Unit 3: Cultural Patterns and Processes
1/76
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Artifact
The material manifestation of culture, including tools, housing, systems of land use, clothing, etc. "What a culture uses"
Mentifact
The central, enduring elements of a culture expressing its values and beliefs, including language, religion, folklore, and etc. "What a culture believes"
Sociofact
The institutions and links between individuals and groups that unite a culture, including family structure and political, educational and religious institutions. "What a culture does"
Acculturation
the modification of the social patterns, traits, or structures of one group or society by contact with those of another
Adopting parts of one culture while maintaining your own cultural traits
Assimilation
process in which a minority group or culture comes to resemble a dominant group or assume the values, behaviors, and beliefs of another group

Syncretism
the combining of different cultural traits/ beliefs, or blending practices of various schools of thought.
Multiculturalism
when various ethnic groups coexist with one another without having to sacrifice their particular identities
Cultural Traits
a characteristic of human action that's acquired by people socially and transmitted via various modes of communication. Culture has five basic characteristics: It is learned, shared, based on symbols, integrated, and dynamic.
Cultural Relativism
the idea that a person's beliefs, values, and practices should be understood based on that person's own culture, rather than be judged through the eyes of another culture
Ethnocentrism
judging people or traditions based on your own cultural standards
Cultural Landscape
landscapes that have been affected, influenced, or shaped by human involvement......the visible imprint of human activity and culture on the landscape....Architecture, language on signs, religious institutions, restaurants, types of stores, etc

Convergence
when two cultures become more similar because of frequent interactions
Divergence
when a culture splits into different cultures because of lack of interaction
Globalization
the growing interdependence of the world's economies, cultures, and populations, brought about by cross-border trade in goods and services, technology, and flows of investment, people, and information.

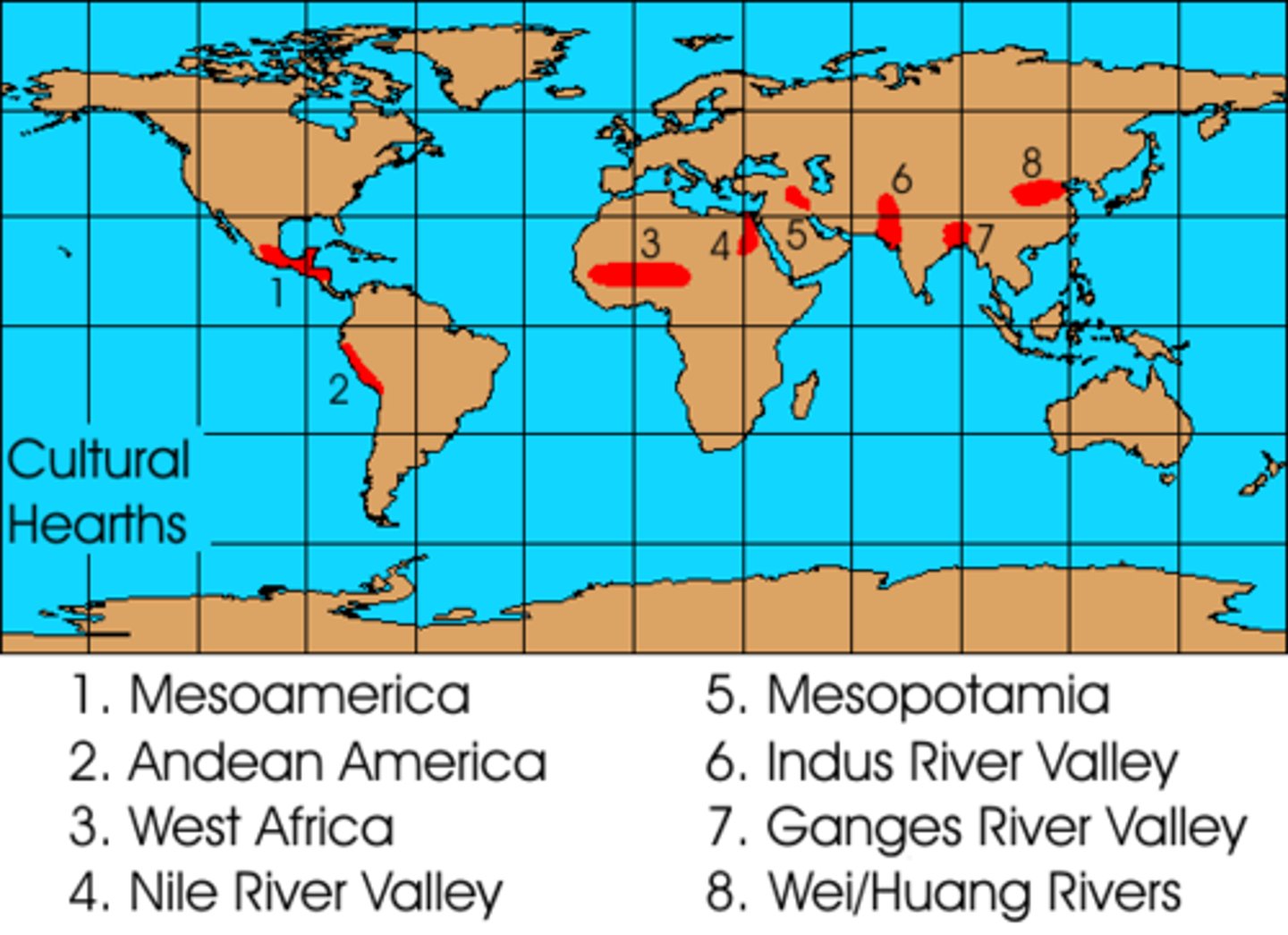
Cultural Hearth
a center where cultures developed and from which ideas and traditions spread outward
Pop Culture
Culture found in a large, heterogeneous society that shares certain habits despite differences in other personal characteristics....the aspects of current culture that make up its arts and entertainment (such as fads, fashions, art, media, music, movies, sports, advertising, etc.)....today is easily transmitted via mass media....can lead to a uniform landscape/placelessness
Habit
A repetitive act performed by a particular individual
Custom
The frequent repetition of an act, to the extent that it becomes characteristic of the group of people performing the act.
Taboo
A restriction on behavior imposed by social custom.
Indigenous (Folk) Culture
Culture traditionally practiced by a small, homogeneous, rural group living in relative isolation from other groups....a culture group that constitutes the original inhabitants of a territory, distinct from the dominant national culture, which is often derived from colonial occupation.
Traditional Architecture
buildings use building materials available and reflect social/environmental customs of the people
Post-modern Architecture
discouraged the use of historical reference in architecture, encouraged creativity, unique visual appeal
Placelessness / Uniform Landscape
the loss of uniqueness of place in the cultural landscape so that one place looks like the next....a result of globalization & pop culture

Sequence Occupancy
notion that societies leave their cultural imprints on a place each contributing to the cumulative cultural landscape
Relocation Diffusion
the spread of an idea through physical movement of people from one place to another
Stimulus Diffusion
The spread of an underlying principle, in which a cultural adaptation is created as a result of the introduction of a cultural trait from another place. People change cultural traits to fit their needs
Contagious Diffusion
The rapid, widespread diffusion of a feature or trend throughout a population.
Hierarchical Diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority or power to other persons or places (think big cities to small cities, celebrities etc)
reverse hierarchical diffusion
diffusion up a hierarchy, such as from a small town to large cities...Example Walmart
Colonialism
the implanting of settlements on a distant territory
Imperialism
policy or ideology of extending the rule or authority of a country over other countries and peoples, often by military force or by gaining political, economic, and/or social control
Language Family
A collection of languages related to each other through a common ancestor long before recorded history....a collection of languages that are all descended from an original, proto-language
Language Branch
A collection of languages related through a common ancestor that existed several thousand years ago. Differences are not as extensive or as old as with language families, and archaeological evidence can confirm that the branches derived from the same family.
Language Group
A collection of languages within a branch that share a common origin in the relatively recent past and display relatively few differences in grammar and vocabulary.
Dialect
A regional variety of a language distinguished by vocabulary, spelling, and pronunciation.
Indo-European Family
World's most spoken Language Family; includes Germanic, Romance, Balto-Slavic & Indo-Iranian
Creole
A language that results from the mixing of a colonizer's language with the indigenous language of the people being dominated....began as a pidgin language that evolves to the point at which it becomes the primary language of the people who speak it
Pidgin
a grammatically simplified means of communication that develops between two or more groups that do not have a language in common: typically, its vocabulary and grammar are limited and often drawn from several languages.
Lingua Franca
A language mutually understood and commonly used in trade (international networks) by people who have different native languages
English is the most used language world wide
Logogram
A symbol that represents a word rather than a sound - a sign or character representing a word or phrase, such as those used in shorthand and some writing systems

Official Language
The language adopted for use by the government for the conduct of business and publication of documents.
Isogloss
A boundary that separates regions in which different language usages predominate.
Extinct Language
A language that was once used by people in daily activities but is no longer used.
Vernacular
everyday language
Syncretism
the combining of different cultural traits/ beliefs, or blending practices of various schools of thought.
Ethnic Religion
a religion that is focused on a single ethnic group (often in a centralized area) that doesn't attempt to appeal to all people
Ex: Judaism, Hinduism, Shintoism
Universal Religion
a religion that attempts to appeal to all people and has a worldwide focus as opposed to a regional focus
Ex: Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Sikhism, Baha'i
Animism
The belief that bodies of water, animals, trees, other natural objects or natural events, like thunderstorms and earthquakes, have a discrete spirit and conscious life.
Secularism
the principle of separation of the state from religious institutions.
Fundamentalism
Literal interpretation and strict adherence to basic principles of a religion (or a religious branch, denomination, or sect).
Theocracy
A government controlled by religious leaders
Caste
The class or distinct hereditary order into which a Hindu is assigned according to religious law.
Monotheism
Belief in one God
Polytheism
Belief in many gods
Religious Branch
A large and fundamental division within a religion
Denomination
A division of a religious branch that unites a number of local congregations in a single legal and administrative body.
Sect
A relatively small group that has broken away from an established denomination.
Intrafaith Conflict
Conflict between people of the same religion.
Ex: Islamic religion between Sunni and Shia
Interfaith Conflict
Conflict between people of different faiths or religions.
Ex: Conflict between Myanmar's Buddhist government and the Rohingya Muslims
Autonomous Religion
A religion that does not have a central authority but shares ideas and cooperates informally.
Hierarchical Religion
A religion that has a well defined geographic structure that organizes territory into local administrative units.
Pilgrimage
A journey to a place considered sacred for religious purposes.
Ex: Islamic Hajj to Mecca
Ethnicity
Identity with a group of people that share distinct physical and mental traits as a product of common heredity and cultural traditions.
Ethnocentrism
judging people or traditions based on your own cultural standards
Ethnic Cleansing
Process in which more powerful ethnic group forcibly removes a less powerful one in order to create an ethnically homogeneous region
Ex: Conflict between Myanmar's Buddhist government and the Rohingya Muslims
Genocide
the deliberate killing of a large group of people, especially those of a particular ethnic group or nation.
Ex: Holocaust, Rwanda Tutsi, Cambodia Khmer Rouge, East Timor
Ethnic Enclave / Neighborhoods
a small area occupied by a distinctive minority culture that is distinct from those in the surrounding area
Ex: Chinatown, Little Italy
Segregation
Separation of people based on racial, ethnic, or other differences
Centripetal Force
An attitude that tends to unify people
Centrifugal Force
A force that divides people
Apartheid
Institutionalized racial segregation laws from 1948-1991 in South Africa that physically separated different races into different geographic areas. Ensured that South Africa was dominated politically, socially, and economically by the nation's minority white population
Balkanization
the process of fragmentation or division of a larger region or state into smaller regions or states, which may be hostile or uncooperative with one another....typically as a result of conflict between different ethnic groups
Nationalism
A strong feeling of pride in and devotion to one's country
Race
Identity with a group of people descended from a common ancestor.
Racism
Belief that race is the primary determinant of human traits and capacities and that racial differences produce an inherent superiority of a particular race.
Blockbusting
Illegal practice of persuading homeowners to sell their property cheaply by telling them that people of a certain race, national origin or religion are moving into the area and thus profiting by reselling at a higher price.
White Flight
working and middle-class white people move away from racial-minority suburbs or inner-city neighborhoods to white suburbs and exurbs