Lecture 6-HLSC3P09 Thyroid Hormones
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
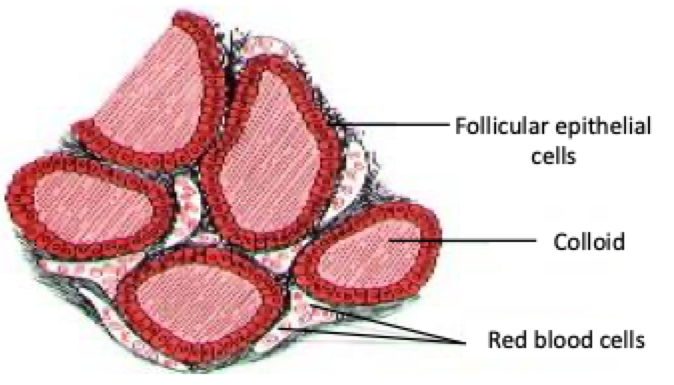
An endocrine gland located over the trachea, composed of two large lateral lobes and responsible for producing thyroid hormones.
What are the large lateral lobes in the trachea connected by?
Isthmus
rT3
Reverse Triiodothyronine- 1 % of the hormones secreted by the thyroid gland, it is an inactive form of T3 that can inhibit the effects of T3 on metabolism.
Which is the most abundant thyroid hormone?
T4
An essential element required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones
True or False: Table Salt is iodized to prevent iodine deficiency
True
True or False: In the Iodine pump, Iodine is 30 times higher in the lumen compared to ECF
True
What is Thyroglobulin made of? What does the formation entail?
A large glycoprotein containing 140 tyrosine aa thyroid hormone are formed within TG
What is the process of the oxidation of Iodide?
Iodide enters the follicular cell
Iodide oxidized by thyroid peroxidase (TPO)
TPO enzyme on the apical (lumen) surface oxidized (active) iodide is formed
What is Iodide oxidized by?
Thyroid peroxidase (TPO)
What is the process of the organification of iodide?
The binding of iodine with the thyroglobulin active iodide added to tyrosine residues of TG iodination is catalyzed by specific enzyme (iodinase)
Tyrosine first iodized to
Monoiodotyrosine (MIT)
Diiodotyrosine (DIT)
What is MIT?
Monoiodotyrosine
What is DIT
Diiodotyrosine
Two DIT (Diiodotyrosine) are coupled to form….?
T4
One DIT and one MIT are coupled to form….?
T3
Where is thyroid hormone stored?
As part of TG in the lumen of the follicle (colloid)
True or False: The total amount stored is sufficient to supply the body with the required thyroid hormone for 2 to 3 months
True
What is the process that removes iodine from thyroxine (T4) to convert it into triiodothyronine (T3)
Deiodination
TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone) is produced by what?
Anterior pituitary
What Digests TG and releases T4 and T3?
Proteinases
What 3 things transport thyroid hormone
Thyroid-binding globulin, Thyroxine Binding Prealbumin, and albumin.
What is TBG?
Thyroxine Binding Globulin
What is TSH controlled by?
Hypothalamus
What does TRH (Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone) do?
Stimulates the release of TSH from the anterior pituitary.
What are the 3 domains on the receptor?
Transactivation domain, DNA-binding domain, Ligand- binding domain
What is TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) produced by?
Anterior Pituitary
What 3 factors effect TSH secretion Regulation
Electrical Stimulation (Increase secretion of TSH) , Cold Temperatures (Increase secretion of TSH), Emotional Reactions can affect is (increase or decrease), Increased thyroid hormone in the body (decreases the secretion of TSH)
How to thyroid hormones act?
Act by binding to thyroid hormone receptors (nuclear receptors)
What are the three thyroid hormone receptors?
Transactivation domain, DNA-binding domain, Ligand binding domain
What sequences of promoter DNA do DNA-binding domain binds to?
Hormone response elements
Excessive thyroid hormone production
Insufficient thyroid hormone production
What are the three effects of the thyroid hormone?
Calorogenic, Sympathomimetic, Cardiovascular
What is Calorogenic?
Increased heat production
What is Sympathomimetic?
Fight or Flight
What are the 3 types of thyroid?
Hypothyroid, Euthyroid, Hyperthyroid
What is Exophthalmos?
Protrusion of the eyeball
What is Cretinism?
Thyroidectomy
A surgical procedure to remove part or all of the thyroid gland, often performed to treat thyroid cancer or hyperthyroidism.
What is Goiter?
An enlargement of the thyroid gland
Thyroid Nodules
Lumps in the thyroid gland, which can be benign or malignant; often detected via ultrasound.
Calcitonin
A hormone produced by the parafollicular cells of the thyroid that helps regulate calcium levels in the blood.
Thyroid Scan
A nuclear medicine test that evaluates the structure and function of the thyroid gland using radioactive iodine.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy
A treatment for hyperthyroidism or thyroid cancer that uses radioactive iodine to destroy overactive thyroid cells.
Myxedema Coma
A life-threatening condition resulting from severe hypothyroidism, characterized by unconsciousness, hypothermia, and respiratory failure.