1. Nervous System Organization
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Neural circuits ___, ____, and ____ responses to _____
detect, process, and effect responses to stimuli
What do sensory neurons contain?
They contain the molecular machinery necessary to detect stimuli and convert them into nervous system activity
What are other names for sensory neurons?
Sensory receptors or sensory afferents
What do effector neurons do?
They synapse onto non-neuronal cells (muscles or glands) that perform (effect) some physiological function
What are other names for effector neurons?
Motor neurons
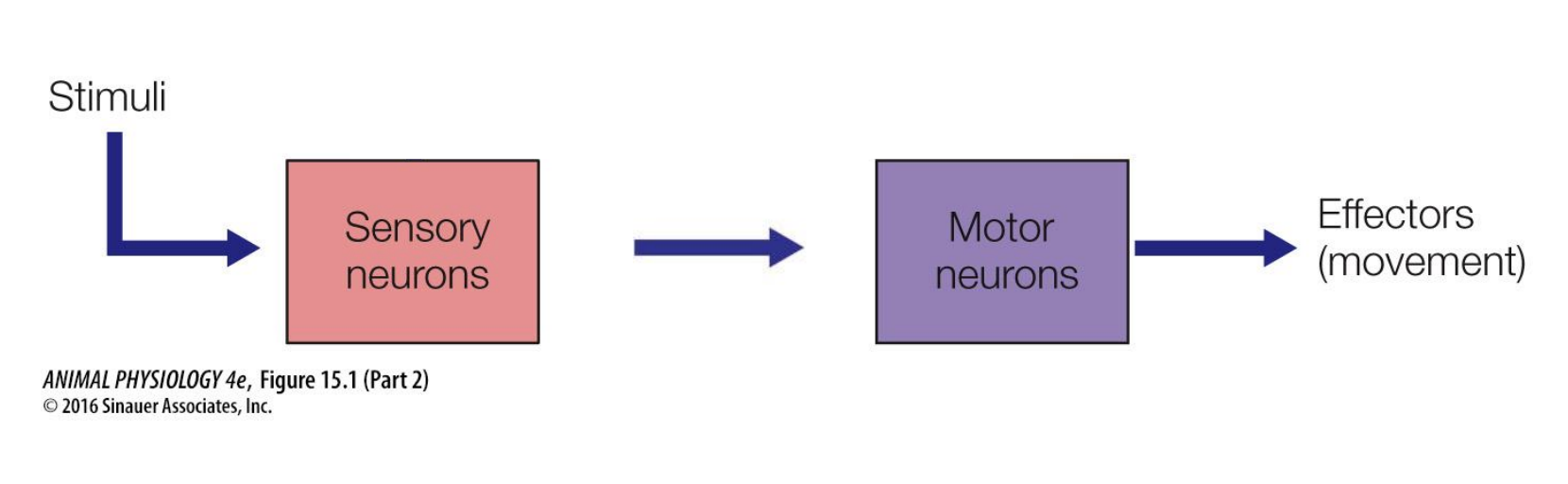
What is the simplest possible circuit?
Monosynaptic reflex where sensory neuron synapses onto motor neuron, and the motor neuron synapses onto a muscle/grand that causes movement
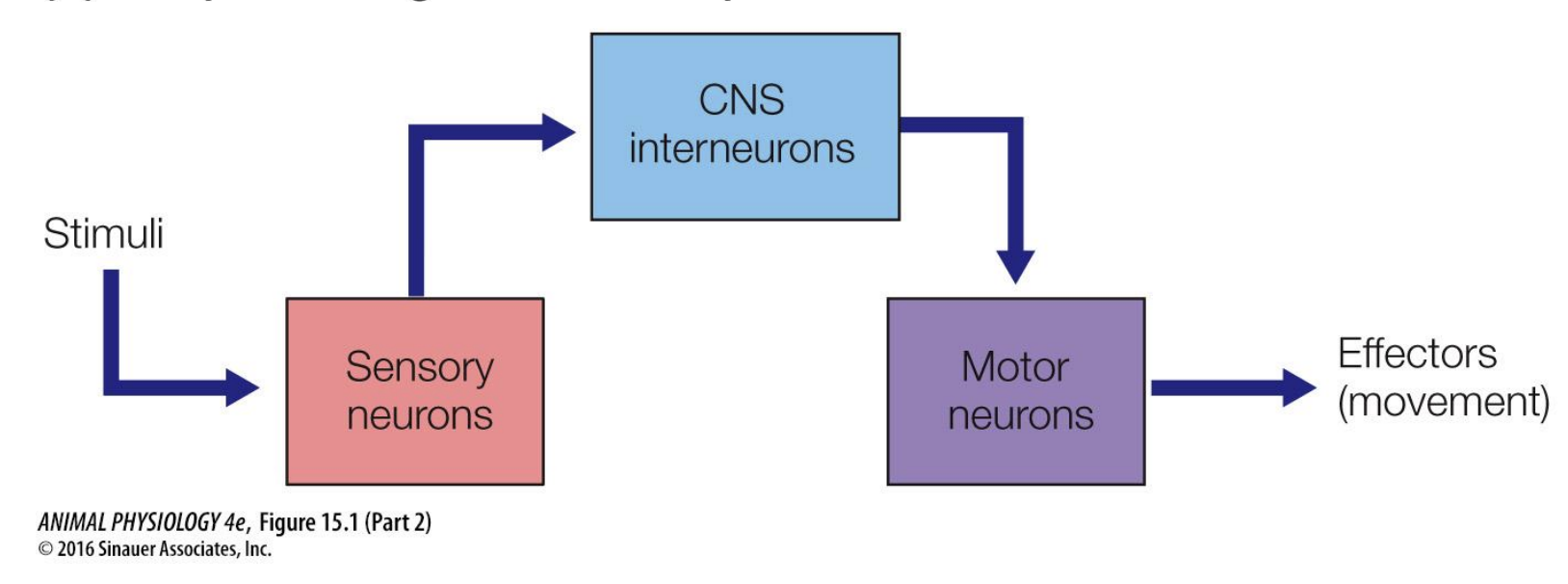
What do more complex behaviors require?
More complex circuits involving interneurons - neurons that locally process information
What are afferent pathways?
They take stimuli from the outside world (sensory receptors) and send the info to the CNS
What are efferent pathways?
They take info out of the CNS and send it to effectors (ex: movement like grabbing)
How many interneurons are there?
None to many - the amount determines how much computation occurs on afferent info
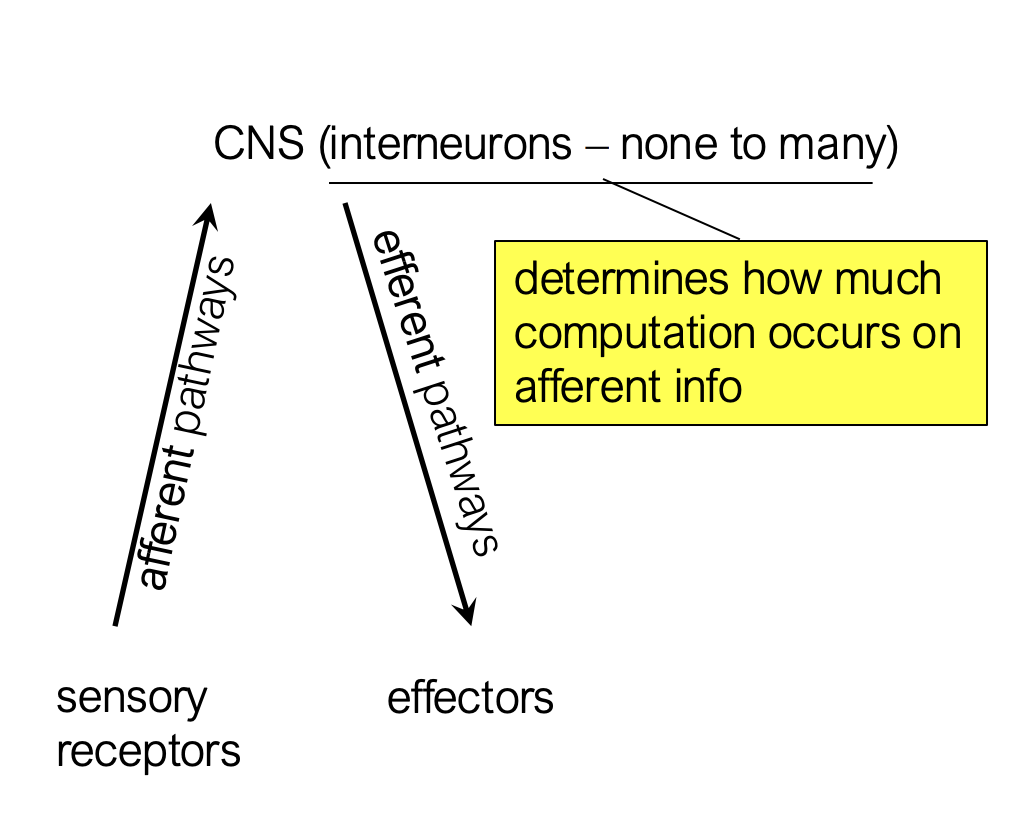
Afferent pathway is synonymous with?
Ascending pathway: sensory receptors to the brain
Efferent pathway is synonymous with?
Descending pathway: brain to the effectors
Division depends on what?
Division depends on how neurons develop and where their cell bodies are located
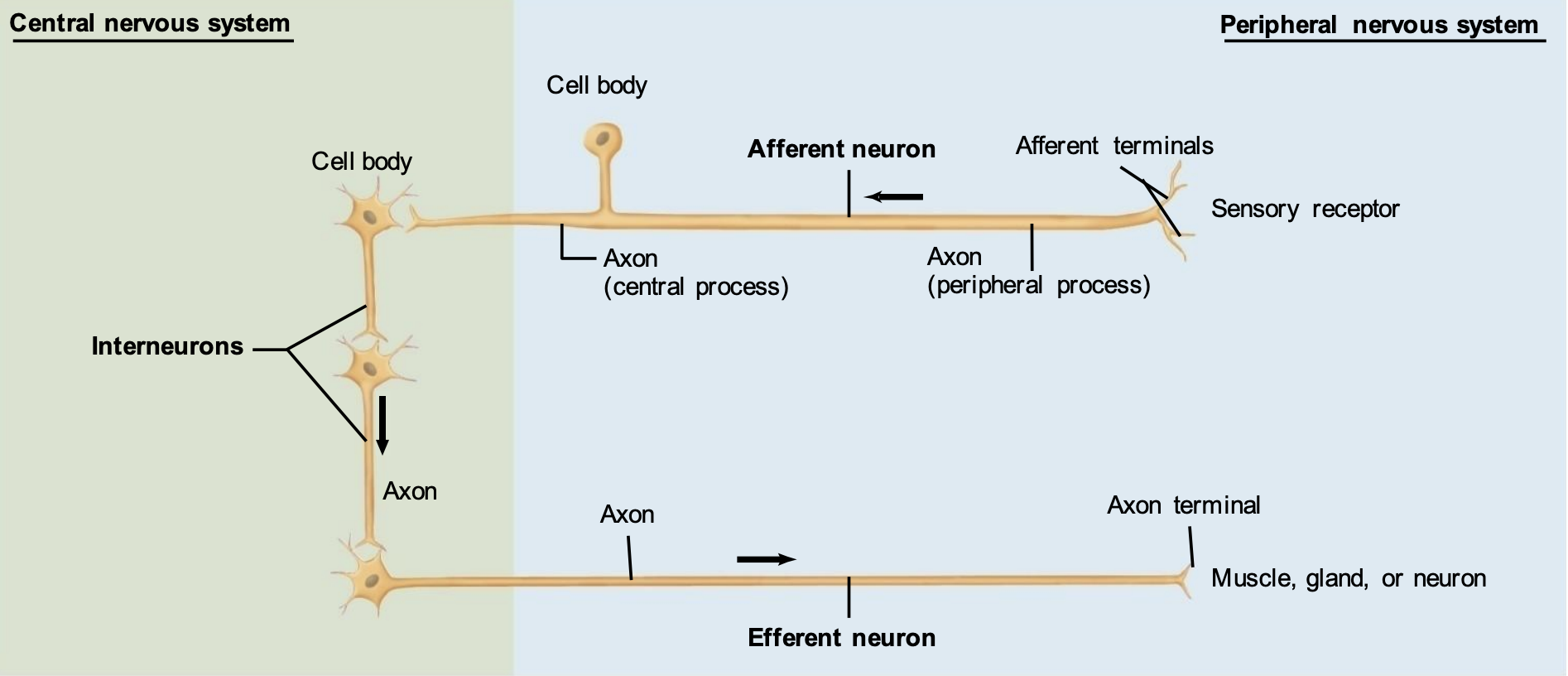
What is the basic anatomical distinction between?
The central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system
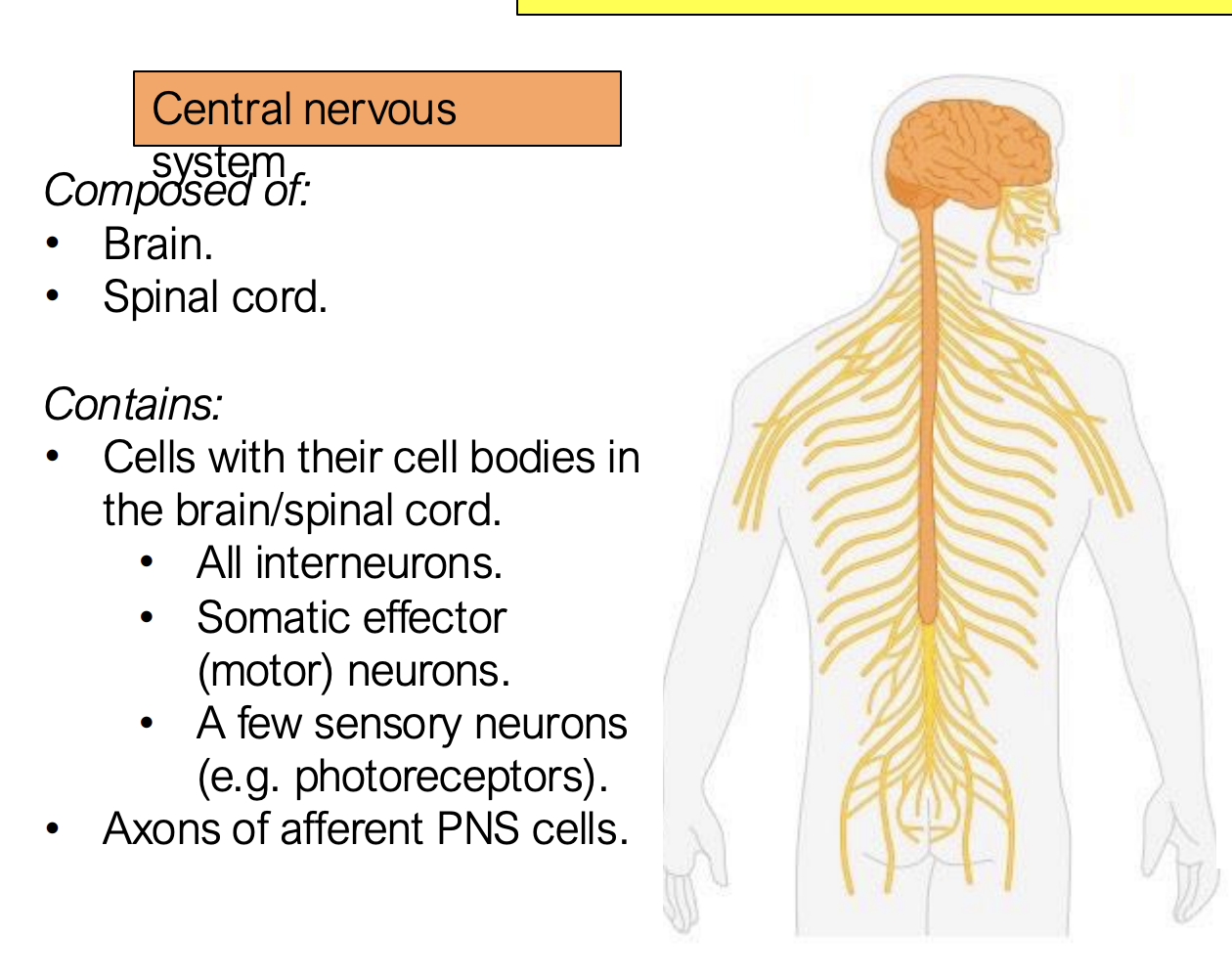
What is the central nervous composed of?
Brain and spinal cord
What does the central nervous system contain?
cells with their cell bodies in the brain/spinal cord
all interneurons
somatic effector (motor neurons)
a few sensory neurons (photoreceptors)
axons of afferent PNS cells
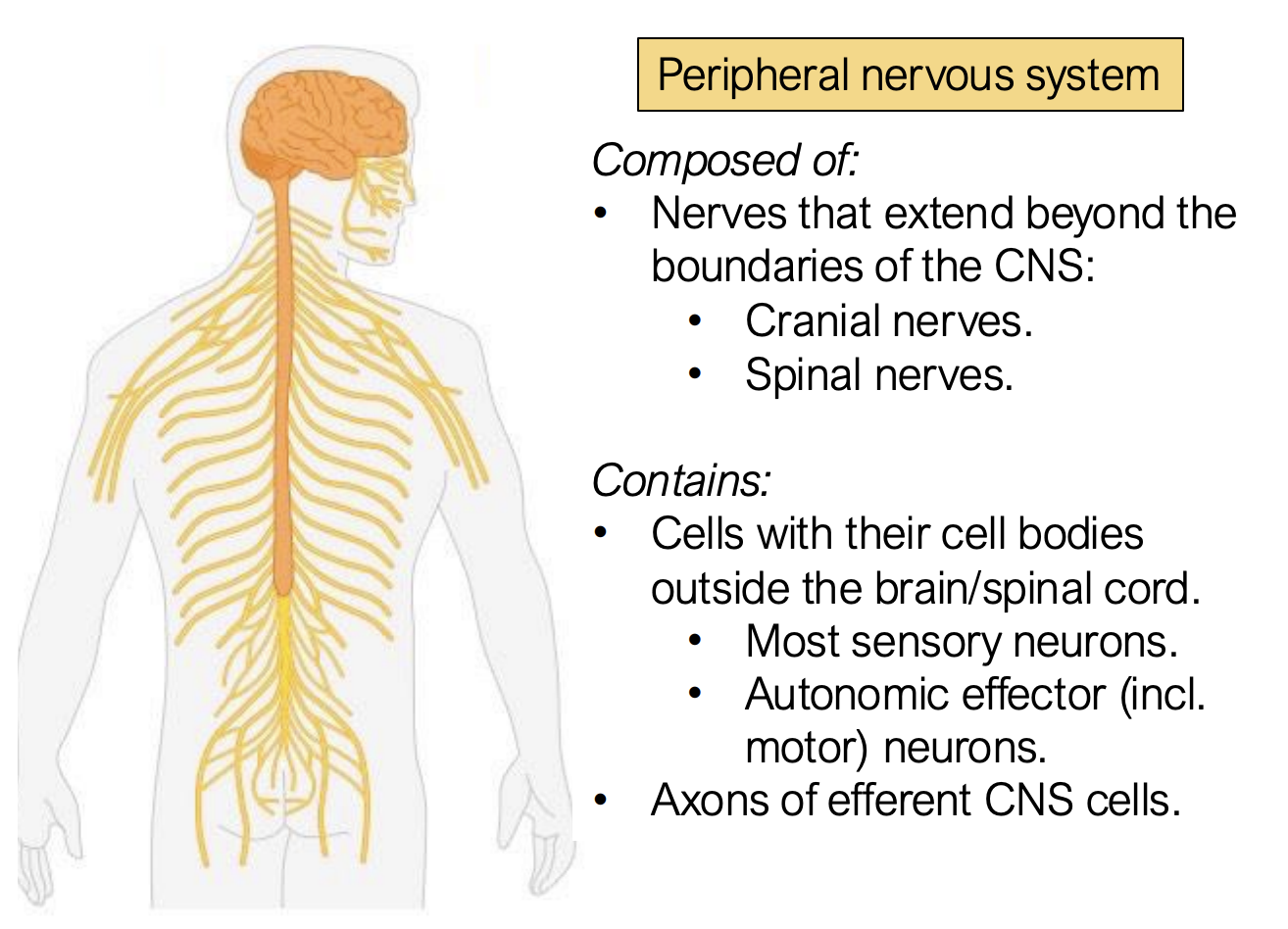
What is the peripheral nervous system composed of?
nerves that extend beyond the boundaries of the CNS
cranial nerves
spinal nerves
What does the peripheral nervous system contain?
cells with their cell bodies outside the brain/spinal cord
most sensory neurons
autonomic effector (including motor) neurons
axons of efferent CNS cells
Map out the steps of an extremely simple neural circuit with locations of the two nervous systems:
PNS: stimuli is picked up by the sensory receptor on the afferent neuron terminals
PNS —> CNS: axon sends message to another afferent neuron to the cell body, and then that axon goes into the CNS to send a message to the cell body of an interneuron
CNS: the interneuron can send message to other interneurons (varying numbers)
CNS —> PNS: the interneuron sends message to the efferent neuron whose dendrite/cell body is in the CNS, and the message travels down the axon in the PNS
PNS: the axon terminal releases information to a muscle, gland, or neuron