Ocular anatomy and histology part 4-6
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
what is the vascular tunic also known as
the uvea
what is the function of the iris in the vascular tunic
acts as a blood aqueous barrier
what muscle of the iris causes it to constrict the pupil
sphincter muslces
what muscle of the iris causes it to dilate the pupil
dilator muslce
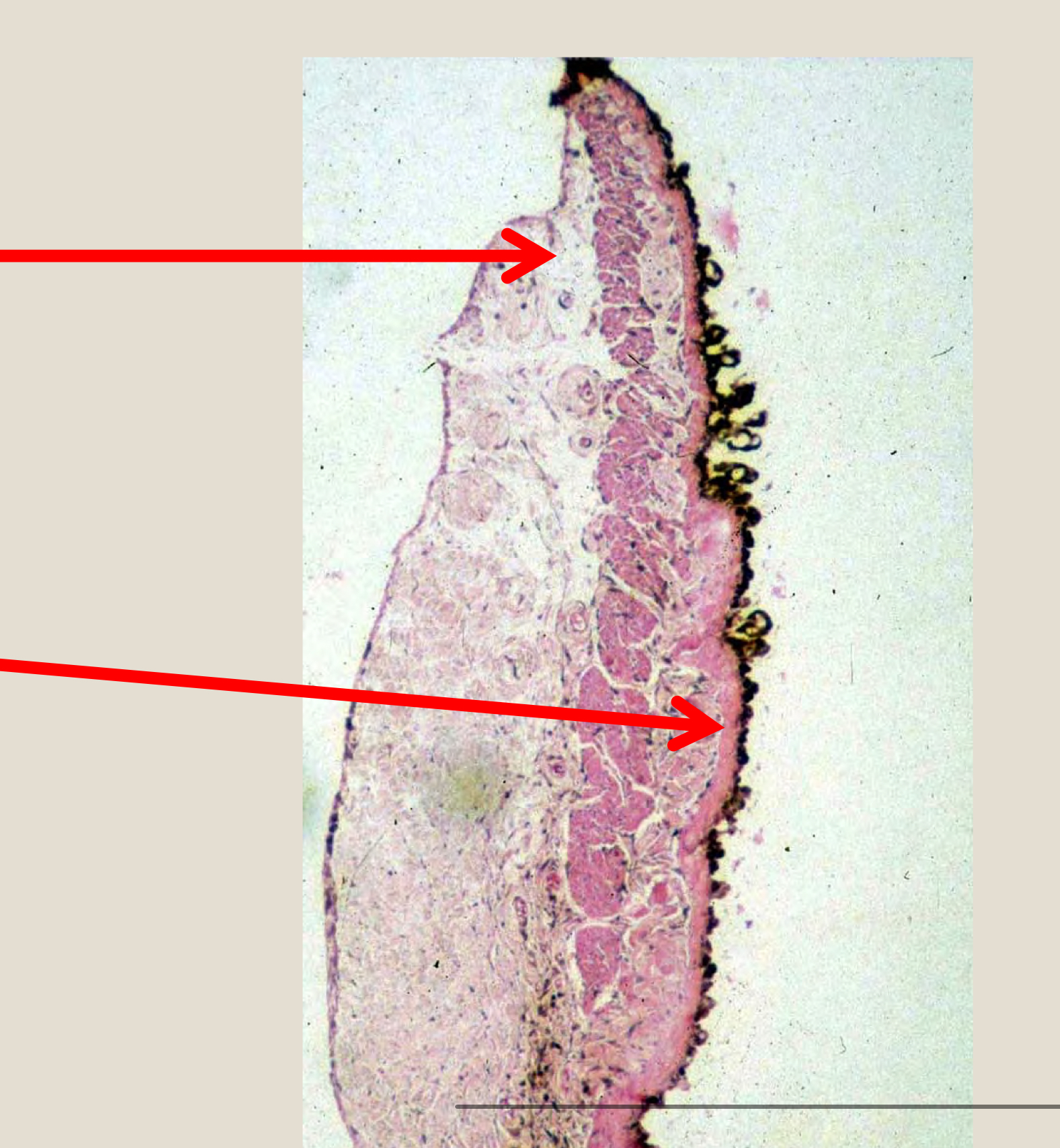
from top top to bottom label the structures of the iris
sphincter muscles
dilator muscles
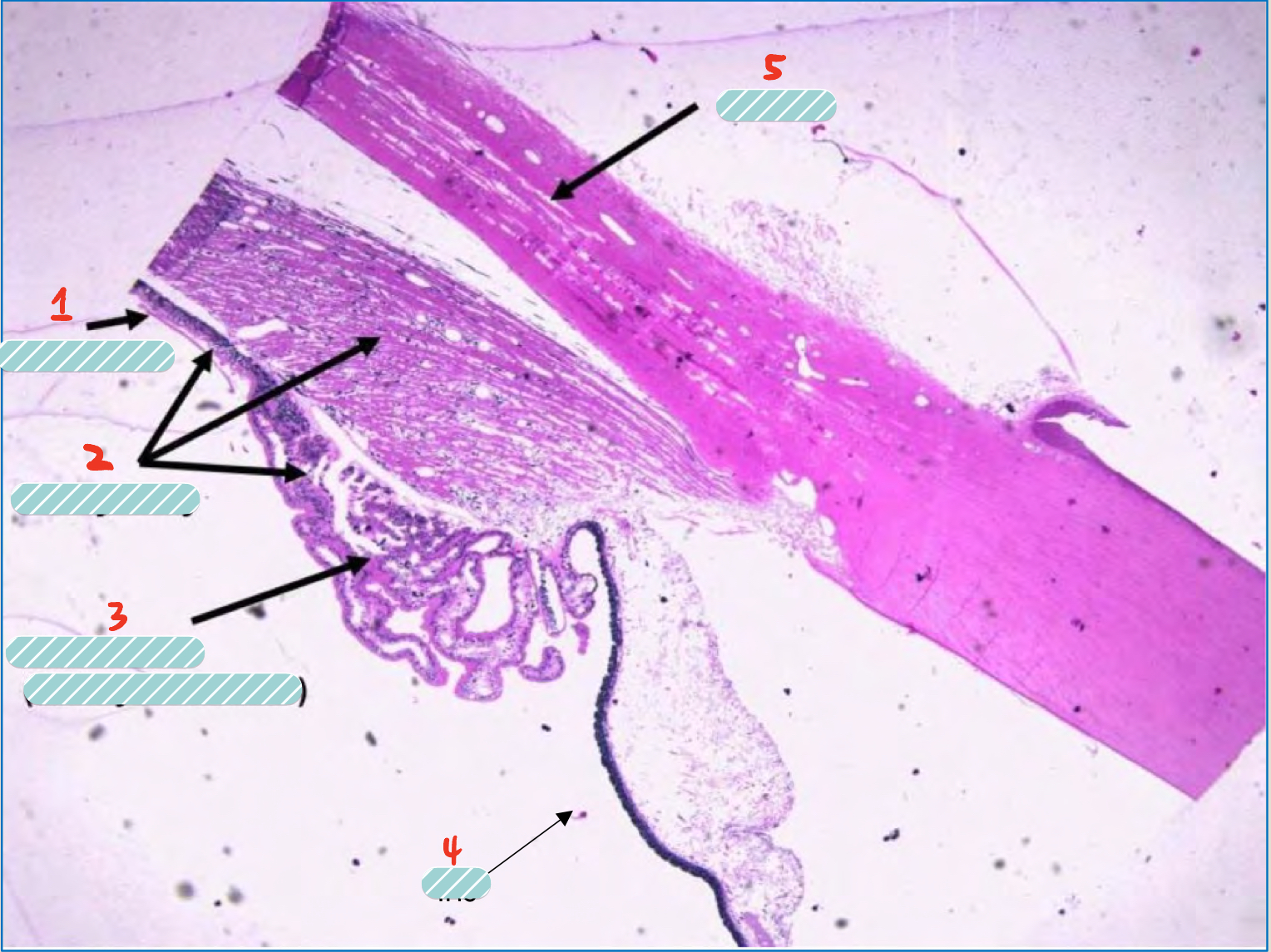
name the structures of the iridocorneal angle
pars plana
ciliary body
par pilcata(ciliary process)
iris
sclera
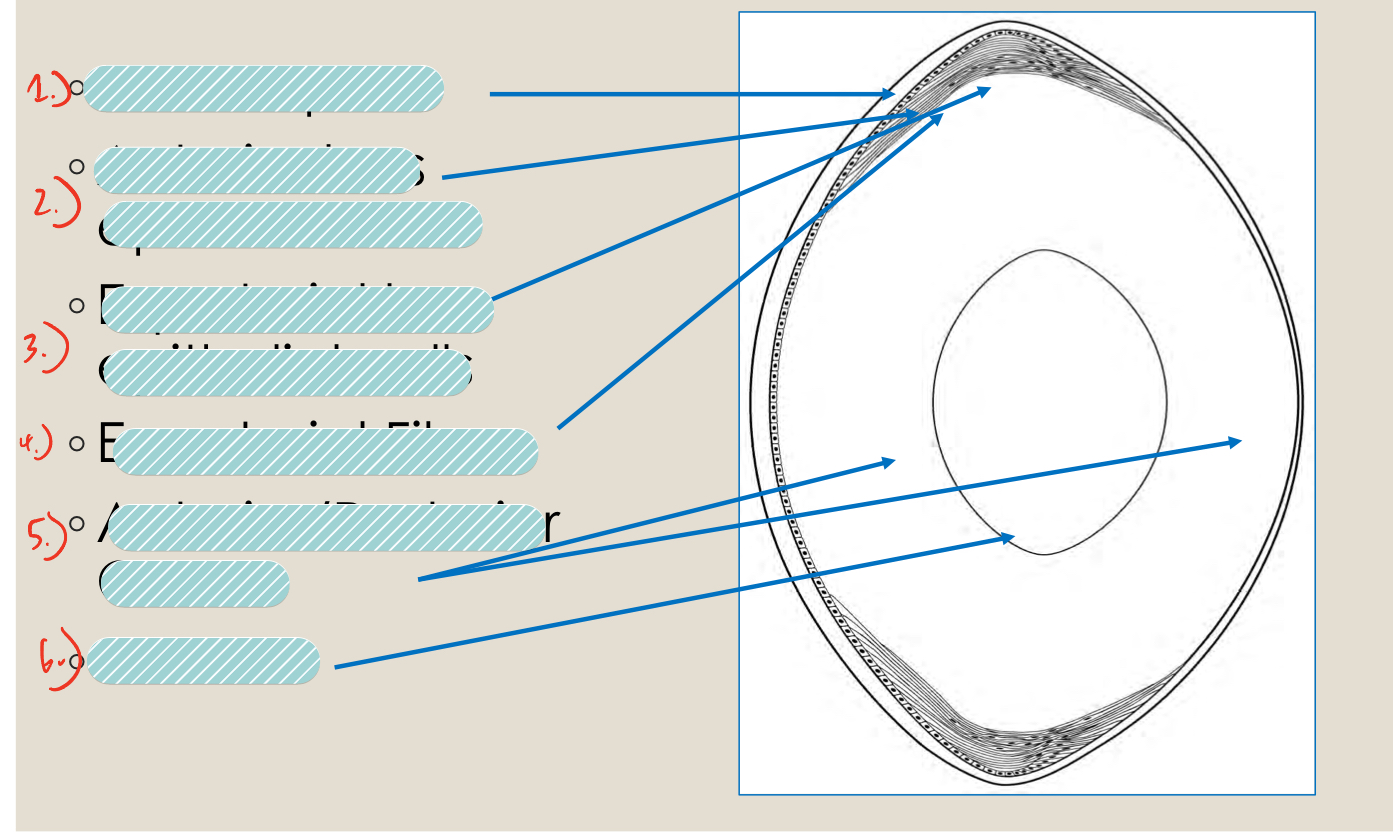
label the structures of the lens
lens capsule
anterior lens epithelial cells
equitorial lens epithelial cells
equatorial fibers
anterior/posterior cortex
Nucleus
where do lens epithelial cells divide and from lens fibers
the equator
what happens to older lens fibers as newer ones are formed
they elongate and are moved internally
as more and more lens fibers made what happens to the central lens fibers
they become compressed and form a nucleus
as lens fibers grow anteriorly and posteriorly where do they meet
they meet at sutures
what do the anterior and posterior suture look like
anterior = y
posterior = upside down y
what lies between lens fibers and the lens capsule
the lens epithelium
what side of the lens capsule is the thickest
the anterior side
With no epithelium present after lens fibers elongate to a point there is no production of basement membrane to make it thicker this is why?
the posterior capsule is thinner
since the eye cannot grow and lens fibers are produced continuously what happens
the lens becomes more compact with age
the continual compaction of the lens can lead to what
nuclear sclerosis
what is cataracts
any opacity of the lens
if cataracts was the cause of opacity you’d see what in lens histology
morgagnian globules
what causes aphakia
loss of lens
what produces the aqueous humor of the anterior chamber
the ciliary body
what cells of the ciliary body produce the aqueous humor
the non pigmented epithelium
where does the aqueous membrane drain out of the eye
the iridocorneal angle
a patient with glaucoma most likely has a blockage of the what
iridocorneal angle
what part of the eye is involved in accommodation of the lens
the ciliary body
what is the difference between dog and cat iris melanin
dogs have darker and rounder granules than cats
what attaches the iris to the cornea
the pectinate ligaments
what is the makeup of the lens
65% water
35% crystalline protein
what are the stages of the vitreous humor
primary
secondary
tertiary
what is the vitreous humor 99% made of
water
what is the function of the vitreous humor
to support the function of the retina and lens
what is the function of the choroid
provides support to the retina
the choroid supplies vessels to what portion of the retina
the outer portion
while the choroid has a tremendous amount of blood flowing through it, the blood is mostly used to do what
regulate heat
where is the tapetum most likely to be in the retina
the dorsal retina
what is the function of the tapetum
reflect light to increase vision in dim light
what lies directly over the tapetum
retinal pigmented epithelium
if RPE lies on the tapetum can it pigmented
no
a detachment took place in the retina and two layers came apart which of the layers was it most likely
the photoreceptors and retinal pigmented epithelium
what does the ganglion cell layer of the retina form
nerve fibers
what is the function of rods
night vision
motion
what is the function of cones
day vision
color
the axons from the ganglion cell layer are supported by what structure in the optic disk
lamina cribosa
in what animal is the optic disc non myelinated and difficult to see
cats
if the entire retina is vascularized that is known as what?
Holangiotic
if only the 3 aclock and 9 aclock positions are vascularized on the retina it is known as what?
merangiotic
if there is poor vasculature on the retina it is known as
paurangiotic
what animal is haloangiotic
cats and dogs
what animal is merangiotic
rabbits
what animal is paurangiotic
Horses
if an animal has no vasculature at its retina it is known as
anagiotic
what animals are anagiotic
birds