skeletal system anatomy
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
support
bones provide a frameowrk that support and anchor all the soft organs
protection
protect our soft organs
movement
muscles use bones to help more the body
storage
bones store minerals (calcium and phosphorous) and 98% of calcium and phosphorus is stored in your bones
bone cell formation
all components of blood are formed inside certain bones
hormone production
osteocalcon deposited in bones to form them andsome hormones are produced in the bones
3 main components
bones, 206 bones in the body, divided into two divisons
axial skeletion (1st divison)
126 bones of the skull, chest, and spinal column
appendicular skeleton (2nd divison)
80 bones, bones of the limbs, gridles that attach them to the axial skeleton, cartilage, ligaments, and other connective tissues
bone classification based on shape
6 shapes
flat bones
thin, flat, and usually curved (rib bones, clavicle, scapula)
stutural/wormiam bones
irregular bones formed between the crancial bones
long bones
long and slender (femur,tibia, fibula,humerus, radius)
short bones
small and boxy (carpsals, tarsals)
sesamoid bones
small, flat, shaped like a seasame seed and develop in the tendons of the knees, hands, and feet (patella)
irregular bones
have complex shapes (vertebrae, hip bones, facial bones)
osseous tissue
bone tissue
1st type of bone tissue
compact/dense tissue
2nd type of bone tissue
spongey bone (cancellous/trabecular)
types of skeletal cartilage
consists of mostly water and has no nerves or blood vessels (hard to repair)
hyaline cartilage
provides support w/ flexibility and resilence
elastic cartilage
similar to hyaline but contains elastic fibers
fibro cartilage
highly compressable and very strong
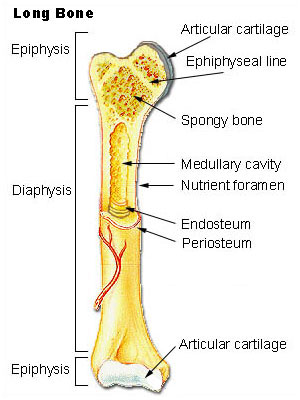
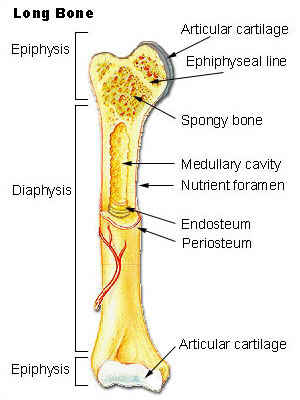
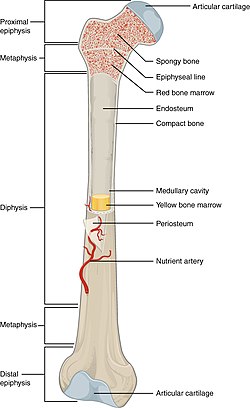
epiphysis
top and bottom of bones w spongey bone inside
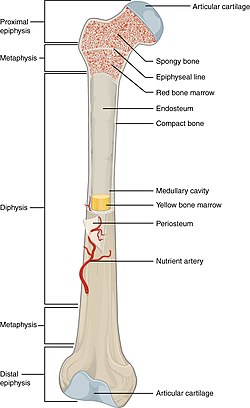
hyaline cartilage
surronds outside of bone
metaphysis
where growth of the bone occurs
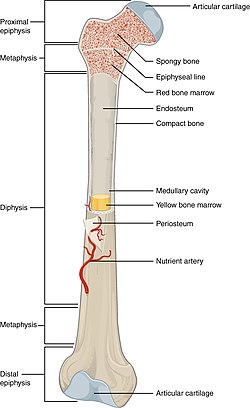
diaphysis
made of compact bones
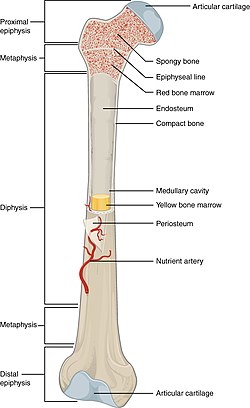
marrow cavity
inner middle cavity of bone
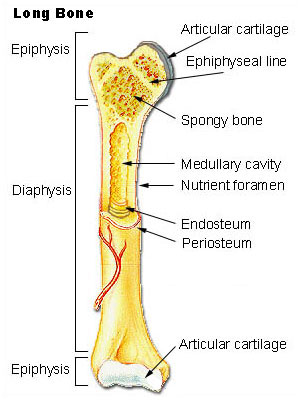
endosteum
lower marrow cavity above periosteum
1st type of marrow cavities
red marrow, makes blood and cell formation
2nd type of marrow cavities
yellow marrow, stores adipose tissue (fats)
adipose
stores fat for starvation, helps keep you warm and provide energy
peri
around
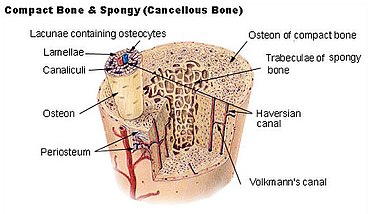
periosteum
layer of tissue surronding the bone and has nerves and blood vessels attached to it
endosteum
lines the marrow cavity (inner surface of bone)
end
inside
osteocyte
mature bone cell that cannot divide and is the most numerous bone type
functions of osteocytes
maintain the protein and mineral content of the adjacent matrix (non-living part of bone)
where are osetocytes found
small pockets called lacune
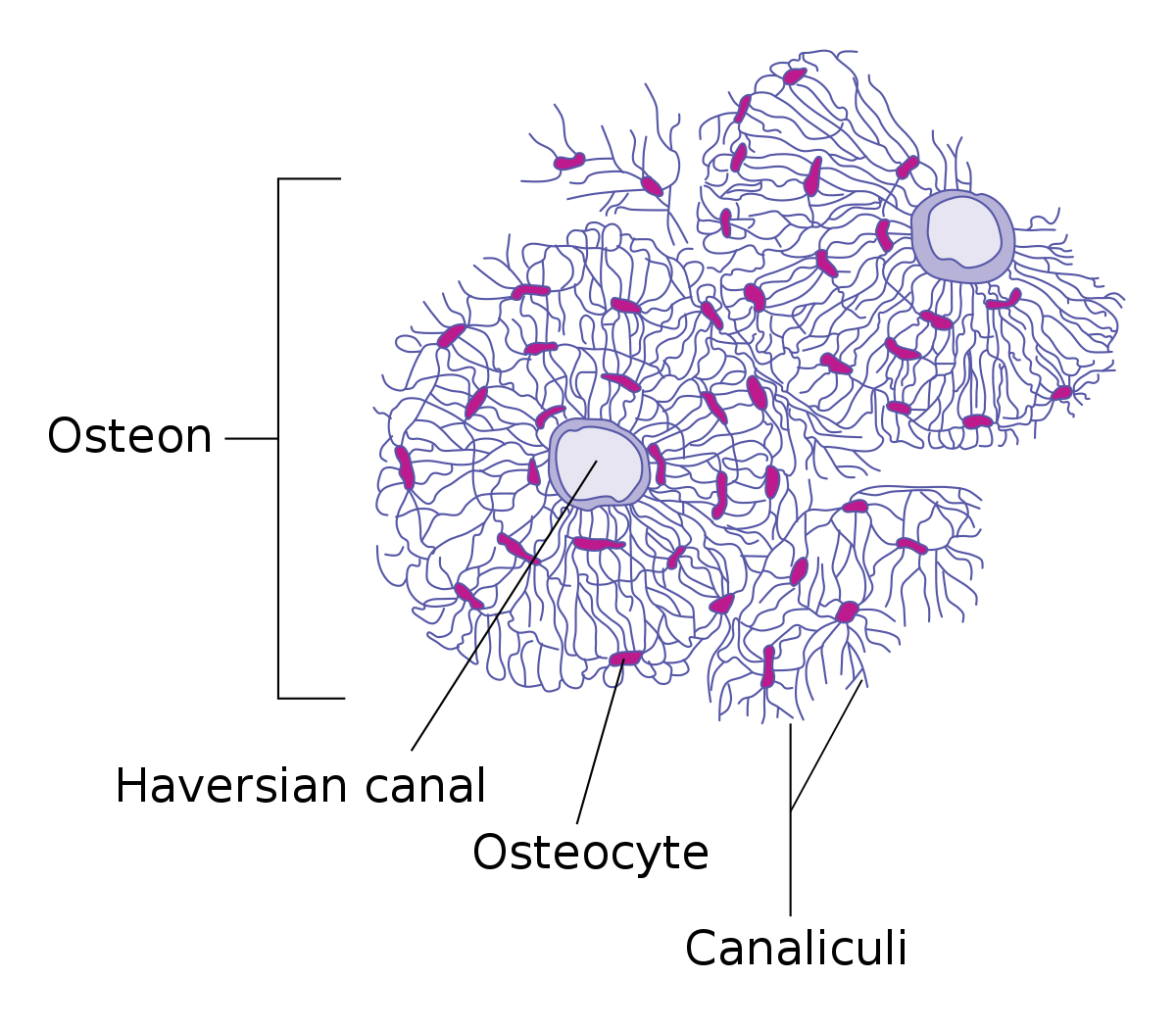
Lacunae are separted from layers of bone matrix called
lamellae
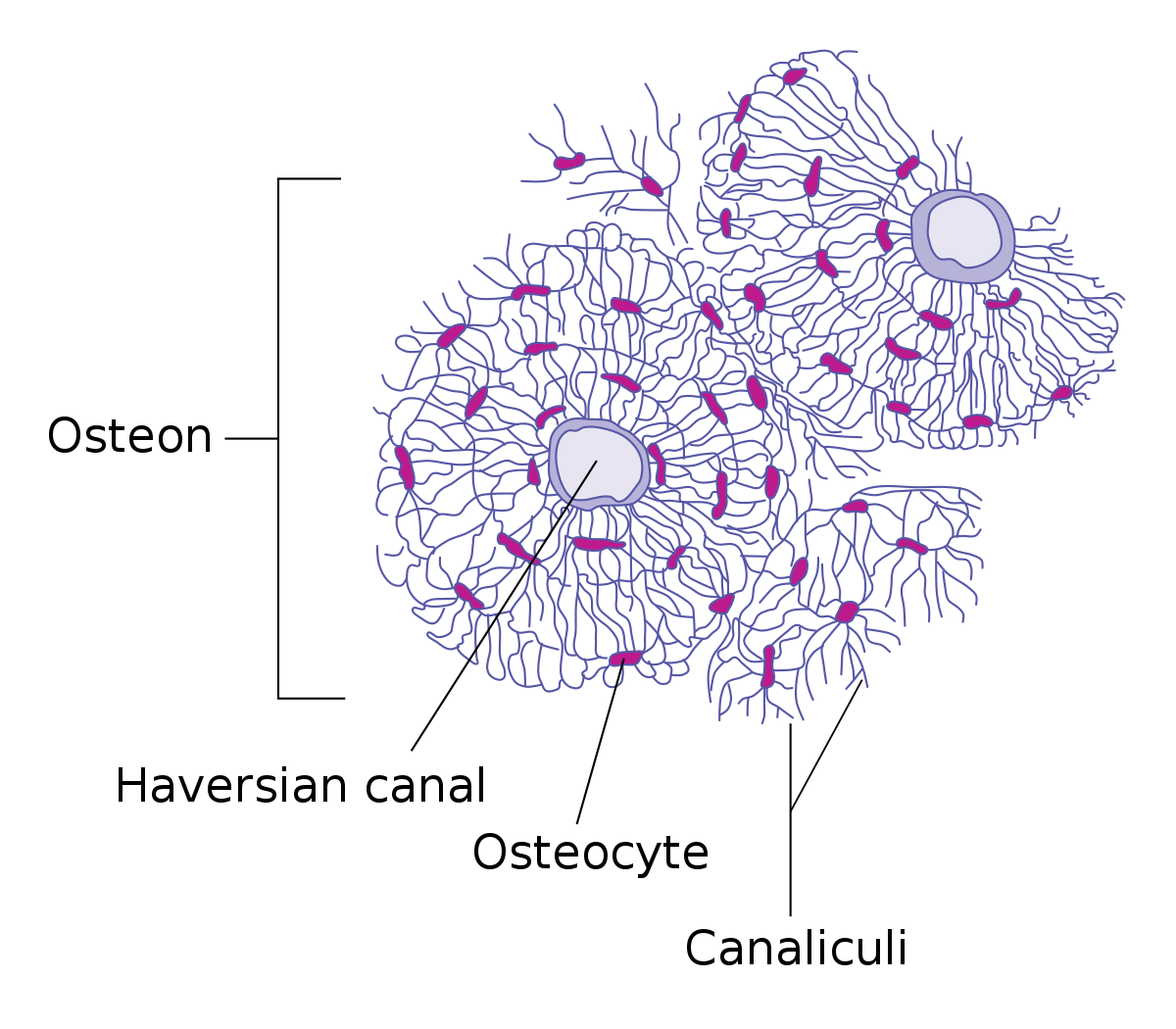
lamellae are connected to each other by small tunnels called
canaliculi
osteoblast
bone building cells
functions of osteoblasts
produce new boney matrix
osteogenesis/ossification
production of new boney matrix
what happens once osteoblasts are surrounded by boney matrix?
they become osteocytes
osteoprogentor
type of stem cell that differentiate into osteoblasts
stem cell
cell that doesnt know its job yet
where are osteoprogentors found?
in the inner lining of the periosteum
endosteum
passageways containing blood vessels
osteoclast
giant cells with more than 50 nucleui
osteoclast function
remove and remodel bone matrix
osteolysis
remove and remodel bone matrix
osteo
bone
lysis
rupture
osteolysis does what
regulates blood mineral levels
1st component of bone matrix
collagen fibers make up 1/3 of bones weight, provides flexibility for the bone
2nd component of bone matrix
calcium phosphate, interacts w/ other minerals and provides strength for the bone and makes up 2/3 of the bone
osteon (flaversion system)
has layers of concentric lamellae around a central canal (Haversion canal)
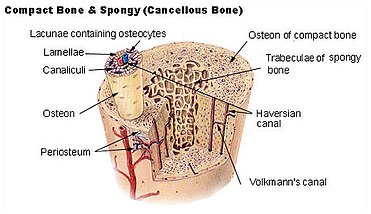
haversion canal
central canal in an osteon
where are osteocytes found
in lacunae between lamellae
central canal contains what
small blood vessels
what do osteocytes do
make the bone strong along its length
where is spongey bone found
where the bone is not heavily stressed
trabeculae
lamellae form struts and plates that form an open network
trabeculae function
reduces the weight of the skeleton
intramembranous ossification
when osteoclasts devlop bone from a fibrous memebrane
where does intramembranous ossification occur
occurs in the flat bones and the clavicale
step 1 of IO
stem cells cluster and differenticate into osteoblasts at an ossification center
step 2 of IO
osteoblasts secrete bone matrix and then become osteocytes
step 3 of IO
bone matrix accumlates around blood vessels to form trabeculae and the periosteum forms
step 4 of IO
trabeculae thicken to form bone and the vessels become red marrow
endochondral ossification (EO)
is when hyaline cartilage is replaced by bone
step 1 of EO
in diaphysis, chondrocytes enlarge and then die, leaving cavities in cartilage
step 2 of EO
blood vessels grow around the cartilage edge and osteoblasts form to create a superficial layer of bone
step 3 of EO
blood vessels penetrate the central region, osteoblasts enter and spongey bone is produced (primary ossification center) and the spongey bone spreads toward bone ends
step 4 of EO
a marrow cavity is created as cartilage is replaced by bone which allows the bone to grow in length or diameter
step 5 of EO
secondary ossification centers form in the epiphysies
step 6 of EO
epiphysies fill w/ spongey bone
step 7 of EO
the bone continues to grow in length until maturity
intramembranous ossification starts as
a membrane
endochondrial ossification starts as
a cartilage model
hormonal control of calcium
perathyroid hormone and calcitionin
perathyroid hormone is released by
parathyroid glands
parathyroid increase what
blood calcium levels
parathyroids stimulate
osteoclast to release calcium
also effects the release of calcitrol
and increases calcium absorbtion
kidneys
increase the release of calcitriol which causes calcium reabsorption in kidneys
calcitionin
released from thyroid gland, decreases blood calcium levels, decreases osteoclast activity in bones, decreases absorbtion of ca
calcitionin in kidneys
is going to inhibit calcitriol release and ca reabsorbtion