Microbiology Lab- Brightfield Microscopy and Microscopic Measurements
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What does the diaphragm of a microscope do?
Regulate the amount of light. Opening it lets in more light, and closing it blocks light.
What does the coarse adjustment of a compound microscope do?
It moves the stage up and down.
What does the fine adjustment of a compound microscope do?
It moves the stage in small increments and allows for sharper focus.
What magnification is the ocular lens?
10X.
What does the condenser lens of a compound microscope do?
It collects and directs light, and has no magnifying power. It can be moved up and down below the stage.
How do you determine total magnification?
Multiply the ocular x objective.
What is resolving power?
The ability to separate two objects or points in the field.
What is the limit of resolution for a compound microscope?
0.2 um.
What is the resolving power of bacterial cells?
1.0 um.
Can internal structures be resolved by a light microscope?
No, as their resolving power is less than 0.2 um.
Why would we want to maximize resolving power?
To limit the loss of light due to refraction.
How do we maximize resolving power?
Set the condenser to the highest position, open the diaphragm, and use immersion oil to see smaller structures.
What are the steps to microscopy?
Turn it on.
Adjust the light to the appropriate brightness.
Focus at 4X using the coarse focus knob first, then use the fine focus.
Adjust the stage and scan the slide to find the specimen of interest and move it to the center.
What kind of objective lenses do we have?
Parfocal, meaning they can be changed with minimal or no refocusing.
What lens is oil immersion used with?
100x.
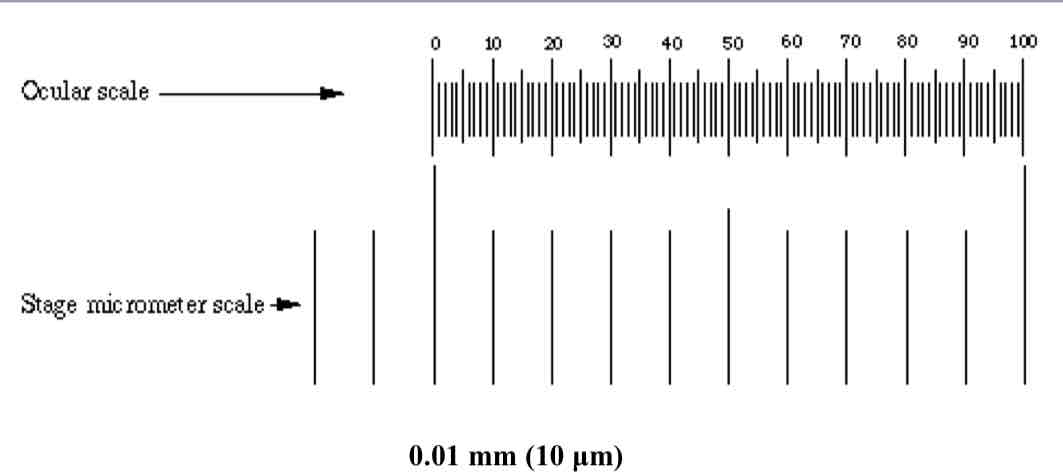
What is the ocular micrometer?
It is built within the microscope. It has arbitrary spacing and must be calibrated for each objective.

What is the stage micrometer?
This is a way of measurement in the form of a slide in which the distance between divisions is known.
Comparison between ocular scale and stage micrometer scale: