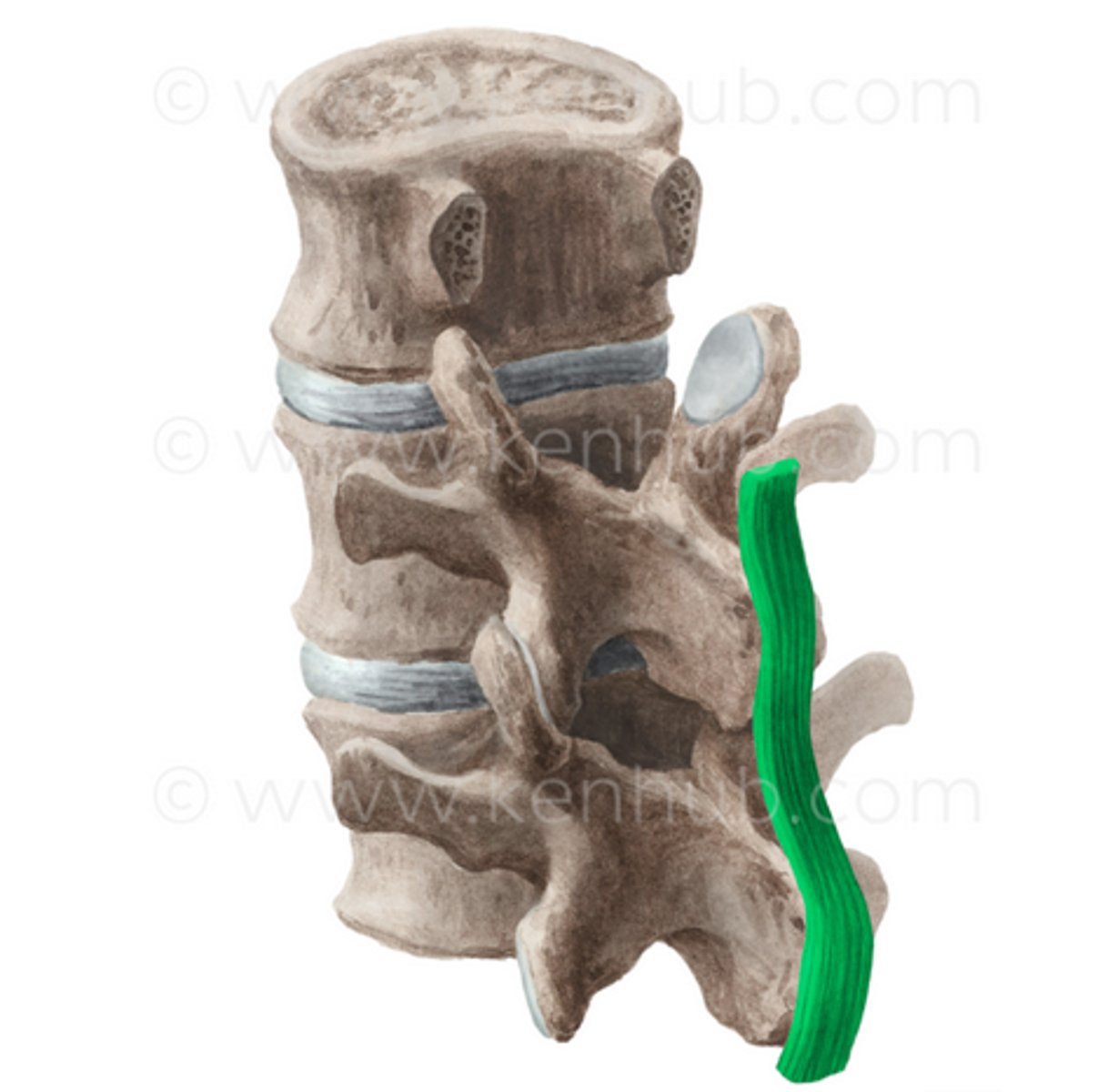
Supraspinous Ligament
Location; Tips of the spinous processes
Start/Stop; C7 to lower lumbar vertebrae
Splenius Muscles
superficial layer of muscles of the spine
Intermediate Layer
erector spinae group (prominent bulge on each side of the vertebral column)
Deep Layer
Transverseospinal group
Spinal Meninges
Form the thecal sac which houses the spinal chord and CSF.
Consist of 3 layers
Dura Layer
Outer Layer
Arachnoid layer
Middle layer
Pia layer
Inner layer
Filum terminale
Descends through the subarachnoid space to inferior border of the thecal sac
Spinal chord
Large nerve cable that connects the brain with the body.
Extends clear down to about T12/L1
Conus Medullaris
Where the spinal cord ends
Cauda equina
a grouping of nerves that appear like a horses tail
Dorsal roots
Sensory/afferent nerve roots
Posterior lateral
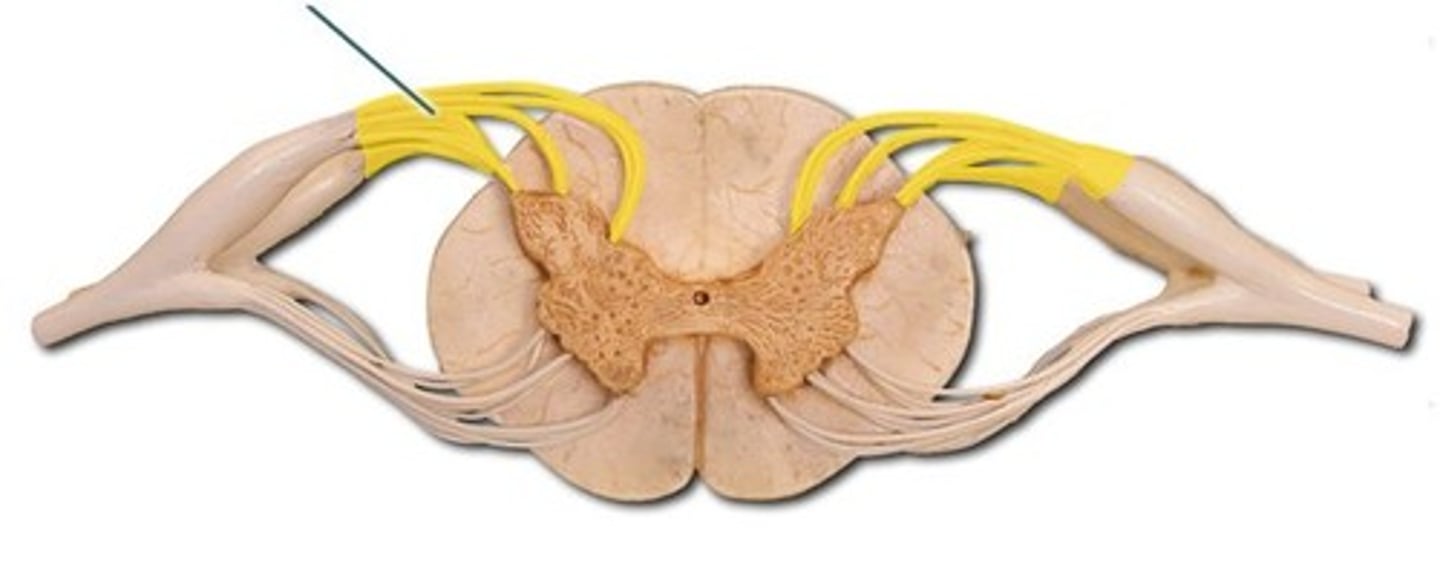
Dorsal Root Ganglion
Oval enlargement of dorsal root containing nerve cell bodies of sensory neurons
Located in intervertebral foramen
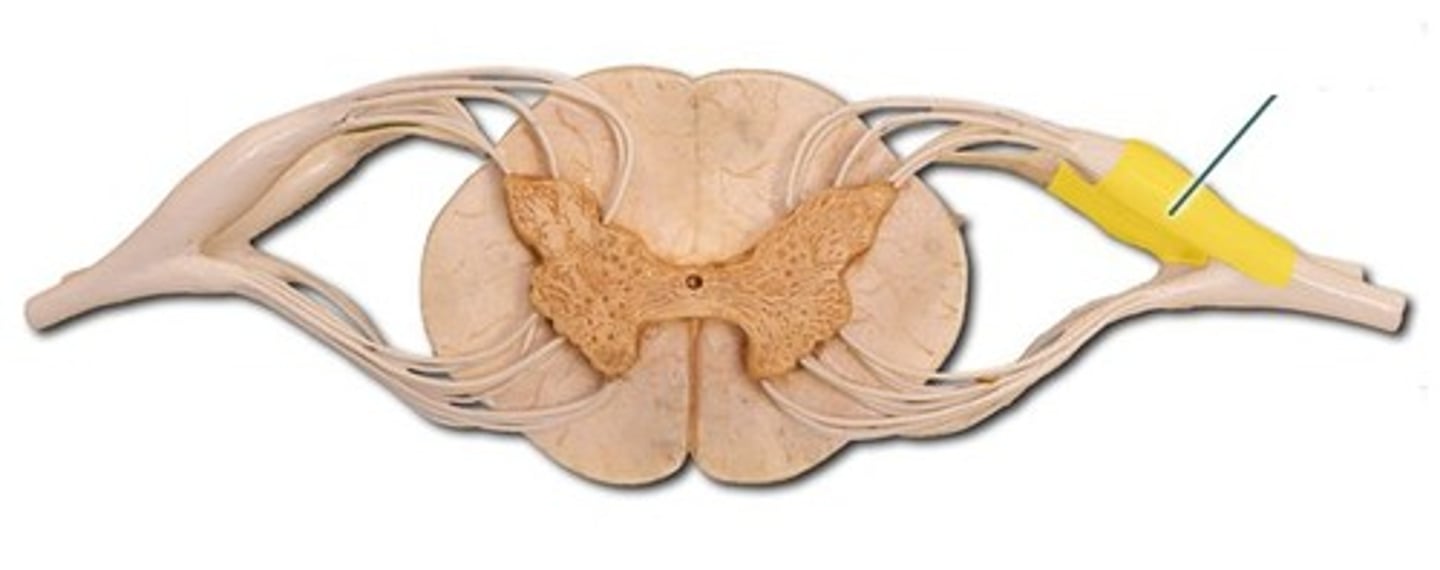
Ventral roots
Motor/Efferent nerve roots
Anterolateral
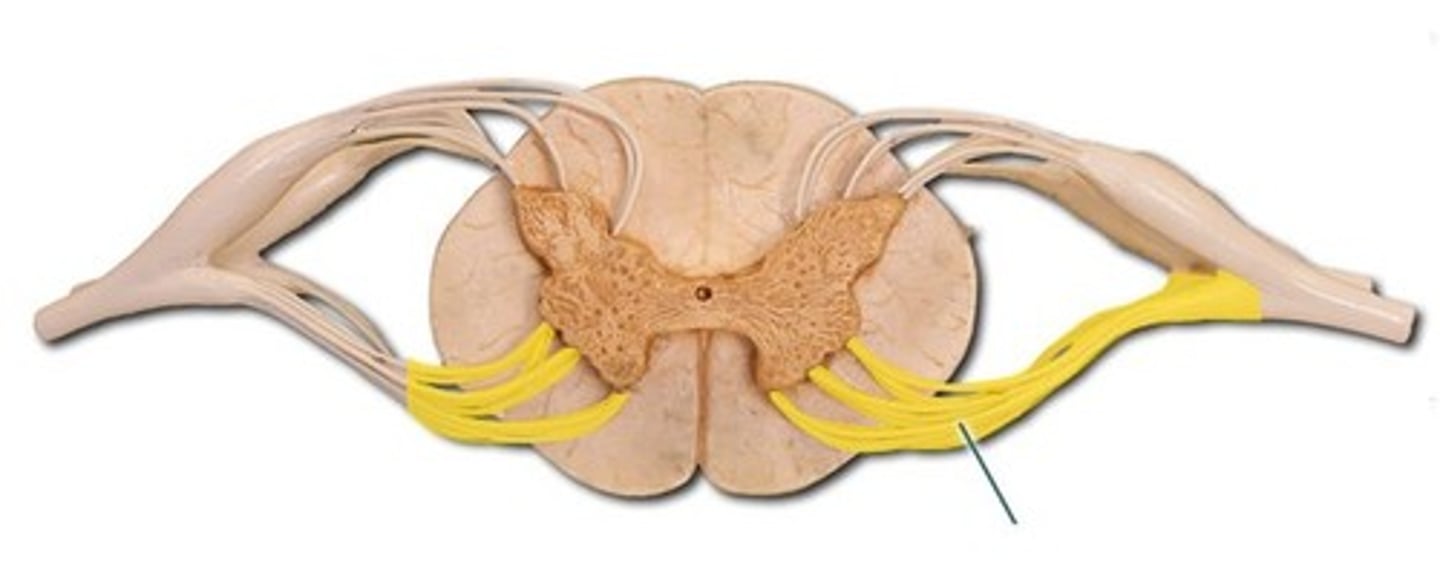
Spinal nerves
Outside the intervertebral foramina ventral and dorsal roots unit to form 31 pairs of spinal nerves