ORAL PATH EXAM 1 LECTURE MATERIAL
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
leukoplakia, tabacco pouch keratosis, oral submucous fibrosis, actinic cheilosis
premalignant white lesions
michels
what is the solution that is used for DIF
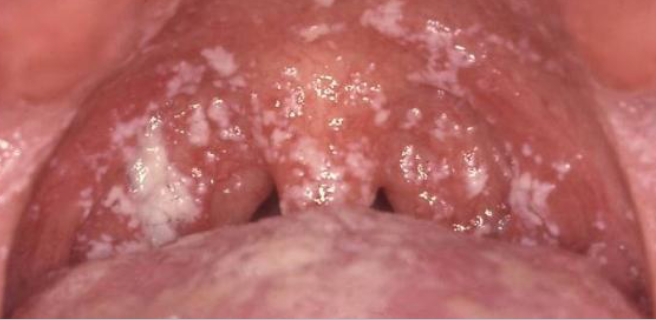
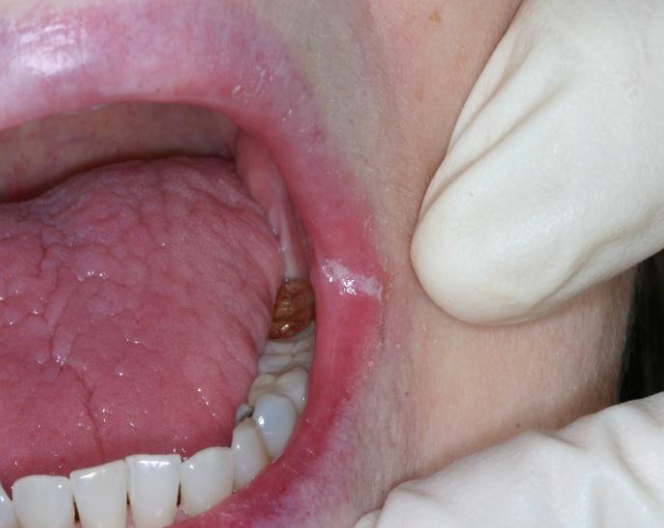
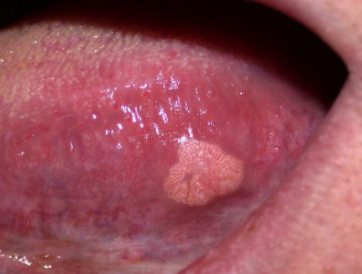
pseudomembranous candidiasis
pt presents with metallic taste and burning sensation, white plaque that can be wiped off
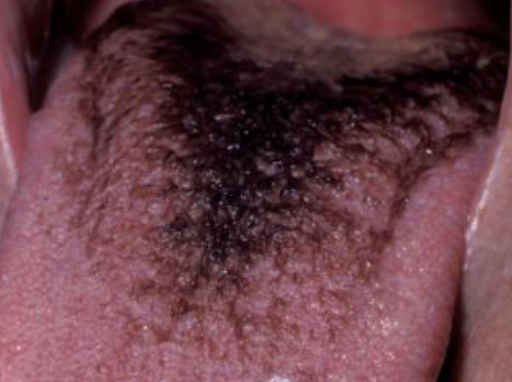
white coated/hairy tongue
white plaque on tongue that can be wiped off, due to imbalance in oral environment
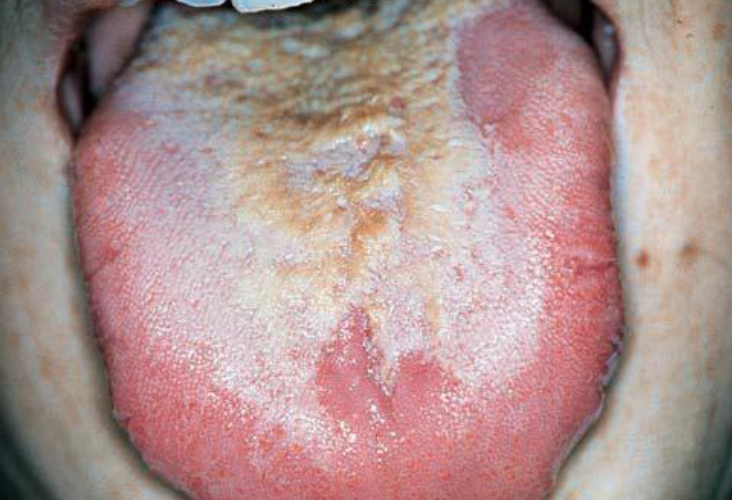
chemical burn
necrotic pseudomembrane that can be scraped off, due to chemical sensitivity
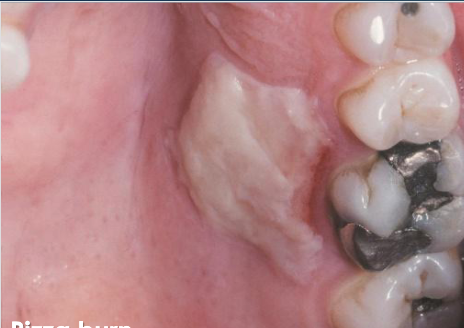
thermal burn
due to contact with hot food/beverage
immunosuppression can cause candida
which of the following is TRUE?
causes complete loss of taste
which statement about candidiasis is FALSE?

white lesions that do not rub off
what do the following have in common:
angular chilitis, lichen planus, linea alba, leukoedema, hairy leukoplakia, white sponge nevus, chewing trauma
angular cheilitis
candidiasis infecttion at angle of mouth that does not rub off
antifungal (nystain)
treatment for angular cheilitis
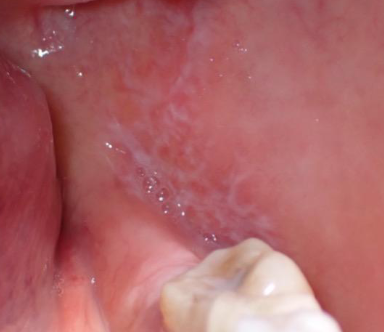
reticular lichen planus
white lacey striations (wickham striae)
topical/systemic steroids if symptomatic
treatment for lichen planus
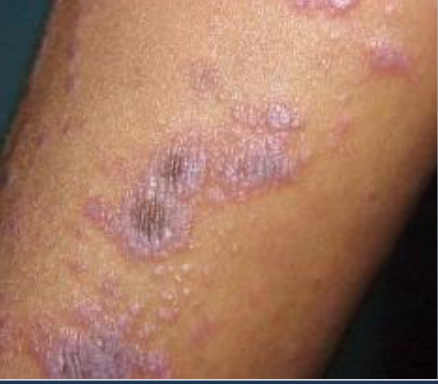
lichen planus
what are these purple puritis, polygonal papules
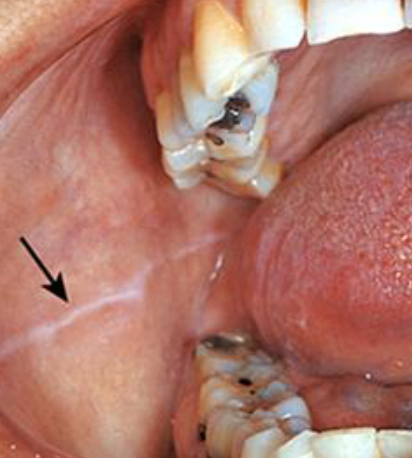
linea alba
white lane prominent if patients with clenching/bruxing
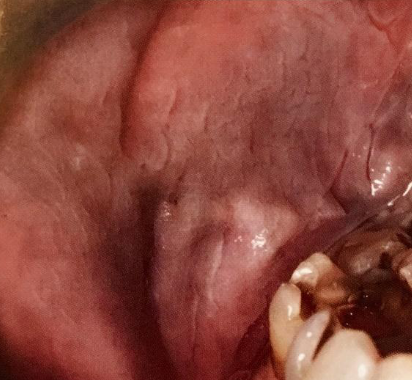
leukoedema
generalized gray-white film, common in AFRICAN AMERICAN individuals, becomes less prominent when mucosa is stretched
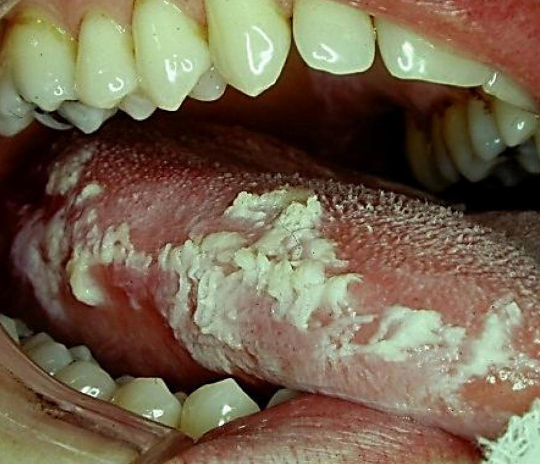
hairy leukoplakia
patient presents with white lesion on tongue, Hx of HIV/AIDs
EBV
which organism is associated with HAIRY LEUKOPLAKIA
white sponge nevus/ cannon disease
asymptomatic white corrugated keratotic surface on BUCCAL mucosa present since CHILDHOOD
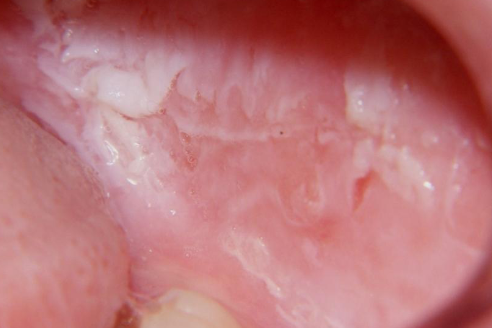
autosomal dominant
inheritance of white sponge nevus
chewing trauma
irregular ragged surface or corrugate white lesion most frequently of buccal mucosa
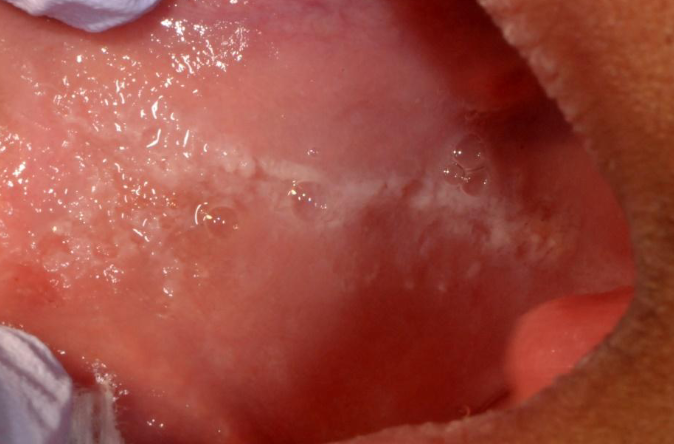
white sponge nevus can disappear when stretching the cheek
which of the following is FALSE

leukoplakia
PREMALIGNANT white lesion that cannot be wiped off
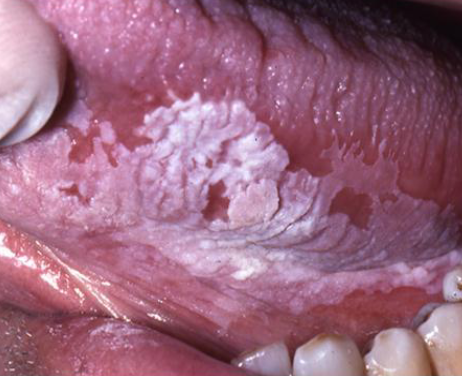
floor of mouth
which site has the highest risk of cancer?
smokeless tobacco keratosis
precancerous white lesion due to chewing tobacco
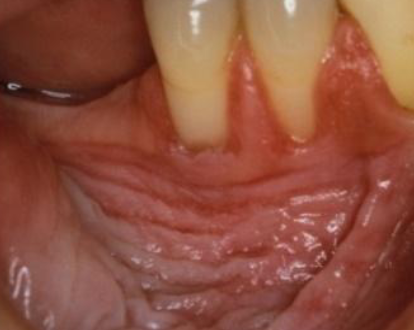
oral submucous fribrosis
chroni, progressive scarring due to BETAL QUID
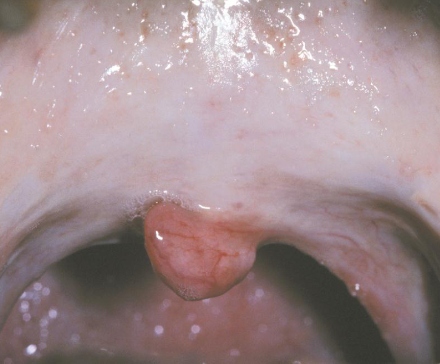
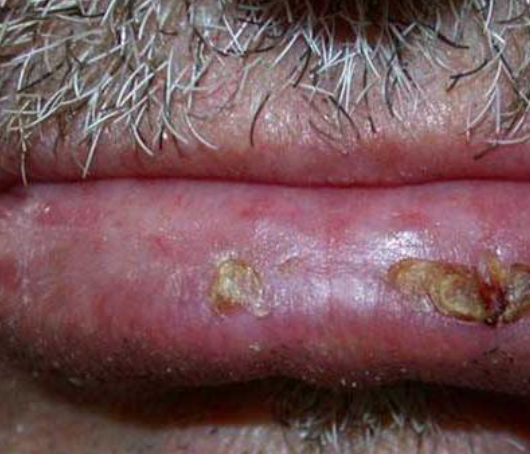
actinic cheilosis
premalignant lesion on lip due to UV light exposure
leukoplakia cannot be rubbed off
which of the following is TRUE

erosive lichen planus
immune mediated disease causing ulcerations and erythema, PAINFUL
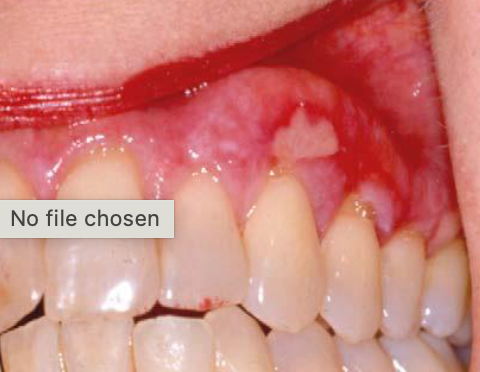
lichenoid mucositis
allergic/sensitivity reaction due to products with flavoring agents with prolonged/frequent contact
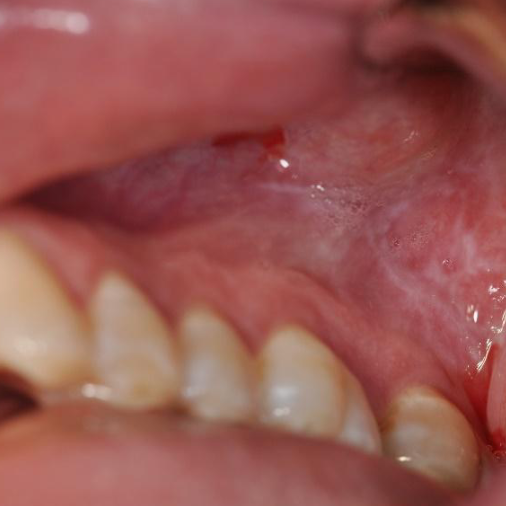
lupus cheilitis
lesion on vermillion zone, associated with autoimmune condition with butterfly rash
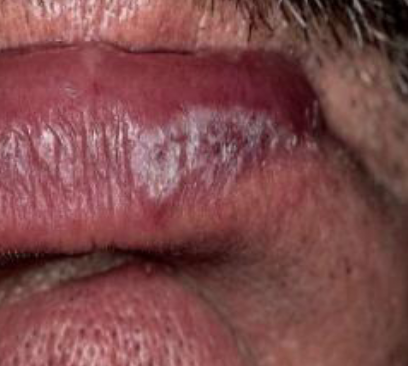
graft versus host disease
lesion with lichenoid features, occurs after transplant
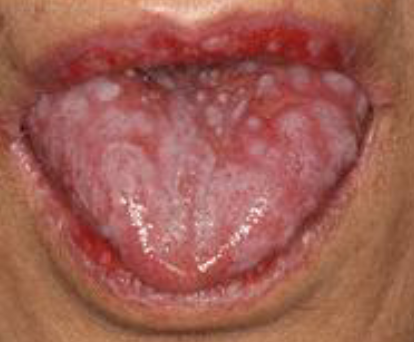
geographic tongue/erythema migrans(mucosa/palate)
harmless, non-contagious inflammatory condition causing smooth, red, map-like patches with white borders on the tongue's surface or buccal mucosa/palate
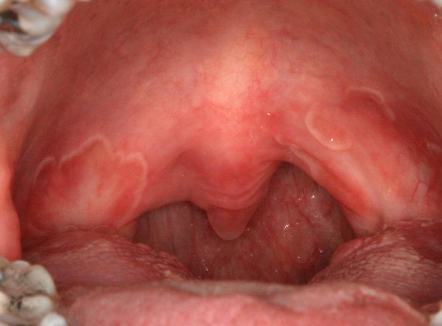
nicotine stomatitis
elevated papules with red central dots due to heat from smoking
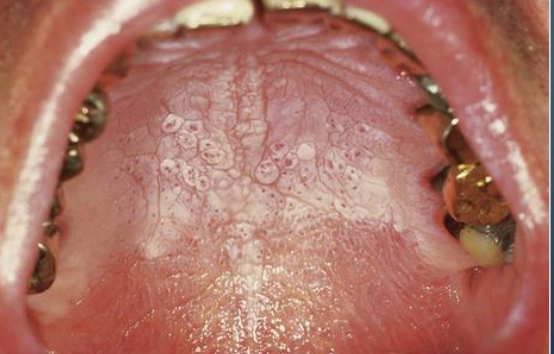
false
T/F nicotine stomatitis is precancerous
erythroleukoplakia
premalignant, red/white patches that show dysplasia on biopsy
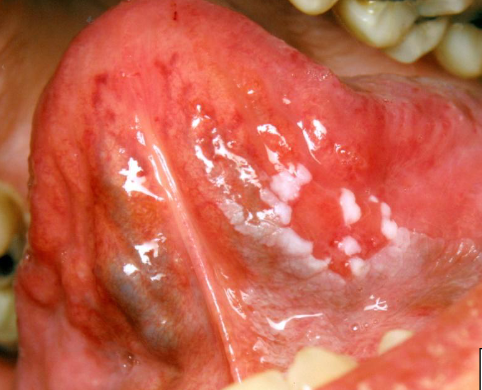
proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
which oral lesion has the HIGHEST risk of oral cancer
1,2,3,4
order the following from lowest to highest malignant potential: (order the numbers)
smooth, thin leukoplakia
granular leukoplakia
erythroleukoplakia
proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
mild dysplasia
atypical morphology in bottom 1/3 of epithelium
moderate dysplasia
atypical morphology up to mid 2/3 of epithelium
servere dysplasia
atypical morphology above mid point to entire thickness of epithelium
carcinoma in situ
atypical morphology involving entire thickness of epithelium
geographic tongue
all of the following are indications for incisional biopsy EXCEPT:

leukoplakia
which of the following does not exhibit lichenoid mucositis

clindamycin
all of the following are prescribed to manage lichen planus EXCEPT:

fordyce granules
clusters of ectopic sebaceous glands, requires no treatment
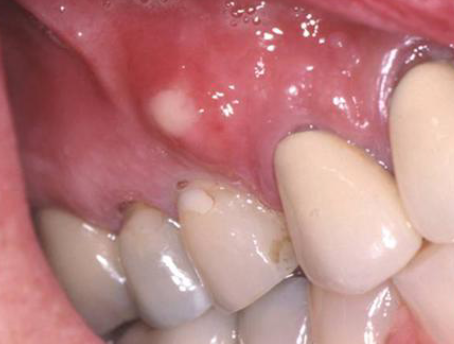
periapical abcess
active infection that presents with pain on percussion of tooth
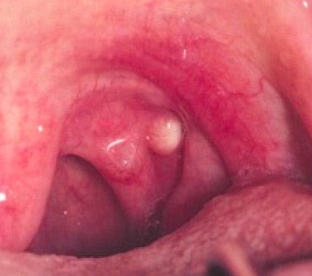
oral lymphoepithelial cyst
smooth no ulcerated, white/yellow lesion that develops in lymphoid tissue on FOM, tonsil or netral tongue
lymphoid hyperplasia
enlargement of lymphoid tissue that appears yellowish
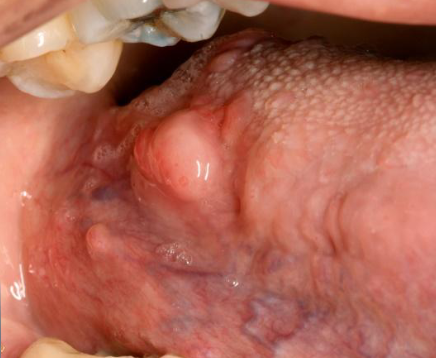
lipoma
soft, movable, yellowish, smooth sessile mass of buccal mucosa
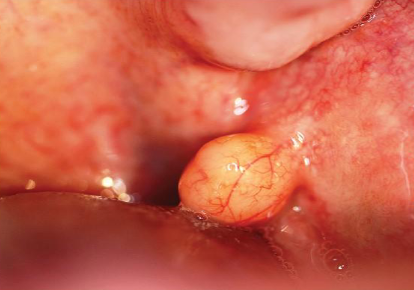
lipoma
most common mesenchymal tumor in the body
sialolithiasis
yellowish calcified structures that may appear on radiograph, causes swelling before or during eating
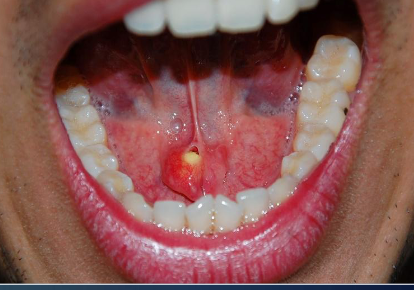
submandibular
most common gland for SIALOLITHIASIS
granular cell tumor
benign pink/yellow mass with granular surface, pseudoepitheliomatous may be mistaken for SCC
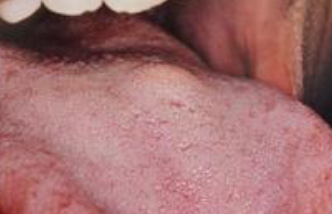
verruciform xanthoma
hyperplastic spithelium with white/yellow/red papillary rough surface
pyostomatitis vegetans
yellowish, elevated pustules with erythematous oral mucosa, “snail track”
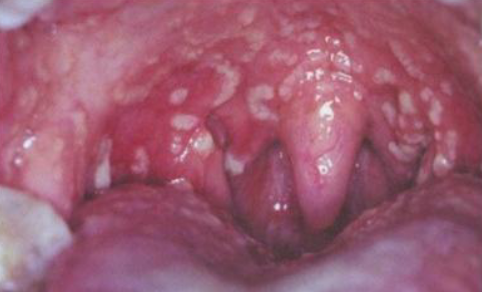
pyostomatitis vegetans
oral lesion associated with ULCERATIVE collitis or CROHNS
periapical abcess is an active infection
which of the following is CORRECT

frictional keratosis
which is NOT a YELLOW lesion:
abcess
oral lymphoepithelial cyst
frictional keratosis
verruciform xanthoma
fibroma
small, painless, elevated lesion on lateral tongue, with rough papillary surface. which is NOT in the differential diagnosis:
squamous papilloma
verruciform xanthoma
fibroma
granular cell tumor
oral submucous fibrosis
irregular ragged white lesion on buccal mucosa. Which is NOT in differrential diagnosis:
white sponge nevus
chewing trauma
frictional keratosis
oral submucous fibrosis
white sponge nevus (only on buccal)
single corrugated white lesion on lateral tongue. which is NOT in differential diagnosis:
leukoplakia
white sponge nevus
hairy leukoplakia
chewing trauma
leukoedema
which of the following does not have SKIN LESIONS:
geographic tongue
lichen planus
systemic lupus
leukoedema
anemia
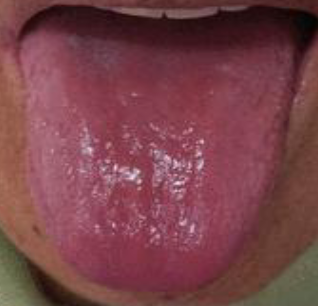
smooth red tongue accompanied by tiredness, headache, lightheadedness
acute atrophic candidiasis
candidiasis causing burning painful, red lesions after course of antibiotics
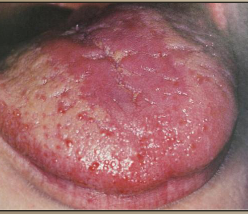
denture stomatitis
candidiasis causing localized erethema in denture areas
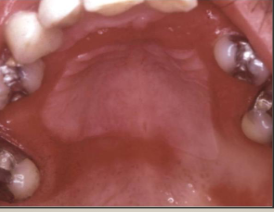
median rhomboid glossitis
candidiasis causing loss of filliform papilla, anterior to circumcallate papilla
nystatin, clotrimazole, diflucan (anttifungals)
treatments for candidiasis
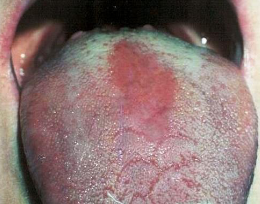
erythroplakia
pre malignant red patch that cannot be diagnosed as any other condition
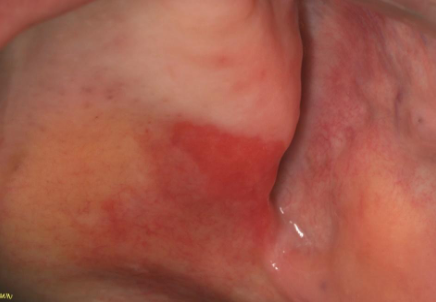
buccal mucosa and gingiva
most common locations for EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS
hemangioma
red/blue, firm, blanches with diascopy
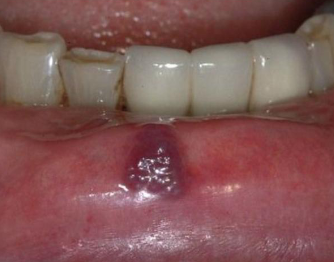
hemangioma
most common tumor of infancy
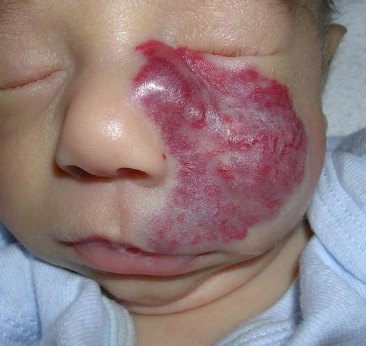
sturge weber angiomatosis
port wine stain, unilateral vascular involvement, gingival hyperplasia, tramline calcifications
false
T/F sturge weber is a hereditary condition
radiation mucositis
localized ulceration following cancer treatment
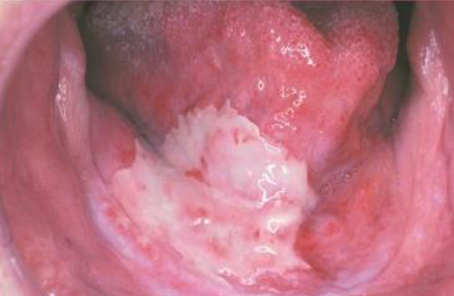
chemotherapy mucositis
generalized ulceration following cancer treatment
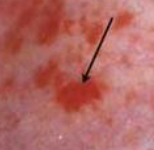
petechiae
minute hemorrahge below ski, small red dots

pupura
slighlty larger than petechiae
ecchymosis
accumulation of blood 2cm> below skin
hematoma
accumulation of blood within tissue producing mass
telangiectasia
dialated small blood vessels near skin surface
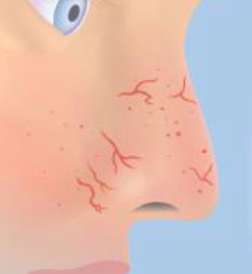
hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT)
autosominal dominant, telangietasia on lips tongue buccal mucosa hands, epitaxis (nosebleed), blanch
crest syndrome
calcinosis, raynauds, esophgeal dysfunction, sclerodactyly, tenlangiectasia
chewing trauma
all of the following could cause erythematous tongue with discomfort EXCEPT:
candidiasis
anemia
chewing trauma
erosive lichen planus
anemia
small red dots on palate could be due to all of the following EXCEPT:
coughing
infectious mononucleosis
crest syndrome
anemia
varicose vein (varix)
abnormally dilated and torturoud veins in OLDER adults, sublingual most common
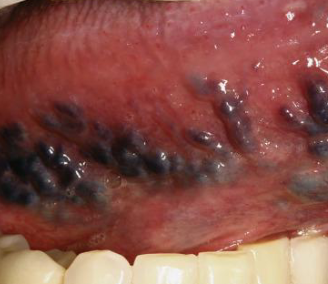
phlebolith
calcified varicose vein
hemangioma
benign tumor of blood vessels
mucocele
most common on lower lip due to trauma of minor salivary gland
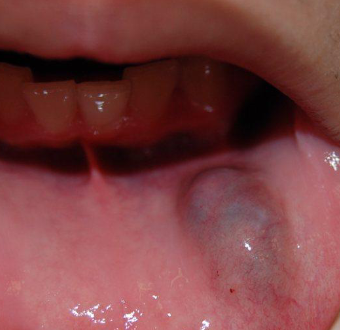
ranula
large mass in floor of mouth from sublingual gland
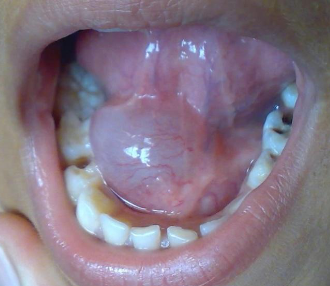
surgical removal, marsuopialization
treatment forr RANULA
upper lip
most common location for salivary duct cyst
epithelial lining
how is a salivary duct cyst different that mucocele
mucoepidermoid carcinoma
salivary gland neoplasm
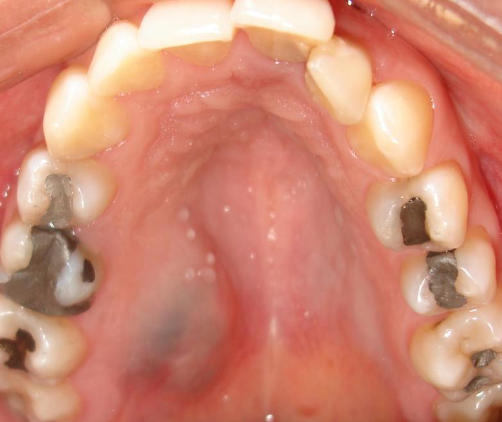
eruption cyst
Children, overlying the crown of erupting deciduous or permanent tooth, subsides whentooth erupts
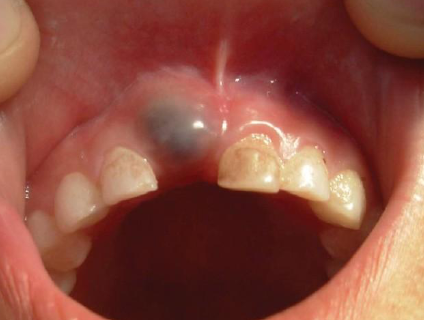
gingival cyst
Adults, most common location is between mandibular canine & PM, surgical excision
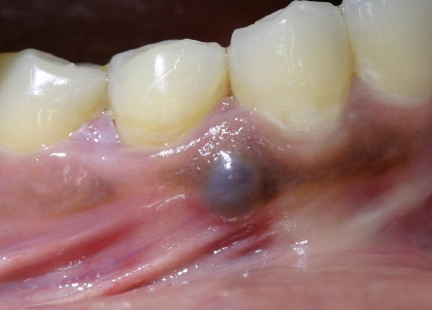
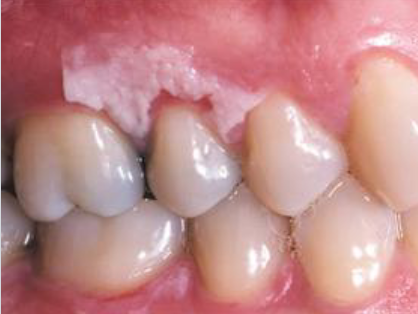
amalgam tattoo
macules or (rarely) as raised lesions which are blue, black, or gray in color, ill defined
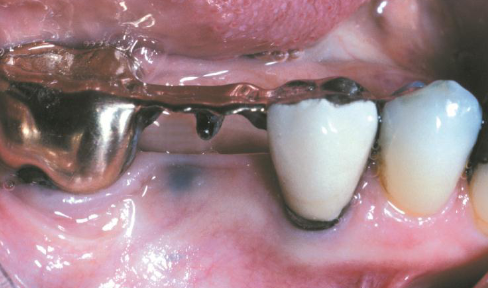
kaposi sarcoma
AIDS related vascular malignant neoplasm
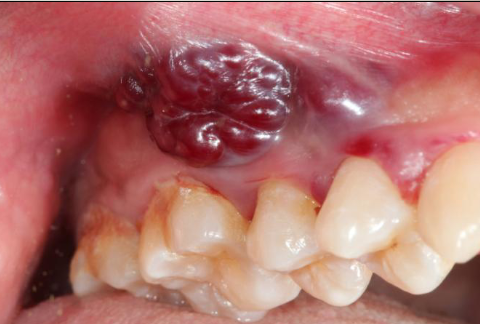
mucoepidermoid carcinoma
which of the following exhibits a large bluish mass on palate:
blue nevue
amalgam tattoo
mucocele
mucoepidermoid carcinoma
hairy tongue
brown/black excess keratin on surface of filiform papillae