Optics Exam 1: Key Terms and Definitions for Success
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
What is the wavelength range for visible light?
400 to 740nm
What is the speed of light in a vacuum?
c=3x10^8 meters per second
What colors exhibit long and short wavelengths?
Red gives long wavelengths and short gives blue wavelengths
What gives an object it's surface color?
wavelengths that are reflected from or produced at a surface/sourse
What happens to light that is not reflected to transmitted?
it is absorbed
What are the colors you see?
colors that are not absorbed, but reflected back into your eye
EX: a blue shirt absorbs red wavelengths and reflects back blue wavelengths
Where does reflection occur?
at any boundary between two different media (EX: air/water or air/lens)
What are the two main/broad types of reflection?
specular and diffuse
What is a specular reflection?
a very smooth surface with a smooth reflection
What is a diffuse reflection?
a rough surface, where light is reflected at strange angles
Where does scattering occur?
non-homogenous optical media
index of refraction
n=c/v
velocity
v=c/n
n for materials other than air is always (greater than or less than) one
greater than one
Snell's Law
n₁sinθ₁=n₂sinθ₂
How does θ change as light travels from lower to higher index?
the angle decreases
How does θ change as light travels from higher to lower index?
the angle increase
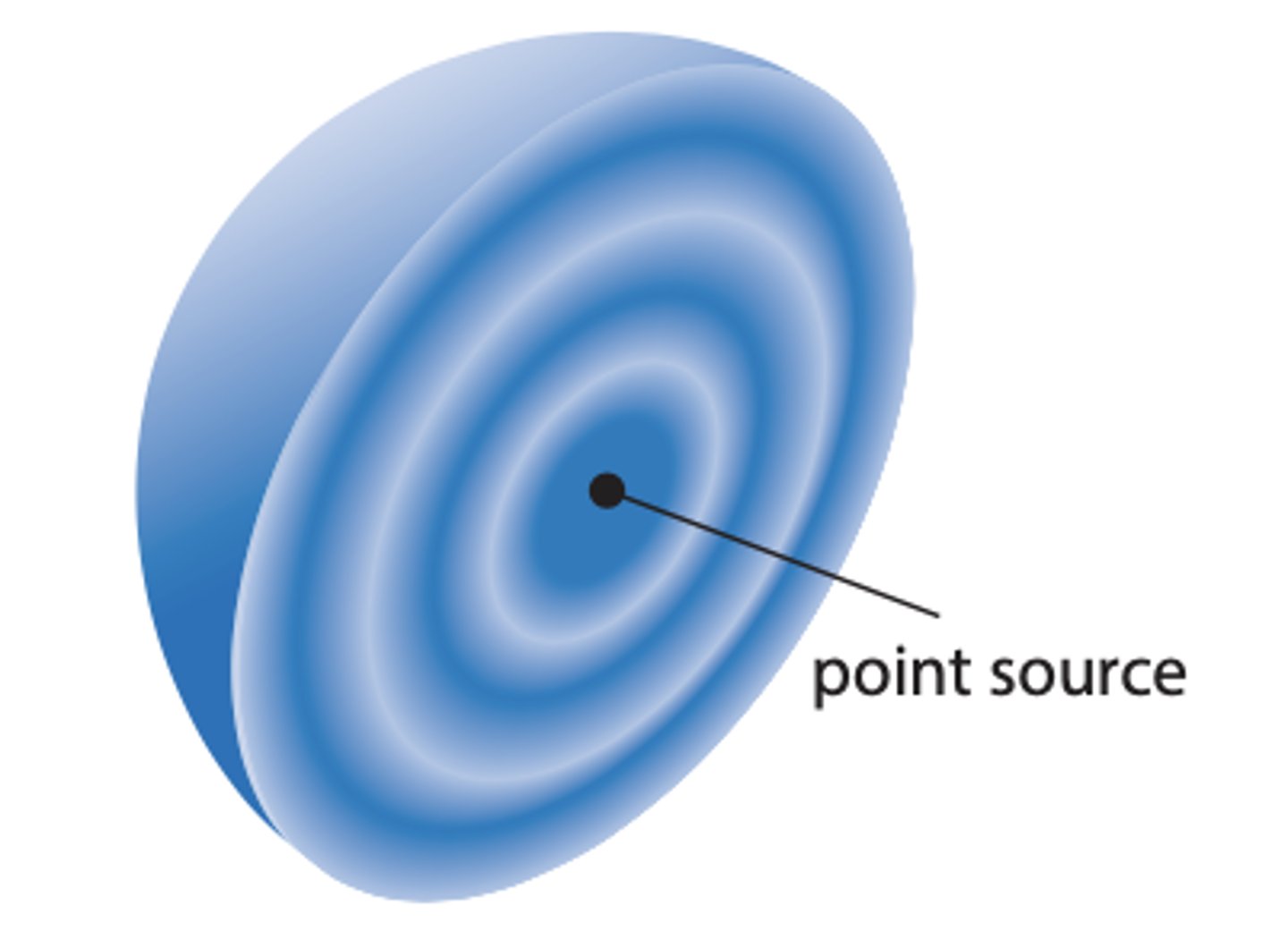
What is a point source?
a source that emits light in all directions
-wavefronts are spherical
-short radius of curvature gives high wave front curvature
-long radius of curvature gives low wave front curvature
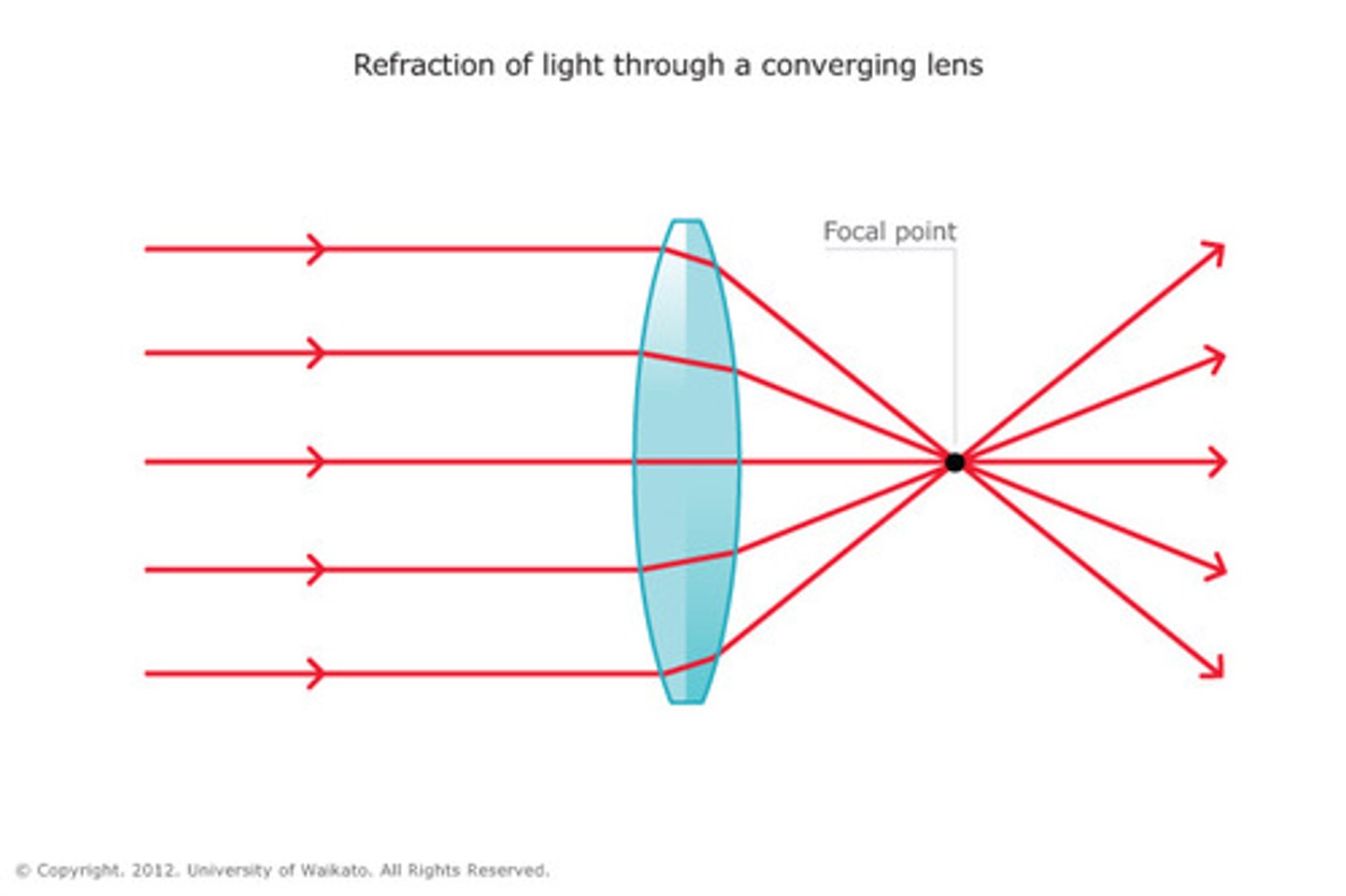
What is a converging wavefront and what is it's center of curvature?
-the center of curvature is the image point
-the rays meet here in a point image
-anywhere else, the image is a blur circle
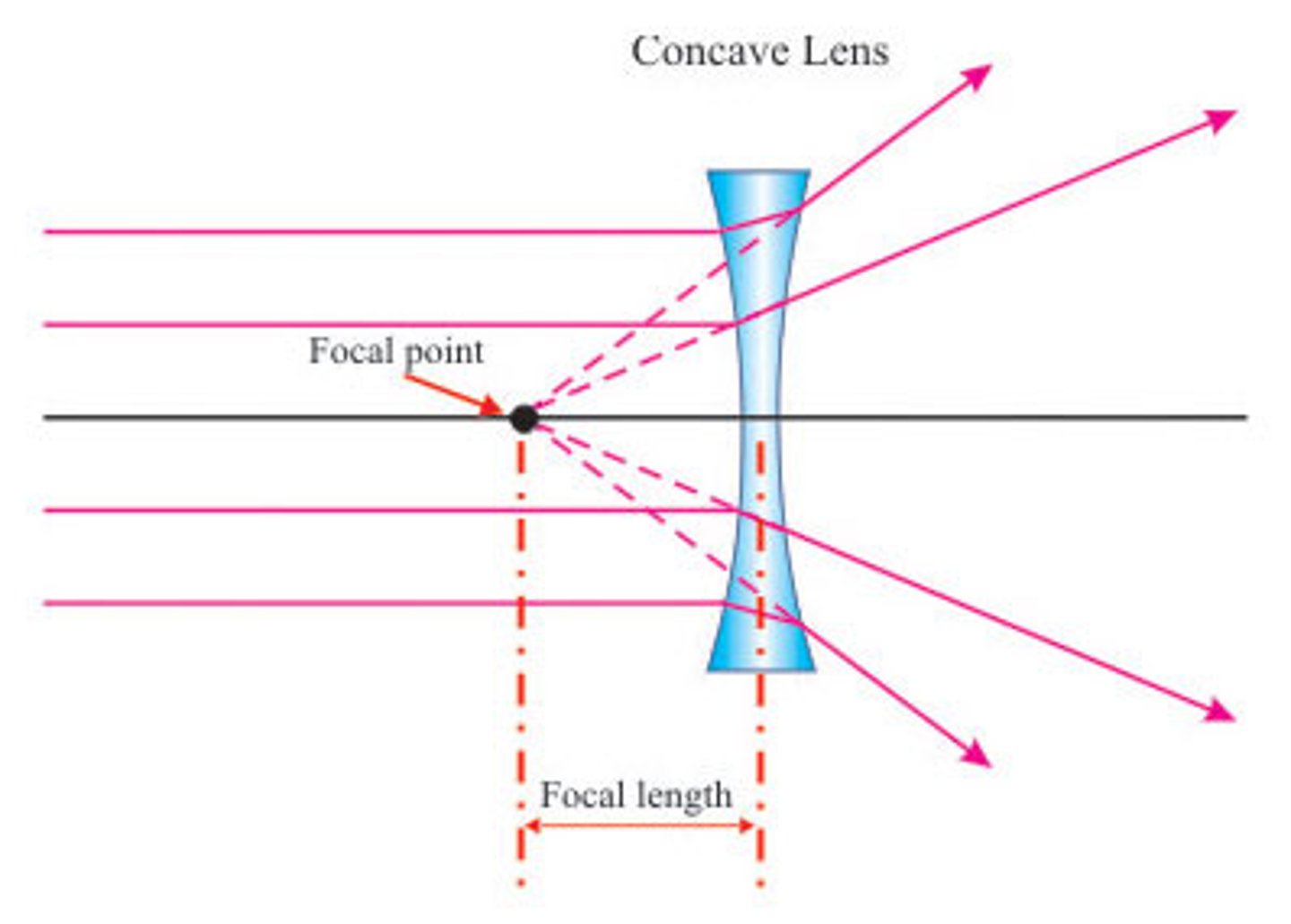
What is a diverging wavefront and what is it's center of curvature?
the center of curvature is the source point (object point)
curvature of a sphere
1/radius of curvature
What is vergence?
the amount of convergence or divergence
vergence equation
Vergence = refractive index (n) / distance from object or image (r)
As diverging light travels, the distance from the source increases and vergence magnitude _________.
decreases
What is the sign for vergence of a converging ray?
positive vergence
What is the sign for vergence of a diverging ray?
negative vergence
What is a ray bundle?
a collection of rays traveling away from a point of object, or traveling towards a point on an image
What is an object at infinity?
parallel rays traveling away from an object
What is an image at infinity?
parallel rays traveling toward the image
What are object rays?
the rays arriving at a lens
What are image rays?
the rays leaving a lens
What is a real object?
diverging light from an object, arriving at a lens
What is the vergence for a real object?
negative
What is a real image?
converging light leaving the lens, towards the image (point at which all the rays intersect)
What is the vergence for a real image?
positive
What is a virtual image?
diverging light leaving a lens (does not converge to a point, cannot be formed on a screen)
What is the vergence for a virtual image?
negative
What is a virtual object?
converging light arriving at a lens
What is the vergence for a virtual object?
positive
What is the optical axis?
the line joining the centers of curvature of the two lens surfaces
What is the secondary focal point?
the on-axis image point for a distant on-axis object point
Where is F₂ for a converging lens?
to the right
What is the primary focal point?
the on-axis object point that produces an image at infinity
Where is F₁ for a converging lens?
to the left
What is the relationship of the focal points for a thin lens in air?
they are equidistant from the lens
For a diverging lens, shorter the focal length, the ____ the lens power.
higher
For a diverging lens, the further the focal length, the ____ the lens power.
lower
How are object distance measured?
From the lens to the object
How are image distances measured?
From the lens to the image
objects or images to the left of the lens...
-distance is negative
-vergence is negative
-objects are real
-images are virtual
objects or images to the right of the lens...
-distance is positive
-vergence is positive
-objects are virtual
-images are real
thin lens vergence equation
image vergence (V) = object vergence (U) + lens power (P)
lens power and focal length equation
f₁=-1/P or f₂=1/P
If U=0 then V=___
P
If U is negative, the object is _____.
real
If U is positive, the object is _____.
virtual
If V is positive, the image is ____.
real
If V is negative, the image is _____.
virtual
If U and P are both negative, then the image is ____.
virtual
If U and P are both positive, then the image is ____.
real
For a converging lens, the primary focal point is to the ___ of the axis.
left
For a diverging lens, the primary focal point is to the ___ of the axis.
right
For a virtual object and a converging lens, the image will be...
real
For a real object and a diverging lens, the image will be...
virtual
For a virtual object and a diverging lens, the image will be...
virtual
If the object is at F1, then the image is...
at optical infinity
If the object is inside F1, then the image is...
real
If the object and image have the same sign (both positive or both negative), then magnification will be...
positive
If the object and image have opposite signs, then magnification will be...
TERM
negative
If the image is smaller than the object, magnification will be greater than or less than 1?
less than 1
If magnification is 1, the object and image are...
the same size
A real object produces a ____ image on the retina.
real
What is the total power of a typical eye model?
+60D
What is the far point?
the object point that results in an image point on the retina
Where is the far point for emmetropes?
infinity
Describe a myopic eye.
too long or too strong
When myopes view distance objects, the image is focused (in front of/behind) the retina.
in front of
For myopes, the far point is always (in front of/behind) the eye.
in front of
For myopes, the far point is a (real/virtual) object point.
real
Describe a hyperopic eye.
too short or too weak
When a hyperope with relaxed accommodation views a distant object, the image is...
behind the retina
For hyperopes, the far point is always (in front of/behind) the eye.
behind
For hyperopes, the far point is a (real/virtual) object point.
virtual
For a myope, vergence LEAVING the eye is (converging/diverging).
converging
For a hyperope, vergence LEAVING the eye is (converging/diverging).
diverging
What is the definition of refractive error correction?
the vergence required to enter the eye to come to a focus on the retina
What is vertex distance?
distance from lens to cornea
For a myope, will their glasses or contact prescription be stronger? (more negative)
glasses
Where will a correcting lens' secondary focal point be?
at the eye's far point
What is lens effectivity?
the effectivity of a lens differs with vertex distance
Plus lenses (gain/lose) effectivity as vertex distance increase.
gain
Minus lenses (gain/lose) effectivity as vertex distance increase.
lose
What happens when the eye accomodates?
the lens changes shape and adds more positive dioptric power
When an object moves closer to the eye, there is (more/less) (positive/negative) object vergence.
more negative
When an object moves closer to the eye (more/less) accommodation is required.
more
What is the near point?
the point where the image is on the retina at maximum accommodation
The Ufp for myopia is always...
negative
The Unp for myopia is always...
negative
The Ao for myopia is always...
positive (or zero)
In myopia, the far point and near point will both be (in front of/behind) the eye.
in front of