AP Euro - McKay Chapter 15 - Absolutism and Constitutionalism (1589-1725)
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Great Chain of Being
European idea that every species was a link on a chain extending from lowest forms to humans and on to spiritual beings. All links and been designed at the same time during creation and would never change. Once all the links were discovered and described, the meaning of life would be revealed.

Patriarchal
relating to a society in which men hold the greatest legal and moral authority

Subsistence
the minimum amount to sustain life

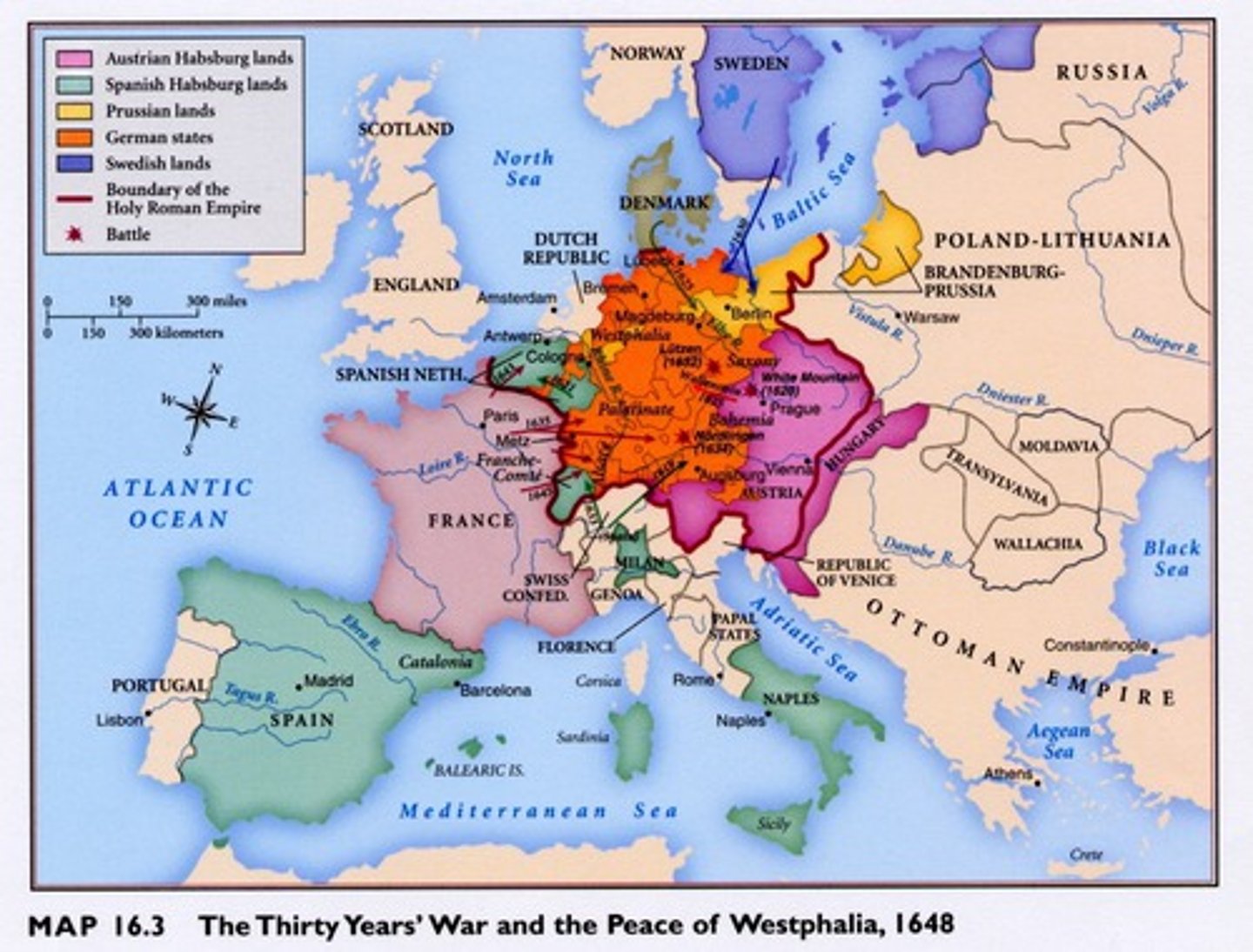
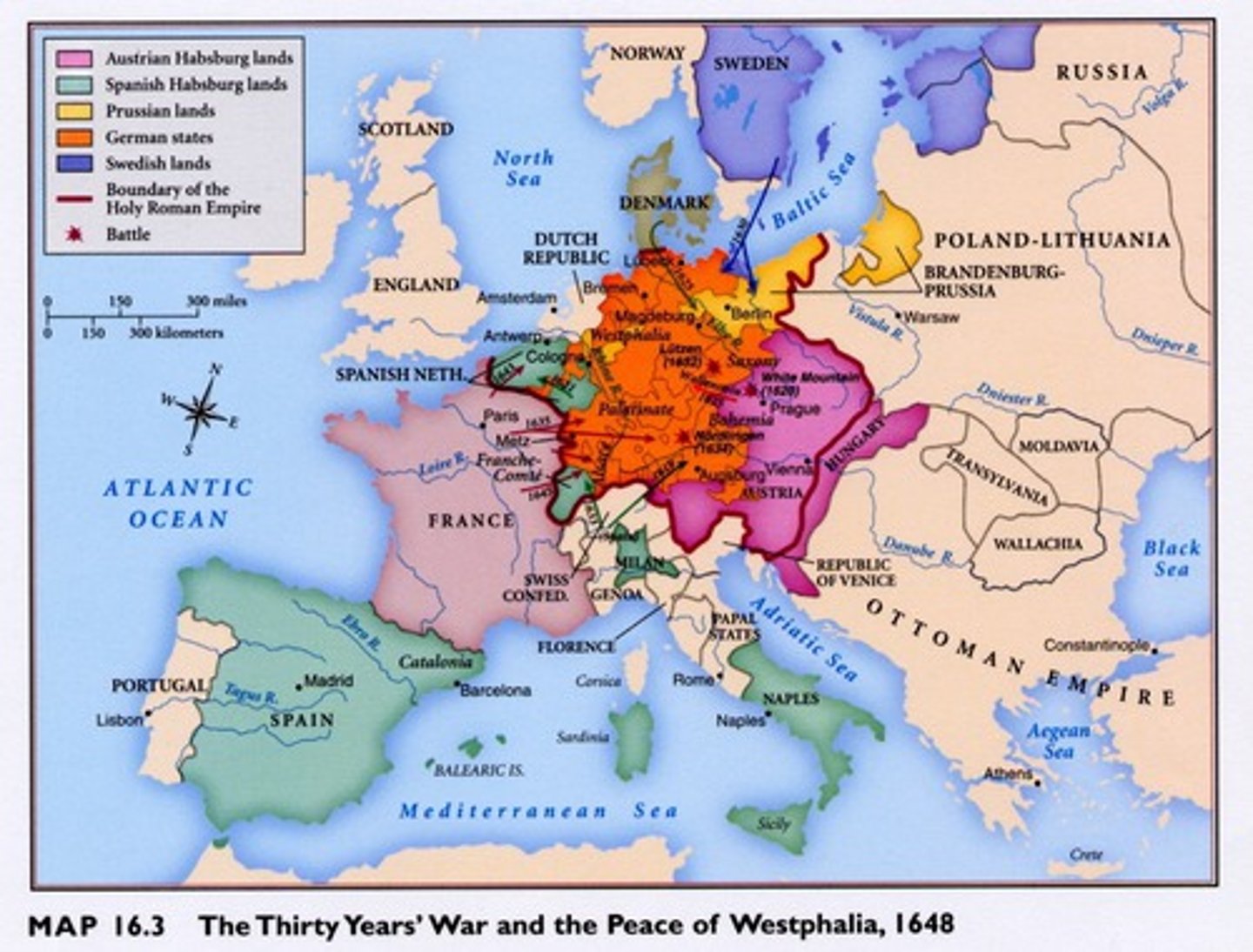
Thirty Years' War
Protestant rebellion against the Holy Roman Empire ends with peace of Westphalia (1618-48) A series of European wars that were partially a Catholic-Protestant religious conflict. It was primarily a batlte between France and their rivals the Hapsburgs, rulers of the Holy Roman Empire.
Peace of Augsburg
A treaty between Charles V and the German Protestant princes that granted legal recognition of Lutheranism in Germany.

Protestant Union
(1608) alliance of German Lutheran princes alarmed at religious and territorial spread of Calvinism and Catholicism. Catholic princes responded with the Catholic League (1609). The two armed camps erupted in the Thirty Years War (1618-1648).

Catholic League
1609 Catholics determined to stop the spread of Protestantism in German states
Bohemian Phase
(1618-1625) 1st phase of Thirty Years' War
HRE Ferdinand II enters Bohemia, Protestant Bohemians get angry and name their own king, Frederick V (he later loses and disappears)
Rebellion in Bohemia spreads to other parts of Euro

Danish Phase
The second phase of the Thirty Years' War in which the Catholic imperial army led by Albert of Wallenstein won a series of major victories against the Protestants.

Christian IV
King of Denmark that was a Lutheran that intervened by leading an army into northern Germany. He was defeated by Wallenstein and ended Danish supremacy in the Baltic.

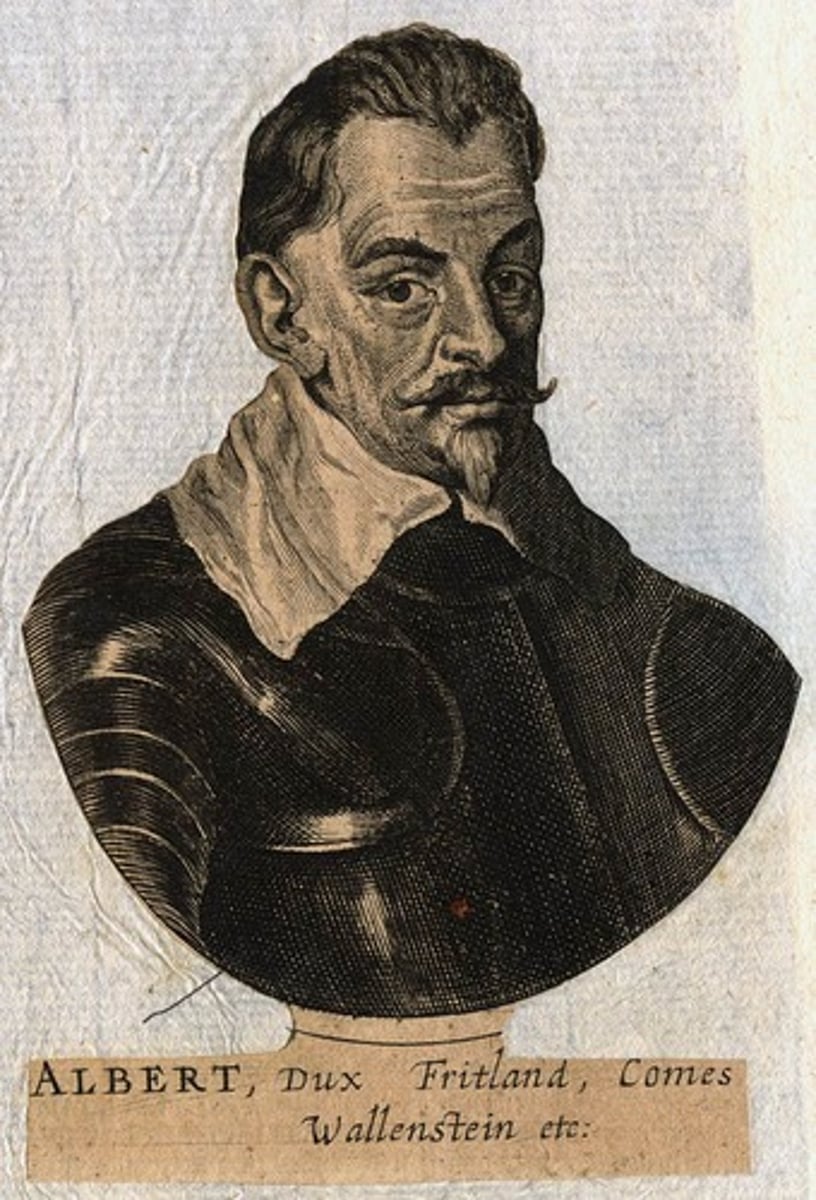
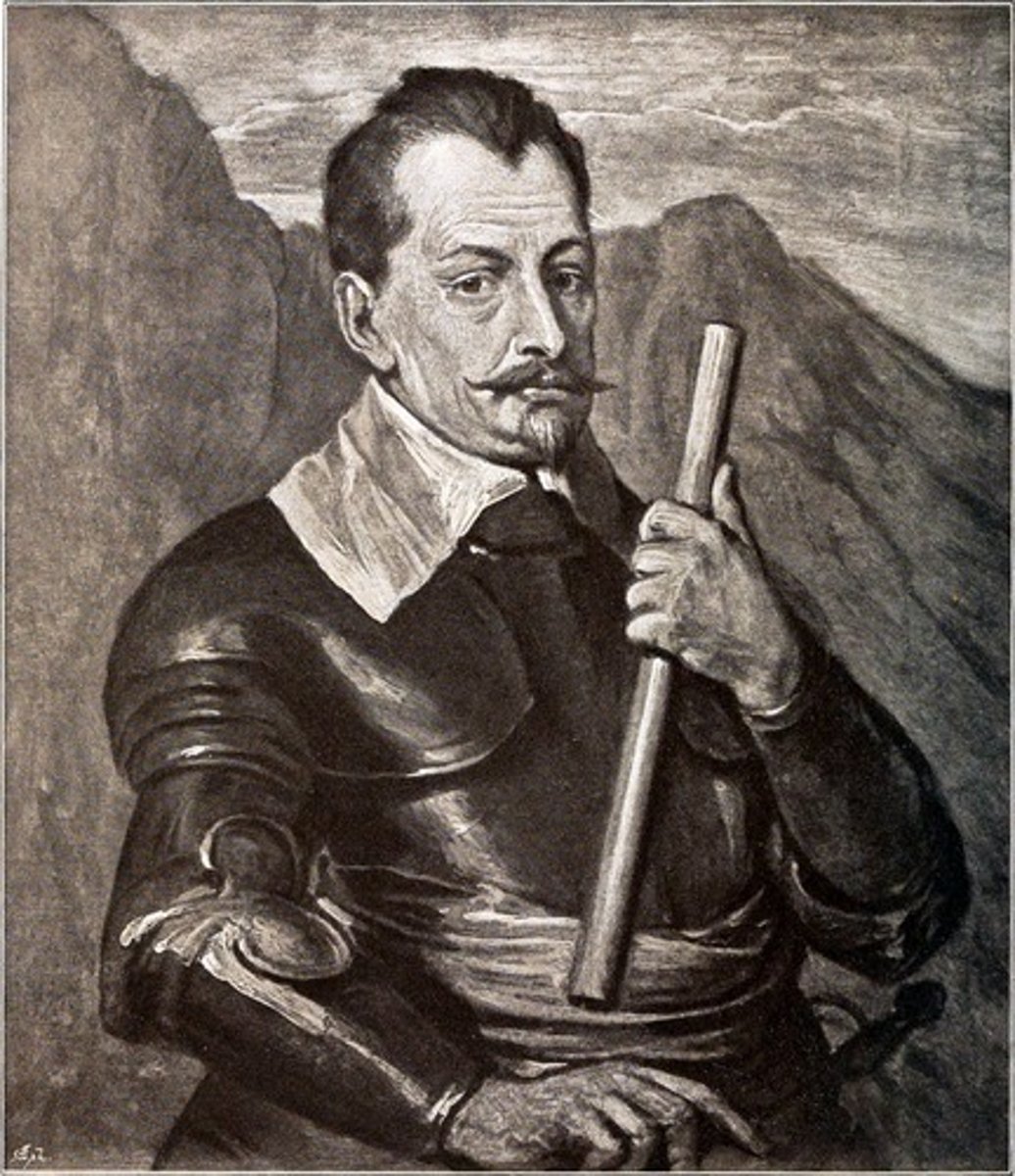
Albrecht of Wallenstein
Protestant mercenary fighting for Catholics, assassinated by Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II. Killed Gustavus Adolphus. Ferdinand killed him because he was threatened by Wallenstein's extreme power over the territories he acquired through the war.

Edict of Restitution
(1629) Emperor declared all church territories that had been secularized since 1552 to be automatically restored to Catholic Church
Swedish Phase
The third phase of the Thirty Years' War marked by Sweden's entrance into the war under King Gustavus Adolphus; during this phase, the Protestants began to defeat the Catholics on many fronts.
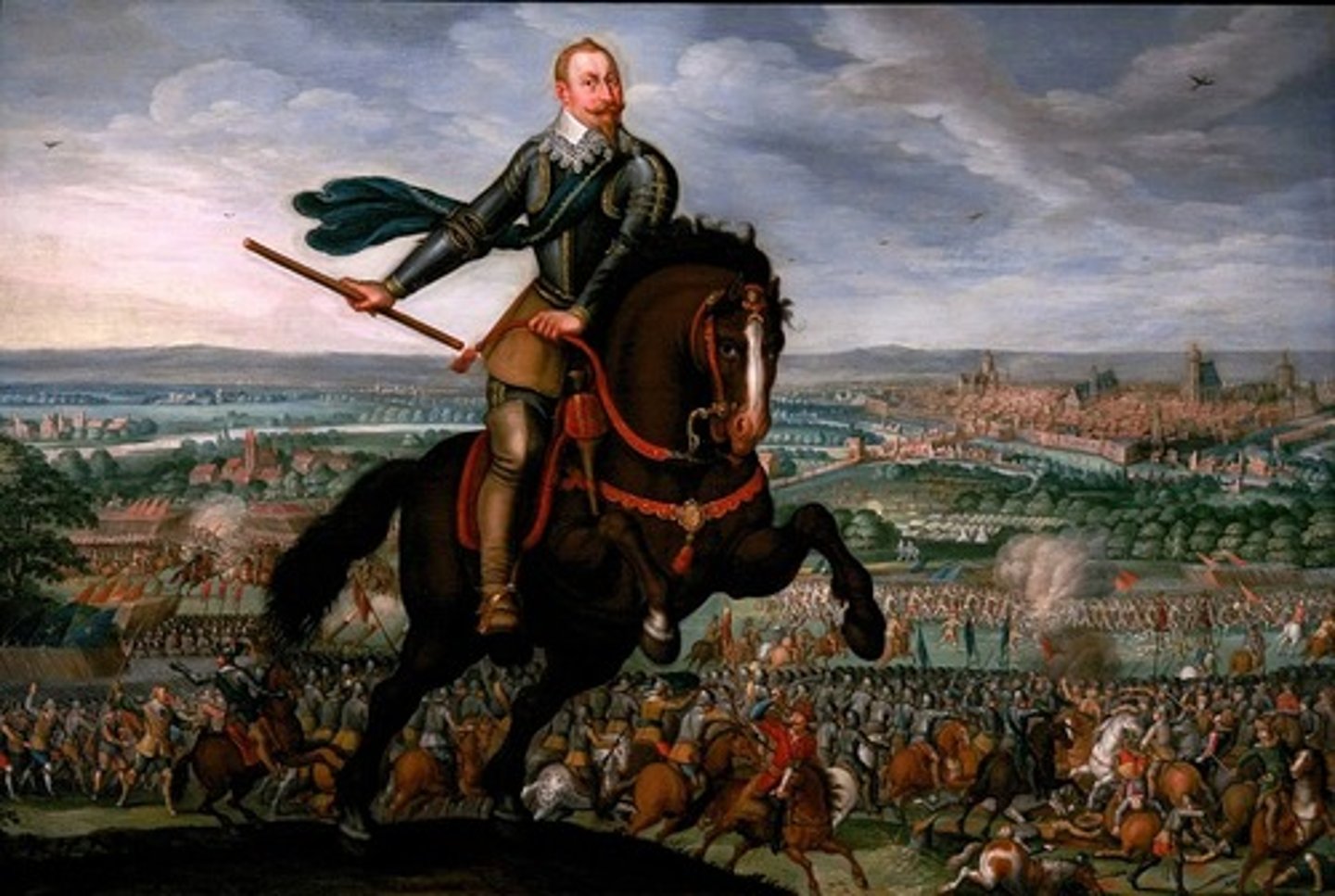

Gustavus Adolphus
(1594-1632) Swedish Lutheran king who won victories for the German Protestants in the Thirty Years War and lost his life in one of the battles.

French Phase
The fourth and final phase of the Thirty Years' War marked by France's entrance into the war on the side of the Protestants; this gave the Protestants the support needed to defeat the Catholics.
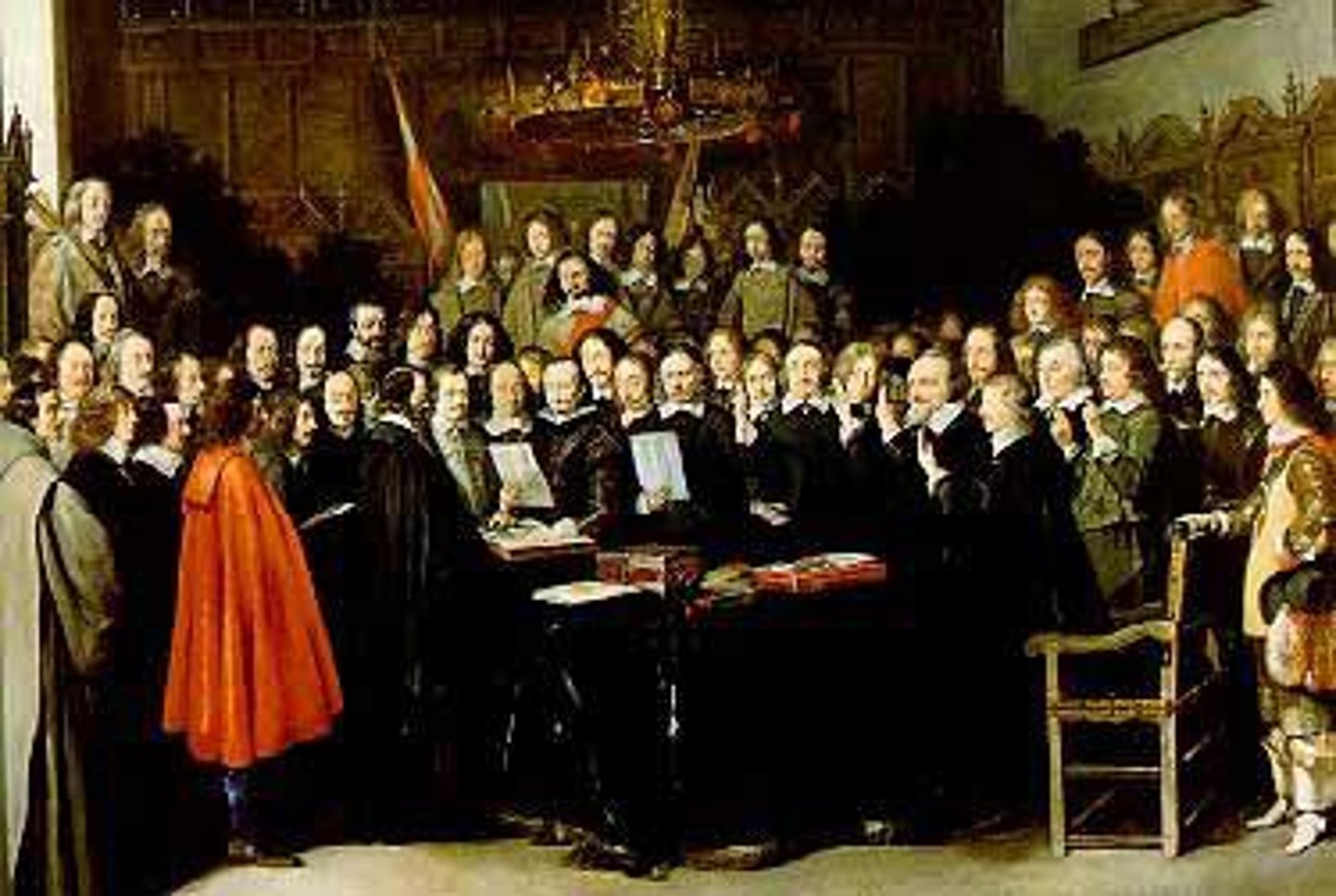
Peace of Westphalia
the name of a series of treaties that concluded the Thirty Years' War in 1648 and marked the end of large-scale religious violence in Europe
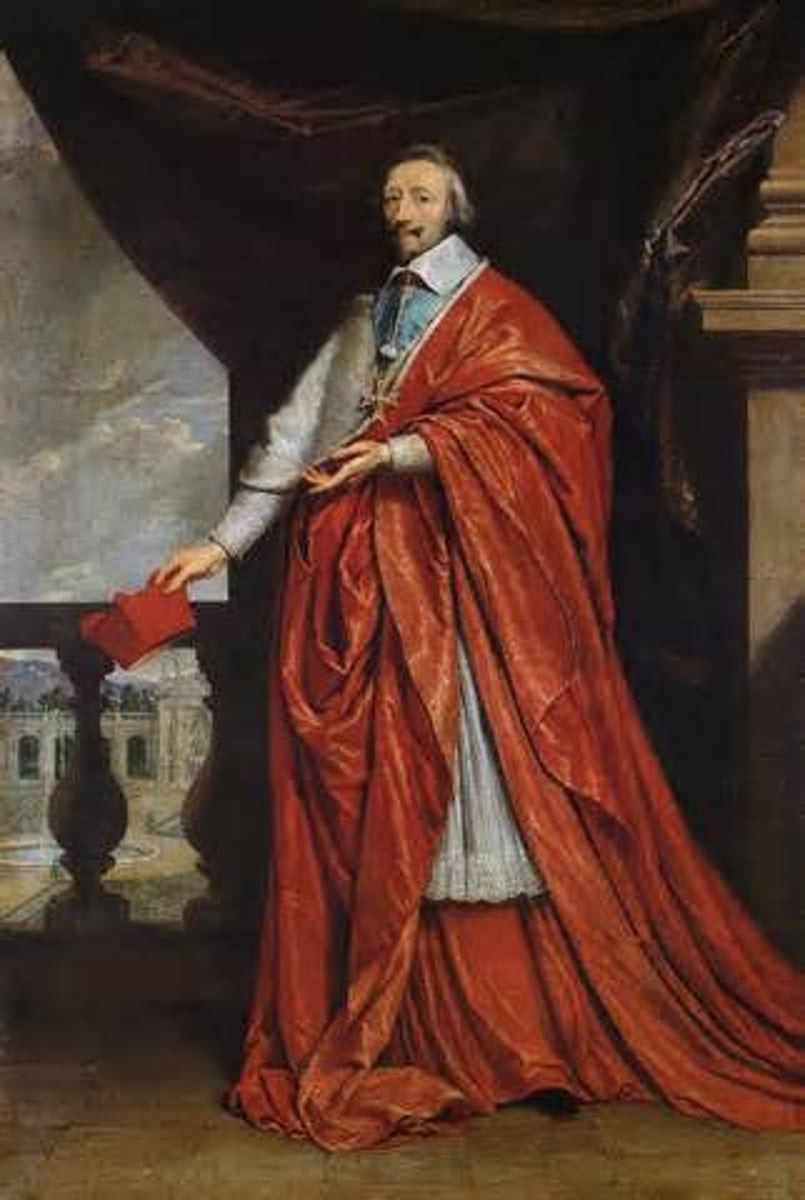
Cardinal Richelieu
(1585-1642) Minister to Louis XIII. His three point plan (1. Break the power of the nobility, 2. Humble the House of Austria, 3. Control the Protestants) helped to send France on the road to absolute monarchy.

Count-Duke Olivares
Phillip IV of Spain left his federal kingdoms to Gaspard de Guzman, Count-Duke of Olivares. Olivares was an able minister. He did not lack energy and ideas; he devised new sources of revenue. However, he clung to the grandiose belief that the solution to Spain's difficulties rested in imperial tradition. Unfortunately, the imperial demanded the revival of the war with the Dutch at the expiration of a twelve-year truce in 1622 and a long war with France over Mantua (1628-1659). Spain thus became embroiled in the Thirty Years' War. These conflicts, on top of an empty treasury, brought disaster. (547-548)

Henry IV
(1589-1610) - Formerly Henry of Navarre; ascended the French throne as a convert to Catholicism. Surrived St. Bartholomew Day, signed Edict of Nantes, quoted as saying "Paris is worth a mass."
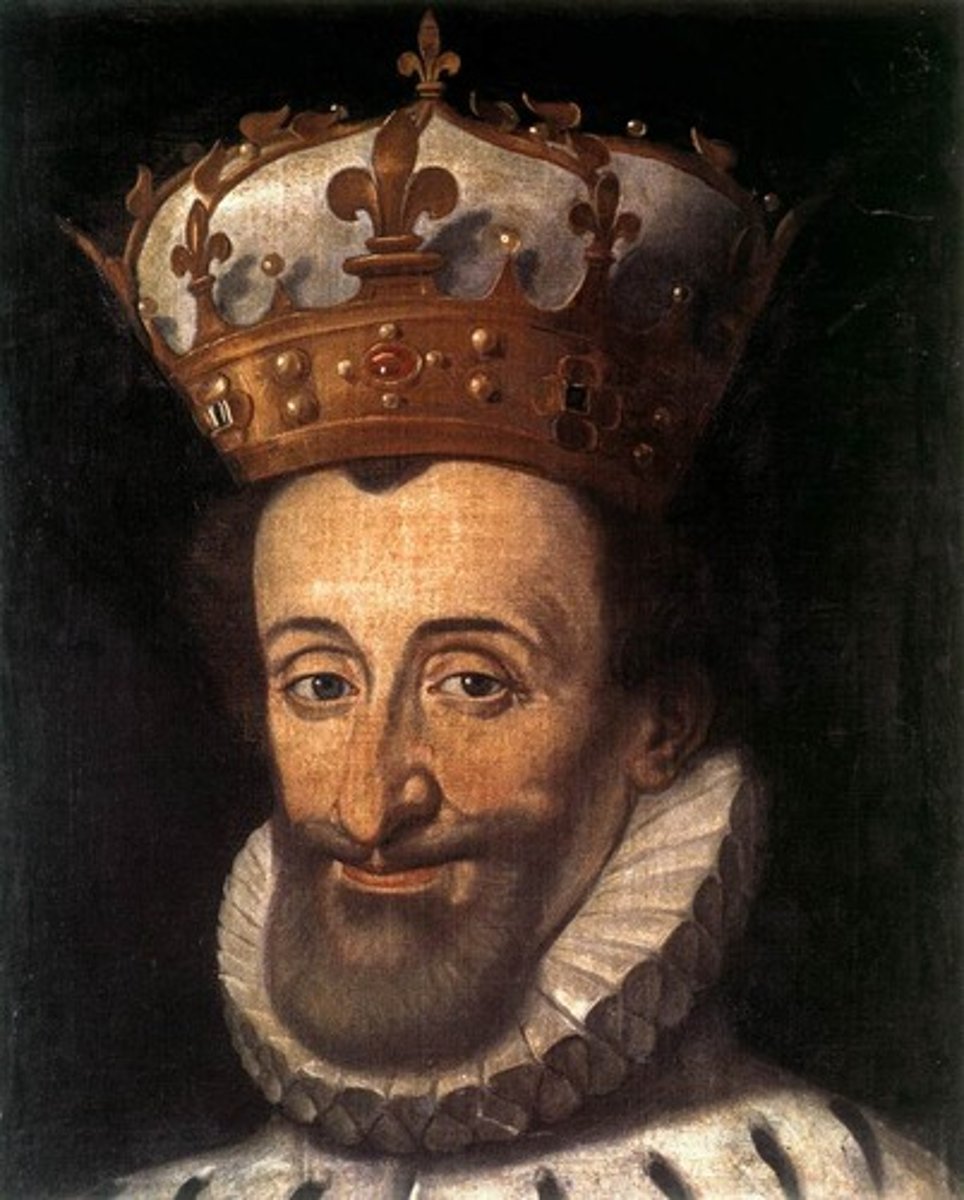

Edict of Nantes
A document issued by Henry IV of France in 1598, granting liberty of conscience and of public worship to Calvinists, which helped restore peace in France.

Intendants
official appointed by French king Louis XIV to govern the provinces, collect taxes, and recruit soldiers

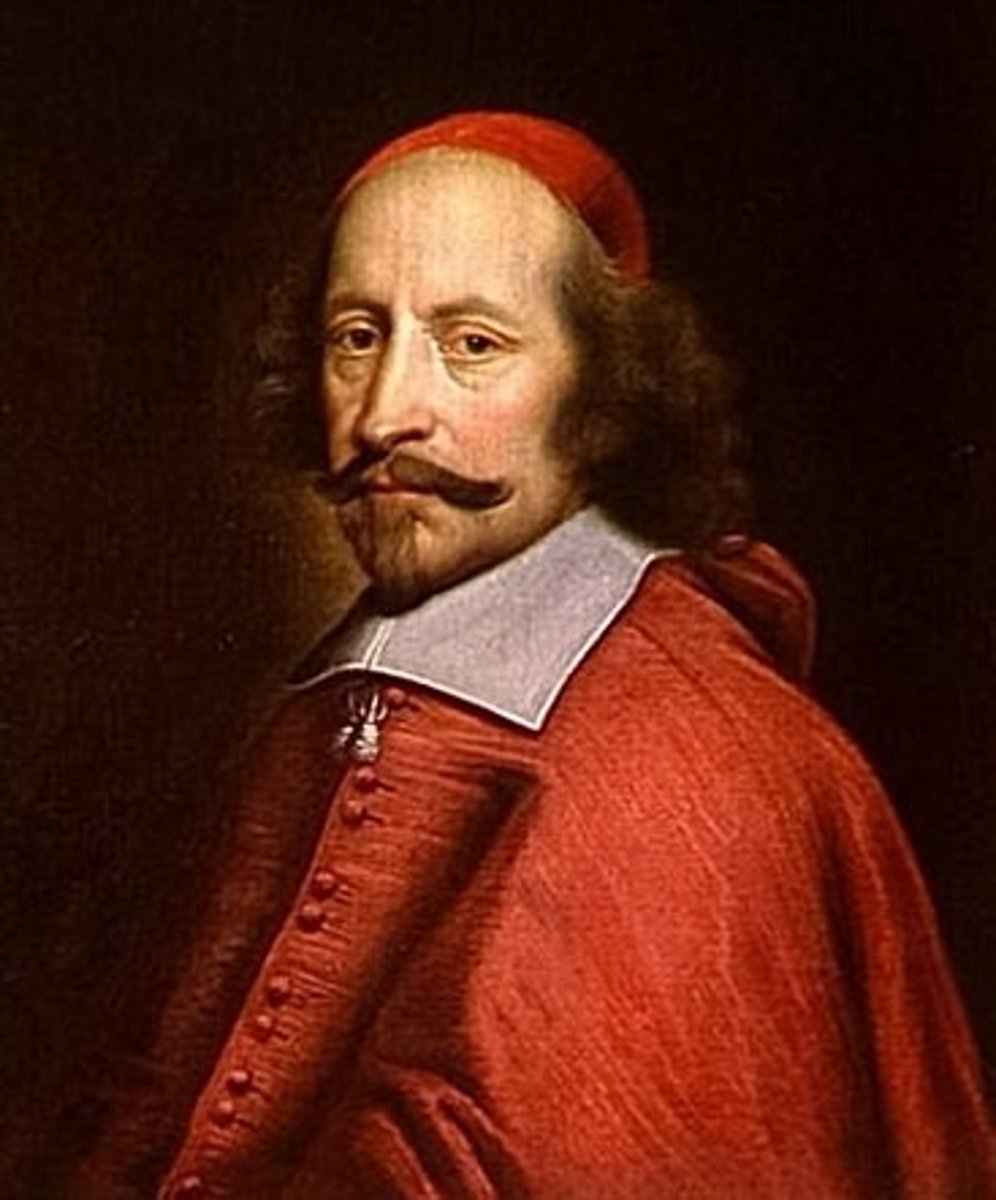
Cardinal Mazarin
(1602-1661), Successor of Cardinal Richelieu and his bad attempts to increase royal revenue and the state lead to the Fronde; ran the government while Louis VIII was still a child

Fronde
a series of violent uprisings during the early reign of Louis XIV triggered by growing royal control and increased taxation

Nobles of the Robe
The nobles whose nobility was either acquired by serving in the bureaucracy or had purchased them.

Louis XIV
(1638-1715) Known as the Sun King, he was an absolute monarch that completely controlled France. One of his greatest accomplishments was the building of the palace at Versailles.
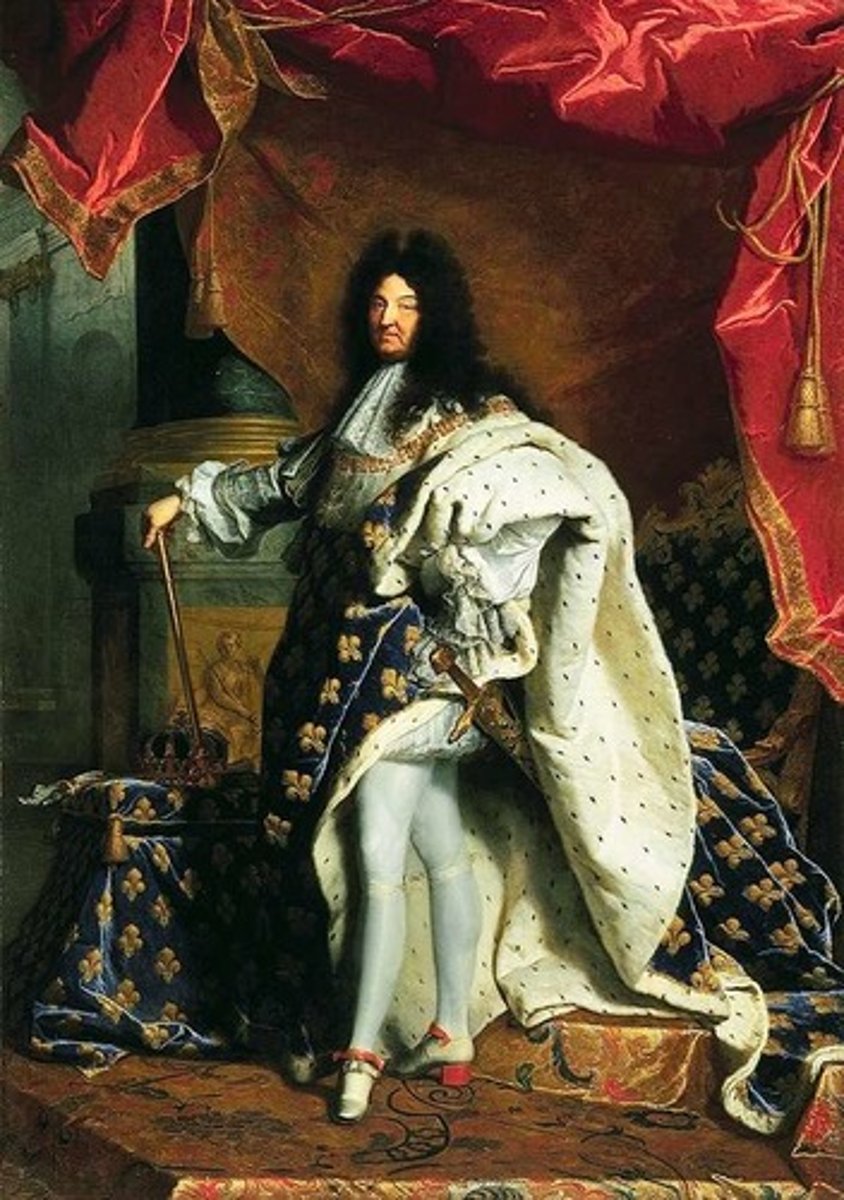

Divine right of kings
Doctrine that states that the right of ruling comes from God and not people's consent

Sun King
A nickname for Louis xiv that captures the magnificence of his court and of the Palace of Versailles, which he built. Louis himself adopted the sun as his emblem.

Estates General
A legislative body in prerevolutionary France made up of representatives of each of the three classes, or estates.
Versailles
Palace constructed by Louis XIV outside of Paris to glorify his rule and subdue the nobility.

Patronage
Granting favors or giving contracts or making appointments to office in return for political support
French classicism
The style in seventeenth-century art and literature resembling the arts in the ancient world and in the Renaissance-e.g., the works of Poussin, Moliere, and Racine.

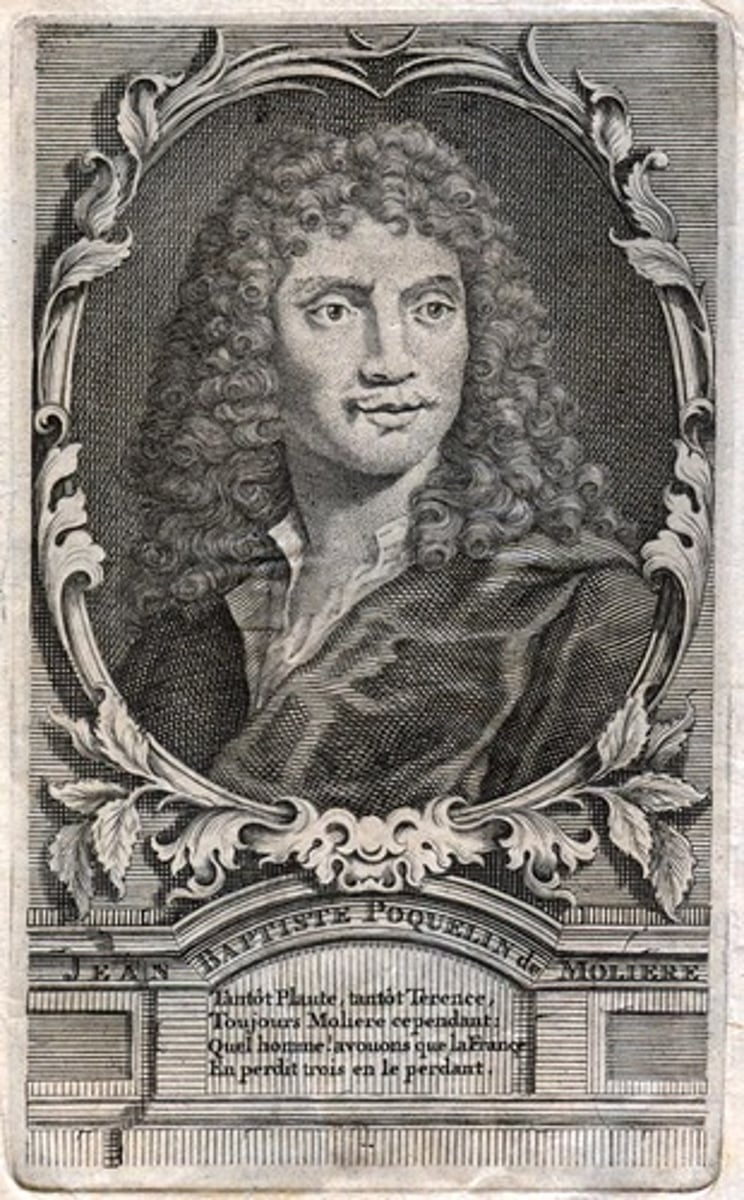
Moliere
French classicist playwright who produced popular comedies that exposed the hypocrisies and follies of society.

Jean-Baptist Colbert
assisted Louis in achieving his goals and believed in the theory of mercantilism and who to prevent wealth from leaving the country and tried to make France self-sufficient

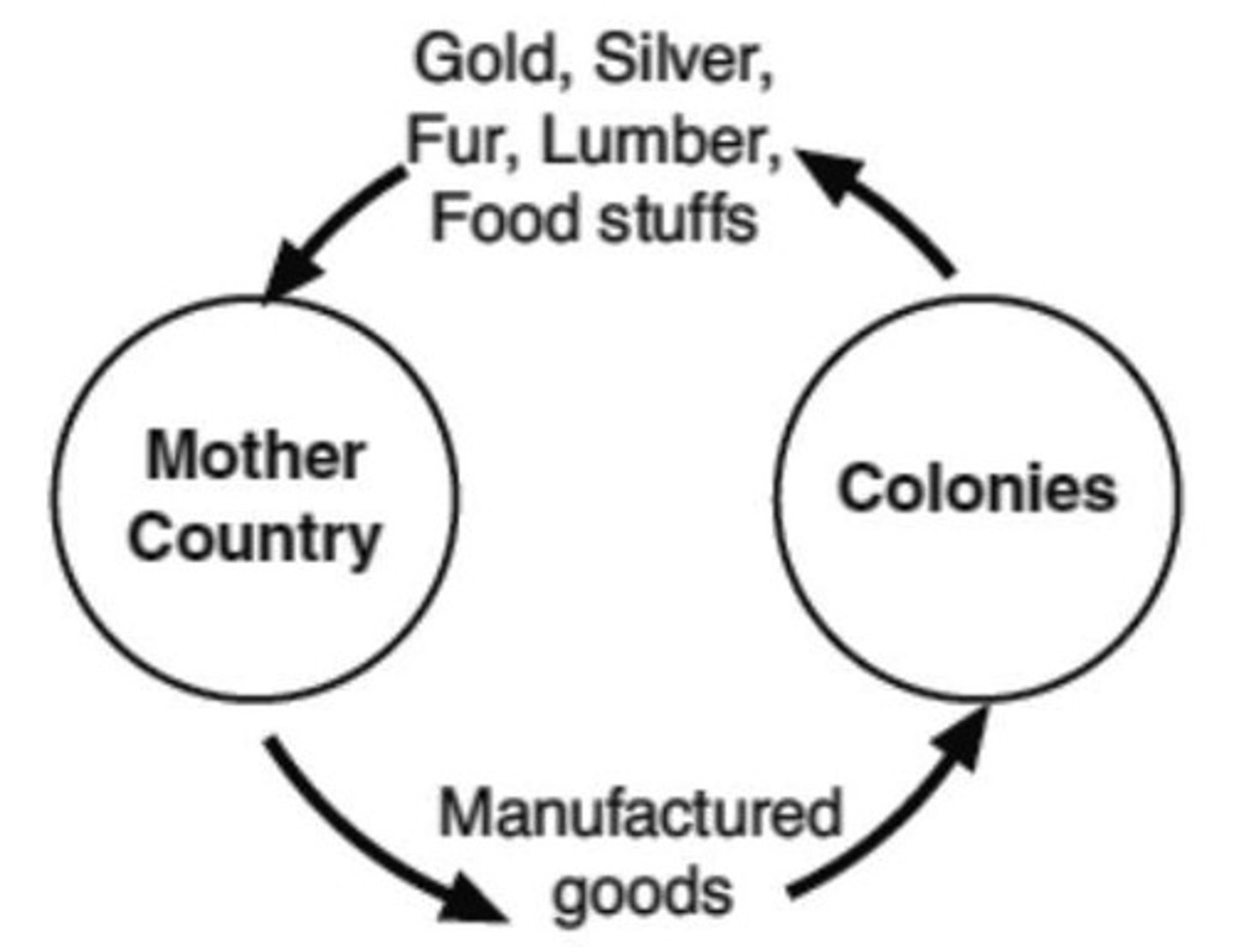
Mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods than they bought
Philip of Anjou
grandson of Louis XIV who was granted the entire Spanish inheritance by Charles II and became Philip V of Spain. His grandfather's domineering actions of invasion as a result caused the War of the Spanish Succession

War of the Spanish Succession
a conflict, lasting from 1701 to 1713, in which a number of European states fought to prevent the Bourbon family from controlling Spain as well as France.
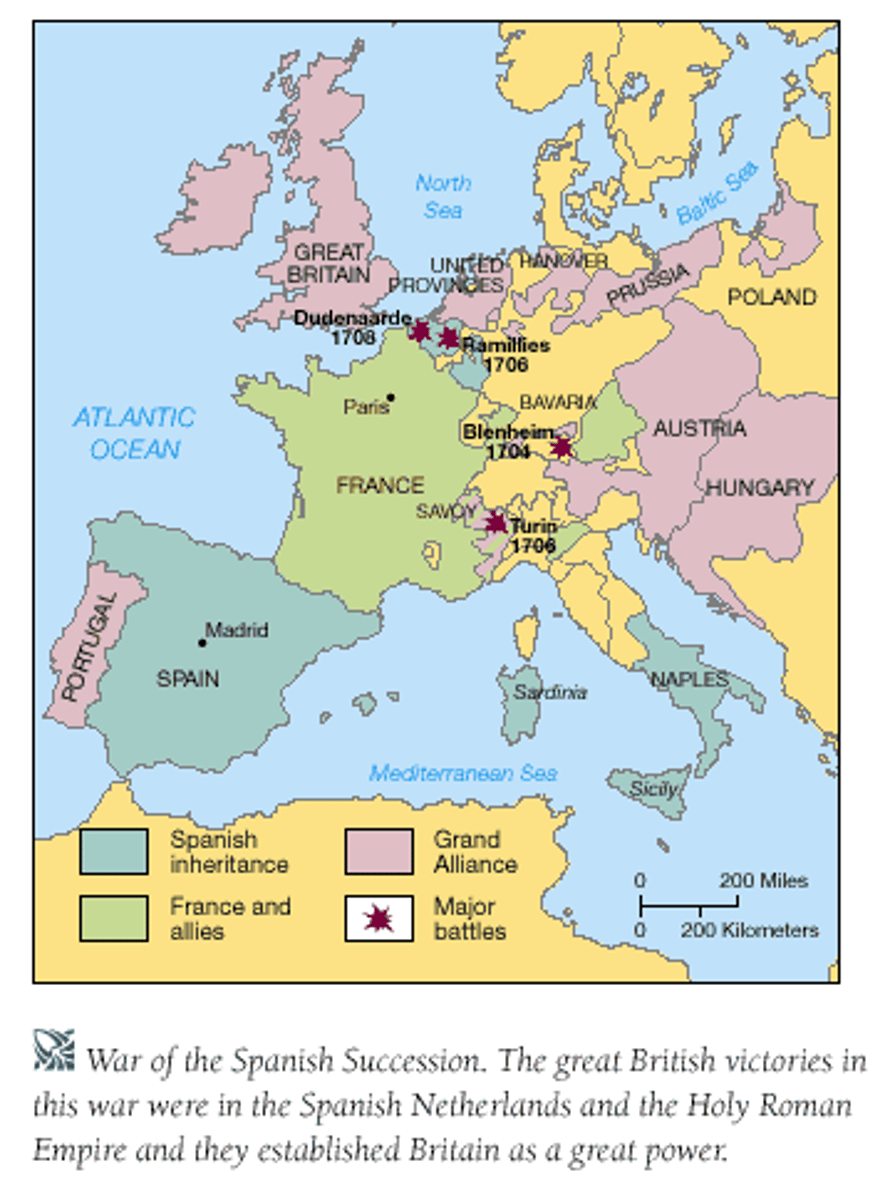
Treaty of Utrecht
1713, ended War of Spanish Succession between Louis XIV's France and the rest of Europe; prohibited joining of French and Spanish crowns; ended French expansionist policy; ended golden age of Spain; vastly expanded British Empire

Moriscos
Muslims who converted to Catholicism after the conquest of Granada to avoid being exiled

Inflation
a general increase in prices and fall in the purchasing value of money.

Serfdom
A type of labor commonly used in feudal systems in which the laborers work the land in return for protection but they are bound to the land and are not allowed to leave or to peruse their a new occupation. This was common in early Medeival Europe as well as in Russia until the mid 19th century.

Ferdinand II
Holy Roman Emperor and king of Bohemia and Hungary who waged war against Protestant forces (1578-1637)

Bohemian Estates
the largely Protestant representative body of the different estates in Bohemia. Significantly reduced in power by Ferdinand II
Vienna
Capital of Austria
Hohenzollem
German royal family who ruled Brandenburg from 1415 and later extended their control to Prussia (1525). Under Frederick I (r. 1701-1713) the family's possessions were unified as the kingdom of Prussia.
Elector
a person who has the right to vote in an election

Frederick William
(1640-1688) The "Great Elector" who built a strong Prussian army and infused military values into Prussian society.

Junkers
Members of the Prussian landed aristocracy, a class formerly associated with political reaction and militarism.
Frederick William I
(1713-1740) Calvinist; his reforms were intended to subordinate both aristocracy and peasantry to the needs of the state + subordinate needs of the states to the demands of the military; integrated economic +military structures of state; appointed only German officers to command troops, eliminating mercenaries who sold their services to the highest bidder; placed noblemen at head of locally recruited regiments; every adult male required to register for service in regiment of local landlord; by end of reign, almost 70% of state expenditures went to army, pacific foreign policy

Mongols
People from Central Asia when united ended up creating the largest single land empire in history.

Ivan the Great
(1462-1505) The Slavic Grand Duke of Moscow, he ended nearly 200 years of Mongol domination of his dukedom. From then on he worked at extending his territories, subduing the nobles, and attaining absolute power.

Muscovite
a citizen of Moscow
Boyars
Russian landholding aristocrats; possessed less political power than their western European counterparts

Third Rome
Russian claim to be successor state to Roman and Byzantine empires; based in part on continuity of Orthodox church in Russia following fall of Constantinople in 1453.
Ivan the Terrible
(1533-1584) earned his nickname for his great acts of cruelty directed toward all those with whom he disagreed, even killing his own son. He became the first ruler to assume the title Czar of all Russia.

Cossacks
Peoples of the Russian Empire who lived outside the farming villages, often as herders, mercenaries, or outlaws. Cossacks led the conquest of Siberia in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries.

Time of Troubles
followed death of Ivan IV without heir early in 17th century; boyars attempted to use vacuum of power to reestablish their authority; ended with selection of Michael Romanov as tsar in 1613.
Michael Romanov
In 1613 an assembly of nobles chose him as the new czar. For the next 300 years his family ruled in Russia (1613-1633)

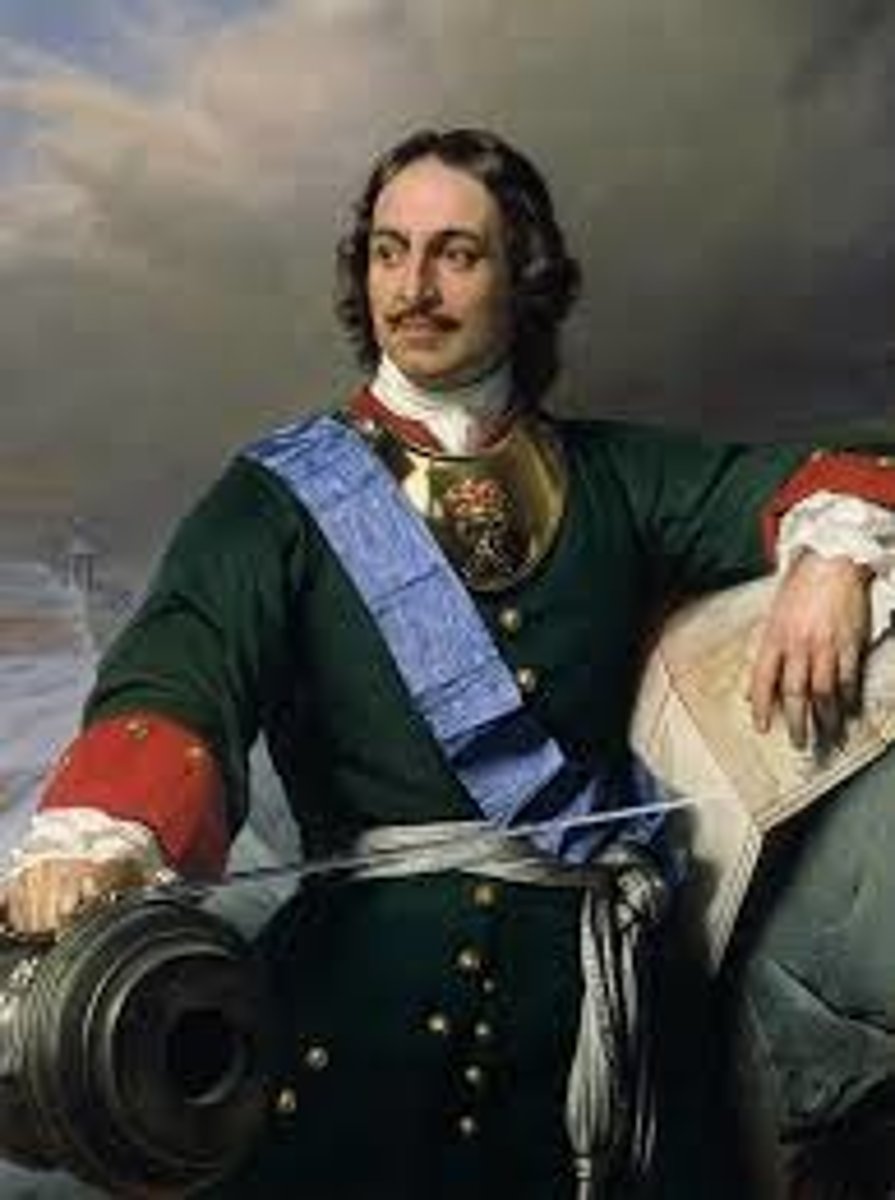
Peter the Great
(1672-1725) Russian tsar (r. 1689-1725). He enthusiastically introduced Western languages and technologies to the Russian elite, moving the capital from Moscow to the new city of St. Petersburg.

Baltic Sea
Sea in Northern Europe bordered by Scandinavian countries and Russia
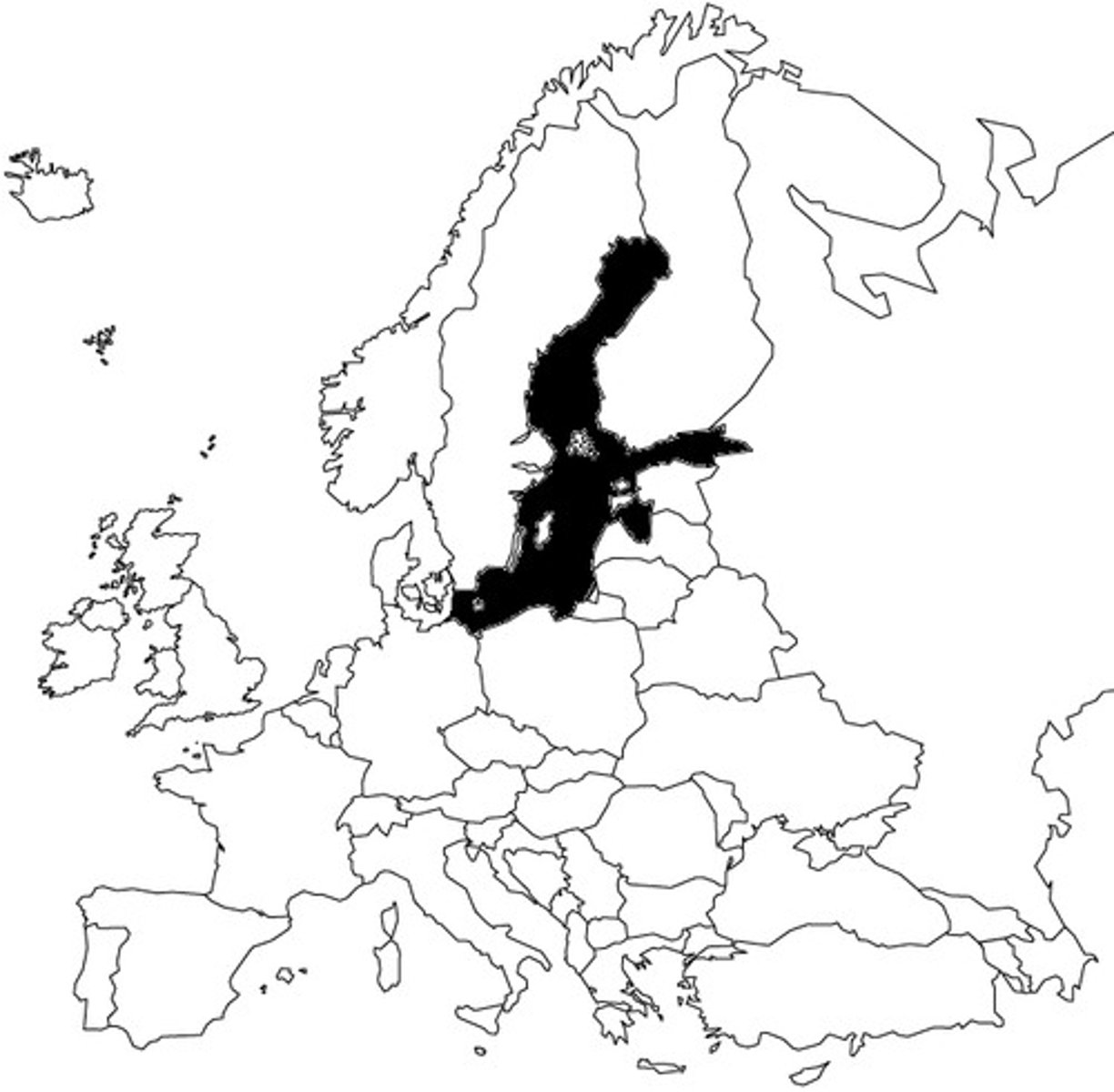
Great Northern War
Russia vs. Sweden. Russia had Poland, Denmark and Saxony as allies. Treaty of Nystad is where Russia gained Latvia and Estonia and thus gained its Window on the West in the Baltic Sea
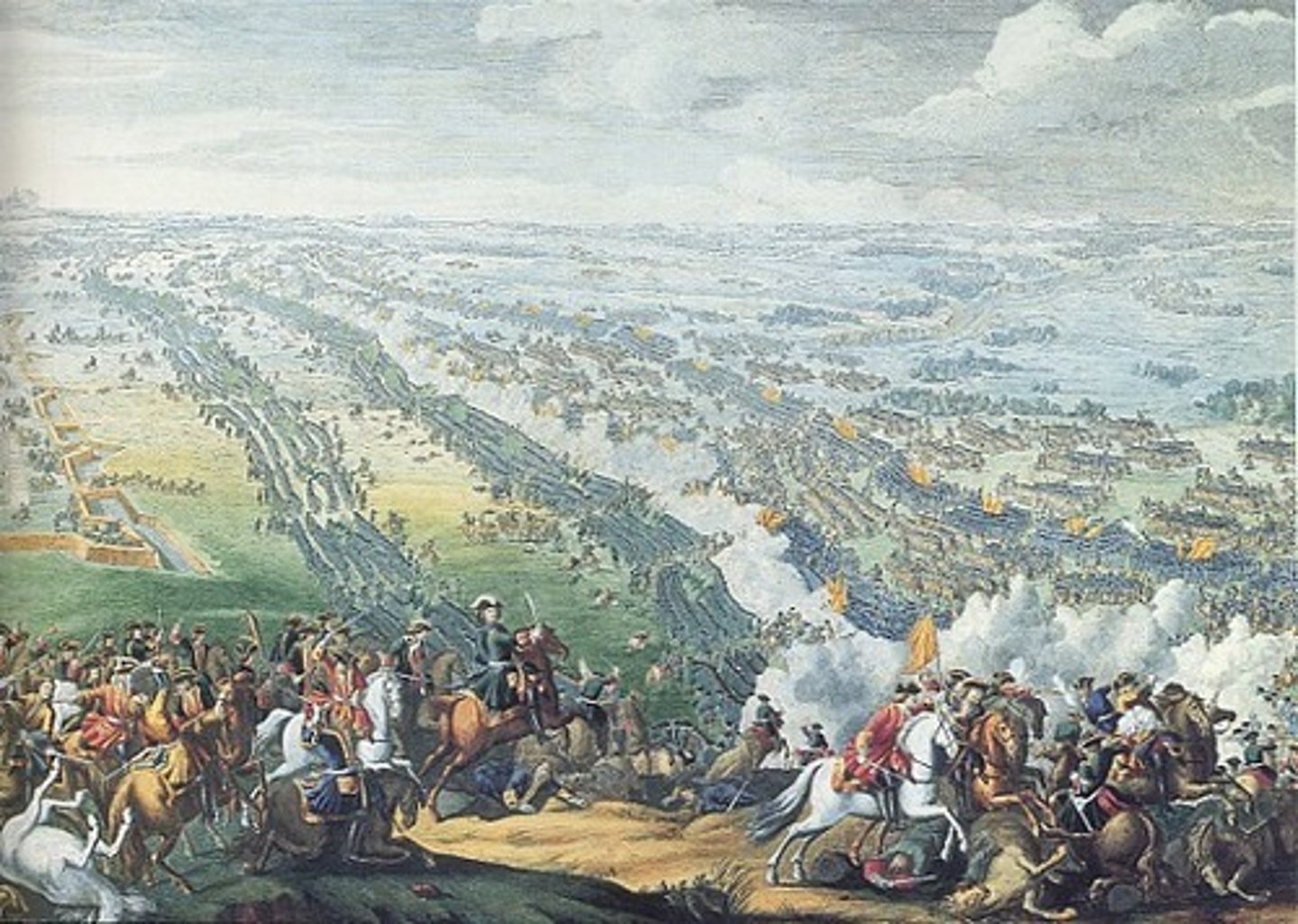
Poltava
A main and decisive battle in the Great Northern War. Afterwards there was a peace treaty and Russia formally became an empire.

St. Petersburg
Built by Peter the Great of Russia to attract europeans and to get warm water ports.
Unigenture
inheritance of land by one son alone
Sultan
"holder of power"; the military and political head of state under the Seljuk Turks and the Ottomans

Janissary corps
The core of the sultan's army, composed of slave conscripts from non-Muslim parts of the empire; after 1683 it became a volunteer force.

Millet
an administrative unit in the Ottoman Empire used to organize religious groups.
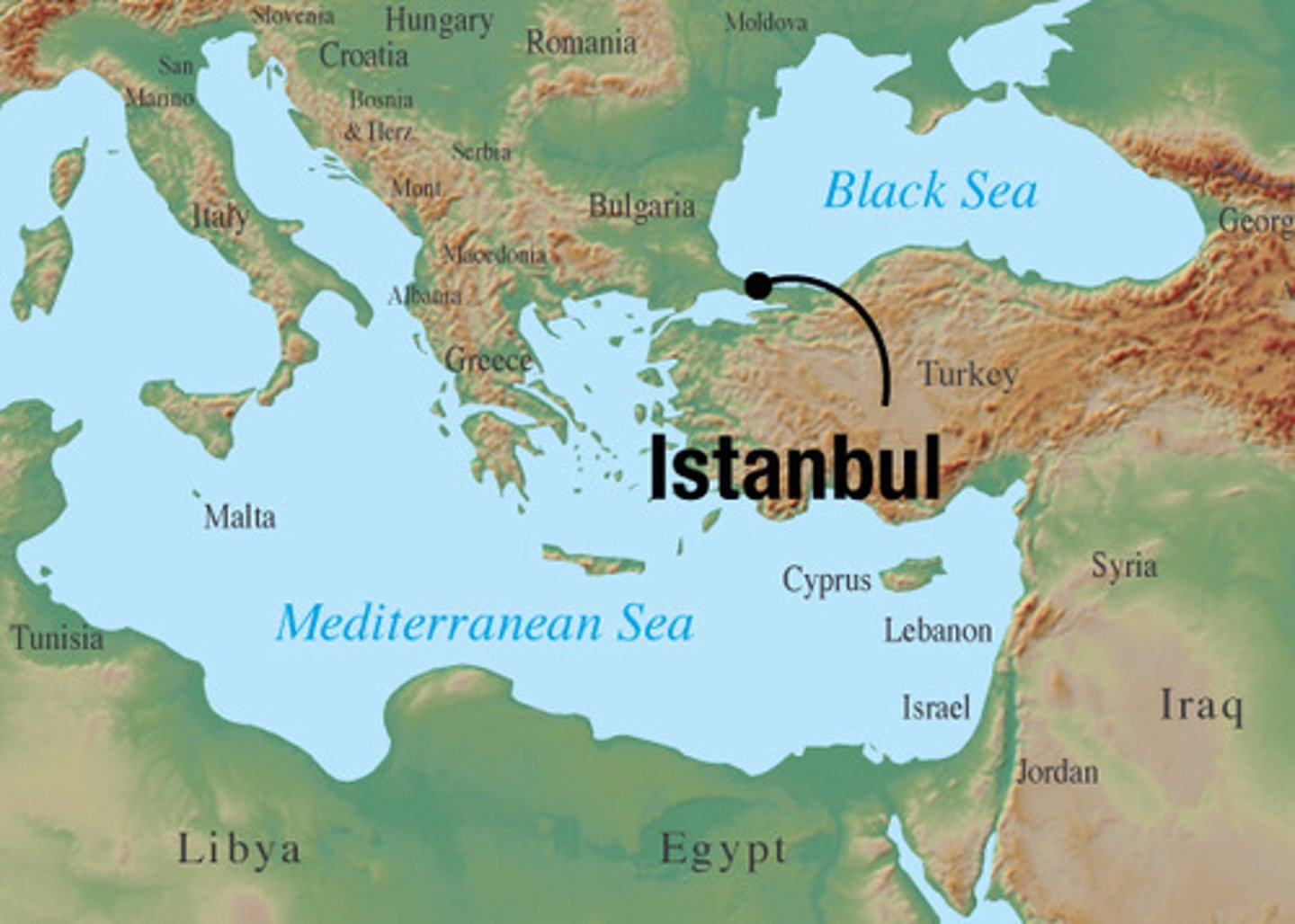
Istanbul
Capital of the Ottoman Empire; named this after 1453 and the sack of Constantinople.
Sultan Suleiman
1520-1566. the magnificent. led the ottomons in becoming the most powerful empire in the world.

Constitutionalism
Basic principle that government and those who govern must obey the law; the rule of law

Republicanism
A philosophy of limited government with elected representatives serving at the will of the people. The government is based on consent of the governed.
James I
(1603-1625) Stuart monarch who ignored constitutional principles and asserted the divine right of kings.

House of Commons
one of the houses of Parliament including wealthy landowners and rich business leaders that represent the middle class and are elected to office

Due process of law
denies the government the right, without due process, to deprive people of life, liberty, and property

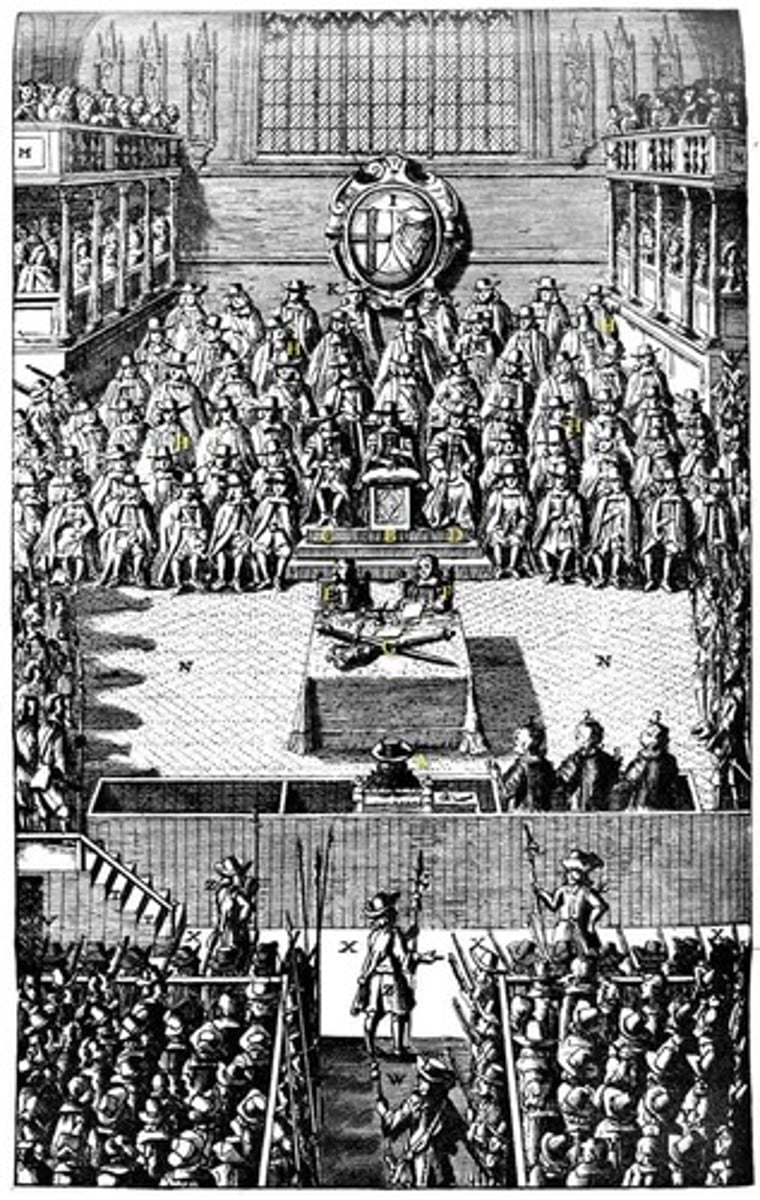
Charles I
King of England, Scotland, and Ireland (1625-1649). His power struggles with Parliament resulted in the English Civil War (1642-1648) in which Charles was defeated. He was tried for treason and beheaded in 1649
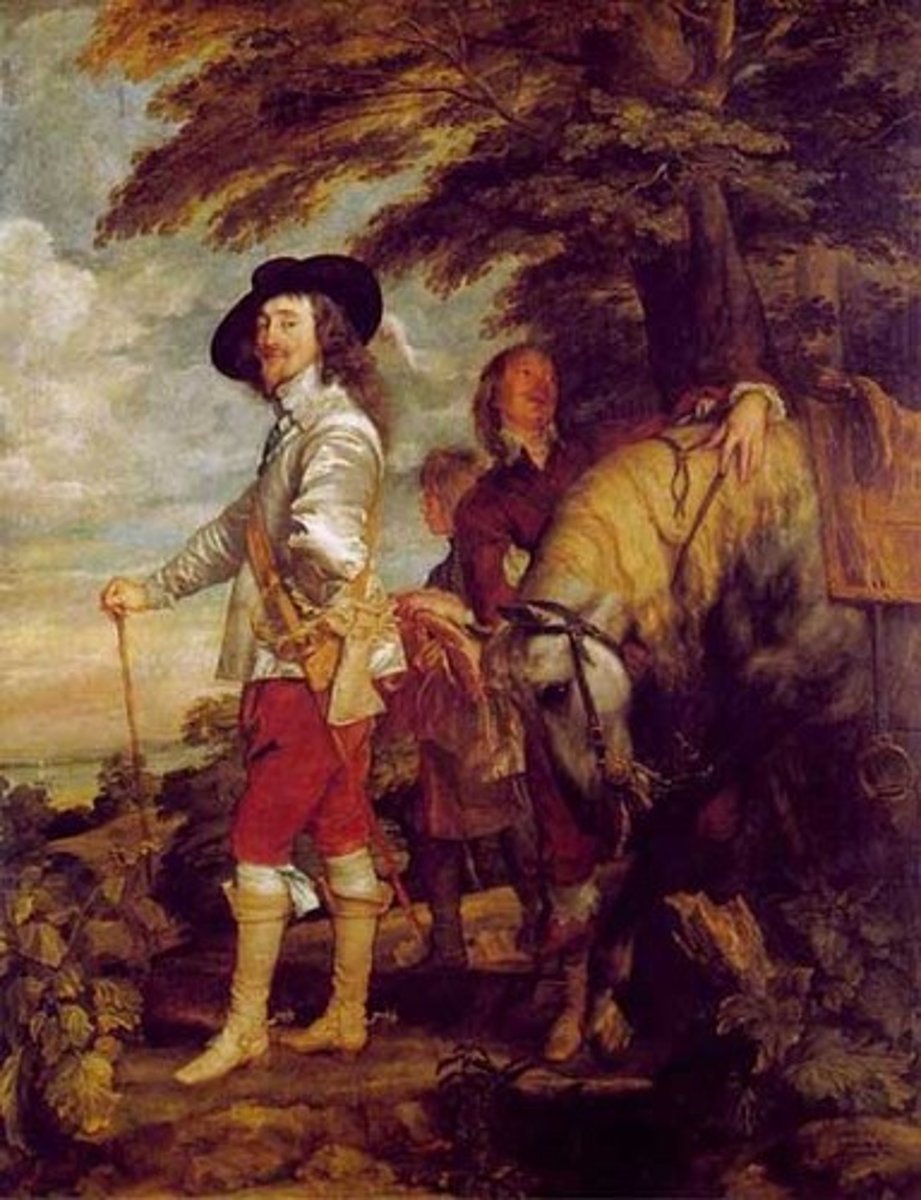

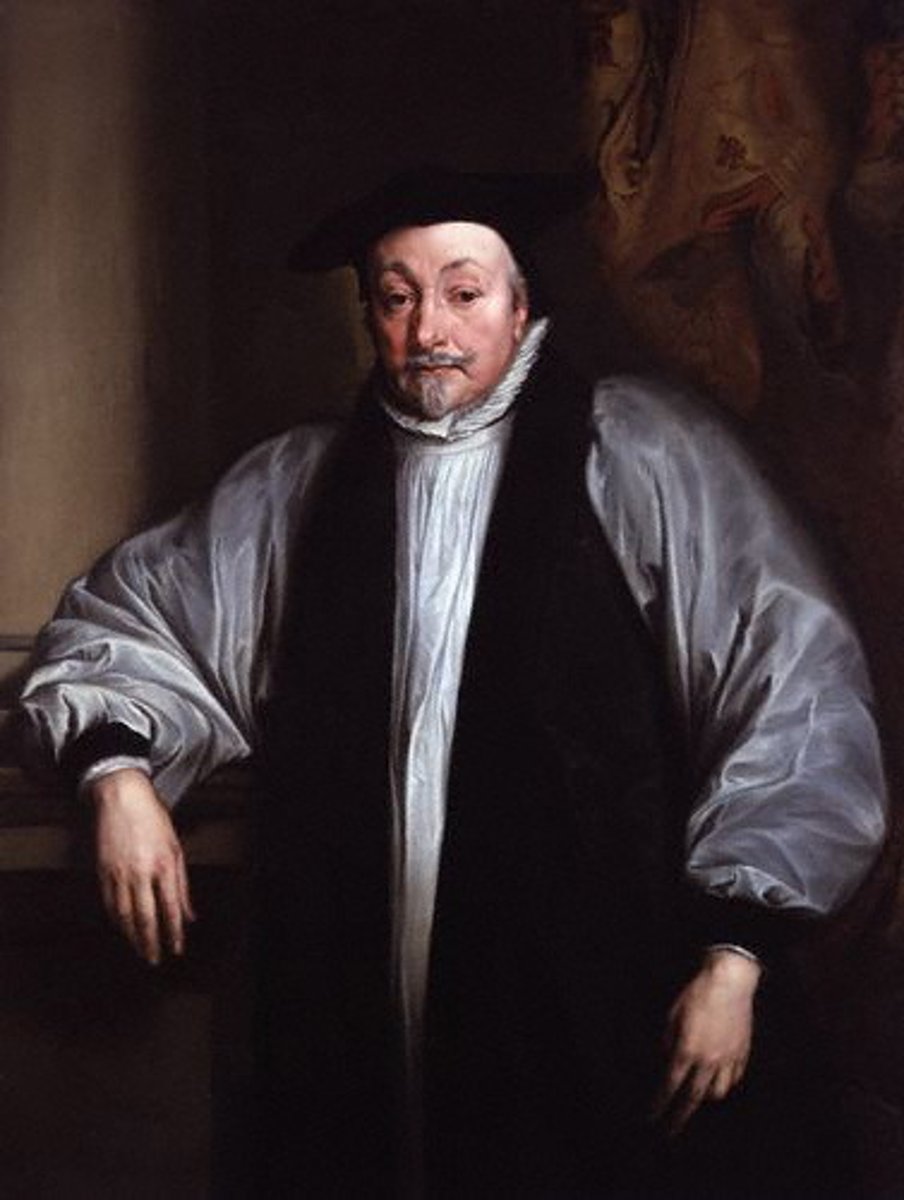
William Laud
Archbishop of Canterbury under Charles I in England. He tried to force the Scottish to use the English Book of Common Prayer. He was later executed by Parliament during the English Civil War.

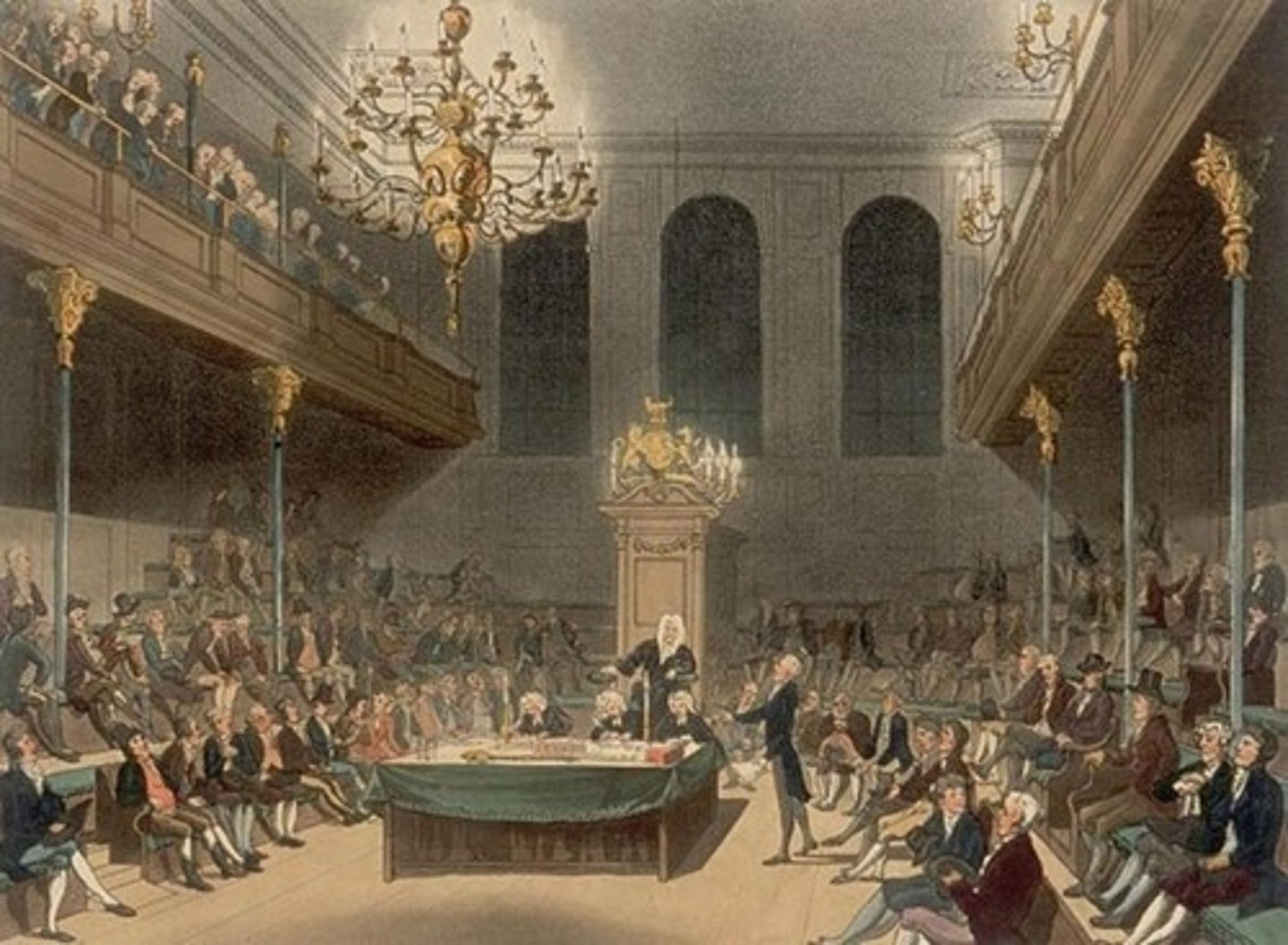
Long Parliament
(1640-1648) desperate for money after Scottish invasion of northern England-Charles finally agreed to demands by Parliament: Parliament could not be dissolved w/o its own consent; had to meet a min. of once every 3 years; ship money abolished; leaders of persecution of Puritans to be tried and executed; Star Chamber abolished; common law courts supreme to king's courts; refused funds to raise army to defeat Irish revolt-Puritans came to represent majority in Parliament

New Model Army
The disciplined fighting force of Protestants led by Oliver Cromwell in the English civil war.

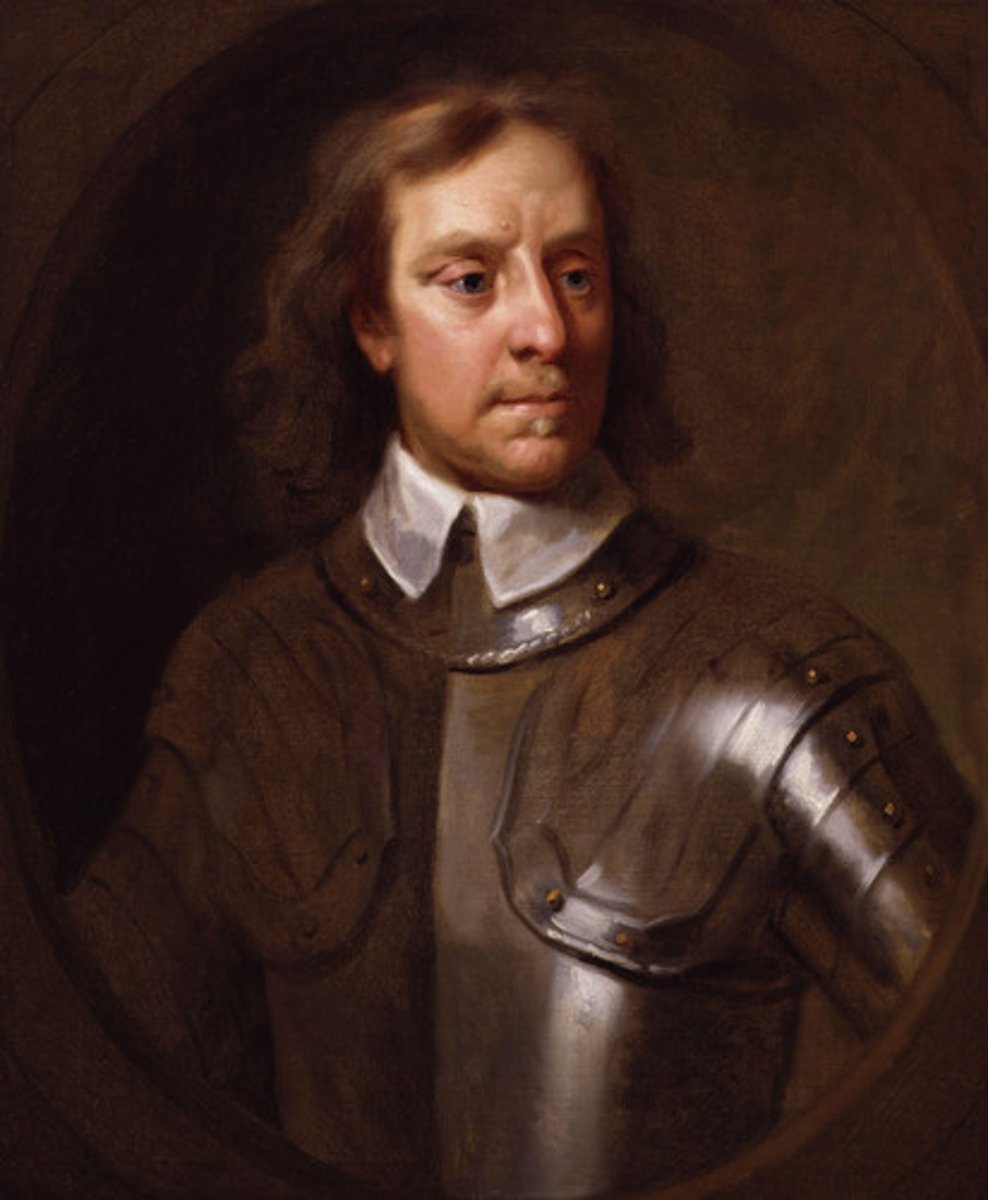
Oliver Cromwell
English military, political, and religious figure who led the Parliamentarian victory in the English Civil War (1642-1649) and called for the execution of Charles I. As lord protector of England (1653-1658) he ruled as a virtual dictator.

Rump Parliament
The Cromwell-controlled Parliament that proclaimed England a republic and abolished the House of Lords and the monarchy.

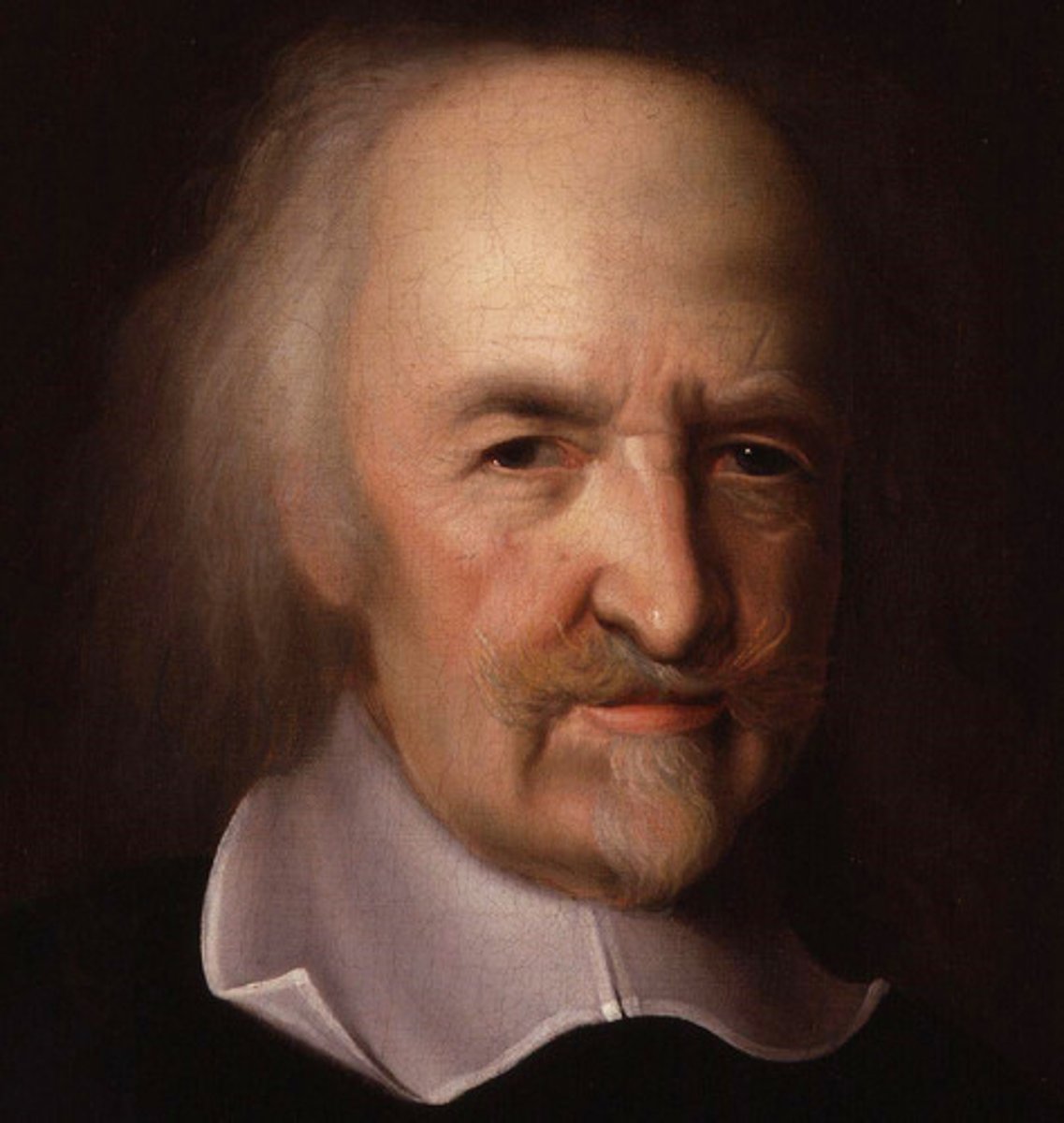
Thomas Hobbes
English materialist and political philosopher who advocated absolute sovereignty as the only kind of government that could resolve problems caused by the selfishness of human beings (1588-1679)

Social contract
A voluntary agreement among individuals to secure their rights and welfare by creating a government and abiding by its rules.
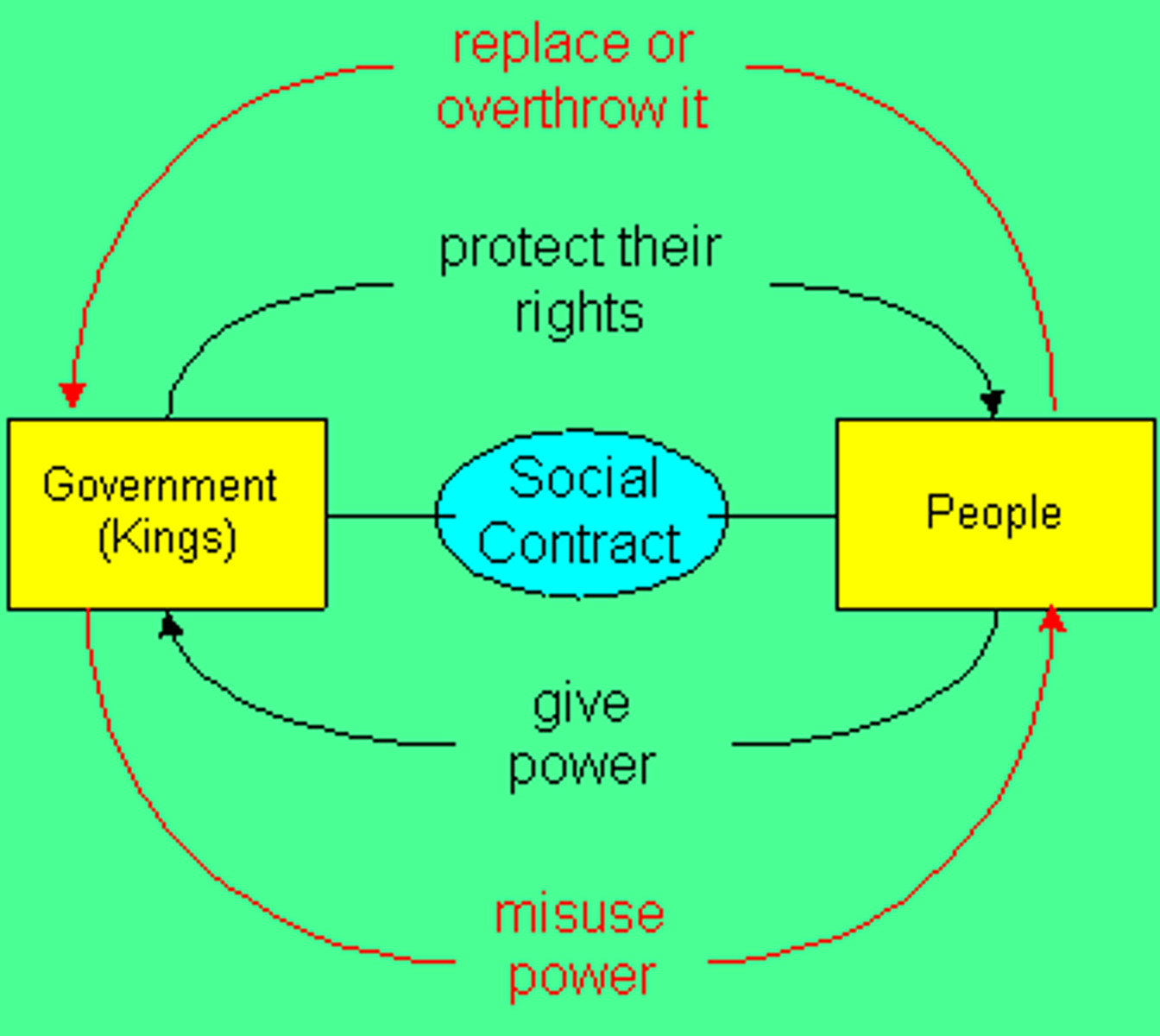
Protectorate
A country whose affairs are partially controlled by a stronger power.
Navigation Act
British regulations designed to protect British shipping from competition. Said that British colonies could only import goods if they were shipped on British-owned vessels and at least 3/4 of the crew of the ship were British.
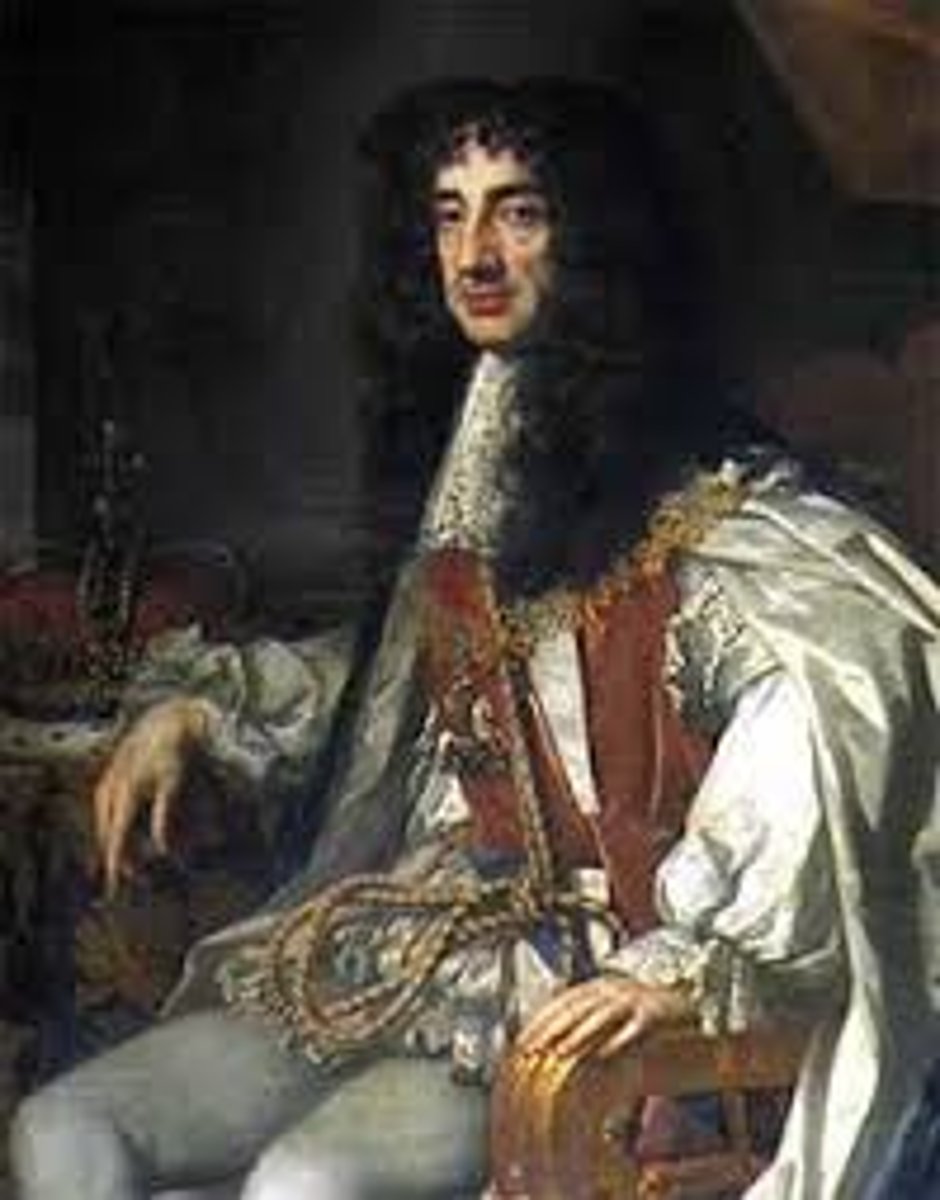
Charles II
King of England, Scotland, and Ireland (1660-1685) who reigned during the Restoration, a period of expanding trade and colonization as well as strong opposition to Catholicism

Test Act
An act forbidding anyone except members of the Church of England from holding political office or entering the professions
William of Orange
Dutch prince invited to be king of England after The Glorious Revolution. Joined League of Augsburg as a foe of Louis XIV.
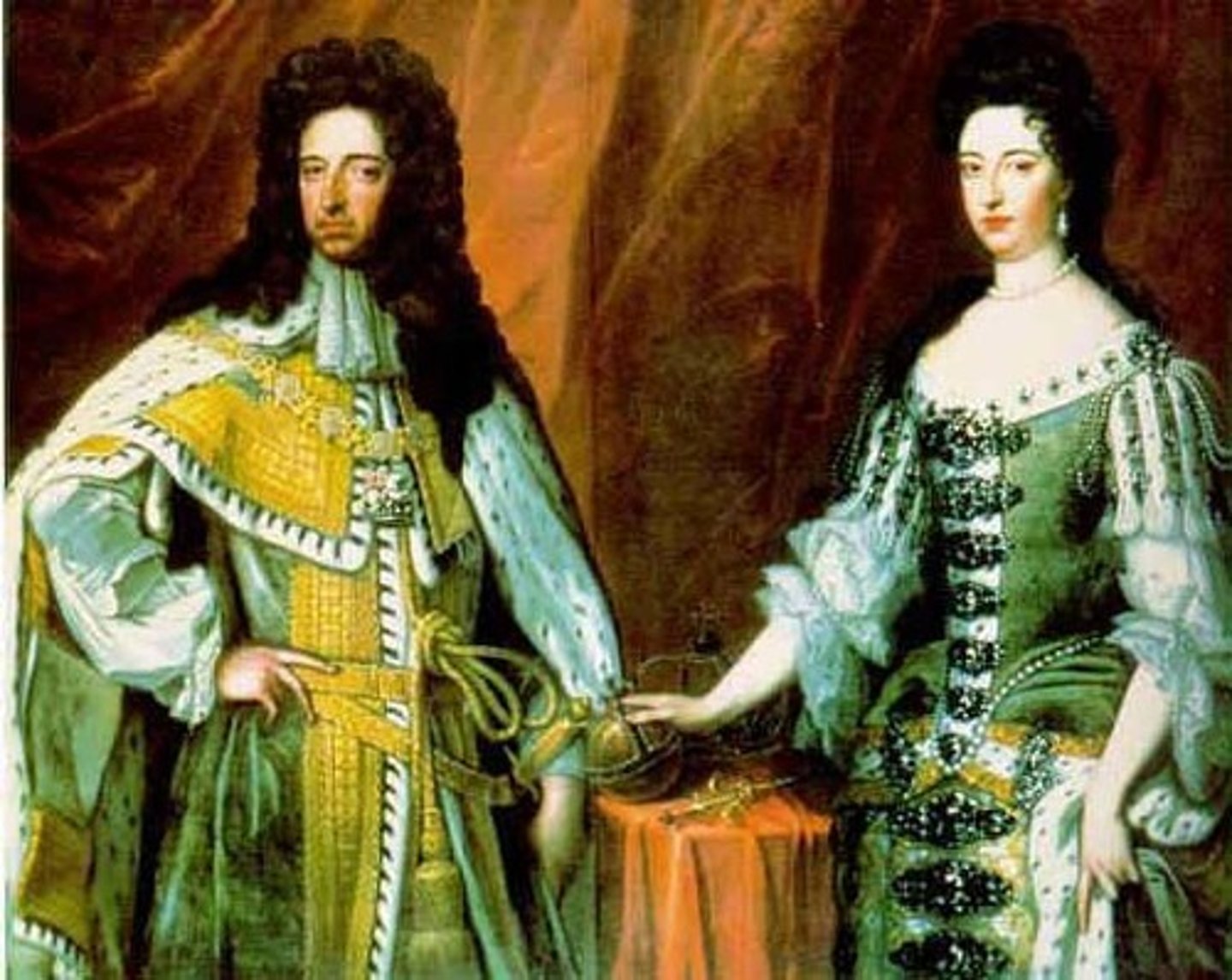

Glorious Revolution
A reference to the political events of 1688-1689, when James II abdicated his throne and was replaced by his daughter Mary and her husband, Prince William of Orange.

John Locke
17th century English philosopher who opposed the Divine Right of Kings and who asserted that people have a natural right to life, liberty, and property.

Robert Walpole
Prime minister of Great Britain in the first half of the 1700s. His position towards the colonies was salutary neglect.

Regent
a person who governs in place of a ruler who is ill, absent, or still a child; ADJ. Ex. the Prince regent
States General
term used by the national assembly of the United Provinces of the Netherlands where the wealthy merchant class held real power; because many issues had to be refereed back to the provinces, the United Provinces was a confederation, or weak union of a strong states.
Holland
Another name for the Netherlands

Stadtholder
a nobleman who represented the king in one or more provinces
House of Orange
Leaders of most of the 7 provinces of the Dutch Republic, favored development of a centralized government with themselves as hereditary monarchs
Baroque
An artistic style of the seventeenth century characterized by complex forms, bold ornamentation, and contrasting elements

Peter Paul Rubens
is the most famous Baroque artist who studied Michelangelo in Italy and took that Renaissance style to the next level of drama, motion, color, religion and animation, which is portrayed in his paintings

Johann Sebastian Bach
Baroque composer
