Ear and Eye, Neuroanatomy of the Brain: Structures, Functions, and Pathways, Muscles & Structures
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
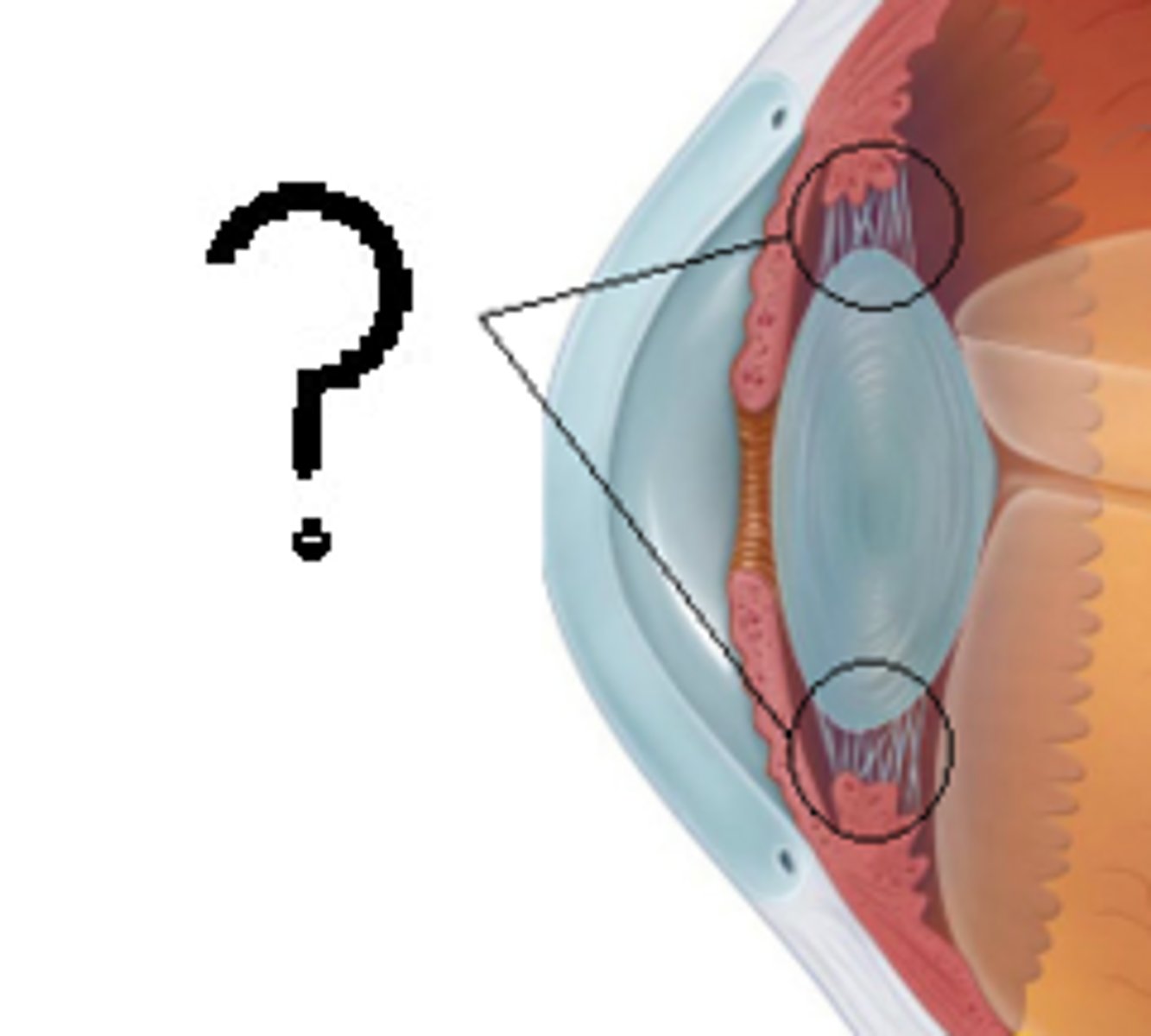
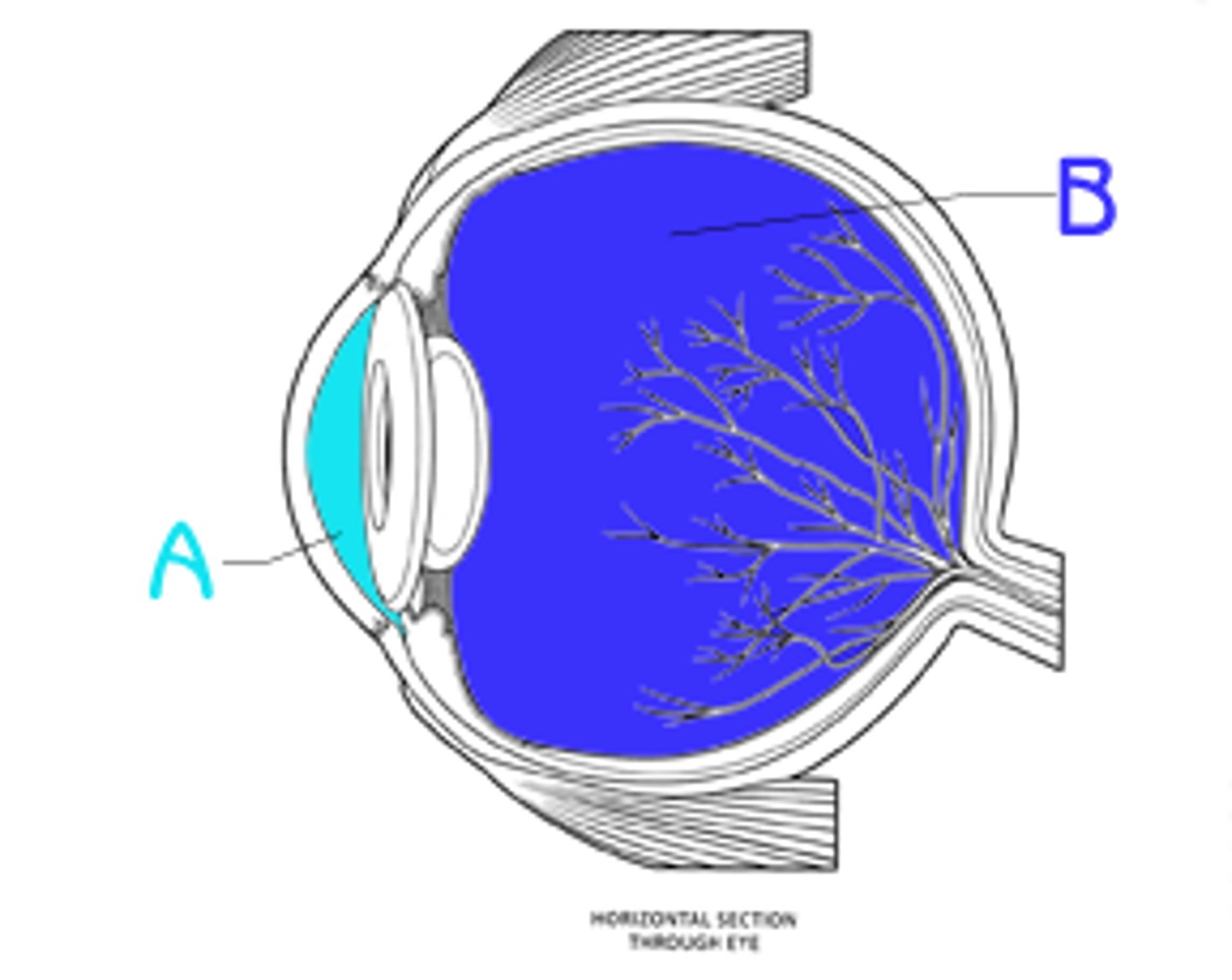
Ciliary Body
Vascular tunic; contains ciliary muscles and processes; controls lens shape
Suspensory Ligament
Connects ciliary body to lens; holds lens in place
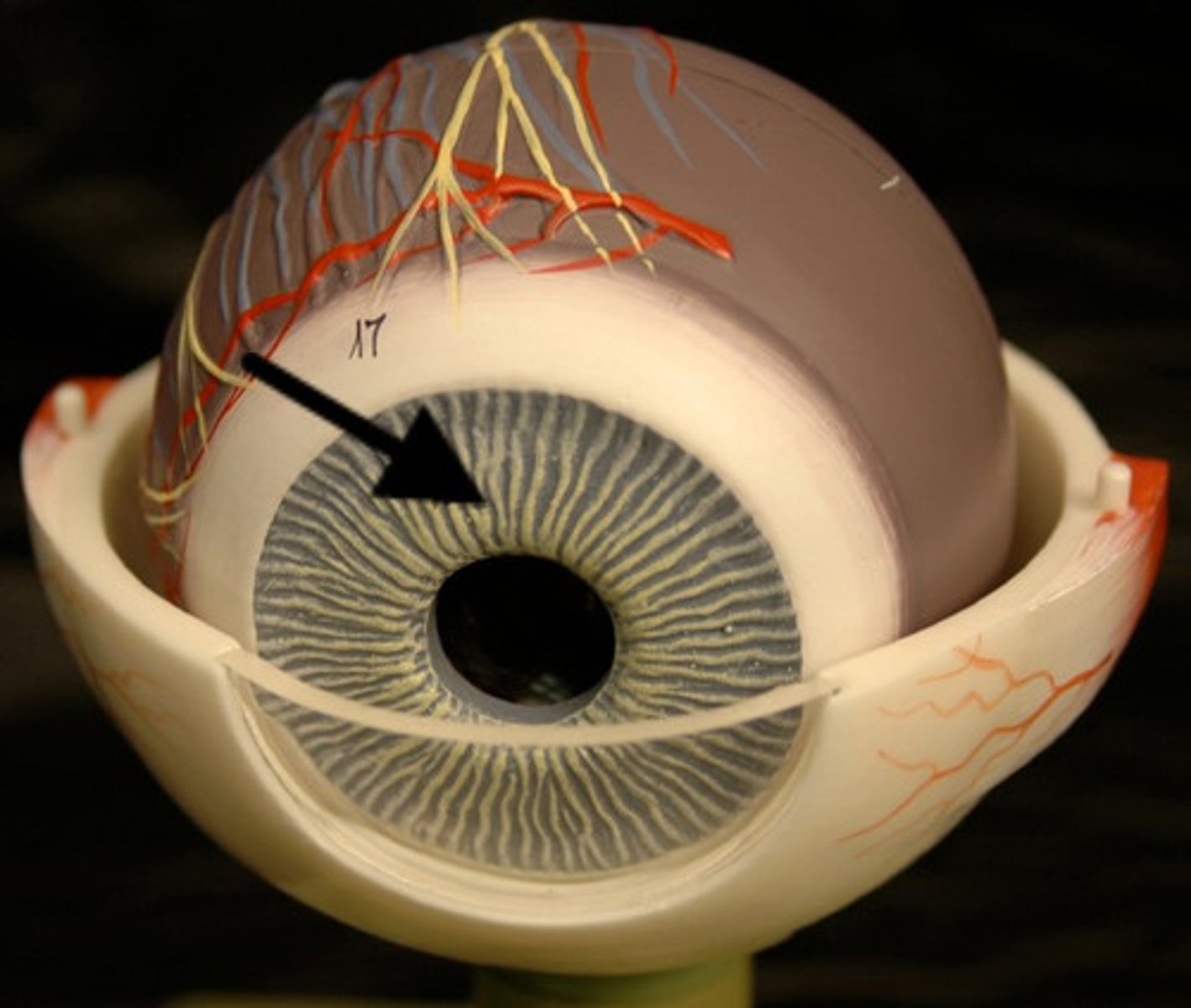
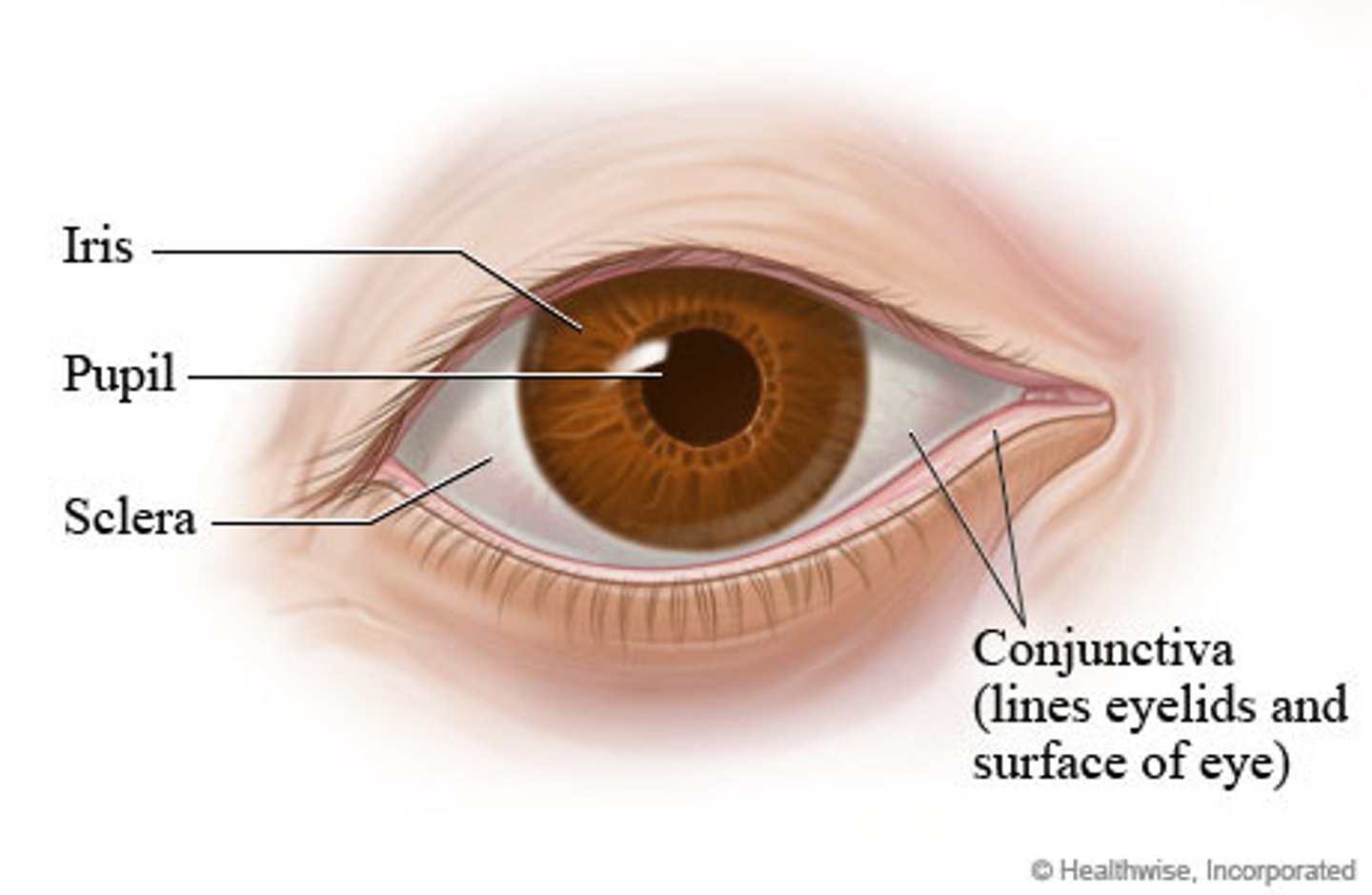
Iris
Part of vascular tunic; controls pupil diameter (light regulation)
Retina
Neural tunic; contains photoreceptors (rods & cones)
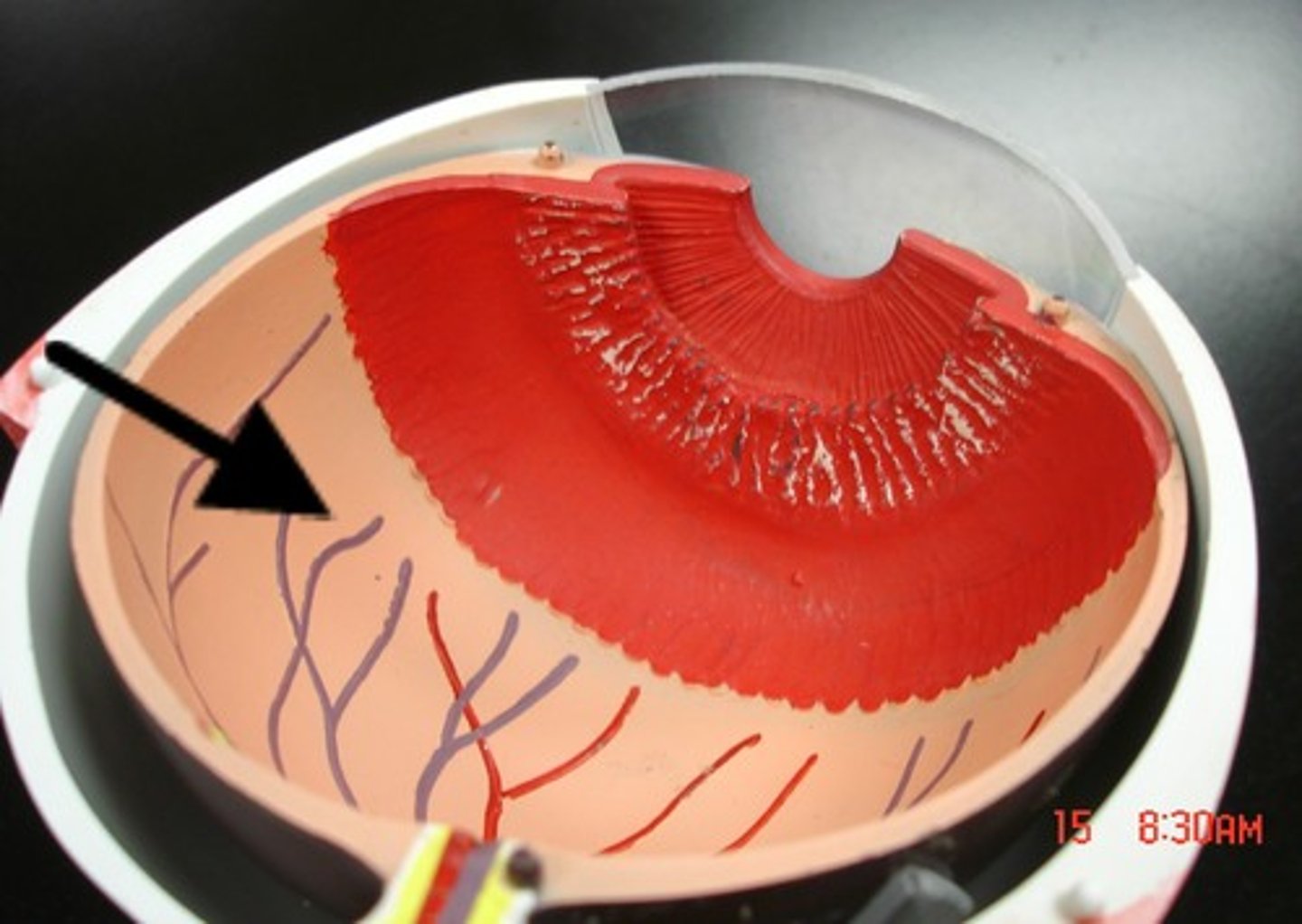
Sclera
Fibrous tunic; outer protective layer ("white" of eye)
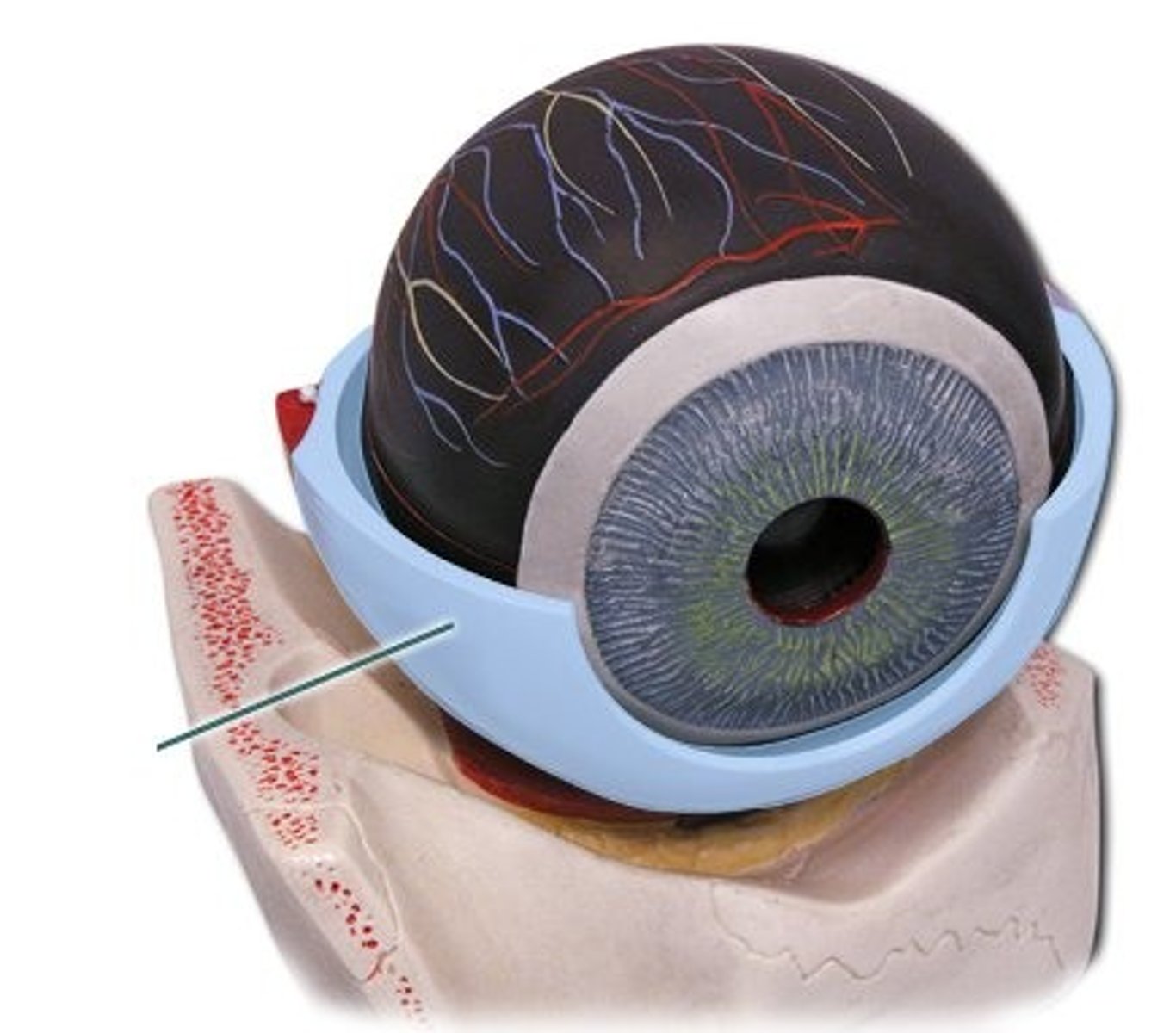
Choroid Coat
Vascular tunic; supplies blood to retina
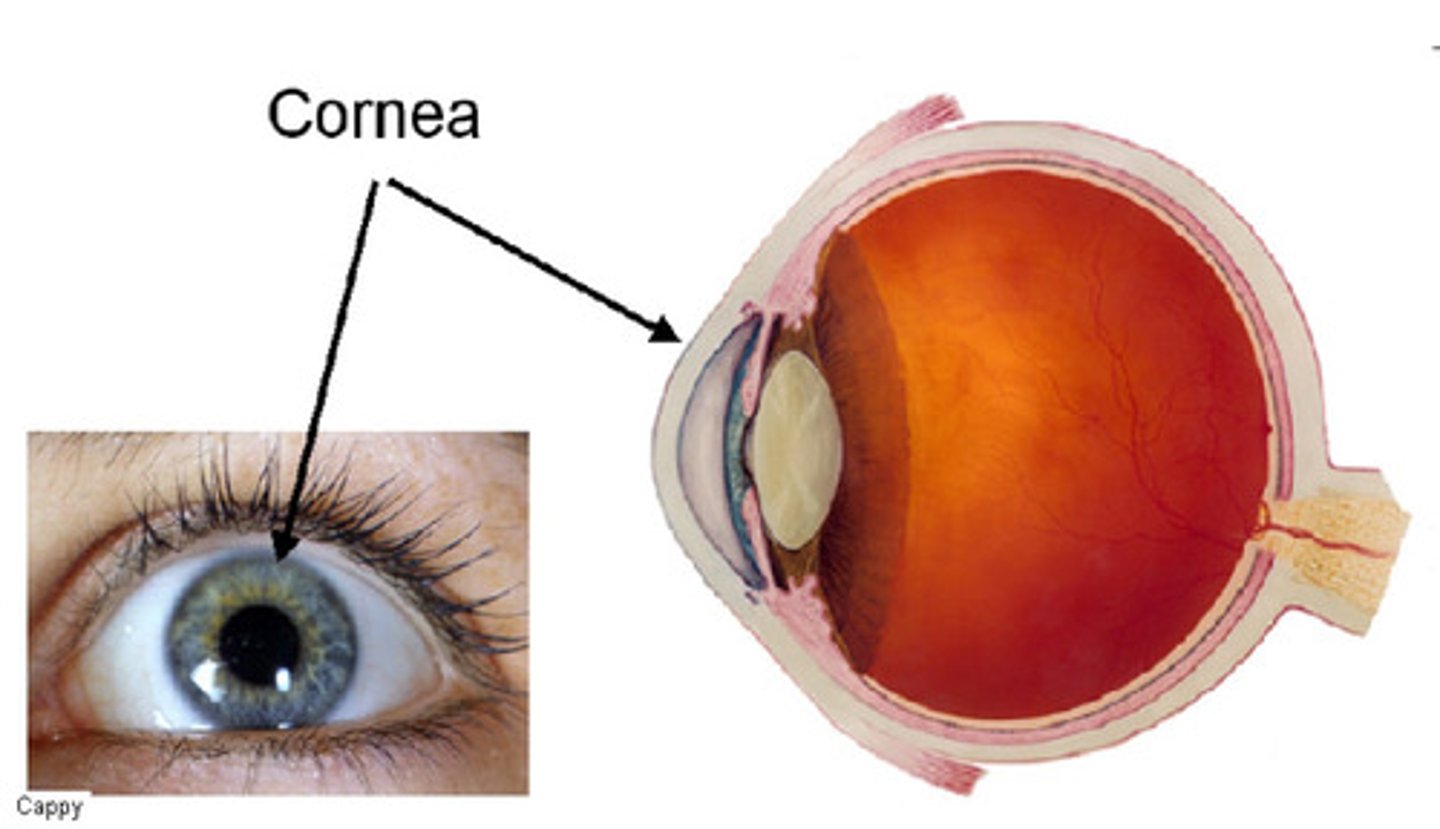
Cornea
Transparent front part; refracts light into eye
Lens
Focuses light on retina; changes shape for near/far vision
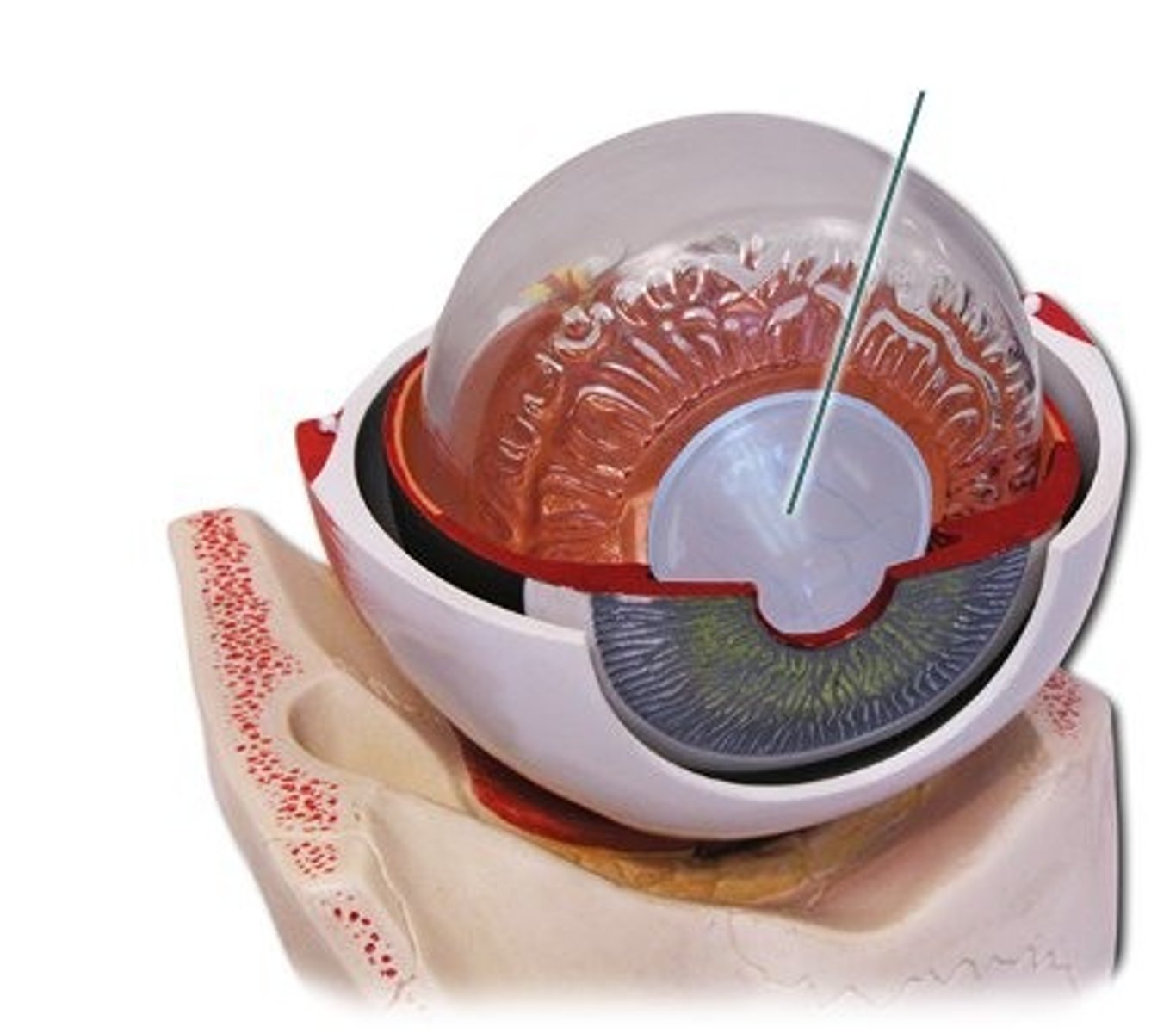
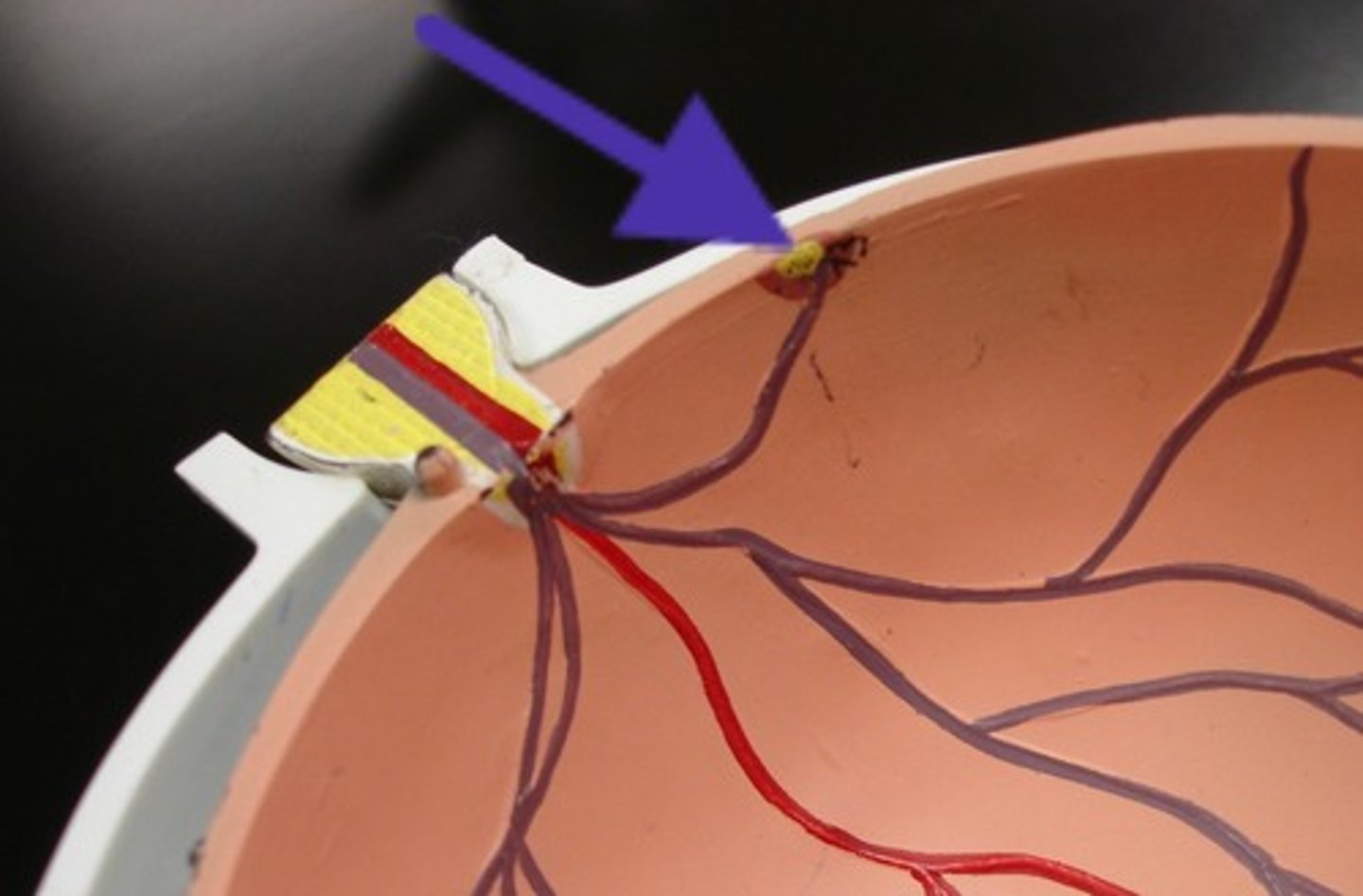
Optic Nerve (CN II)
Transmits visual info to brain
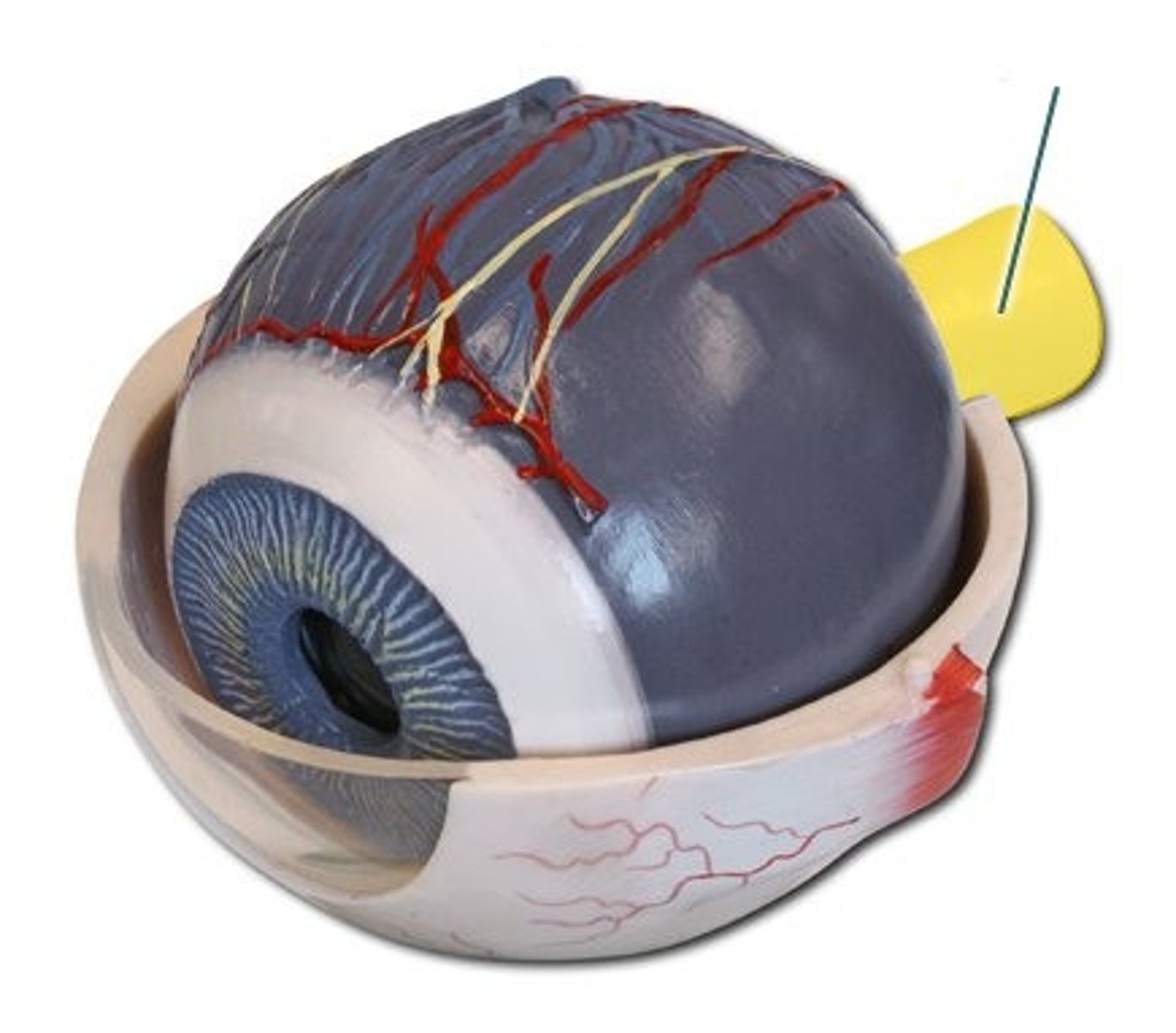
Vitreous Humor
Gel-like fluid filling posterior segment
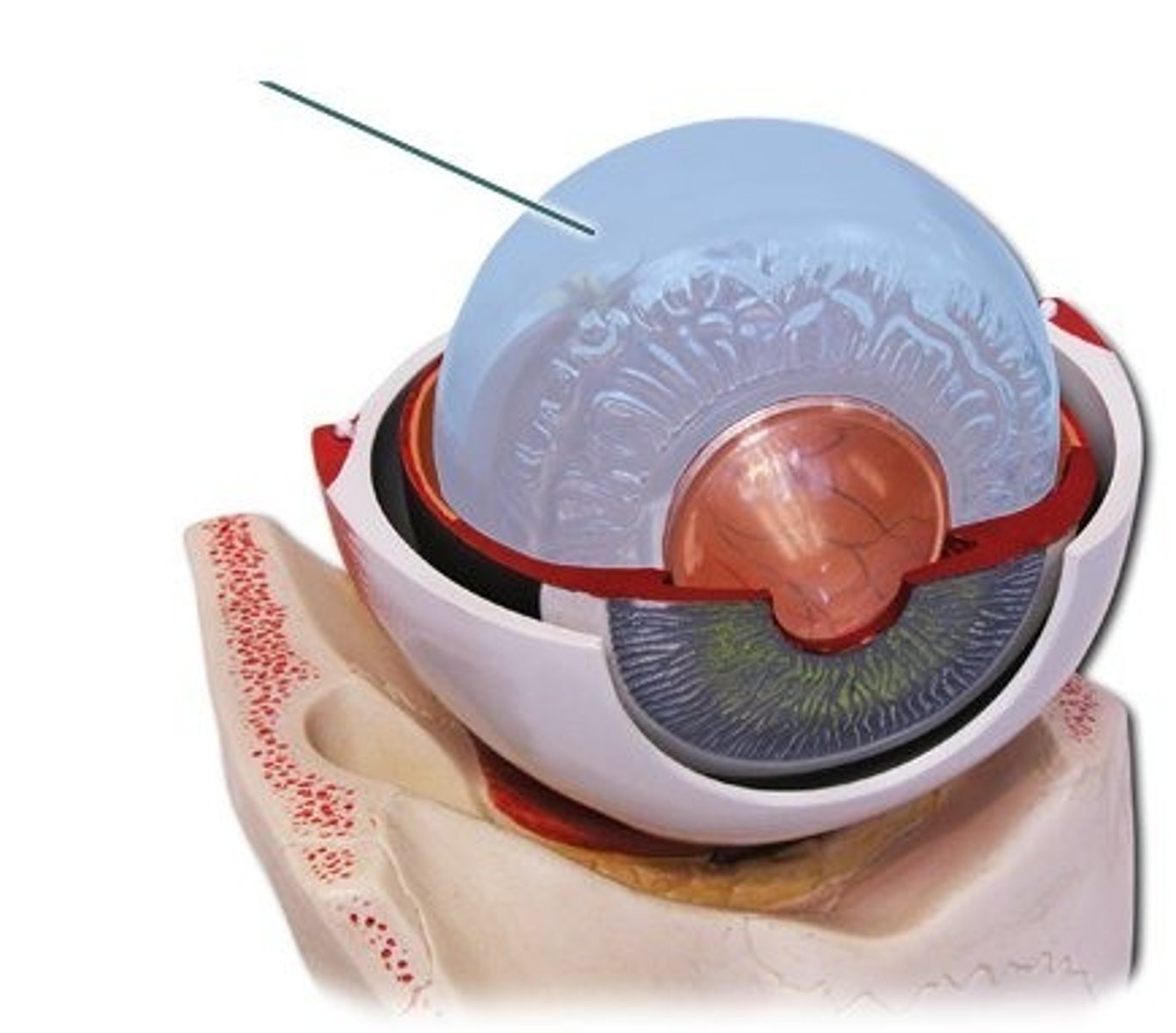
Aqueous Humor
Fluid in anterior and posterior chambers
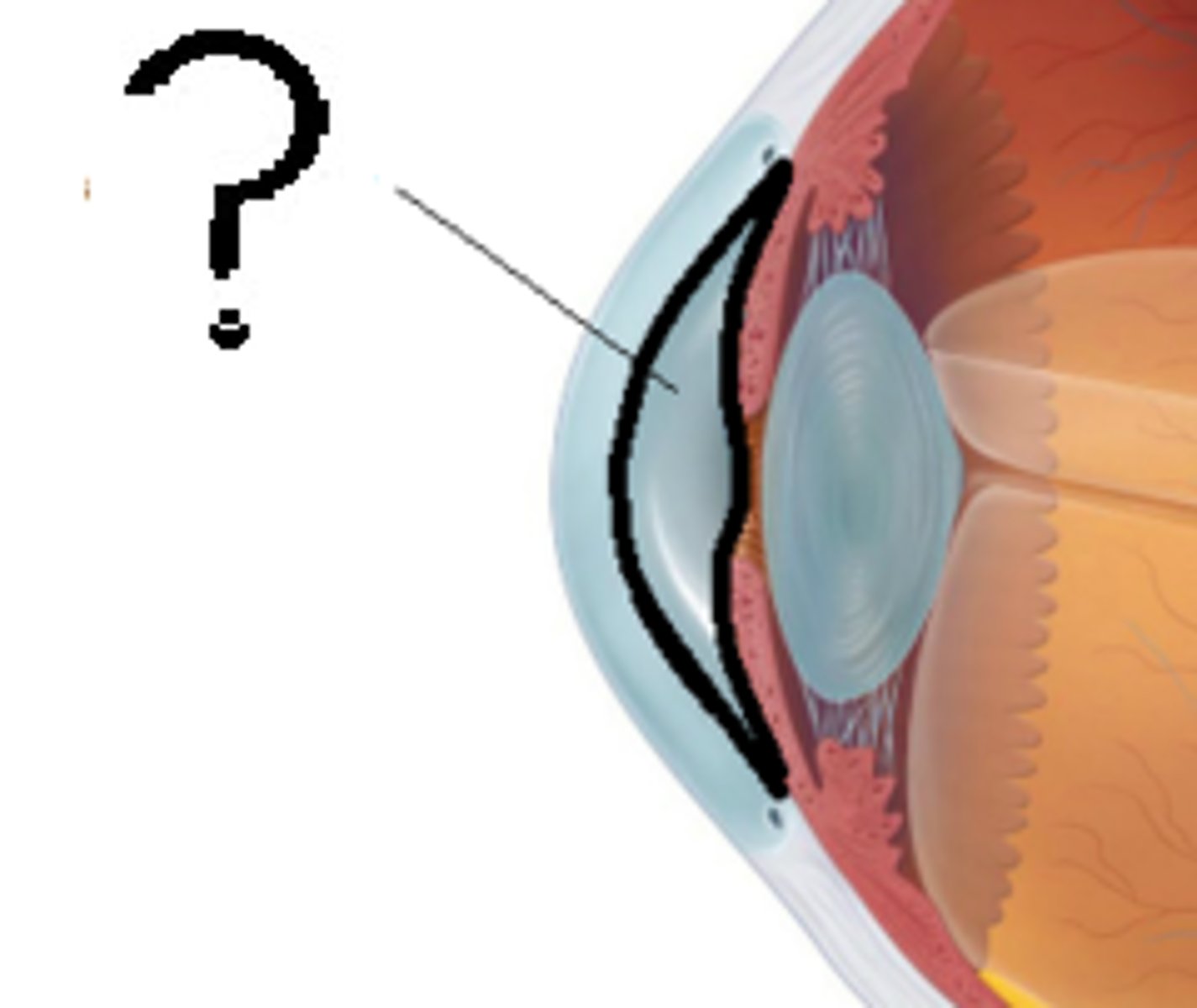
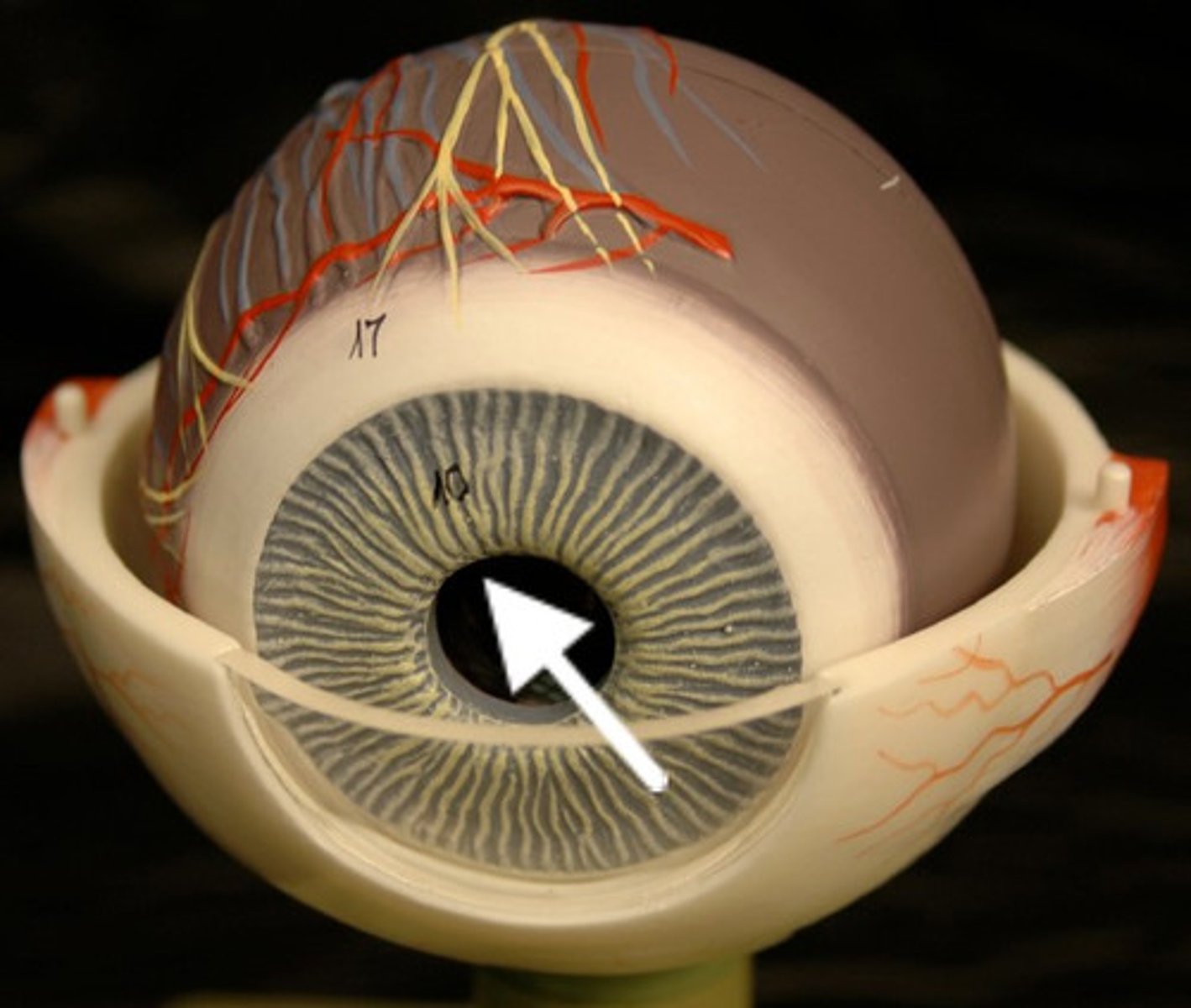
Pupil
Central opening of iris; allows light in
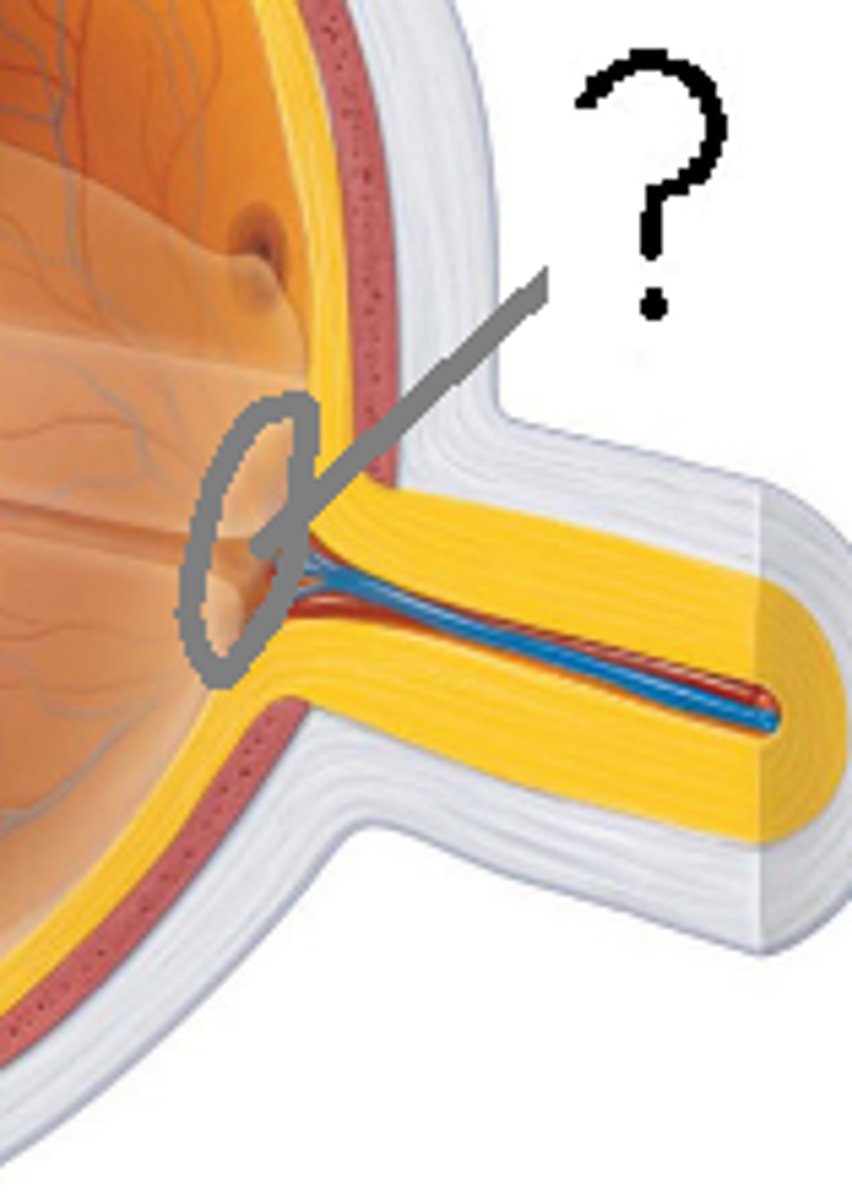
Optic Disc
"Blind spot" — where optic nerve exits, no receptors
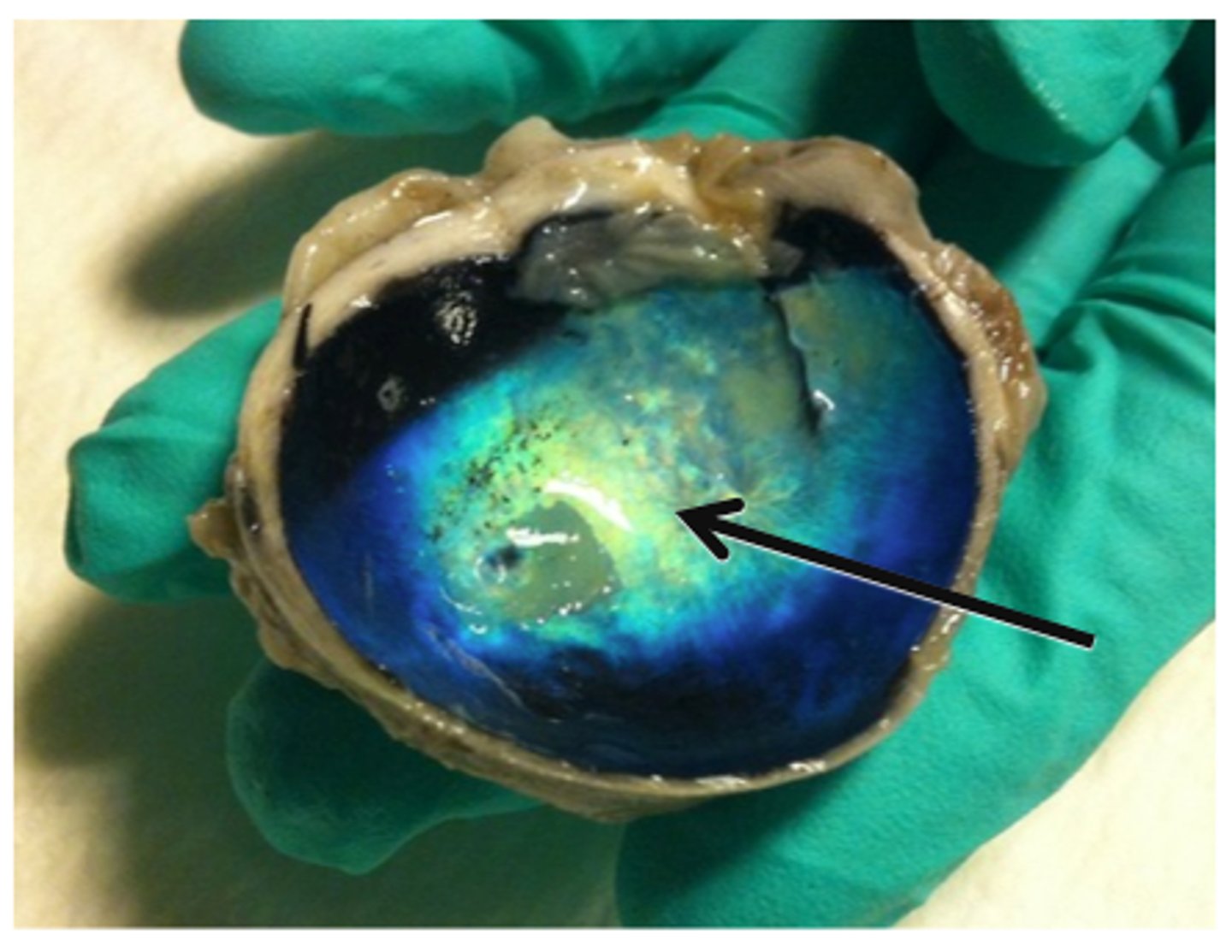
Tapetum Lucidum
Reflective layer in animals (night vision)
Fovea Centralis
Sharpest vision point; high cone density
Conjunctiva
Mucous membrane lining eyelids & sclera
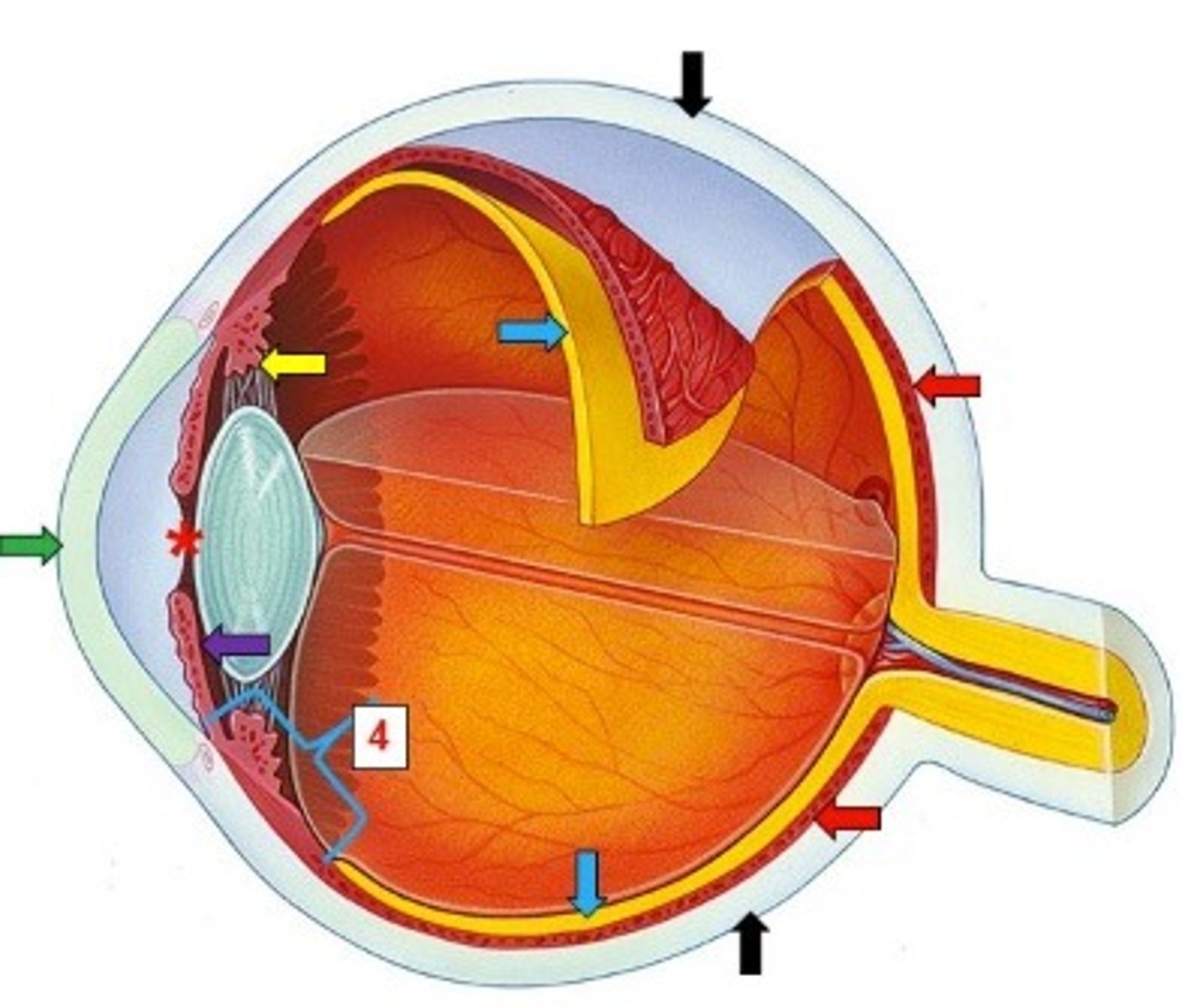
Ciliary Process
Secretes aqueous humor
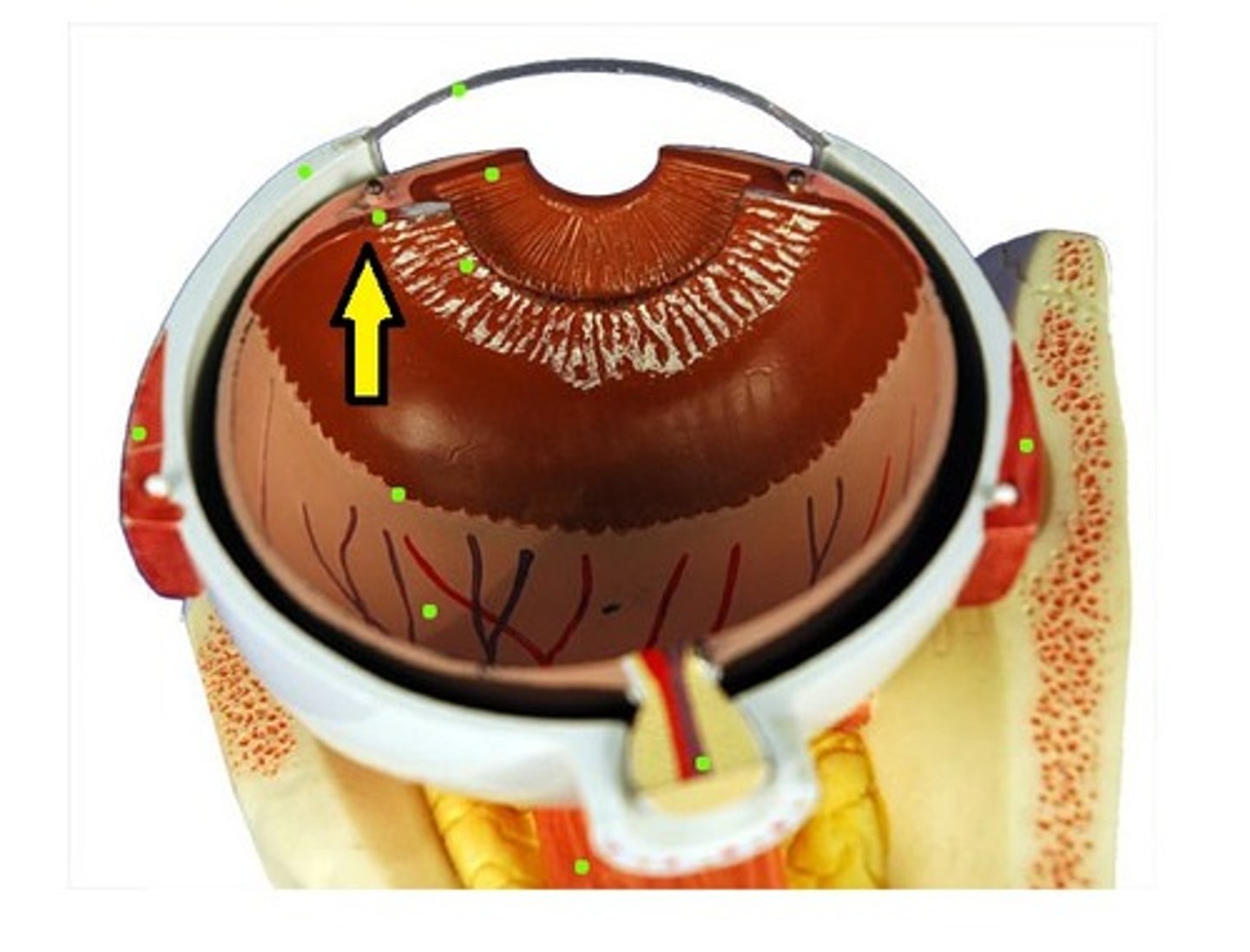
Ciliary Muscle
Alters lens shape for focus (accommodation)
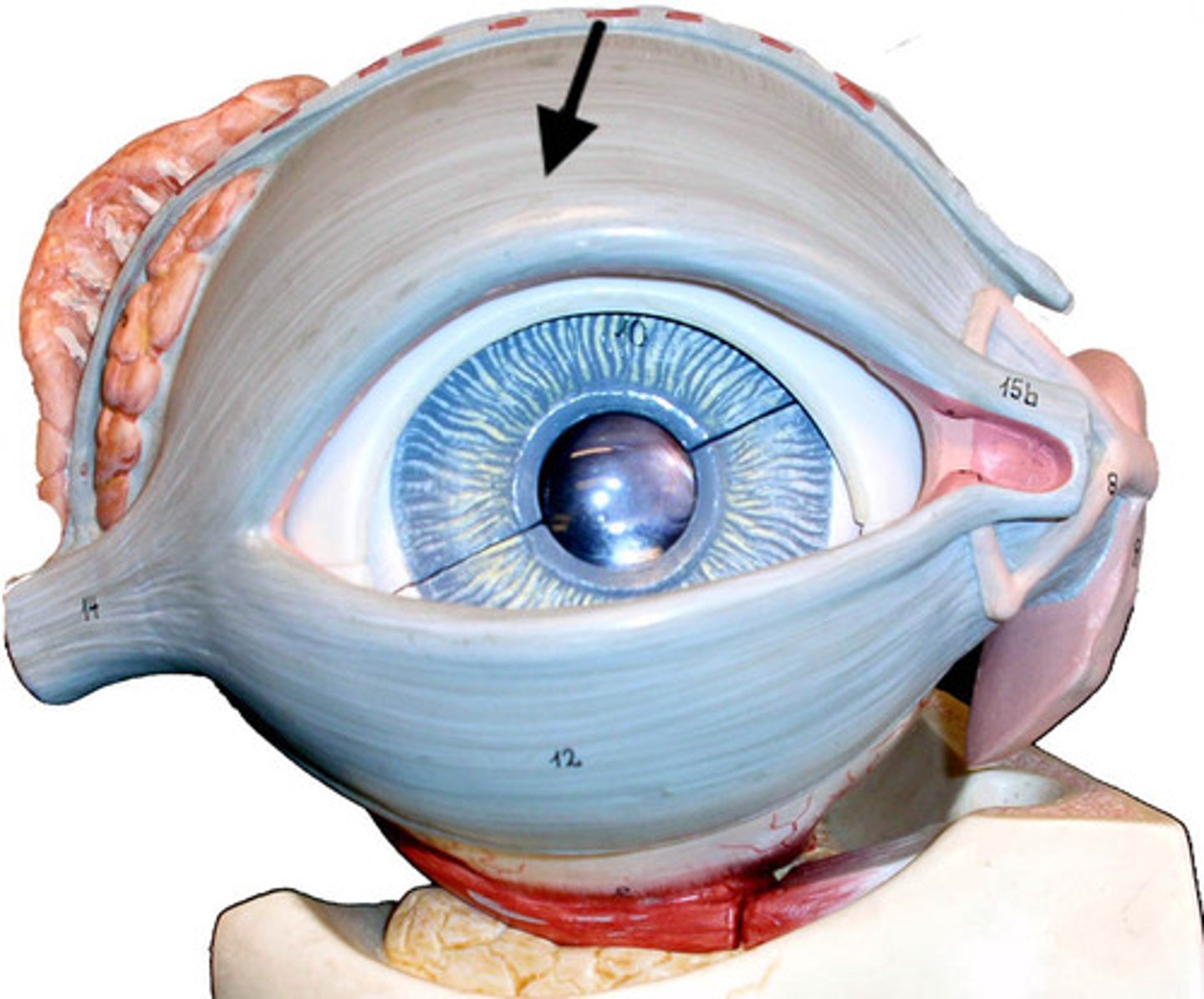
Eyelid
Protects eye; lined with palpebral conjunctiva
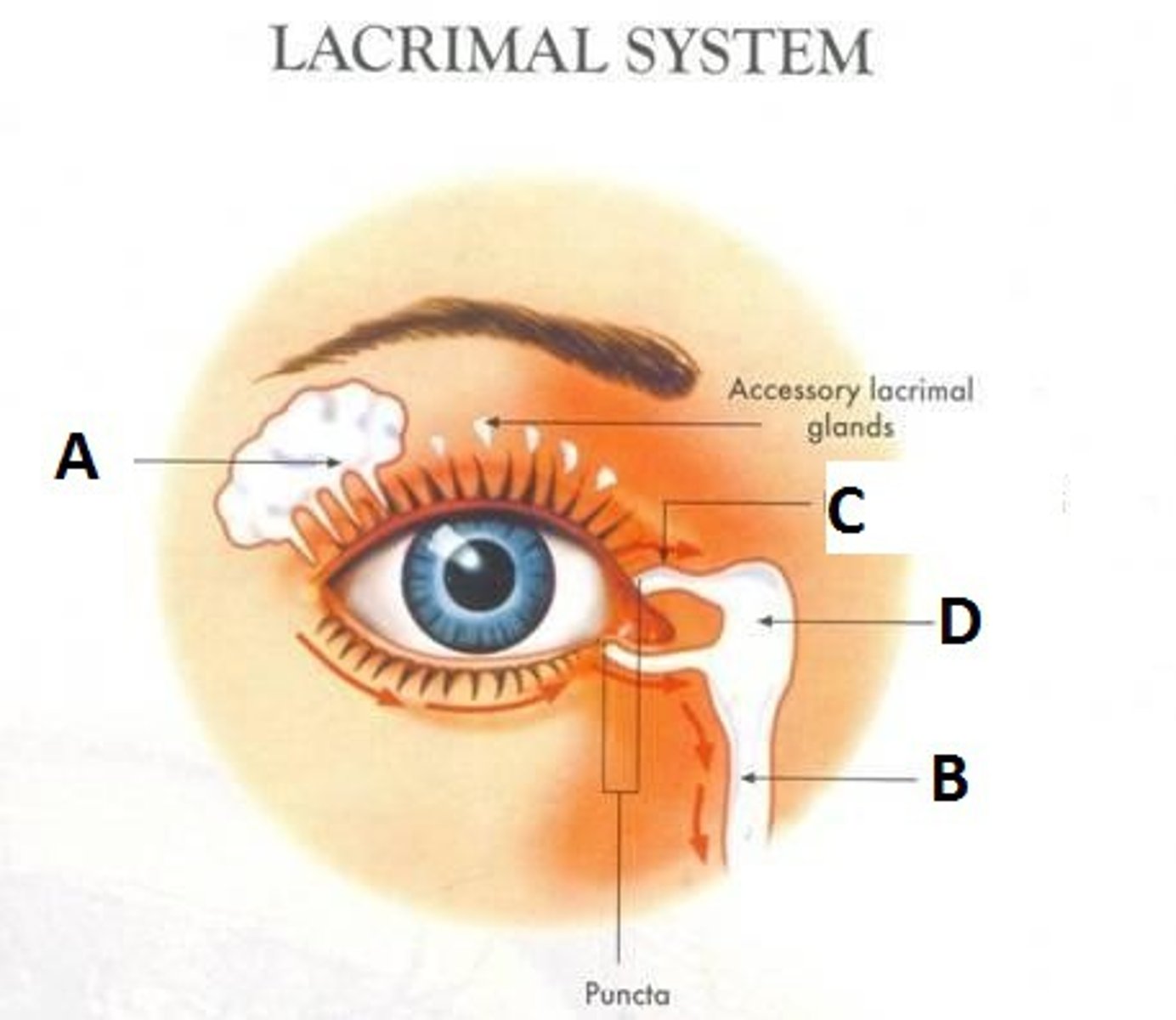
Lacrimal Gland
Produces tears
Lacrimal Duct
Drains tears to nasal cavity
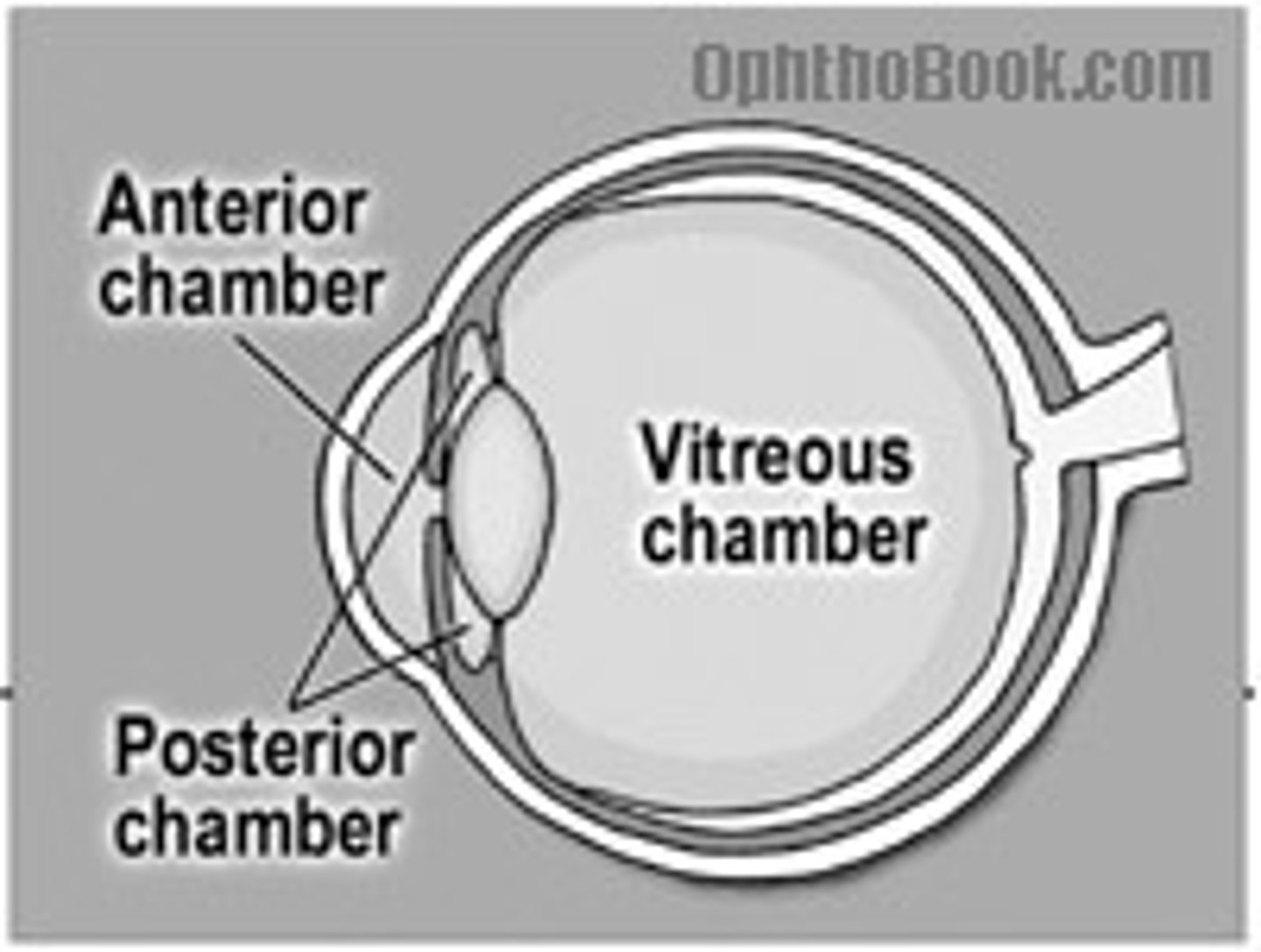
Anterior Chamber
Space between cornea and iris (aqueous humor)
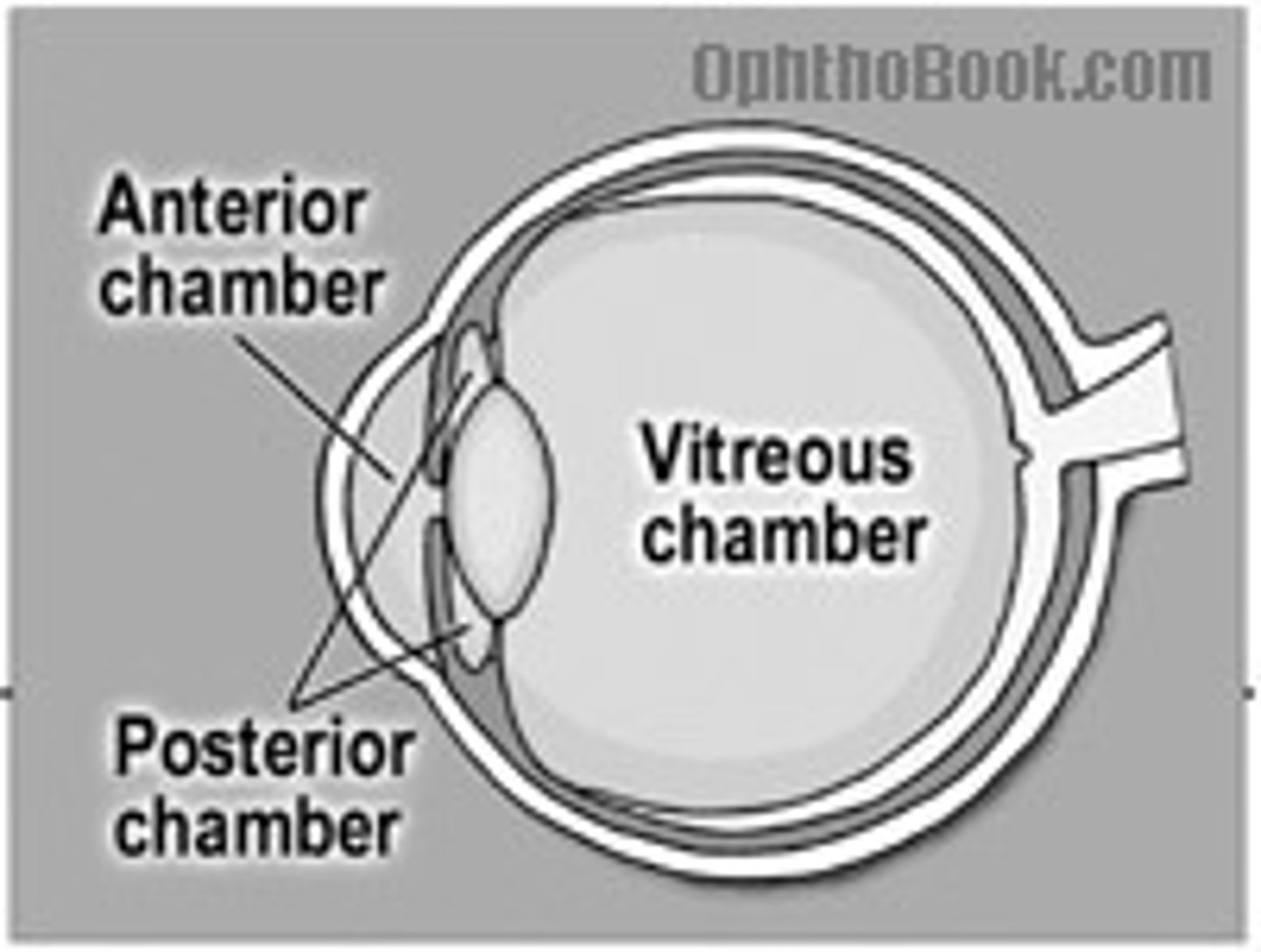
Posterior Chamber
Between iris and lens (aqueous humor)
Posterior Segment
Behind lens; filled with vitreous humor
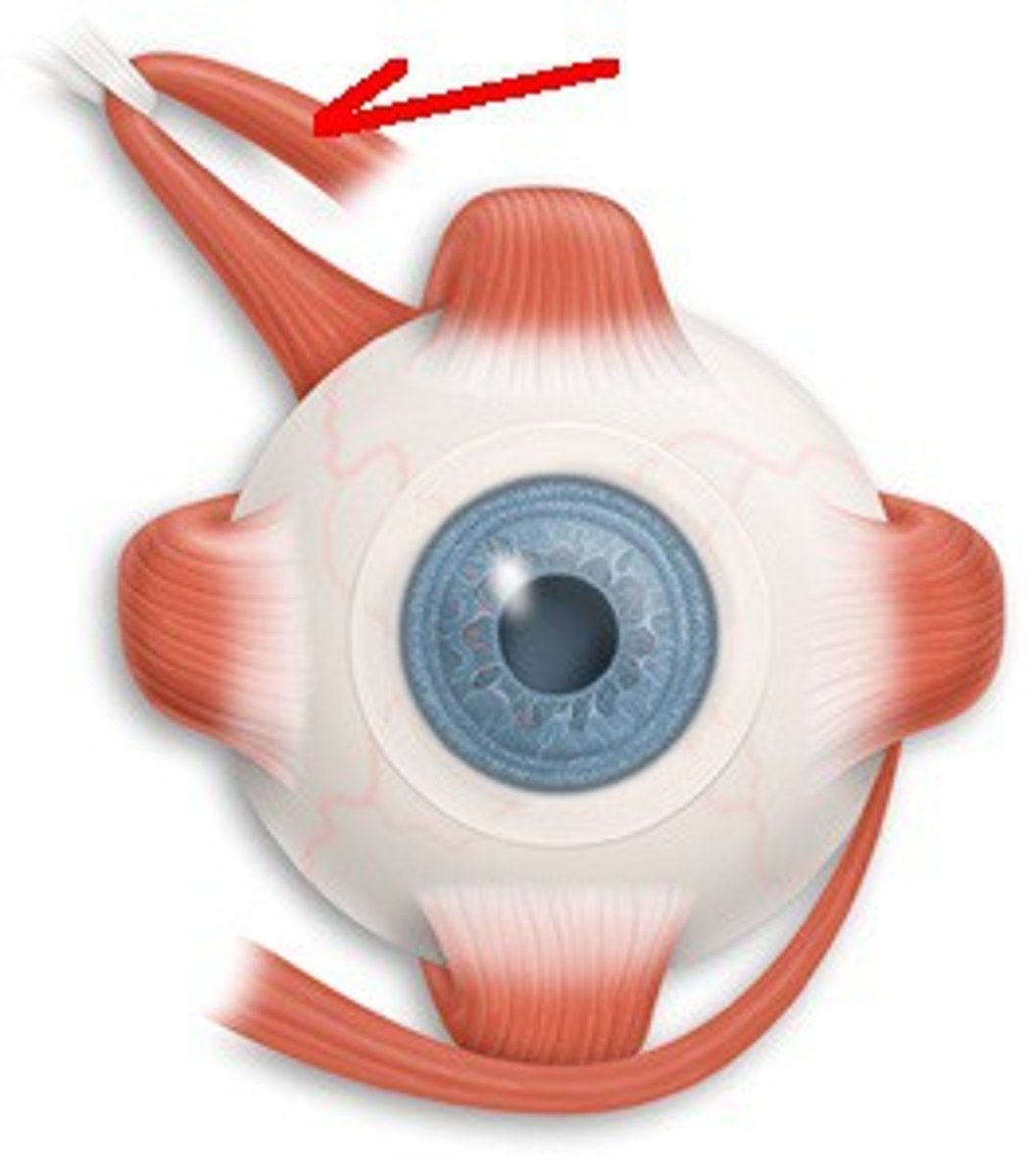
Superior Oblique
CN IV; Moves eye down & out
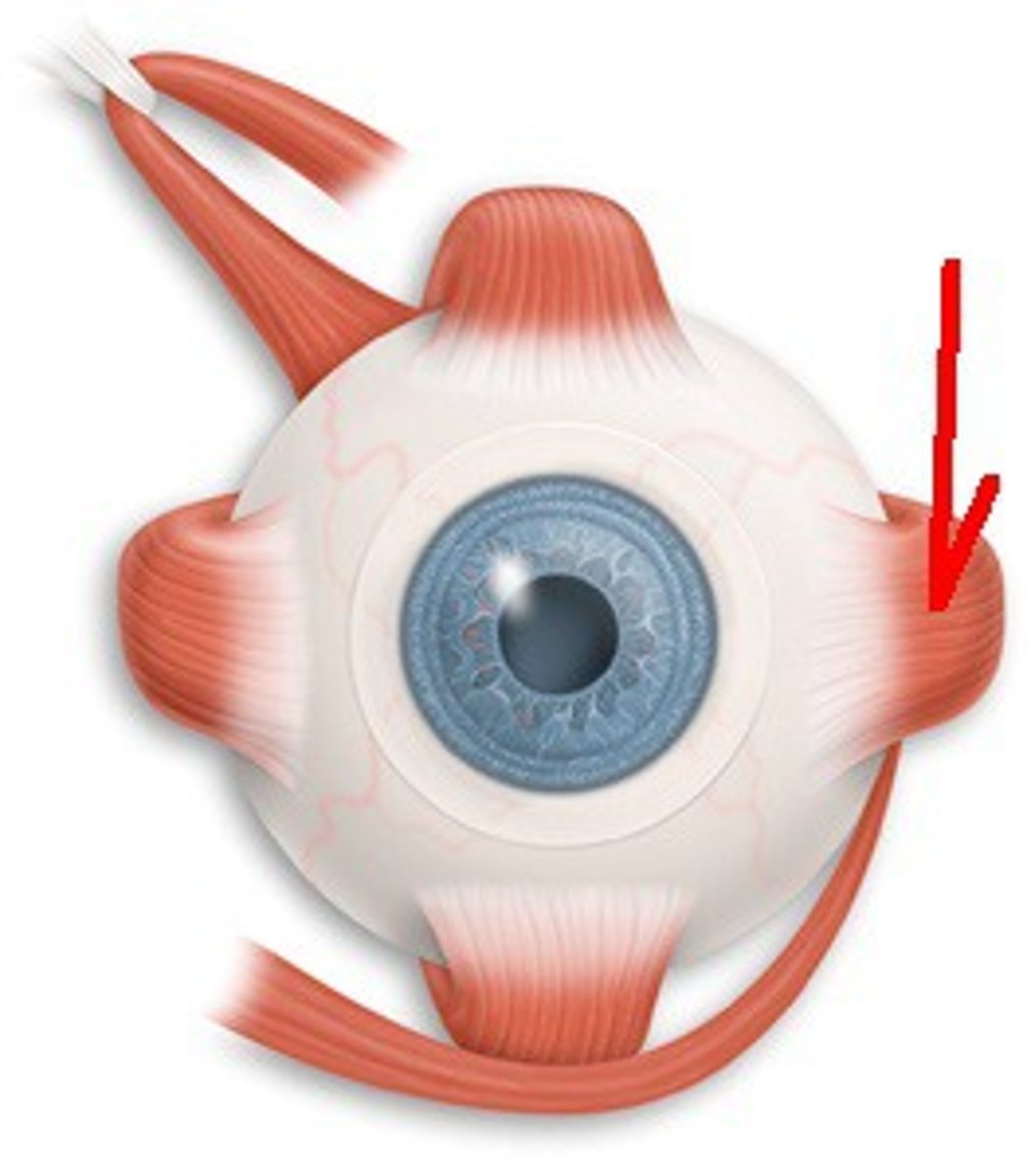
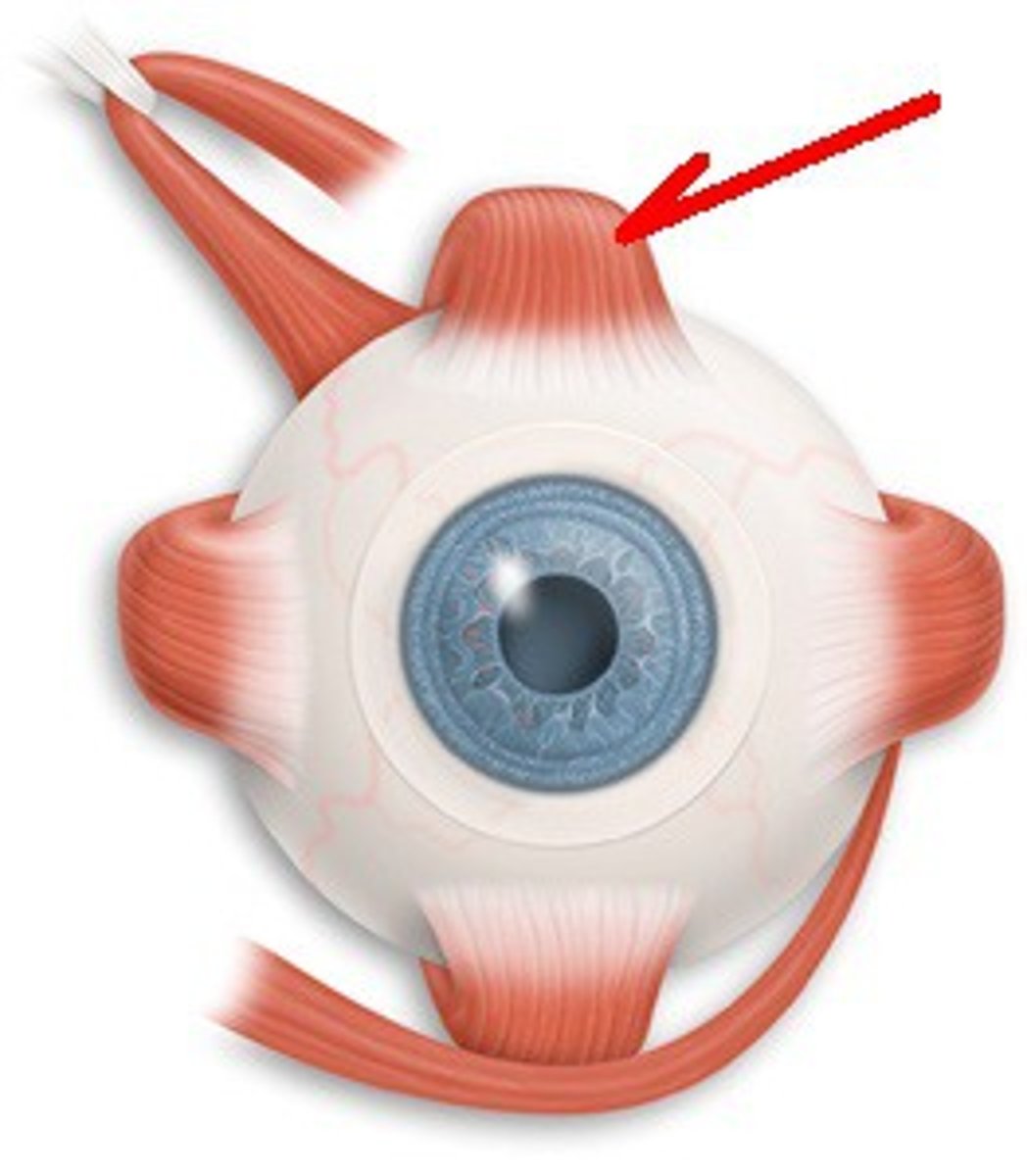
Inferior Oblique
CN III; Moves eye up & out
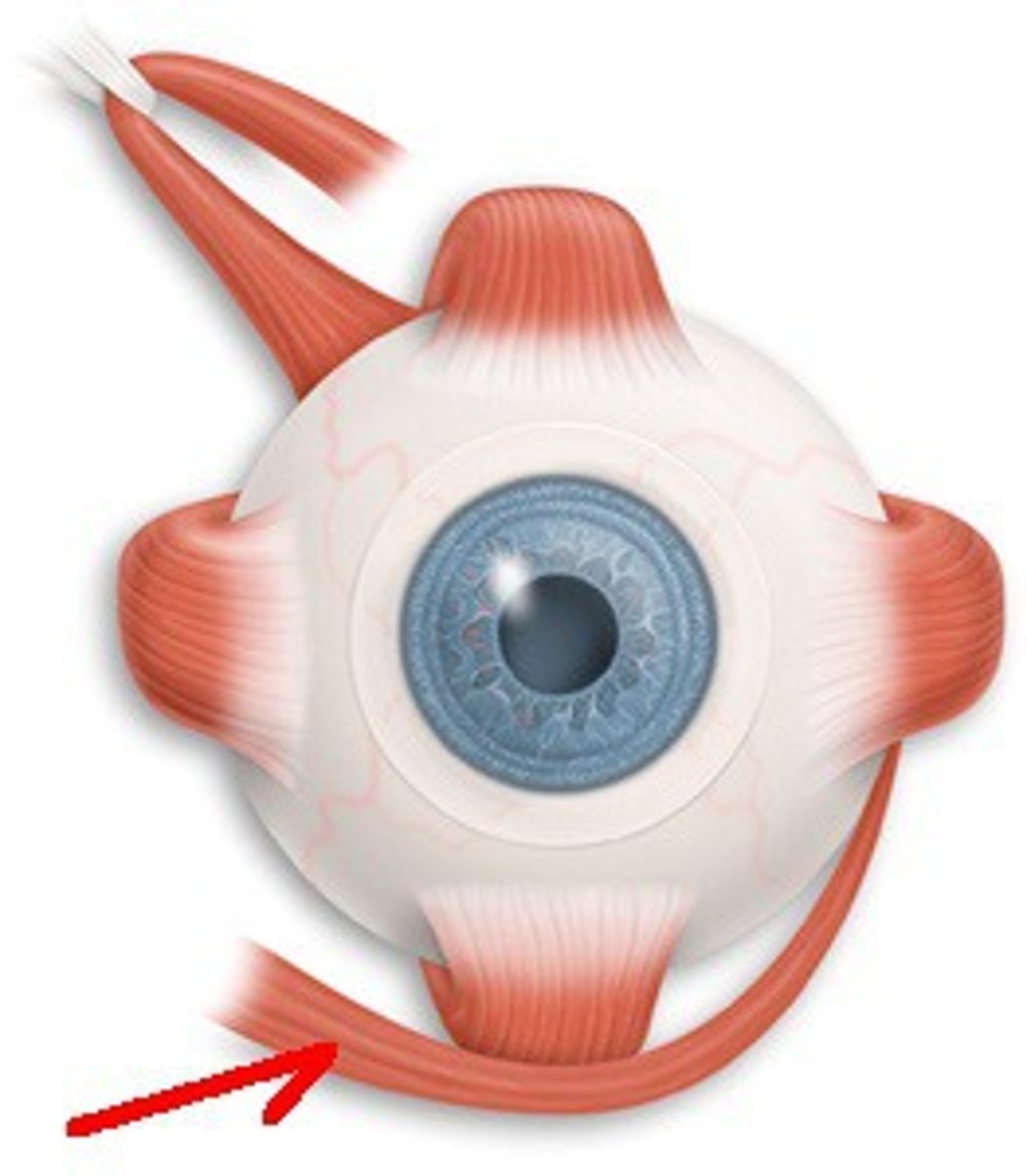
Lateral Rectus
CN VI; Moves eye out (abduction)
Medial Rectus
CN III; Moves eye in (adduction)
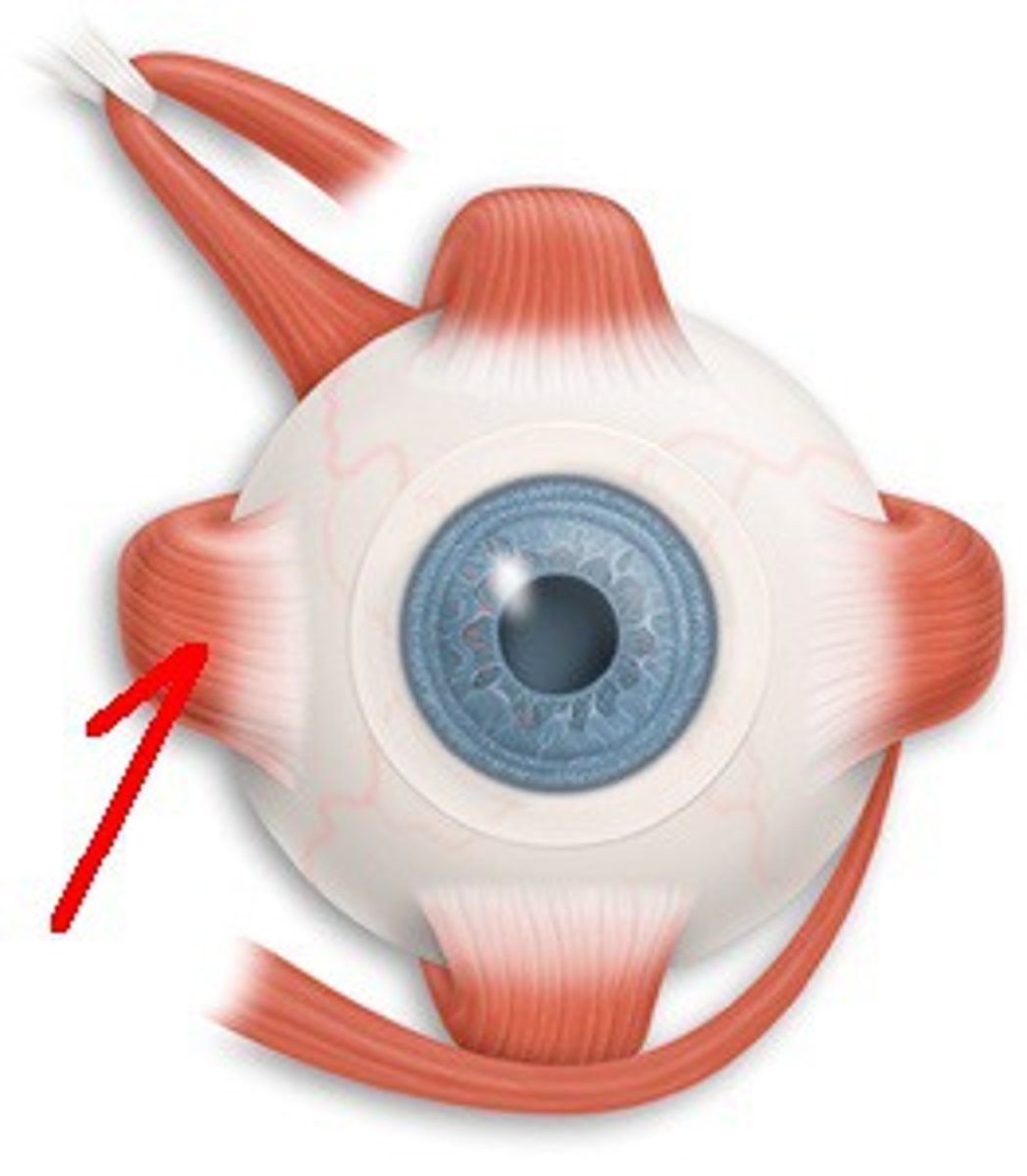
Inferior Rectus
CN III; Moves eye down & in
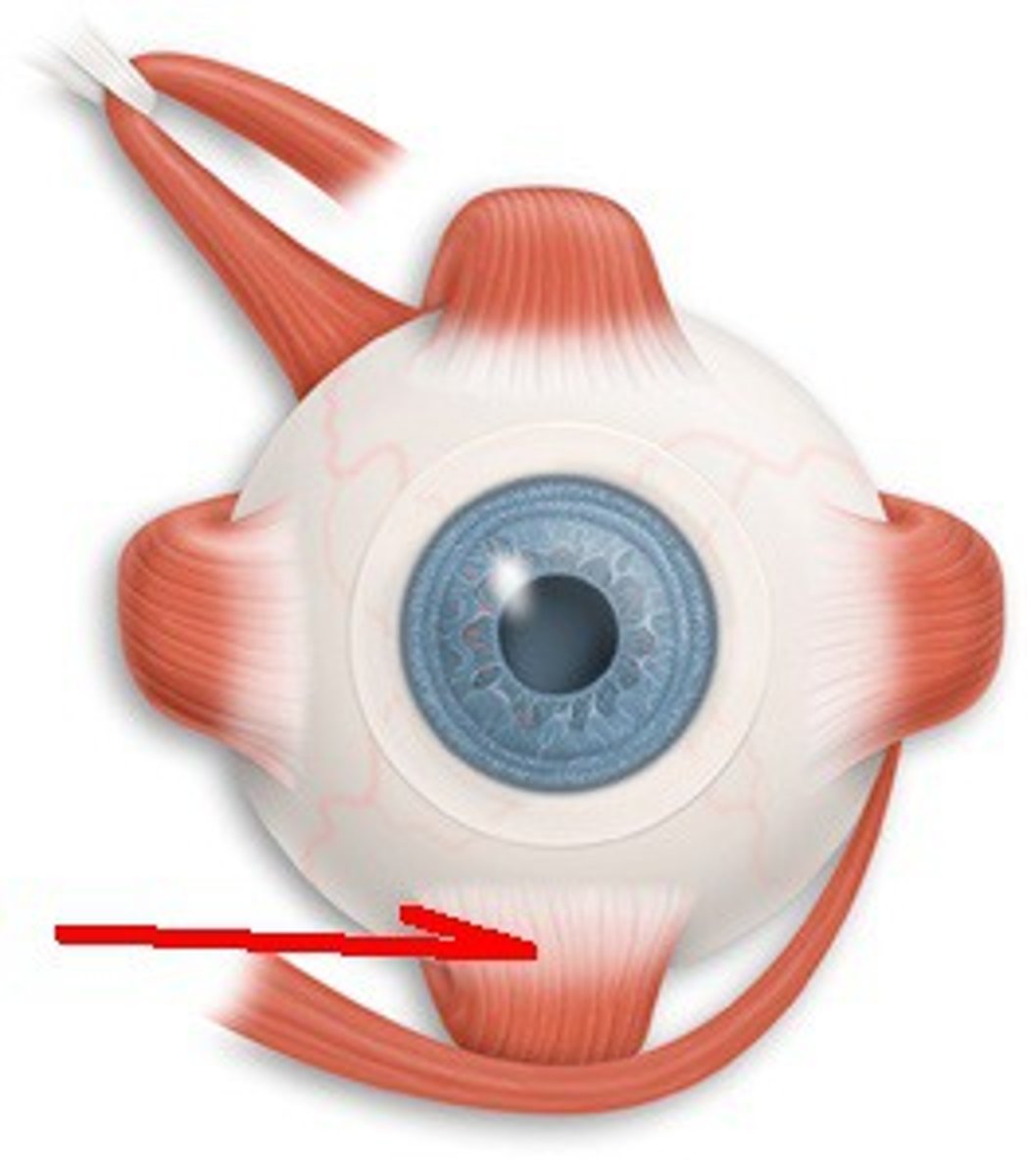
Superior Rectus
CN III; Moves eye up & in
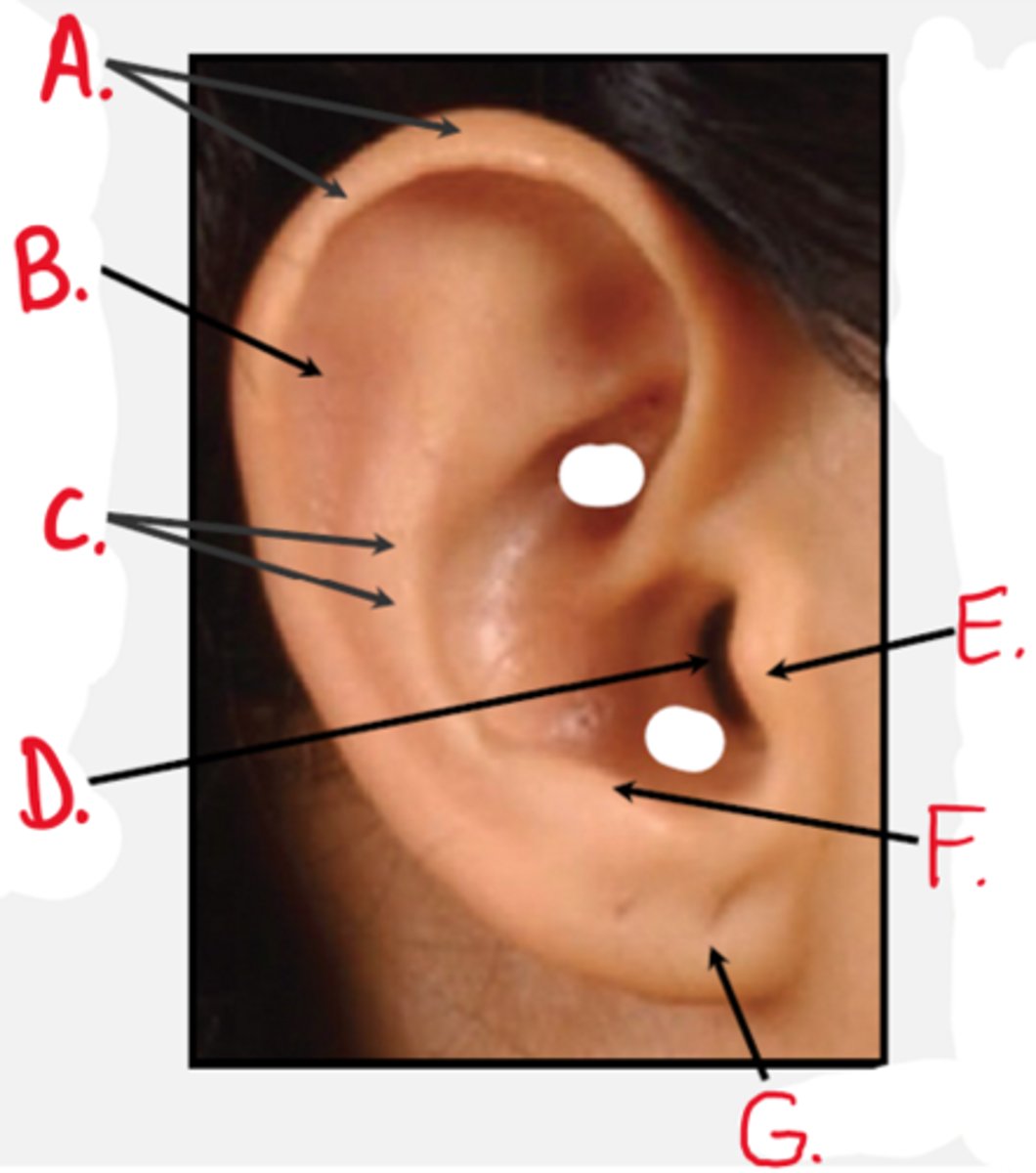
Auricle (Pinna)
Outer ear flap; collects sound
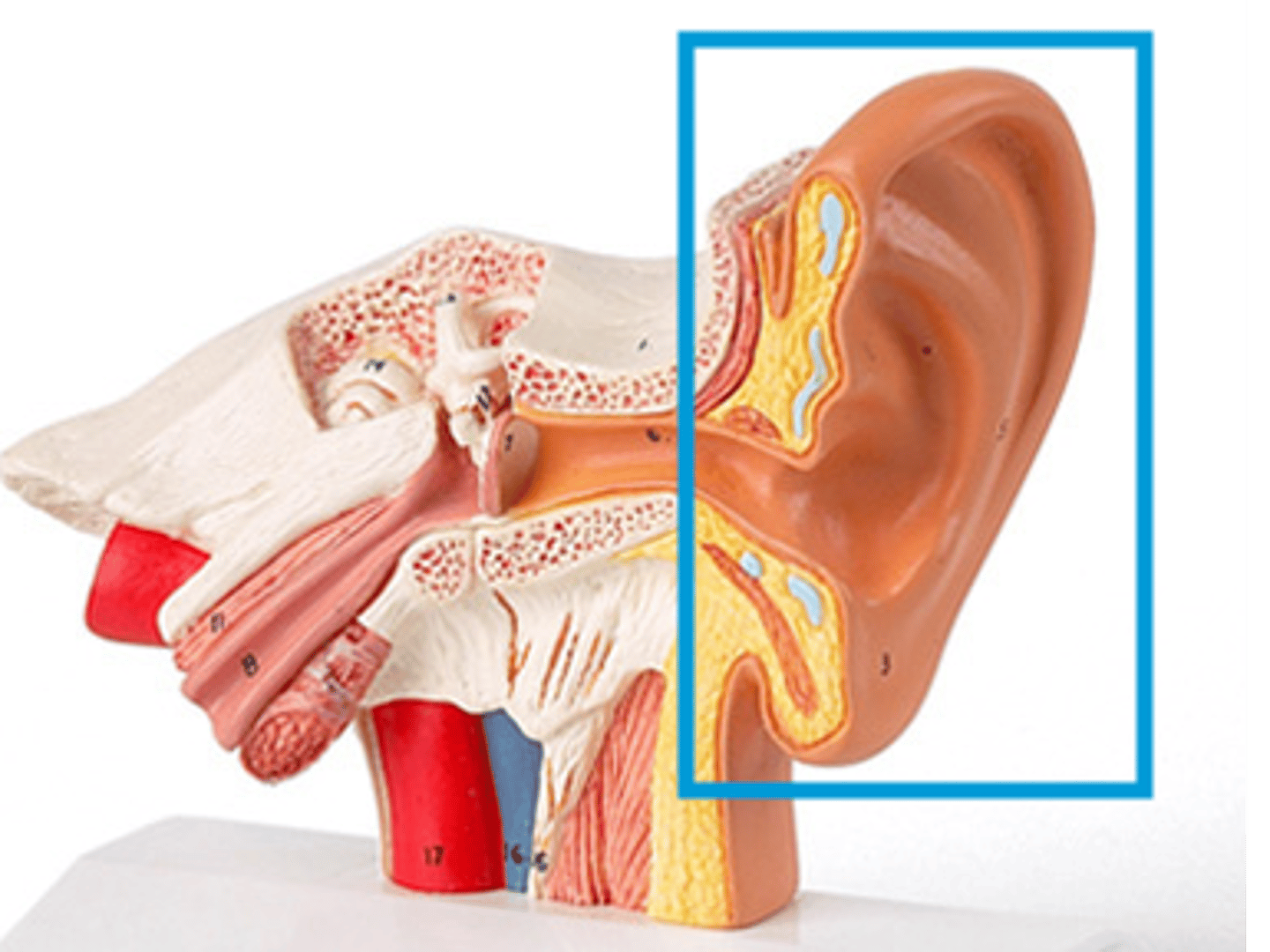
Lobule
Lower soft part of pinna
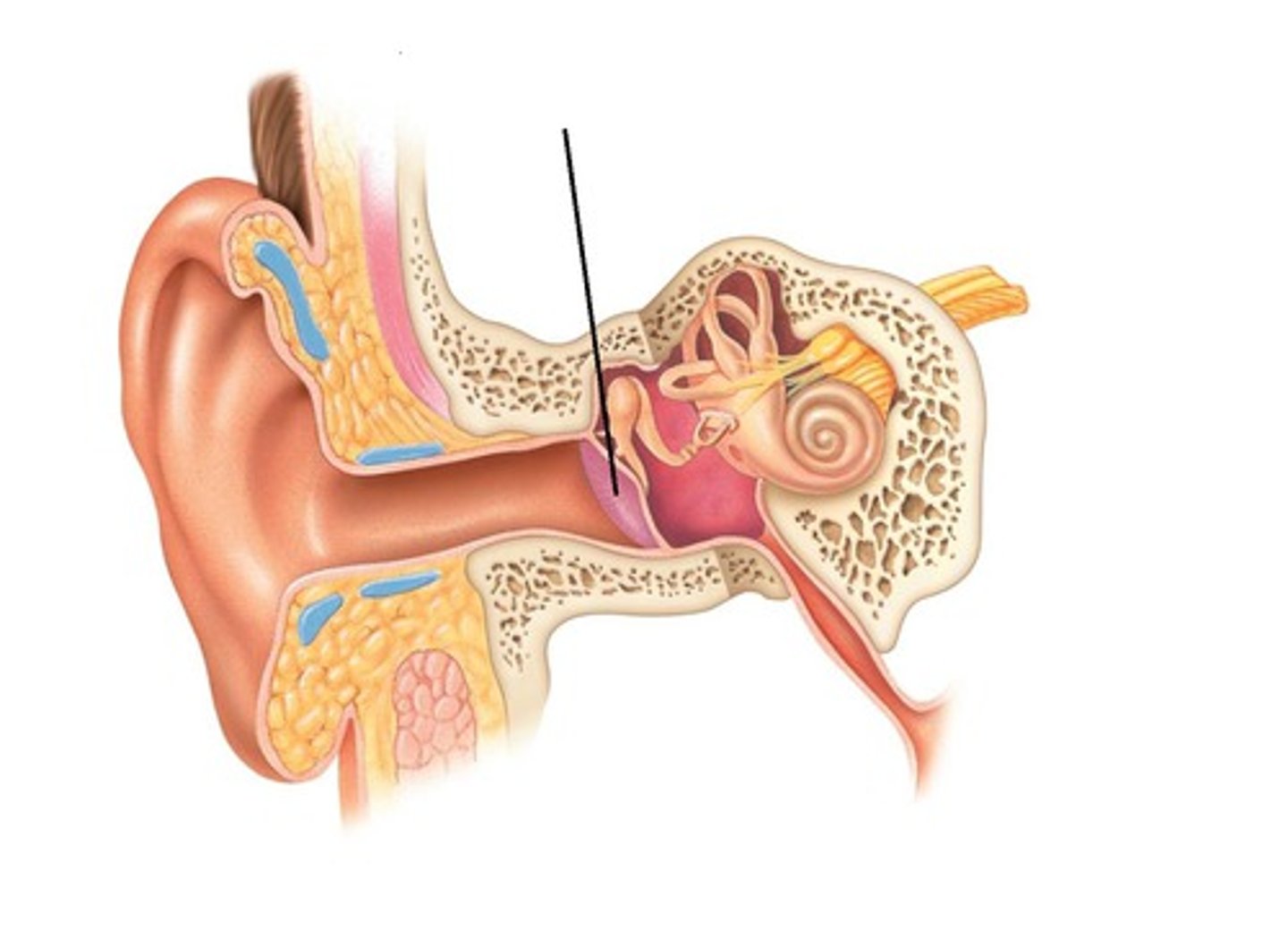
External Auditory Canal / Meatus
Directs sound to tympanic membrane
Tympanic Membrane
Eardrum; vibrates with sound waves
Malleus (Hammer)
Attached to eardrum
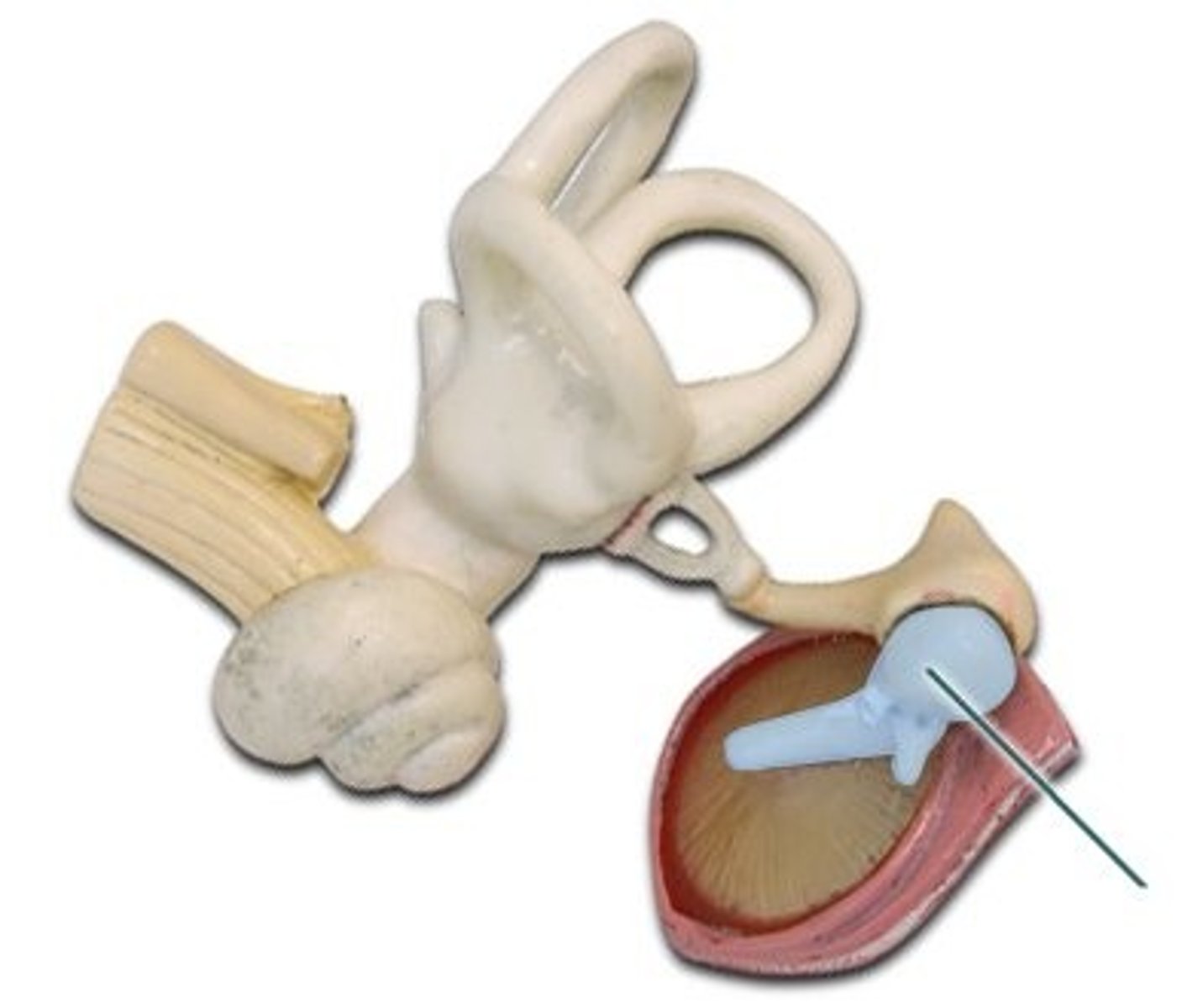
Incus (Anvil)
Middle bone
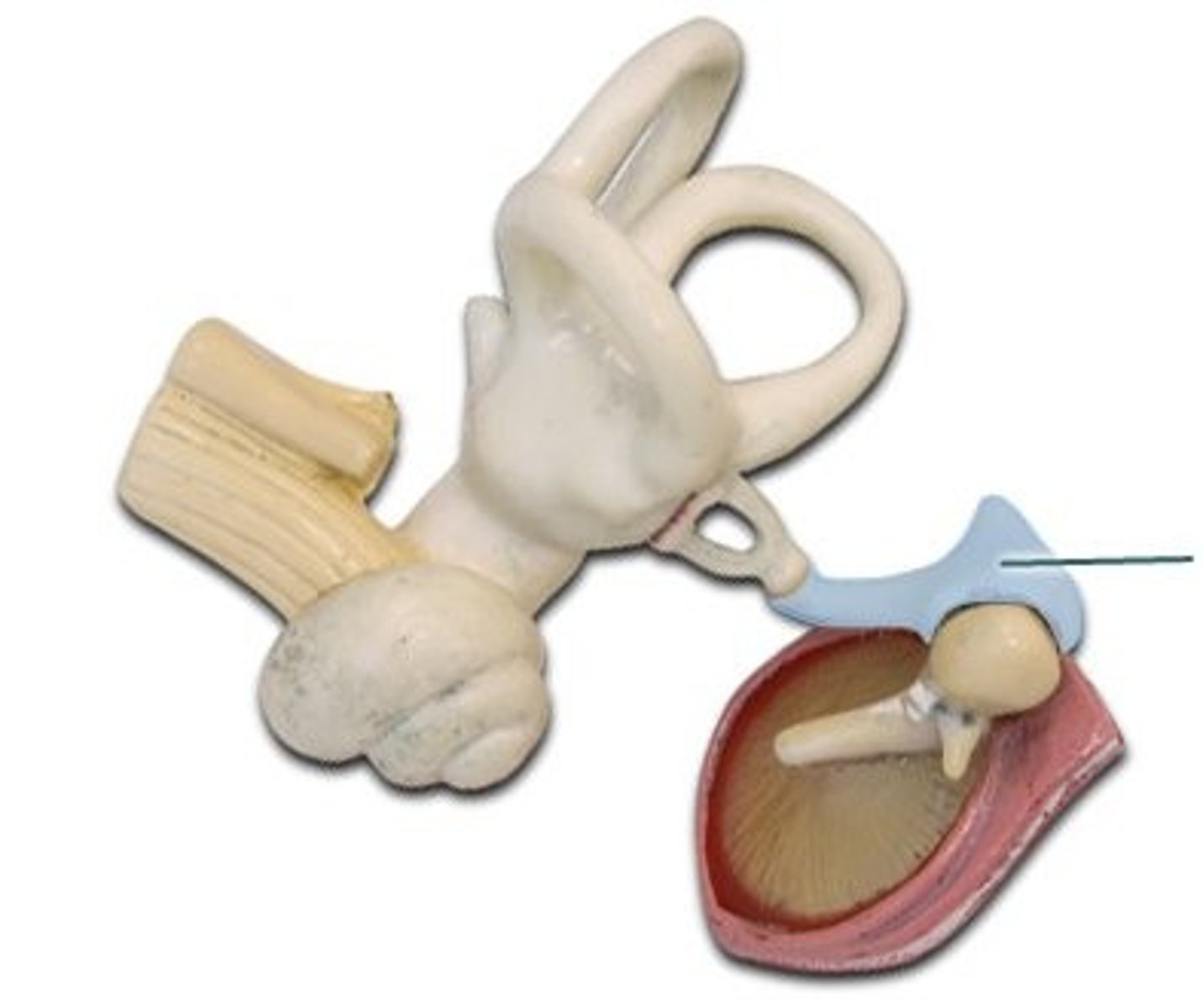
Stapes (Stirrup)
Transmits vibrations to oval window
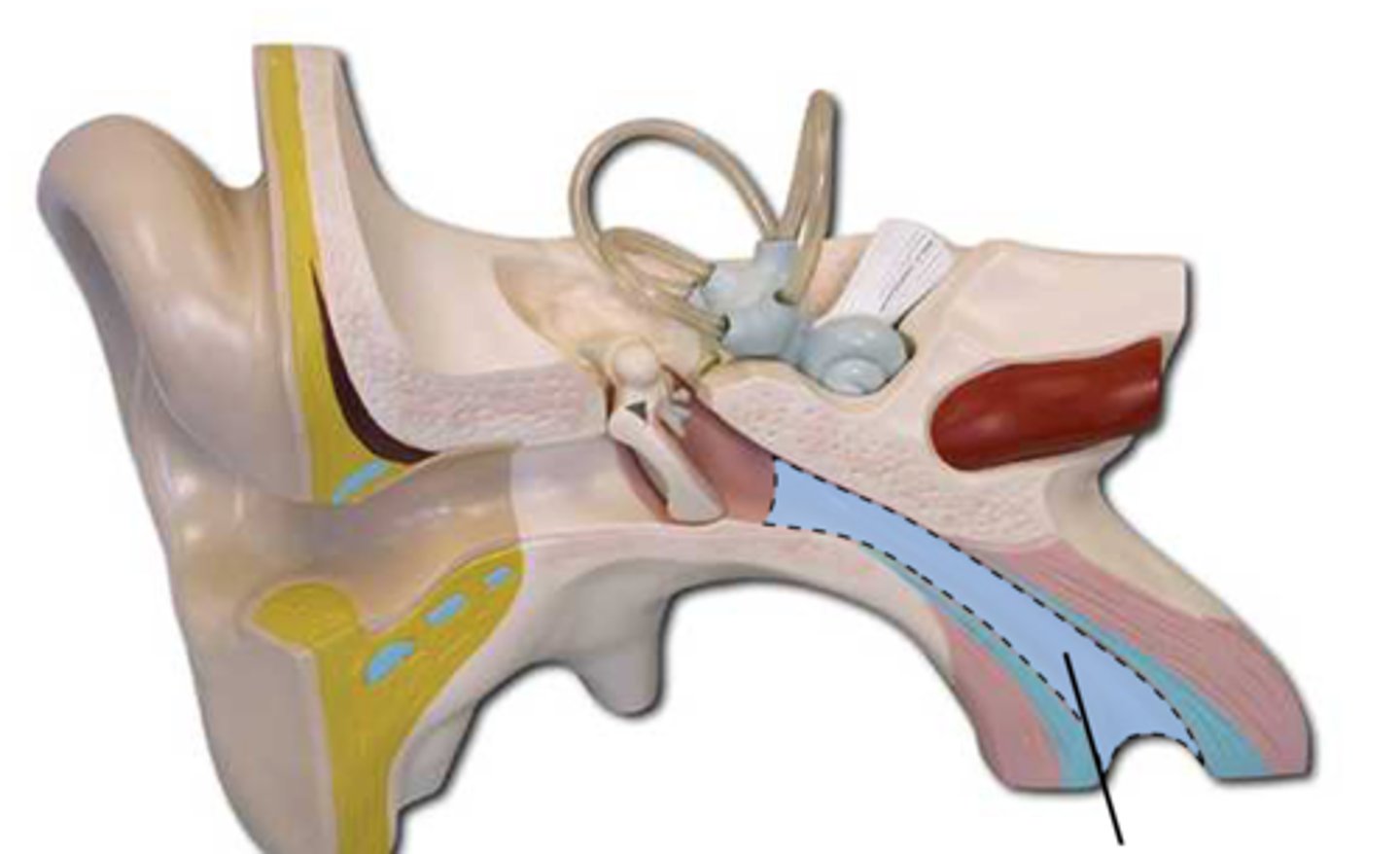
Eustachian (Pharyngotympanic) Tube
Connects middle ear to nasopharynx; equalizes pressure
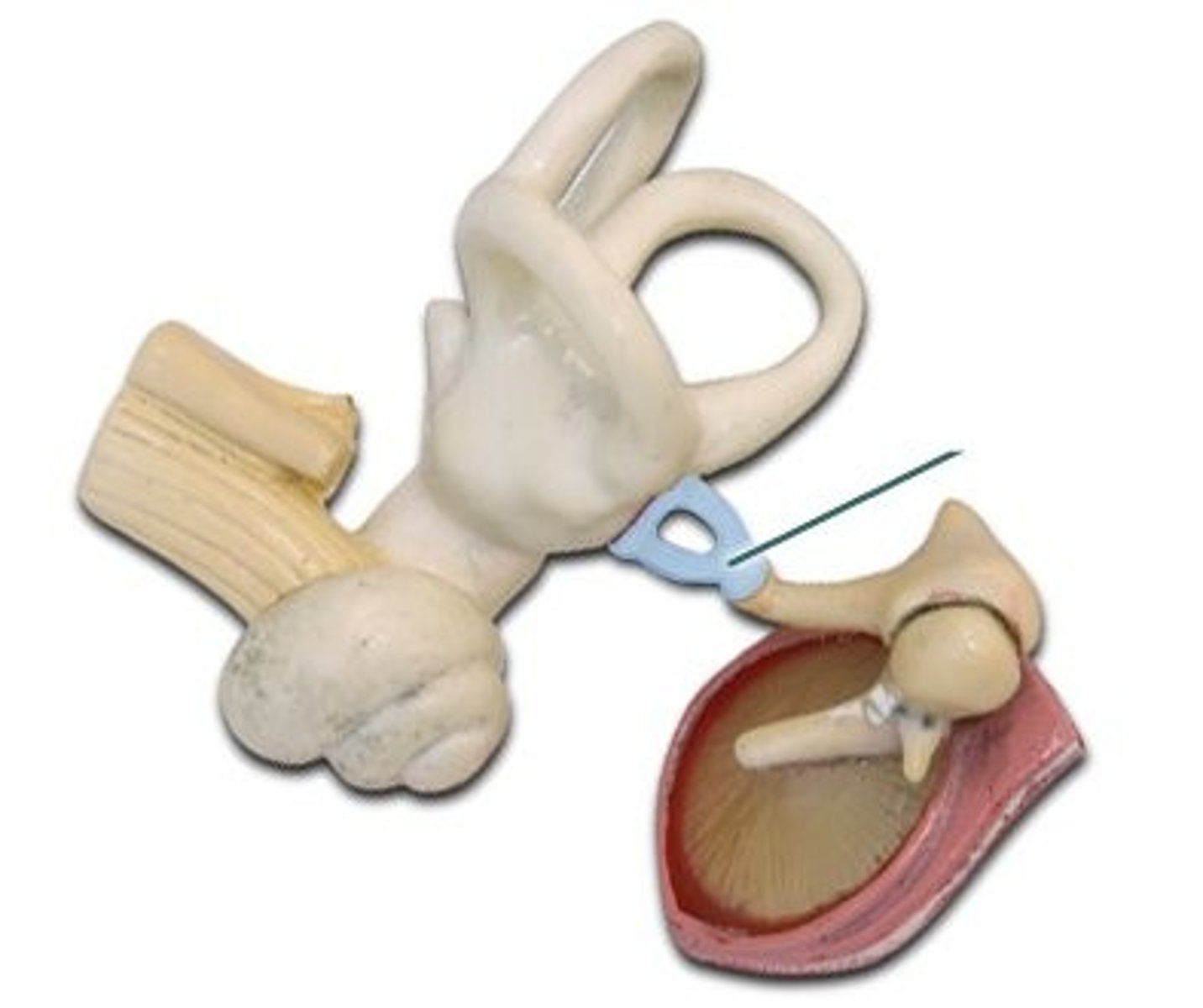
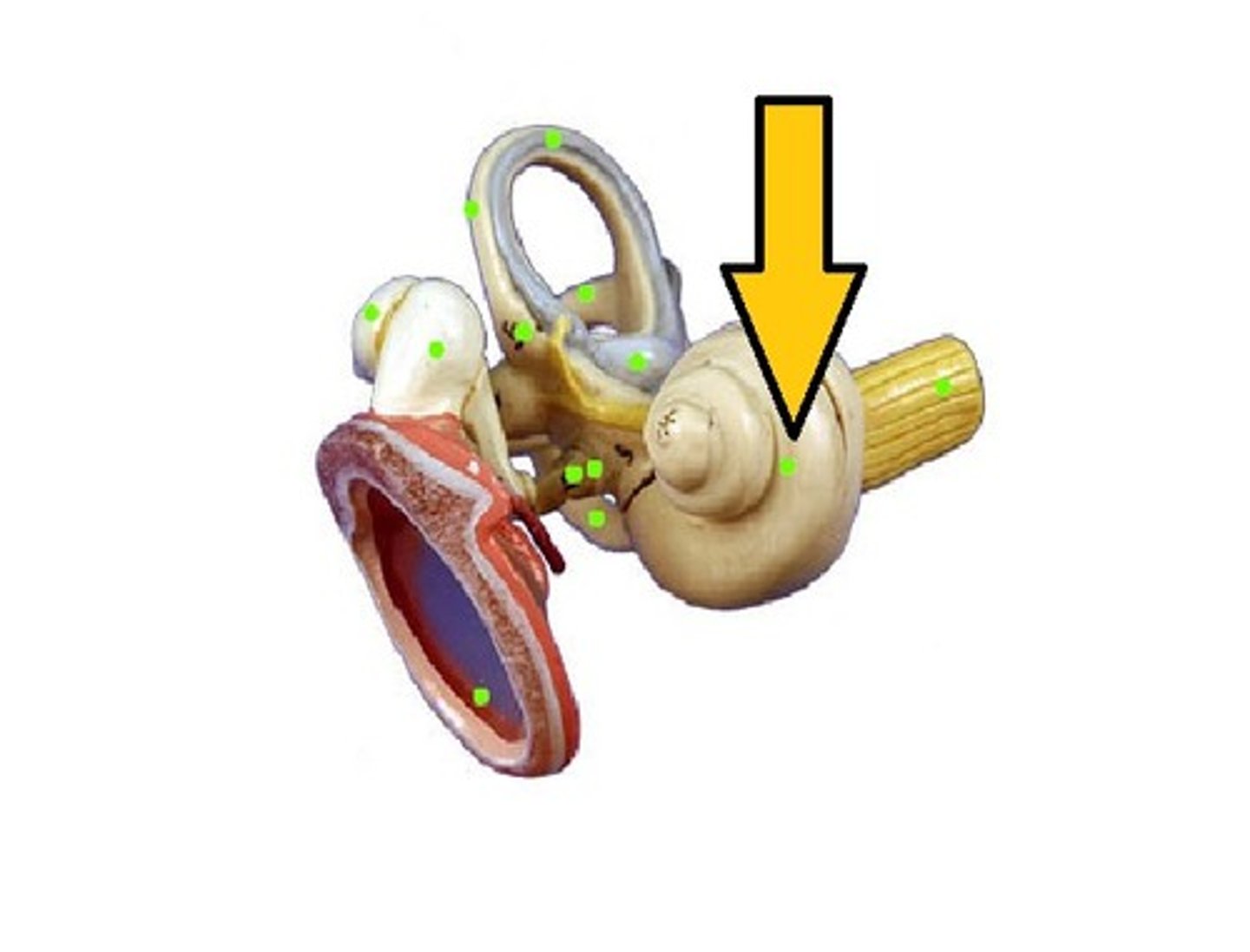
Cochlea
Hearing; spiral-shaped
Round Window
Releases pressure from cochlea
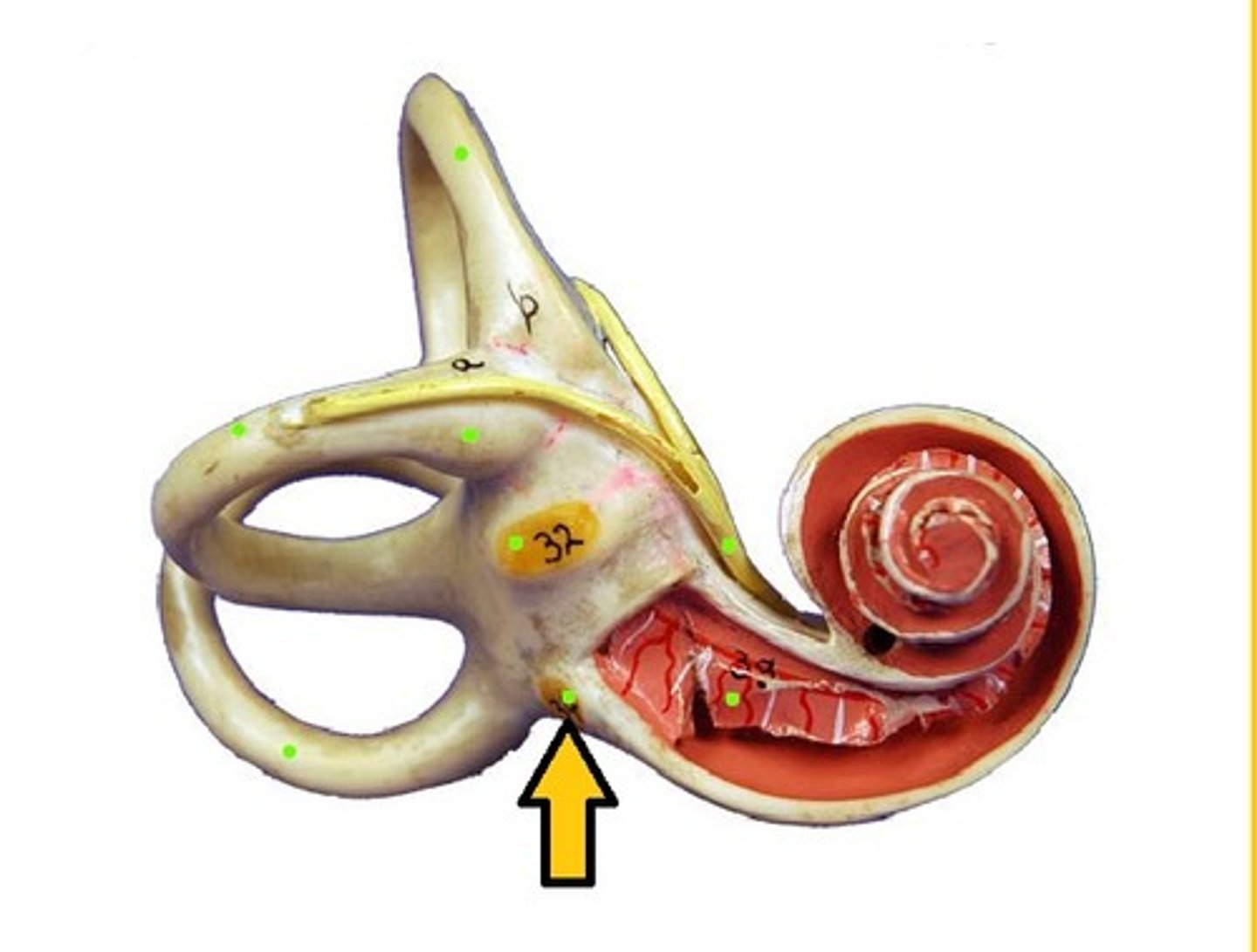
Oval Window
Where stapes attaches; transmits vibrations
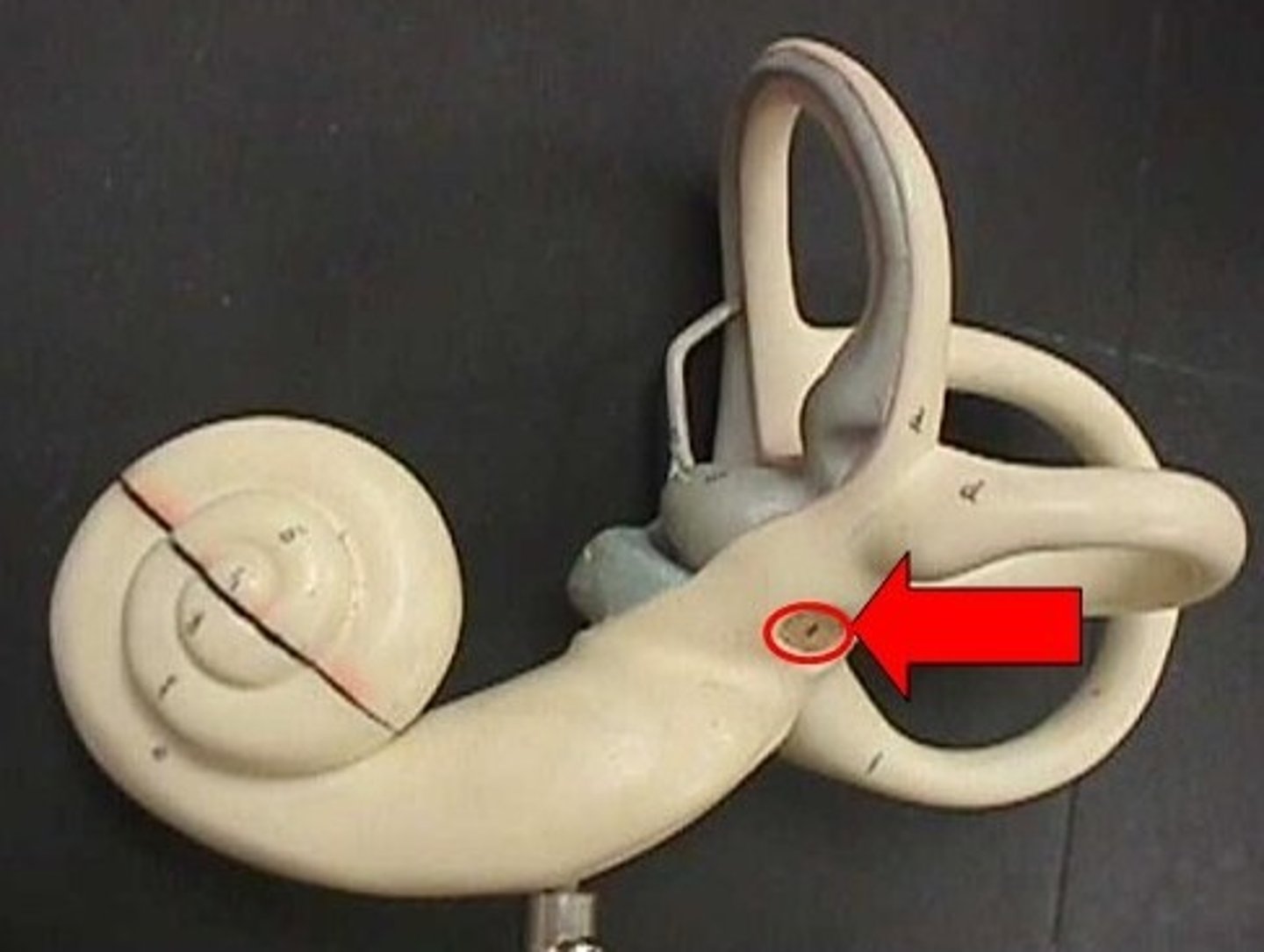
Vestibule
Static balance (utricle & saccule)
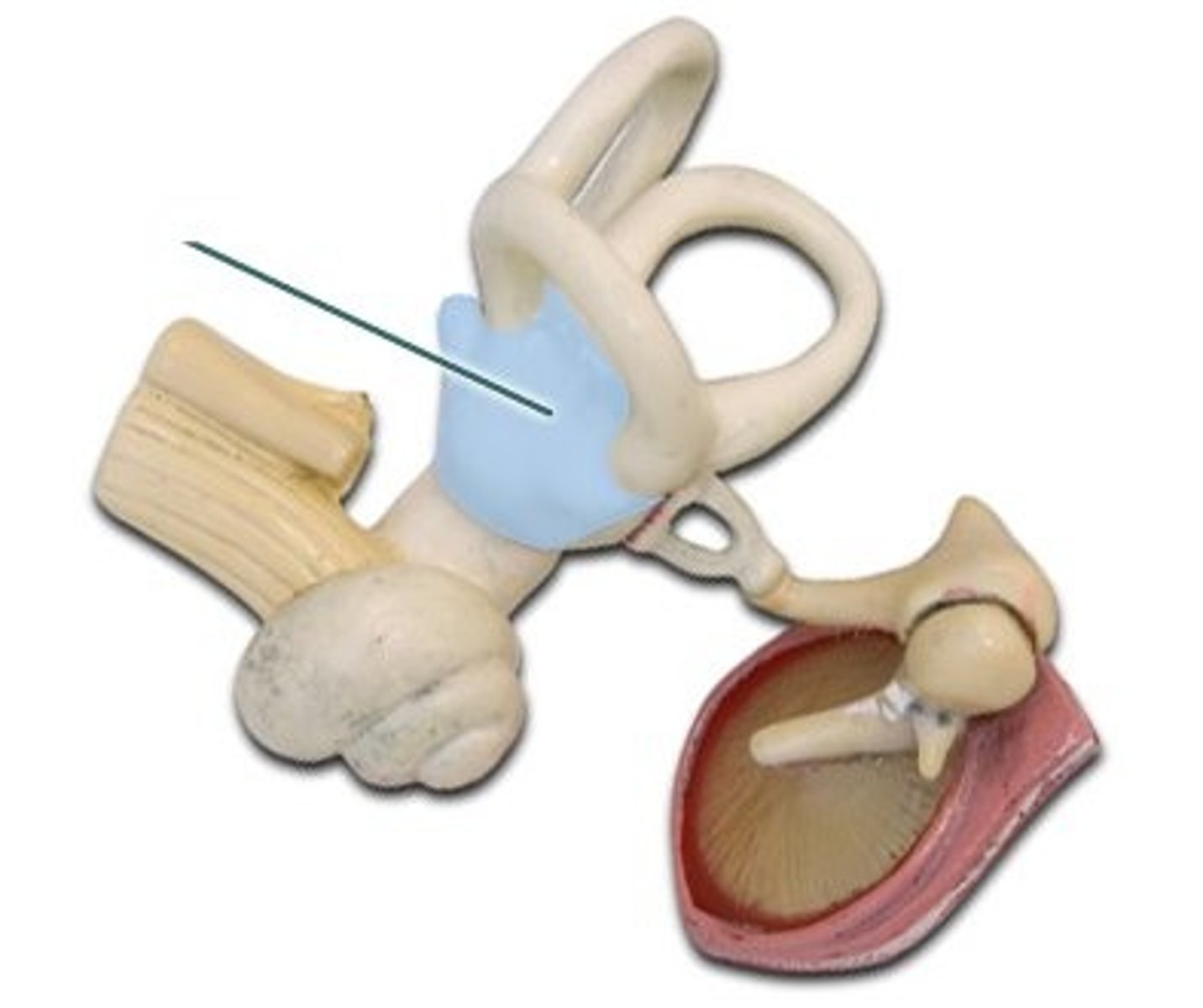
Semicircular Canals
Dynamic equilibrium
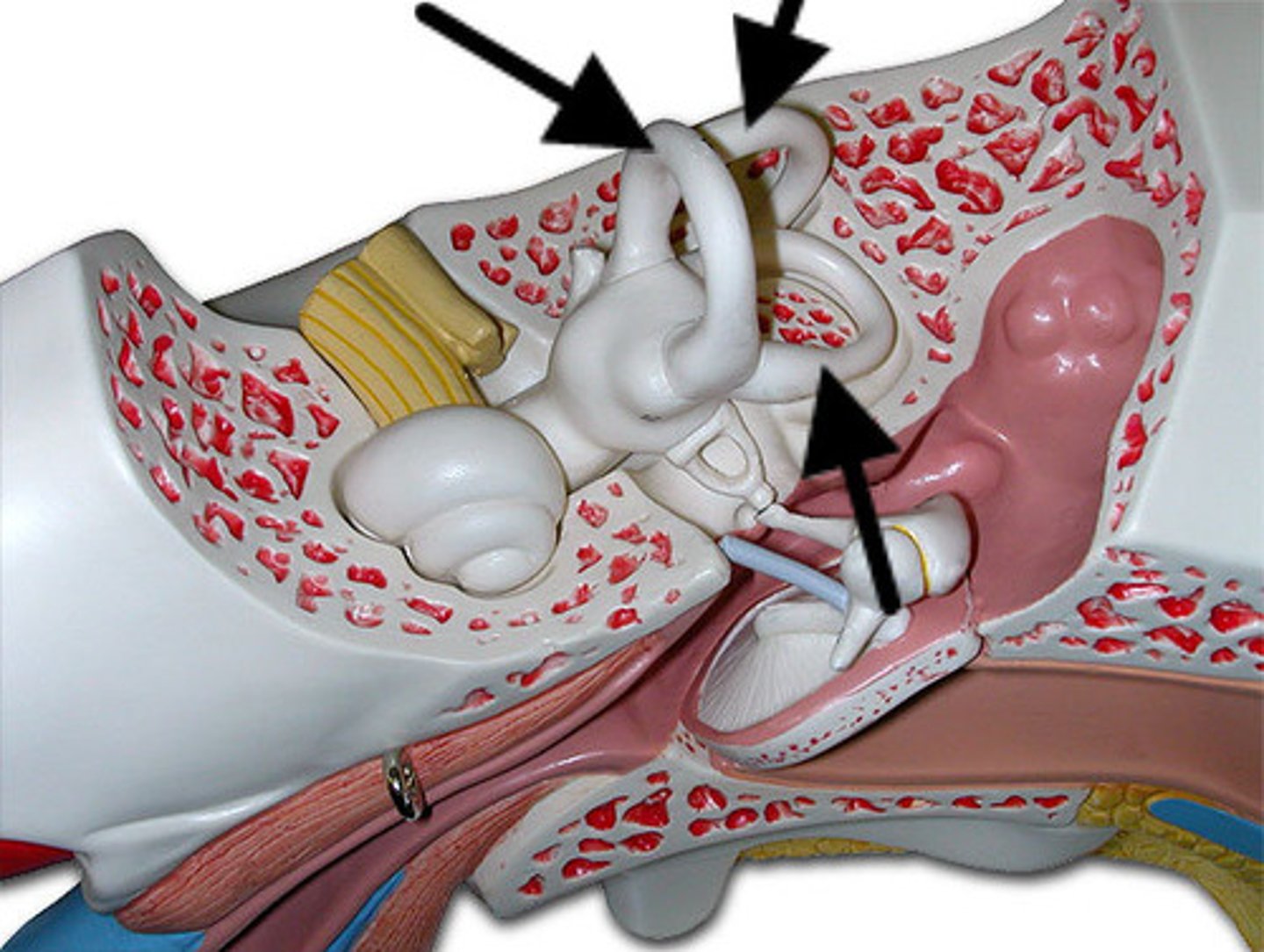
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII)
Hearing & balance
Scala Vestibuli (Vestibular Duct)
Upper chamber; perilymph

Scala Tympani (Tympanic Duct)
Lower chamber; perilymph
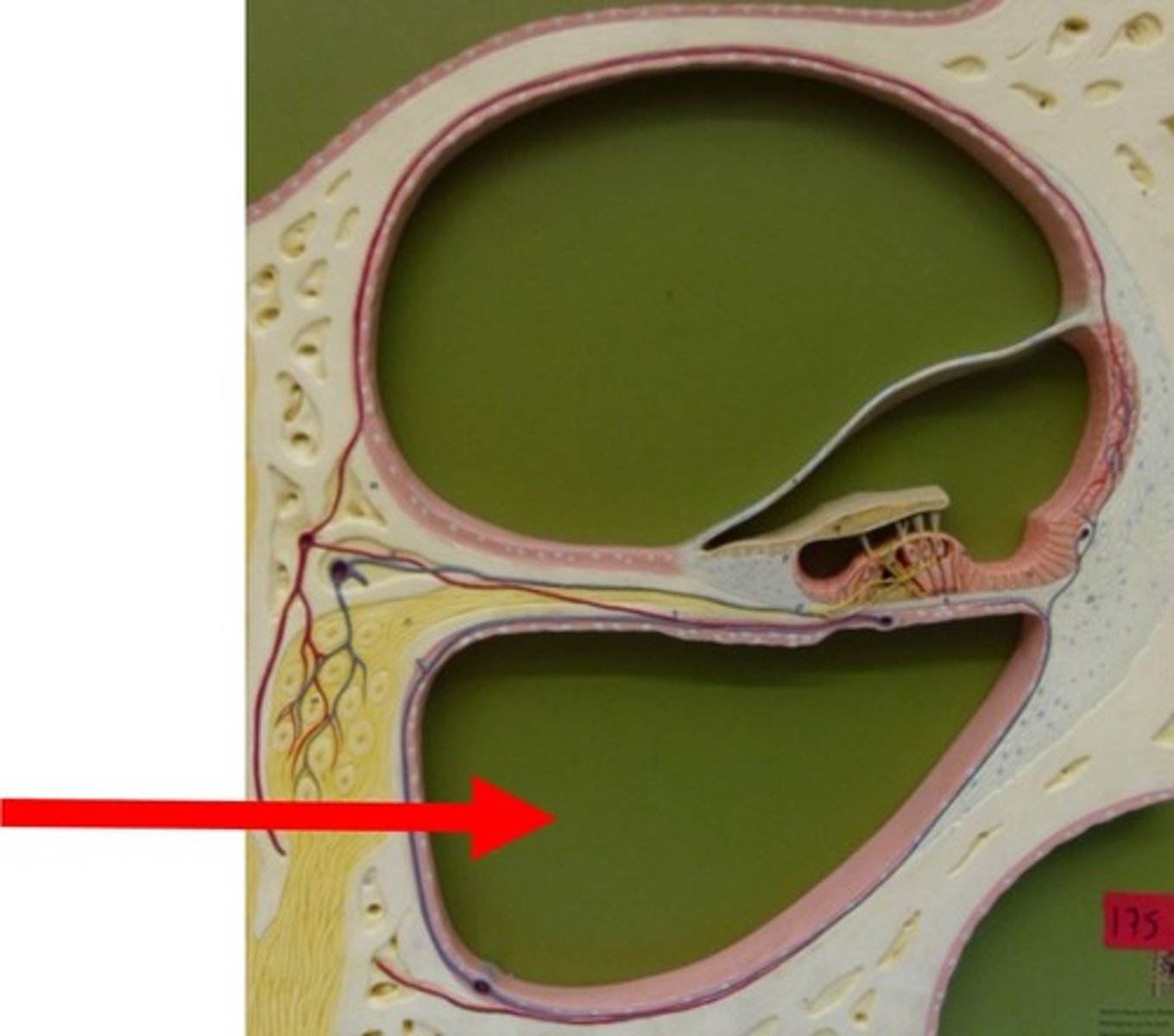
Scala Media (Cochlear Duct)
Middle chamber; endolymph
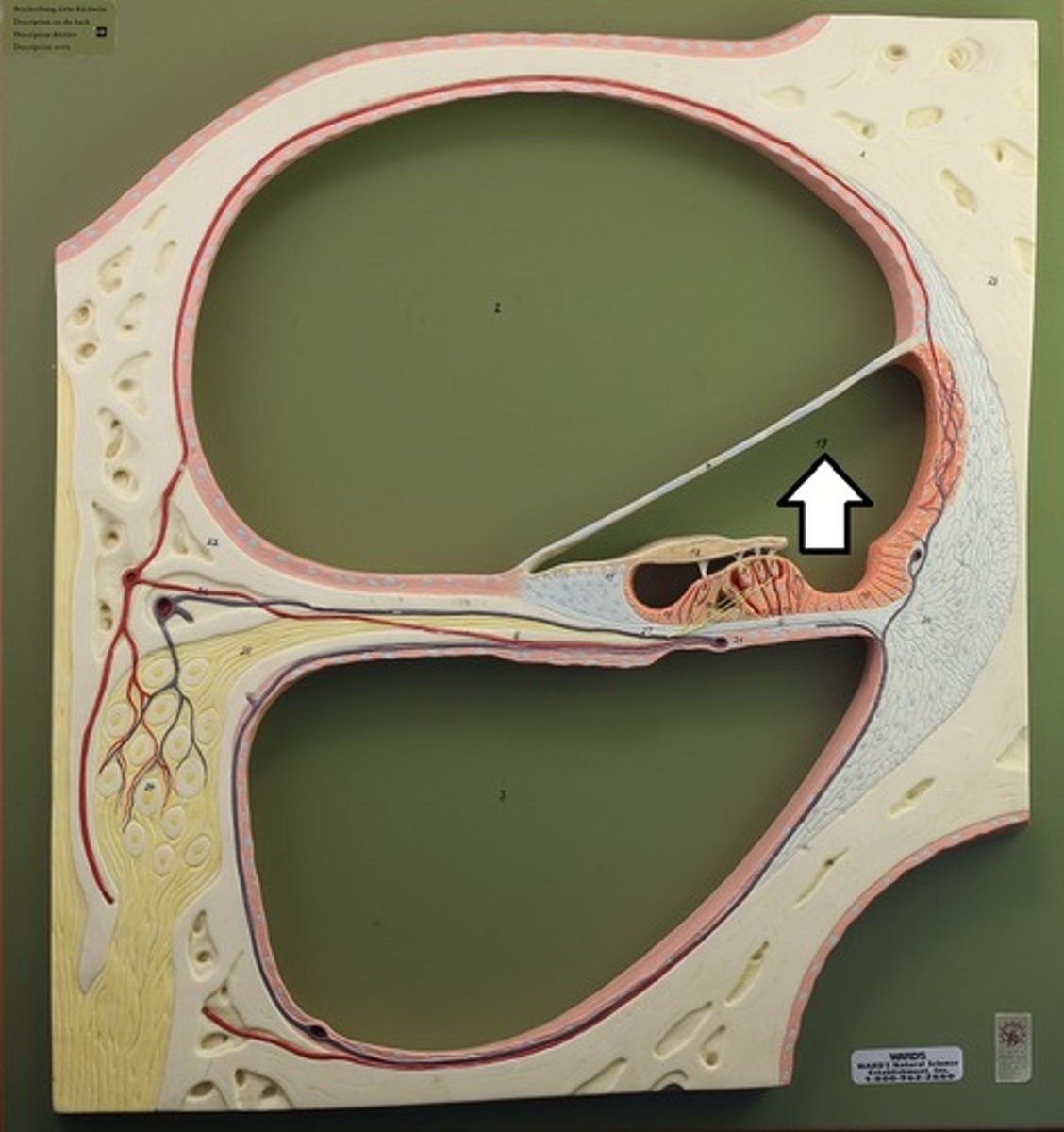
Vestibular Membrane
Roof of cochlear duct
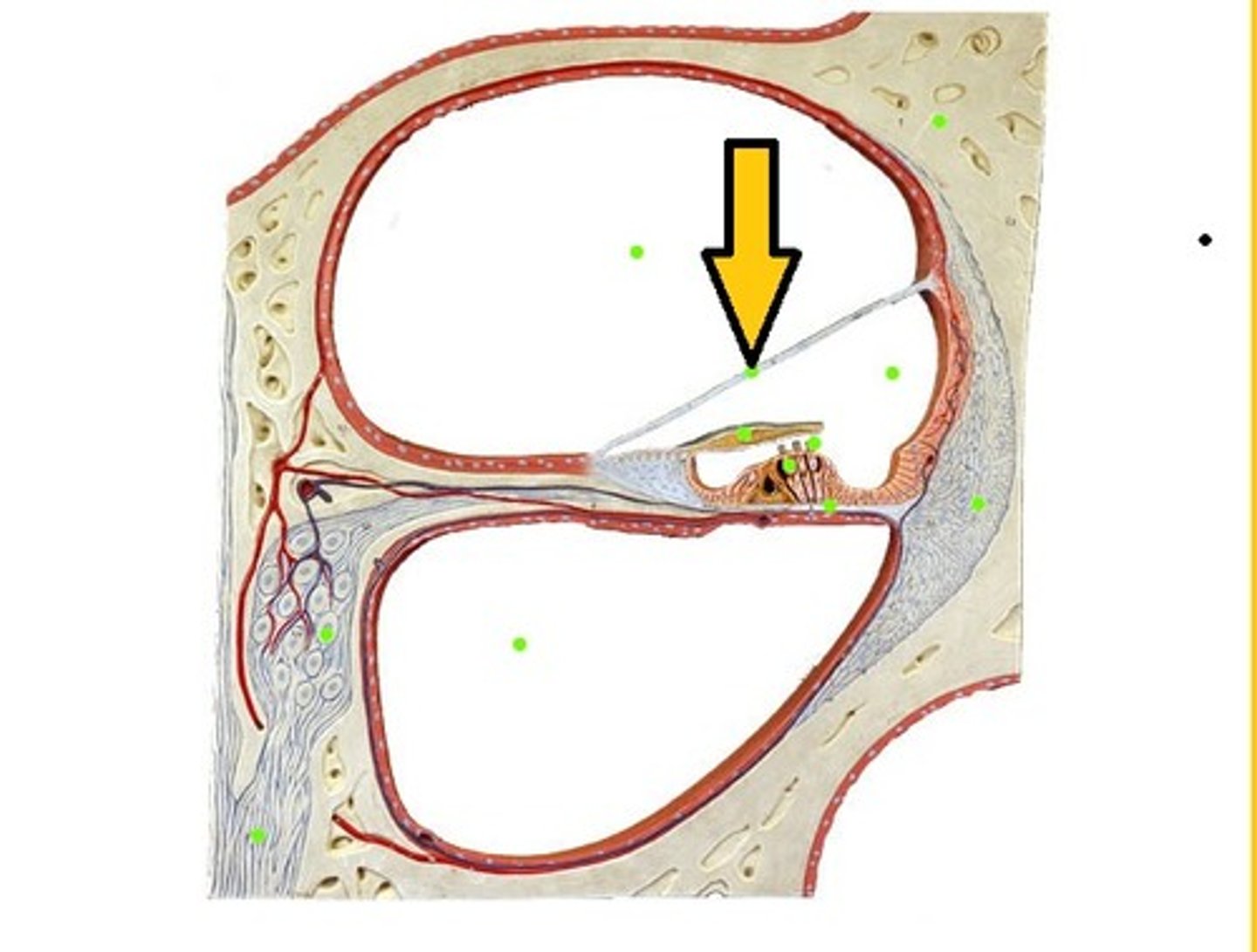
Basilar Membrane
Floor of cochlear duct; supports hair cells
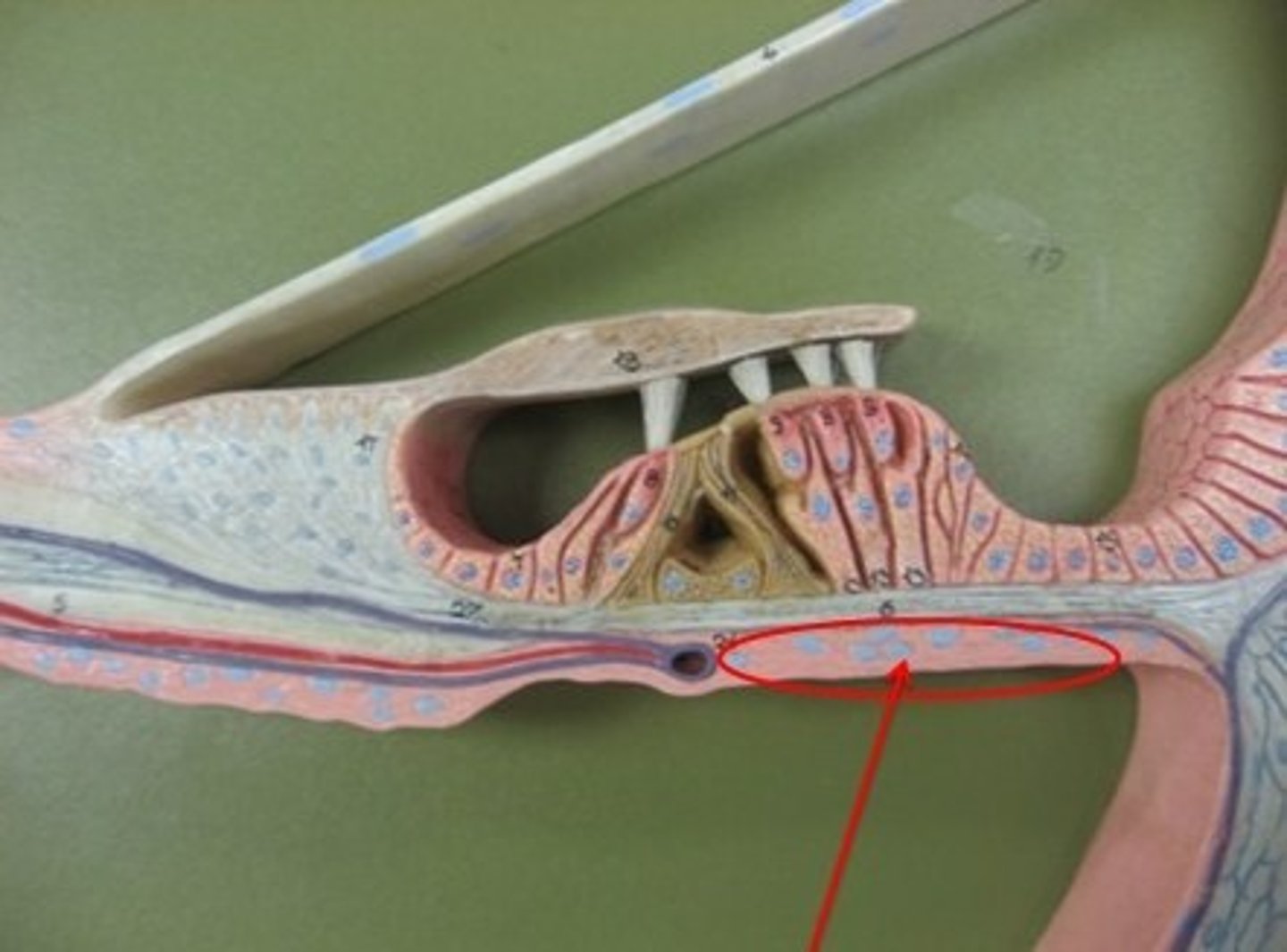
Tectorial Membrane
Contacts hair cells of Organ of Corti
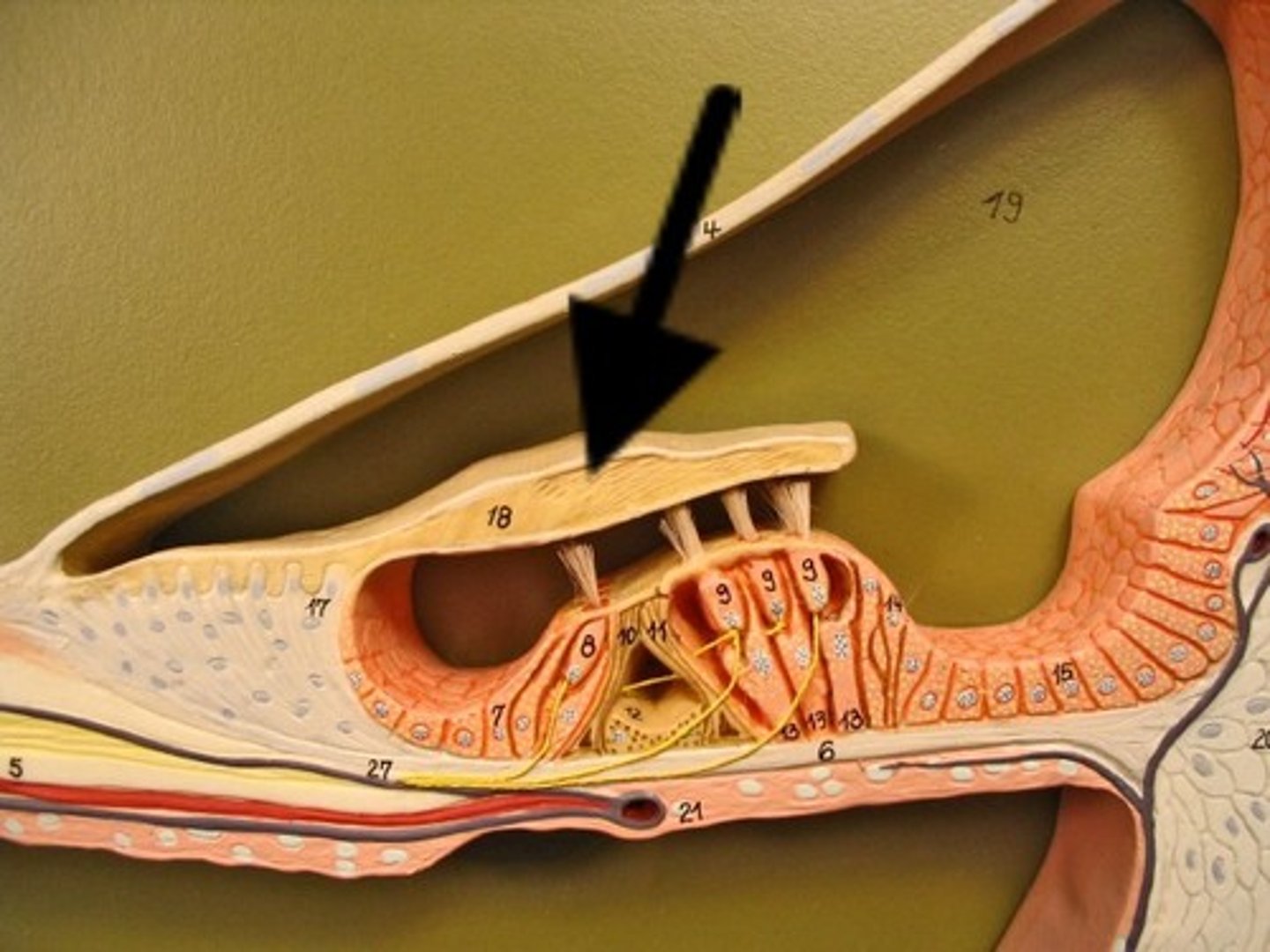
Hair Cells
Sensory receptors for hearing
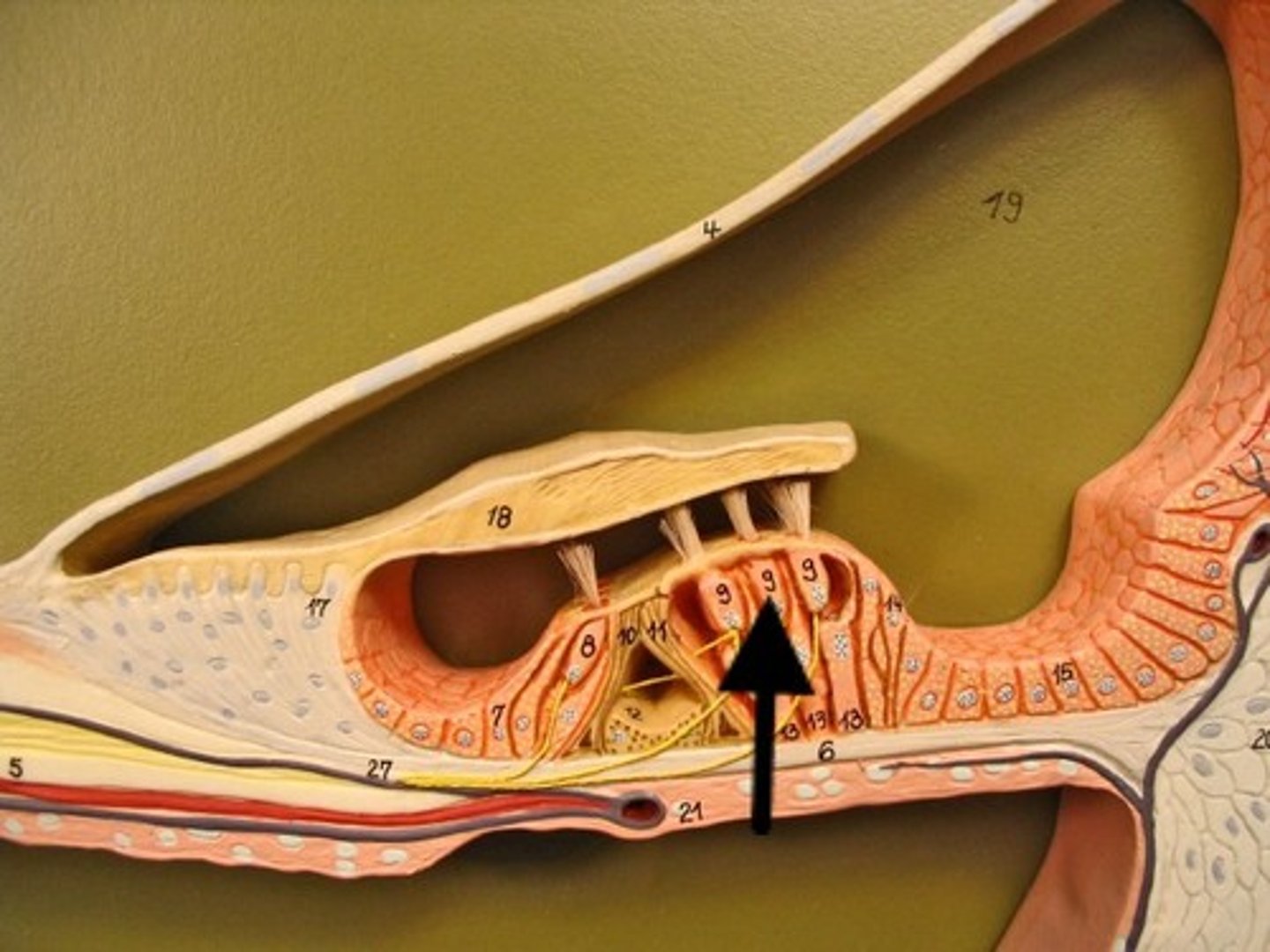
Organ of Corti
Hearing receptor organ within cochlear duct
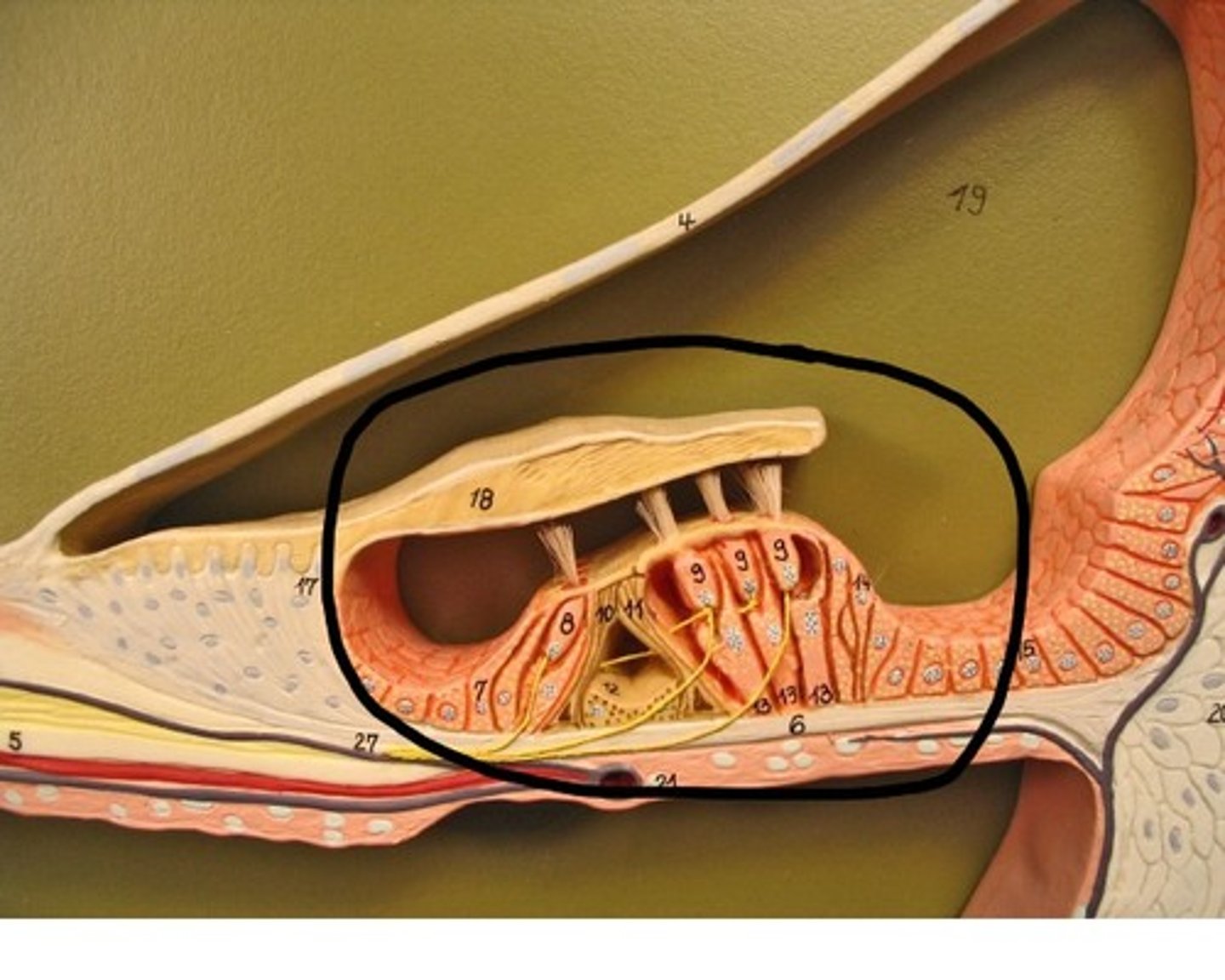
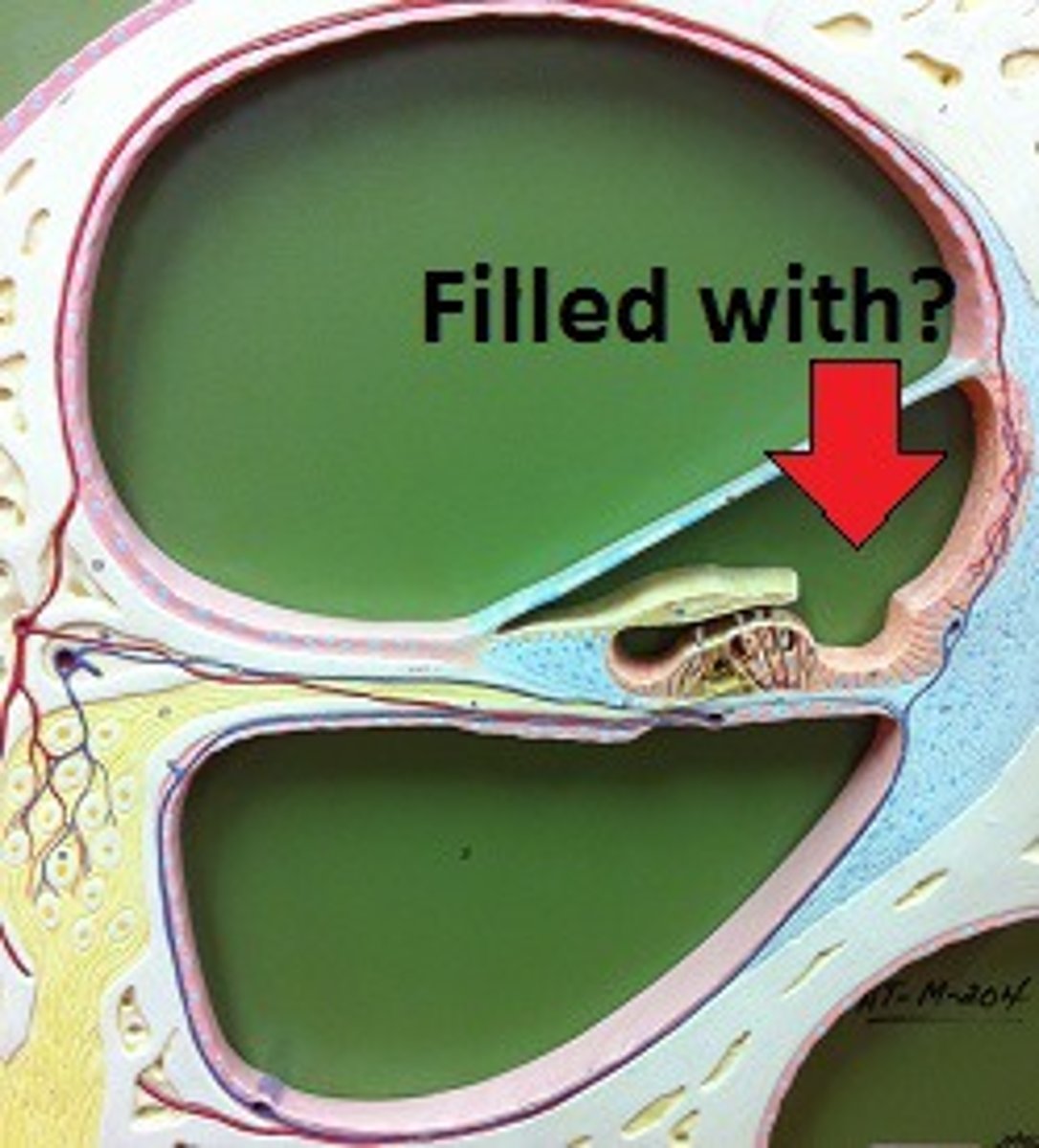
Perilymph
Fluid in vestibuli & tympani
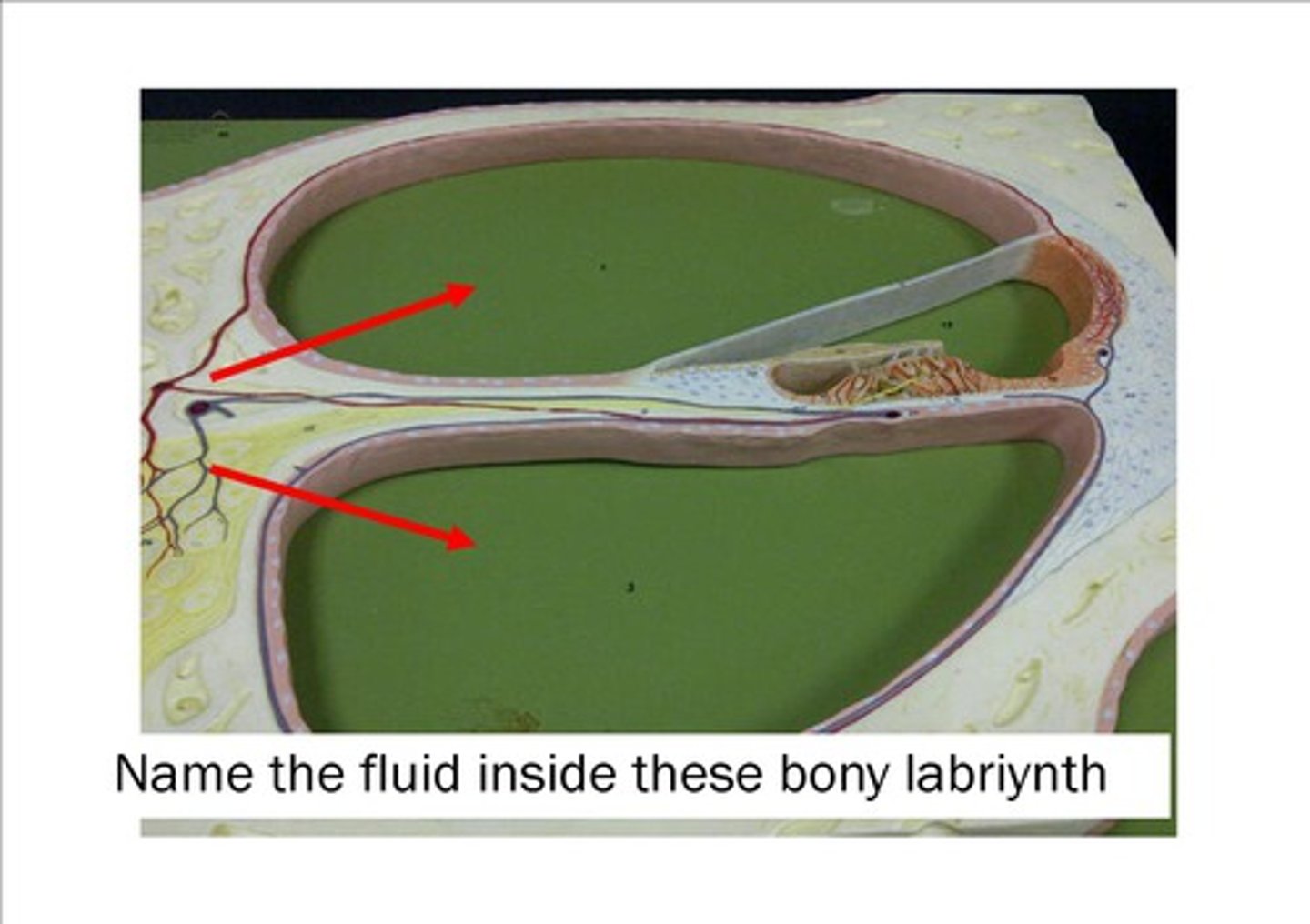
Endolymph
Fluid in cochlear duct
External Ear
Pinna
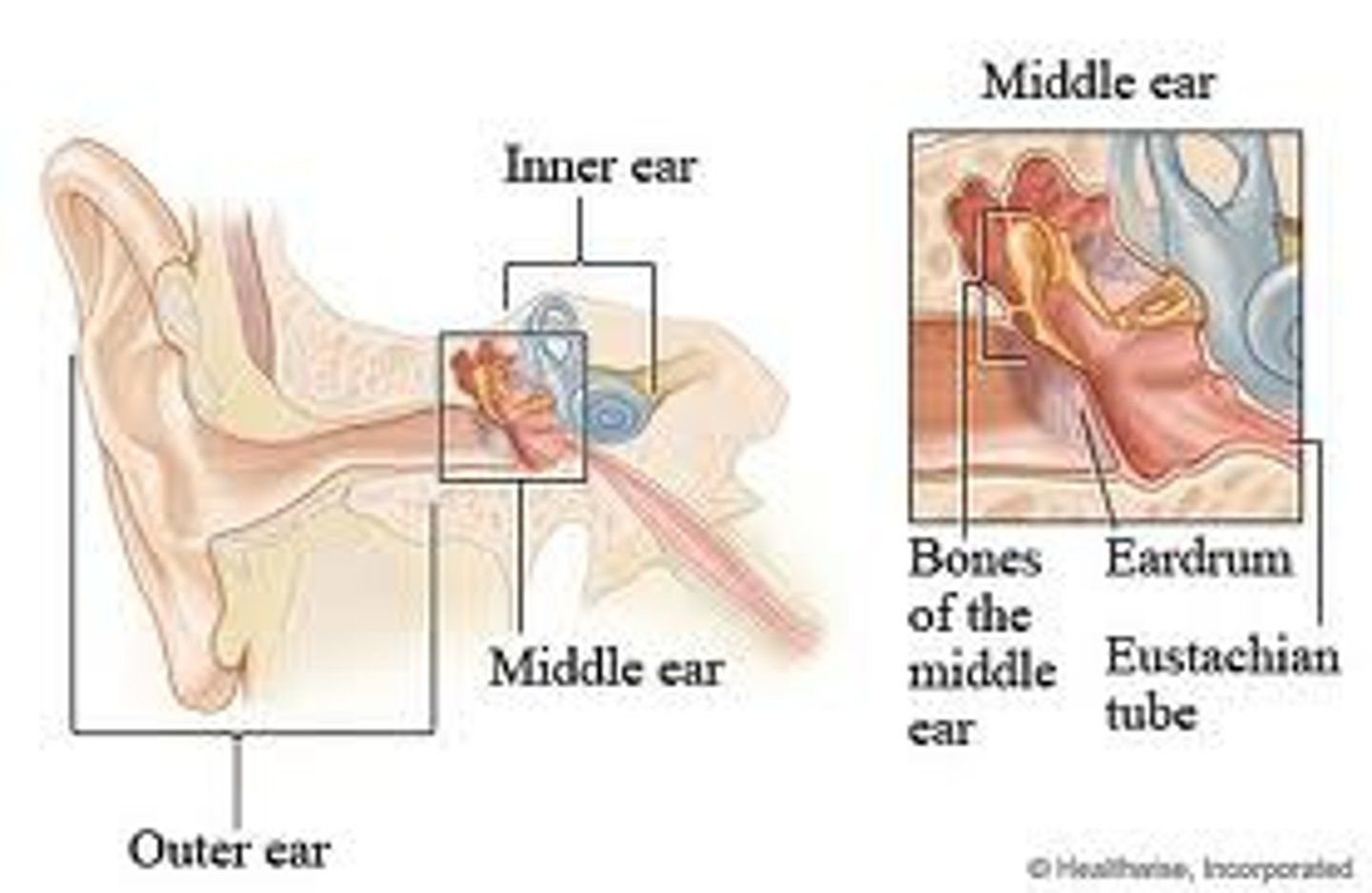
External Auditory Meatus
Canal leading to the eardrum
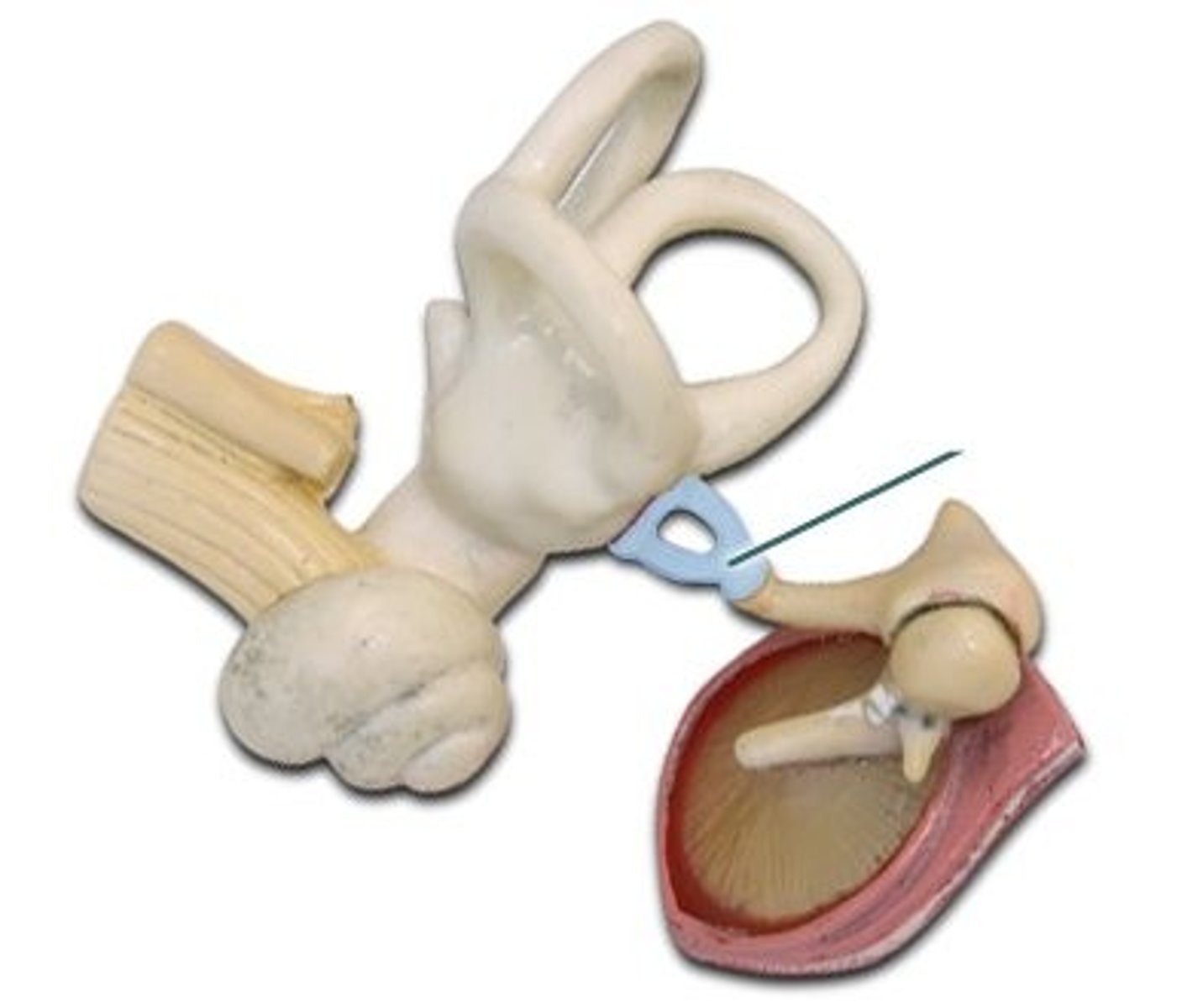
Malleus
Hammer-shaped bone in the middle ear
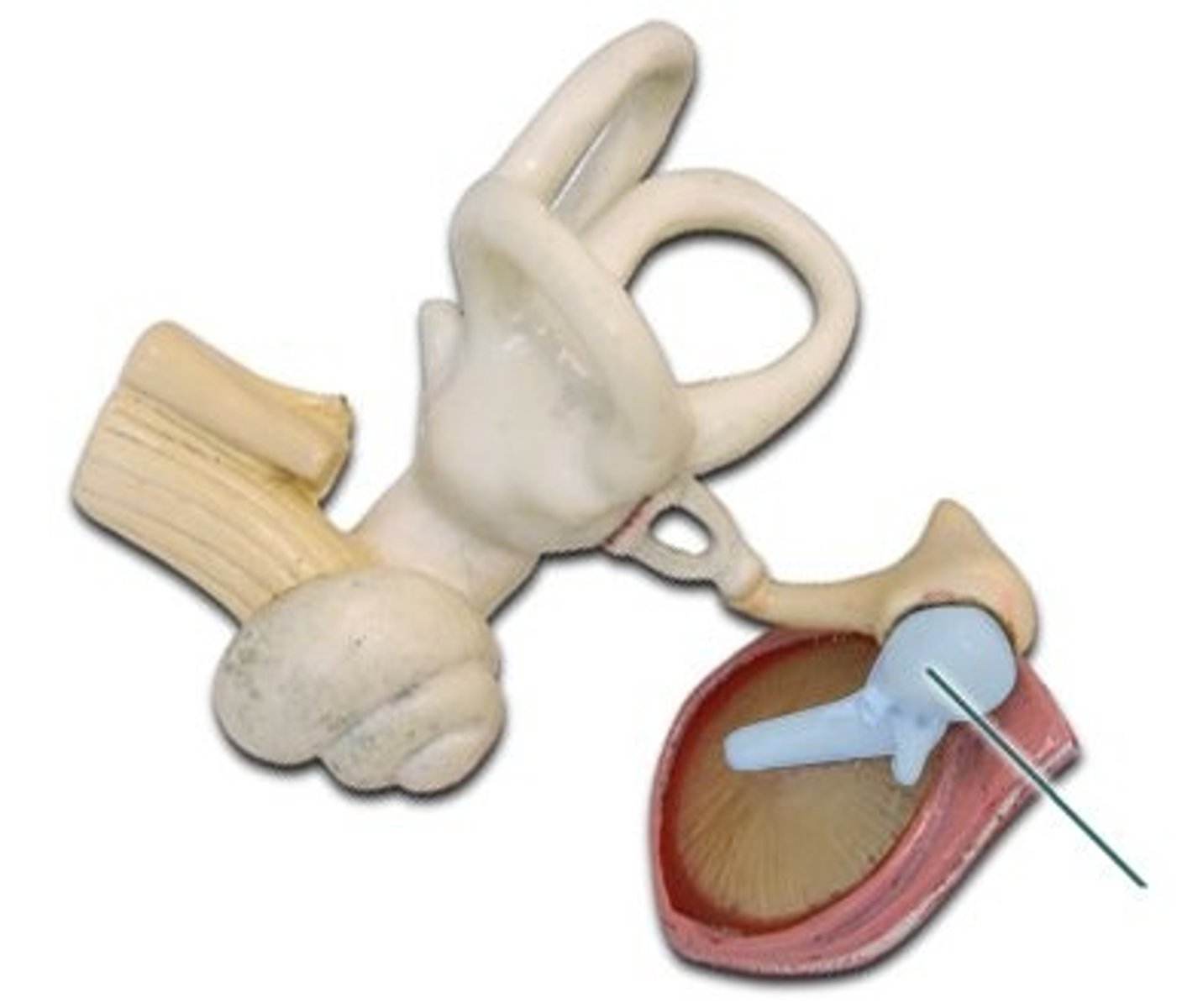
Incus
Anvil-shaped bone in the middle ear
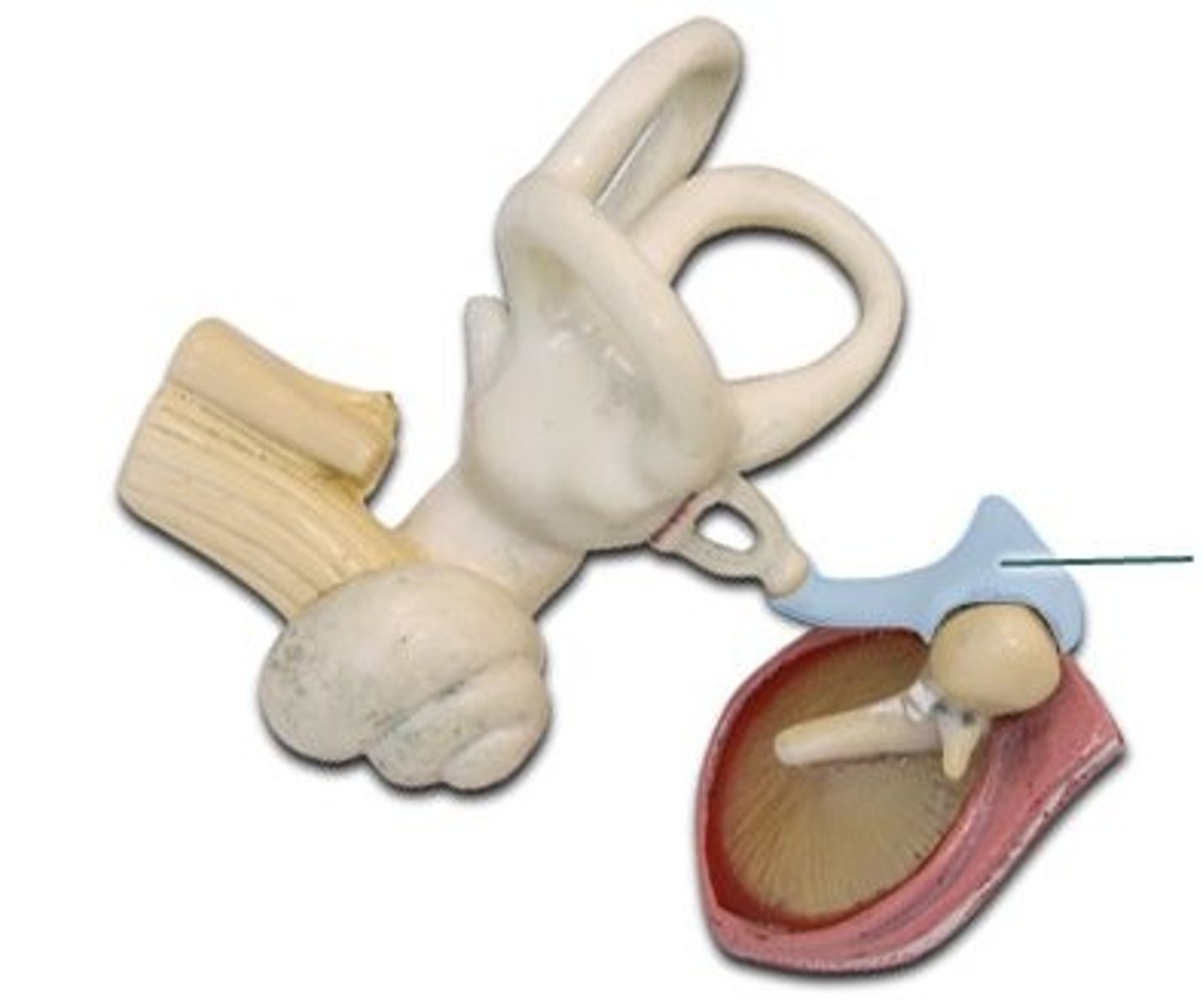
Stapes
Stirrup-shaped bone in the middle ear
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain; responsible for thinking, learning, emotion, sensory processing, and voluntary movement.
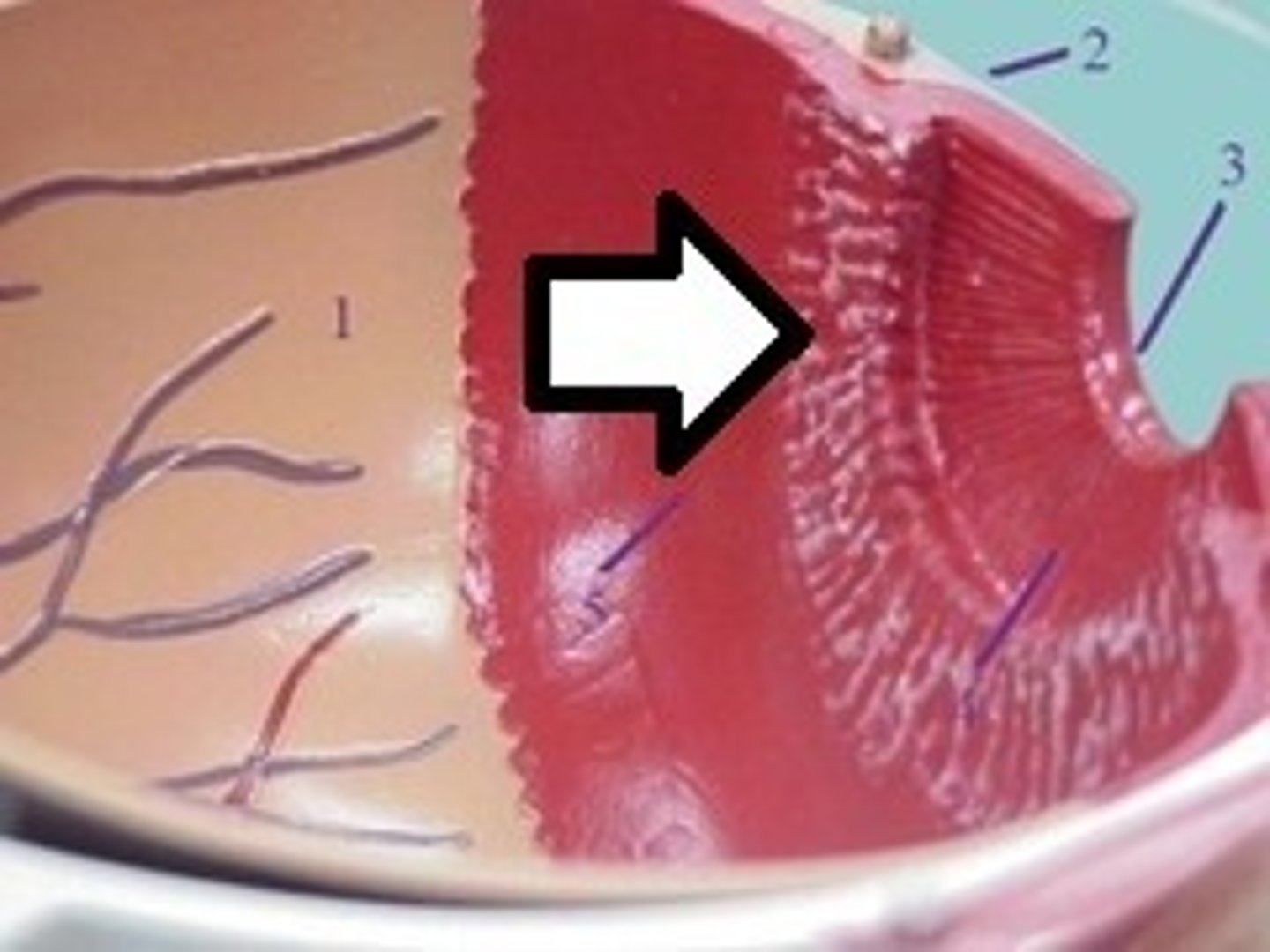
Cerebellum
Located under the cerebrum at the back of the brain; coordinates balance, posture, and fine motor control.
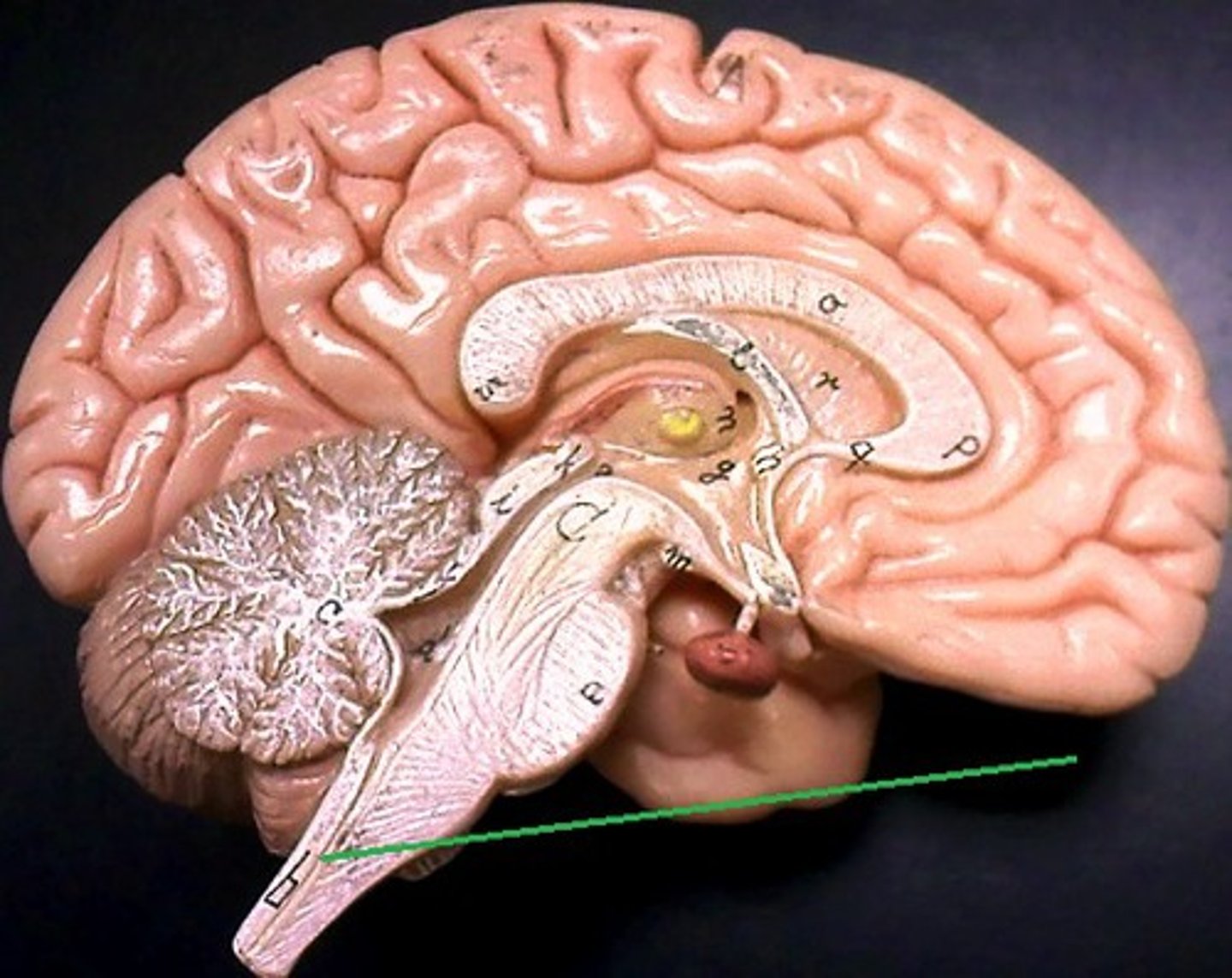
Spinal Cord
Connects brain to the rest of the body; transmits nerve signals between brain and body.
Medulla Oblongata
Lowest part of brainstem; controls vital functions like heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure.
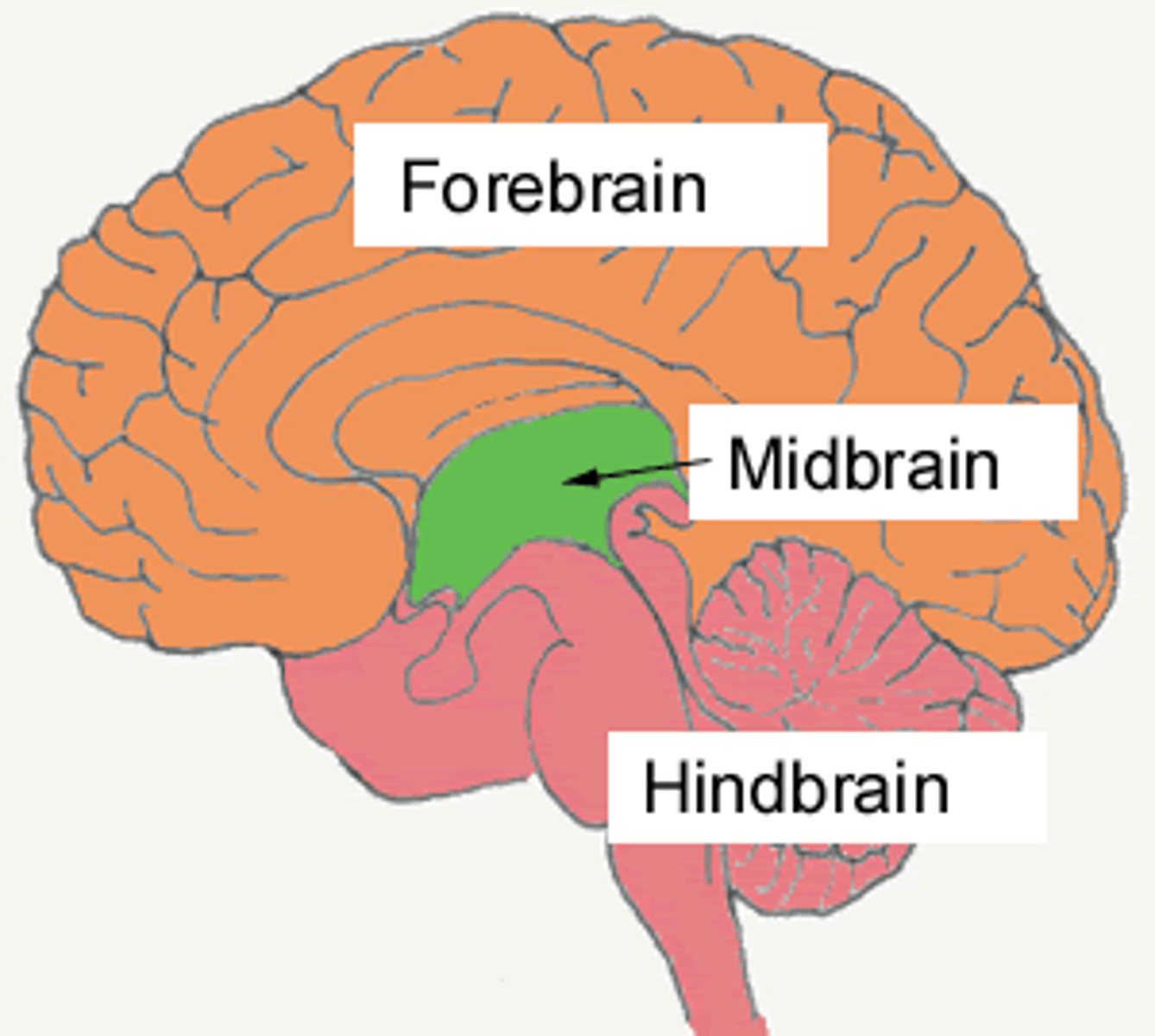
Midbrain
Uppermost part of brainstem; controls eye movement and auditory/visual reflexes.
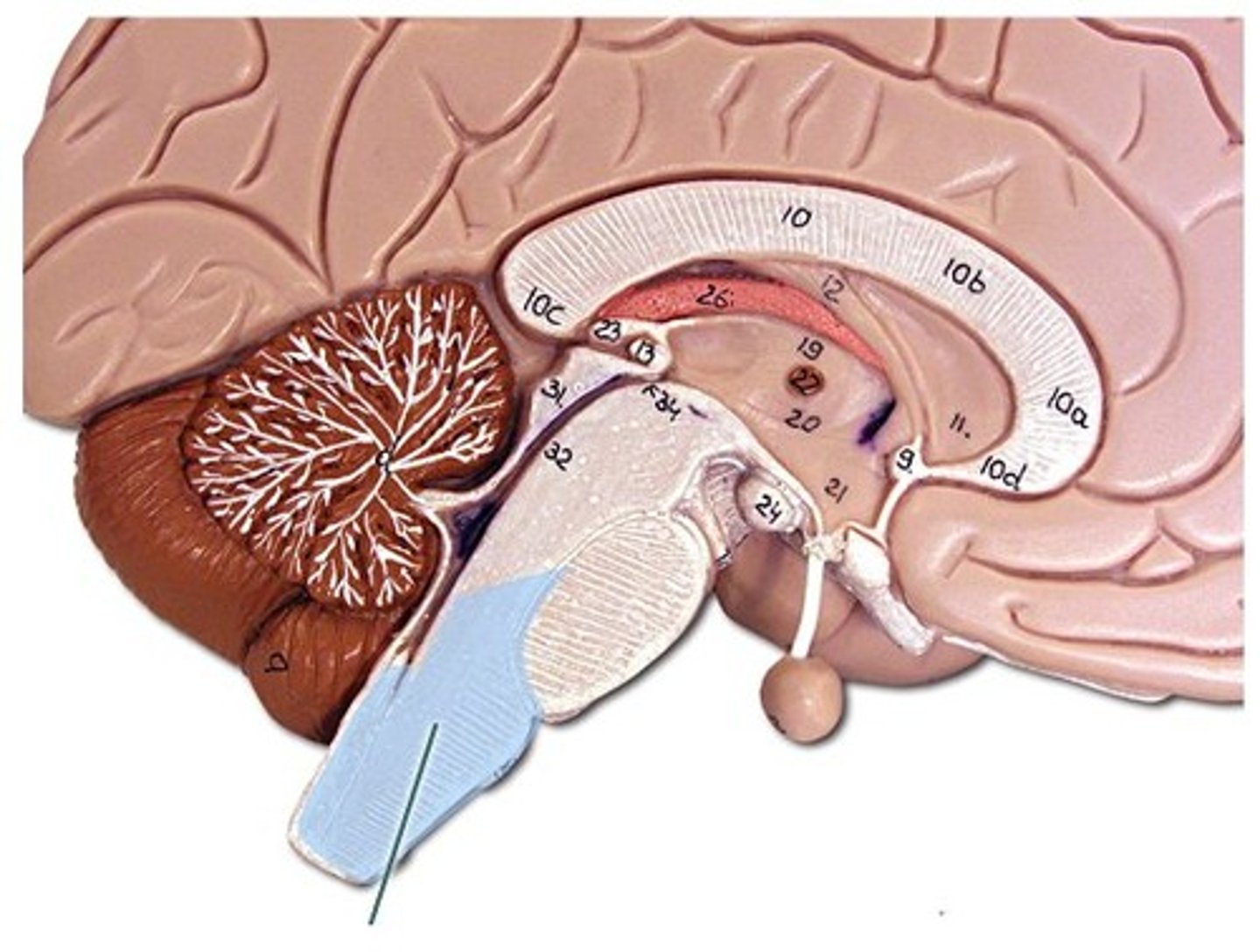
Cerebral Peduncles
Fiber tracts on anterior midbrain; carry motor signals between cerebrum and brainstem.
Corpora Quadrigemina
Four rounded bumps on posterior midbrain; involved in reflexes to visual (superior) and auditory (inferior) stimuli.
Superior Colliculi
Visual reflex centers; track moving objects.
Inferior Colliculi
Auditory reflex centers; respond to sound.
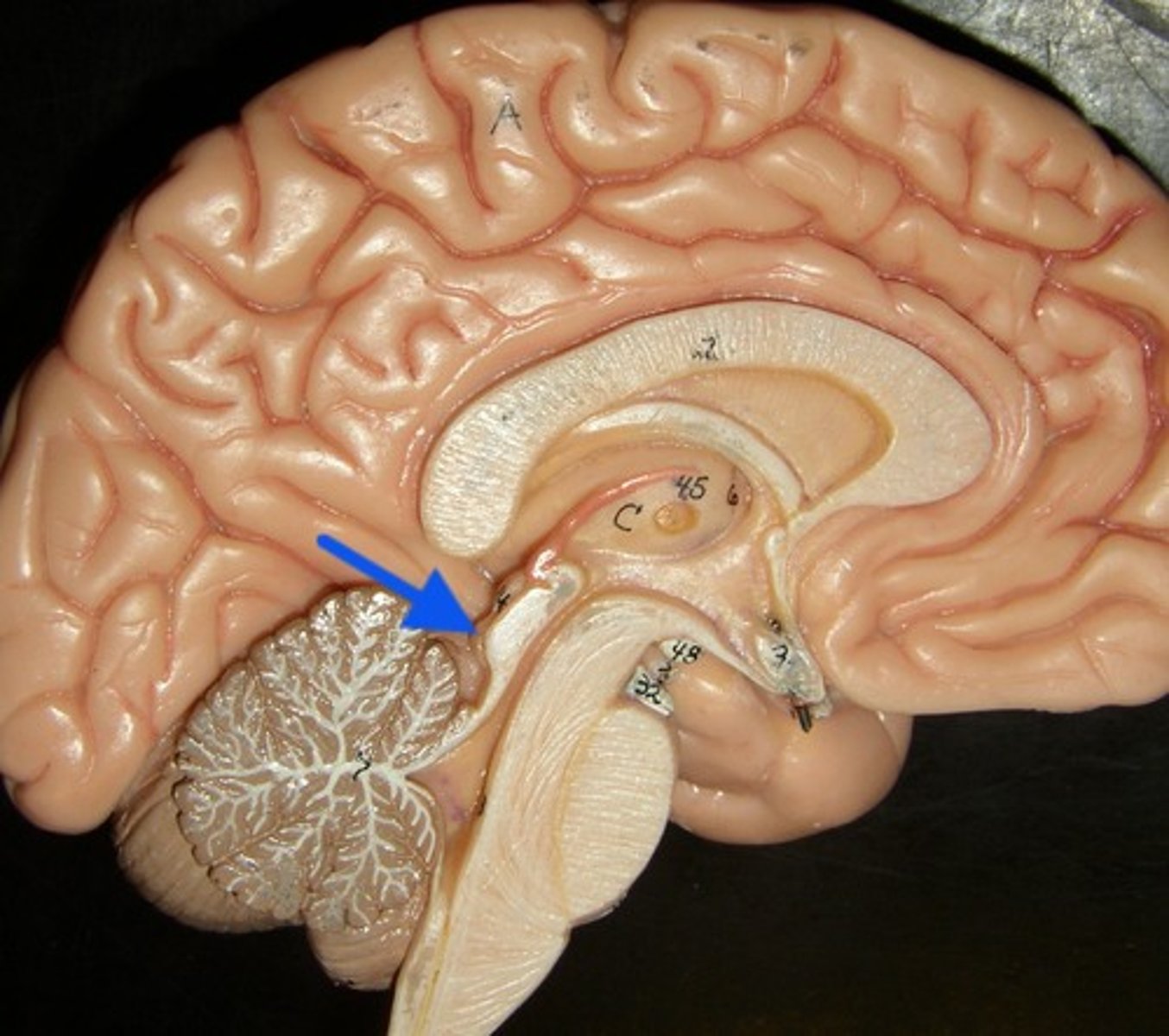
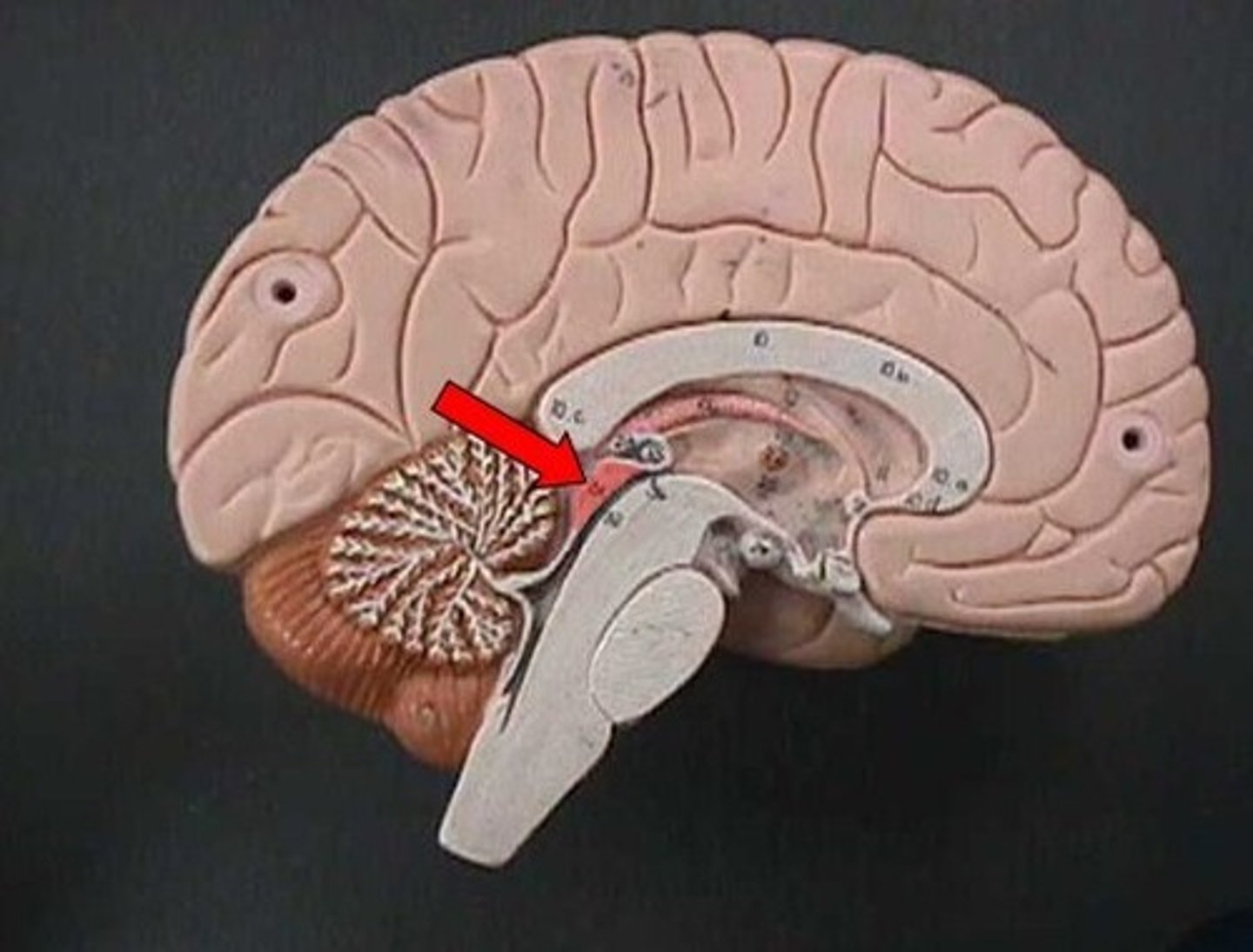
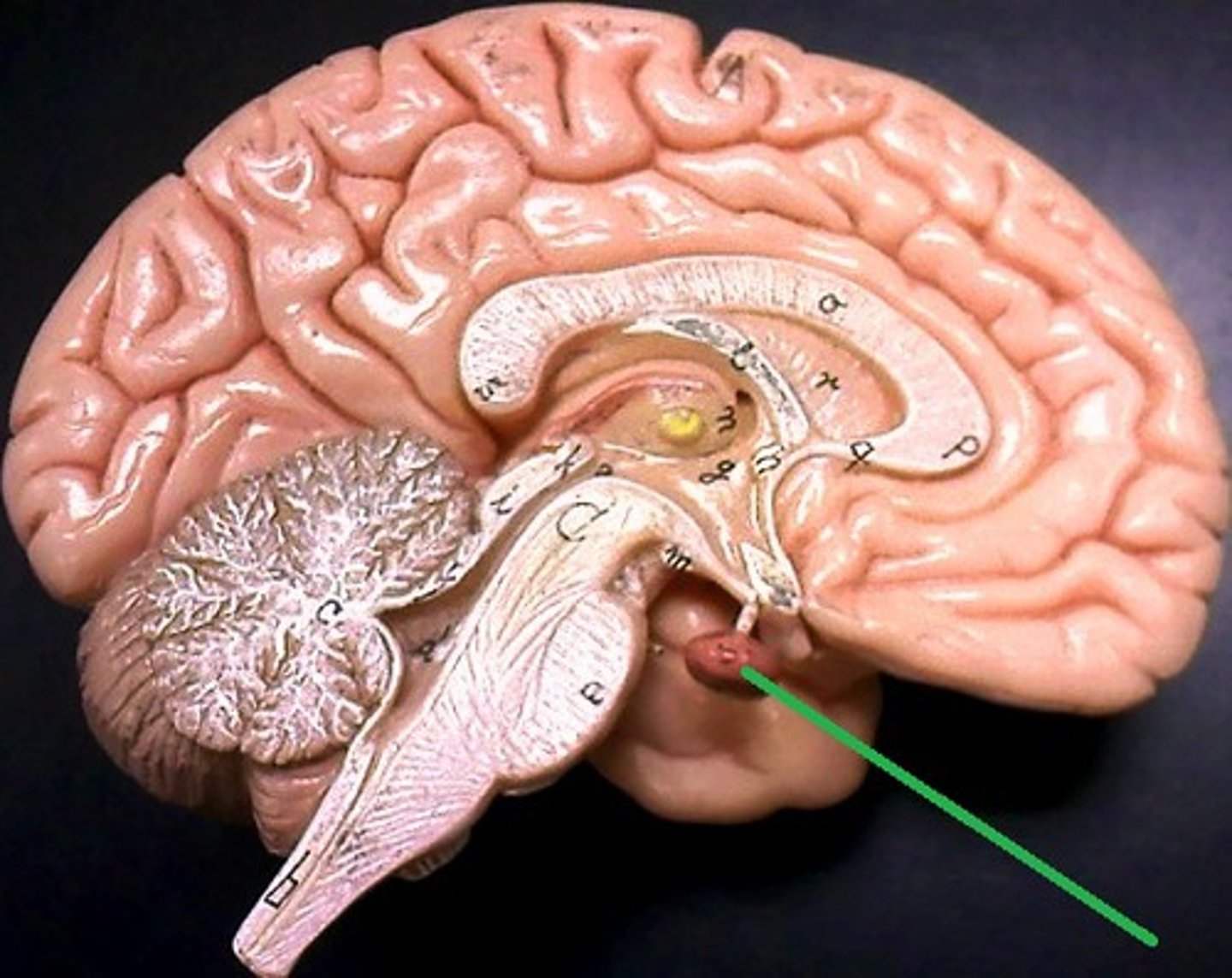
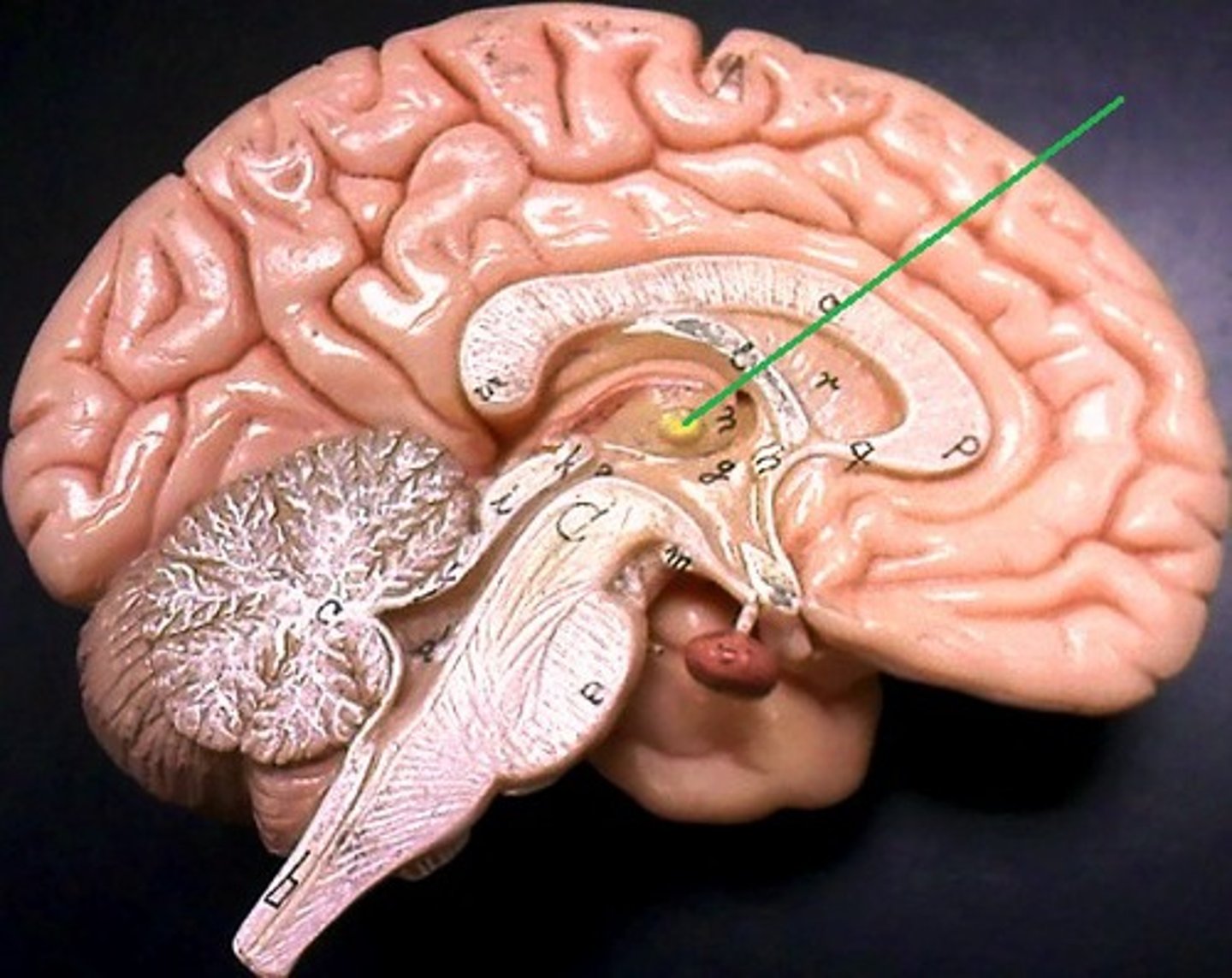
Pituitary Gland
Small endocrine gland under hypothalamus; secretes hormones controlling growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
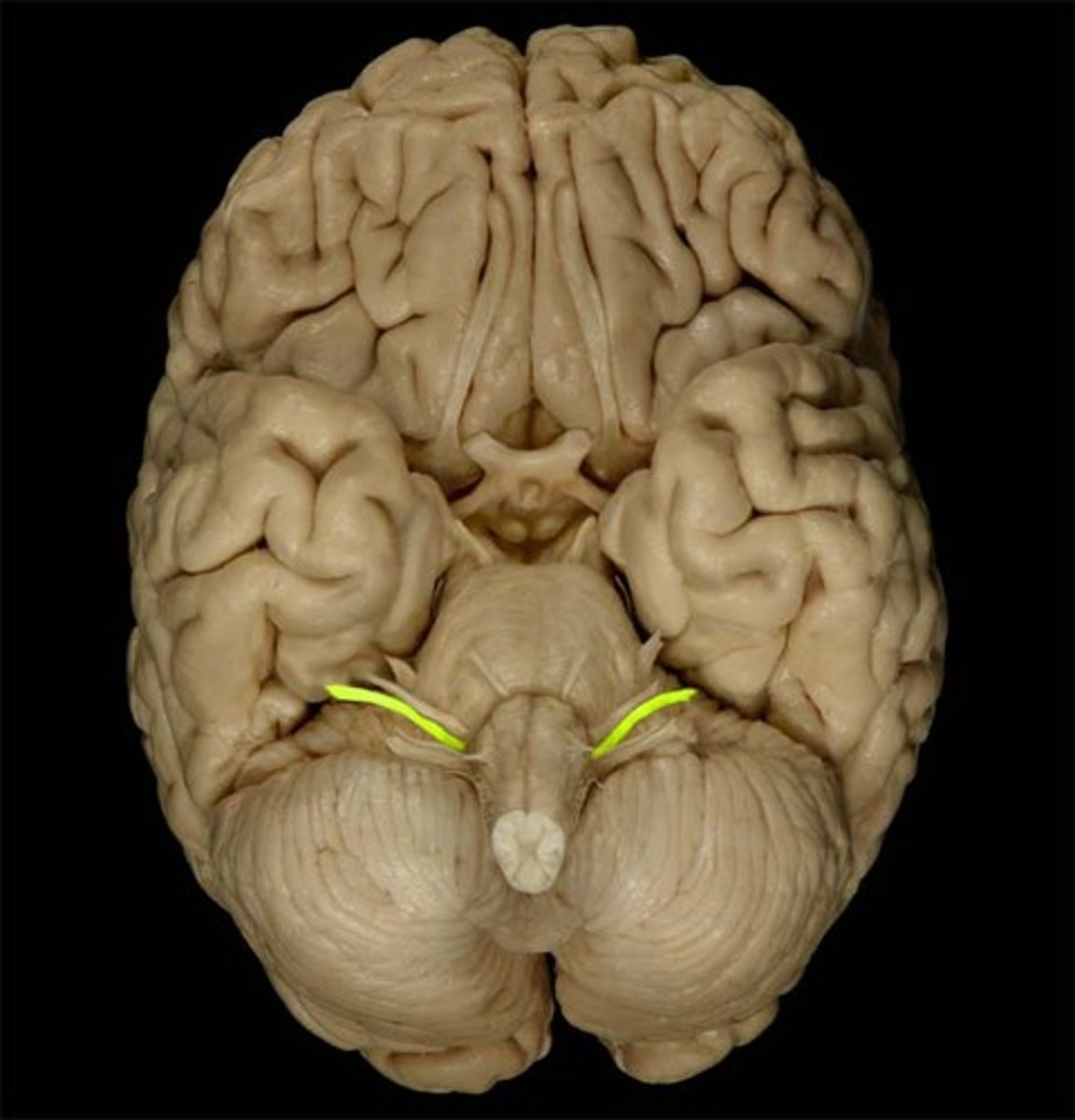
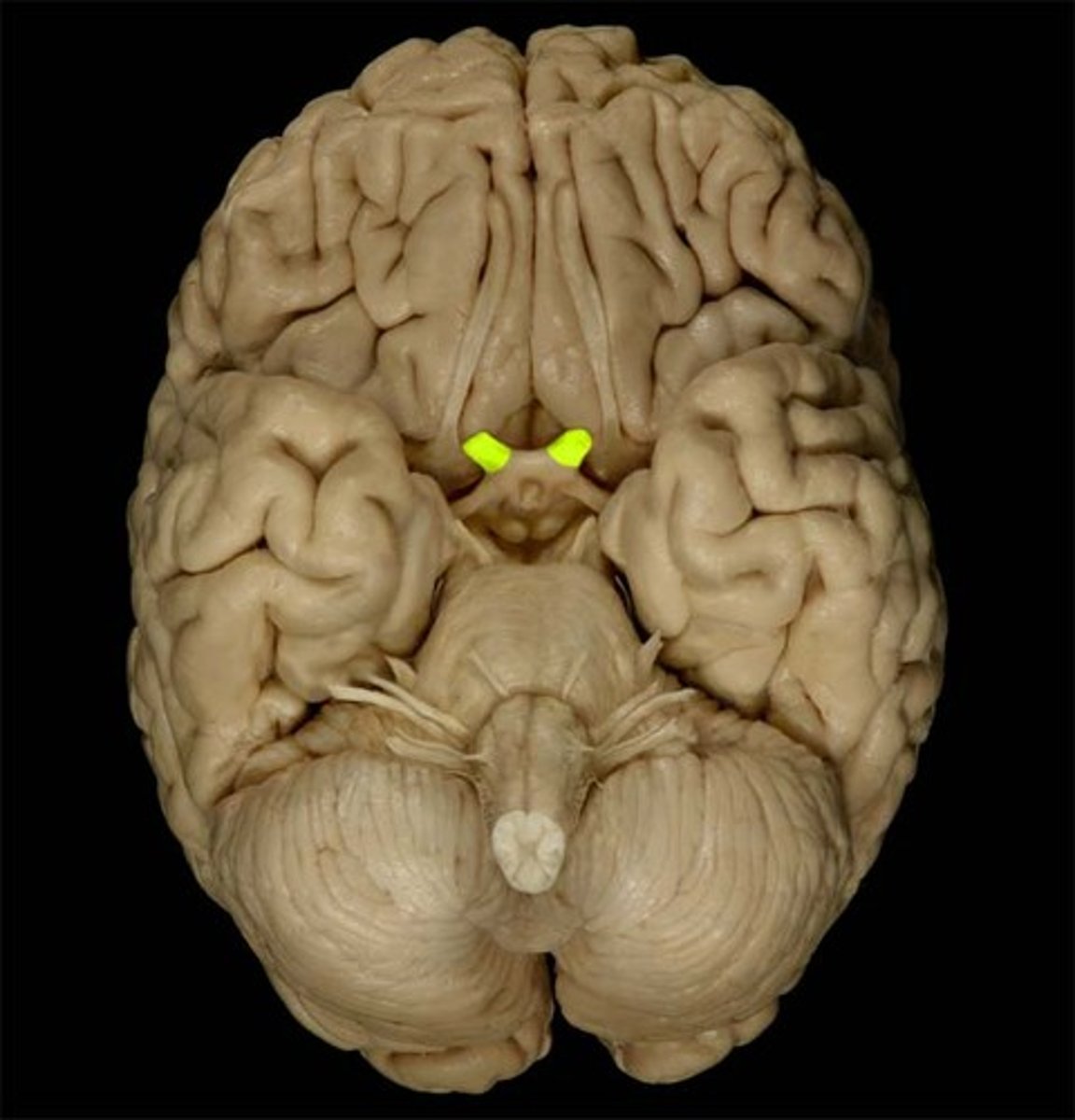
Olfactory Bulb
Front underside of brain; receives smell input from nasal cavity.
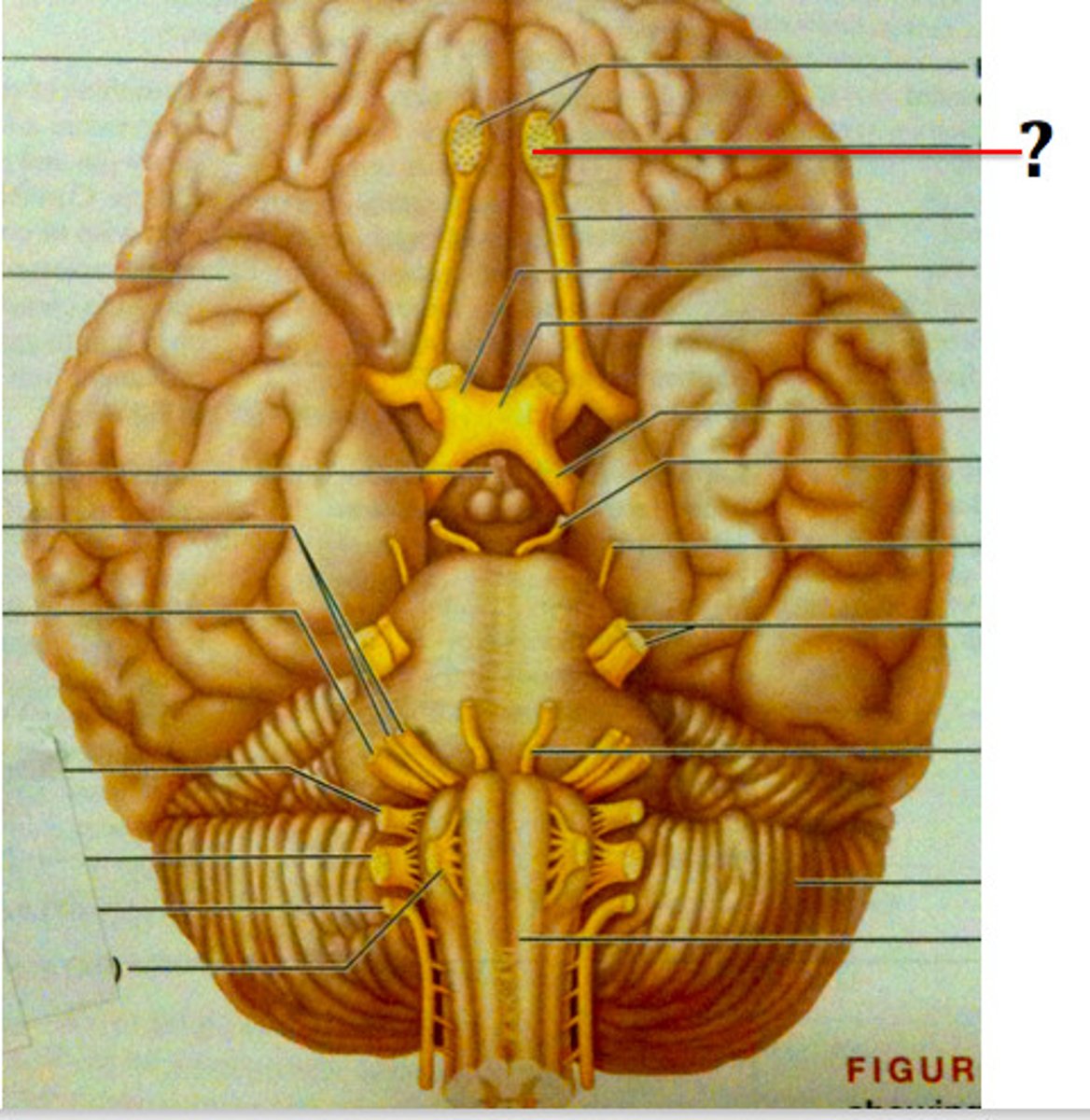
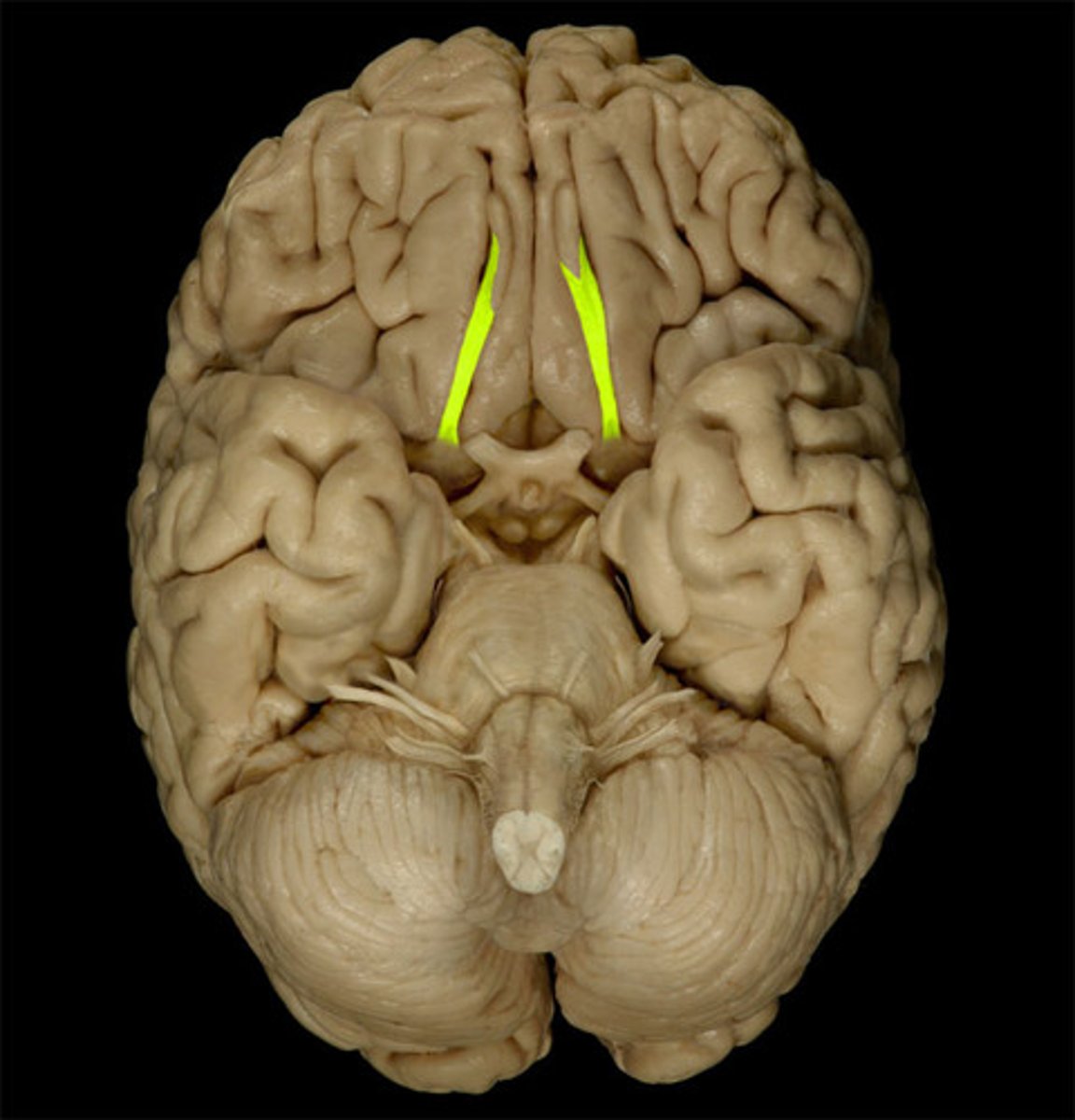
Olfactory Tract
Carries smell signals from olfactory bulbs to cerebrum.
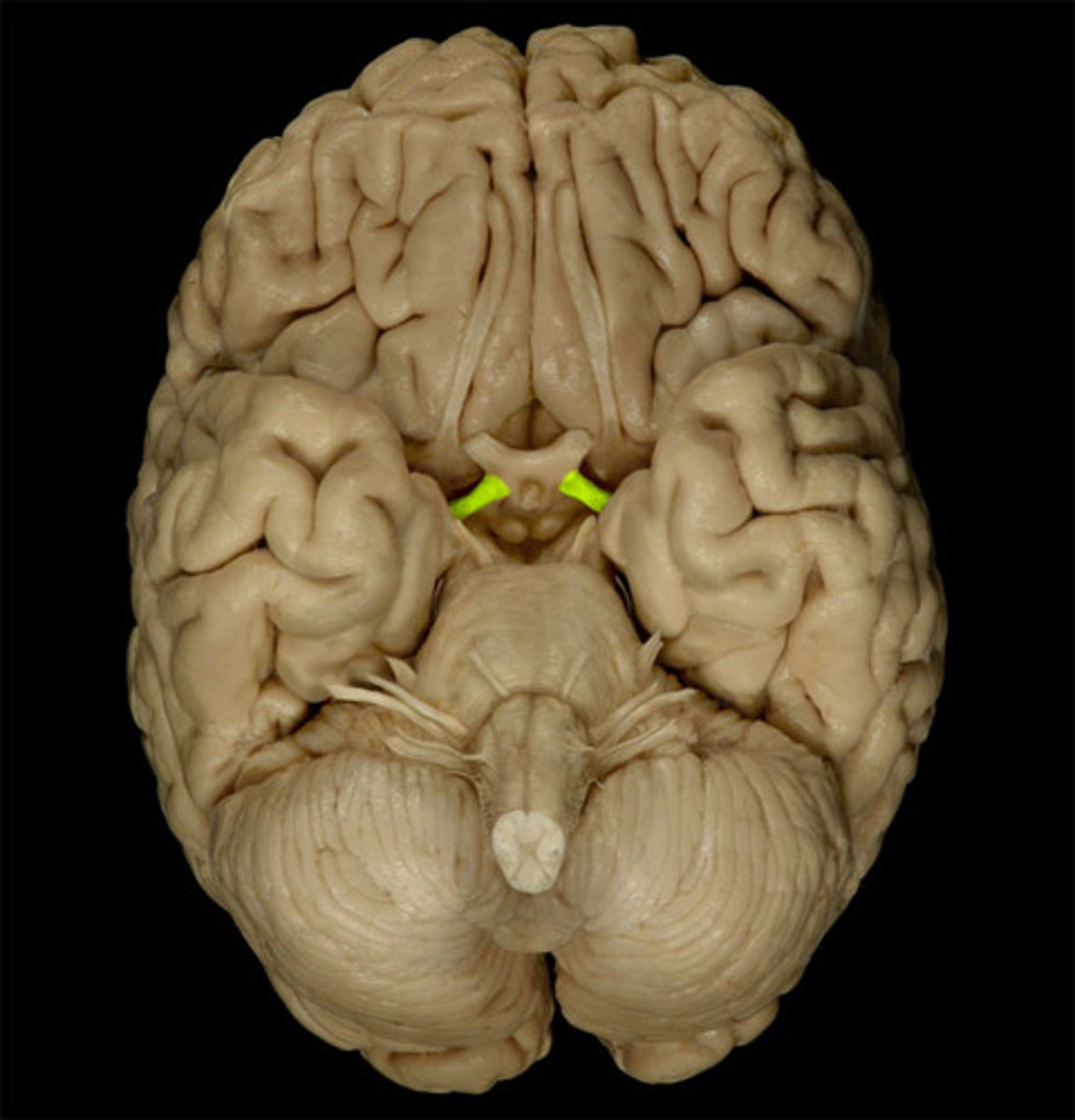
Optic Nerve
Transmits visual information from eyes to optic chiasma.
Optic Chiasma
X-shaped crossing where some optic nerve fibers switch sides.
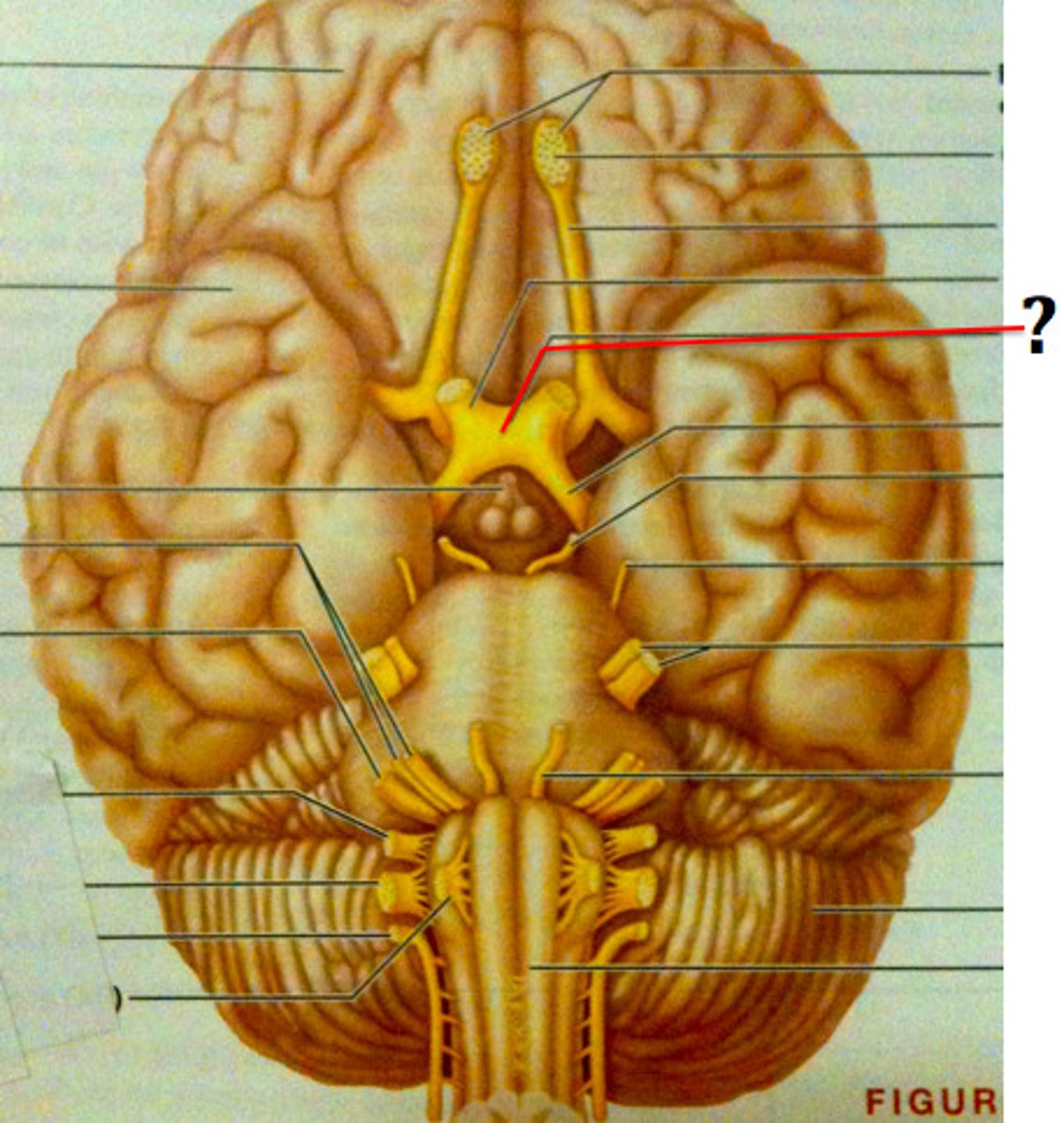
Optic Tract
Carries visual information from chiasma to occipital lobe.
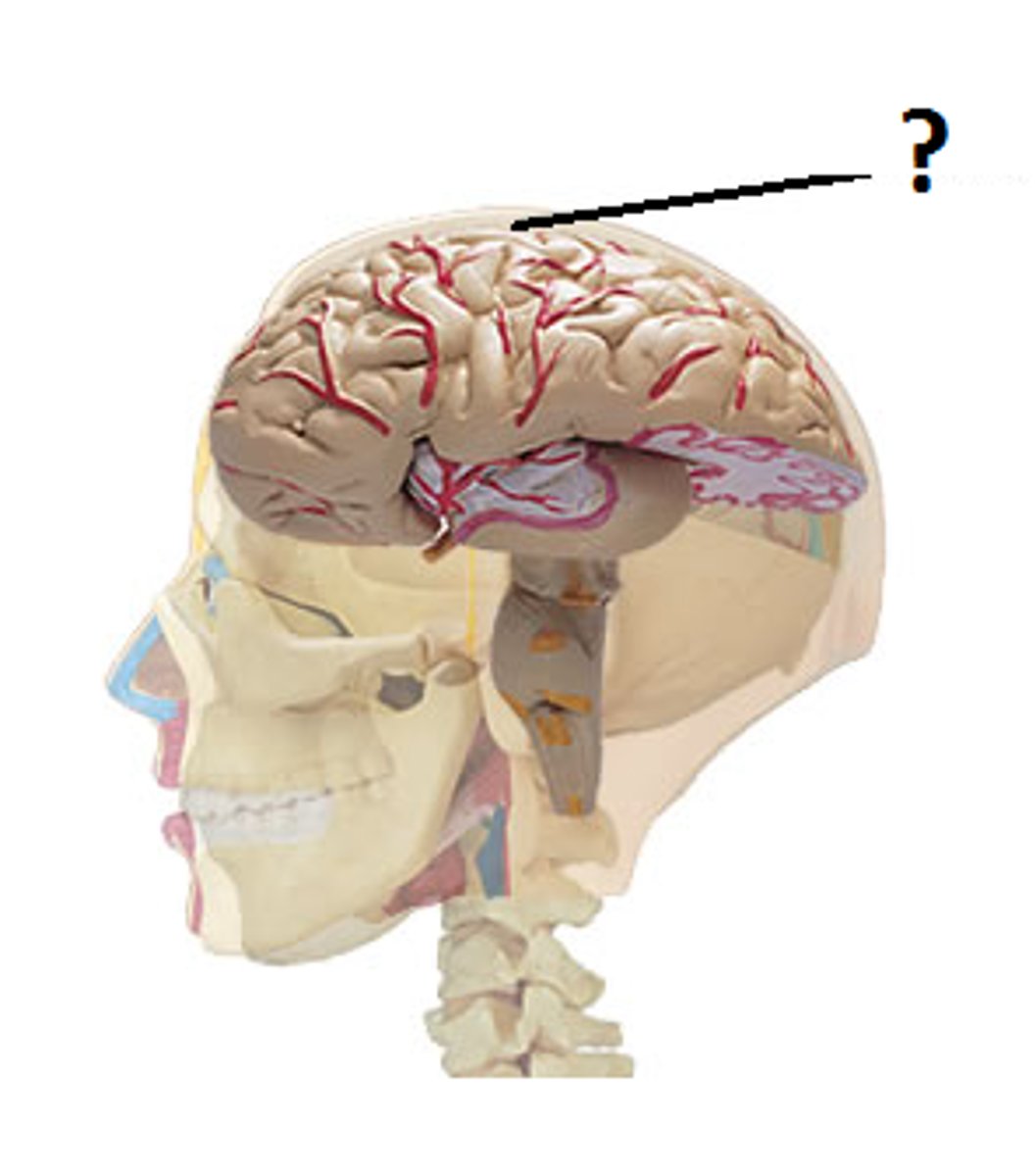
Cerebral Cortex
Outer gray layer of cerebrum; site of consciousness, reasoning, and sensory interpretation.
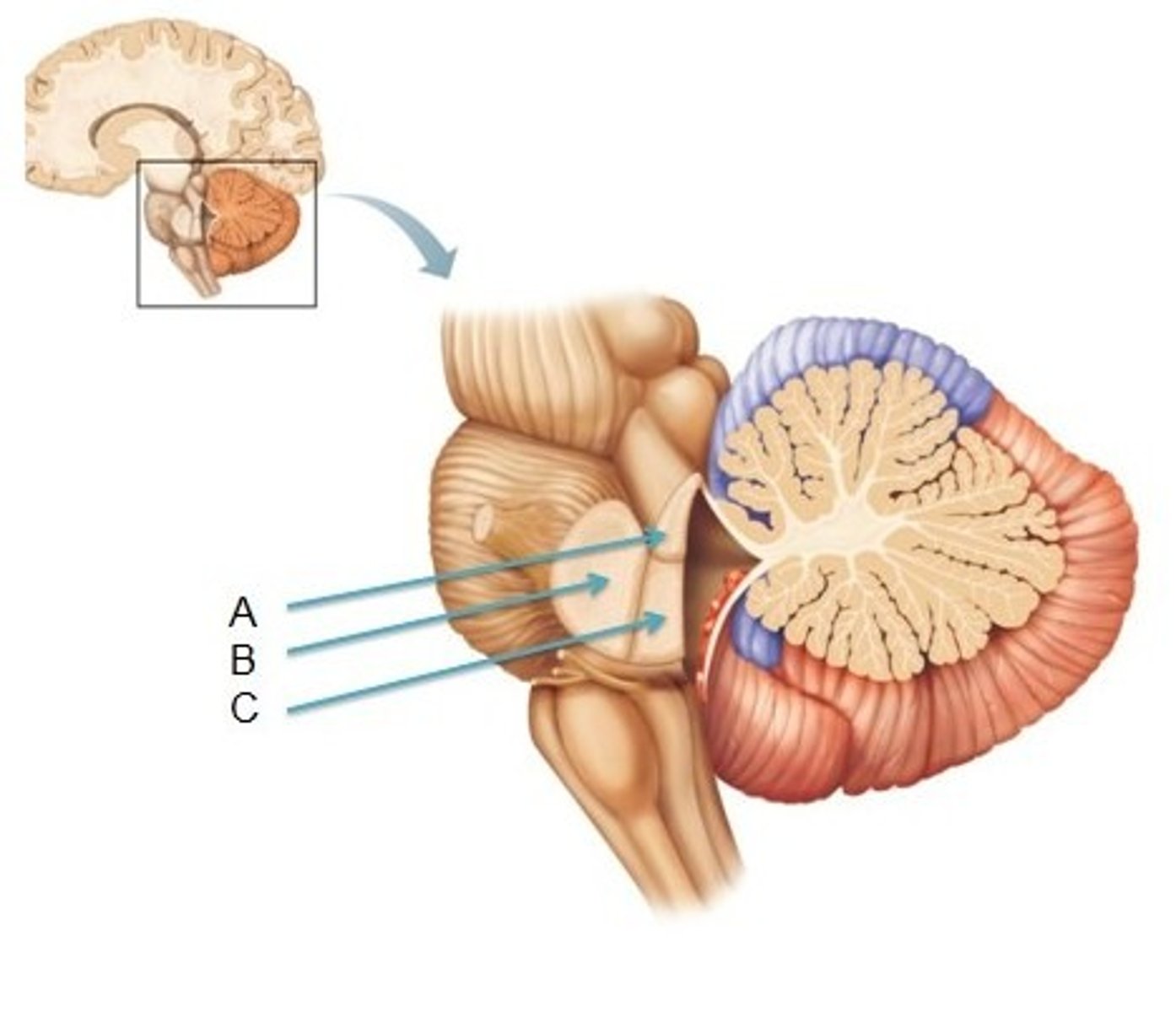
Arbor Vitae
White matter of cerebellum shaped like a tree; coordinates muscle movements.
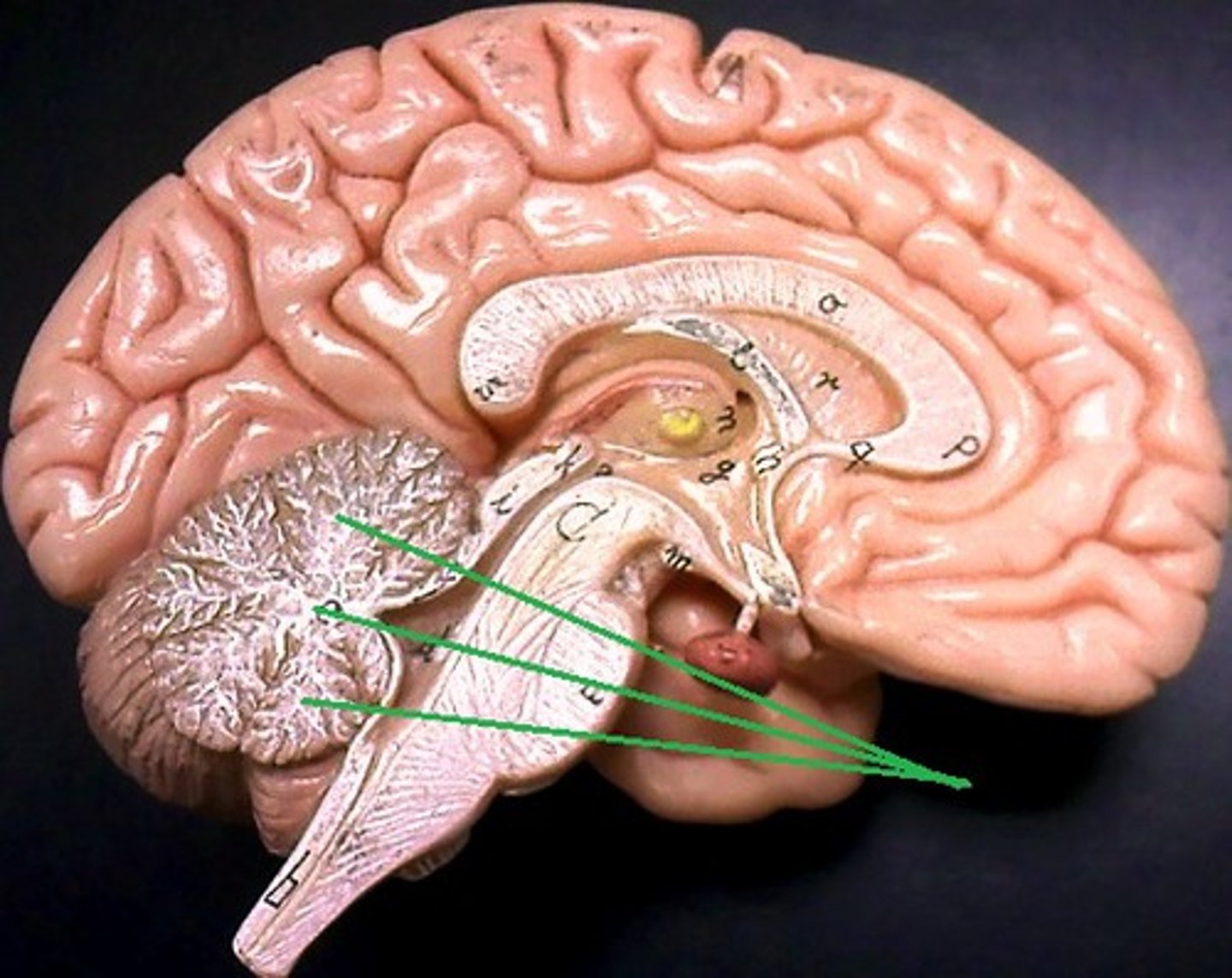
Cerebellar Peduncles
Three fiber tracts connecting cerebellum to brainstem; carry sensory and motor information.
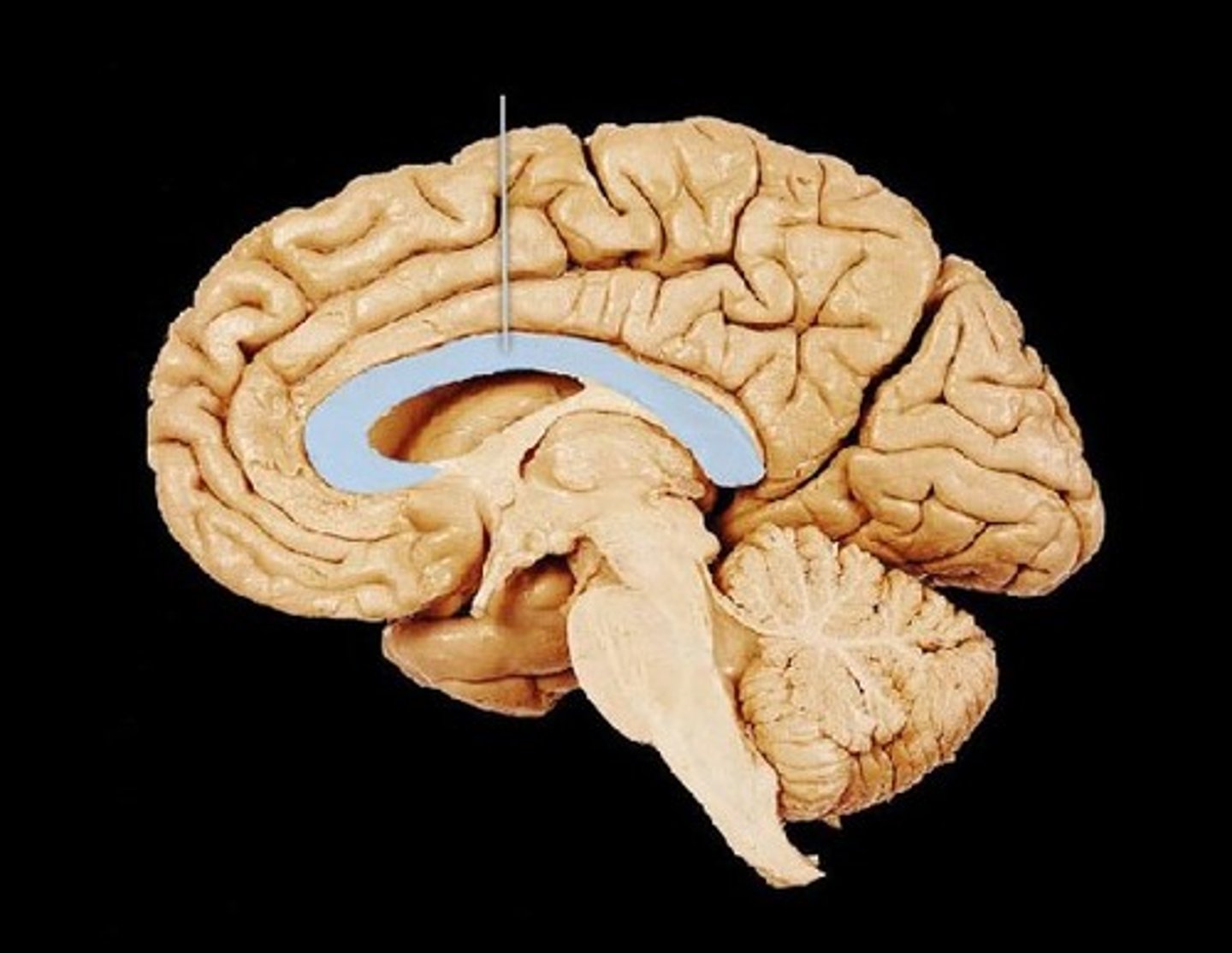
Corpus Callosum
Thick band of white matter connecting left and right hemispheres; allows communication between them.
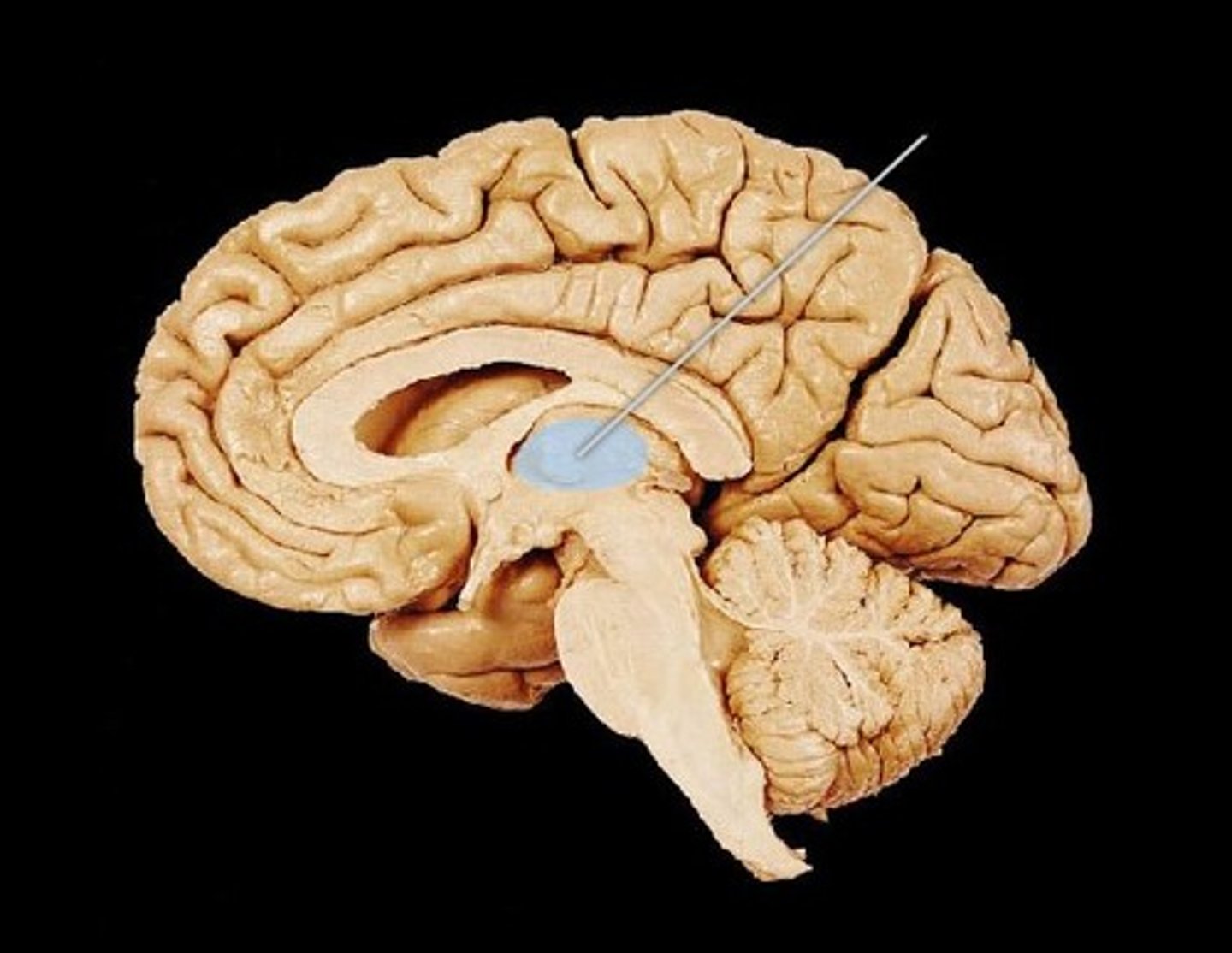
Thalamus
Central relay station for sensory information going to the cerebral cortex.
Hypothalamus
Below thalamus; regulates hunger, thirst, temperature, hormones, and autonomic functions.
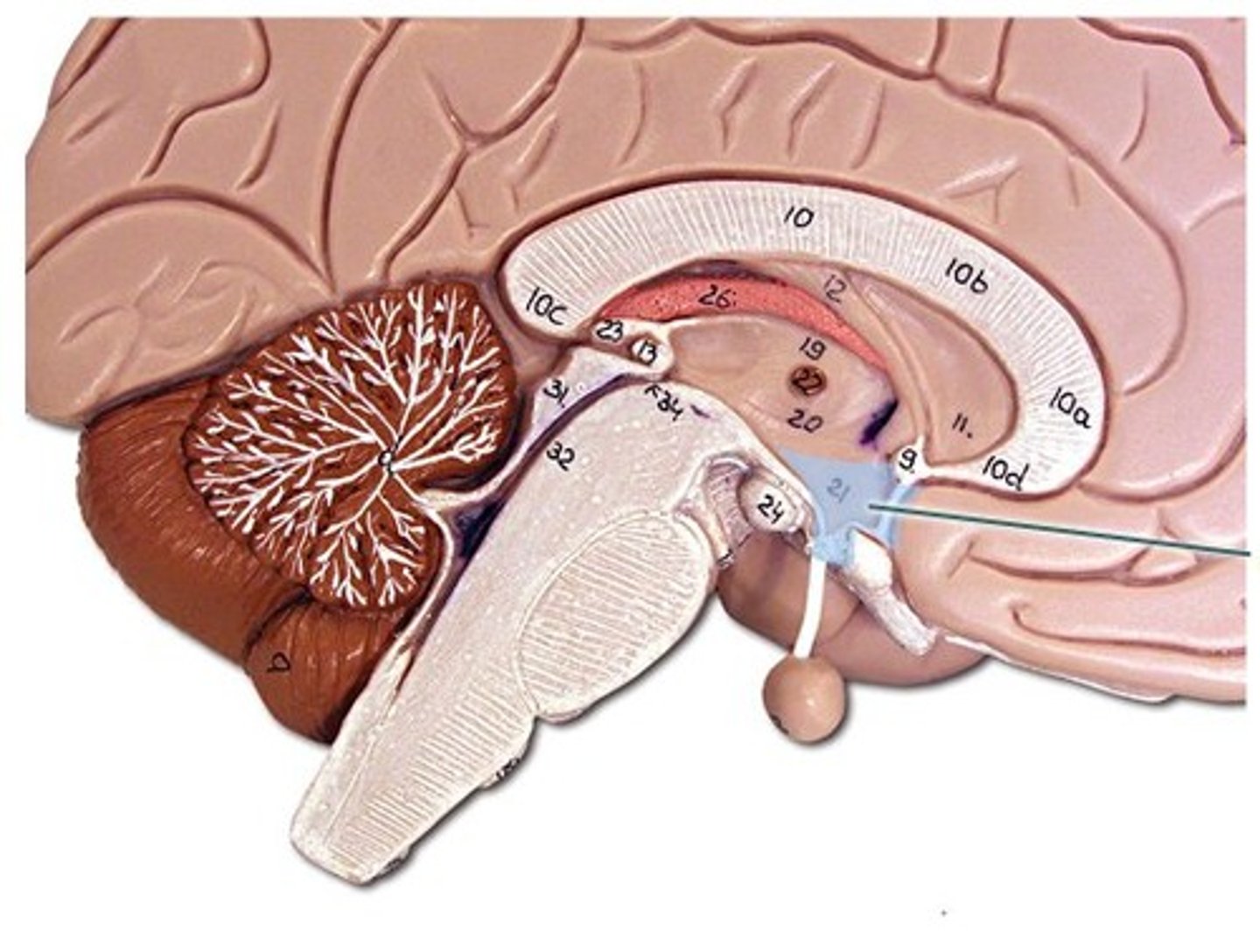
Pineal Gland
Small gland behind thalamus; produces melatonin for sleep regulation.
Lateral Ventricles
Paired chambers within cerebrum; contain CSF.
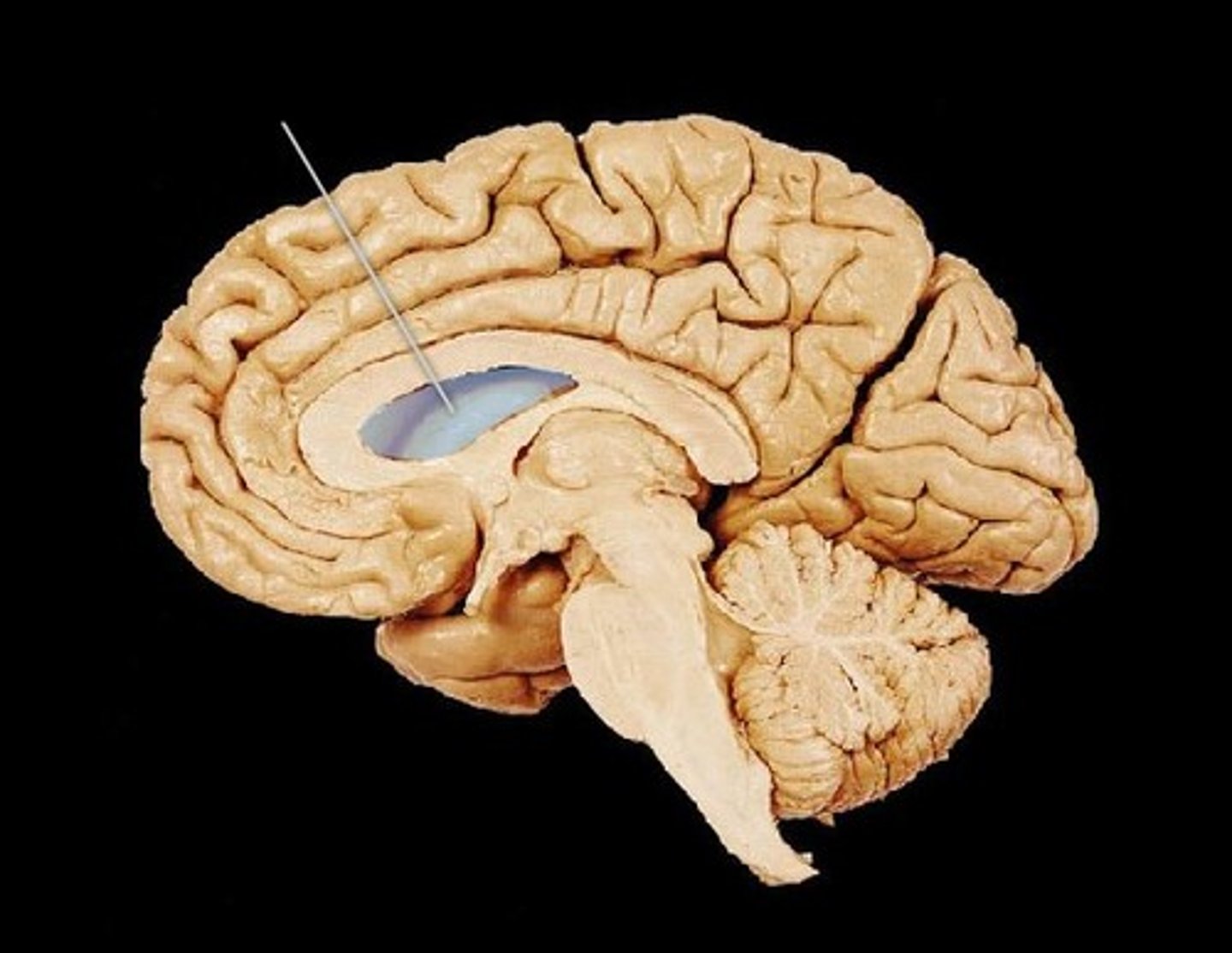
Third Ventricle
Narrow cavity between thalamic halves; filled with CSF.
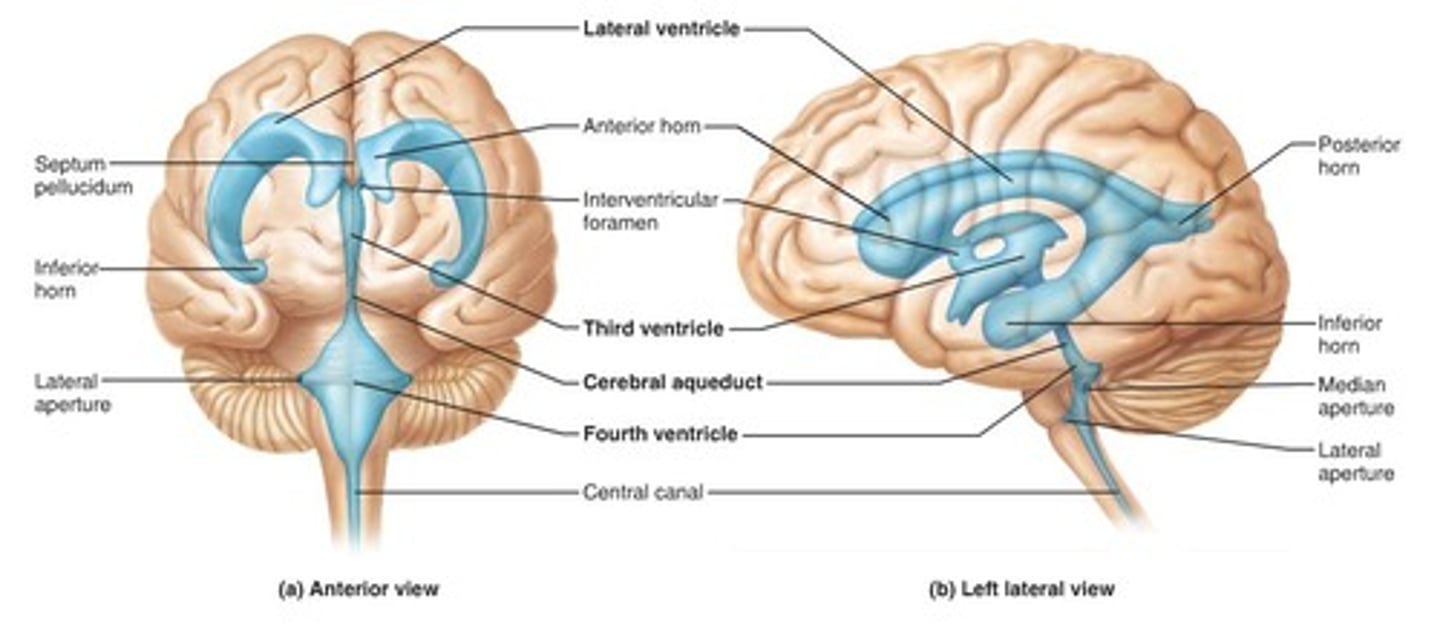
Cerebral Aqueduct
Narrow channel through midbrain connecting 3rd and 4th ventricles.
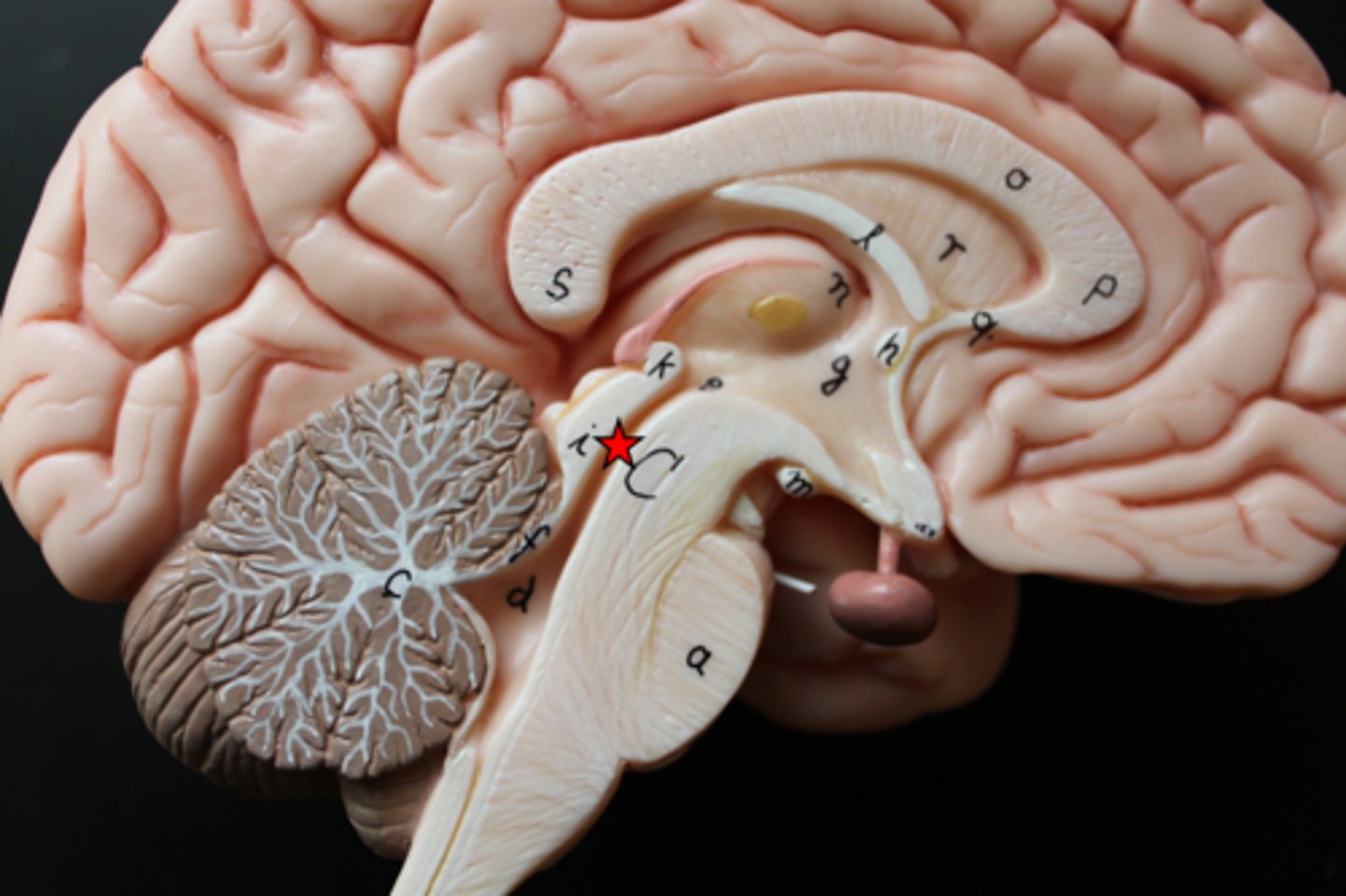
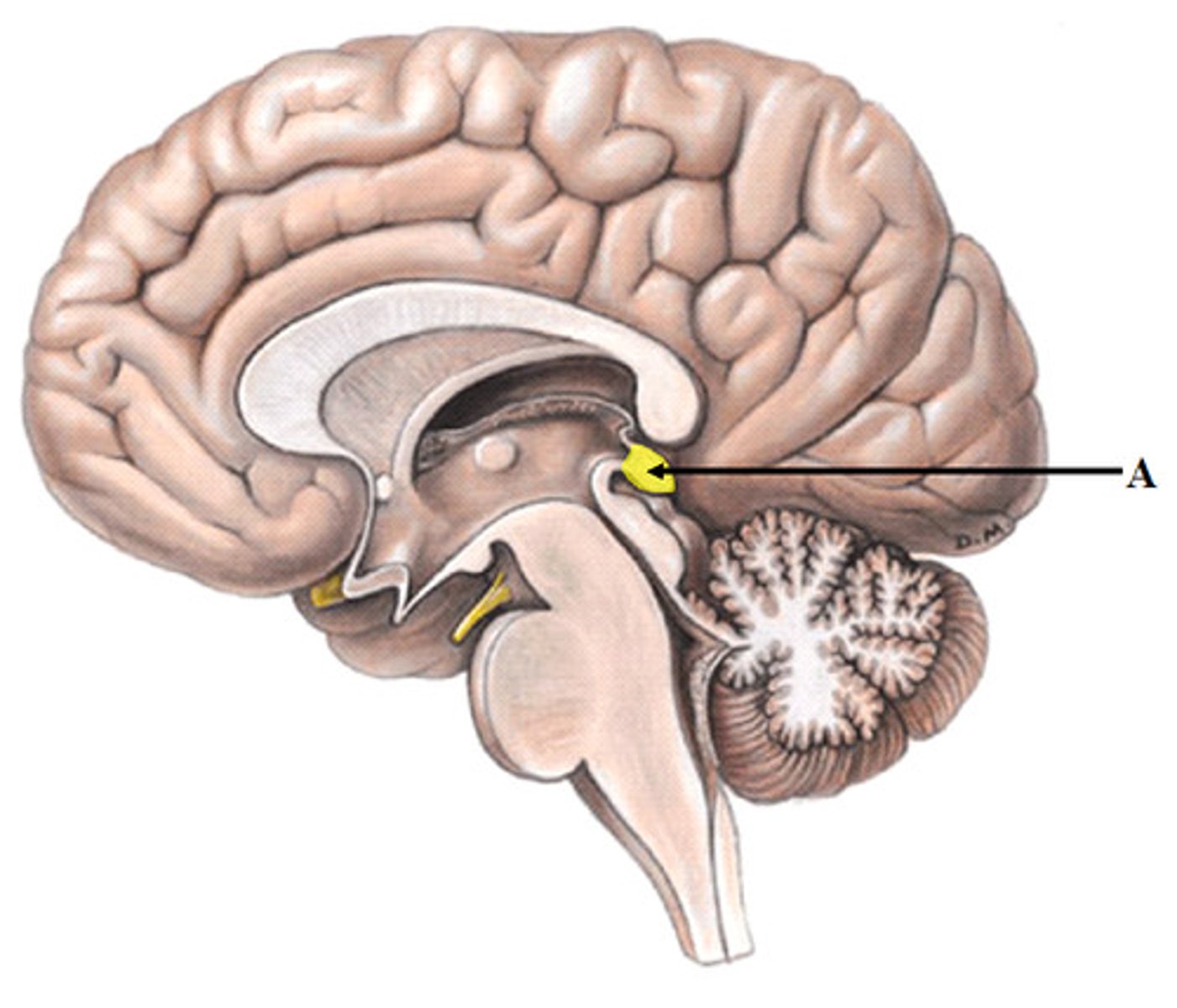
Mammillary Body
Round structure beneath hypothalamus; involved in memory and smell reflexes.
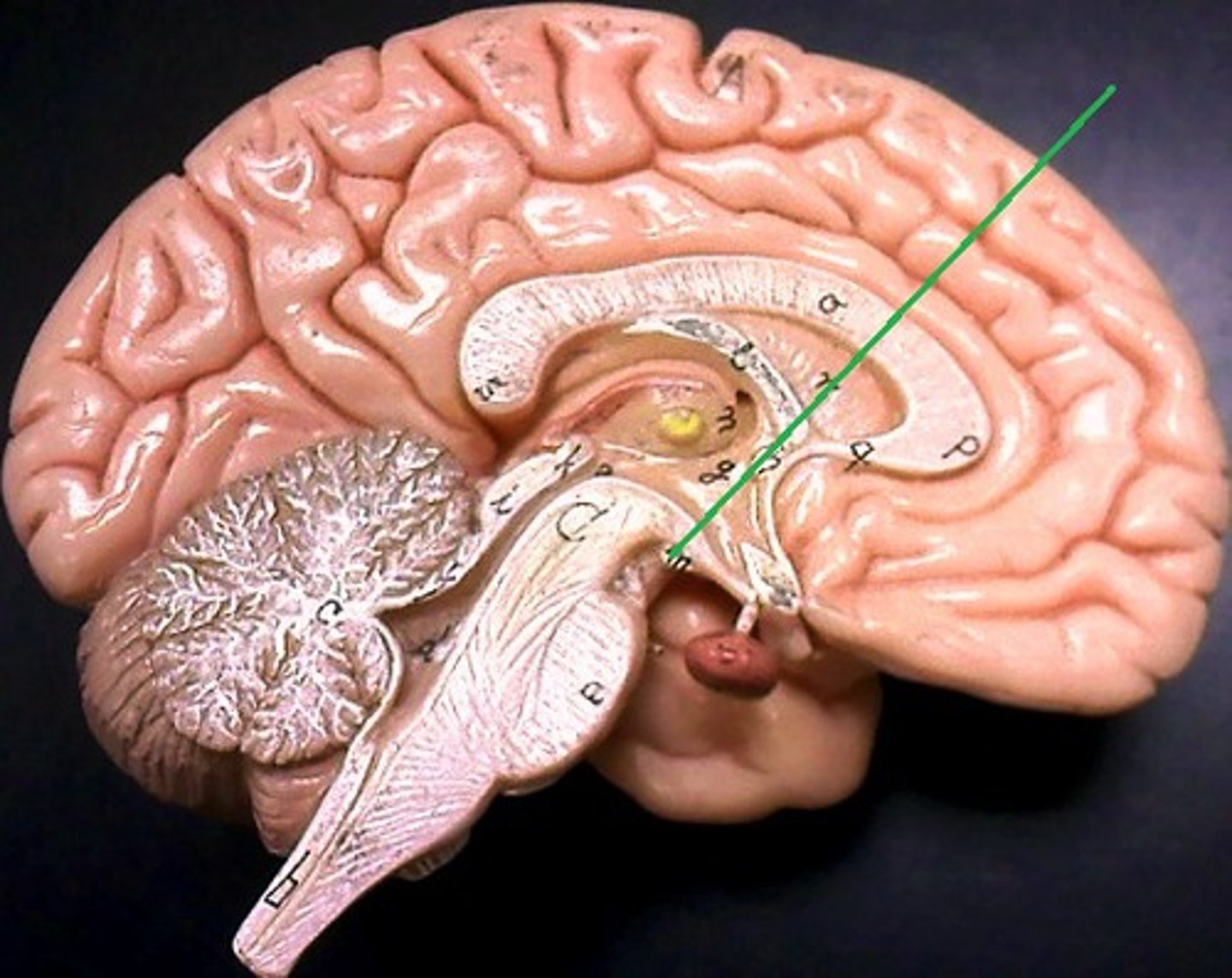
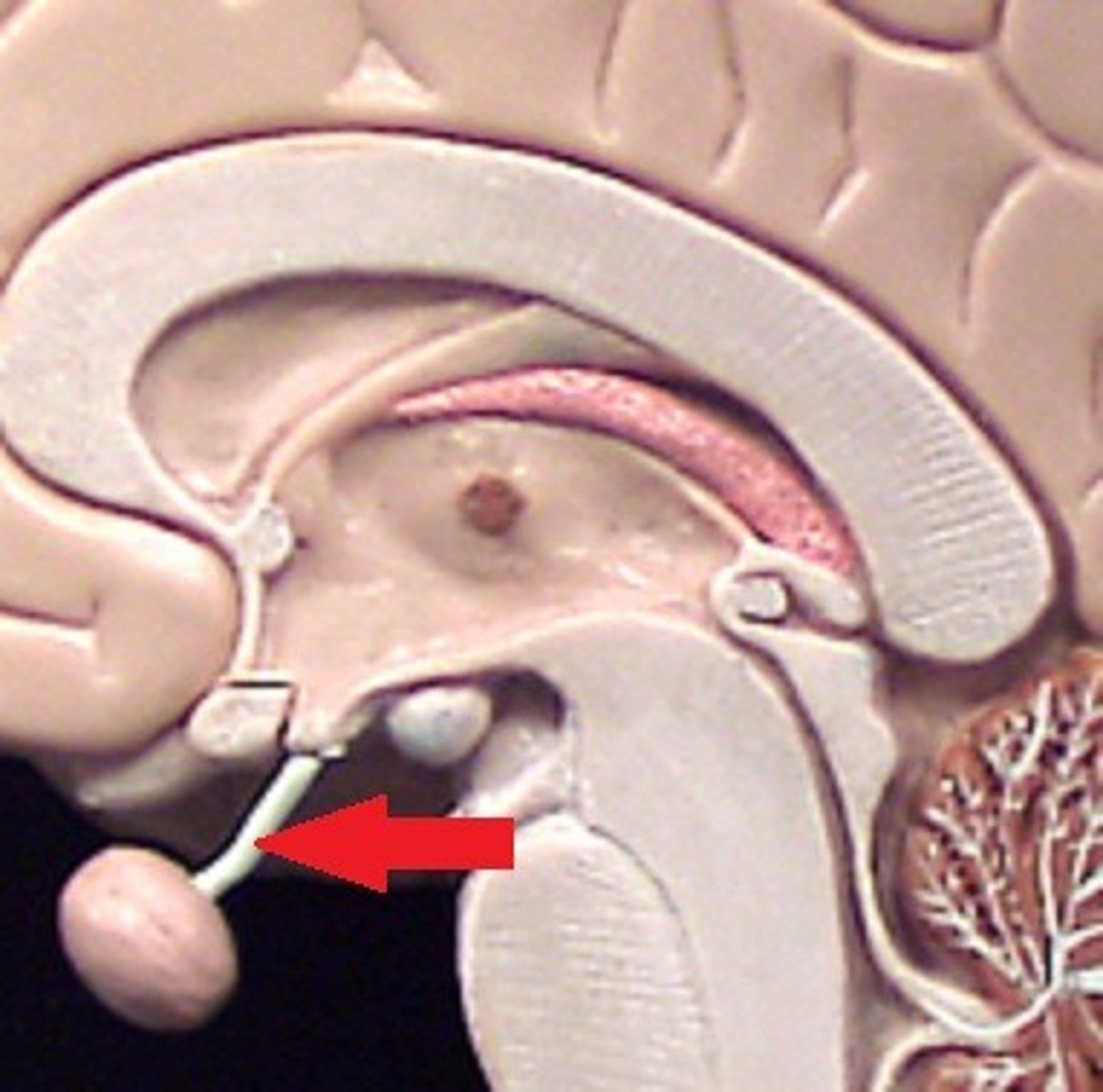
Infundibulum
Stalk connecting hypothalamus to pituitary gland; transmits hormones.
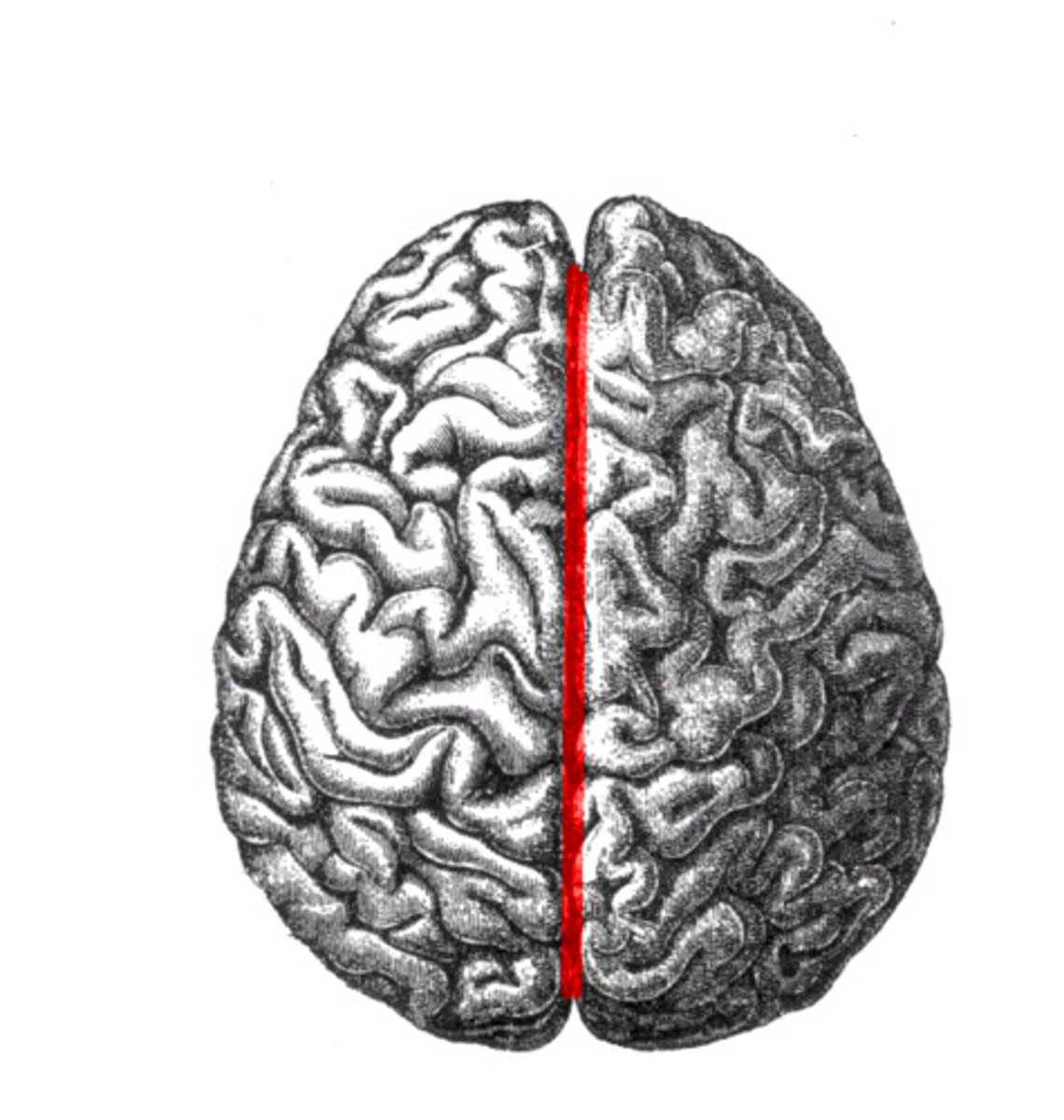
Longitudinal Fissure
Deep groove separating left and right cerebral hemispheres.
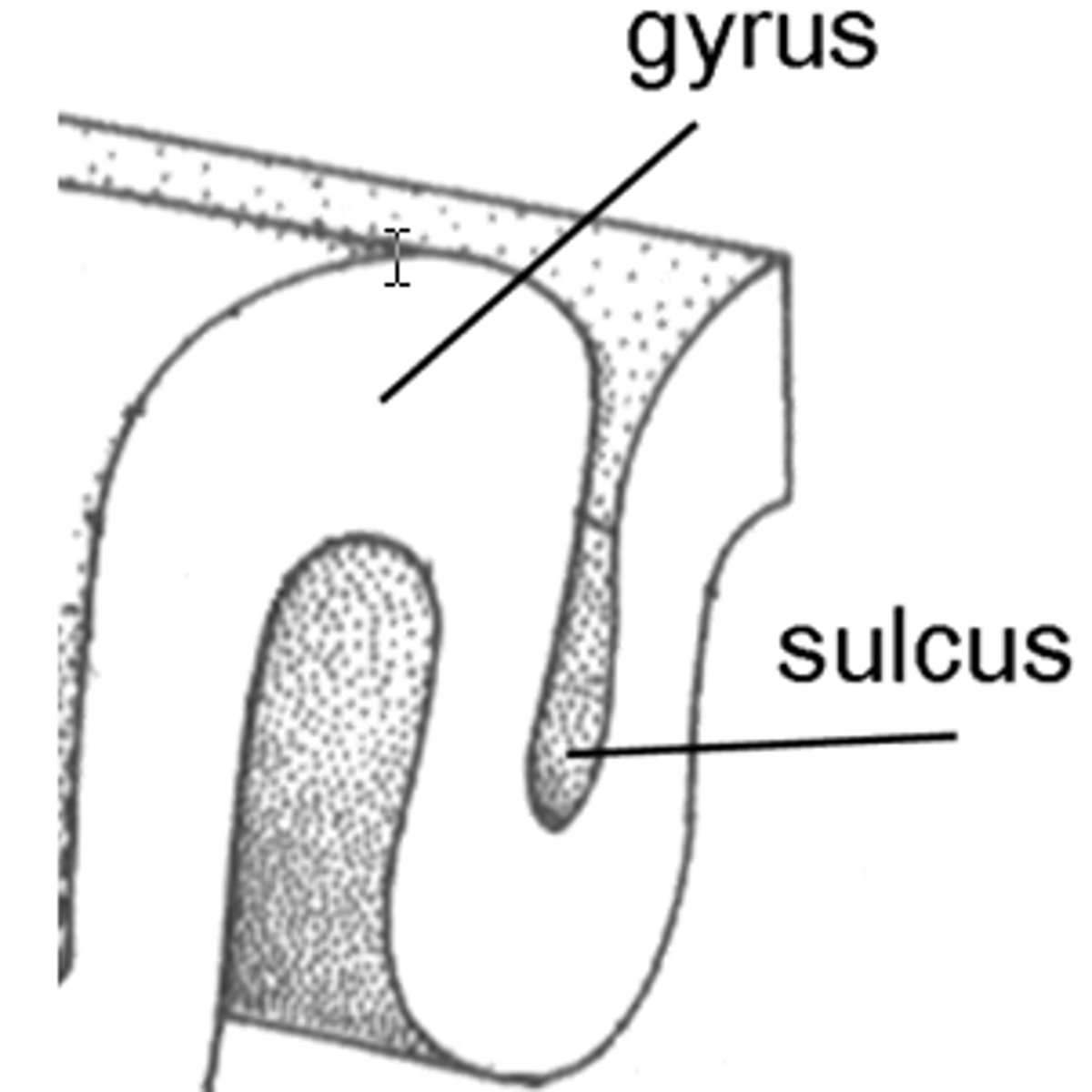
Sulcus
Shallow grooves between folds (gyri) of the brain.
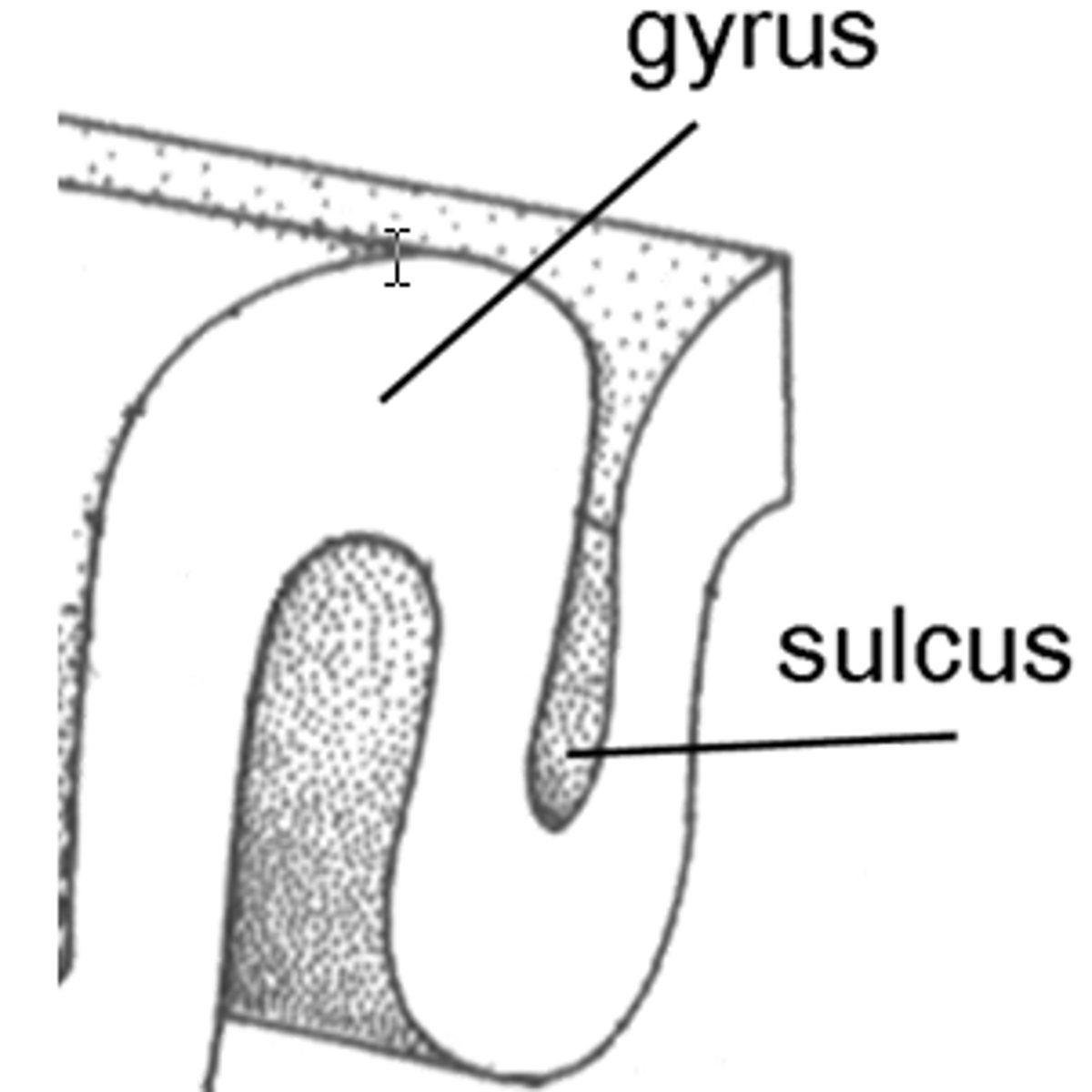
gyrus
Raised folds on the brain's surface that increase surface area for neural processing.
Dura Mater
Tough, outer protective layer of meninges.
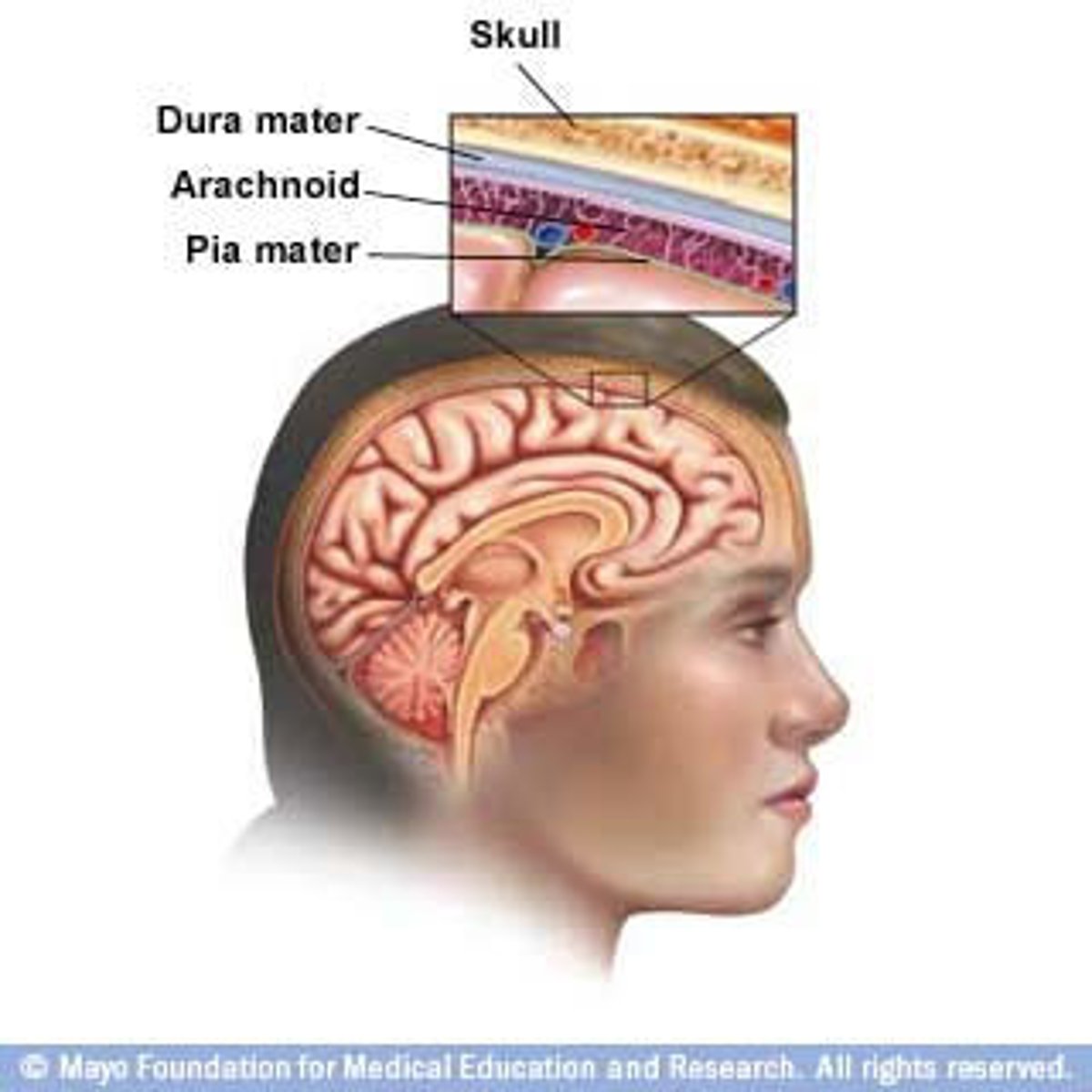
Arachnoid Mater
Middle, web-like meningeal layer containing cerebrospinal fluid.
Pia Mater
Thin, inner layer that clings tightly to the surface of the brain and spinal cord.
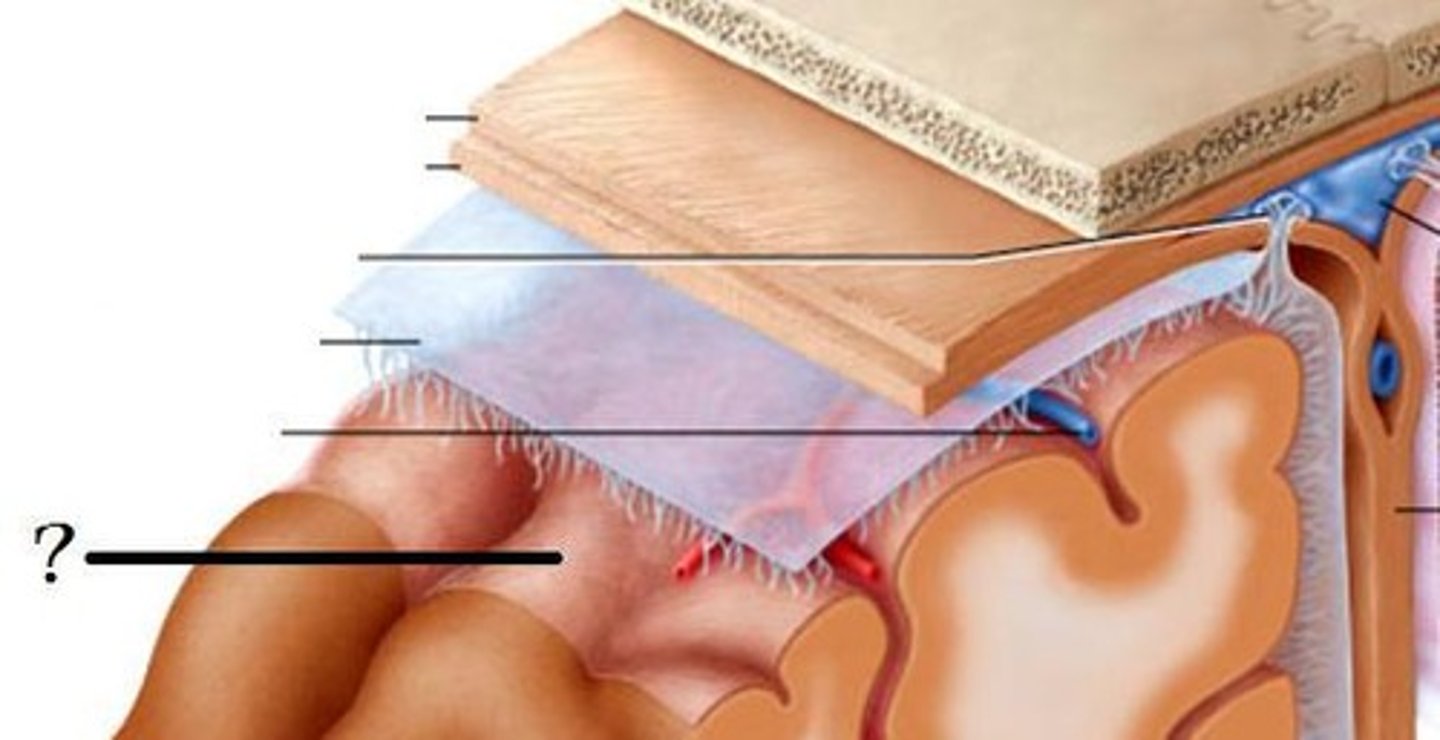
Fourth Ventricle
Cavity between the pons and cerebellum; filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
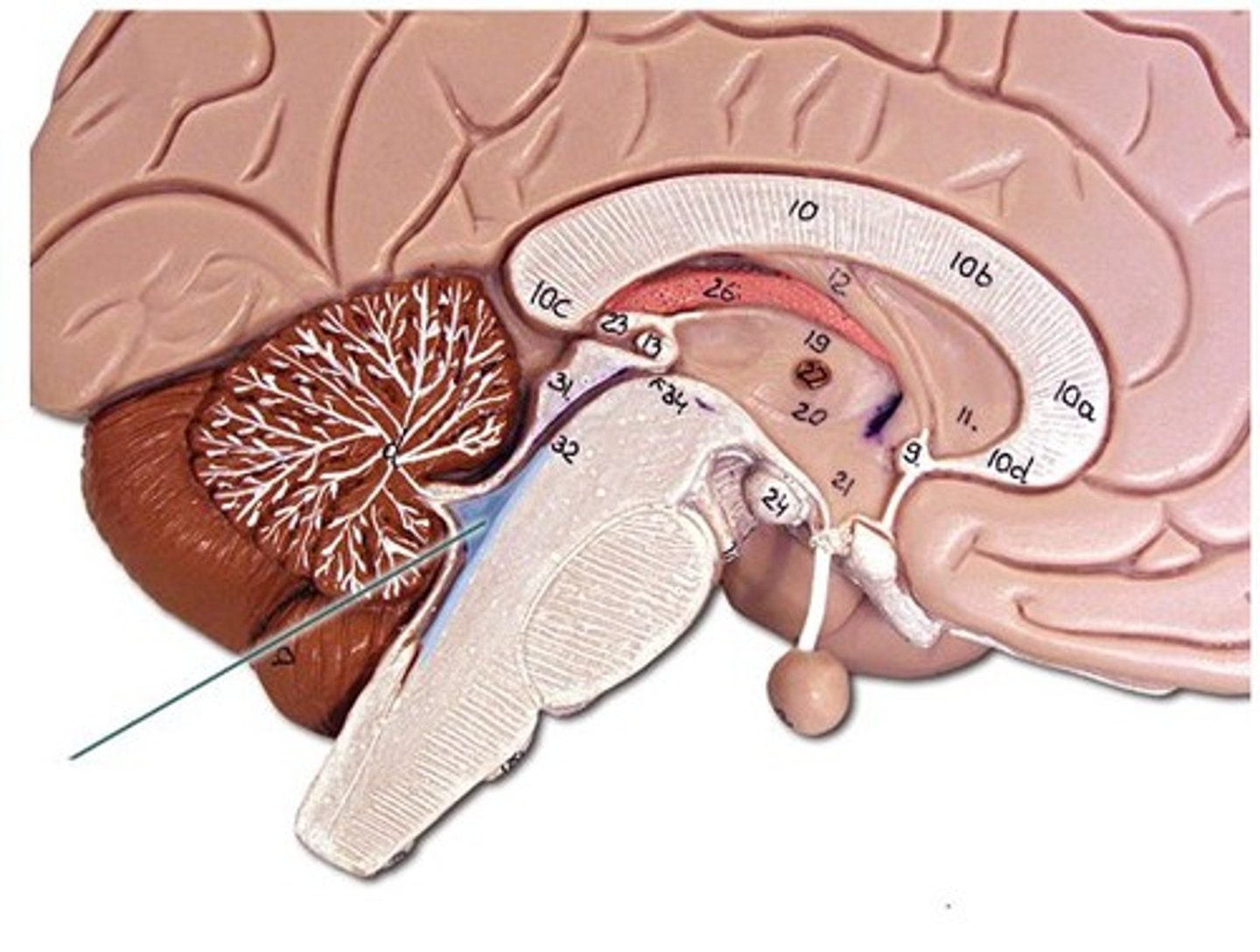
Fornix
Fiber tract arching below corpus callosum; connects hippocampus and hypothalamus.
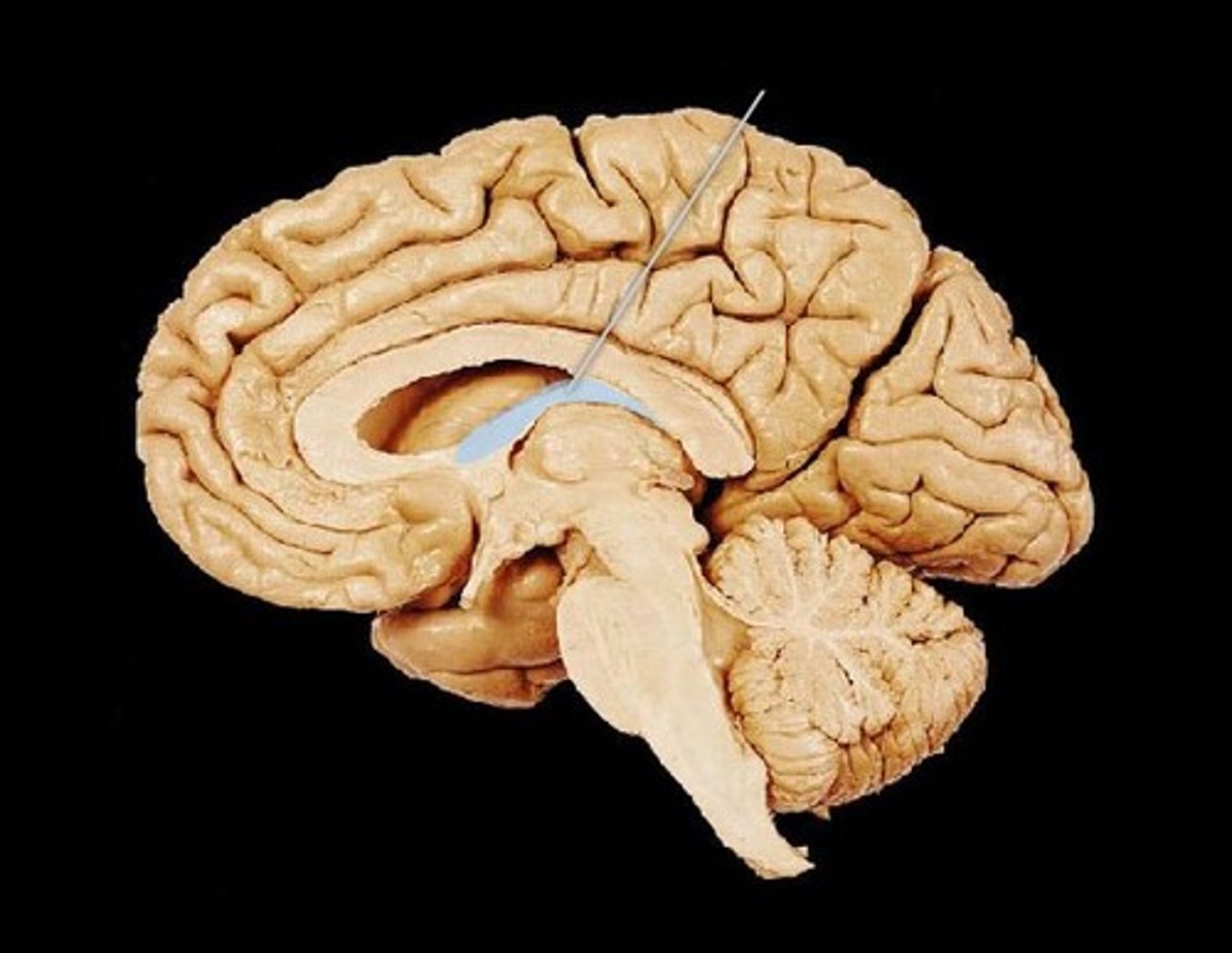
Pons
Bridge between medulla and midbrain; assists in regulating respiration.
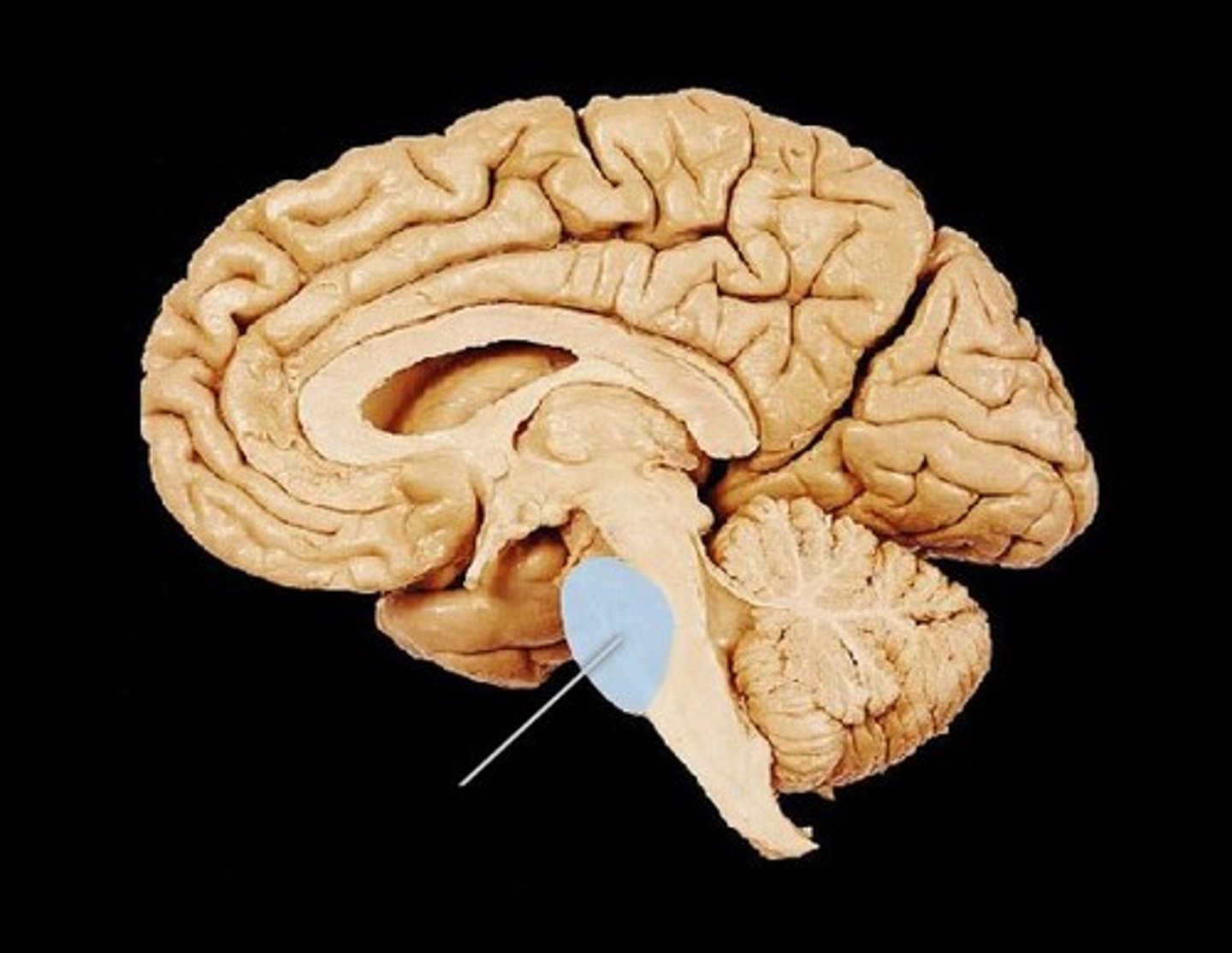
Choroid Plexus
Network of capillaries in ventricles that produce cerebrospinal fluid.
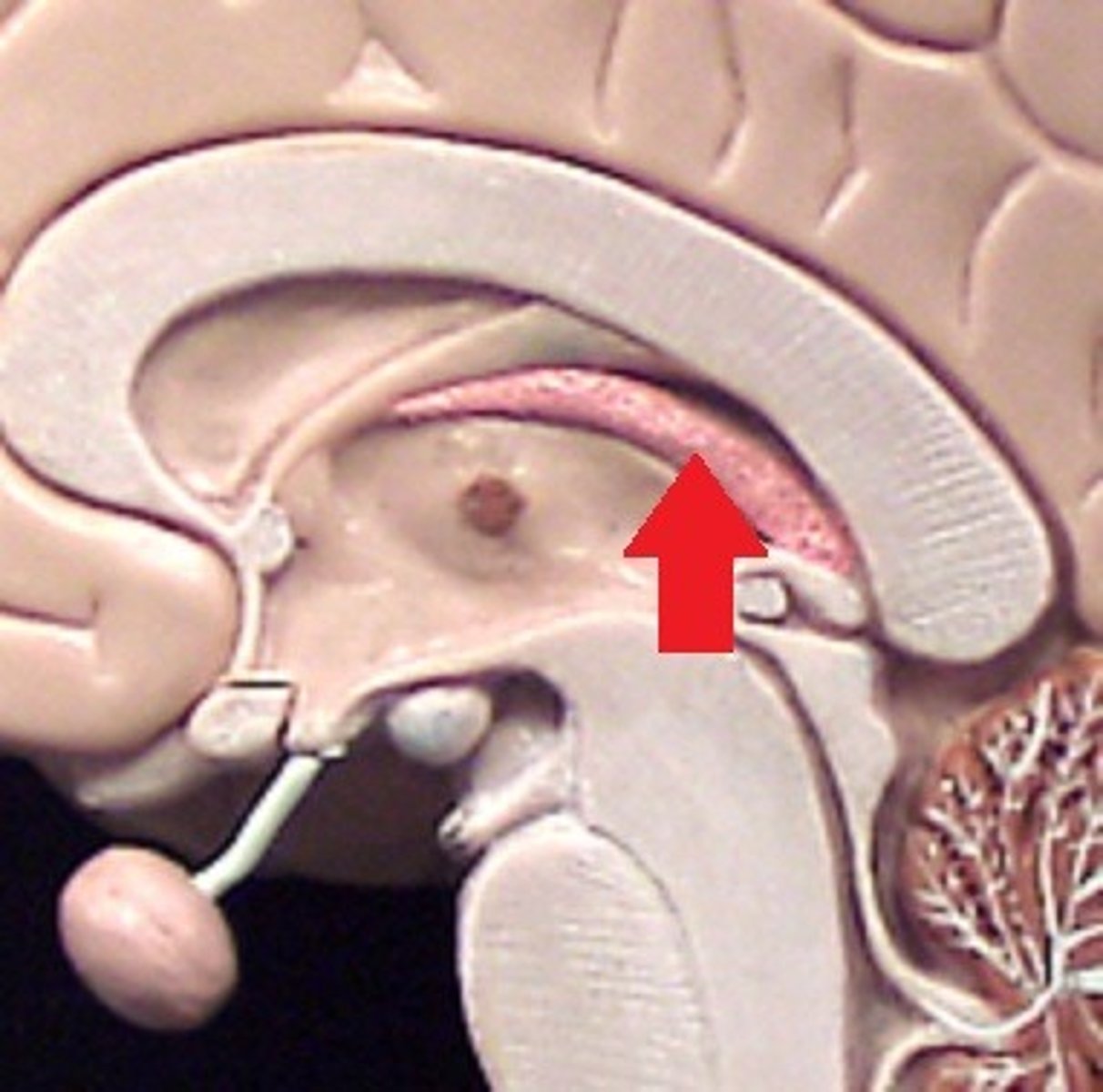
Intermediate Mass of Thalamus
Small bridge joining the two thalamic halves.
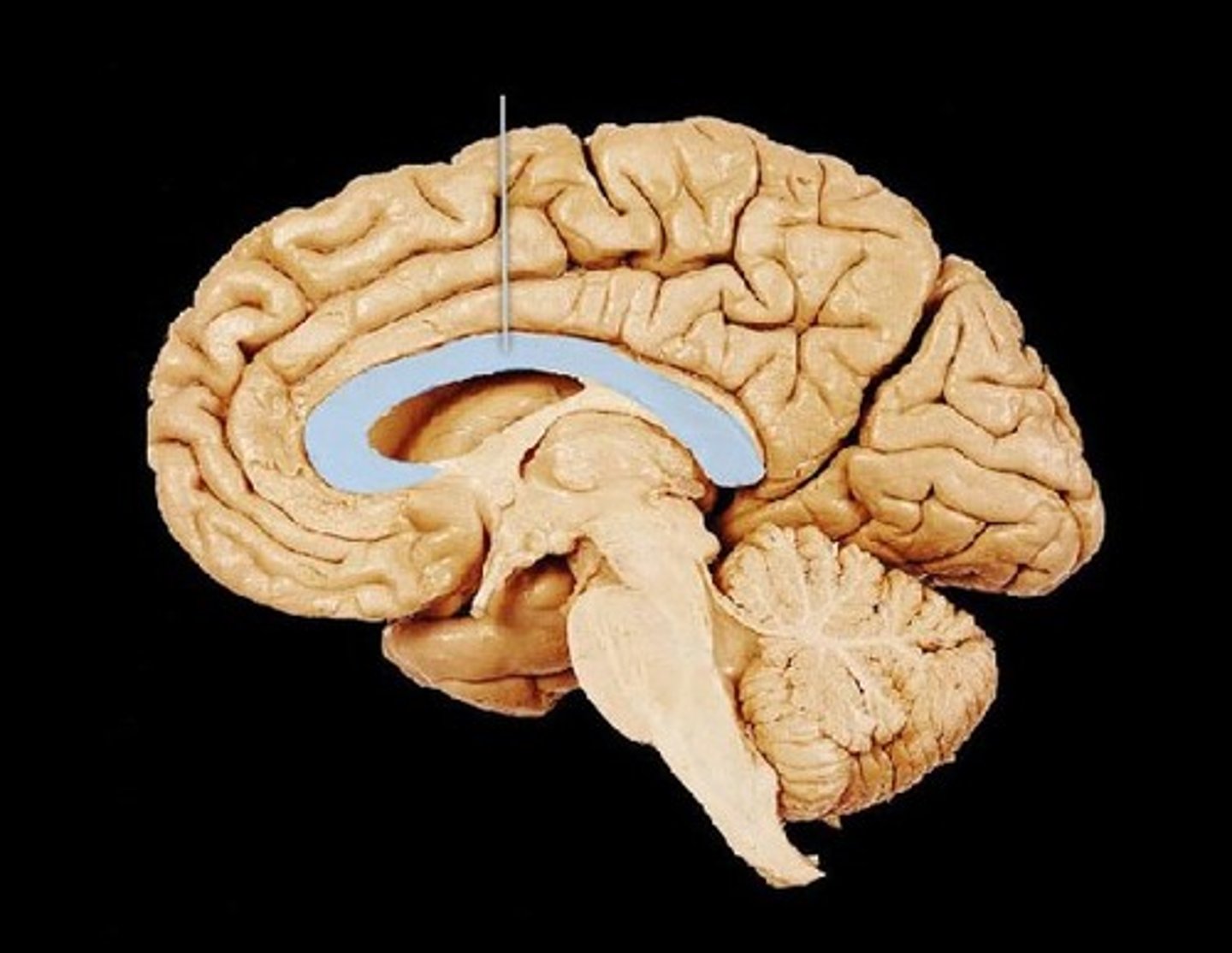
Corpus Callosum (Body, Genu, Rostrum, Splenium)
Large fiber tract connecting left and right cerebral hemispheres; Genu (front), Body (middle), Splenium (back), Rostrum (below front).
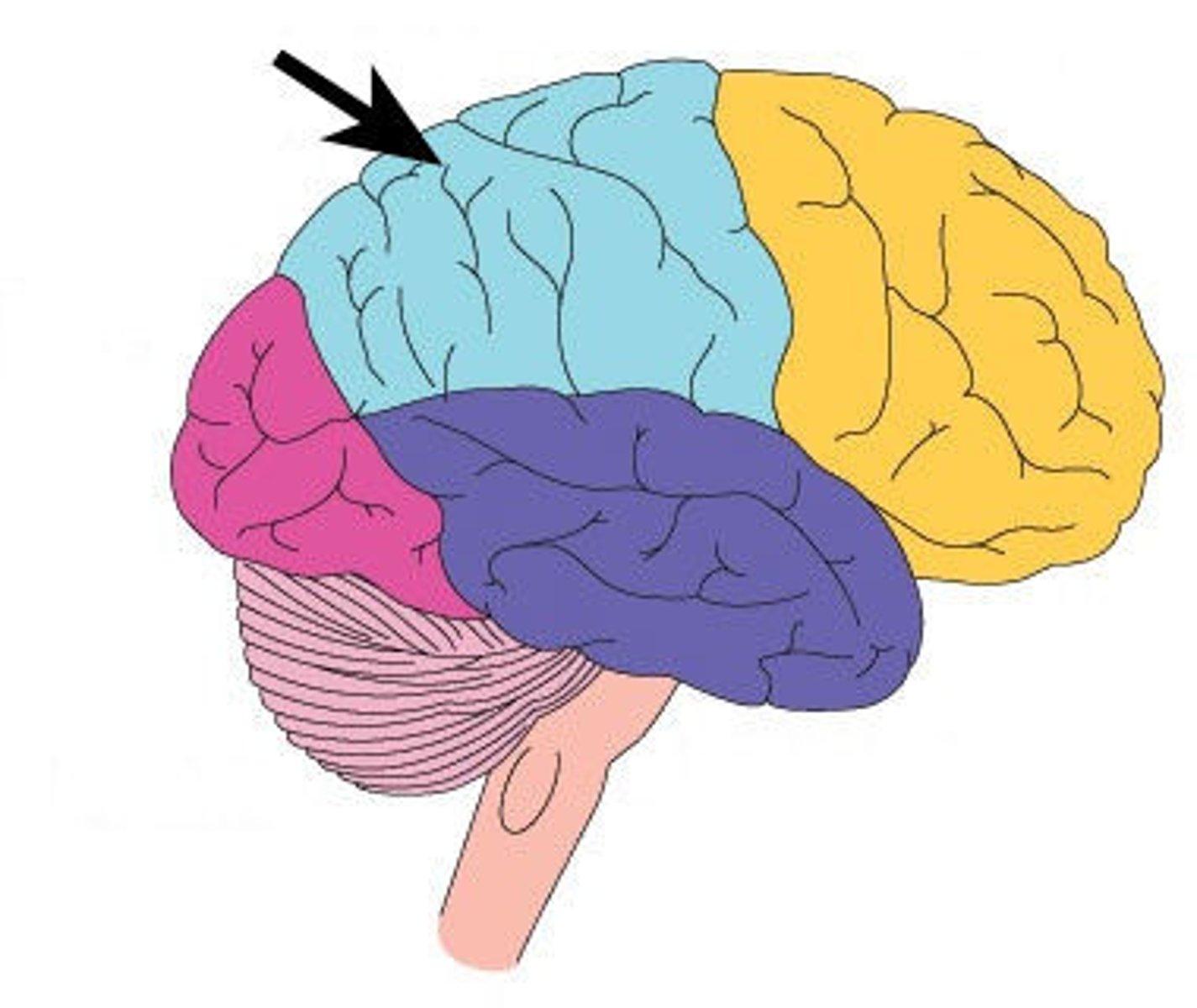
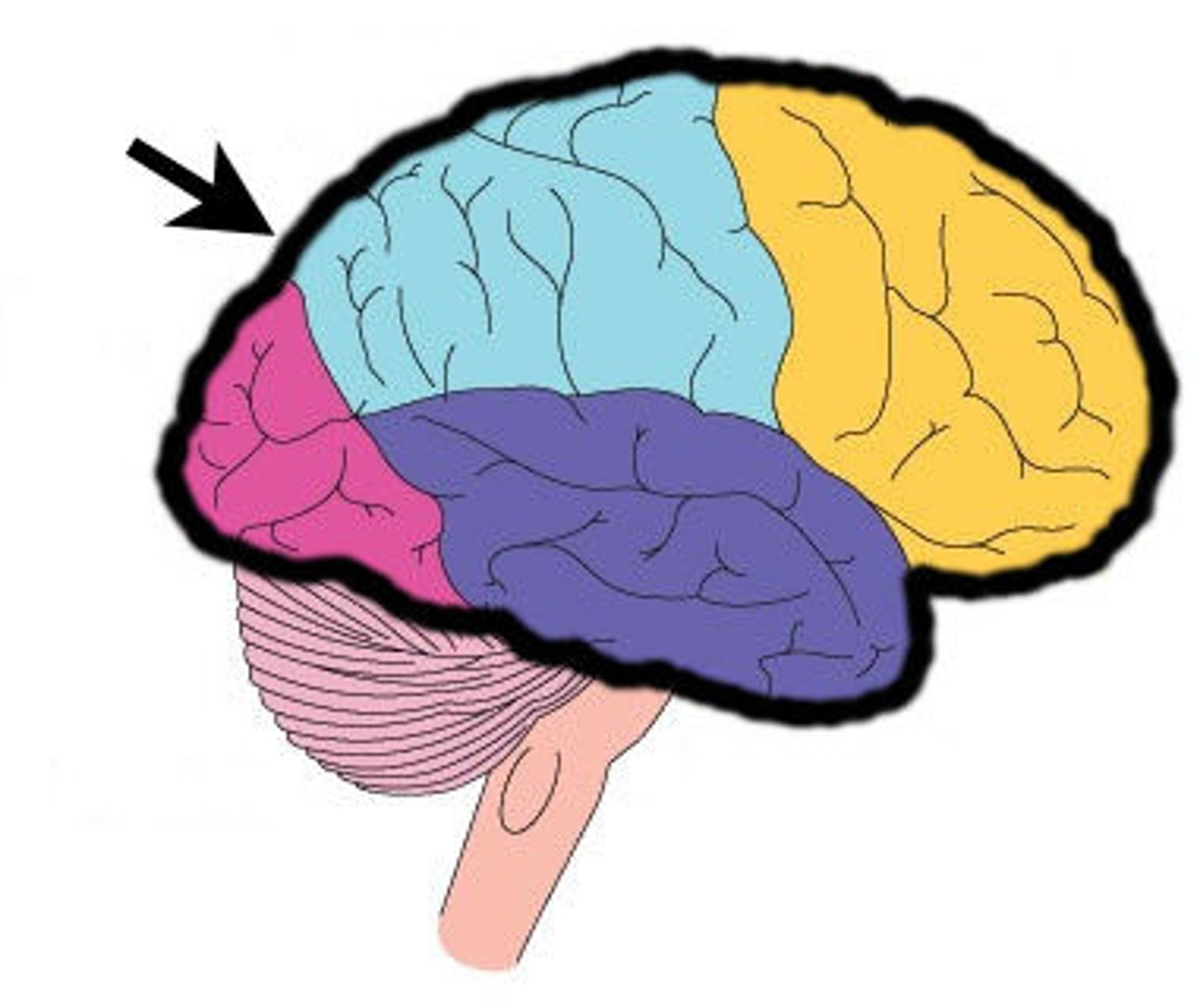
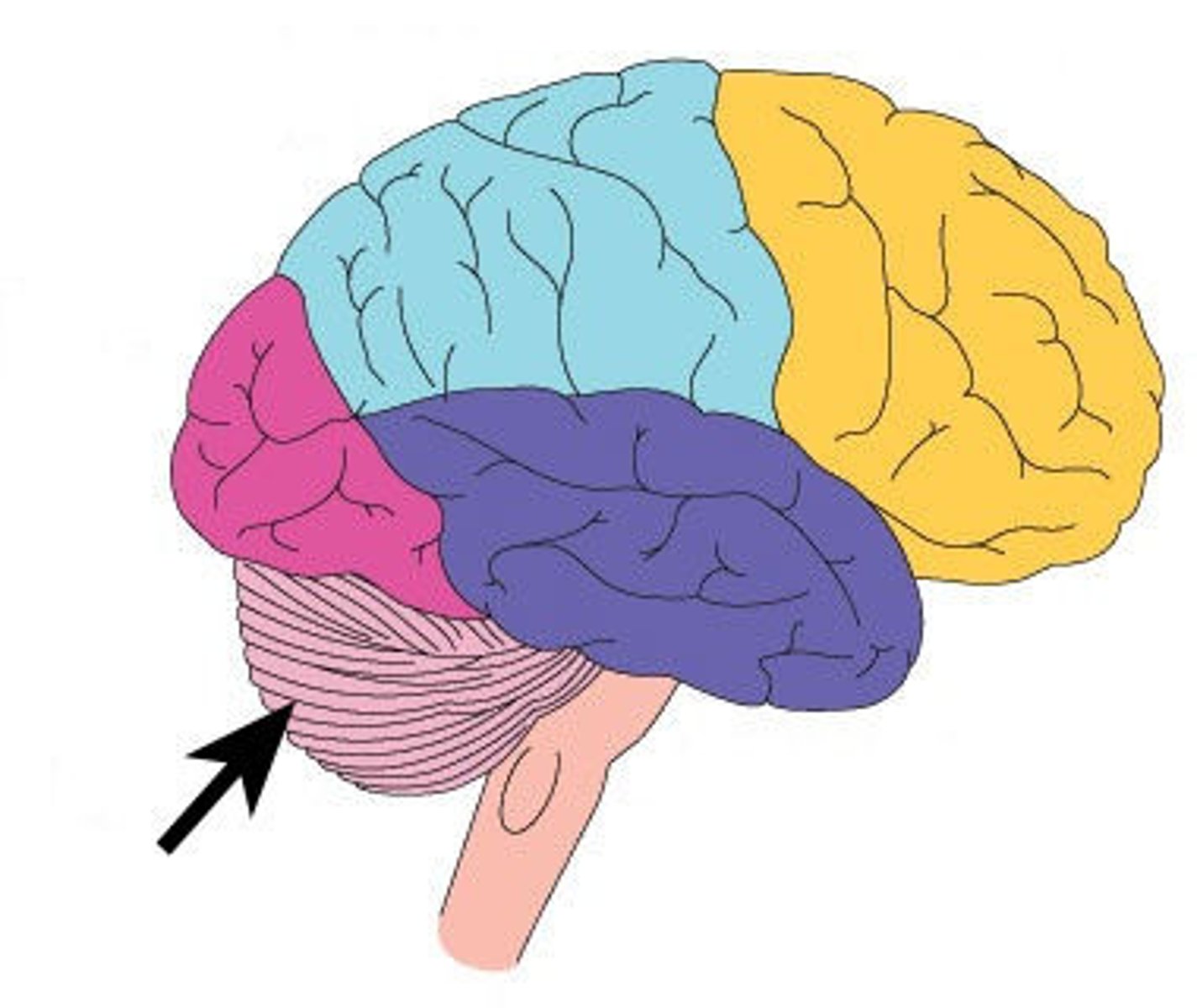
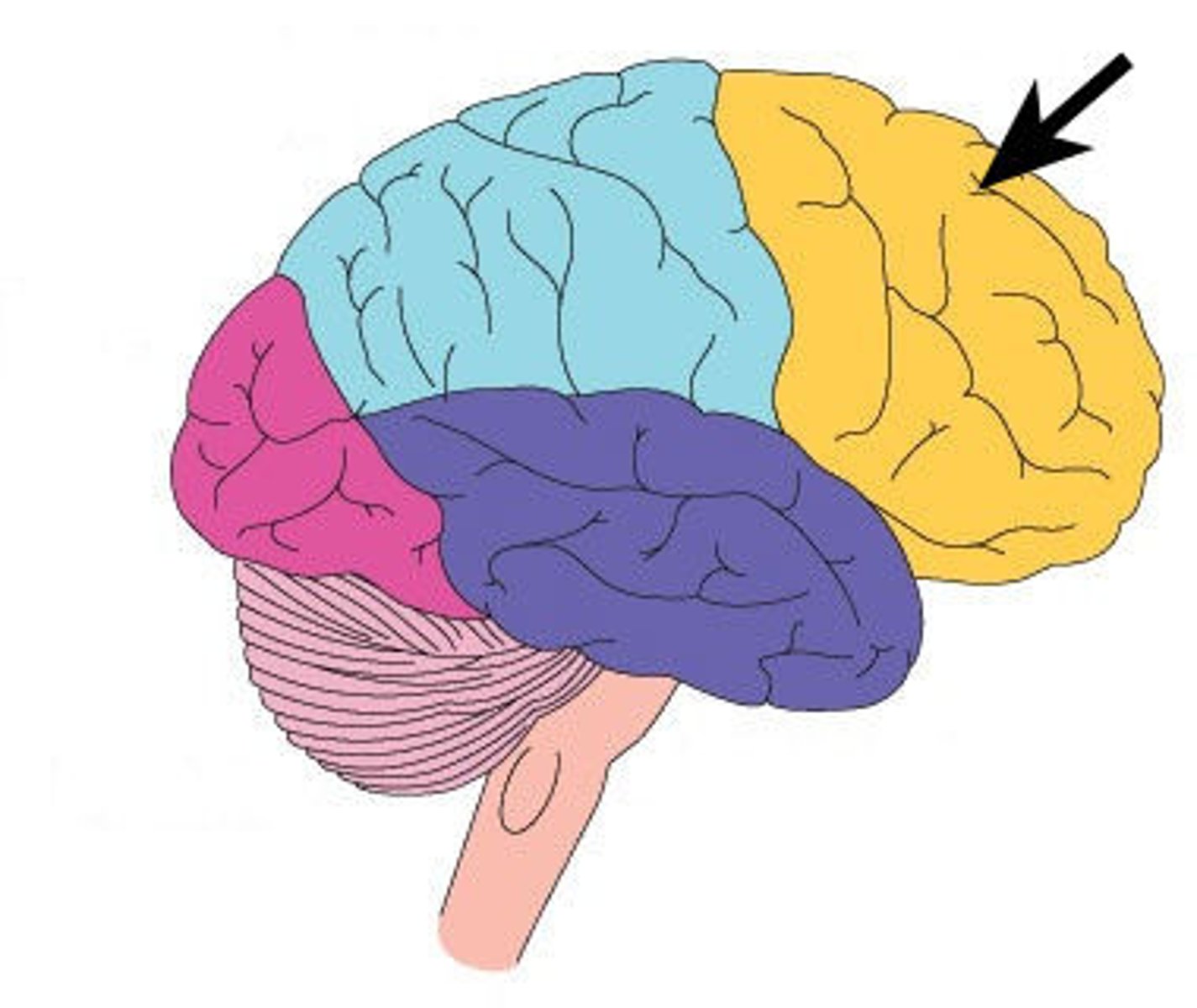
Frontal Lobe
Responsible for cognition, reasoning, planning, and voluntary motor function.
Parietal Lobe
Processes sensory input and body awareness; involved in movement coordination.