Visual field
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Q: Where is visual sensitivity greatest?
A: In the center, decreasing toward the periphery
Q: Give an example of a generalized visual field defect A: Retinitis pigmentosa
Q: Give an example of a localized visual field defect A: Central scotoma from AMD
Q: What is a scotoma? A: An area of depressed visual function (central, paracentral, cecocentral)
Q: What is a sector-shaped defect? A: From small scotomas to complete sector loss (e.g., nasal optic disc defects)
Q: What is an altitudinal defect? A: Affects superior/inferior quadrants, respecting the horizontal meridian
Q: What is an arcuate defect? A: Narrow temporally, spreading nasally (e.g., glaucoma)
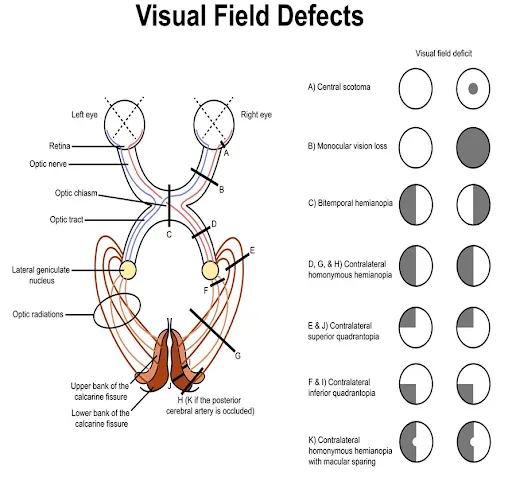
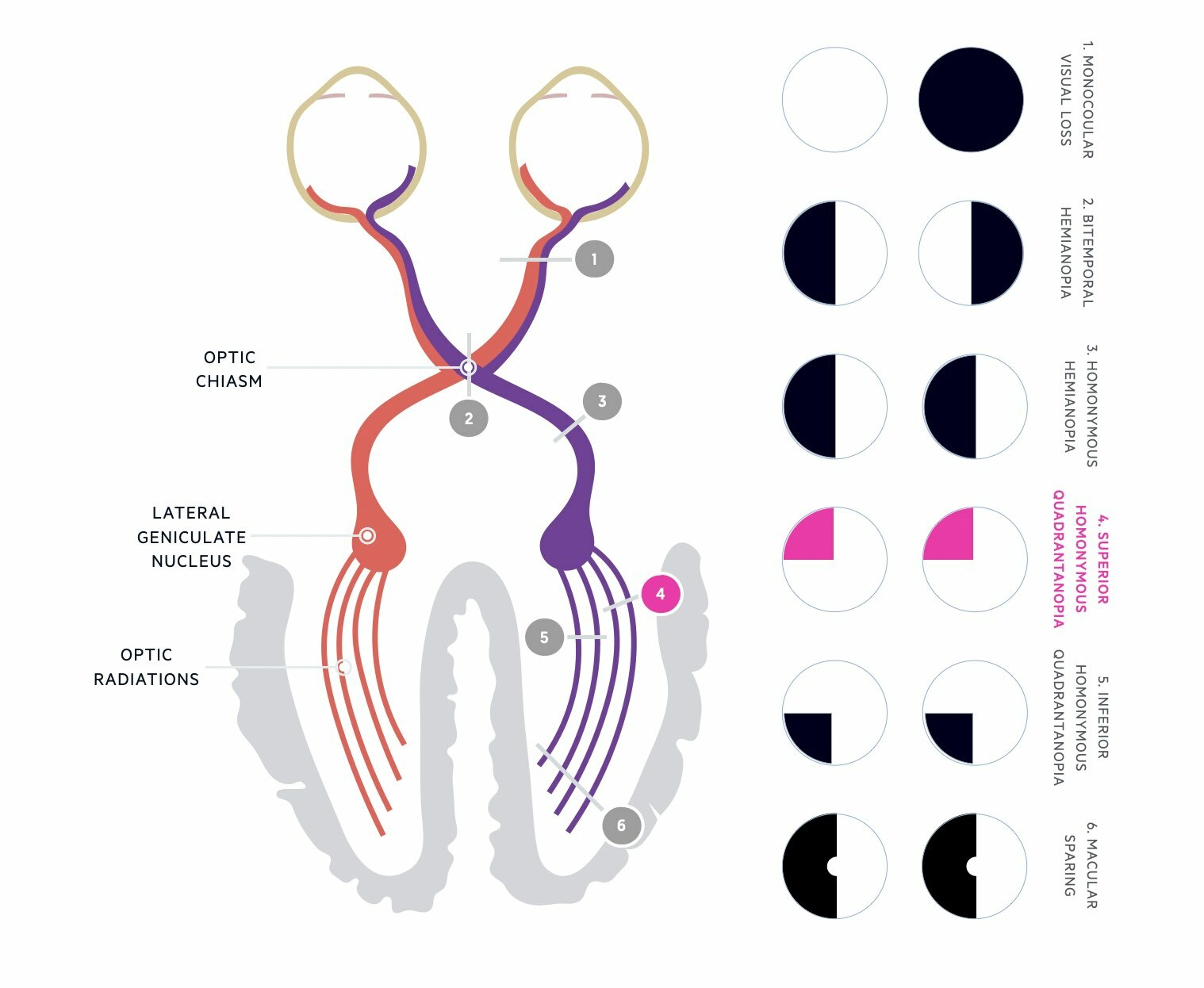
Q: What is hemianopia? A: Loss of one half of the visual field (homonymous or heteronymous)
Q: What is bitemporal hemianopia? A: Temporal loss of both eyes, usually involving the chiasm (e.g., pituitary tumor)
Q: What is quadrantanopia? A: Defects in one quadrant of the visual field
Q: List common causes of retinal defects
Congenital (e.g., coloboma)
vascular (e.g., ischaemia), inflammation (e.g., uveitis)
hereditary (e.g., retinitis pigmentosa)
systemic (e.g., MS), degeneration (e.g., retinal detachment)
Q: List some causes of optic disc/nerve pathology
A: Congenital issues, neuropathy (e.g., optic neuritis), oedema, tumors, glaucoma
Q: What types of visual field defects can result from optic disc/nerve pathology? A: Scotomas, arcuate defects, or complete unilateral VF loss
Q: What pathologies can affect the optic chiasm and what visual field defects do they cause?
A: Pituitary tumors (causing bitemporal hemianopia) or aneurysms, causing characteristic visual field defects (junctional scotoma)
Q: What type of visual field defects do optic tract lesions cause?
A: Homonymous hemianopias, often asymmetric (incongruous defects)
Q: What is the function of the LGB in the visual pathway?
A: It's the first synapse for retinal fibers
Q: What types of visual field defects can LGB lesions cause?
A: Sector-shaped defects or hemianopias, often affecting the macula
Q: How are optic radiations divided?
A: Into superior and inferior groups
Q: What type of visual field defects do optic radiation lesions cause?
A: Quadrantanopias, often due to temporal/parietal/occipital lobe damage
Q: What types of visual field defects do visual cortex pathologies produce?
A: Congruous VF defects (hemianopias, keyhole defects, macular sparing)
Q: What are common causes of visual cortex pathologies?
A: Vascular lesions, trauma, tumors
Q: What is Static Perimetry?
A: Measures retinal sensitivity using stationary lights
Q: What is Kinetic Perimetry?
A: Moving stimuli from non-seeing to seeing areas to map visual fields
Q: What are some examples of Automated Perimetry devices?
A: Octopus 900, Humphrey, Goldman
Q: What is Confrontation testing?
A: Manual tests (finger counting, hat pin method)
Q: What are some key steps in performing automated perimetry?
A: Ensure glasses are removed, calibrate machine, and maintain head/eye position
Q: How do kinetic and static tests differ in automated perimetry?
A: Kinetic tests map points seen by the patient; static tests vary brightness to assess sensitivity
Potential Artefacts in Visual Field Testing
Q: What factors can interfere with visual field test results? A: Lenses, cataracts, pupil irregularities, and poor positioning
Confrontation Testing
Q: What is confrontation testing and how is it performed? A: It's a simple bedside method using finger counting