chem things i keep forgetting
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
alpha decay
emission of 4/2 He
beta decay
neutron becomes a proton
positron emission
1/1 proton —> 1/0 neutron + beta+ particle
electron capture
proton absorbs e- and becomes a neutron
gamma decay
emission of energy
What species undergo alpha decay?
atomic number > 83
What species undergo beta decay?
n:p ratio high
What species undergo positron emission?
n:p low, light nuclei
What species undergo electron capture?
n:p low, heavy nuclei
What species undergo gamma decay?
most nuclear decays are gamma
If rate quadruples when concentration doubles…
the reaction is second order
If rate doubles when concentration doubles…
the reaction is first order
If the rate does not change when concentration is doubled…
the reaction is zeroth order
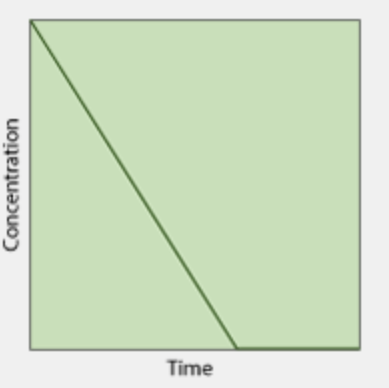
What is the order of this concentration vs time graph?
zeroth order
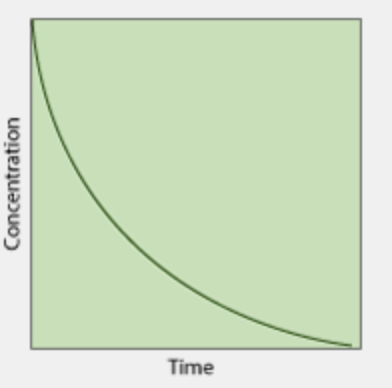
What is the order of this concentration vs time graph?
1st order
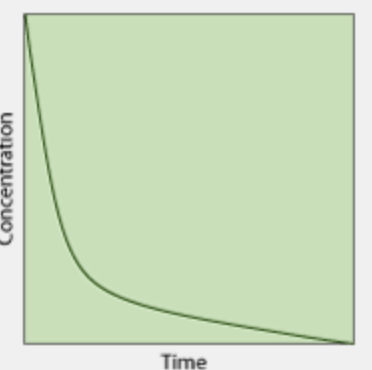
What is the order of this concentration vs time graph?
2nd order
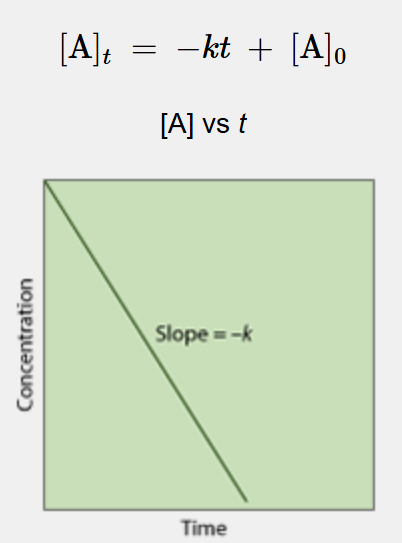
What is this a linearization of?
zeroth order reaction
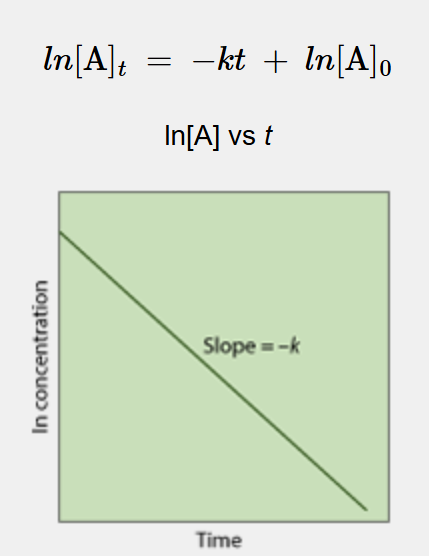
What is this a linearization of?
1st order reaction
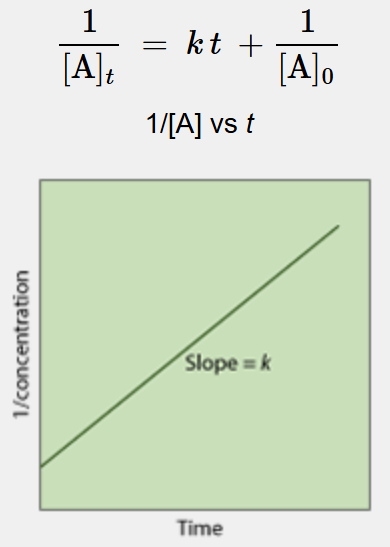
What is this a linearization of?
2nd order reaction
microstate
a specific microscopic configuration of a system; more microstates = more entropy
delta S and qrev
delta S = qrev/T = delta H/T
standard/absolute entropy
the entropy value for the standard state of a species; standard state elements S=/= 0
How do you predict boiling point using ghost equation?
delta G = 0 so delta H =T * delta S
Keq = Q
equlibirum
Keq > Q
rxn will shift right
Keq < Q
rxn will shift left
strong acids
HClO4, HClO3, HBr, HCl, HI, HNO3, H2SO4
strong bases
Ba(OH)2, Ca(OH)2, CsOH, LiOH, KOH, RbOH, NaOH, Sr(OH)2
higher charge and smaller size makes…
a better Lewis acid
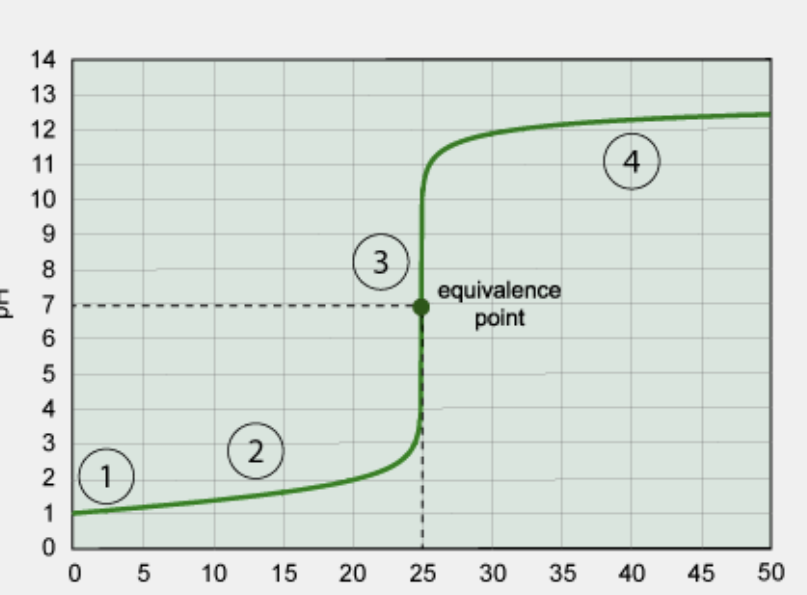
What kind of titration is this?
strong acid/strong base
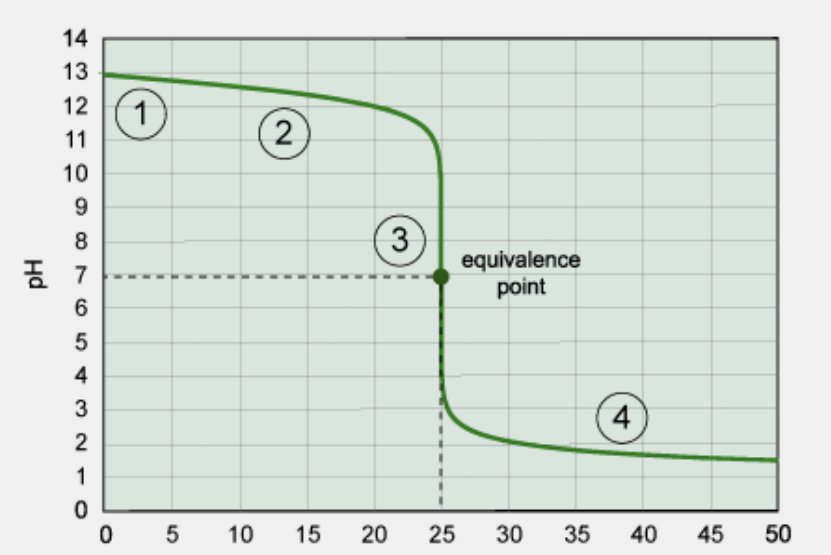
What kind of titration is this?
strong base/strong acid
Titration at any point
ICF, divide by Vtot to find molarity if needed
Acid/Base dissociation equilibria
ICE
n AOs
= n MOs
sigma bonds
e- density on internuclear axis
pi bonds
e- density above and below internuclear axis
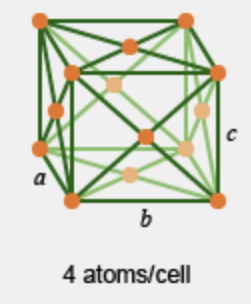
What crystalline cell is this?
face centered cubic; CN = 12
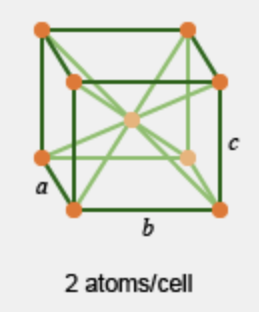
What crystalline cell is this?
base centered cubic; CN = 8
atomic/molecular solids
low BP/MP; van der Waals/LDF
network covalent solids
High BP/MP; covalent bonds
ionic solids
Highest BP/MP; electrostatic attraction
metallic solids
metallic bonding
for complexes: Kf > Q
shift R; soluble
for complexes: Kf < Q
shift left; insoluble
field splitting energy…
is in Joules/photon
unpaired d shell e-…
means the complex is colored and influenced by a magnetic field
m = ItM/nF
mass plated = current x time x molarity / # of e- x Faraday’s constant
arrhenius acid
acid that increases the H+ concentration of a solution
lewis acid
acid that accepts lone pairs of electrons
bronsted-lowry acid
acid that dissolves and releases protons
nuclear activity
activity = initial activity x (0.5)^(t/t1/2)