Brain Anatomy
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Part 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Brain regions
cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brain stem, cerebellum
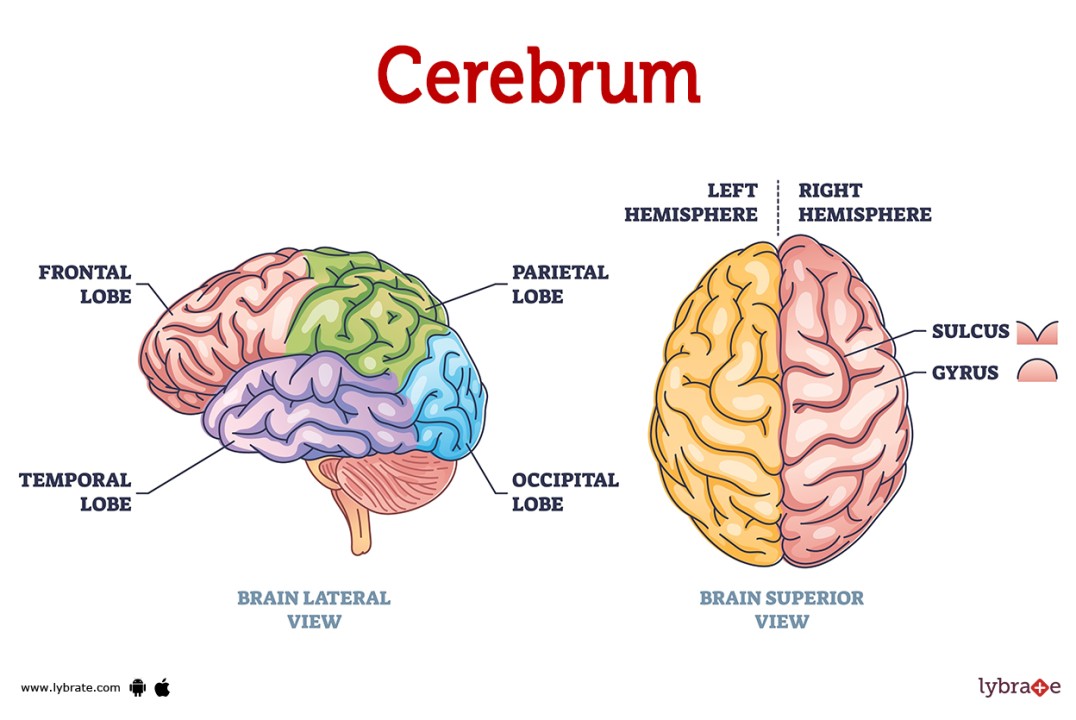
Cerebral hemisphere
paired superior parts of the brain; most conscious behavior known as the “executive suite”
surface lobes include: frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal
Frontal lobe
controls voluntary motor functions (right controls left)
Parietal lobe
recieves/interprets impulses for paint, touch, heat, cold, distances, size and shapes
Occipital lobe
controls eye sight
Temporal lobe
auditory and olfaction area
Insula lobe
taste; gustatory
Somatic sensory area
receives impulses from the body’s sensory receptors
Primary motor area
sends impulses to skeletal muscles
Gyri
grooves and ridges
Sulci
furrows or indents
Fissures
deeps grooves divide the cerebrum into lobes
Cerebral cortex
Broca’s area; motor speech area usually in the left hemisphere on top of the cerebrum
Gray matter
outer layer composed of neuron cell bodies
White matter
inner layer made of myelinated fibers
Corpus callosum
connects the left and right hemispheres
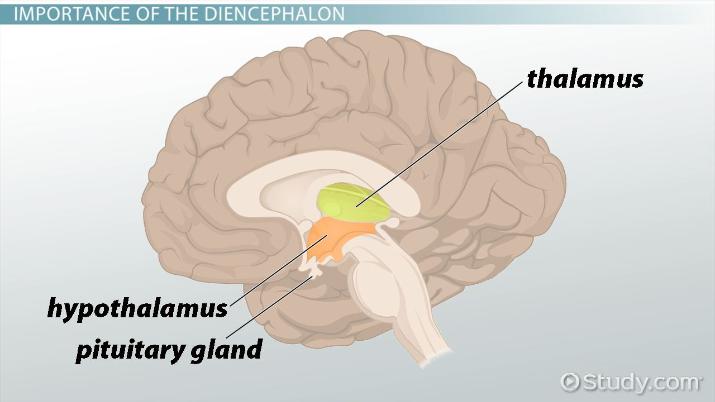
Diencephalon
sits on the brain stem, enclosed the cerebral hemispheres, made of thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus
Thalamus
egg-shapes mass of gray matter that surrounds the third ventricle, relay station for sensory impulses passing upward to cerebral cortex, transfers impulses to the correct part of the cortex for localization and interpretation
Hypothalamus
floor of the diencephalon, important autonomic nervous system center, (regulates body temp, regulates water balance, regulates metabolism) houses limbic system to emotions, regulates the pituitary gland, houses mammillary bodies for smell
Epithalamus
forms the roof of the 3rd ventricle, houses the pineal body (endocrine gland) and includes the choroid plexus (forms cerebrospinal fluid)
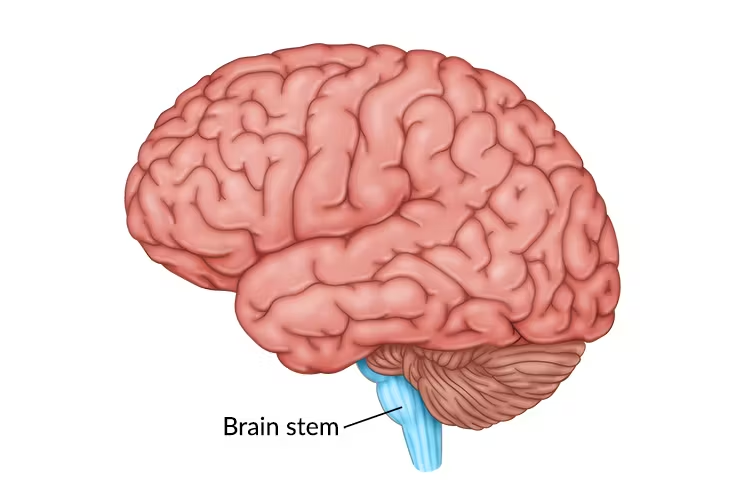
Brain stem
attaches to spinal cord and made of midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
Midbrain
composed of tracts of motor nerve fibers and reflex center for vision and hearing
Pons
bulging center part of the brain stem, bridge between medulla and midbrain, composed of two-way fiber tracts, includes nuclei involved in the respiratory center
Medulla
most inferior part of the brain stem that merges into the spinal cord and contains important centers that control: heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, swallowing, vomiting
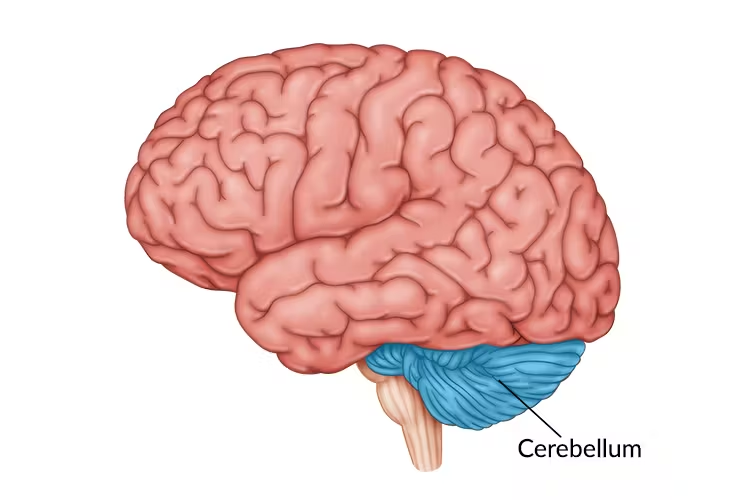
Cerebellum
provides involuntary coordination of body movements (balance, muscle tone, muscle coordination) and thin outer gray matter and internal white matter (arbor vitae)