nat & var (variety, characs) AND (structure and function (levels of org, cell structure)
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
characteristics of living organisms (MRS GRENC), variety of living organisms (cell structures)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
MRS GRENC
movement
respiration
stimulus (responds to surroundings)
growth
reproduction
excretion
nutrition
controls internal conditions
define organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system
organelle → small structure within cell that carries out a function
cell → small fundamental unit that makes up an organism
tissue → group of (usually similar) cells working together to perform a function
organ → groups of tissues working to together to perform a shared function
organ system → group of organs (with related functions) working together to perform a function
eukaryote vs prokaryote
eukaryote has a nucleus
EU
PLANT | ANIMAL | BACTERIA | FUNGI | |
nucleus | ||||
cytoplasm | ||||
cell wall | ||||
cell membrane | ||||
mitochondria | ||||
ribosomes | ||||
chloroplasts | ||||
permanent vacuole | ||||
plasmid | ||||
flagellum | ||||
uni/multicellular | ||||
carbohydrates stored as: |
PLANT | ANIMAL | BACTERIA | FUNGI | |
nucleus | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
cytoplasm | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
cell wall | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
cell membrane | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
mitochondria | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
ribosomes | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
chloroplasts | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
photosynthesis? | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ *but some rarer bacteria have chlorophyll in cytoplasm | ❌ saprotrophic |
permanent vacuole | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
plasmid | ❌ | ❌ | ✅* and circular chromosome of DNA | ❌ |
flagellum | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
uni/multicellular | multi | multi | uni | uni: yeast multi: mushroom |
carbohydrates stored as: | starch/sucrose | glycogen | glycogen | glycogen |
example | pea plant | dog | e.coli | Amoeba |
basic structure | function | |
nucleus | ||
cytoplasm | ||
cell membrane | ||
cell wall | plant: fungi: [bacteria: ] | |
chloroplasts | ||
vacuole | ||
ribosomes | ||
mitochondria |
basic structure | function | |
nucleus | contains genetic material in chromosomes | contains genetic information, controls cell activities |
cytoplasm | jelly-like substance | site of chemical reactions |
cell membrane | controls what goes in/out of cell holds cell together | |
cell wall | plant: cellulose fungi: chitin [bacteria: peptidoglycan] | give cell structure and shape, prevent bursting |
chloroplasts | contains chlorophyll | site of photosynthesis, chlorophyll absorbs sunlight |
vacuole | sack | contains cell sap: water, salts/sugars, mineral ions starch storage holds shape of cell |
ribosomes | protein synthesis | |
mitochondria | site of aerobic respiration |
define pathogen
microorganism that causes disease
virus features
include: size, contains either ___ or ___
example
protein coat
parasitic; cannot reproduce without living host
very small
contain either DNA or RNA
example: influenza
NOT LIVING
what is cell differentiation
process by which a cell becomes specialized to perform a specific function
animal vs plant cell differentiation
animal: as organism develops, animal cells lose ability to specialise early on
only some adult STEM cells remain undifferentiated
these are involved in replacing/repairing cells e.g. blood, skin.
plant: many types of plant cells can differentiate into anything at any stage in their lifetime
A stem cell is an _______ cell of an organism that is capable of ______ an _____ number of times
A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism that is capable of dividing an unlimited number of times
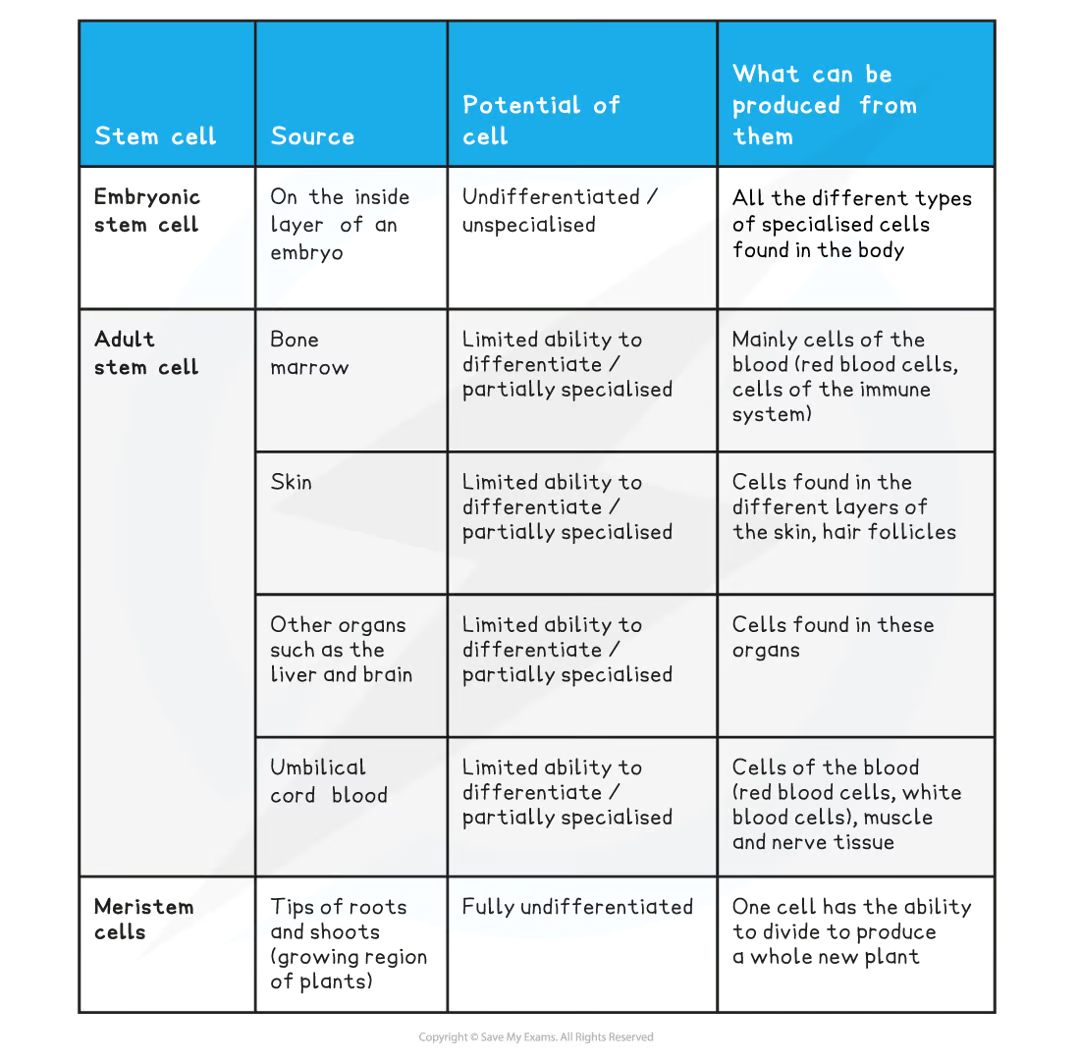
stem cell | source | potential | product |
embryonic | |||
Adult | bone marrow | ||
adult | skin | ||
adult | other organs e.g. liver, brain | ||
adult | umbilical cord blood | ||
meristem |
problem | how stem cells could be used to treat it | source of stem cells | |
diabetes II | |||
paralysis |

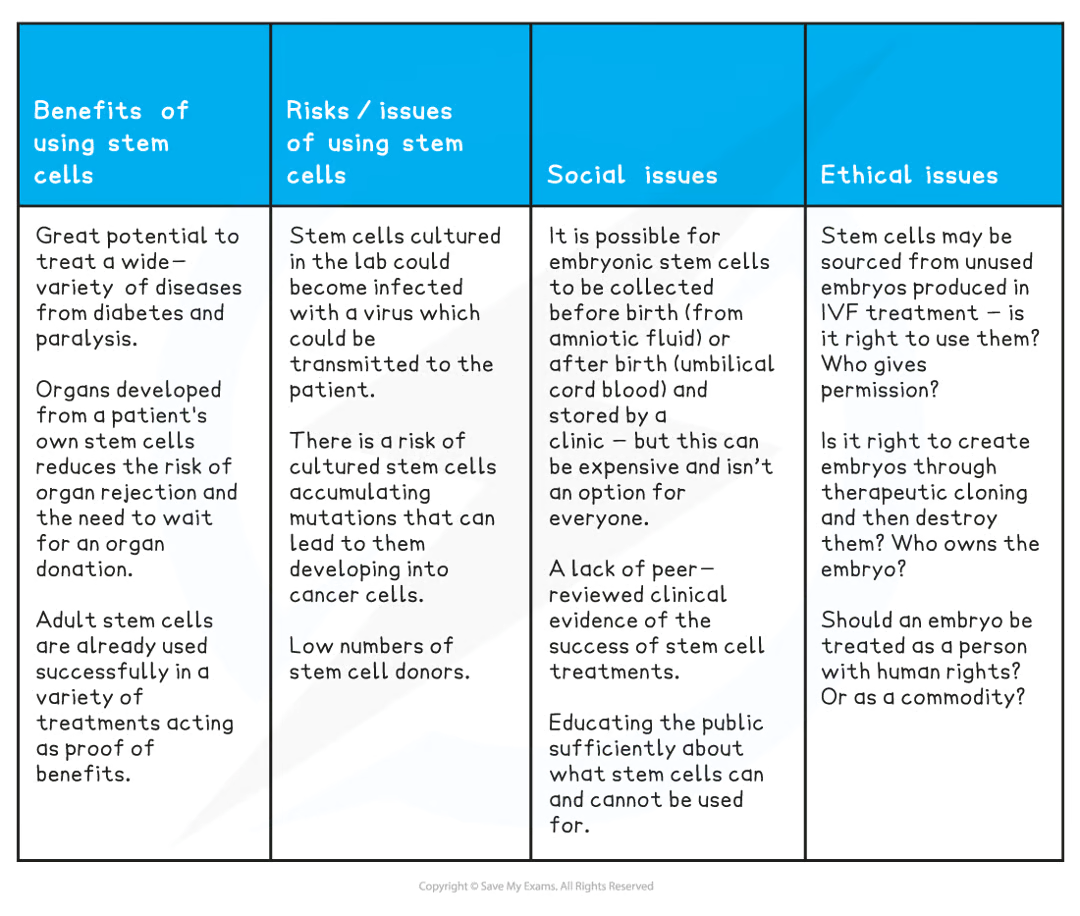
benefits of using stem cells | risks/issues of using stem cells | social issues | ethical issues |