structure and function (gas exchange in humans)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
5 features of exchange surfaces and what they do
many molecules can diffuse across at the same time → faster diffusion, more space for diffusion
very thin → short diffusion distance → faster diffusion
permeable → allows substances to cross exchange surface
(in animals) - good blood supply → maintains steep concentration gradient
good blood supply of external media → maintains steep concentration gradient

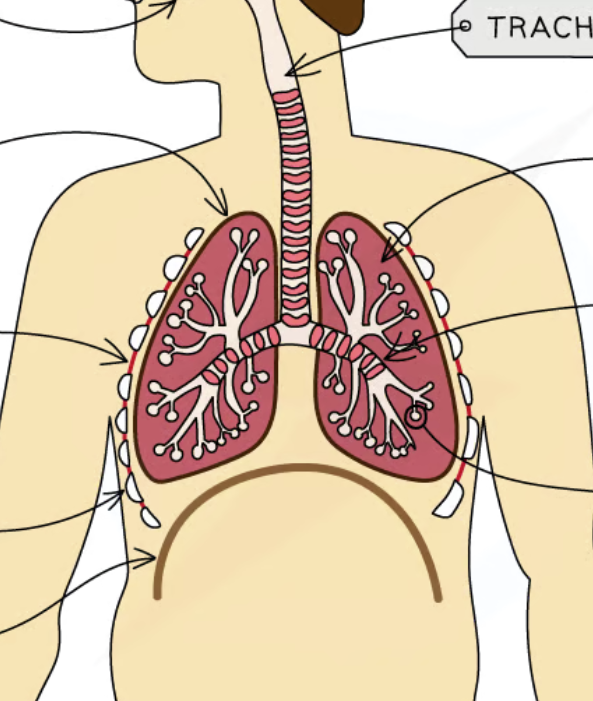
label body diagram
*where is nasal cavity, pleural cavity + fluid inside, bronchiole
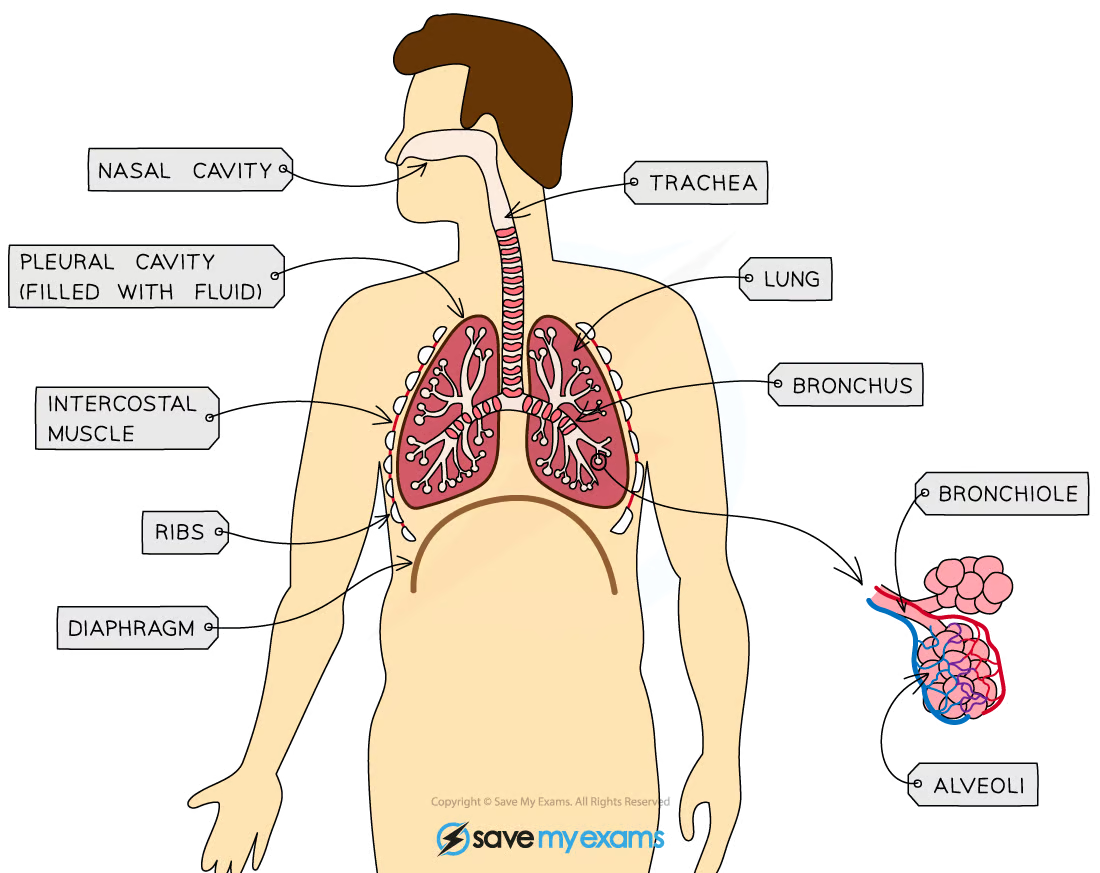
definition and why | |
|---|---|
ribs | |
intercostal muscles | |
diaphragm | |
trachea | |
larynx | |
bronchi | |
bronchioles | |
alveoli | |
pleural cavity | and why its there |
definition | |
ribs | bones that protect internal organs like the lungs/heart |
intercostal muscles | muscles between the ribs that control their movement (for inhalation/exhalation) |
diaphragm | sheet of connective tissue and muscle at the bottom of the thorax to help change volume of thorax to allow for inhalation/exhalation (is a muscle) |
trachea | windpipe that connects mouth/nose to the lungs |
larynx | voice box, air passes through and makes a sound |
bronchi | 2 tubes branching off trachea into lungs |
bronchioles | many smaller tubes branching off bronchi to connect to alveoli |
alveoli | tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs |
pleural cavity | fluid-filled space between pleural membranes - reduces friction so lungs can move freely |
what are the cilia and mucus
passages down to lungs have ciliated epithelial cells - ells have tiny hairs that beat and push mucus up the passages towards the nose and throat where it can be removed
The mucus is made by goblet cells
mucus traps particles, pathogens, and dust and prevents them from getting into the lungs and damaging the cells there
muscles can only _____ on bones, not _____ on them
muscles can only pull on bones, not push on them
External intercostal muscles, pull the rib cage _____
Internal intercostal muscles pull the ribcage ______
External intercostal muscles, pull the ribcage UP
Internal intercostal muscles pull the ribcage DOWN
even simpler definition of diaphragm, without breathing
it separates the ___ cavity from the _______
domed thin sheet of muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdomen
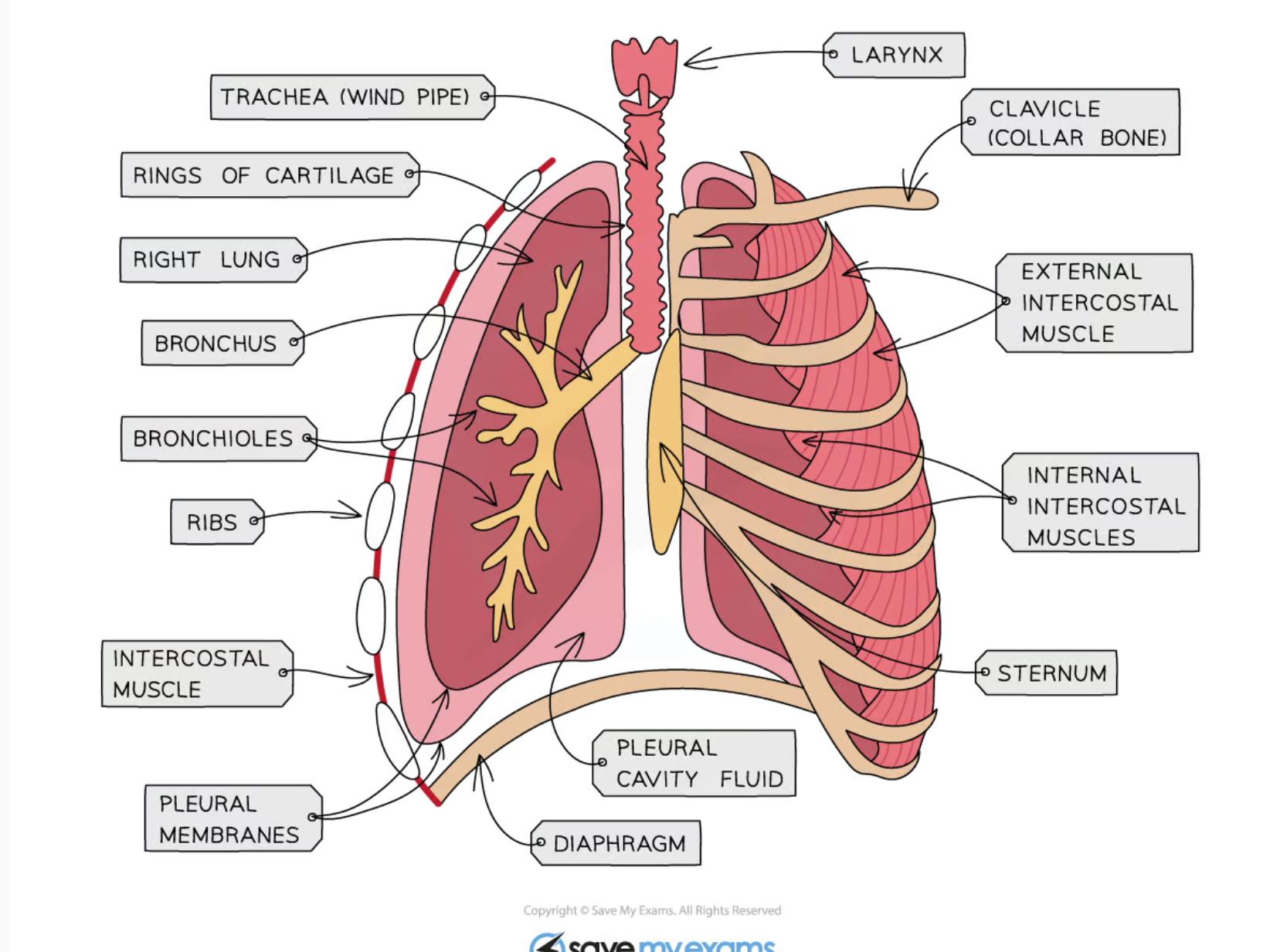
label lungs
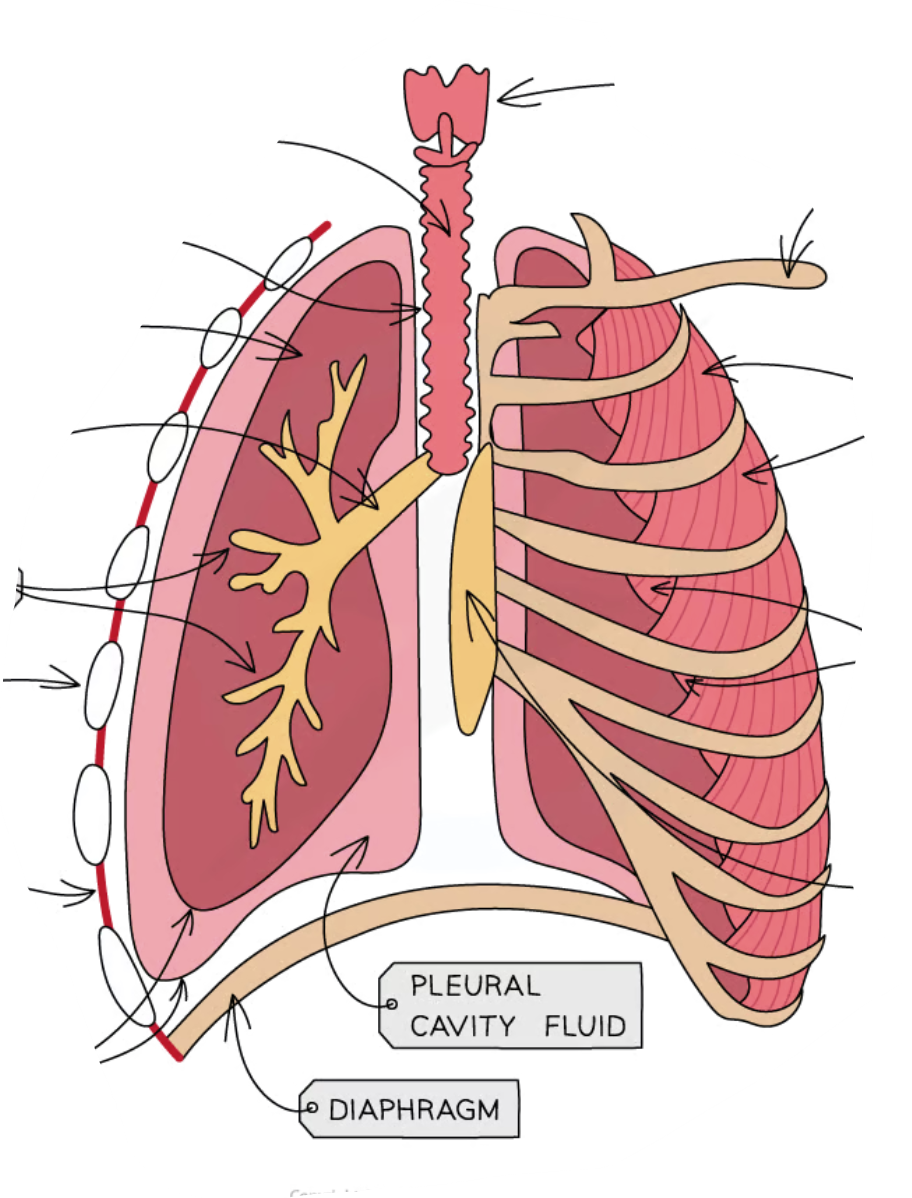
why does trachea have rings of cartillage
to prevent trachea from collapsing during inhalation
where are the internal vs external intercostal muscles
There are 2 sets of intercostal muscles: the external, on the outside of the rib cage, and the internal, on the inside of the rib cage
what is ventilation
the process of moving air into and out of the lungs
what happens during inhalation (5)
external intercostal muscles and diaphragm contract.
external intercostal muscles pull ribs up and out, diaphragm flattens.
volume of thorax increases
air pressure decreases inside lungs
air is drawn into lungs
why is inhalation an ____ process?
active process
involves muscle contractions, so energy is required
describe the process of exhalation (5)
diaphragm relaxes (upwards) into original domed shape
external intercostal muscles relax - ribs drop down and in
volume of thorax decreases
increased air pressure inside lungs
air is forced out
during regular breathing, exhalation is a _____ process. why?
passive process
external intercostal muscles relax, and diaphragm relaxes, returns to domed shape
when is exhalation not a passive process, why
during intense exercise, forceful/strong exhales
internal intercostal muscles contract, pull ribs down and inwards, forcing air out of the lungs. external intercostal muscles relax (antagonistic pair - work in different directions to each other))
volume increase = pressure _______
volume decrease = pressure ________
volume increase = pressure DECREASE
volume decrease = pressure INCREASE
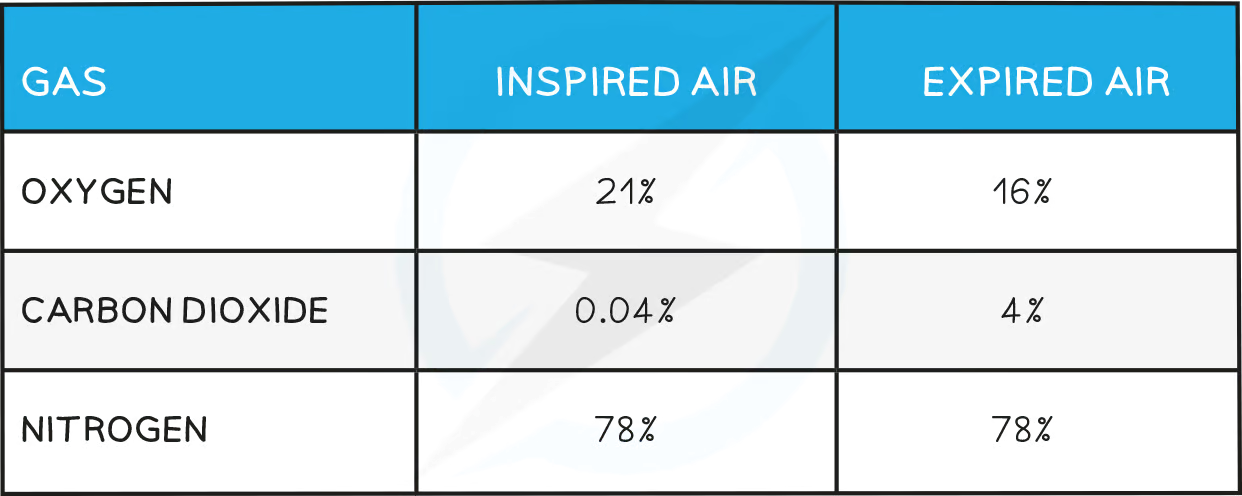
oxygen, co2, nitrogen in air vs what is exhaled
what that shows
don’t use nitrogen
produce co2
use oxygen (but not all)
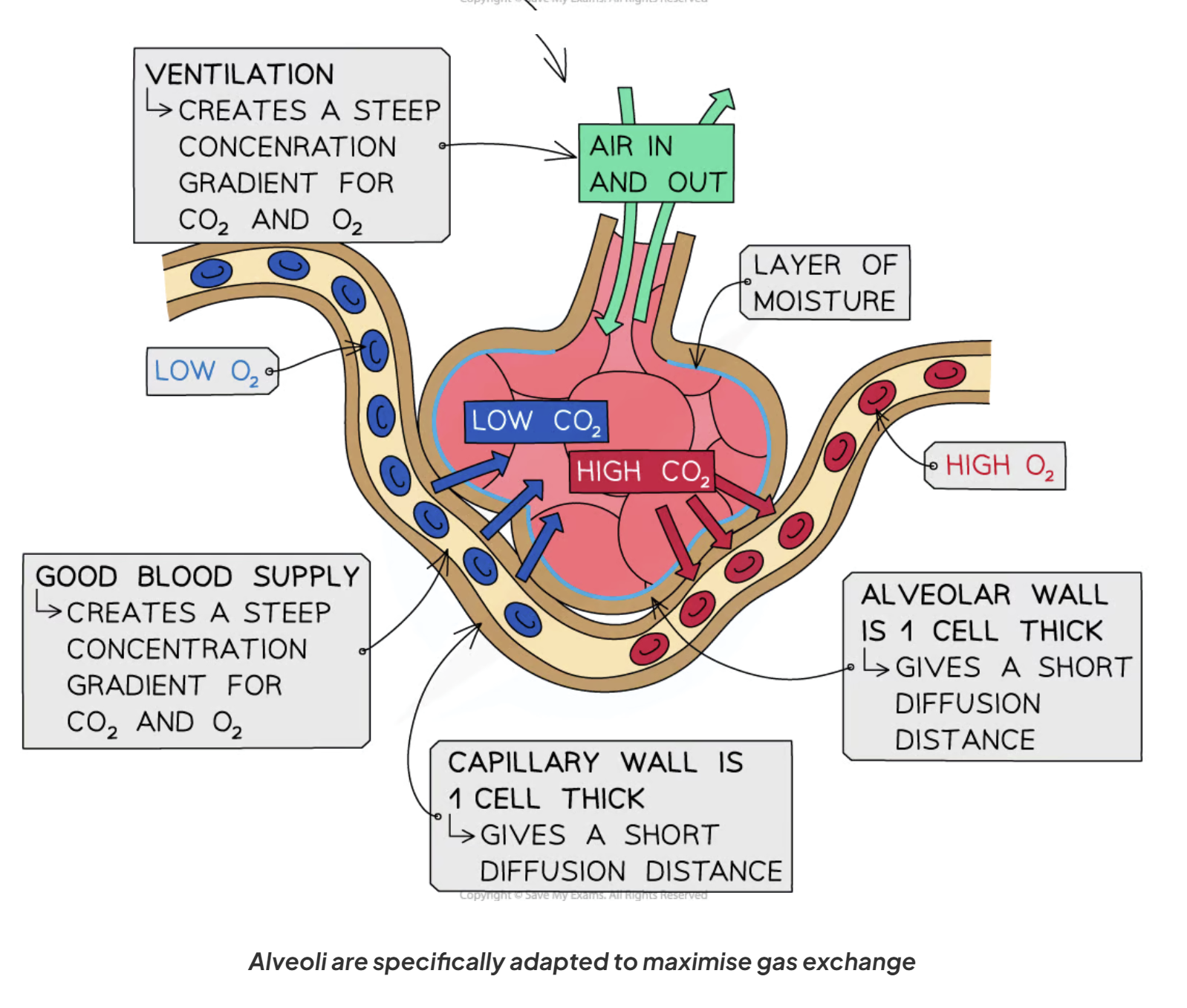
how are alveoli adapted for gas exchange (5)
think wet
Moist walls/layer of moisture - gases dissolve in the moisture helping them to pass across the gas exchange surface, faster diffusion.
many alveoli so a massive surface are for gas exchange
alveoli walls are one cell thick - short diffusion distance, faster diffusion
good supply of external medium (of air via ventilation - inhalation/exhalation)- so steep concentration gradient maintained
good blood supply - steep concentration gradient maintained
3 specific diseases smoking causes
COPD - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
coronary heart disease
lung cancer - increased risk
3 main bad chemicals from cigarettes
Tar - carcinogen (a substance that causes cancer)
Nicotine - an addictive substance which also narrows blood vessels
Carbon monoxide - reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood
why is nicotine bad
addictive
narrows blood vessels → increased blood pressure
also increases heart rate
Both of these effects can cause blood clots to form in the arteries leading to heart attack or stroke
why is carbon monoxide bad (3)
binds to ____
puts strain on ____ as ______ ______ and ____ need to increase to get the same amount of _______ into the blood
also puts strain on ____ ___ to pump the blood ______ around the body. This increases the risk of _____ and _______
binds irreversibly to haemoglobin - reduces capacity of blood to carry oxygen
strain on the breathing system as breathing frequency and depth need to increase in order to get the same amount of oxygen into the blood
also puts strain on circulatory system to pump the blood faster around the body. This increases the risk of CHD and strokes
two diseases basically caused by tar
Chronic bronchitis is caused by tar which stimulates goblet cells and mucus glands to enlarge, producing more mucus
It destroys cilia and mucus (containing dirt, bacteria and viruses) builds up blocking the smallest bronchioles and leading to infections
A smoker's cough is the attempt to move the mucus
effect of Exercise on Breathing rate
CORMMS
Change - change whether the student has exercised or not
Organisms - same age, gender, size and general fitness
Repeat - repeat the investigation several times to ensure our results are reliable
Measurement 1 - measure the change in breathing rate
Measurement 2 - ...immediately after exercise and each minute for the subsequent 5 minutes
Same - type of exercise carried out, temperature of the environment, food intake of the students prior to the investigation
effect of exercise on breathing results and WHY
what about after exercise has finished, what happens to breathing rate, WHY
Frequency of breathing increases when exercising
This is because muscles are working harder and aerobically respiring more and they need more oxygen to be delivered to them (and carbon dioxide removed) to keep up with the energy demand
If they cannot meet the energy demand they will also respire anaerobically, producing lactic acid
After exercise has finished, the breathing rate remained elevated for a period of time
This is because the lactic acid that has built up in muscles needs to be removed as it lowers the pH of cells and can denature enzymes catalysing cell reactions
It can only be removed by combining it with oxygen - this is known as ‘repaying the oxygen debt’
This can be tested by seeing how long it takes after exercise for the breathing rate to return to normal
The longer it takes, the more lactic acid produced during exercise and the greater the oxygen debt that needs to be repaid