CHP 15 Autonomic Nervous System
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is the Autonomic Nervous System
(ANS) or Visceral Motor System
motor nervous system that controls glands, cardiac muscle, smooth muscle
primary organs
viscera of thoracic and abdominal cavities
structures of body wall (cutaneous blood vessels, sweat glands, piloerector muscles
General properties of the ANS
-INVOLUNTARY actions without conscious intent or awareness
-note: visceral effectors do not depends on the ANS to function, ANS just adjusts them
Denervation Hypersensitivity
exaggerated responses of cardiac and smooth muscles if autonomic nerves are severed
Visceral Reflexes
-unconscious, automatic, responses to stimulation
-reflex arc
receptors = sense and detect
Afferent neurons = send to the CNS
Integrating Center = within the CNS that process
Efferent neurons = carry away from CNS
Effectors = carry out end response
Divisions of ANS
1) Sympathetic division = fight or flight or freeze, STRESS
2) Parasympathetic division = rest and digest, repair, calm
Autonomic Tone
normal background rate of activity that represents the balance of the two divisions according to the body’s needs
Parasympathetic Tone + Sympathetic Tone
Autonomic Output Pathways compared to a Somatic Pathway
Somatic = motor neuron from brainstem/spinal chord has a myelinated axon that goes all the way to the skeletal muscle
Autonomic = travel across TWO neurons to get to target organ + cross a synapse where those neurons meet (called an autonomic ganglion), goes from a presynaptic neuron to a postganglionic neuron to along an axon to a target cell
Sympathetic Division Pathways using communicating Rami
-short preganglionic fibers (in the lateral horns + regions of spinal chord gray matter) send signal through white communicating ramus (myelinated)
-leads to sympathetic chain of ganglia called paravertebral ganglia
-leave the chain by postganglionic fibers using gray communicating ramus (unmyelinated) of three ways:
synapse immediately with a postganglionic neuron
travel up and down the chain and synapse with other ganglia at other levels
pass through chain w/o synapsing and continue as splanchnic nerves
-goes all the way to the target organ
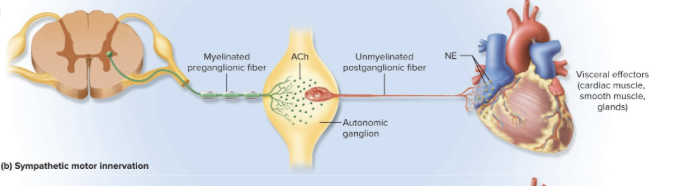
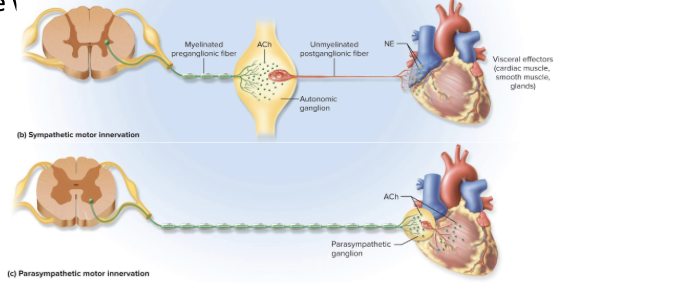
difference between parasympathetic division and sympathetic division output pathways
sympathetic: shorter preganglionic fibers and longer postganglionic fibers
parasympathetic; very long preganglionic fibers and super short postganglionic fiber
Adrenal Glands
-located on superior poles of kidneys with two parts
1) Adrenal Cortex: outer layer, secretes steroid hormones
2) Adrenal Medulla: inner core, modified postganglionic neuron w/o fibers, secretes a mixer of hormones into bloodstream
Parasympathetic Division pathways
-super long preganglionic neurons from midbrain, pons, medulla or sacral spinal chord segments
-goes to terminal ganglia either in or near target organ
-then super short postganglionic fibers
*VERY SELECTIVE in the stimulation of target organ
Nerves to the Parasympathetic division
-Oculomotor Nerve (III) = narrows pupil and focuses lens
-Facial Nerve (VII) = tear, nasal, and salivary glands
-Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) = parotid salivary gland
-Vagus Nerve (X) = viscera as far proximal half of colon
Enteric Nervous System
-nervous system of the digestive tract
-technically subdivision of parasympathetic division
-NO CNS components
-innervates smooth muscle and glands
-regulated by the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems