Acute Exam 2 Lab
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Water seal should be ___cm
2
Suction chamber should be ___cm
20
The middle water seal chamber allows air to exit pleural space on ____ and keeps air from entering pleural space in inspiration
exhalation
Tidaling def
rise and fall of fluid with inhalation and exhalation
Continuous bubbling indicates an
air leak
Water in the small arm of water seal rises as intrapleural pressure becomes more
negative
Traditional closed chest drains regulate amount of suction by height of
water
____ level in the suction control chamber regulates amount of negative pressure suction transmitted to the pleural cavity, NOT the setting on the source
water
Dry suction allows for ____ pressure levels
higher
Dry suction uses a control valve to balance force of suction with atmosphere so it can respond and adjust to changes in atmosphere
yes
Indications for high pressure dry suction
massive air leak, empyema, viscous pleural effusion
Sump port is for collection of _____ for autotransfusion
autologous blood
Heimlich valve is a one way ____ valve that allows air to ____ but wont let it back in
flutter, escape
Blue end connects to _____, transparent end has sterile dressing for tubes that have minimal/no ______ or connects to collection bag
chest tube, drainage
Arrow on the valve should always point ____ from patients chest
away
Heimlich valve is for small or partial _____ and does not collect fluid
ptx
Pneumostat is another one way valve for ______ with small amounts of ____
ptx, liquid
Pneumothax white end to ____, clear end is for _____ or removing drainage. Collects ____ of drainage
patient, sampling, 30mL
Pneumostat air leak well confirms air leak if there is bubbling after adding ____ of water to the well
1 ml
Empty pneumostat with a
plunger
Pleural space is a small cavity between ____ and ____ pleura that contains serous fluid that allows movement without friction during respiration
visceral, parietal
Fluid in lung can create _____ which prevent lungs from expanding fully
counterpressure
Tension ptx
injury to chest wall/lungs allows air to enter pleural space but keeps it from leaving
Tension ptx is
emergency
In tension ptx, the mediastinal shift displaces trachea towards the _____ side
unaffected
Diminished/absent lung sounds indicate that the lung has not
reexpanded
Chest chest tube dressing at least every
4 hrs
When to replace disposable chest tube drainage system?
when full
Drainage amount

Clamping chest tube is risk for
tension ptx
IF chest tube detaches from drainage system
Exhale and cough, submerge in 1 inch of sterile water
Palpate area around dressing to check for ____ or ____ which indicate that __ is leaking into subq tissue surrounding insertion site
crepitus, subq emphysema, air
During first 24 hrs of chest tube insertion check every
1 hr
Chest tube assess regular
character, consistency, amount of drainage
Mark drainage level by noting time and date at drainage level on chamber every
8 hrs
Assess fluid level q _____ because water can evaporate
shift
Tidaling expect ____cm of fluctuation
5-10 (2-4 inch)
keep sterile gauze at bedside to cover insertion site if tubing becomes dislodged
yes
Tubing should remain _____ level of insertion site or else fluid could go back into pleural space
below
stripping/milking tubing can increase negative pressure in the system to a level that can ____ pleural tissue
damage
report to providor
difficulty breathing, cyanosis, rapid/shallow breathing, subq emphysema, chest pain, bleeding
After lung has reexpanded and minimal drainage, can clamp or disconnect tube before removing to observe for distress. Can also verify ok by cxr
yes
Ambulate every _____ to allow lung expansion and drainage
4-6 hrs
If transporting and detaching suction source, should make sure
air vent is open
After first few hours, report any drainage over ___ml/hr, because losing 100mL of blood q16min might require autotransfusion
70
Nasal cannula Fio2 range is ____, liter flow rate is ____L
24-44, 1-10
high flow nasal cannula fio2 ____% and flow rate of up to ___L
100, 60
Oxygen conserving cannula/oximizer fio2 range ____%. Good because it has higher fio2 with lower ___ flow
24-60, o2
Face tent fio2 of ____%, ___L, good for ___
24-100, 10, humidification
Oxymask is Fio2 of ___%, and has low ___ high fio2 so good for long term use
24-90, flow
nono rebreather mask fio2 of ___% and uses a reservoir bag. It can administer almost 100% oxygen.
80-95
CPAP has fio2 of ___% at ___cm of water pressure. it is invasive and right before ventilation
21-100, 5-20
If chest tube is pulled out, apply ___ and tape only ___ sides so air can escape
occlusive, 3
Half life of norepi is very ___ so as soon as bag is used up the pt can crash right away
short
Sepsis vs septic shock diff by need/no need of
vasopressors
Rebound reaction within ___ hrs
72
3rd spacing means dry ___ but body still has fluid
intravascularly
norepi vasopresses the periphery so the ___ are safe but extremities are vulnerable
vital organs
chest tube breaks what to do
cut end of tube and put in ns/water
blebs that pop usually resolve on its own once the ___ __ is taken away
positive pressure
Leopald maneuvers help to determine
number of fetus, presenting part, fetal lie, fetal attitude, degree of descent, point of max intensity for fhr
Leopald maneuver prereqs/positioning
pee, supine, knees flexed, pillow under head and hip
Leopald maneuver steps
palpate fetal part at funds, fetal back, attitude of head
Leopald document
fetal lie, fetal presentation, attitude of head, presentation head and face for cephalic
First stage of labor def
initiation of regular uterine contractions and cervical dilation/effacement
First stage, latent phase characteristics
0-6 dilation, little effacement and descent
Latent phase contractions are mild-mod and are around q _____ mins, lasts ____ seconds
5-20, 30-60
Active phase characteristcs
6-10 dilation, significant descent
Active phase has mod-strong contractions q___mins that last ____seconds. THis is when mother feels desire to ___ ___
2-5, 40-90. bear down
Second stage of labor def
complete dilation and effacement-birth
Ferguson reflex def
spontaneously bear down
Second stage of labor equpment
radiant heat warmer, emergency neonatal equipment
Third stage of labor def
birth to placenta
Fourth stage of labor def
stabilization to 2 hrs after placenta delivery
Stage 4 monitor
vs, fundal location, bleeding, bladder, perineum
C section additional documentation
approximate edges, edema, ecchymosis
apgar check at min and _
1, 5
APGAR test
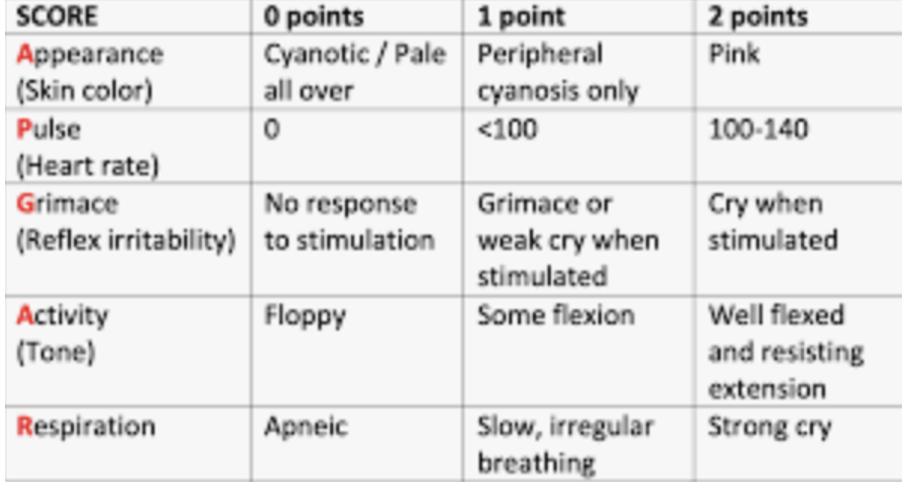
In newborns assess ____ first
rr
newborn VS top 3
rr, pulse/hr, temp
Newbor RR should be ___ bpm with breathless cessation under __ seconds
30-60, 19
INfant hr should be taken on apex for 1 min. Should be ___ and ___ with ___bpm when sleeping and ___ when awake
sharp, clear, 80-100, 110-160
Baby length should be ___cm
45-55
Head circumference right above ____ line and should be ___cm
brow, 32-37
Chest circumference taken at nipple line and should be _____cm, or ___cm less than head
30-33, 2-3
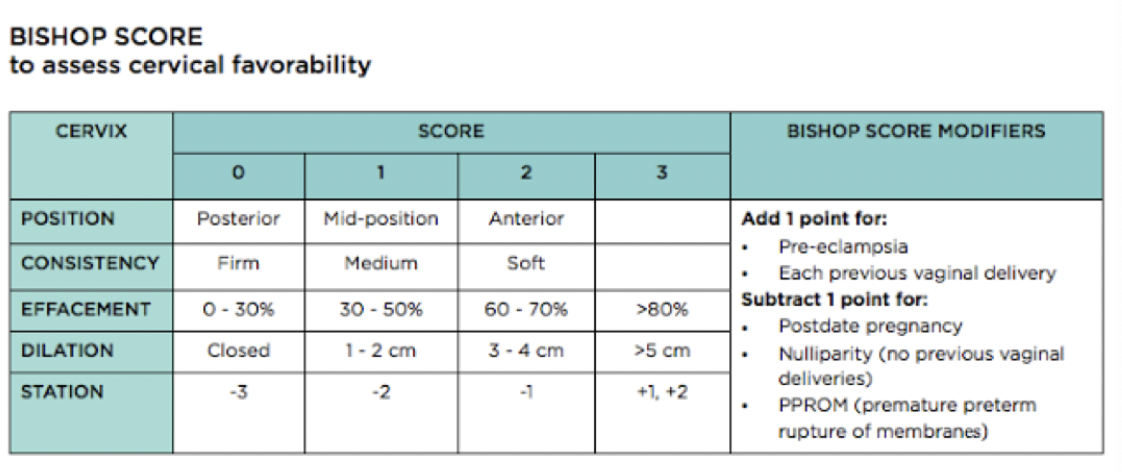
Bishop score
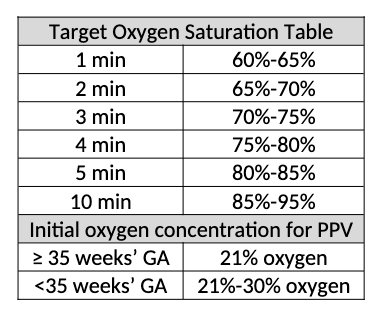
Target saturation table
Bubble assessment
Breast, uterus, bladder, bowels, lochia, episiostomy/lacerations extremeties emotions