Microscopic Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle: Sarcomeres, Neuromuscular Junctions, and Contraction Types
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Sarcolemma
Plasma membrane of the muscle fiber
Sarcoplasm
Cytoplasm of a muscle fiber
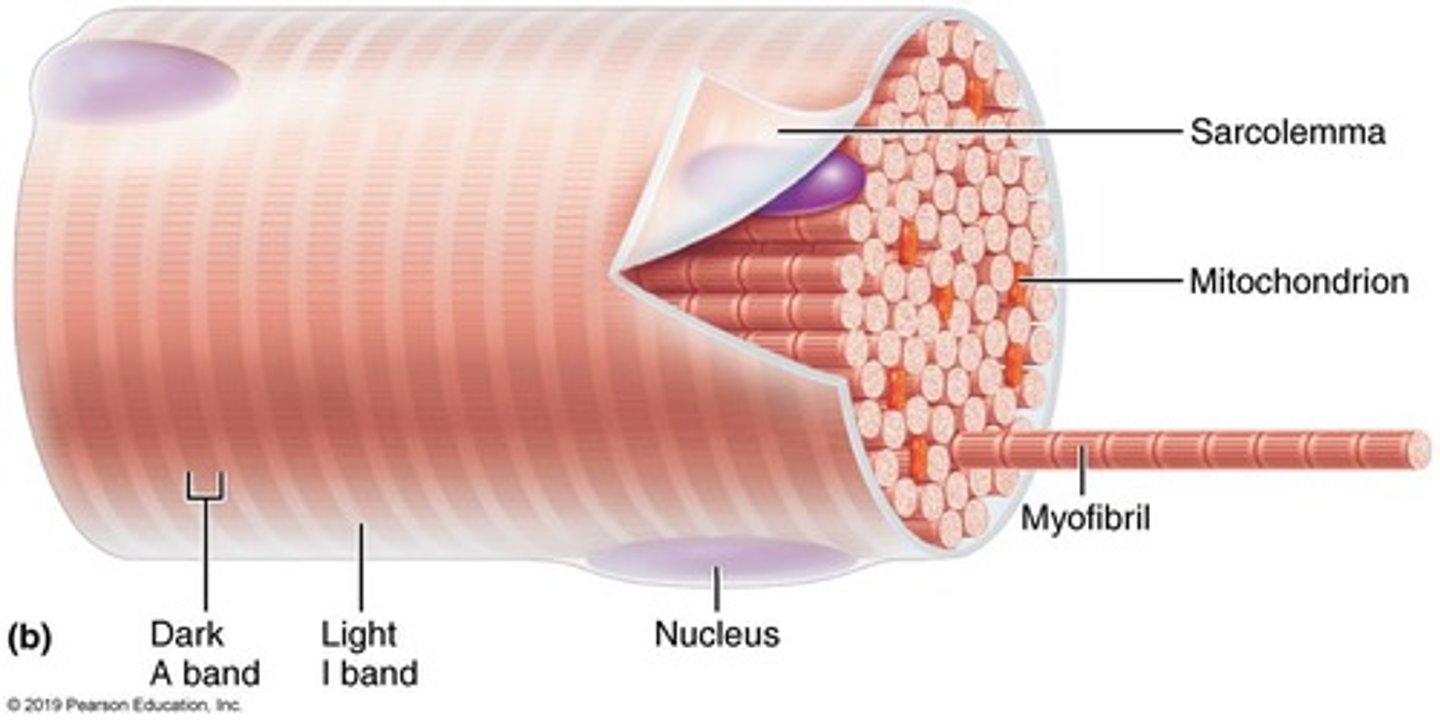
Myofibrils
Rod-like structures that run the entire length of the muscle fiber
Mitochondria
Perform aerobic respiration to produce energy for muscle activity
Myoglobin
Protein that binds and stores oxygen, located in the sarcoplasm
Inclusions
Glycosomes - granules of stored glycogen
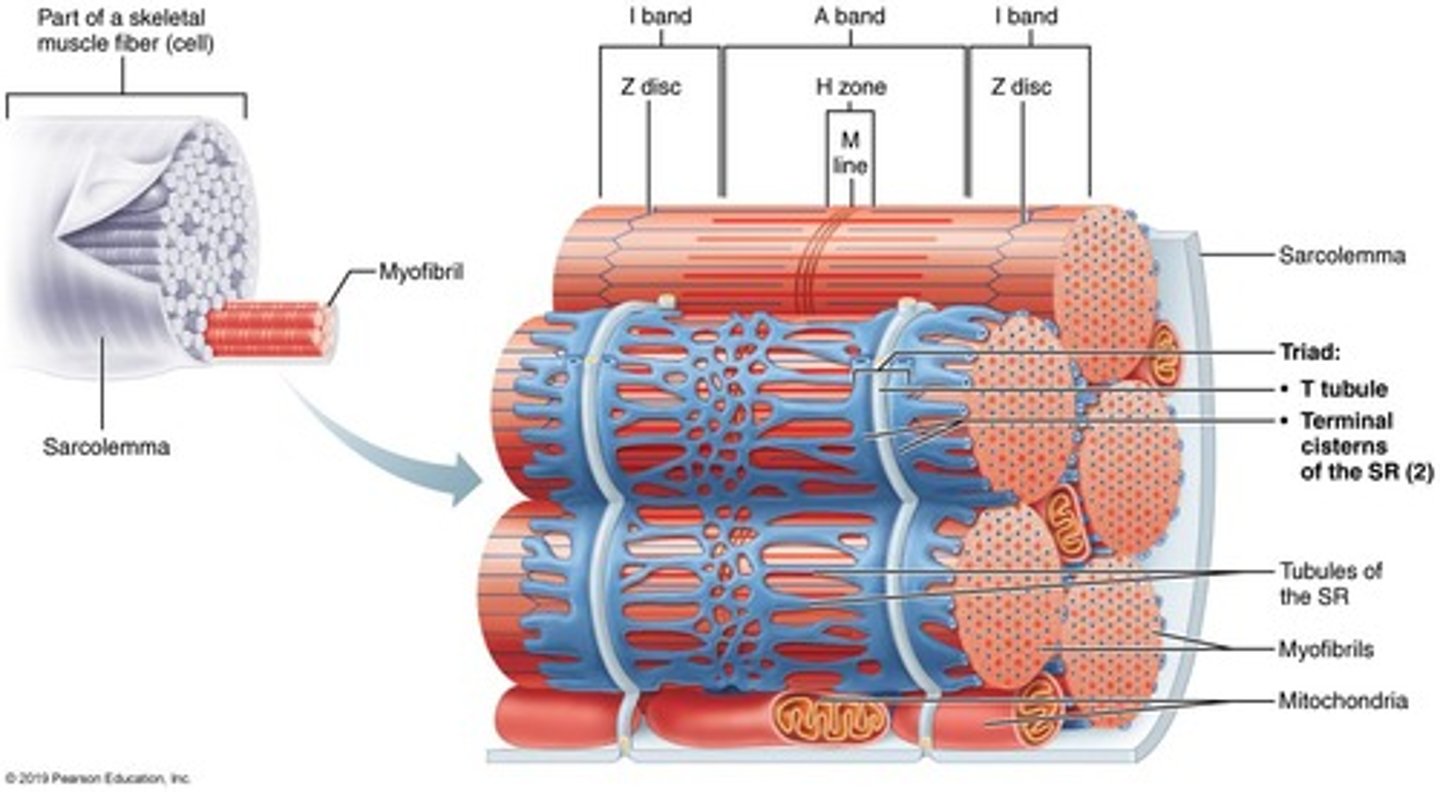
Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
Specialized smooth ER; stores and releases Ca2+ into the sarcoplasm
Terminal cisternae
Expanded ends of the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Transverse tubules (T tubules)
Involutions of the sarcolemma into the sarcoplasm
Triad
Composed of one T tubule, sandwiched between two terminal cisternae
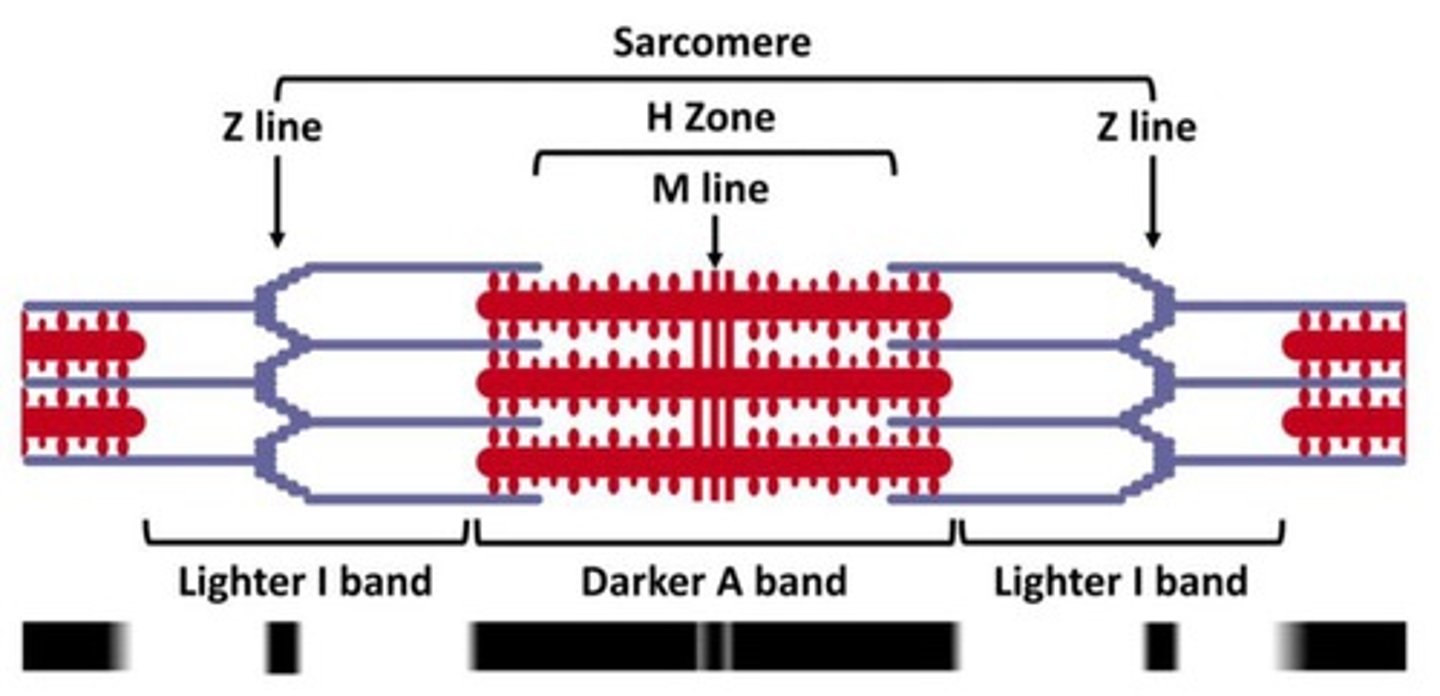
Sarcomere
Bounded by two Z discs, the structures of the sarcomere underlie muscle contraction
Myofilaments
Thick (myosin) and thin (actin) filaments of the sarcomere
A band
Region of thick filaments
H zone
Middle region of the A band (doesn't overlap with the thin filaments)
M line
Anchors the thick filaments
I band
Region of thin filaments (doesn't overlap with the A band)
Z disc
Anchors the thin filaments
Neuromuscular junction
Where a motor neuron meets a muscle fiber
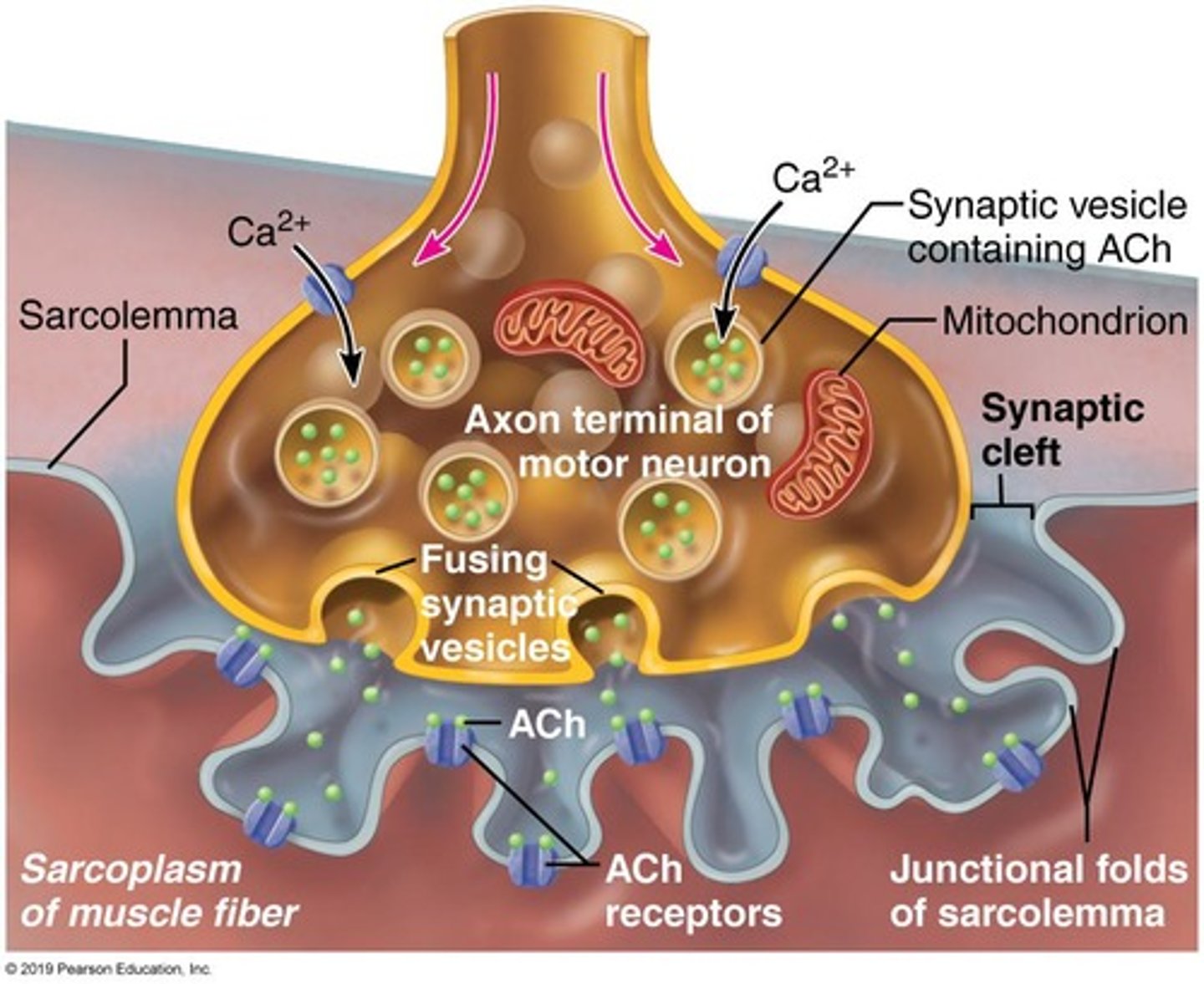
Motor neurons
Induce movement by sending impulses to skeletal muscles that stimulate contraction
Axon terminals
Terminals of the motor neuron that make contact with the skeletal muscle
Motor unit
The motor neuron and all of the skeletal muscle fibers it innervates via its axon terminals
Excitation-contraction coupling
Action potential reaches axon terminal, inducing Ca2+ channels to open
Acetylcholine (ACh)
A neurotransmitter contained in synaptic vesicles
ACh
ACh is released into the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the sarcolemma.
Ion channels
Ion channels in the sarcolemma open, allowing an influx of ions that depolarizes the sarcolemma.
Triads
Triads propagate rapid depolarization throughout the muscle fiber.
Ca2+
Ca2+ is released from the SR, enabling the contraction of sarcomeres (and of the muscle fiber).
Isometric contraction
Isometric: force generated by the muscle increases at a constant muscle length.
Isometric contraction example
Plank: isometric contraction.
Isotonic contraction
Isotonic: force generated by skeletal muscle is constant and the muscle length changes.
Isotonic contraction example
Bicep curl: concentric isotonic contraction.
Concentric contraction
Concentric: muscle shortens.
Eccentric contraction
Eccentric: muscle lengthens (but doesn't relax).
Aerobic exercise
Aerobic or endurance exercise increases the capillaries, mitochondria, and myoglobin content in muscle fibers.
Aerobic exercise examples
Examples: jogging, biking, swimming.
Resistance exercise
Resistance exercise or strength training increases the number of myofibrils in muscle fibers to increase the size of skeletal muscles.
Resistance exercise examples
Examples: weight lifting or other isometric exercises where muscles are pitted against immovable objects.
Muscle fiber composition
Muscle fibers contain many myofibrils (long series of contractile sarcomeres).
Sarcomere contraction
Thick and thin filaments of the sarcomere slide against each other during contraction.
Critical elements in contraction
ACh and Ca2+ are critical to several steps of the contraction process.
Isotonic vs Isometric
Isotonic: force increases, muscle length is steady; Isometric: force is steady, muscle length changes.
Exercise effects on muscles
Different kinds of exercise increase muscle stamina or the size of muscles.