Transportation and Respiration
1/168
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 4 part 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
169 Terms
What is blood:
Blood is a liquid tissue.
What is the color of oxygen-rich blood:
Scarlet red.
What is the color of oxygen-poor blood:
Dull red.
What is the pH level of blood:
Between 7.35 - 7.45
What are the functions of blood:
Transportation, regulation and protection.
What is meant by transportation as one of the functions of blood:
Blood transports respiratory gases (O2, CO2), nutrients, waste, hormones and other things that can be absorbed through skin
Where does blood circulate:
Blood circulates in the heart, capillaries, arteries and veins.
What is meant by regulation as one of the functions of blood:
Blood regulates body temperature, water volume and the pH levels. (body pH level must be kept at 7.4)
What is blood clotting:
The mechanism that protects against blood loss after injury.
What is meant by protection as one of the functions of blood:
Blood clots to protect the body after the injury, white blood cells protect against disease. (White blood cells make antibodies)
What makes up blood:
Plasma (non cellular, liquid)
Blood cells/cell fragments (cellular, solid).
What makes up plasma:
Water (91%)
Proteins (7%)
Nutrients/hormones/ions (2%).
What makes up the buffy coat:
White blood cells, platelets.
What is a hematocrit:
The ratio of red blood cells to the total blood volume. Prepared using a centrifuge (an instrument that spins blood, separating its components based on their densities.)
What is the color of plasma:
Plasma has a straw color.
What percent of blood volume is plasma:
50%-60%.
What is an alternative name for red blood cells:
Erythrocyte
Where are the red blood cells produced:
In the bone marrow.
What is the shape of a red blood cell:
It is disc shaped (donut but without the hole)
What does a red blood cell not have:
Red blood cells don’t have a nucleus and a mitochondria.
What breaks down the red blood cells:
Spleen and liver.
How long does a red blood cell live:
120 days.
What do red blood cells contain:
Hemoglobin.
What is the role of the red blood cell:
Transportation of O2 and a small amount of CO2 around the body.
What is hemoglobin:
A protein that carries O2 around the body.
What makes up hemoglobin:
4 heme groups that bind to oxygen.
To how many molecules of oxygen can a hemoglobin bind to:
One hemoglobin molecule can bind to 4 molecules of oxygen.
What is an alternative name for white blood cells:
Leukocyte.
Where are the white blood cells produced:
White blood cells are produced in the bone marrow and in the lymph tissue
How much of the blood volume do white blood cells take up:
2%-3%.
What is the shape of a white blood cell:
Amoeboid. (no basic shape, always changes)
What is the difference between a red and white blood cell:
The white blood cell has a nucleus, the red blood cell DOESN’T have a nucleus.
What is the role of the white blood cell:
Part of the immune system, detects germs (antigens), produces antibodies, cleans up dead cells.
What is an alternative name for a platelet:
Thrombocyte.
Why is a platelet different from red/white blood cells:
The platelet is a cell fragment, NOT a cell.
How is a platelet different from a white blood cell:
A platelet has no nucleus, but the white cell does.
How long does a platelet live for:
A platelet lives for about 10 days.
What is the role of a red blood cell:
Blood clotting.
What makes the platelets:
A Megakaryocyte.
What is coagulation:
The formation of a blood clot.
Why is clotting important:
It helps prevent major blood loss after injury.
What are anticoagulants:
Proteins that prevent blood from clotting.
Give examples of anticoagulants:
Heparin, Fibrinolysin.
Why are clots in the blood vessels dangerous:
They can travel throughout the body and can lead to death.
Give examples of where the blood clots can travel:
Brain - causes stroke
Heart- causes heart attack
Lungs - causes pulmonary embolus
What is hemophilia:
An inherited bleeding disorder where the person’s blood does not clot properly.
Why does hemophilia happen:
An important clotting factor is missing. (Clotting factor VII, or anti-hemophilia factor)
Clotting factor:
The enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. (Also known as thromboplastin)
How many blood groups there are:
There are 4 blood groups. A, B, AB, O.
How are blood groups determined:
Determined by antigens present on the surface of the red blood cells.
What is the Rh factor:
A third antigen that can be present on the surface of a red blood cell.
What is the blood type with the Rh factor called:
If the antigen is present, then the blood type is positive.
Describe the clotting process:
A blood vessel is injured - Blood leaves to clean the wound and blood vessel undergoes vasoconstriction
Platelets migrate to the site of injury and then burst, releasing an enzyme called thromboplastin
Thromboplastin initiates the conversion of prothrombin (a plasma protein) into thrombin
Thrombin coverts the soluble plasma protein fibrinogen into insoluble strands of fibrin
The fibrin forms a network of fibers that trap red blood cells and platelets to form a clot
What is Animal Circulatory System:
Series of tubes and pumps that transports circulatory fluid throughout the body.
What is 3 component of most animal circulatory system:
Circulatory fluid = “Blood”
Tubes = Blood Vessels
Muscular pump = Heart
What are 3 types of Blood Vessels:
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries

What are each role of 3 types of Blood Vessels:
Arteries = Carry blood away from the heart
Veins = Return blood to heart
Capillaries = Connect arteries to veins
Arterioles:
Arteries “narrow version”
Venules:
Veins “narrow version”
Capillary beds:
Networks of capillaries
What is the structure of the arteries:
Three tissue layers:
Connective tissue
Thick muscular wall or smooth muscle
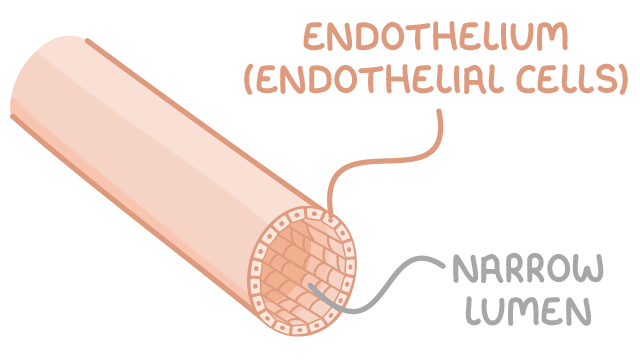
Endothelium (They line the blood vessel)
Lumen have a narrow diameter in arteries
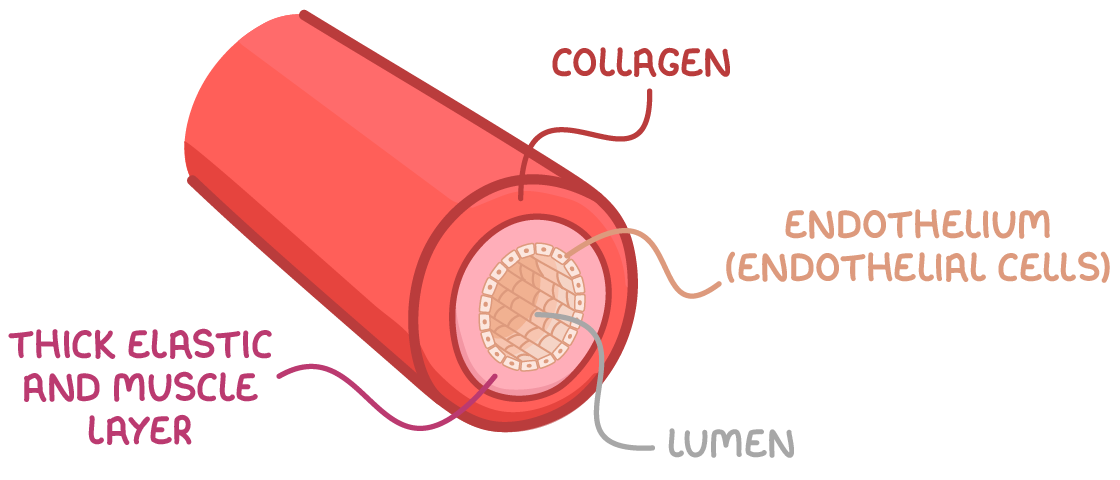
Lumen:
A hollow passage way through which blood flows
Elasticity:
Elastic recoils helps maintain blood pressure even when the heart relaxes.
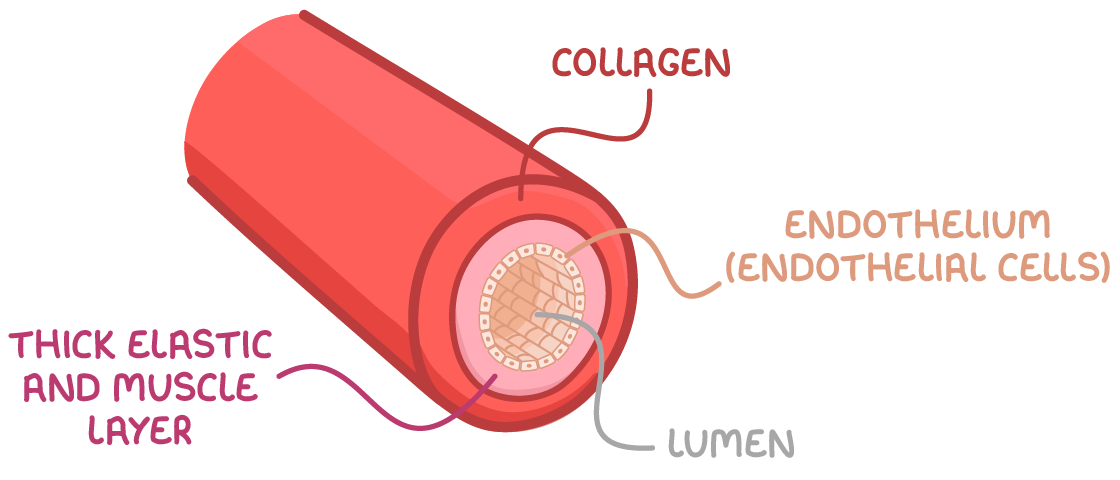
What is the structure of veins:
Three tissue layers:
Connective tissue
Thin muscular wall or Smooth muscle
Endothelium (They line the blood vessel)
Lumen have a wide diameter in veins
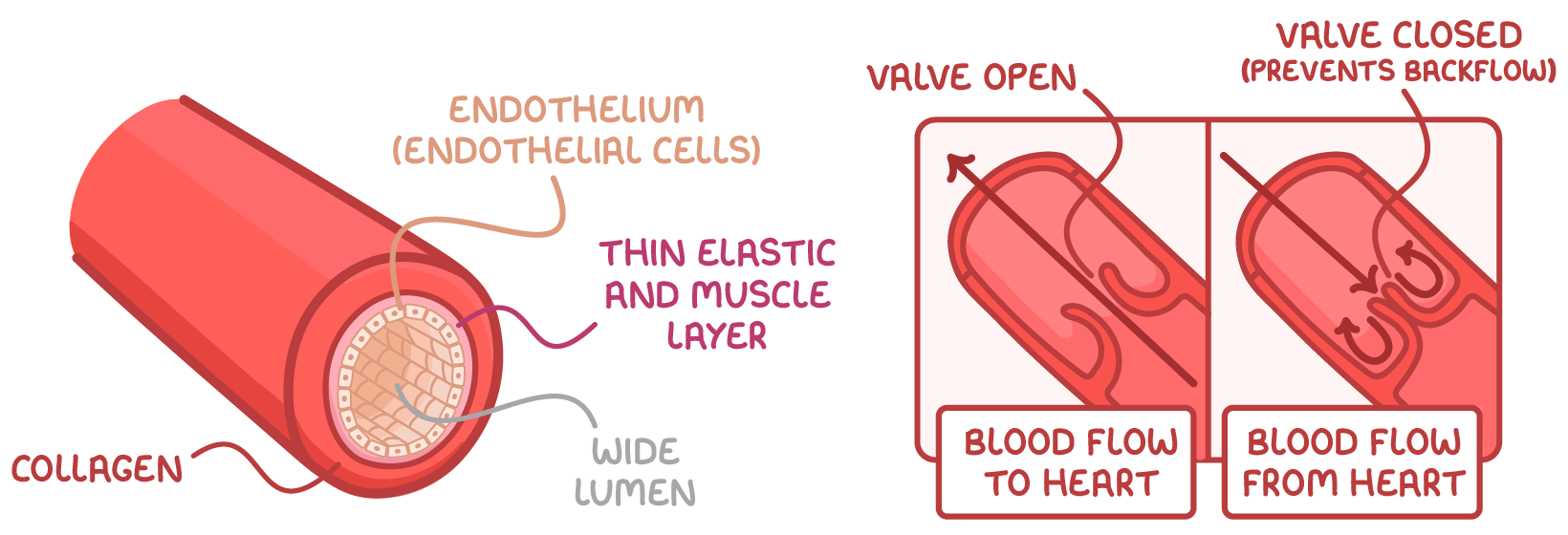
Why is the blood pressure in arteries, vein and capillaries are different:
The heart pumps blood into arteries at high force. Veins receive blood after it has passed through low-pressure capillaries.
Arteries have thick, muscular walls to handle high pressure. Vein walls are thinner and less elastic than arteries, allowing them to stretch and hold more blood at low pressure.
Blood pressure drops as blood moves from arterioles into the narrow capillaries, slowing flow for nutrient/waste exchange.
How are veins maintain their blood pressure:
“Muscle pump” - Skeletal muscle contractions (squeeze blood through veins during movement)
One way valves - Prevent backflow and only allow blood to flow toward heart
Varicose Veins:
Caused by defective valves
Blood accumulates within the veins, causing them to distend, twist, and become visible on the surface of the skin
Capillaries function & example:
Exchange materials between blood & cells.
Example: Oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, waste, water.
What is the structure of capillaries
Tissue Layer:
Very thin walls
Lack 2 outer layers
No muscle layer
Only endothelium
How can water & solutes flow out of capillaries to
tissues:
Due to blood pressure
“Bulk flow”
How can interstitial fluid flows back into capillaries:
Due to osmosis
Plasma proteins increase osmosis pressure - solute potential
Interstitial fluid
The watery fluid that fills the spaces between body's cells
Crucial transport medium that delivers oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and signals from blood capillaries to cells, while also collecting waste products for removal, eventually draining into the lymphatic system
What is controlled the blood flow in capillaries:
Pre - capillary sphincters - “Open & Close” muscle
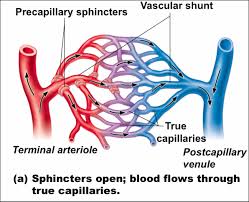
What is the main vessel through is called:
Vascular shunt
When is supply varies of blood is needed:
After a meal, blood supply to digestive tract increases.
During strenuous exercise, blood is diverted from digestive tract to skeletal muscles.
Capillaries in brain, heart, kidneys & liver usually filled in capacity to maintain homeostasis
What are mammalian heart composed of:
Pericardium
Myocardium
Endocardium
Pericardium
Outer layer enclosing the heart
Contains pericardial fluid that lubricate and protects the heart
Prevents friction from damage
Thin layer of tissue
Myocardium
Middle layer, composed of cardiac muscle.
Made up of cardiac muscle cells
Cardiac muscle cell
Myogenic - Pulse independently
Gaps junctions create gap that connect these cell to allow exchange of material and impulse to spread in heart
Endocardium:
Inner layer of smooth muscle that lines the heart cavity and
covers valves and chambers
Allows blood to flow and prevents blood clotting
How many chambers does the heart has:
The heart has four chambers:
• 2 atria = filling chambers (blood enters)
• 2 ventricles = pumping chambers (blood exits)
Why does blood flow from atrium to ventricle doesn’t need much “muscle”:
Because they relying on gravity and passive transport
Heart valves:
Four valves in the heart
They are flaps of connective tissue
• 2 Atrioventricular (AV) valves
• 2 Semilunar valves
Function of heart valves:
To prevent back flow and ensure blood flows in the correct direction through the heart.
Why is the heart considered a double pump:
Because it pumps the blood to the lungs and to the body.
General pathway of blood:
Heart → Lung → Heart → Body

What are 3 type of Circulation:
1. Systemic Circulation
2. Pulmonary Circulation
3. Coronary (Cardiac) Circulation
Systemic Circulation:
The blood flows between the heart and all the body
systems.
“Carrying oxygenated blood from the heart's left side, through the aorta, to supply all organs and tissues, then returning deoxygenated”
Pulmonary Circulation:
Blood flow between the heart and the lungs.
Coronary (Cardiac) Circulation:
Blood flow throughout the tissues of the
heart itself.
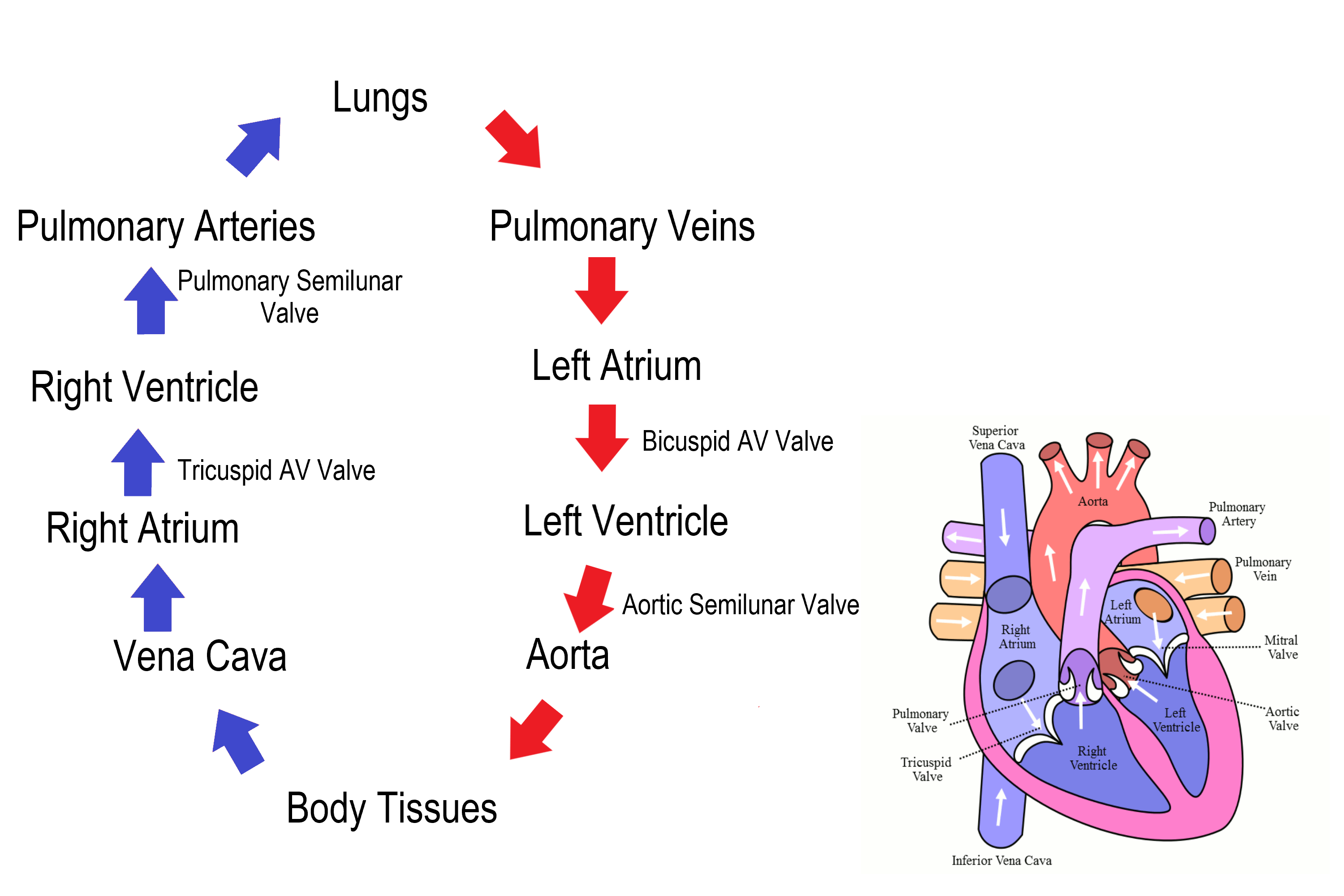
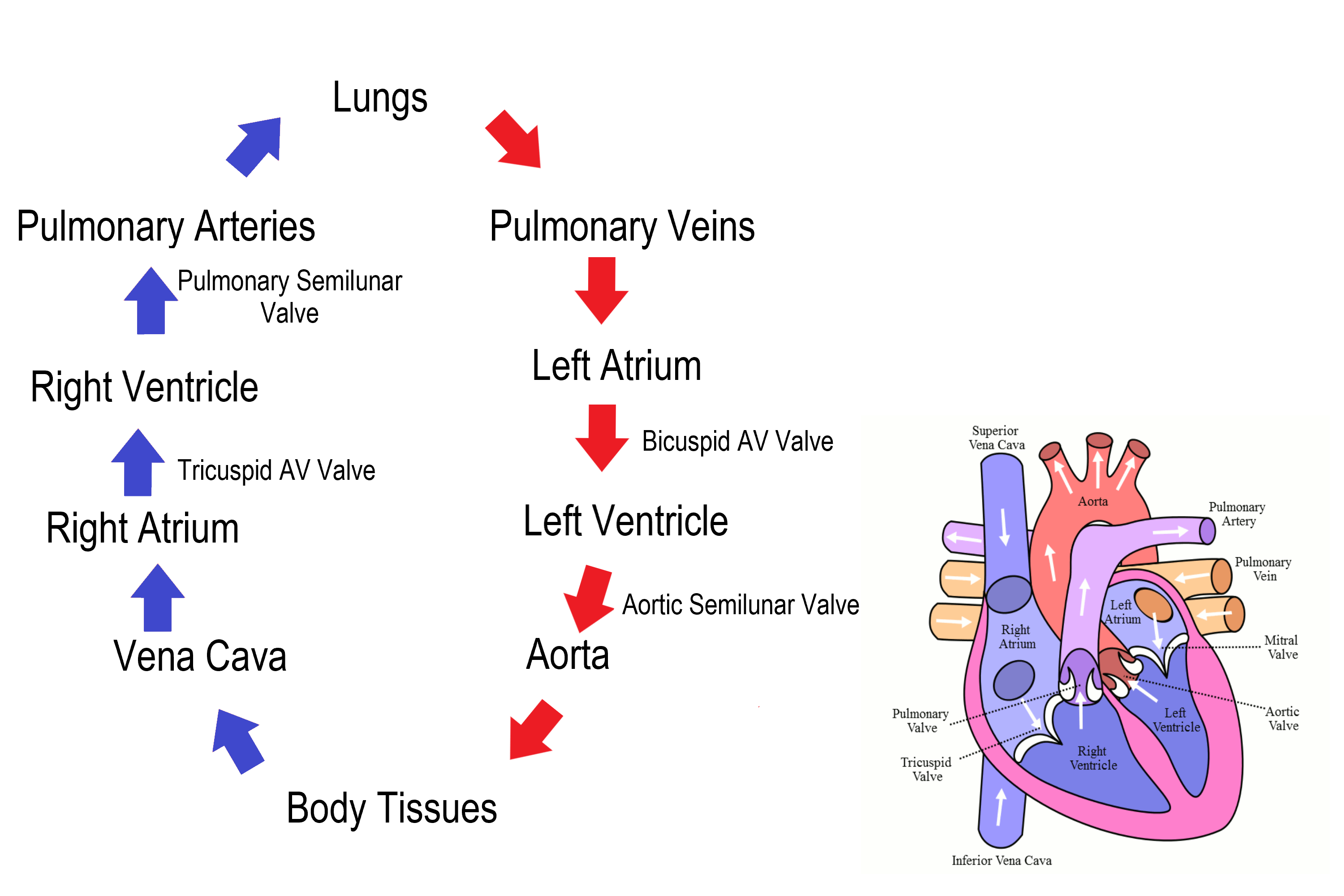
Pathway of oxygenated blood:
1. Lungs
2. Pulmonary Vein
3. Left Atrium
4. Left Atrio-ventricular Valve
5. Left Ventricle
6. Aortic/ Semi-Lunar Valve
7. Aorta
8. Body Cells and Organs
Pathway of deoxygenated blood:
1. Body Cells and Organs
2. Inferior Vena Cava & Superior Vena Cava
3. Right Atrium
4. Right Atrio-ventricular Valve
5. Right Ventricle
6. Pulmonary Semi-Lunar Valve
7. Pulmonary Artery
8. Lungs
What are the only arteries carry deoxygenated blood?
The pulmonary arteries are the ONLY arteries in the body that
carry deoxygenated blood.
What are the only pulmonary carry oxygenated blood?
The pulmonary veins are the ONLY veins in the body that carry
oxygenated blood.
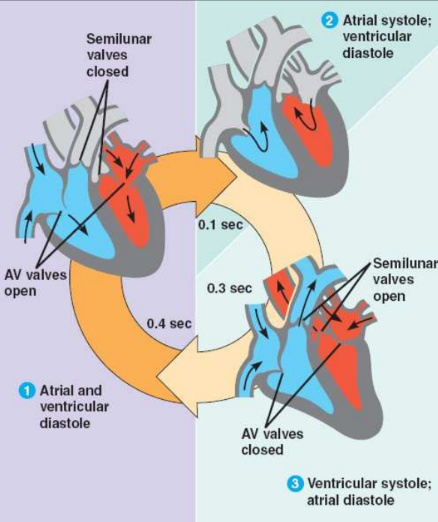
Cardiac Cycle
The heart beat “process”
Systole
A period of muscle contraction.
Atria and ventricles force blood out.
Diastole
A period of rest or relaxation.
Atria and ventricles fill with blood
What are 3 main stage of cardiac cycle:
Atrial and ventricular diastole (0.4)
Atrial systole ventricular diastole (0.1)
Ventricular systole atrial diastole (0.3)
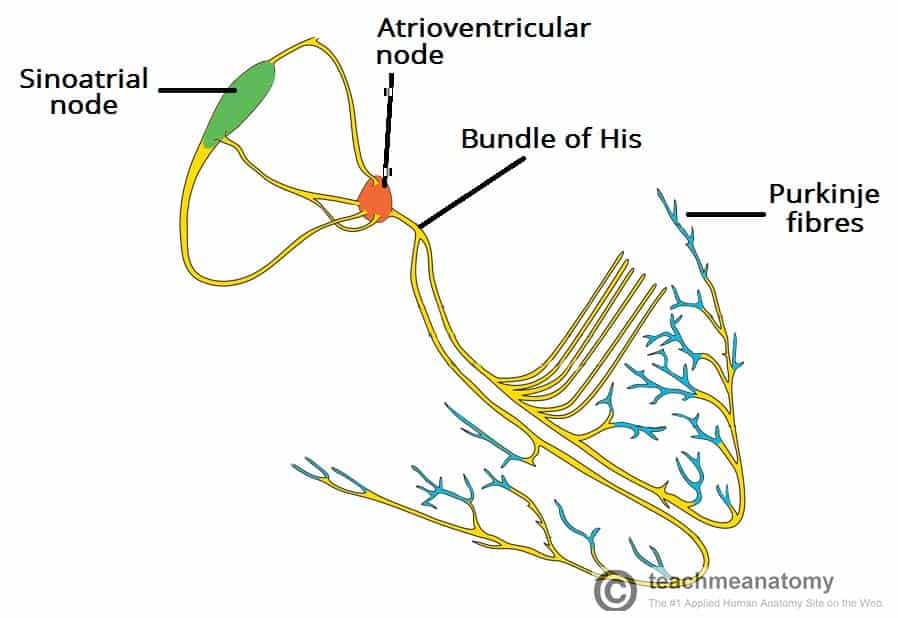
How is the heart beat control and spread:
“Send → A → Big → Pulse”
S - SA Node
A - AV Node
B - Bundle of His
P - Purkinje fibers
Sinoatrial Node:
“SA Node” or “Pacemaker” - Control/Start the heart beat
A specialized bundle of neurons (nerve cells) located in the wall of the right atrium.
It releases a wave of contraction in the muscle fibers of the atria, forcing blood out (making them contract)