3) Crystal Defects
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Give the equation for change in energy caused by vacancies
U = ε_f N; ε_f = vacancy formation energy; N = number of vacanies
Why don’t perfect crystals form
imperfections increase the entropy o
Give the equations for entropy
S = kln(g); g = (Na + Nv)!/(Na!Nv!); Na = number of atoms; Nv = number of vacancies
Give the equation relating energy to vacancy formation
Nv/(Na + Nv) = exp(-ε_f/kT); ε_f = vacancy formation energy
Give the equation for free energy and what happens at eqm
U-TS; at eqm d(U-TS)/dNv = 0
Interstitial atoms
atom not on lattice site; adopts site with largest free volume; pushes neighbours slightly costing energy
How does weak atomic bonding affect vacancy formation
easier for vacancies/interstitials to form; less E required to overcome E loss of bonds
How does density affect interstitials
low density makes it easier for interstitials to form; more space for it to sit
What are substitutional impurities
different atoms replaces native atom on a site; requires similar size and chemistry
Give the equation for the formation of point defects
N_eq = nt exp(-ε_f/kT); N_eq = defects at eqm; nt = lattice sites; ε_f = formation energy
Describe the diffusion of point defects
diffusion low in solids; defects have higher E; easier to escape and diffuse; controlled by bond strength
Interstitial displaces a native atom becoming a substitution is more likely to occur when:
interstitial E of native atom < impurity; subs E of impurity < native atom
Interstitial diffuses into another interstitial site is more like occur when
large free volume in the lattice structure; impurity is smaller than native atom
Give the equation for Ficks law of diffusion
D = A exp(-ε_a/kT); D = diffusion rate (m²/s); ε_a = activation energy; A = prefactor (depends on diffusion distance, lattice, vibrations etc)
How can defects aggregate
vacancy and interstitial annihilate; vacancies aggregate forming large voids; interstitials aggregate forming high density regions
Why might defects aggregate
double vacancy breaks fewer bonds so more energetically favourable; but requires atoms with fewer interactions (not favourable); double interstitials disrupt fewer atoms; hindered by diffusion; aggregation requires work
Describe defects in an ionic structure
substitutions must be of same charge; imbalance of charge is not energetically favourable; interstitial sites are v limited as ions must have opposite charge to neighbours
What is Kroger Vink terminology
M^C_S; M = species (atoms, vacancies, e or h); C = resulting charge (.=+ve, ‘=-ve); S = lattice occupied (atom or i)
Charge neutral pairs
ceramics need to be neutral; formation of a charged defect will require one of opposite charge too
Schottky pairs
anion and cation vacancy
Frenkel pairs
anion/cation vacancy and same interstitial
How is diffusion of defects different in ceramics
dominated by energy of coulomb repulsion
Clustering
multiple defects (of opposite charge) aggregate together inducing large relaxations in surrounding lattice; if enough can form effectively different lattice (and phase separation); likelihood influenced by strength of attraction (size, charge, mobility)
What makes clustering more likely in ceramics
greater difference between defect and lattice; but harder to form defects due to larger activation energy
How can defects affect lattice strain
inbuilt strain from large/small ions can be relieved by defects if of a better size for the site
Give the equation for gibbs free energy
G = U + PV - TS; lower G is more favourable
U
sum of internal energies; find lowest energy arrangement of atoms; maximise low energy interactions; clustering defects to reduce loss of bonds
PV
generally small; crystals dont compress or expand much
TS
disordered system has higher entropy; prefers no clustering
What factors govern mixing in solid solutions
same as defects: similar sized cations have greatest solubility
Vergards law
lattice parameter is weighted mean of components lattice parameter; rarely accurate (better in ordered systems) as atoms not linearly interpolatable
Vergards law equation
a = xA aA + (1-xA)aB; xA = mole fraction of A present; aA/B = lattice parameter of A/B
List the larger defects found in crystals
stacking faults; voids; grain boundaries; twin boundaries (two orientations); dislocations
Stacking faults
disruption in layers; fcc/ccp: missing layer (intrinsic) or extra layer (extrinsic)
What are dislocations
line defects in crystal created by natural shear within crystal; separates slipped and unslipped region
Slip
one crystal plane slides over another
Slip plane
crystal plane on which the slip occurs; its the plane separating the two perfect crystals that slips; normally highest atom density (close packed planes)
Line vector
t; vector along dislocation line; +ve when looking along the line
Burgers vector
shows slip caused by dislocation movement; want as small as possible to minimise energy; must be conserved
How to define a Burgers vector
draw a RH loop around the disloc along atom bonds; draw same loop on a perfect crystal; b vector joins end to start on the perfect lattice
A burgers vector of an edge dislocation is
perpendicular to the dislocation line
A burgers vector of a screw dislocation is
parallel to the dislocation line
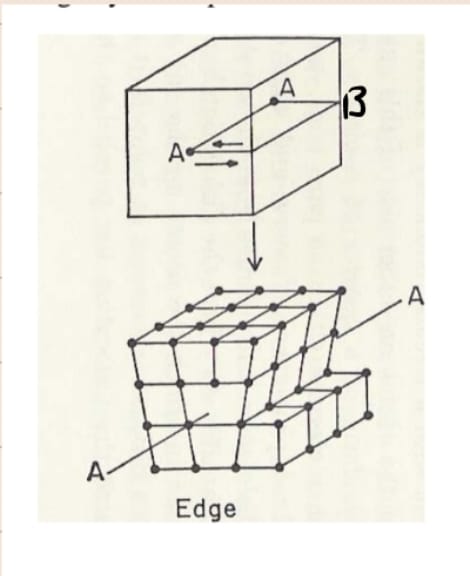
Use this image to explain how an edge dislocation forms
slice from edge to line AA; apply shear force perpendicular to the slice in opposite directions at top and bottom; AA is the dislocation line and AABB is the slip plane
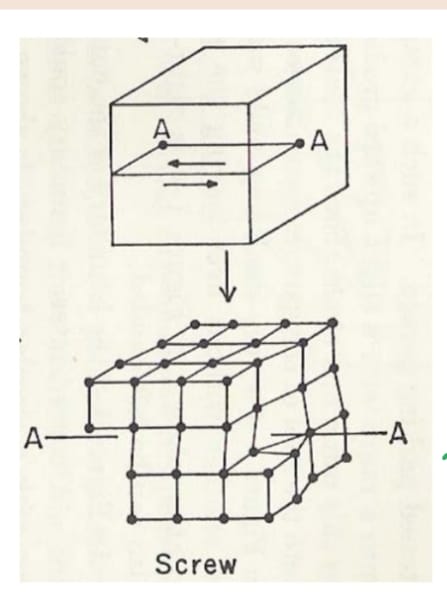
Use this image to explain how a screw dislocation forms
slice from edge to line AA; apply shear force parallel to line of dislocation (AA); slip plane is AABB
What are mixed dislocations
when disloc forms a loop or ends on two perpendicular edges; at one edge stress is perpendicular to the dislocation line (edge disloc); at the other edge stress is parallel to dislocation line (screw disloc); in between it is mixed
What happens to dislocations at a boundary
must end at a surface (or loop) to conserve Burgers vector; collecting together can form a low angle boundary
How do dislocations affect lattice stress
can relieve stress from lattice mismatches; shift the atoms to reduce distortion lowering the energy
What is glide
dislocation motion in the slip plane; edge dislocations glide in their plane; screw dislocations can cross slip to another plane
Sessile dislocations:
cannot glide
Glissile dislocations
can glide
What is slip
movement of many dislocations resulting in permanent deformation; concentrated in slip bands
What is a slip system
slip plane+direction; specific to crystal system
Wide dislocation core =
distortion spread over larger area; lower energy to move as less lattice distortion; plastic deformation easier
Wide space slip planes
atoms have more space to move without repulsion from neighbours; lower energy for movement
Describe the slip systems in fcc
close packed on the {111} planes; there are 4 of these planes and 3 slip directions on each one so 12 slip systems; fcc tends to be soft
What are partial dislocations
sometimes favourable to slip in smaller steps; AB stacking: B moves onto C site instead of another B; lower energy to move; causes stacking fault; two partials
Describe the energetics of dislocations
b vectors are conserved; dislocations can combine (or annihilate) or split
Give the equation for Franks rule for elastic energy of a dislocation
E = alpha Gb²; alpha=parameter:0.5-1; G = shear modulus; b=burgers vector
What is the condition for it to be energetically favourable for a dislocation to split
b1² > b2² + b3²; splitting reduces energy
What is the condition for it to be energetically favourable for dislocations to combine
b1² < b2² + b3²; combining reduces energy
What is cross slip
screw disloc moves to a different slip plane due to local stresses; as line and burgers vectors are parallel there are infinite planes containing both (an edge dislocation cannot do this)
What is climb
edge dislocation moves up or down a plane by gaining a vacancy (moves up) or extra atom (moves down)
What is a dislocation lock
a sessile disloc; two dislocs on different glide planes intersect producing a b vector that doesnt allow glide along either plane