Compensation, Job Evaluation, and Salary Structure
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of flashcards covering key concepts from the lecture on Compensation, Job Evaluation, and Salary Structure.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Job description
Outlines the requirements, duties, and responsibilities of a specific role or position. includes clear and specific title reflecting the role.
Compensation
impacts an employer’s ability to attract and retain employees and ensures optimal levels of employee performance in meeting organization’s strategic objectives. refers to the form of wages or salary.
Title VII of Civil Rights Act of 1964
The is a federal law that protects workers’ rights to fair treatment.
Equal Pay Act of 1963
The is a law that protects workers’ rights to equal pay for equal work.
The is a systematic process of determining the relative worth of jobs within an organization to establish a fair and equitable compensation structure.
Job Evaluation
is defined as fairness of pay differentials among individuals in the same job.
Individual Equity
compares levels of fairness in compensation for different jobs within an organization.
Internal Equity
Pay transparency can consist of making public individual salaries and/or the process by which salaries are set. This concept is contrasted with .
Secrecy
In the context of compensation, the outlines the classification system used by federal government jobs.
GS System
The three Hay Compensable Factors include Know-How, Accountability, and .
Problem-Solving
Equity Theory suggests that an individual senses inequity when perceiving ratios are not equal concerning and of contributions and rewards.
Inputs/Outputs
The defines a framework that determines how salaries are structured and distributed within an organization.
Job Salary Structure
Job description
outlines the requirements, duties, and responsibilities of a specific role or position
Job Title
clear and specific title reflecting the role
Job Summary
highlights main purpose of the role and how it fits within the organization,
captures interest of potential candidates
Key Responsibilities
list of duties and tasks the candidate will perform
Required Qualifications and Skills
Education
Experience
Technical Skills
Soft Skills
Certifications
Compensation
impacts an employer’s ability to attract and retain employees and ensures optimal levels of employee performance in meeting organization’s strategic objectives
Direct compensation
wages or salary
Base pay (hourly, weekly, monthly)
Incentive Pay (sales bonuses and/or commissions)
Indirect compensation
form of benefits
Legally required benefits (e.g Social Security)
Optional (e.g group health benefits)
Title VII of Civil Rights Act of 1964
Protects workers’ rights to fair treatment
Equal Pay Act of 1963
Protects workers’ rights to fair treatment and prohibits wage discrimination based on sex.
Comparable Worth
standards of equal pay for equal work should be replaced with equal pay for equal value
objective, measurable data to support assessment of value of different jobs is lacking
there is no basis in current law for arguments of comparable worth.
Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938
regulates minimum wage
sets overtime policy
establishes exempt classes for managers and other professional employees
“duties” test ultimately determines whether a position is exempt
delineates independent contractor versus employee status
Inquiries of current salaries as a means of determining salary offers are coming under increased scrutiny
States and cities have passed laws which prohibit employers from making such inquiries
Massachusetts Pay Equity Act
first prohibited inquiries of both job applicants and their employers regarding current salaries of applicants until after a job offer is made, and then only with written permission of the applicant
EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
No real average or standard
Protects workers’ rights to fair treatment
Typical annual compensation for senior executives:
20% salary
30% annual incentives
50% long-term incentives
Stock Grants
require organization to meet specific financial goals
Stock Options
provide opportunity to purchase shares at some future date, at price determined when options are awarded
focus employee attention on creating shareholder value
do not have to be reported as expenses
can create culture obsessed with improving stock performance at expense of other concerns
can prompt executives to engage in creative accounting practices
KEY STRATEGIC ISSUES IN COMPENSATION
Determining compensation relative to market
Striking balance between fixed and variable compensation
Deciding whether or not to utilize team-based versus individual pay
Creating appropriate mix of financial and non-financial compensation
Developing cost-effective compensation program resulting in high performance
EQUITY
provides fair and equal opportunities and resources while also recognizing that different individuals need different levels of support to succeed, allowing for inclusivity.
INDIVIDUAL EQUITY
Defined as fairness of pay differentials among individuals in the same job
INTERNAL EQUITY
Defined as fairness of pay differentials between different jobs in organization
Methods of establishing internal equity: (1) job ranking, (2) job classification, (3) point method, or (4) factor comparisons
PAY TRANSPARENCY VERSUS SECRECY
Local governments require pay transparency for public employees but private employers generally have discretion
Transparency can consist of making public individual salaries and/or the process by which salaries are set
GS 1
perform, under immediate supervision, with little or no latitude for the exercise of independent judgment
jobs: typist, messenger
GS 2
perform, under immediate supervision, with limited latitude for the exercise of of independent judgment
jobs: engineering aide
GS 5
perform, under general supervision, difficult and responsible work; exercises judgment in a limited field
jobs: chemist, accountant, civil engineer, statistical clerk
HAY COMPENSABLE FACTORS
Used as a basis for determining the value of a position has three factors: Know-How, Accountability, and Problem-Solving
Know-how
the sum total of every kind of skill, however required, necessary for acceptable job performance; it comprises overall “fund of knowledge” and has three elements:
Knowledge of practical procedures, specialized techniques, and learned disciplines.
The ability to integrate and harmonize the diversified functions involved in managerial situations (operating, supporting, and administrative)
Active, practicing skills in the area of human relationships
Accountability
the answerability for an action and for the consequences thereof. It has three dimensions:
Freedom to act: degree of personal or procedural control and guidance
Job impact on end results
Magnitude: indicated by the general dollar size of the area(s) most clearly or primarily affected by the job
Problem-Solving
the original “self-starting” thinking required by the job for analyzing, evaluating, creating, reasoning, and arriving at conclusions. It has two dimensions:
The environment in which the thinking takes place
The challenge presented by the thinking to be done
EXTERNAL EQUITY
Fairness of organizational compensation levels relative to external compensation;
in other words, comparing how different companies pay for the same job/position
Assessed by collecting wage and salary information to guide in setting organization’s pay strategy to lead, meet, or lag labor market wages
Lag Policy
EQUITY THEORY
An individual senses inequity when perceiving ratios are not equal
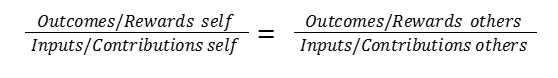
JOB EVALUATION
Job evaluation is a systematic process of determining the relative worth of jobs within an organization to establish a fair and equitable compensation structure.
It helps in comparing different jobs based on factors like skills, responsibilities, effort, and working conditions to ensure that employees are fairly compensated for their contributions.
5 PURPOSE OF JOB EVALUATION
1. Ensures Internal Equity
Helps maintain fairness in pay among employees
2. Guides Compensation Decisions
Provides a basis for salary structures
3. Supports HR Planning
Helps in workforce planning, promotions, and career progression
4. Improves Organizational Efficiency
Aligns job roles with business goals
5. Enhances Employee Motivation
Ensures employees feel valued and fairly rewarded
4 COMMON JOB EVALUATION METHODS |
1. Ranking Method
jobs are ranked from highest to lowest based on overall importance
2. Classification Method
jobs are grouped into predefined categories or levels
3. Point Rating Method (most common)
jobs are scored based on compensable factors like skill, responsibility, effort, and working conditions
assigns numerical values based on compensable factors
4. Factor Comparison Method
jobs are compared based on key job factors with benchmark jobs and assigned monetary value
STEPS IN CONDUCTING JOB EVALUATION |
Step 1: Job Analysis
Gather job descriptions, responsibilities, qualifications, and working conditions through interviews, questionnaires, observations, and reviewing existing documents
Step 2: Selecting the Job Evaluation Method
Choose method based on organizational needs (e.g: ranking, classification, point rating, factor comparison method)
Step 3: Identifying Compensable Factors
define key job attributes used to assess job worth.
Skill – Education, experience, technical knowledge.
Effort – Physical and mental workload.
Responsibility – Level of decision-making, financial accountability.
Working Conditions – Physical environment, hazards, stress levels
Step 4: Assigning Weights & Scores (Point Rating Method)
allocate points to compensable factors based on their importance
*Score of last level = given weight x 10
*Score of level 2 - 4 = score in level 5 - score in level 1 4 then add to prior level
Step 5: Evaluating Jobs and Creating a Job Hierarchy
compare the scores of each job and rank them accordingly
group similar jobs into pay grades for fair compensation
Step 6: Implementing & Reviewing the Evaluation
validate the results with management and employees
adjust and update job evaluations periodically to reflect changes in roles
JOB SALARY STRUCTURE |
is a framework that defines how salaries are determined and distributed within an organization
establishes pay grades, salary ranges, and compensation levels based on factors like job evaluation, market rates, experience, and organizational policies
KEY ELEMENTS OF A SALARY STRUCTURE |
1. Pay Grades
Helps maintain fairness in pay among employees
2. Salary Ranges
The minimum, midpoint, and maximum pay assigned to each pay grade
3. Broadbanding
flexible pay structure with wider salary bands
4. Market-based Pay
aligning salaries with industry benchmarks
5. Internal Equity & External Competitiveness
balancing fair pay within the organization while remaining competitive externally