Anatomy Exam #4 - Skin
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
integumentary system
skin, hair, nails, sebaceous gland, sweat glands (accessory structures)
function of integumentary system
- barrier
- protection
- termo regulation
- energy storage
-vitamin D synthesis
layers of the skin
epidermis and dermis (cutaneous layer), hypodermis (subcutaneous layer)
thin skin
Covers most of the body
Has four layers of keratinocytes
layers of thin skin
stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum corneum
thick skin
Covers the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
Has five layers of keratinocytes
layers of thick skin
stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum
stratum corneum
outermost layer of epidermis
- dead cells (15-30 layers)
- keratin protein
stratum lucidum
a layer of the epidermis found only in the thick skin
- eleian protein (makes it have a dark appearance)
- 1 layer
stratum granulosum
third layer of the epidermis
- 3 to 5 layers
- not dividing
stratum spinosum
fourth or third epidermis
- 7 to 10 layers
- active
- lesser degree of dividing
- produce keratohyaline (protein)
stratum basale
bottom layer of epidermis
- mitotically active cells
- 1 layer
- stem cells
keratinocyte
dying cells (alive on the bottom and dead on top layer)
what type of tissue is epidermis
stratified squamous epithelium
epidermal ridges
downward waves of epidermis
dermal papilla
extension of the papillary layer of the dermis that increases surface contact between the epidermis and dermis
layers of the dermis
papillary layer and reticular layer
epidermal ridge + dermal papilla
wave pattern
papillary dermis
areolar connective tissue
reticular dermis
dense irregular connective tissue
accessory structure
are in the dermis but are not made from that tissue...is made from the epidermal tissue
what is the dermis made up of?
connective tissue
What is the hypodermis made up of?
adipose tissue
langerhans cells
epidermal macrophages that help activate the immune system
melanocyte
cell in the basal layer that gives color to the skin
dendritic
shape of langerhan cells
epidermis function
- dry surface is unacceptable for growth of most microorganism
- langerhans cells are found in all but the stratum corneum
- antigen presenting cells (phagocytosis in foreign objects)
- first line of defense
factors affecting pigmentation
- type of melanin produced
- how much the malanosomes are filled with melanin gransules prior to transfer
- number of size of melanosome produced
- how long the melanosome persist in the keratinocytes
- degree of transfer within the dermis
how are melanocytes produced?
- melanocytes produce melanin from tyrosin in specialized organelles (melanosome)
- melanosome are transferred to keratinocytes upon stimulation
- melanosomes in keratinocytes contribute to skin's pigmentation
skin color
biological trait and polygenic trait
race
social construct
sources of vitamin D
- sunlight (7-dehydrocholesterol)
- steroid compound
- cholecalciferol (vitamin D)
- intermediary product (calcifediol) in liver
- calcitriol (calcium re-absorption) in kidney
- diietary cholecalciferol (calcium absorption) in digestive tract
free nerve ending
- found in epidermis
- sense pressure/pain/temp
tactile discs
- found on boarder between epidermis and dermis
- sense texture and pressure
meissner's corpuscles
- found in papillary dermis
- sense fine touch and vibration
lamellated corpuscles
- found in papillary dermis
- sense deep vibrations
ruffinin corpuscles
- found in reticular dermis
- sense stretch
thermoregulation of hot
-Sweat glands are activated
-No shivering
-Vasodilation (in dermis)
- muscle is relaxed
- heat loss by evaporation
thermoregulation of cold
-No sweat
-Shivering (muscle causes the hair to stand up)
-Vasoconstriction (in dermis)
hair follicles
- protection
- epithelial column
exocrine glands
- outside
- epithelial column
- sweat glands and sebaceous glands
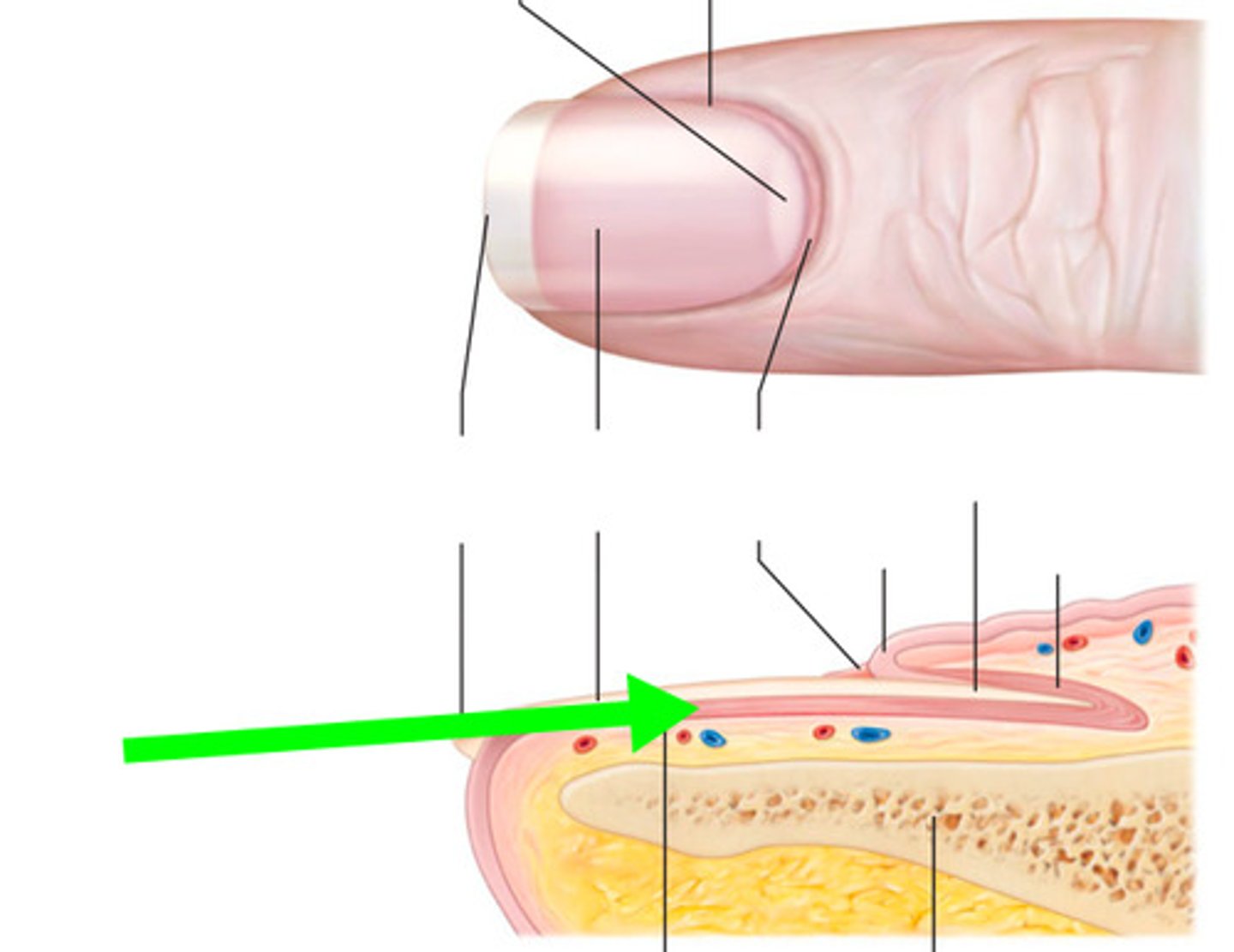
nails
- protection
- nail field
hair shaft
visible part of the hair
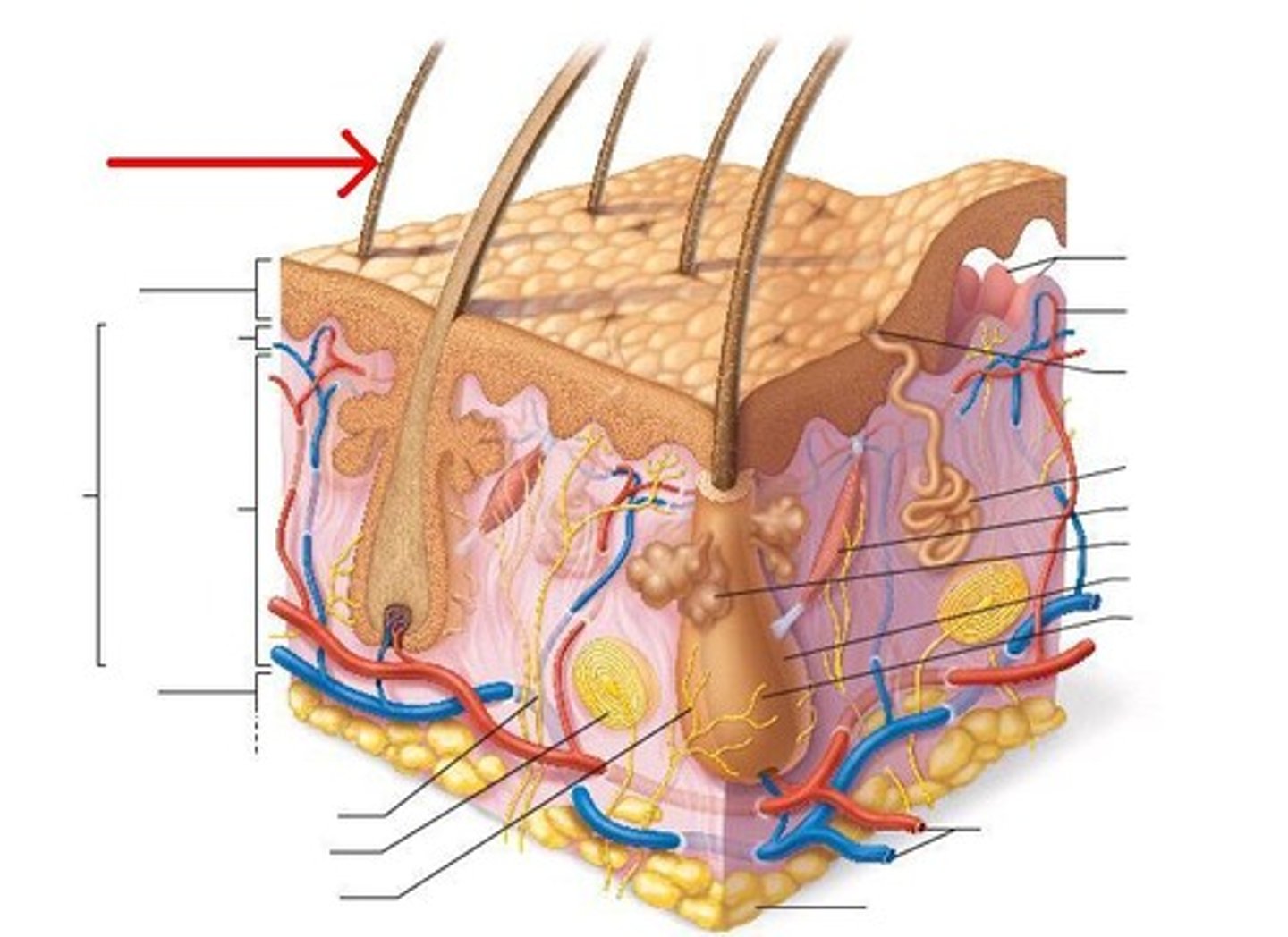
hair follicle
a small tubular cavity containing the root of a hair
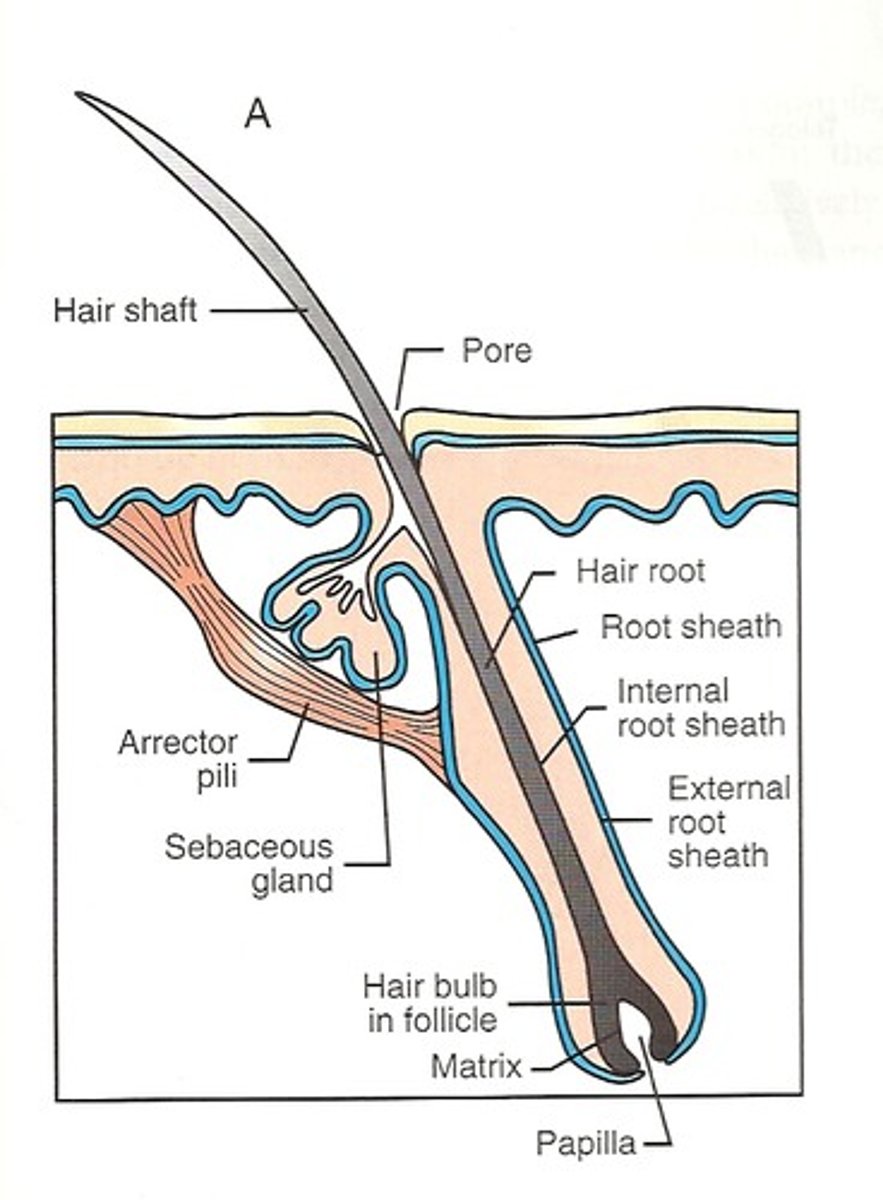
hair matrix
actively dividing area of the hair bulb that produces the hair
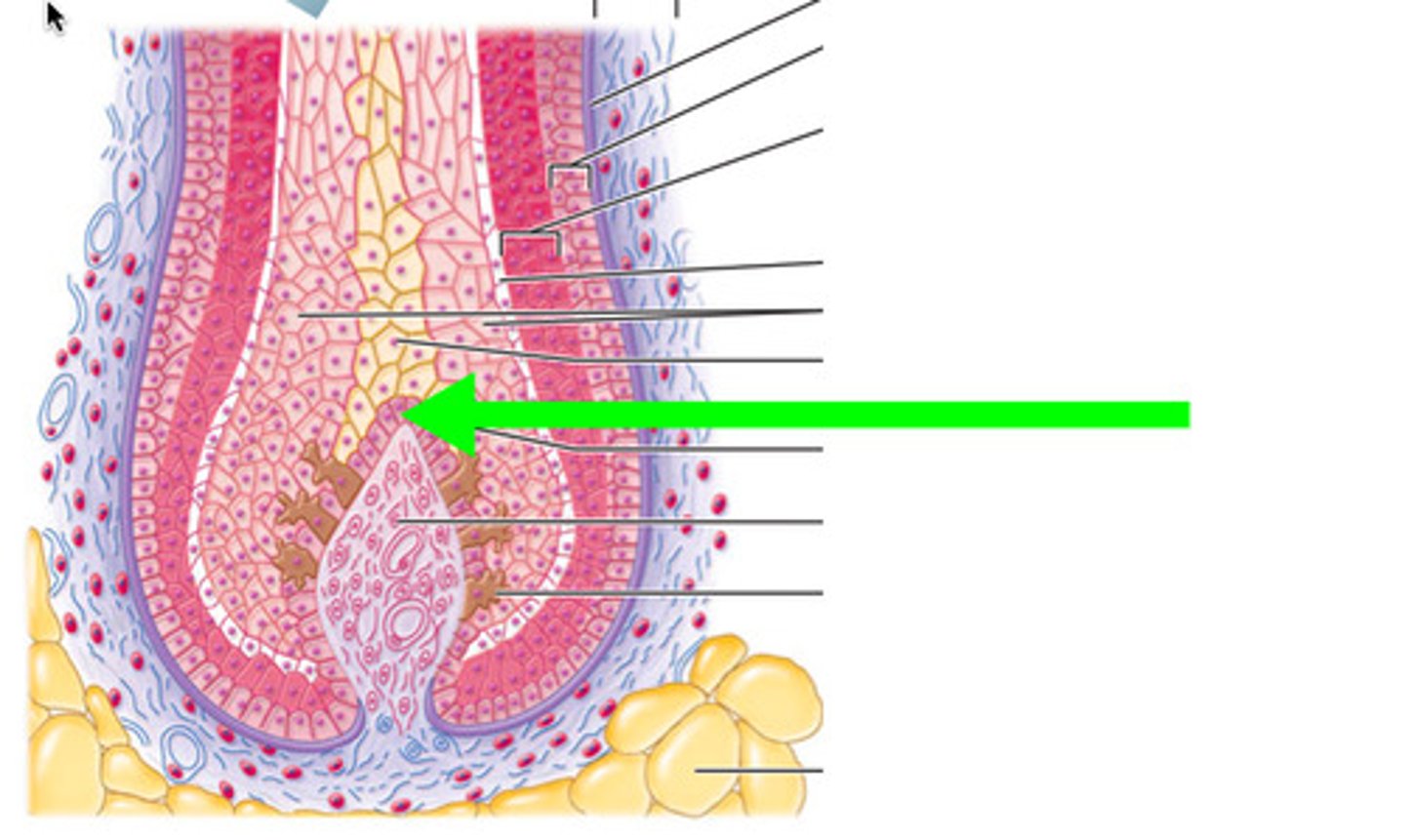
hair bulb
The rounded, club-shaped part of hair located at the end of the hair root
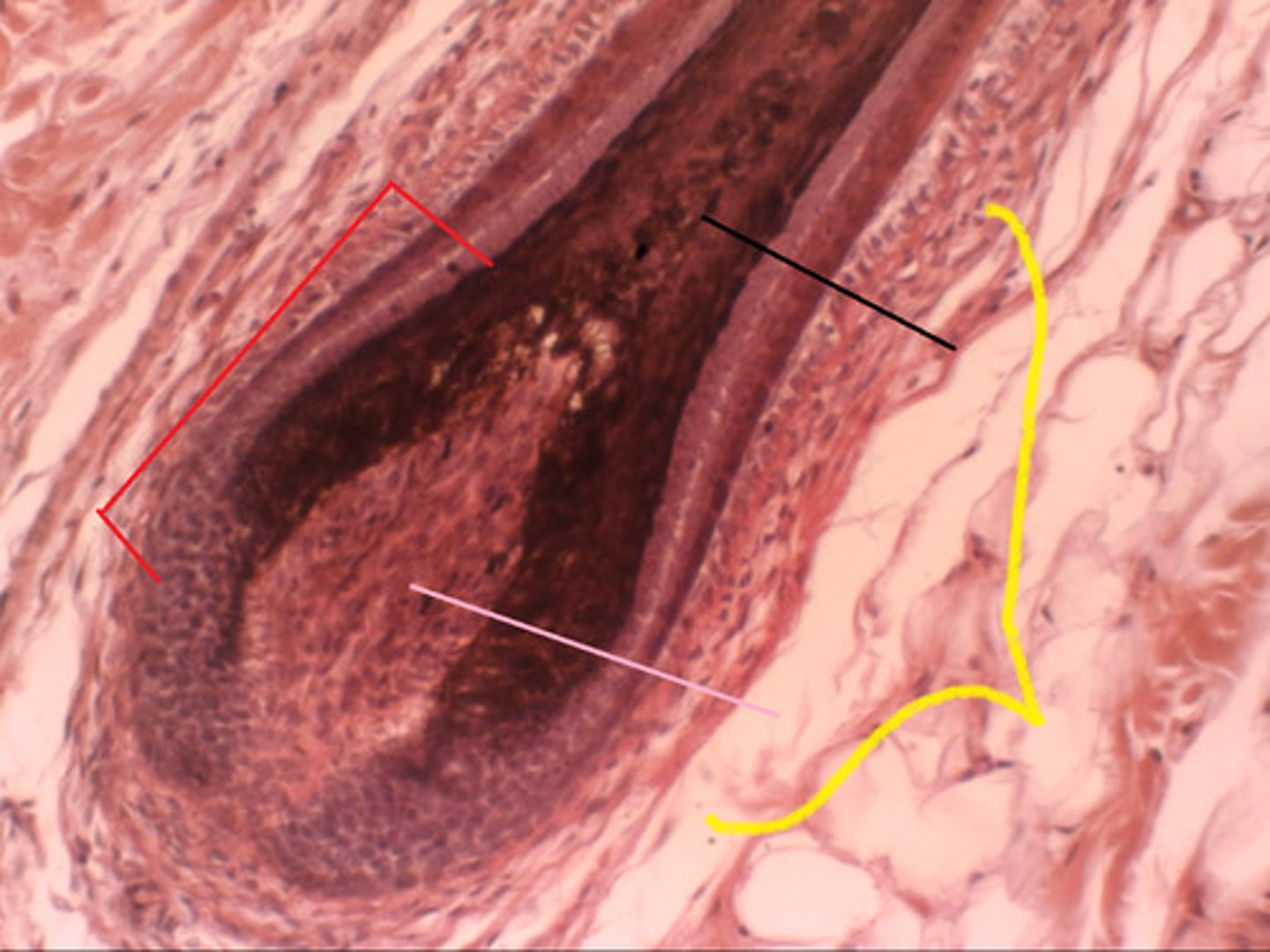
hair papilla
mass of connective tissue, blood capillaries, and nerve endings at the base of the hair follicle
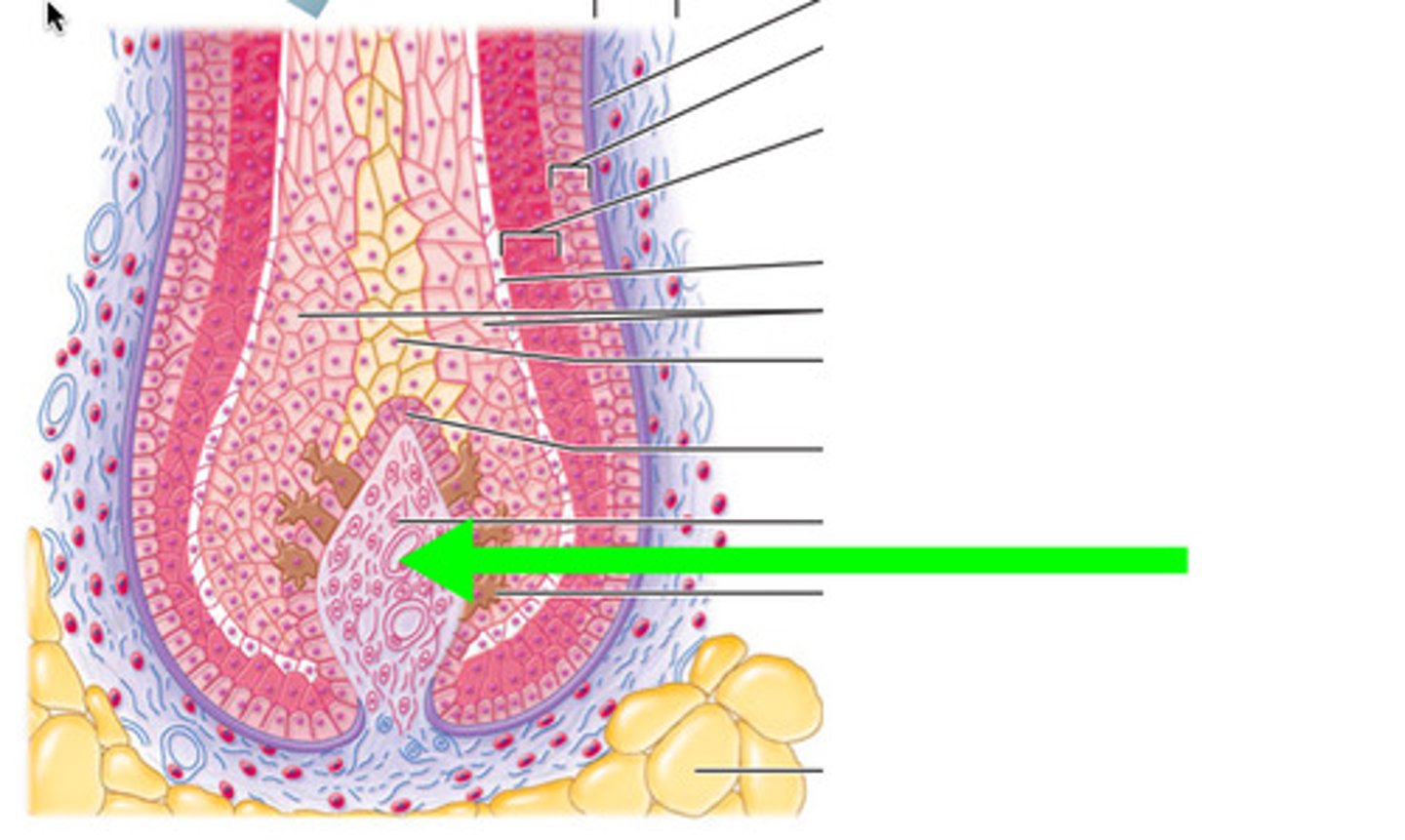
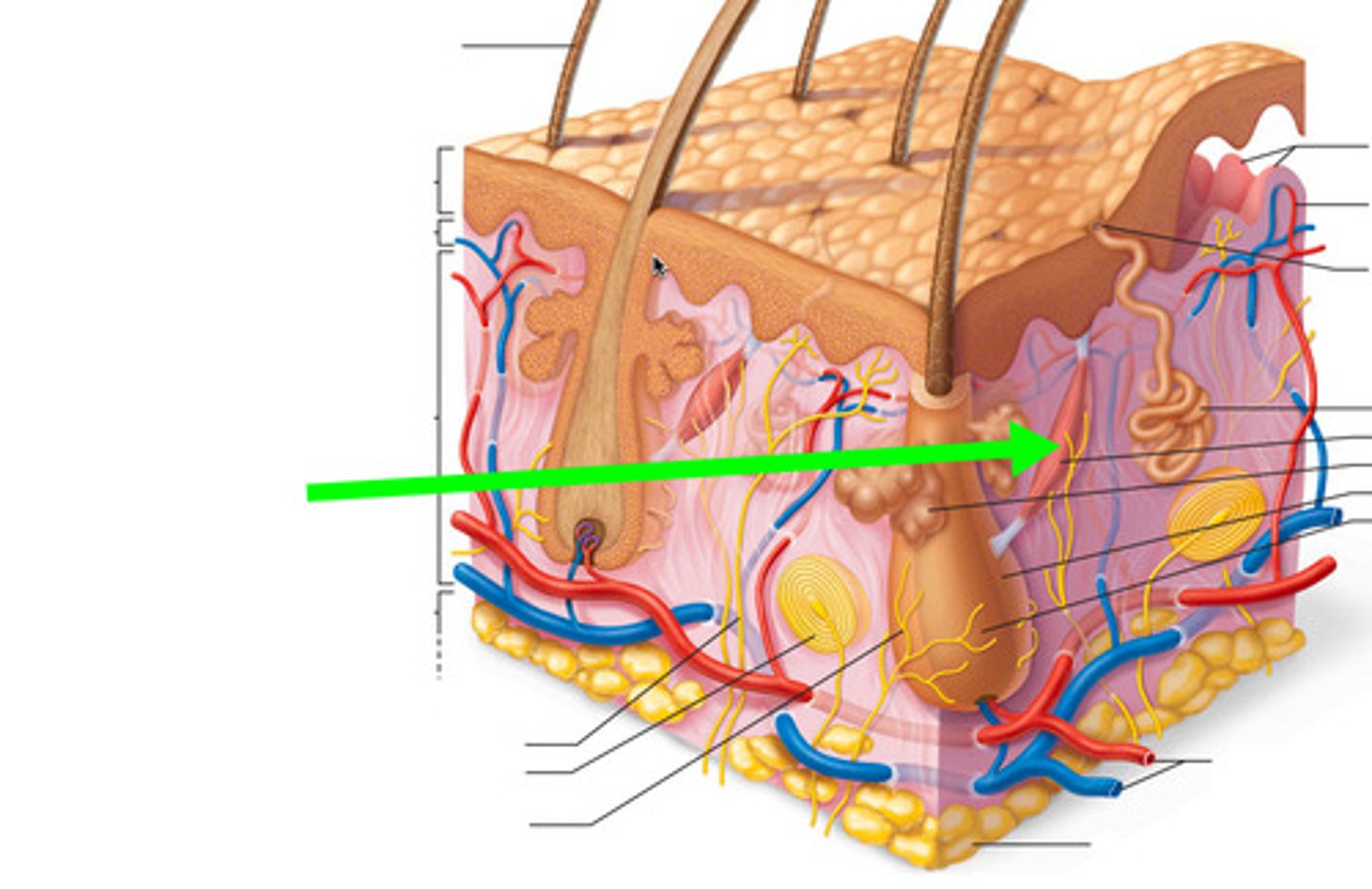
arrector pili muscle
An involuntary muscle fiber attached to the underside & base of the hair follicle
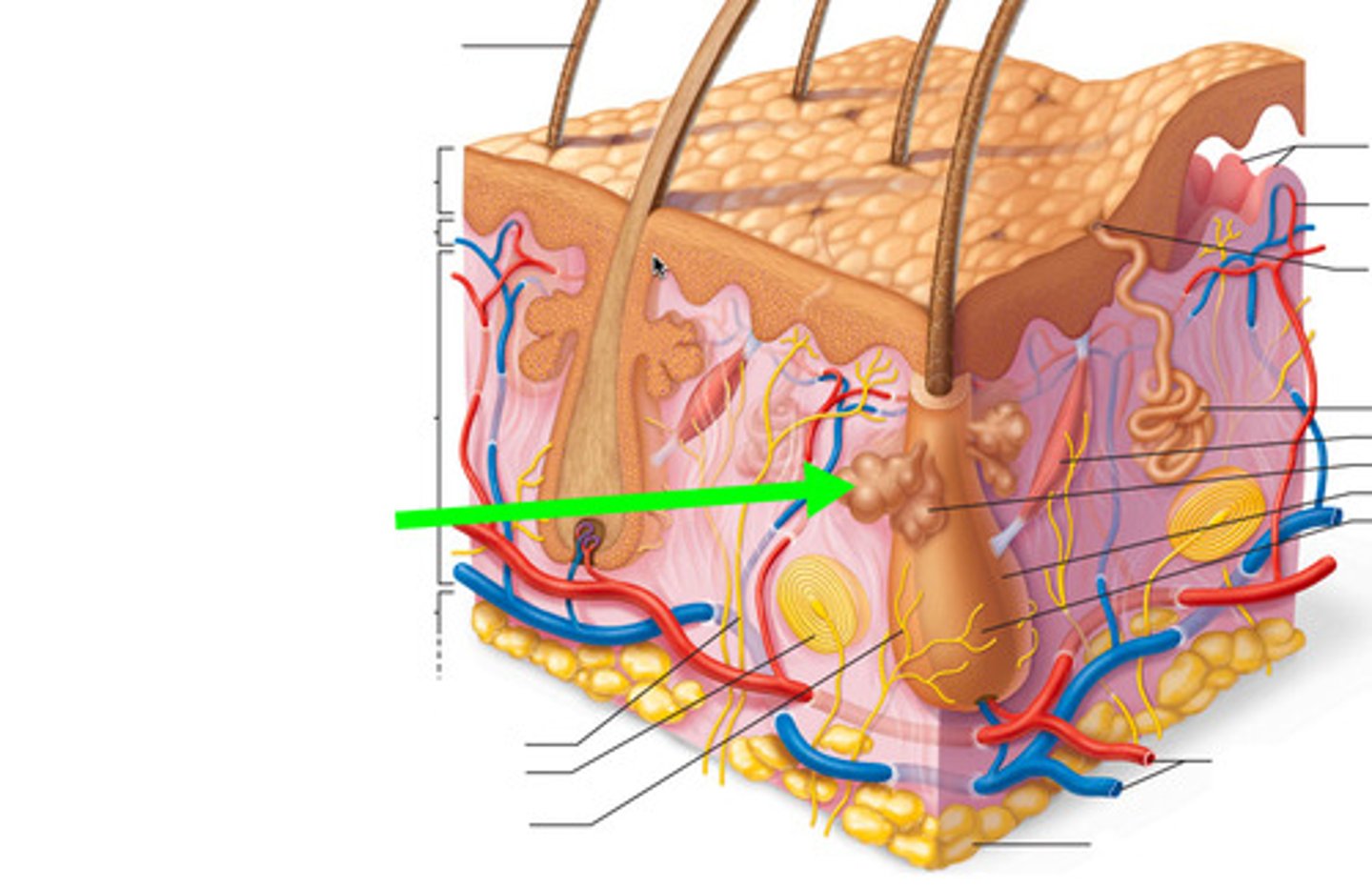
sebaceous glands
secrete sebum (oil) into the hair follicles where the hair shafts pass through the dermis
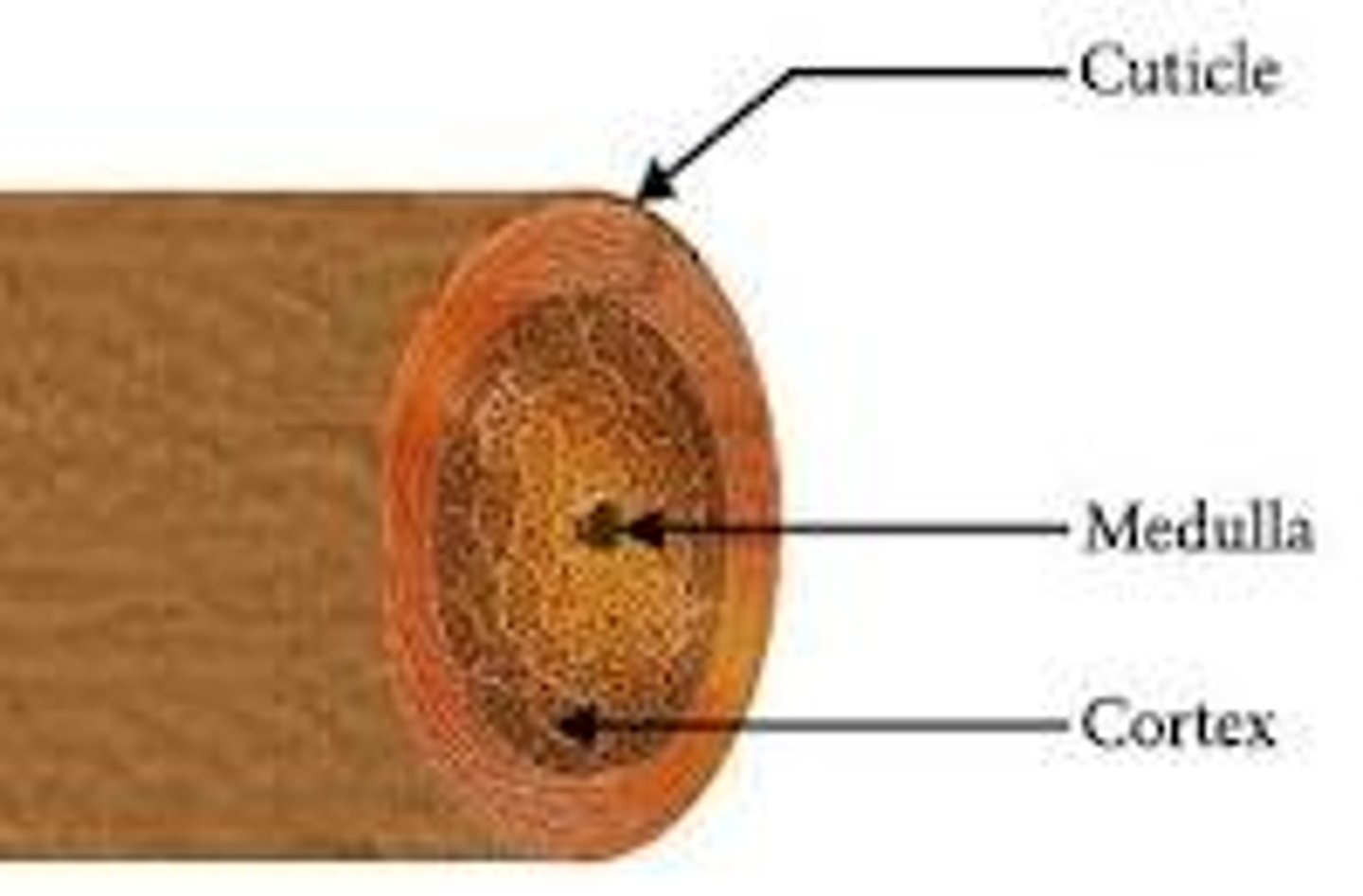
parts of hair shaft (outside to inside)
- cuticle (hardest keratin)
- cortex (hard keratin)
- medulla (soft keratin)
stages of hair growth
-Anagen (Growth stage - active growth by nourishment from blood supply) (2-7 years)
-Catagen (Transition stage - detach from papilla) (10 days)
-Tetagen (Final resting stage - papilla shirk, angiogenesis, fall out of hair follicle) ( 3 months)
nail plate
hard part of the nail (hard keratin)
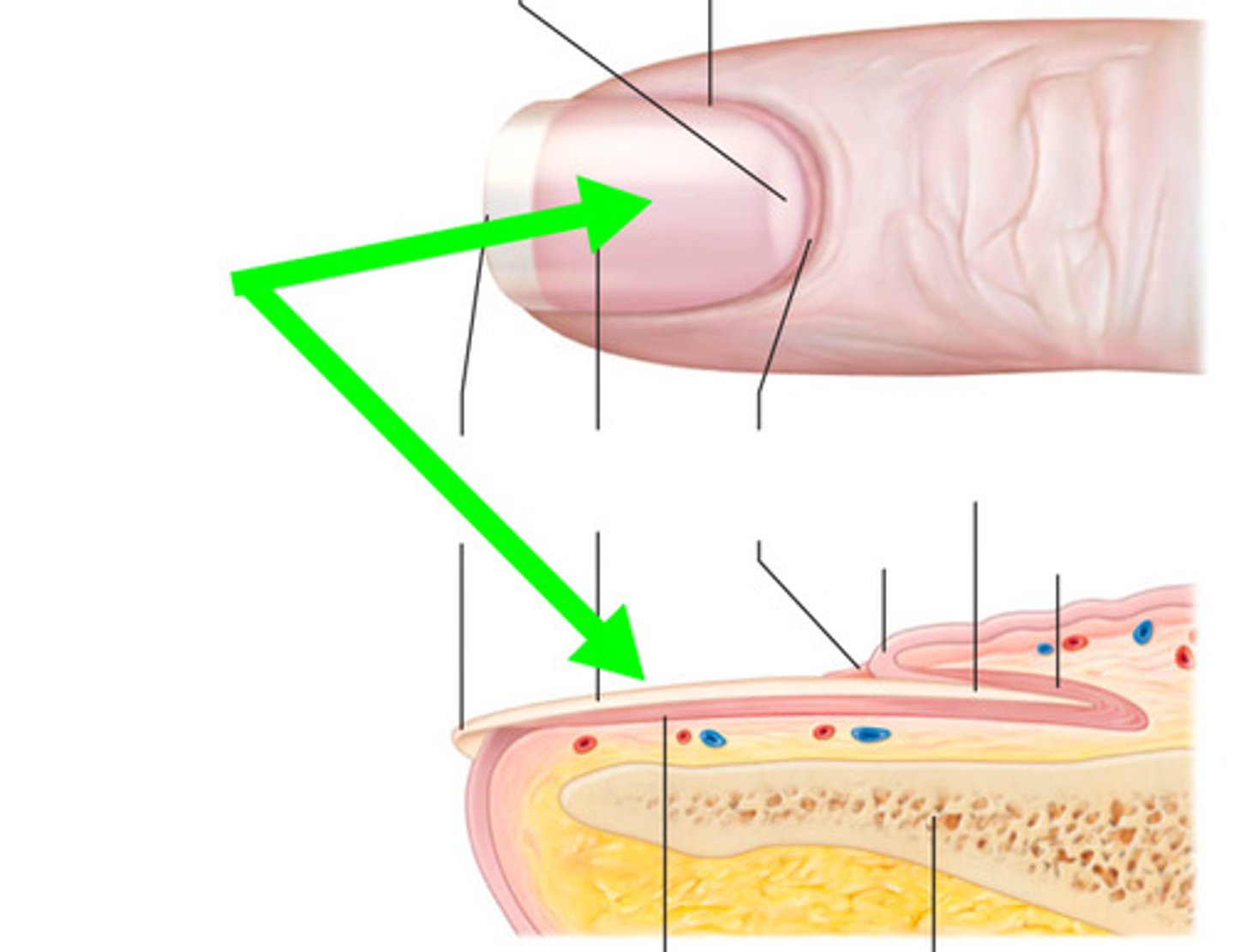
lunula
The half-moon-shaped, whitish area at the base of a nail
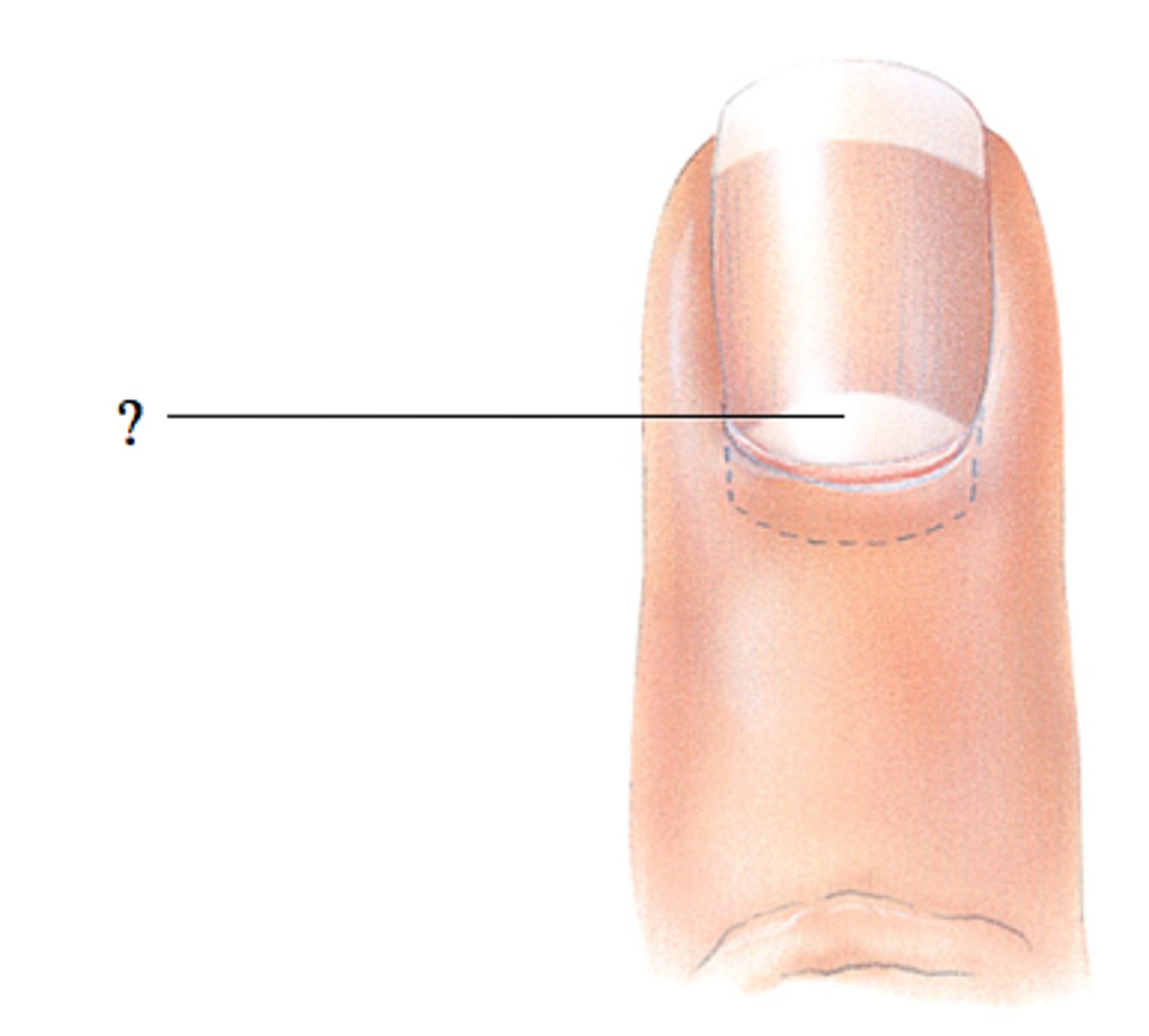
nail matrix
the part of the nail beneath the body and root from which the nail is produced
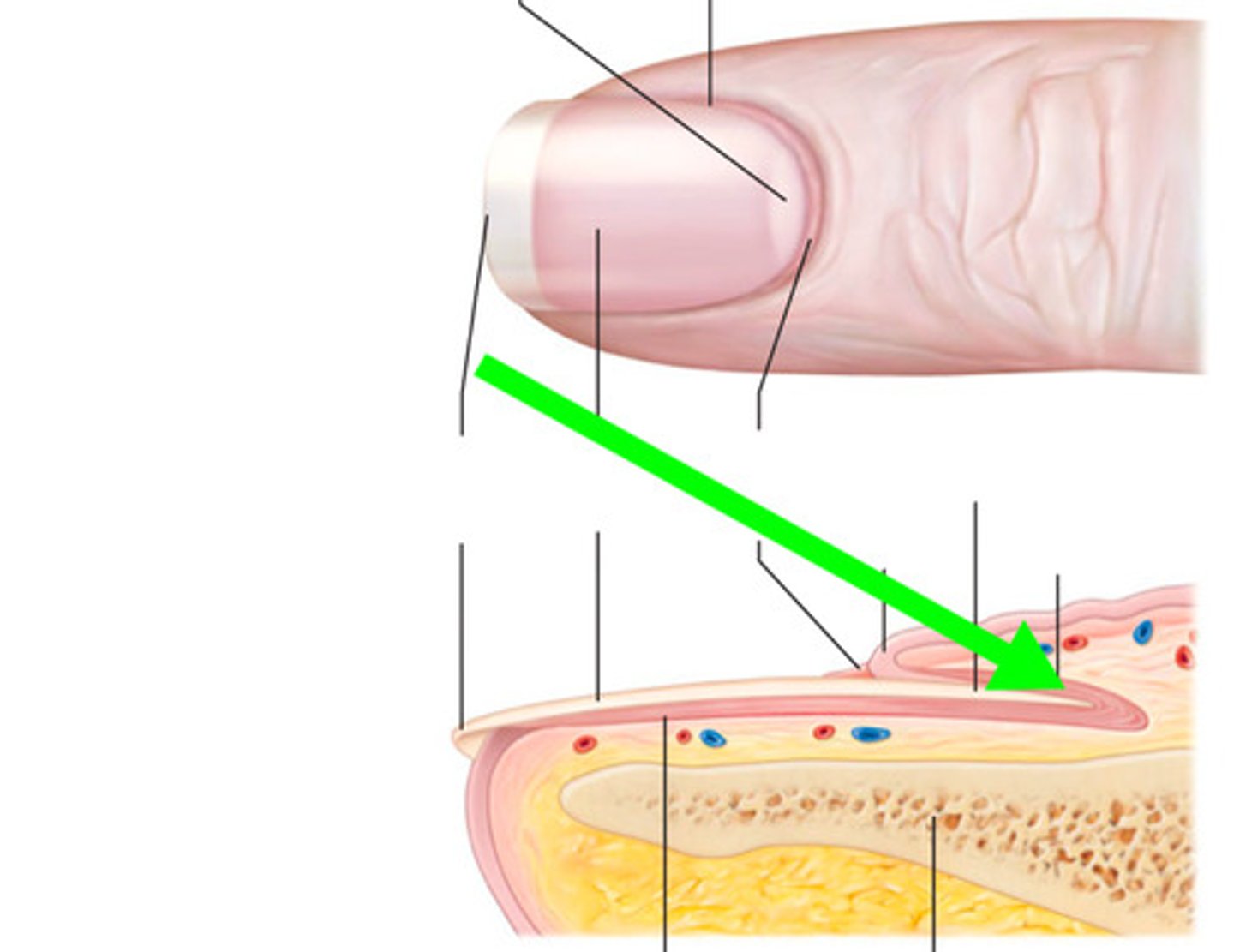
Eponychium
cuticle
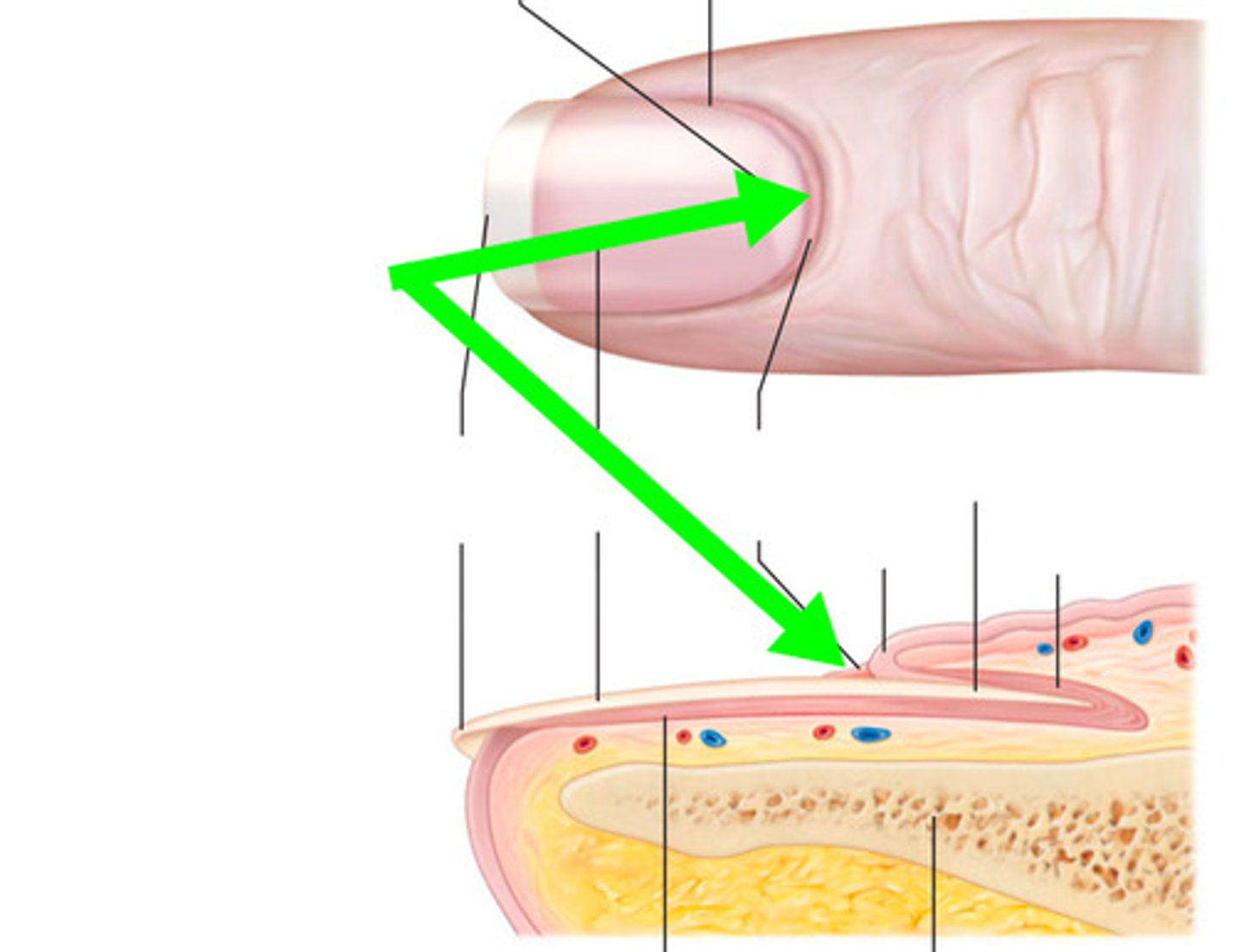
Hyponychium
Skin between the free edge and fingertip of the natural nail
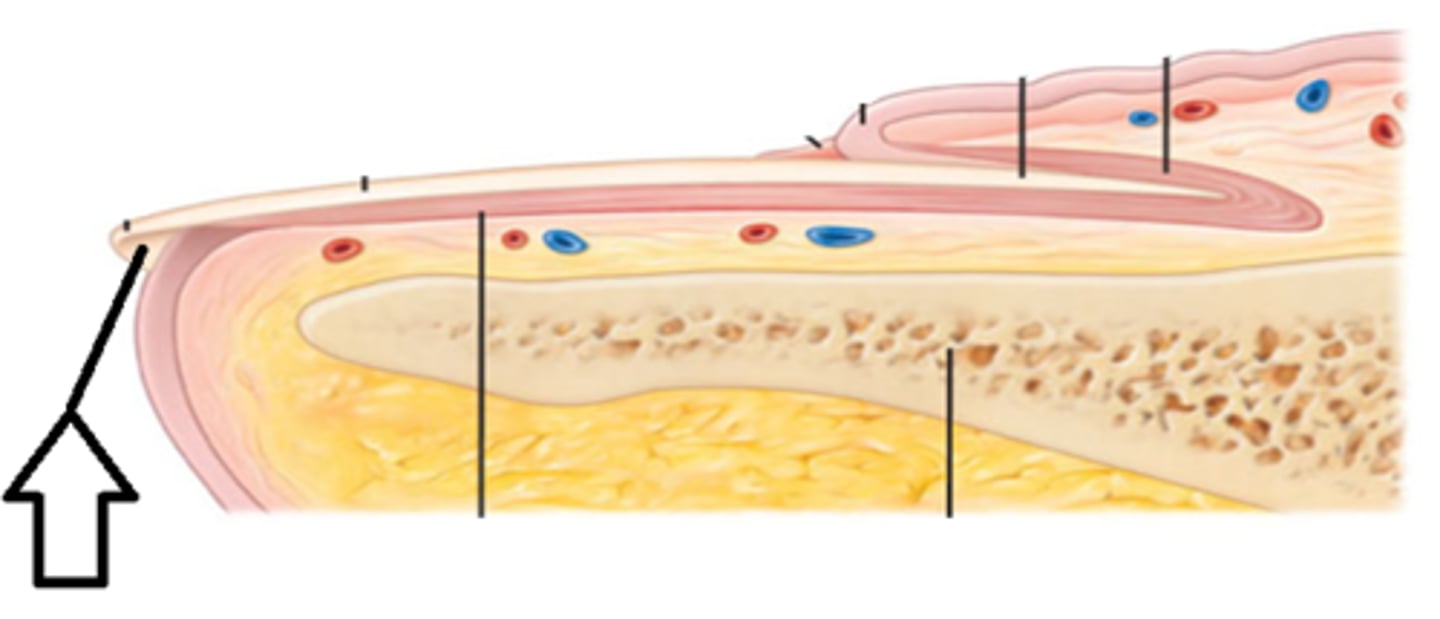
nail bed
skin underlying the nail plate (top layer of epithelia tissue)
Sebaceous (oil) glands
-Produce sebum to keep skin and hair soft, and prevent bacteria from growing on the skin
- prevent H20 loss
- anti bacateria
- holocrine secretion
merocrine sweat glands
- secrete a watery fluid directly onto the surface of the skin
- most common
- thermo regulation
apocrine sweat glands
- produce true sweat plus fatty substances and proteins; - found in the axillary (armpit) and anogenital areas of the body
sudoriferous glands
sweat glands
temperature control of body
negative feedback
burn
arrhythmia
first degree burn
epidermis
second degree burn
epidermis and papillary layer of dermis
third degree burn
epidermis, papillary and reticular dermis, and can be hypodermis is serve
rule of 9's
Head and neck = 9%,
Chest and upper back = 9% each
Arm = 9% each
Abdomen and lower back = 9 % each
Genital area - 1%
Leg - 18% each
pressure ulcers (1)
epidermis
pressure ulcers (2)
epidermis and dermis
pressure ulcers (3)
epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis
pressure ulcers (4)
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis, muscle, bone, superficial fascia
what does sebaceous glands cause?
acne
- whitehead (no opening)
- blackhead (opening to outside)
- papule (buildup)
- pustule (even more)
- cyst/nodule (goes down into bottom of follicle)
psoriasis
hyperactive disease (increased division in keratinocytes)
warts
hyperplasia and metaplasia
- can cause HPV infected cells
age
- fewer melanocytes
- drier epidermis (decrease in sebum)
- thinning of epidermis (ulcers)
- thinning of dermis (ulcers)
- diminished immune response (langerhan cells)
- decreased perspiration (sweat glands on/off)
- reduced blood supply
- fewer active follicles (less anagen)
- slower skin repair
- altered hair and fat distribution
eleidin
clear protein-bound lipid found in the stratum lucidum that is derived from keratohyalin and helps to prevent water loss (produce color)
keratohyalin
granulated protein found in the stratum granulosum
hair cuticle
Outermost layer of hair; consisting of a single, overlapping layer of transparent, scale-like cells that look like shingles on a roof.
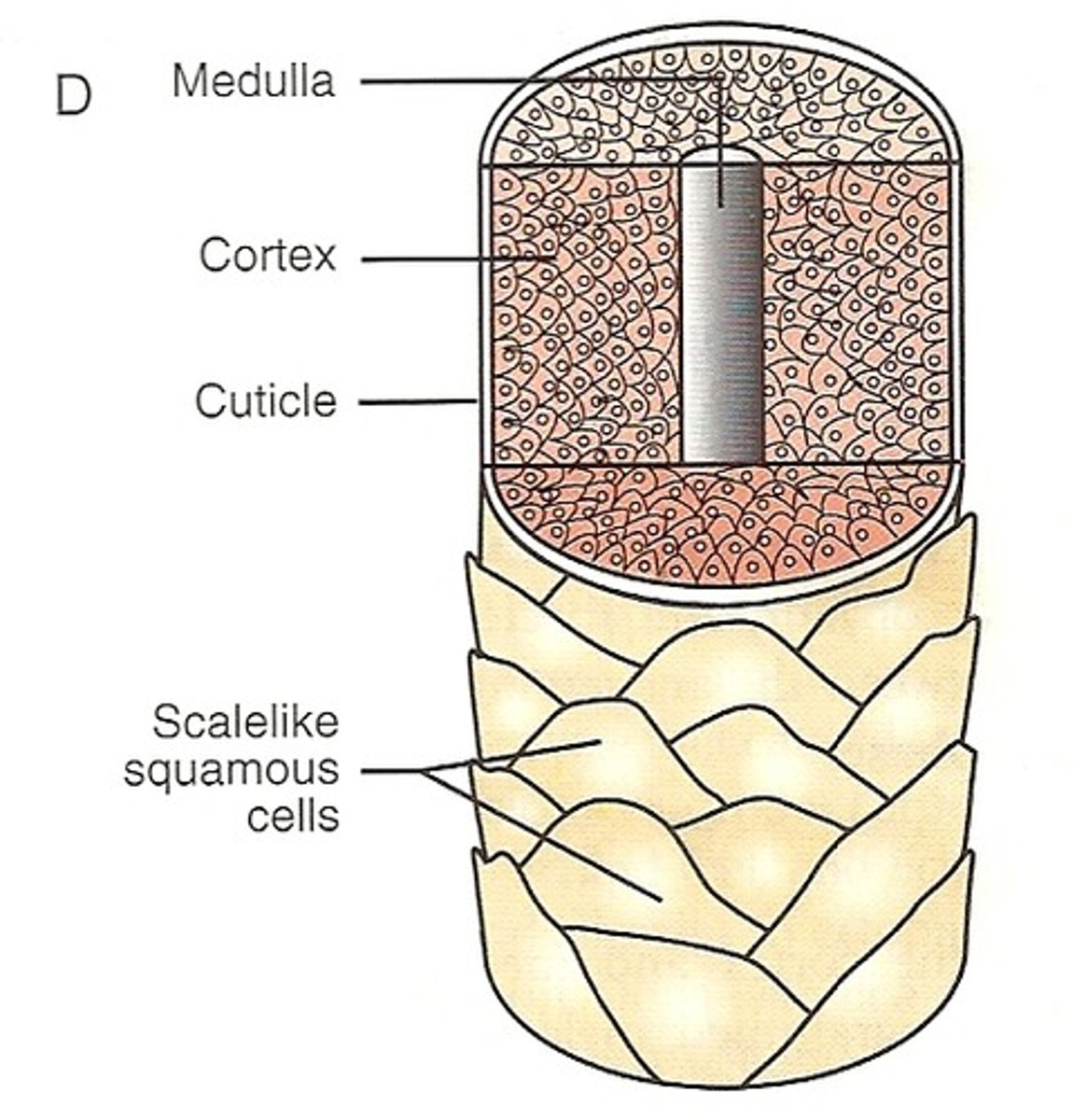
hair cortex
Middle, thickest portion of a hair shaft
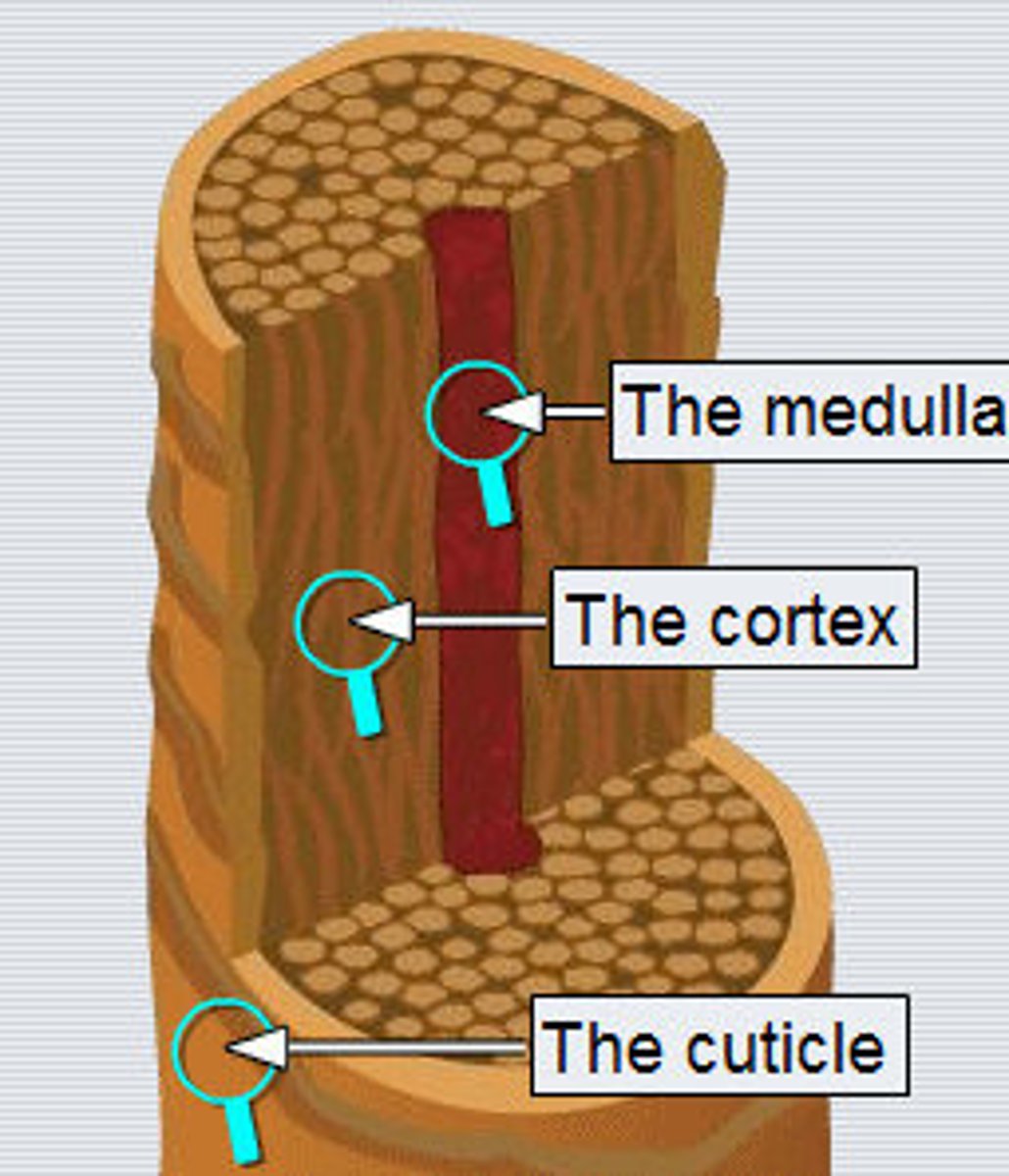
hair medulla
innermost portion of a hair shaft
anagen
The period of active growth
catagen
The period of break down and change of hair growth
telogen
Resting phase of hair growth