Biology Carbon
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Carbon
has the ability to form single, double, and triple bonds, mostly covalent bonds
covalent bonds
electrons are shared in this bond
macromolecules
large organic molecules found in living things
monomer
the individual pieces of a polymer
polymer
multiple monomer joined together
Polymerization
monomers become polymers by this process
dehydration synthesis
monomers form a bond by losing one molecule of H2O to become a polymer, covalent bond
hydrolysis
the chemical breakdown of a compound due to reaction with water
carbohydrates
living things use carbohydrates as soures for energy and for structural purposes, made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a fixed ratio of 1:2;1 Glucose: C6H12O6; monomer is monosaccharide
polysaccharide
multiple sugars, or monomers; are complex carbohydrates and may be hundreds or thousands of monomers long
monosaccharides
one sugar, or monomer; monomer of carbohydrates
disaccharides
two sugars, or monomers
glucose
serves a primary fuel to generate energy that the body’s cells use to carry out their metabolic and biological functions; primary fuel
glycogen
animals and humans store excess glucose in the liver and muscle cells as-
starch
plants store their energy in the form of-
cellulose
plants also use a structural carbohydrate to maintain their shape, support found in their cell walls called-
chitin
the cell walls of fungi and the exoskeletons of arthropods are made of-
lipids
long term energy; mostly made of carbon and hydrogen and some oxygen. Composed of a Glycerol head and Fatty Acid Tails; Generally not soluble in water- hydrophobic; EX: fats, oils, waxes, and steroids; Phospholipids make up the cell membrane
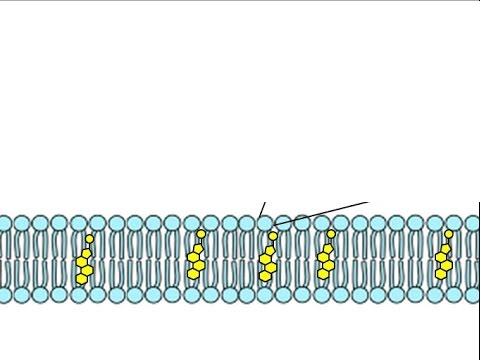
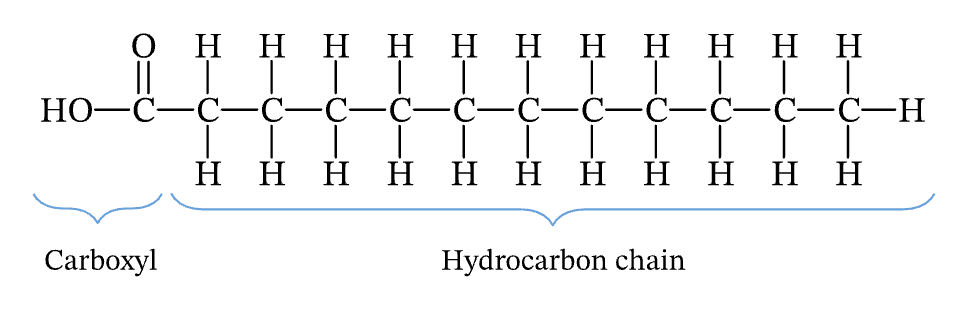
saturated bond
carbon to carbon single bonds; more solid in room temperature
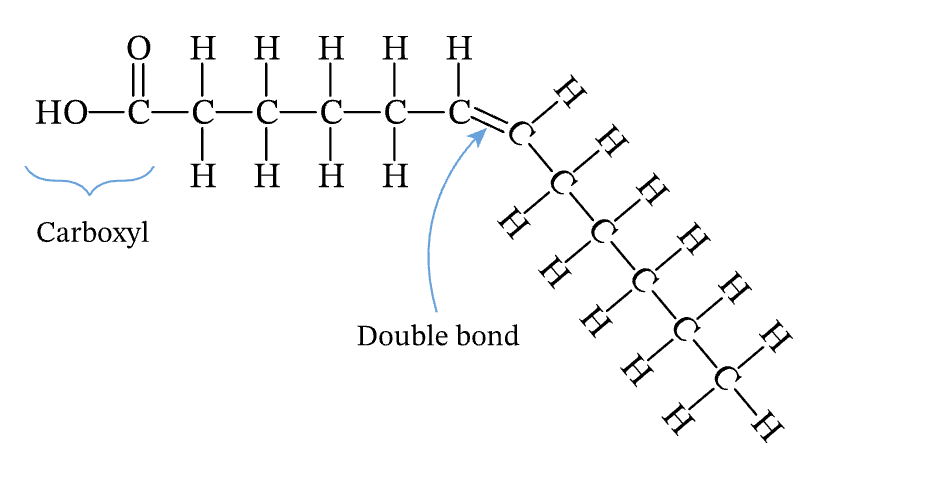
unsaturated
carbon to carbon double bonds; more liquidy in room temperature
Nucleic Acids
store and transmit heretitary or genetic information. Polymers are nucleic acids;
Nitrogenous base
caries the base pair; held together with hydrogen bonds
Deoxyribose
the sugar of deoxyribonucleic acid
deoxyribonucleic acid
double stranded; carries genetic information; sugar is deoxyribose
Purines
adenine and guanine are considered-
pyrimidines
thymine and cytosine are considered-
ribonucleic acid
Single stranded; sugar is ribose; adenine pairs to uracil
Proteins
polymers made of amino acid monomers; has an R group as a placeholder; are used for enzymes, hormones, and antibodies; consists of the elements O, H, C, N, and sometimes S
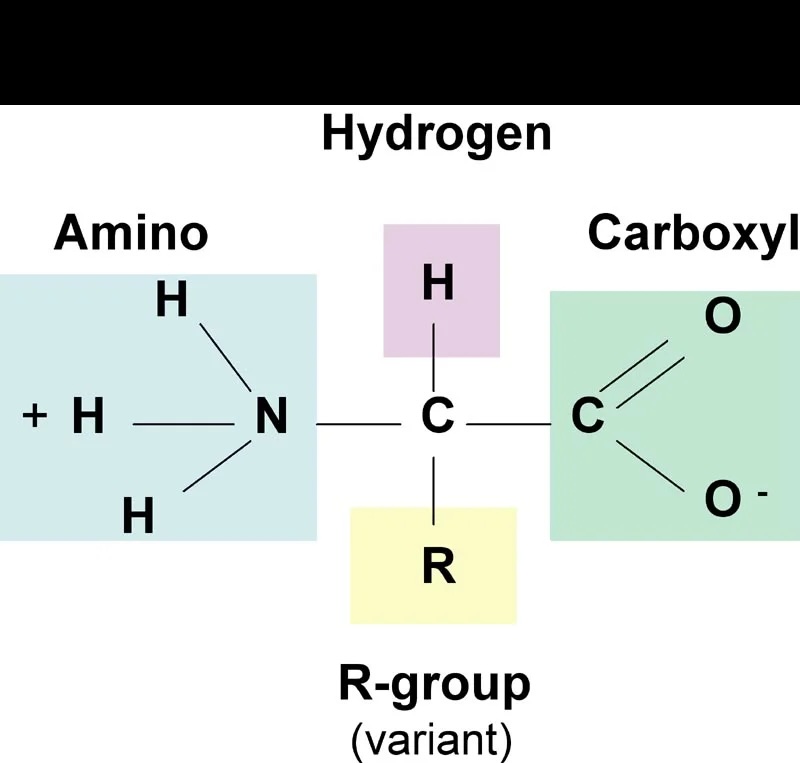
amino acid
monomers of the polymer protein
peptide bond
the bond connecting two amino acids; covalent bond; made by dehydration synthesis
enzymes
control the rate of chemical reactions; lowers the activation energy
horomones
regulate cell processes
antibodies
helps fights diseases
primary
the linear sequence of amino acids
secondary
results from hydrogen bonds between the different R groups; starts to fold in on itself and hydrogen bonding begins between R groups
Tertiary
the finalized 3-D shape of the polypeptide
quaternary
not all proteins reach this structure, only occurs when two or more polypeptides attach and work together, such as with HEMOGLOBIN
Hemoglobin
transports oxygen in our blood
activation energy
the minimum amount of energy that is required to activate atoms into chemical reactions
Substrate
name for the reactants
active site
the place at which the reactants bind to the active site
denature
if an enzyme is not in its optimal conditions; can result from temperature, pH, salt concentration(salinity)