Universe, Galaxies, and Stars
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
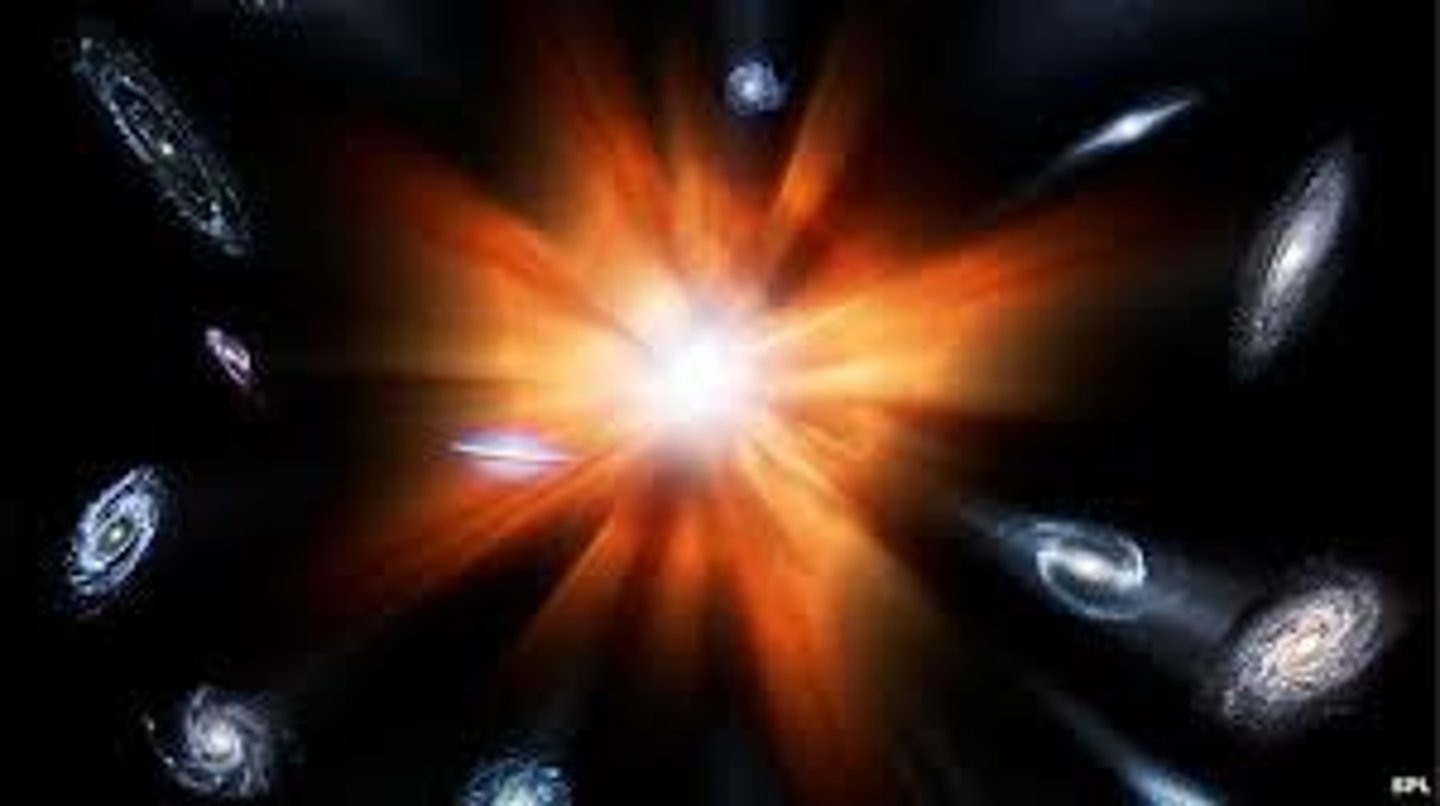
Big Bang Theory
the theory that the universe originated due to an explosion of small mass of matter at extremely high density and temperature

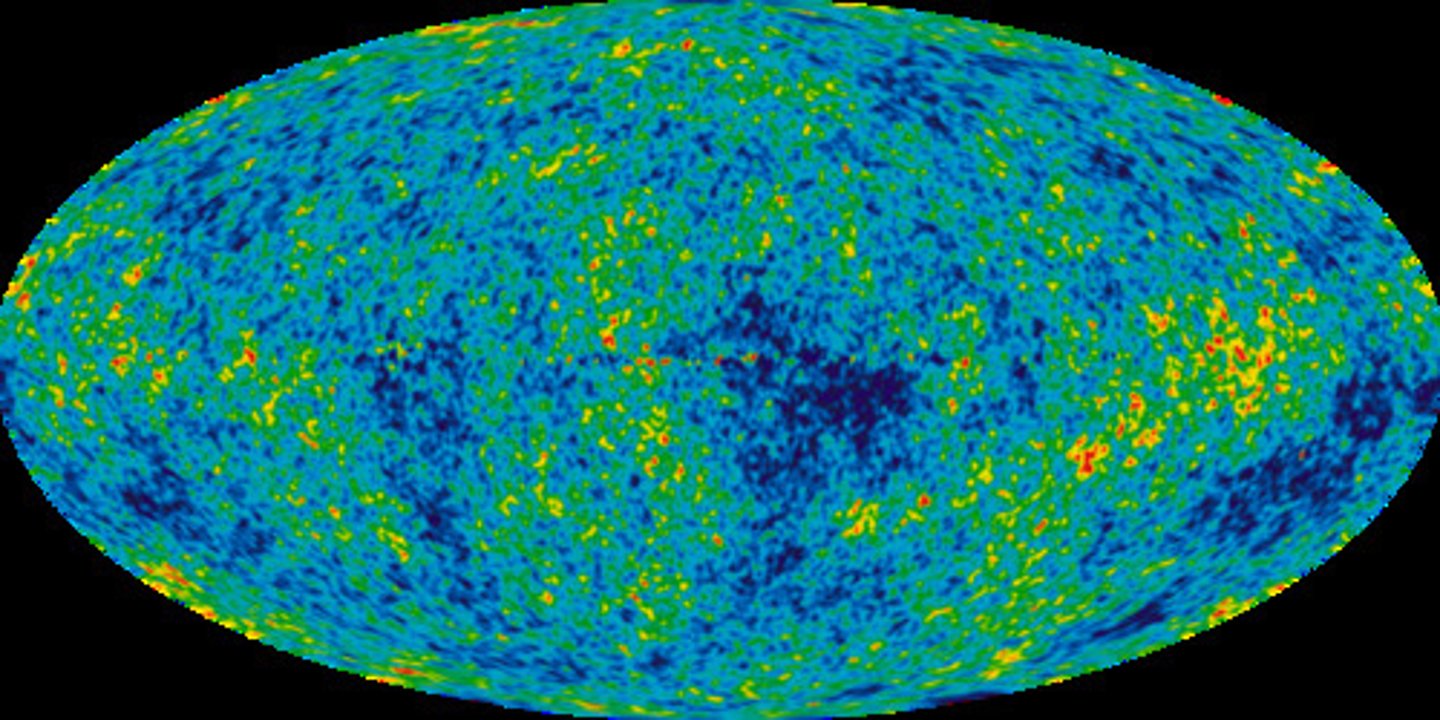
Cosmic Background Radiation
The electromagnetic radiation left over from the big bang

Temperature (Big Bang)
Evidence that states there is still heat in the universe left over from the Big Bang
Expanding Universe
the idea that the space between galaxies or clusters of galaxies is growing with time.
Open Universe
It is believed that the universe will continue to expand forever.
Closed Universe
The theory that the universe will continue to expand so much that it runs out of momentum and collapses on itself
Flat Universe
The theory that the universe will reach a size and stay that size
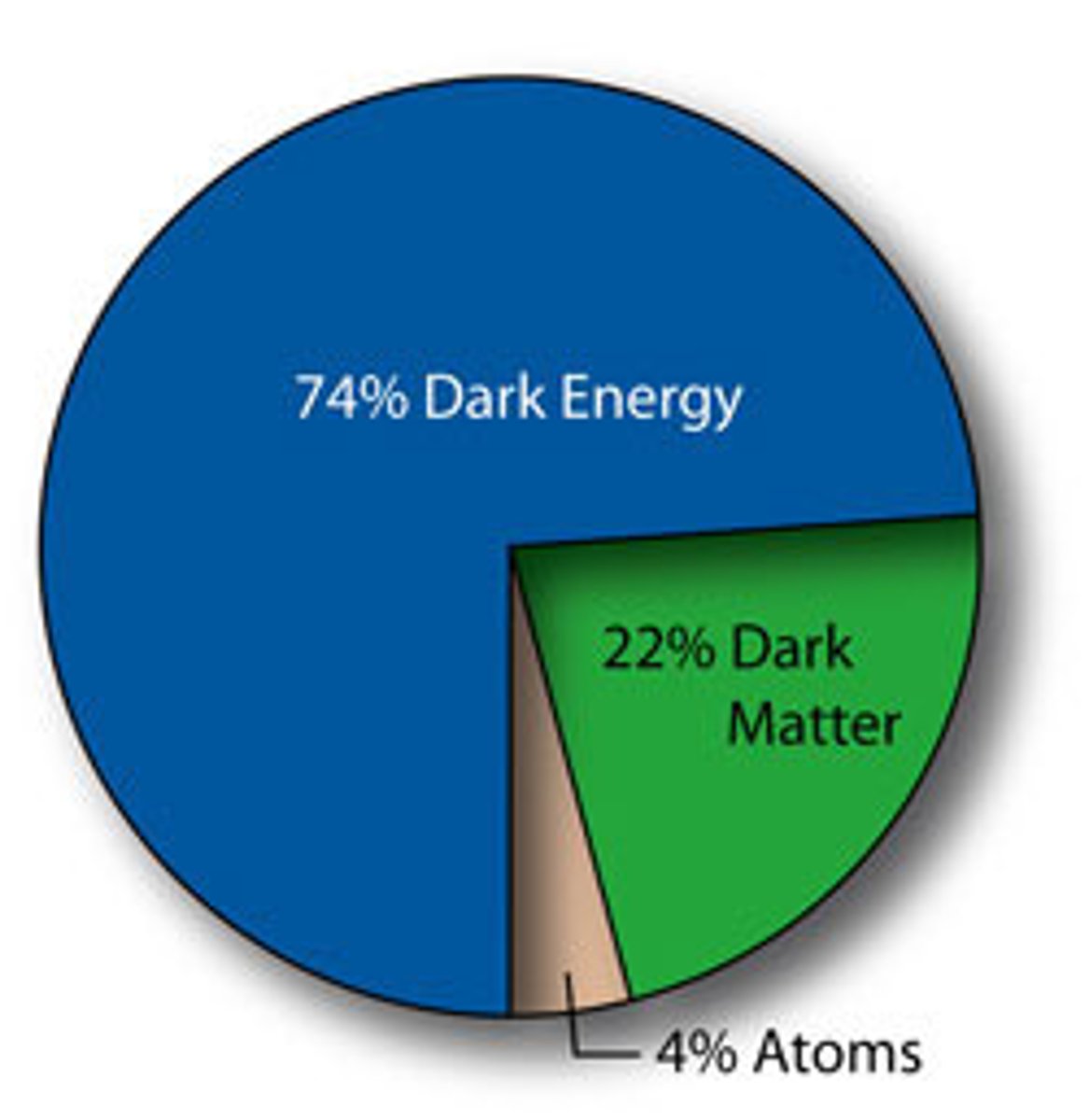
Dark Matter
matter that does not give off electromagnetic radiation but is quite abundant in the universe
Dark Energy
a mysterious force that appears to be causing the expansion of the universe to accelerate
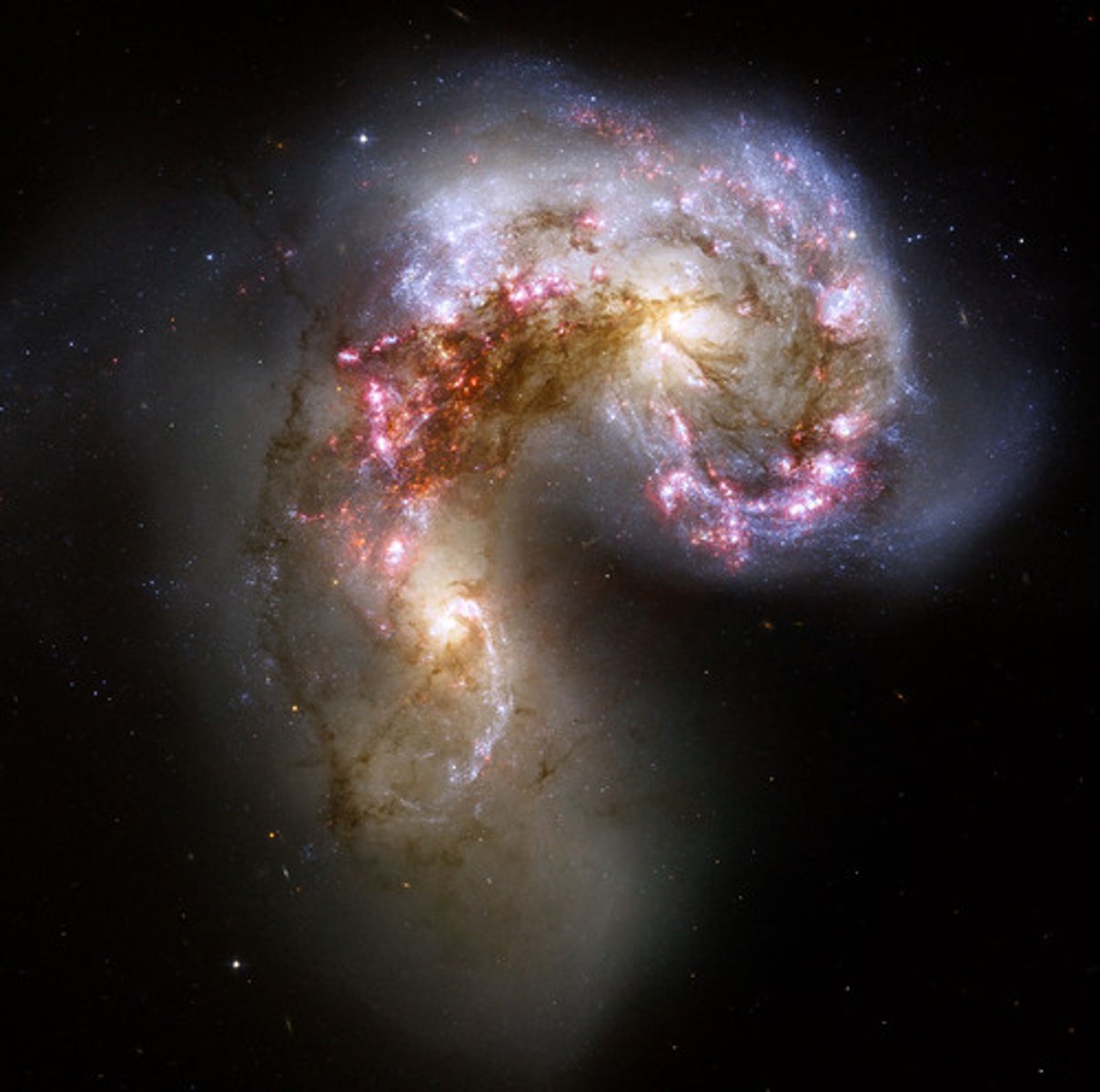
Galaxy
A large collection of planets and stars held together by gravity

Elliptical Galaxy
A galaxy shaped like a round or flattened ball, generally containing only old stars
An oval-shaped galaxy that contains mainly older stars, a few new stars, and very little gas and dust.
Lenticular Galaxy
Central buldge, no spiral arms
Spiral Galaxy
a galaxy with a bulge in the middle and arms that spiral outward in a pinwheel pattern
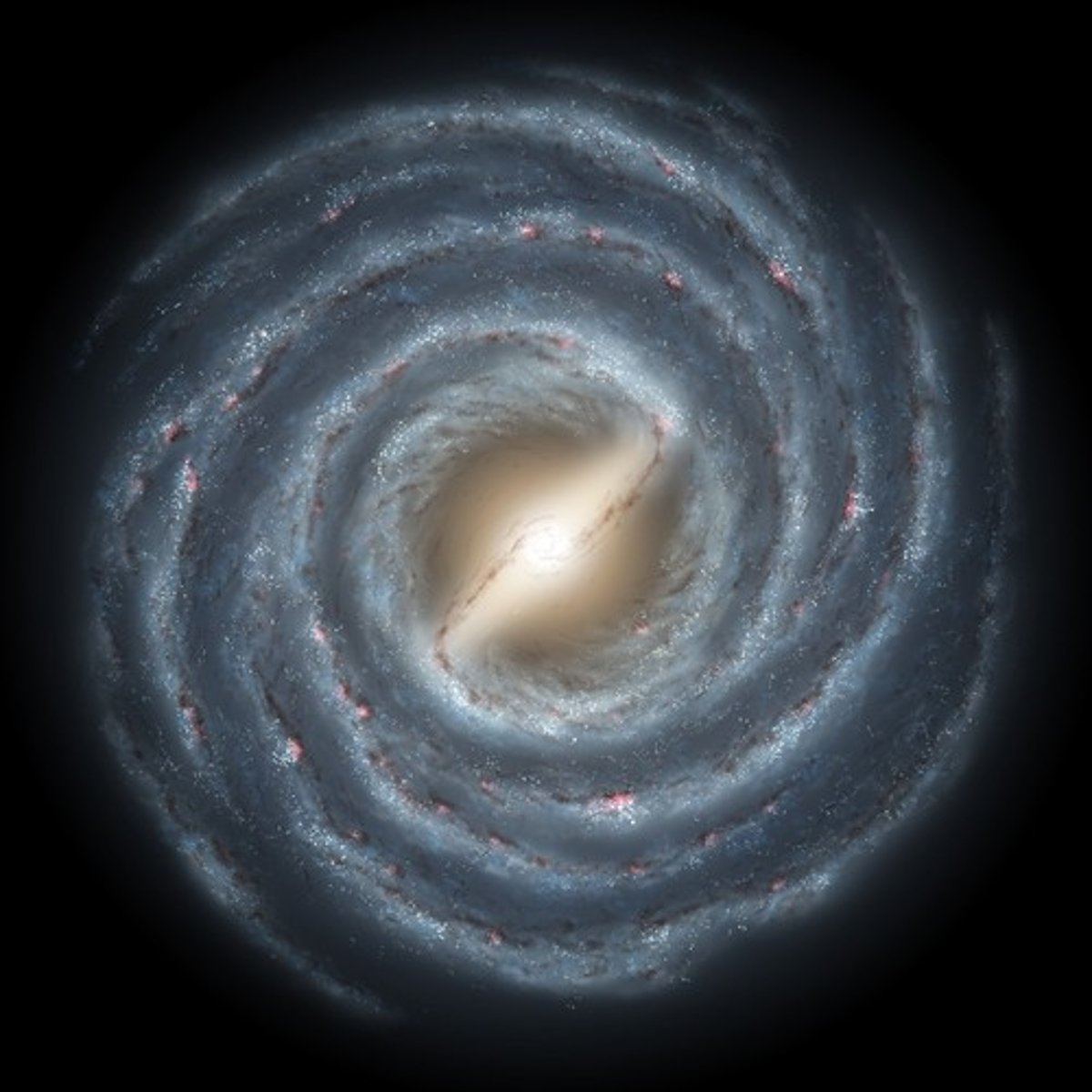

Local Group
A small group of two dozen galaxies
Galaxy Supercluster
Huge swarm of galaxies
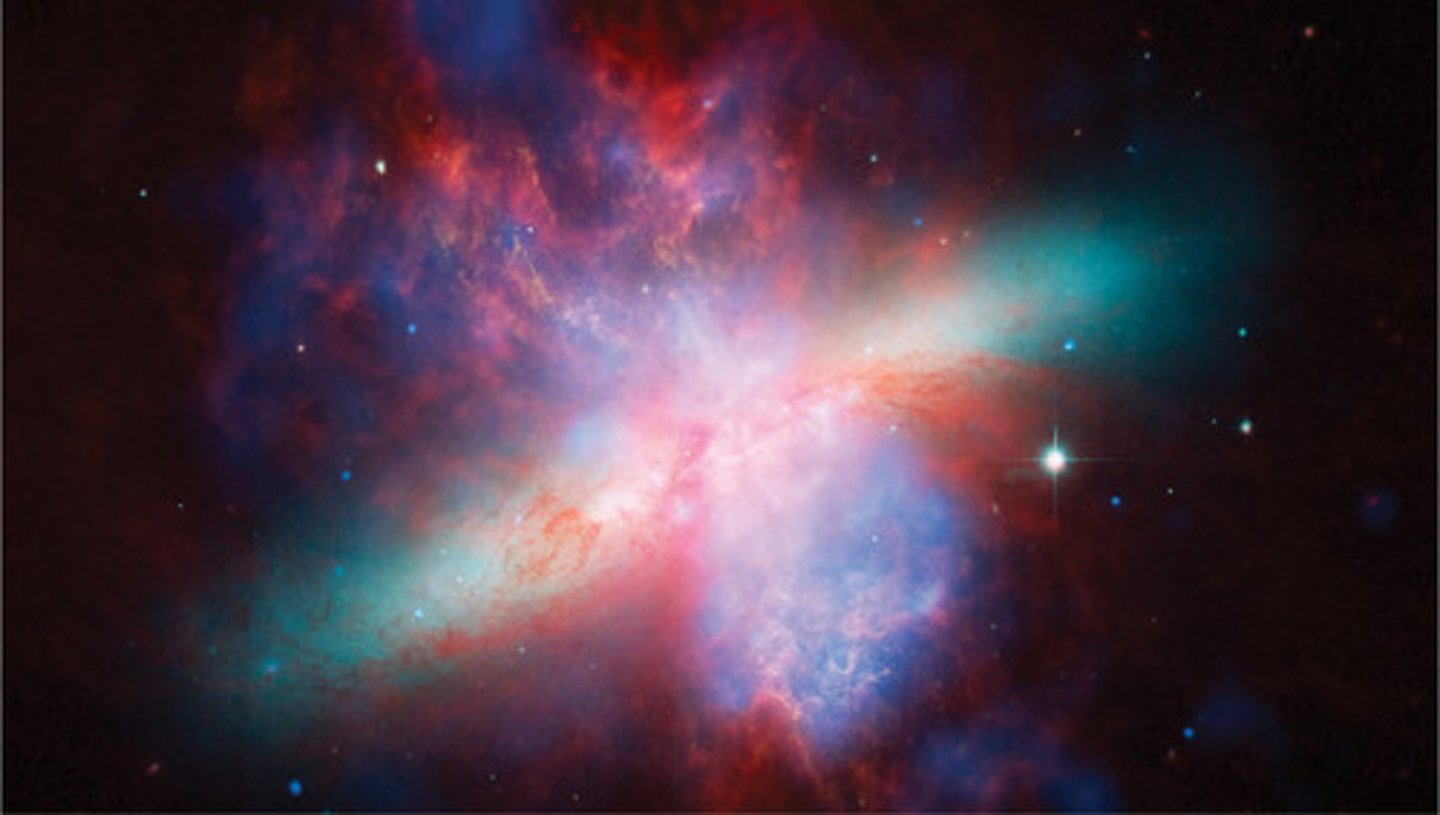
Active Galaxy
a galaxy with an unusually luminous nucleus

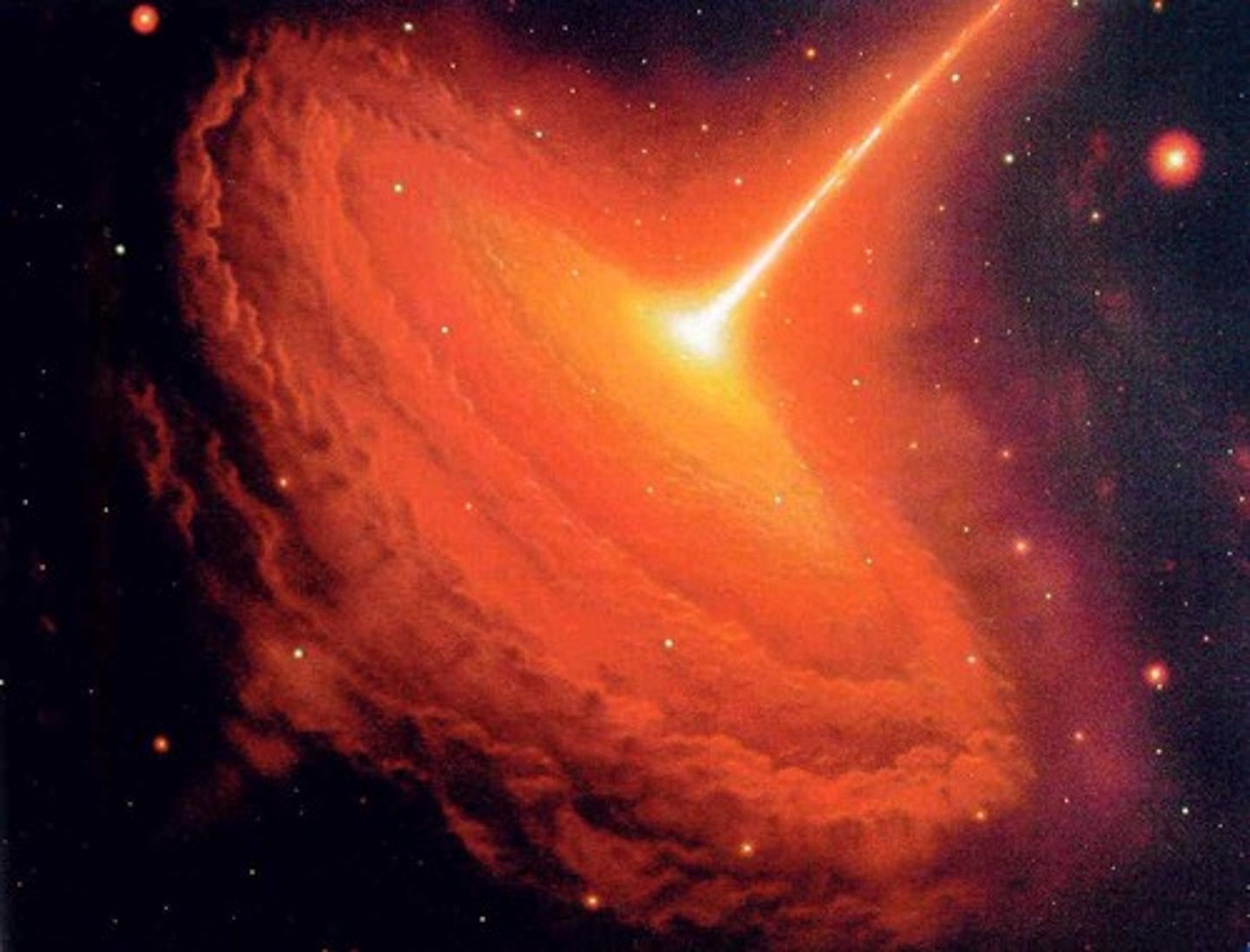
Quasar
distant yet high energy astronomical object

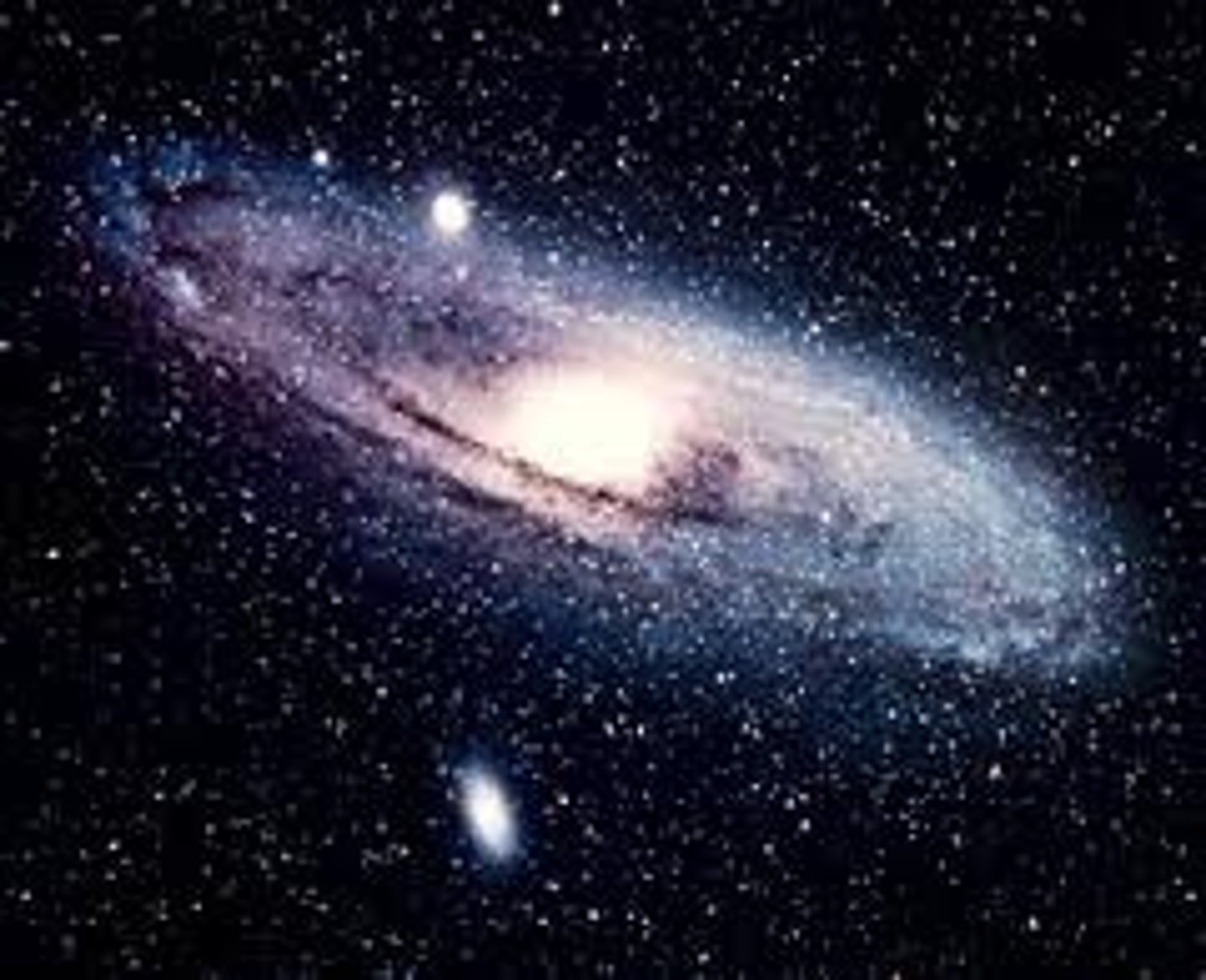
Milky Way
our galaxy, has trillions of stars

Spiral Arms
The curved swirling regions of a spiral galaxy where stars, gas, and dust are more concentrated.
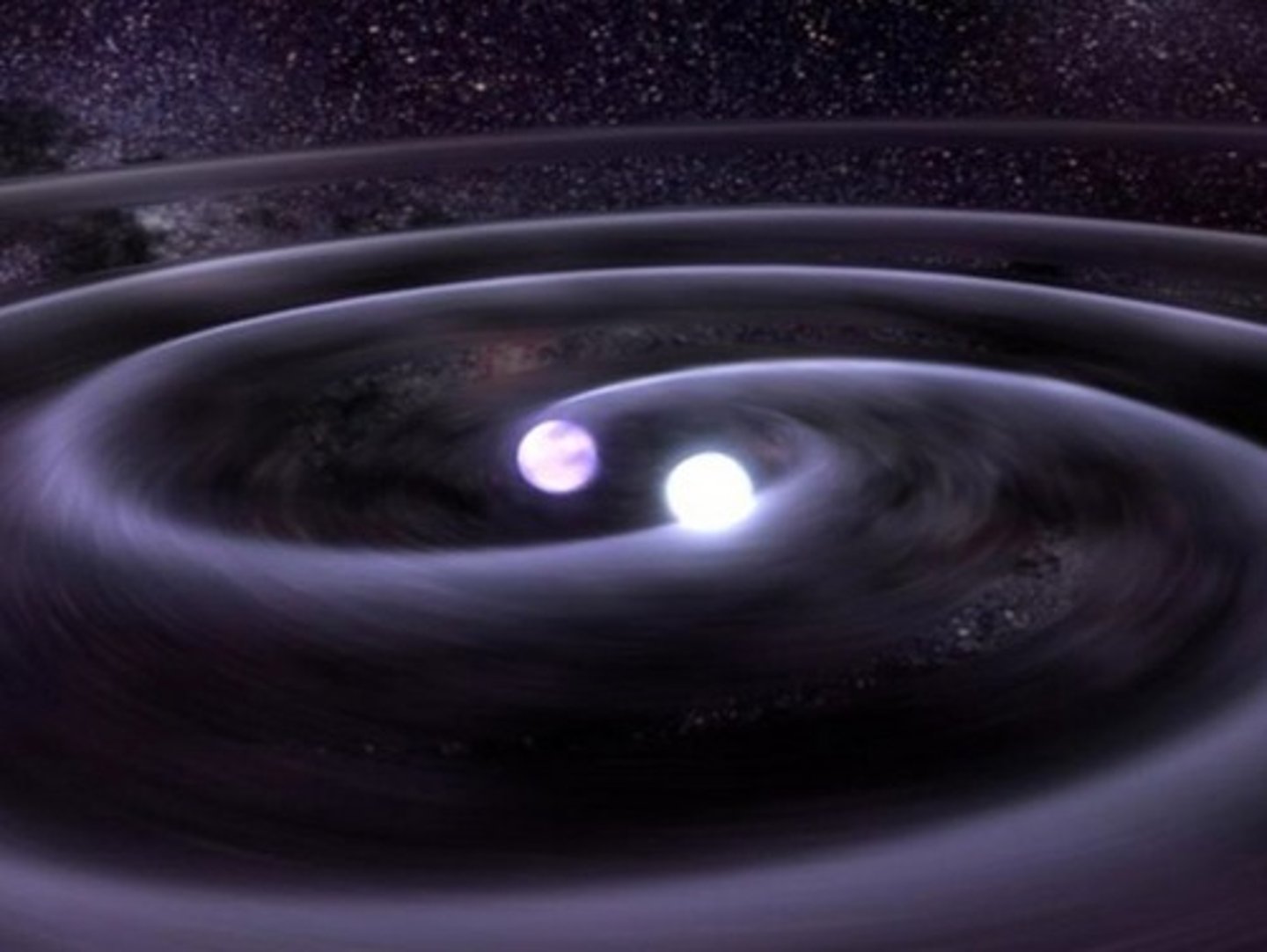
Binary Stars
Star systems that have two stars

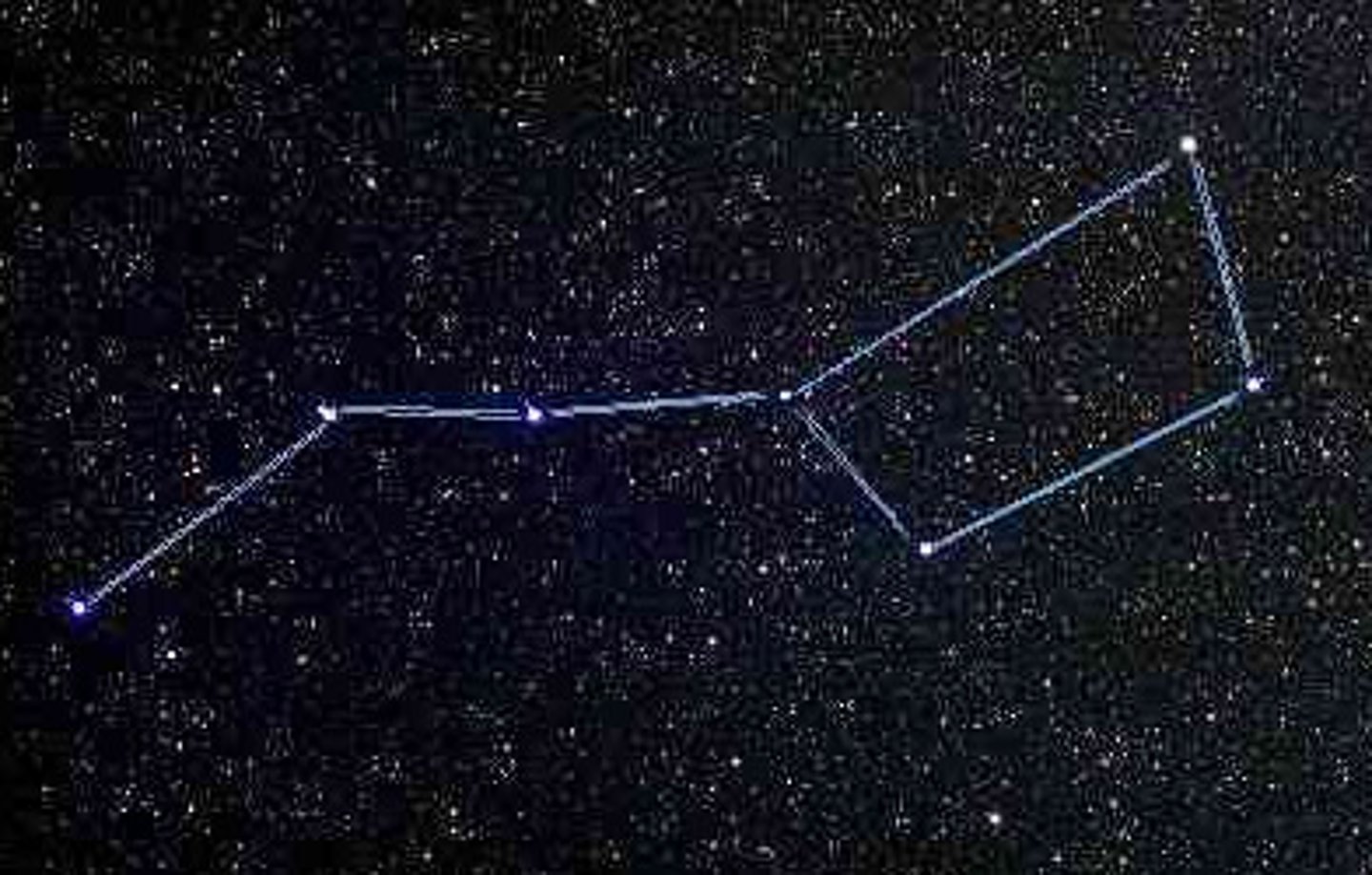
Constellations
Imaginary patterns of stars in the sky.

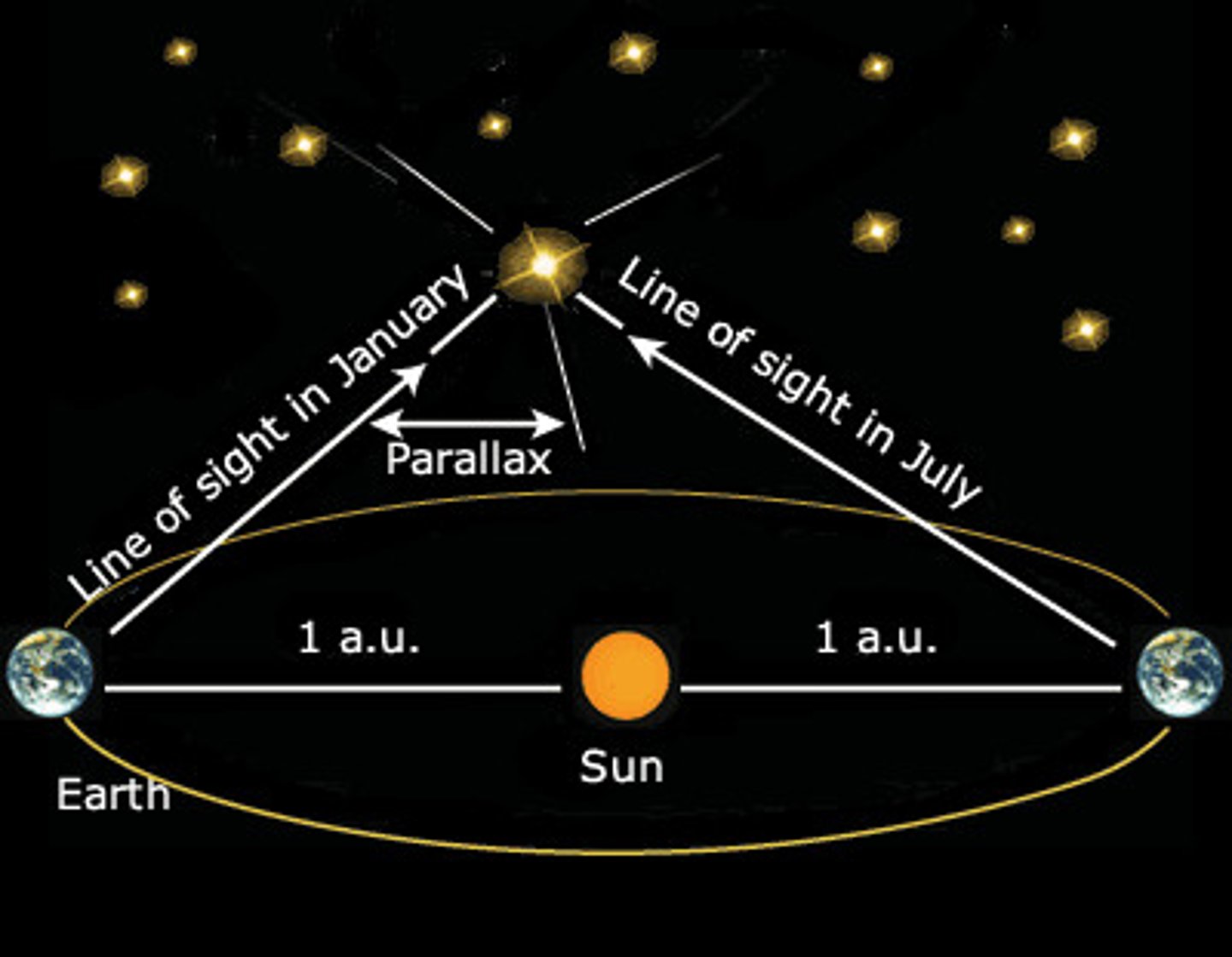
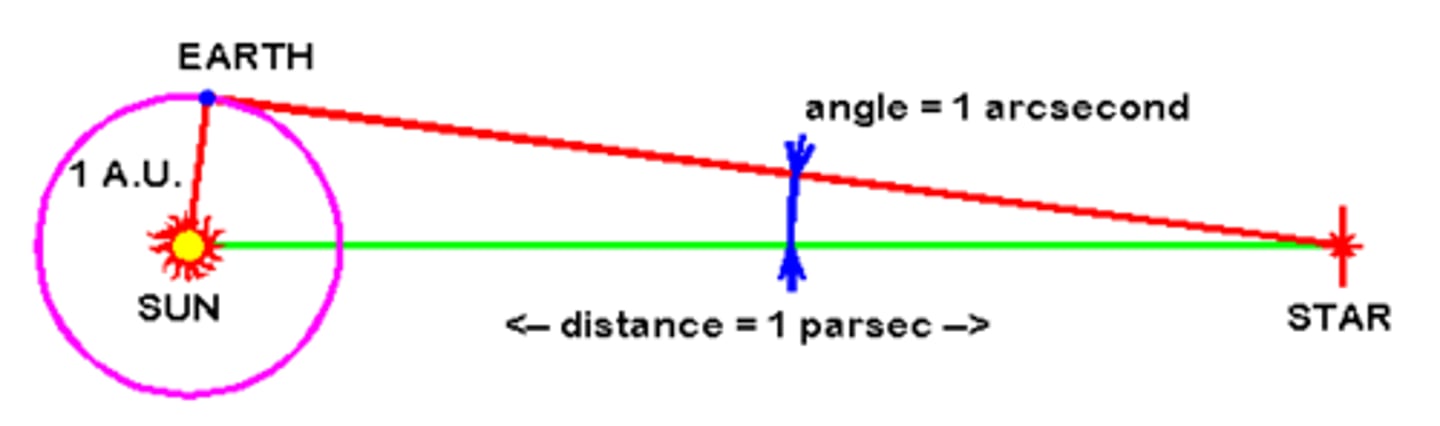
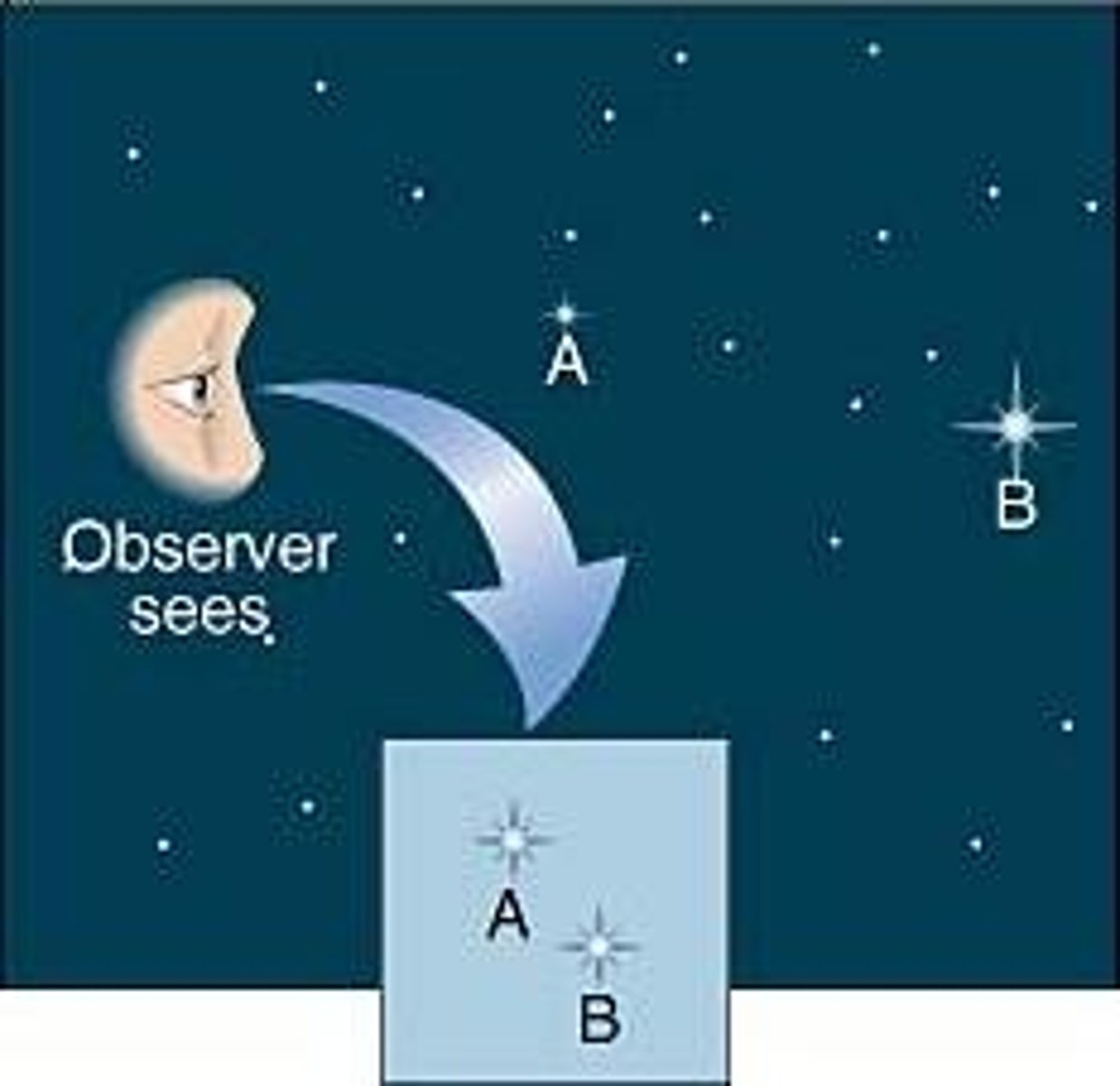
Parallax
The shift of an object when viewed from different positions
Light Year
Distance light travels in one year.
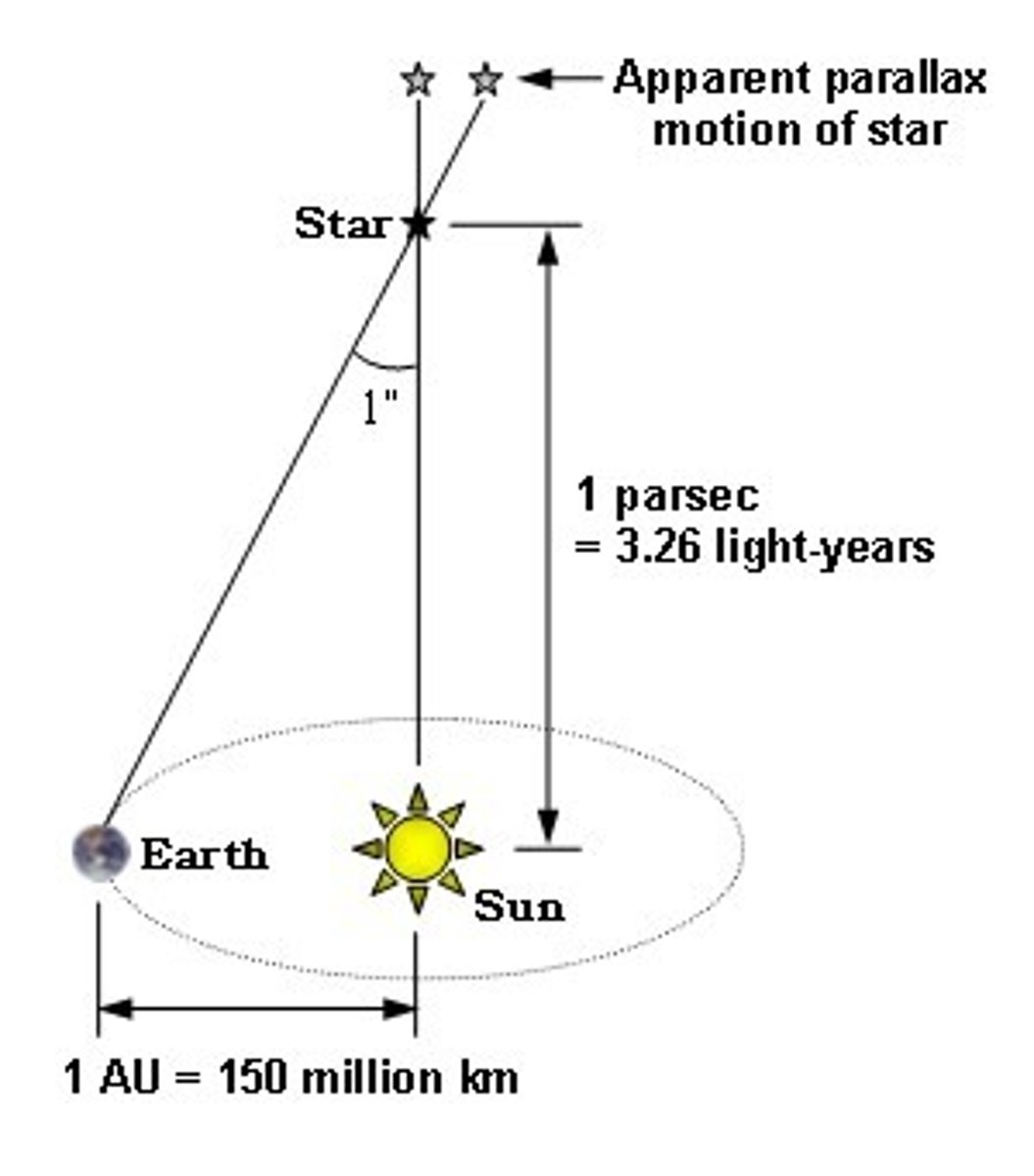
Parsec
3.26 light years
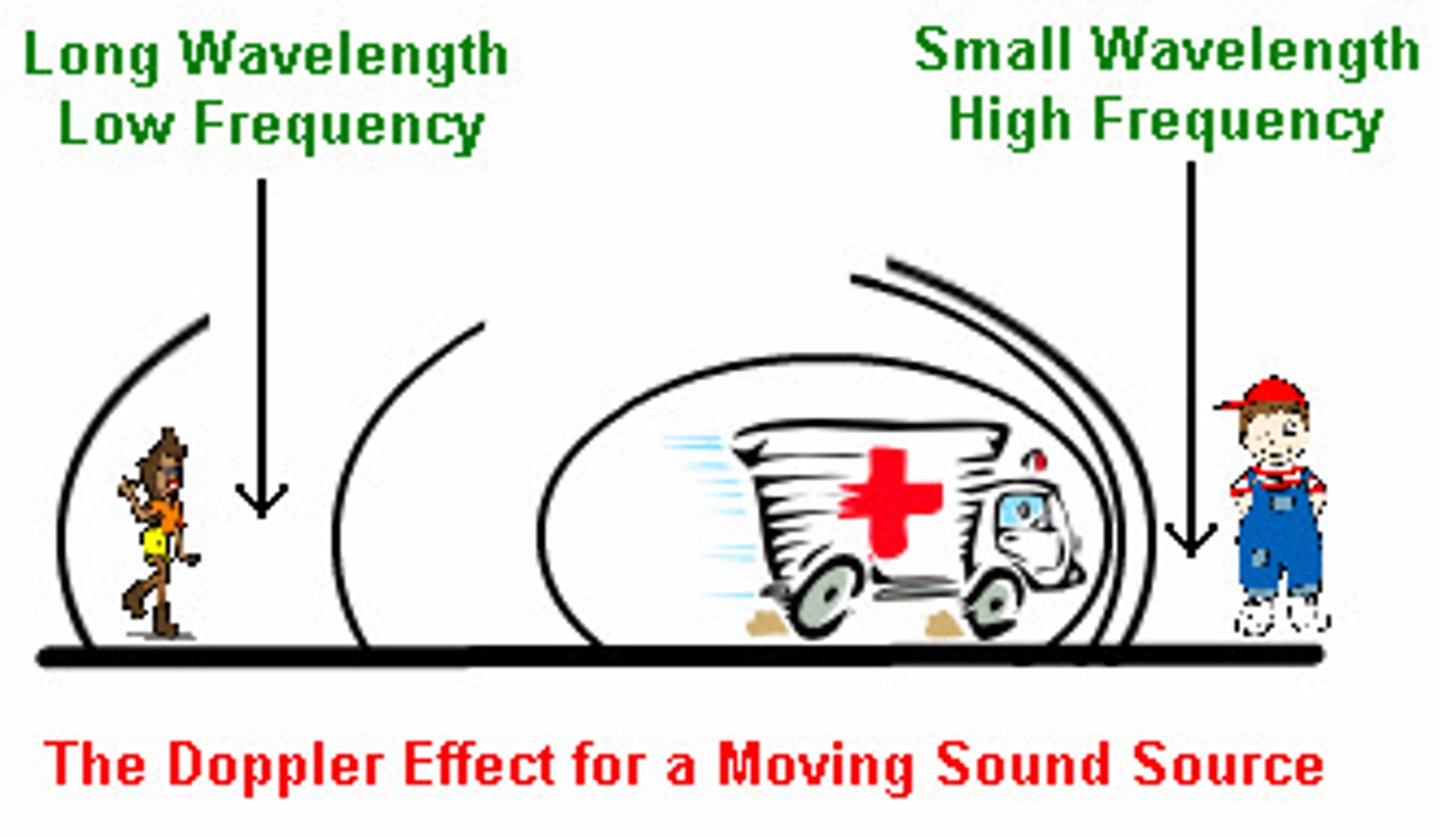
Doppler Shift
the shift to a different wavelength on the electromagnetic spectrum (when light source is moving away it is red shifted and when light source is moving closer it is blue shifted)
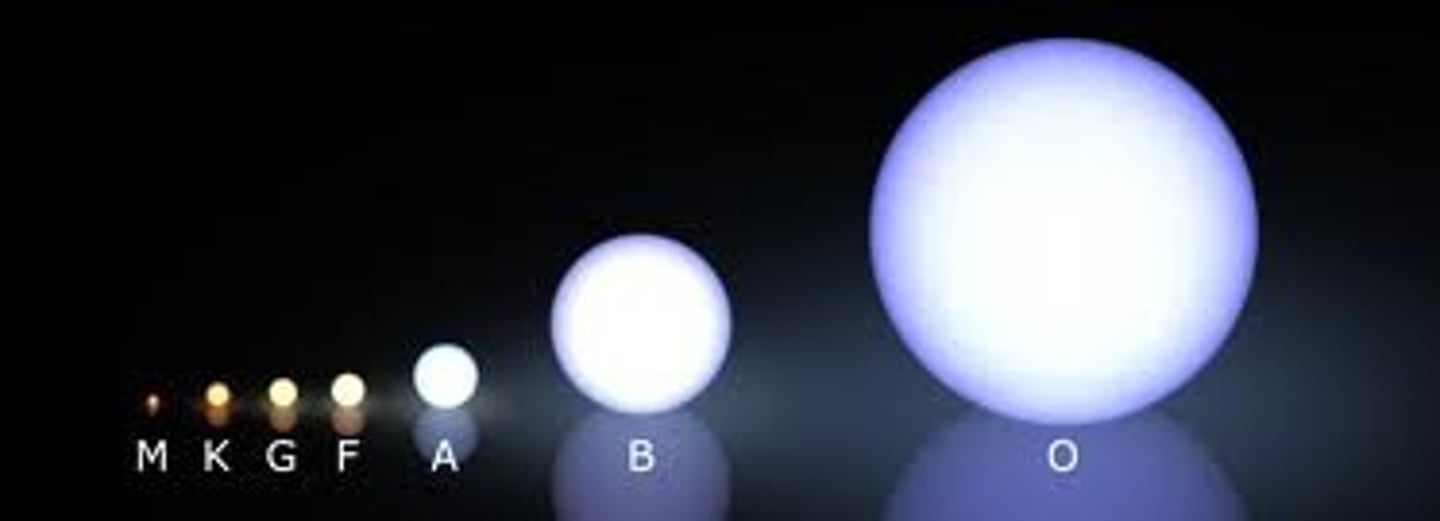
Star Magnitude
The brightness of a star on a scale of -8 to +17.

Apparent Magnitude
The brightness of a star when viewed from Earth
Absolute Magnitude
how bright a star actually is

Hydrostatic Equilibrium
the balance of the inward gravitational force and the outward force of fusion within a star. This balance of forces is what keeps a main sequence star stable.
Nebula
A large cloud of dust and gas in space
Protostar
A cloud of gas and dust in the shape of the star, but without nuclear fusion
Average Mass Star
What is a main sequence star
Red Giant
A star that expands and cools once it runs out of hydrogen fuel
Planetary Nebula
A huge cloud of gas that is created when the outer layers of a red giant star drift out into space
White Dwarf
A small, hot, dim star that is the leftover center of an old star
Black Dwarf
A white dwarf but dark and cool
Nuclear Fusion
The process of hydrogen turning into helium and releasing energy
Red Supergiant
Red giant increases in size and brightness
Supernova
a star that suddenly increases greatly in brightness that ejects most of its mass.
Neutron Star
a star that is made of electrons and protons smashed together, they form neutrons
Black Hole
An object in space whose gravity is so strong light cant escape