large scale networks
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
white matter fibres / tracts
arcate fasciculus= key language tract
white matter tracts helps us understand the anatomical interconnections between regions
structural connectivity
the roadways of the brain = cant have good communication without good ways to connect areas
diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
tracks the direction of movement of water molecules
systematic flow in one direction indicates a large white matter tract
DTI clinical applications
identifying diseases that affect long axons e.g multiple sclerosis
psychologically; if basic scans down show anything but there are cognitive problems
diffuse axonal injury in head injury and concussion, twisting and tearing large white matter tracts
know a lot more from these methods about structural problems that underlie amnesia
corpus colosseum
people experiencing significant amnesia tend to have lower white matter fibre volume
corpus colosseum damage itself is occurring, but also predictive of greater amnesia, along with many other areas
functional connectivity
the crosstalk between interconnected regions during a particular activity
traffic on the road
degree of cross talk between regions varies depending on the task
can measure the degree of synchrony between activity in different regions - how does the bold signal change over time to map connection and communication between areas
dynamic networks
Lots of large scale networks operate as inhibitors of each other, so the networks will ebb and flow as the brain moves between thought and focus
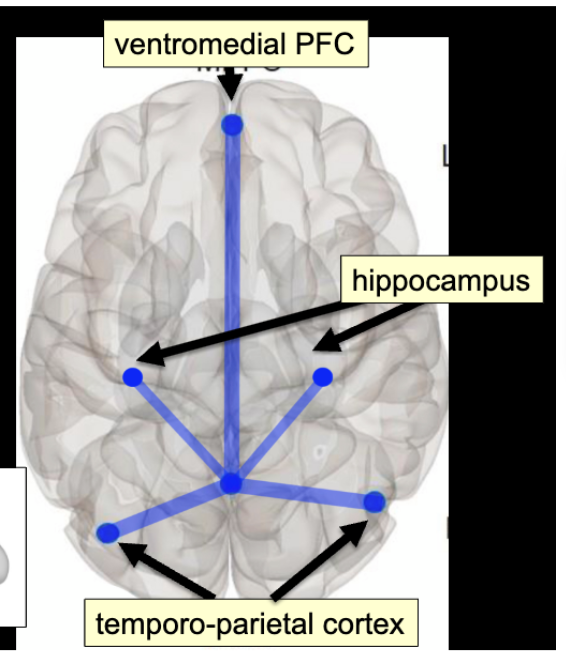
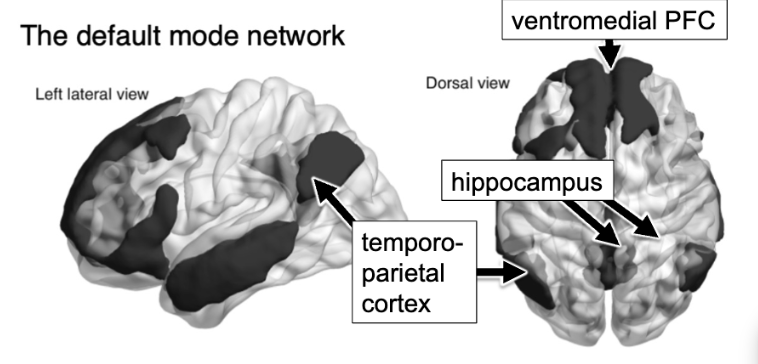
default mode network
‘day dreaming’ network
active at rest
active when focused on internal thoughts
deactivated when focus shifts to external stimuli
inner reflection exploring ideas / solutions
super portion of the
prefrontal cortex
number of lateral structures, but lots of key ones on the medial surface
temporoparietal cortex, hippocampus, ventromedial PFC, posterior cingulate cortex
DMN activities
retrieving memories for past experiences, reliving mentally (hippocampus)
making judgements about themselves relative to others (VMPFC, social cognition and judgments on others)
mind wandering
mind wandering
button press tasks
greater activation of the DMN when day dreaming
able to measure beyond activities that require an external focus
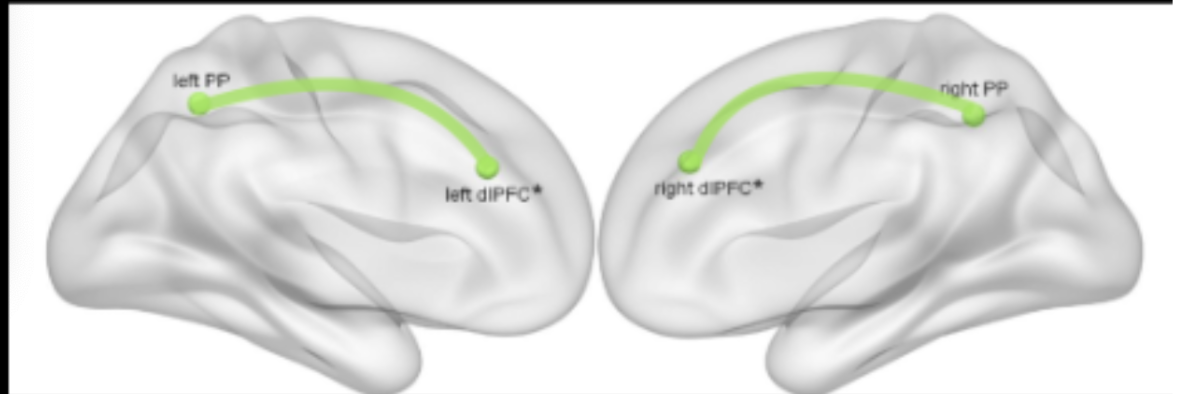
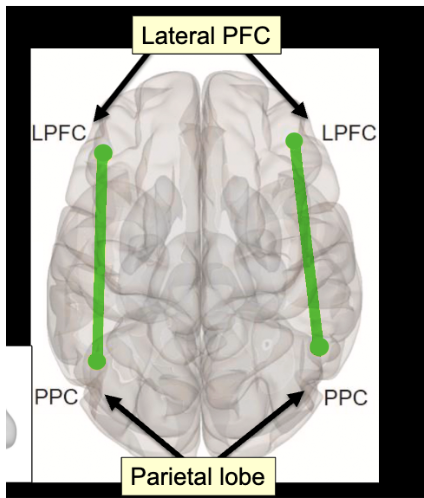
frontoparietal control network
activated when performing a demanding task
highly externally focused cognitive control & effortful tasks
controlling behaviour to achieve a goal
large portion of the lateral PFC
parietal lobe
interparietal sulcus
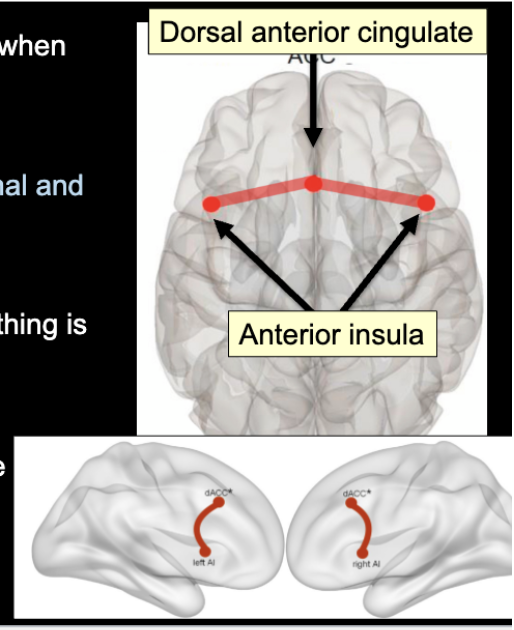
the salience network
signals when something is aversive or emotionally salient
can respond to a thought or emotion
helps to initiate rapid switches between networks
dorsal anterior cingulate= signals when we need to exert effort on a task
anterior insula= evaluates emotional and bodily states
anterior PFC
the hotel task & complex problem solving
real life problems & multi tasking involve dynamic switching between modes
damage to the anterior PFC; people get fixed in one network and then cannot switch to the other one
depression
increased connectivity, synchronicity, and overall activation within the default mode network
more time being introspective, more time ruminating
unclear as to wether cause or effect
creativity in healthy people
high scorers: tightly synchronised activity in parts of the default mode and fronto parietal control networks
low scorers: primarily posterior cross talk
suggests that creative thought involves flexible interplay between;
1. Default mode network (internal thoughts, reflection, imagining, remembering)
2. Frontoparietal control network (goal directed top-down control of cognition, evaluation of ideas, etc.)