N209 - Male Genitourinary System
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Frequency, urgency, and nocturia
Dysuria
Hesitancy and straining
Urine color
Past genitourinary history
Penis—pain, lesion, discharge
Scrotum—self-care behaviors, lump
Sexual activity and contraceptive use
Sexually transmitted infection (STI) contact
What are related health hx questions to ask male patients?
5-6 times a day (vaires with fluid intake & individuals habits)
What is the average adult voids?
oliguria
diminshed voids (<400 mL/24 hours)
UTI
What does cloudy urine indicate?
hematuria
What is a danger sign in the urine that warrants further workup?
urge incontinence
= involuntary urine loss from overactive detrusor muscle in the bladder
stress incontinence
= involuntary urine loss with physical strain, sneezing or coughing caused by weakness of the pelvic floor
nocturnal enuresis
= involuntary urinating @ night after age 5 to 6 years
gloves
glass slide/materials for cytology
flashlight
What equipment is needed to examine the male genitalia?
standing with underwear down and appropriate draping
What position should the male be in for examination?
hairless, wrinkled and free of lesions
dorsal veins may be aparent
How should the skin on the penis normally look?
smooth and w/o lesions
have uncircumsized males move back the foreskin (should move easily)
some cheesy smegma may have collected underneath
make sure to slide the foreskin into it’s original position
How should the glans of the penis appear?
just above centrally
where is the urethral meatus positioned?
follows male developmental patterns (diamond) and course, curly
What is normal hair distribution?
no male pattern (diamond), lice or scabies
What might you see with abnormal hair distribution?
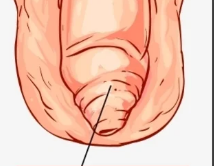
Phimosis
= narrowed opening of prepuce so the foreskin cannot retract
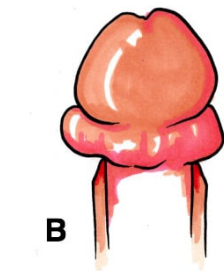
Paraphimosis
painful constriction of glans by retracted foreskin
medical emergency
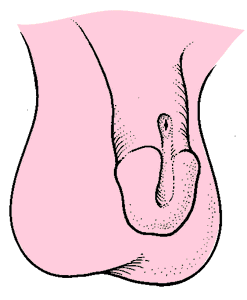
Epispadias
= abnormality where the meatus is located dorsal
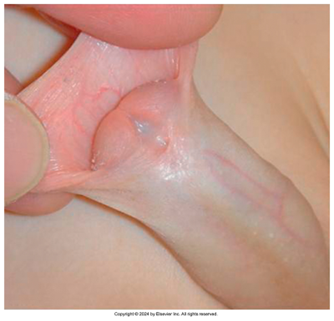
Hypospadias
= abnormality where the meatus is located ventrally (most common congenital disorder in baby boys)
meatus edge should appear pink, smooth & without discharge
When you compress the glans anteroposteriorly b/t your thumb & forefinger, what should you note?
b/t your thumb & 1st 2 fingers
feels smooth, semifirm, and nontender
How would you palpate the shaft? What should you feel?
asymmetrical
skin rugate (wrinkled)
darker in color
can be contracted or relaxed (depending on the temperature)
Have the male hold his penis out of the way (or do it yourself) and note size, symmetry and appearance, what is a normal finding?
left; right
The ______ scrotal half is usually lower than the _______ half.
sebaceous cysts
= yellowish, 1-cm nodules that are firm, nontender, and often multiple on the scrotal surface
contents move easily & there is slight tenderness to compression
testes are oval, firm, rubbery and equal
You palpate each scrotal half gently b/t your thumb and 1st 2 fingers. What are normal findings of the testes?
discrete, soft and smooth
What is a normal finding when palpating the epididymis?
epididymitis
= indurated, swollen and tender epididymis
severe pain relieved by elevation
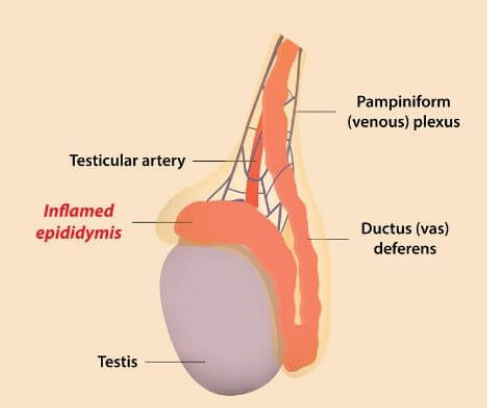
Cord is smooth and nontender
You palpate each spermatic cord b/t your thumb and forefinger along its length from the epididymis up to the external inguinal ring. What is a normal finding?
transillumination
= darkening the room & shining a strong light from behind the scrotal contents.
Solid tissue and blood do not transilluminate (hernia, epididymitis, or tumor)
Serous fluid transluminates and shows as a red glow (hydrocele or spermatocele)
What is an abnormal finding when transilluminating the testes?
hydrocele
= A condition where the scrotum is swollen due to fluid accumulation in the sheath which surrounds a testicle.
spermatocele
= painless fluid filled cyst in the epididymis
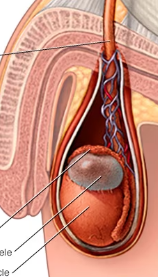
if you note a swelling or mass
When would you perform transillumination?
inspect the inguinal region for any bulges as a person stands and strains down
normally none is present
How would you inspect for a hernia? What should you see?
have the person shift their weight to the left side
How would you palpate the right side of the inguinal canal for a hernia?
herniating mass bumps your fingertip or pushes against the side of your finger
What is an abnormal finding when palpating the inguinal canal for hernias?
Nerve
Artery
Vein
Empty space
Lymphatics
What technique should you use to palpate the inguinal canal?
no bulging
What is a normal finding when palpating the femoral area for hernias?
13 to 14 through adulthood
At what age should Testicular Self-Examination (TSE) be taught?
Knowing their own normal consistency (so they will know when something is abnormal and detect it early)
What should the emphasis be on when teaching TSE?
Timing - should be done once a month
Shower - warm water relaxes the scrotal sac
Examine - check for and report changes immediately
What 3 points should be included during TSE teachings?
clear and slightly acidic (4.5-8.0)
What is the normal color and pH of urine?
specific gravity
What measures the concentration of urine?
1.003
What is a very dilute concentration of urine?
1.030
What is a very concentrated concentration of urine?
proteinuria
= high protein in the urine, indicates glomerular disease
Glycosuria
= high glucose in the urine; occurs with hyperglycemia with diabetes
WBC; RBC
Increased ____ and ___ occurs with UTIs.
glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
What does creatinine measure?
125mL/min
what is a normal GFR?
the GFR decreases and creatinine levels increase
How does decreased kidney function affect GFR and creatinine levels?
creatinine
What is the end-product of muscle metabolism that ranges from 0.7-1.5 mg/dL and is used to assess kidney function?
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
What is the end-product of protein metabolism that ranges from 10-20 mg/dL and rises with dehydration or an increase in protein intake?
Cryptorchidism
= undescended/absent testes
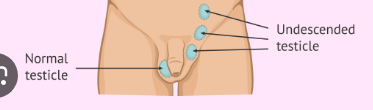
in abdominal cavity near kidneys
Where do the testes develop prenatally?
1.5 to 2 cm long and 1 cm wide
Only a slight increase in size occurs during prepubertal years
What is the measure of the testis at birth? How does this change in prepubertal years?
enlargement of testes
What is the first sign of puberty?
pubic hair appears, then penis size increases
What is the second stage of puberty?
Pubic hair decreases & penis size decreases
Due to decreased tone of dartos muscle, scrotal contents hang lower, rugae decrease, & scrotum becomes pendulous
Testes decrease in size and are less firm to palpation
Increased connective tissue is present in tubules, so these become thickened and produce less sperm
What changes can you see in the OA males genitals?
Male does not experience a definite end to fertility as female does
What is the difference b/t male and female fertility?
40
80 to 90
@ what age does the sperm begin to decrease? When does it stop?
Testosterone
_______________ production declines after age 30 but continues very gradually so resulting physical changes are not evident until later in life
Preschool-age to young school-age child, 3 to 8 years of age, leave underpants on until just before examination
Older school-age child or adolescent, offer an extra drape, as with adult; reassure child and parents of normal findings
What considerations should be taken for pediatric examinations?
Sexual Maturity Rating (SMR) in boys stage 1
no pubic hair
size and proportion of the penis and scrotum are the same as during childhood
Sexual Maturity Rating (SMR) in boys stage 2
testes and scrotum begin to enlarge
few hairs at the base of the penis
Sexual Maturity Rating (SMR) in boys stage 3
sparse hair growth over the entire pubis
penis begins to enlarge and scrotum continues to enlarge
Sexual Maturity Rating (SMR) in boys stage 4
thick growth over pubis (but not on thighs)
penis grows in length and diameter
scrotum darkens
Sexual Maturity Rating (SMR) in boys stage 5
hair growth spreads over medial thighs
penis and scrotum are their adult size and shape
Urethritis
= inflammation of the urethra that causes painful, burning urination, urethral pruritis, and discharge.
meatal edges are reddened, everted, & swollen with purulent discharge
urine is cloudy w discharge and mucus shreds
can be caused by certain STIs
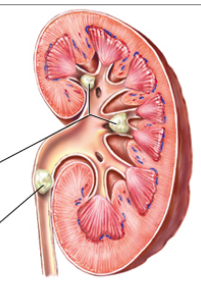
Renal Calculi
= stones (crystals of calcium oxalate or uric acid) form in kidney tubules and migrate.
can get lodged and obstruct urine flow (causing hydronephrosis)
abrupt, severe flank pain, nausea and vomiting, restlessness, hematuria
Acute Urinary Retention
= inability to pass urine with bladder distention and lower abdominal pain
can cause UTI from stasis
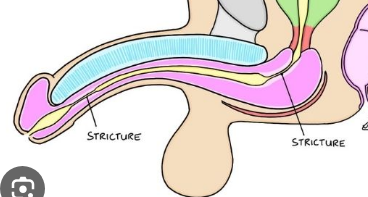
Urethral stricture
= pinpoint, constricted opening at meatus or inside along urethra.
congenital or secondary to urethral injury
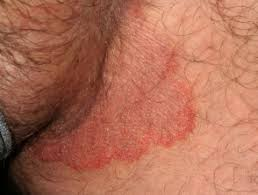
Tinea Cruris
= fungal infection in the crural fold from sweating or wearing layers of occlusive clothing
forms a red-brown half-moon shape w well-defined borders
“jock itch”
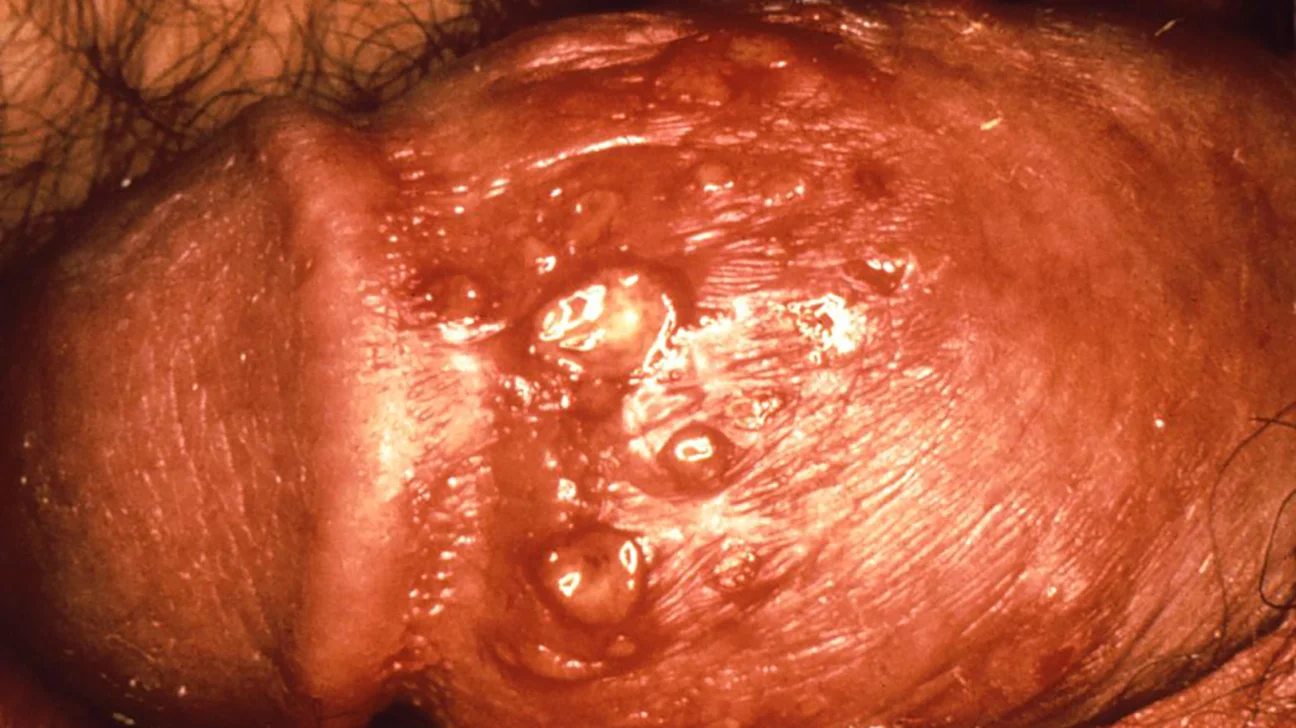
Genital Herpes (HSV-2 Infection)
= an STI (initial infection lasts 7 to 10 days, then remains dormant indefinitely) where clusters of small vesicles with surrounding erythema erupt on the glans, foreskin, or anus
gardasil
Which vaccine prevents HPV-related diseases?
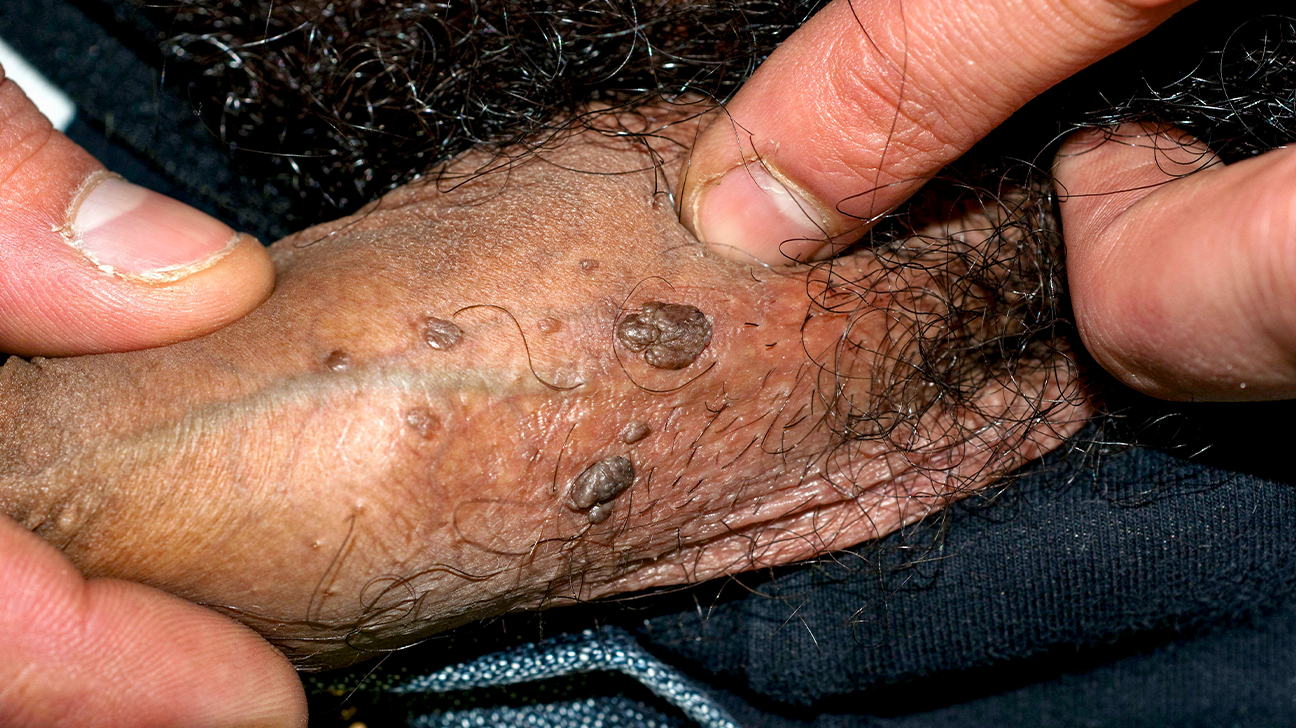
Genital Warts
= soft, pointed, fleshy, painless papules that occur on shaft of penis, behind corona, and around the anus.
caused by human papillomavirus (HPV)
one of the most common STIs
Primary Syphilis (chancre)
= small, solitary, silvery papule that erodes to a red, round or oval, superficial ulcer with yellowish serous discharge
occurs within 2-4 weeks of infection
carcinoma
= Very rare cancer on the glans or inner lip of foreskin. Begins as red, raised, warty growth or as an ulcer with watery discharge
priapism
= prolonged painful erection of penis without sexual stimulation and unrelieved by intercourse or masturbation
Peyronie Disease
= hard, nontender, subcutaneous plaques on dorsal or lateral surface palpated by stretching the penis
usually occurs after age 45
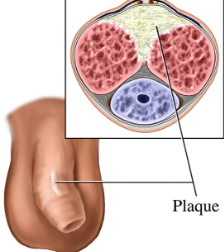
Testicular Torsion
= sudden twisting of the spermatic cord that requires emergency surgery
S: excruciating unilateral pain in testicle
O: red, swollen scrotum; one testis higher than the other
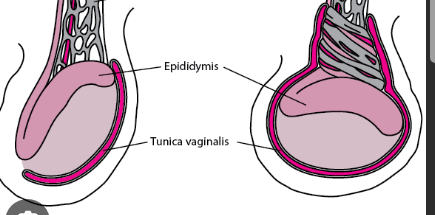
Varicocele
= dilated, totuous internal spermatic vericose veins caused by incompetent valves, which permit reflux of blood
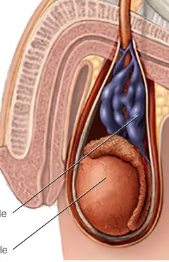
Diffuse Tumor
= enlarged testis that does not transilluminate bc of a tumor that maintains the shape of teste
Scrotal Hernia
= nontender swelling of scrotum
requires surgery
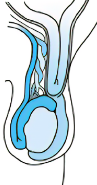
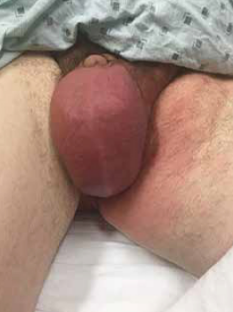
Orchitis
= tender swelling of testis (acute inflammation)
enlarged, edematous, reddened
does not transilluminate
Scrotal Edema
= scrotum that is enlarged, tender & taut with pitting
indirect
An inguinal hernia that is through the internal inguinal ring and is most common of all hernias.
common in infants
congenital or acquired
pain with straining
direct
An inguinal hernia that is directly behind and through the external inguinal ring.
acquired weakness
common in older men
usually painless
Femoral
A hernia that is through the femoral ring and canal, more often on the right side.
acquired
least common of all hernias
more common in women
severe pain