Freaking GeNeTiCs unit 2 Mitosis part 1
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BOOOO GENETICS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Telomere
What is A?
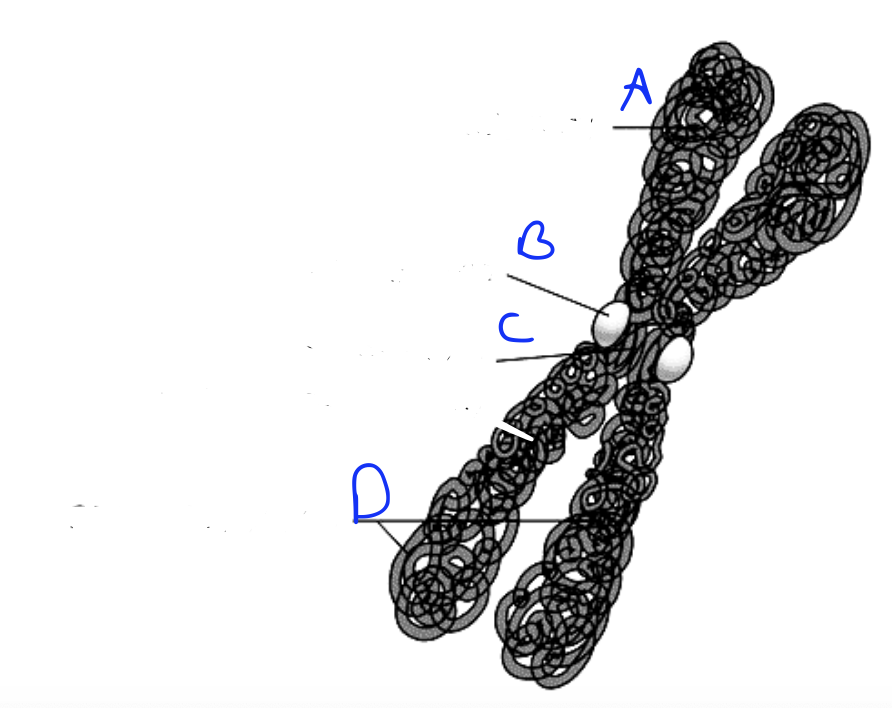
Kinetochore
What is B?
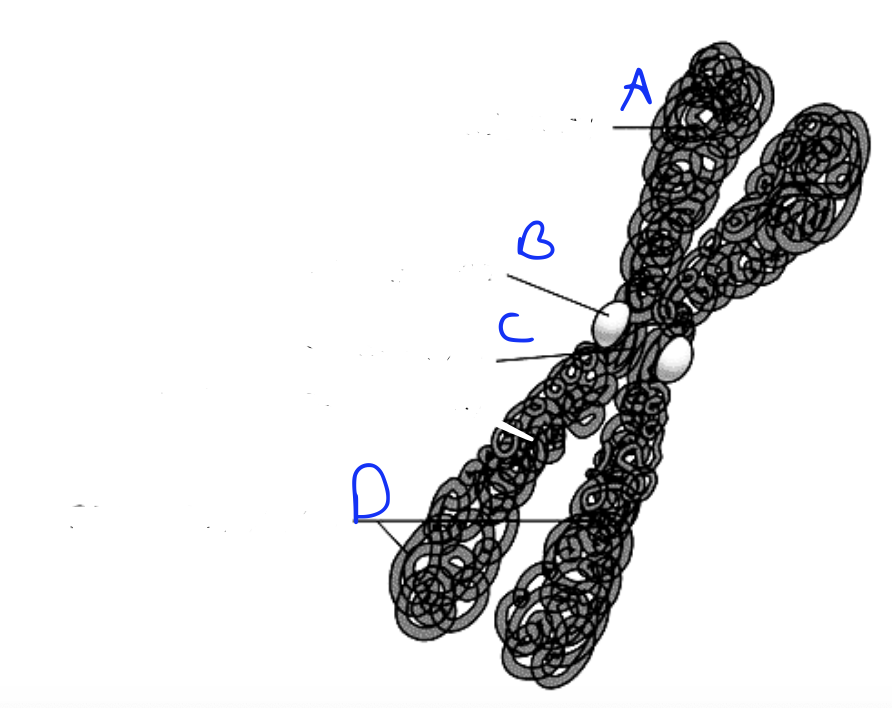
Centromere
What is C?
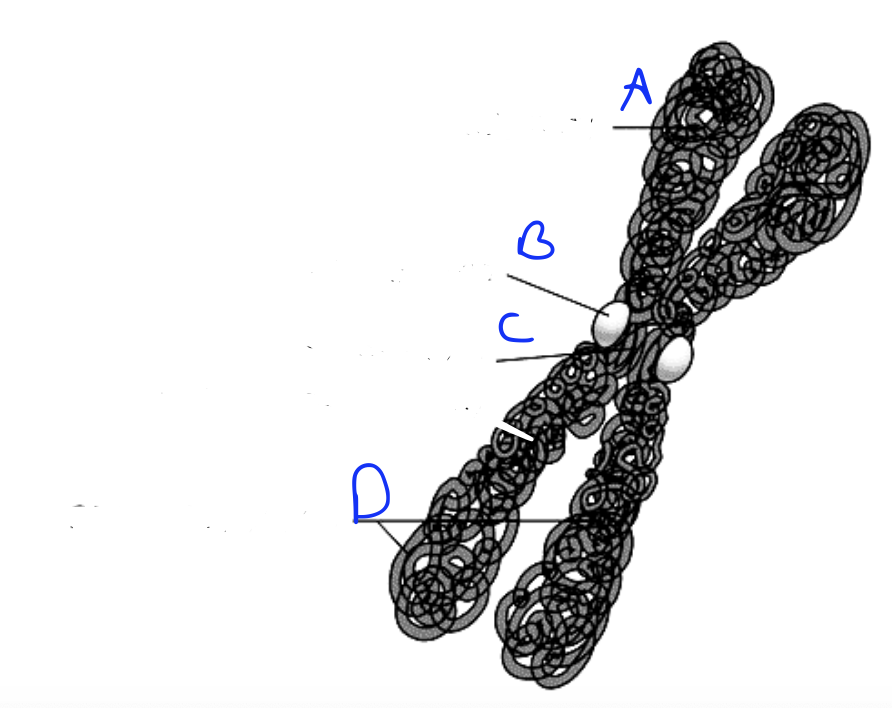
Sister chromatids
What are D?
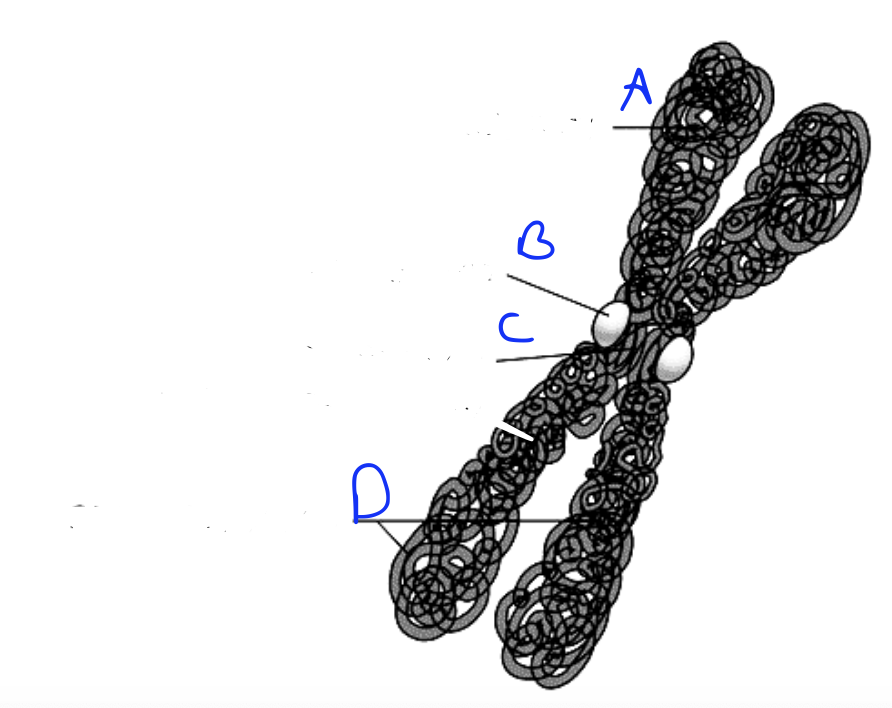
P arm
The shorter arm on a chromatid
Q arm
The longer arm on a chromatid
Metacentric
When the centromere is located in the middle of the chromosome
Submetacentric
When the centromere is located slightly off center on the chromosome
Acrocentric
When the centromere is close to the end of the chromosome
Telocentric
When the centromere is at the end of the chromosome
Monad
Chromatid state: one chromatid; (not typically visible, before replication)
Dyad
Chromatid state: two chromatids (after replication)
Sister chromatids are identical and homologs are different, one from each parent
What is the difference between sister chromatids and Homologs(or homologous chromosomes)
tetrad
When homologous chromosomes in the dyad state pair they create a ____ (4 chromatids intertwined)
Bivalent
Another name for tetrad
chromatin
DNA and histone proteins in the nucleus which condense to form
chromosomes
Kayrotype
number and appearance
of chromosomes in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell
G1 S G2 M
List the Phases of the cell cycle
rapid growth of the cell
What occurs in G1 of the cell cycle?
Genome replication, sister chromatids are formed
What occurs in S phase of the cell cycle?
Prep for Mitosis, organelles and mitochondria duplicated, Microtubules formed
What occurs in G2 of the cell cycle?
Mitosis
What occurs in M phase of the cell cycle?
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
List the 4 phases of mitosis
Mitosis
Mitosis or meiosis: equational division
Chromosomes condense and become visible, Spindle fibers form spindle Apparatus, Organelles migrate to opposite ends of the cell, nuclear envelope breaks down, nucleolus disappears
What occurs during prophase?
Chromosomes/pairs of sister chromatids align in the middle of the cell on the equatorial plate
What occurs during Metaphase?
Sister Chromatids are pulled apart by microtubules
What occurs during Anaphase?
Spindle apparatus is disassembled, nuclear envelope reforms, chromosomes uncoil and begin expression
What occurs during Telophase?
cytokinesis
cytoplasm division after nuclear division
Have
Spindle fibers in animal cells have/do not have centrioles
Do not have
Spindle fibers in plant cells have/do not have centrioles
pinching with cleavage furrow
Animal cytokinesis:
Cell wall and cell plate form
Plant cytokinesis
Meiosis
Mitosis or meiosis: reductional division
The separation of homologues
Meiosis 1 can be generalized as
The separation of sister chromatids
Meiosis 2 can be generalized as
homologs pair and exchange info
What occurs in prophase1?
Leptonema, Zygonema, Pachynema, Diplonema, Diakinesis
List the stages of prophase 1
Duplicated chromosomes (a pair of homologous chromosomes in the dyad state) condense and become visible
What occurs during Leptonema?
Homologs pair and form a tetrad/bivalent
What occurs during Zygonema?
Crossing over occurs between homologs and synaptonemal complex is formed
What occurs during Pachynema?
Chiasmata
What is the site of cross over in pachynema?
Homologs unpair and pull away from each other
What occurs during Diplonema?
Diplonema
Which stage of prophase 1 do humans eggs rest at until ovulation?
Homologs thicken and move towards the center, preparing for metaphase 1
What occurs during Diakinesis?
paired homologs align in middle of the cell
What occurs during Metaphase 1?
paired homologs separate & are pulled toward opposite ends of the cell
What occurs during Anaphase 1?
homologs made form two sister chromatids arrive at poles
What occurs during Telephase1?
chromosomes condense
What occurs during Prophase II?
haploid number of chromosomes in dyad state align in middle
What occurs during Metaphase II?
Chromatids separate, change to monad state, 1N
What occurs during Anaphase II?
4 haploid cells with chromosomes in the monad state
What are the Products of Meiosis?
Reduction of ploidy, the paternal and maternal chromosomes are randomly assorted in metaphase, crossing over ensures diversity among the products
List the three most important aspects about meiosis
Non-disjunction
What is the failure of homologs or sister chromatids to separate properly in Meiosis 1 or 2?
Trisomy in chromosome 21
What causes down sydrome?
Trisomy in chromosome 13
What causes Patau syndrome
Trisomy in chromosome 18
What causes Edward syndrome
Down syndrome, Patau syndrome, and Edwards syndrome
What are three syndromes caused by trisomy
What causes Klinefelter Syndrome
Lacking and X chromosome in Females
What causes Turner Syndrome
extra X chromosome in females
What causes Triple X syndrome
extra Y chromosome in males
What causes XYY syndrome
Nullisomy
What is it called when you are missing a pair of homologs (form of nondisjunction)
Monosomy
What is it called when you are missing one chromosome (form of nondisjunction)
Trisomy
What is it called when you have an extra chromosome (form of nondisjunction)
Mitosis
Mitosis or Mitosis: Occurs in somatic cells
Meiosis
Mitosis or Mitosis:occurs only in specialized cells of the germ line
Meiosis
Mitosis or Mitosis: both reductional and equational divisions –
homologous pairs and sister chromatids are
separated
diplonema
What is this?
