a. abd + general anatomy
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
normally, what changes occur in the waveform of the SMA POSTprandially
.
a) resistance increases
b) diastolic flow decreases
c) resistance decreases
d) resistance and diastolic flow decrease
c. resistance decreases

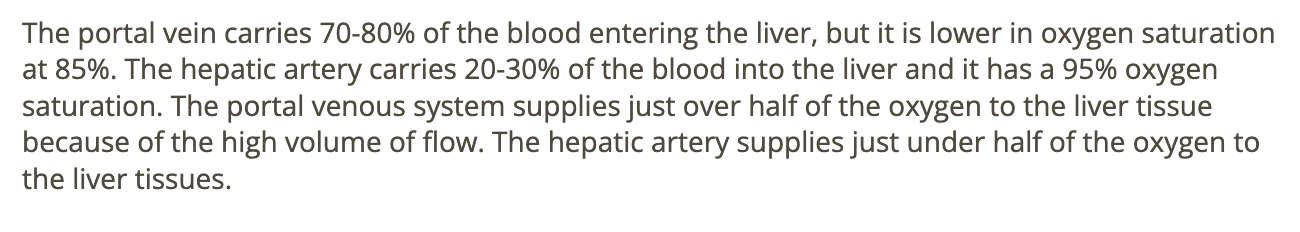
the hepatic artery carries ____ of the blood [95% O2 saturation] entering the liver
.
a) 20-30%
b) 50-60%
c) 80-90%
d) 100%
a. 20-30%
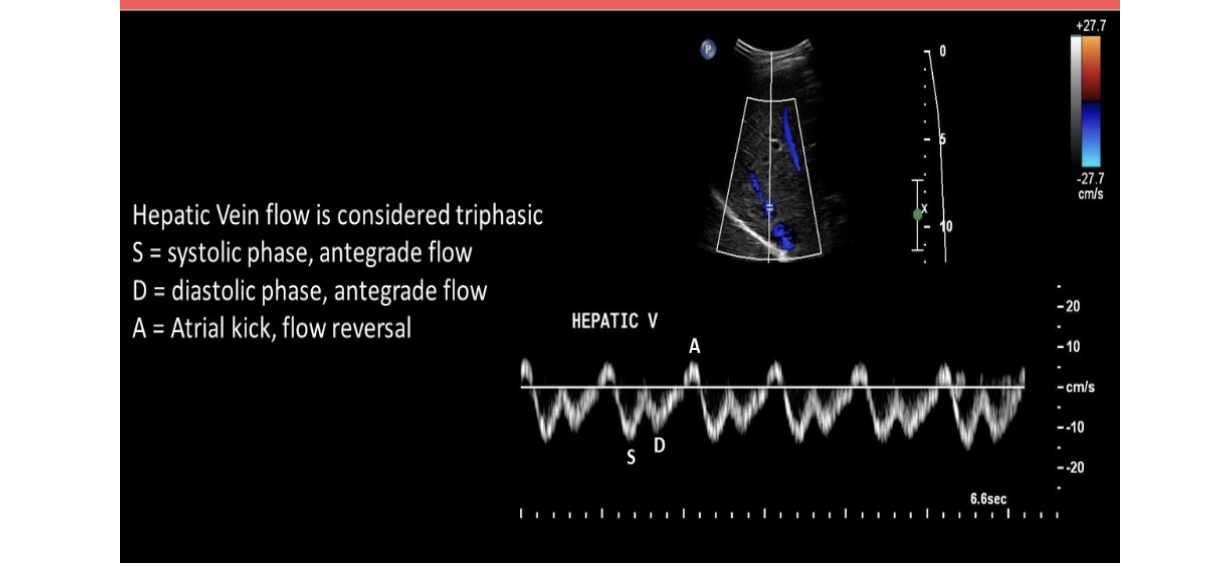
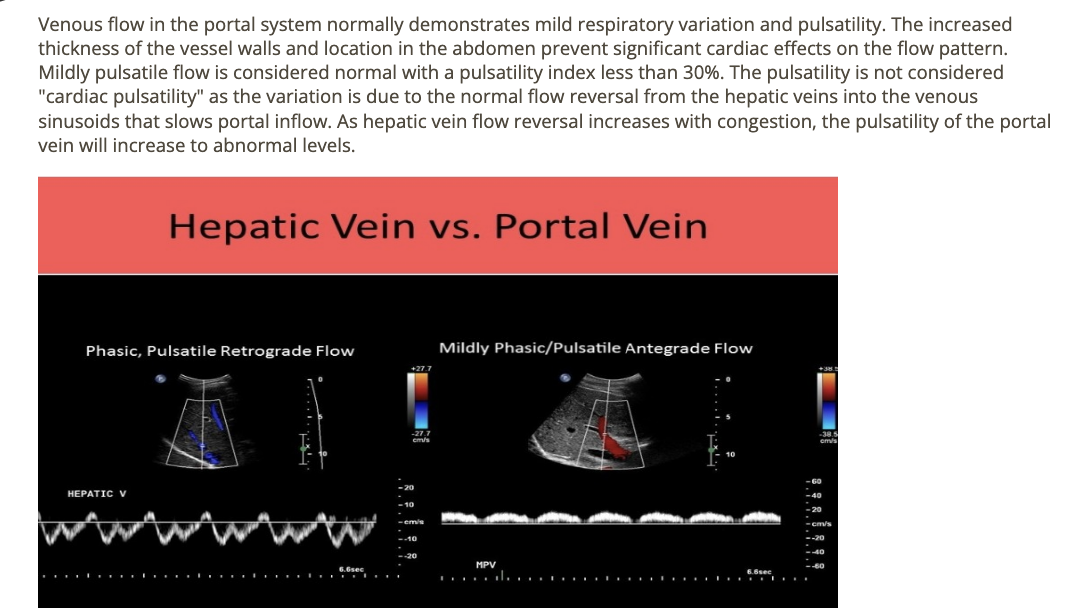
normal hepatic venous flow will show
.
a) 2 large RETROgrade diastolic + systolic waves follow by a small ANTEgrade component that corresponds w/atrial contraction
b) 2 large RETROgrade diastolic + systolic waves follow by a small RETROgrade component that corresponds w/atrial contraction
c) 2 large ANTEgrade diastolic + systolic waves follow by a small ANTEgrade component that corresponds w/atrial contraction
d) 2 large ANTEgrade diastolic + systolic waves follow by a small RETROgrade component that corresponds w/atrial contraction
d. 2 large ANTEgrade diastolic + systolic waves follow by a small RETROgrade component that corresponds w/atrial contraction

which blood vessel courses anterior to the AO + posterior to SMA
.
a) inferior mesenteric vein
b) superior mesenteric vein
c) right renal vein
d) left renal vein
d. left renal vein
![<p>which describes the normal doppler waveform in the <strong><u>proximal renal vein </u></strong>[not at renal hilum]</p><p>.</p><p>a) respiratory phasicity + mild pulsatility</p><p>b) mild pulsatility w/no respiratory changes</p><p>c) respiratory phasicity w/no pulsatility</p><p>d) continuous flow</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1042b305-b118-435e-a9d7-e318a0a629f0.png)
which describes the normal doppler waveform in the proximal renal vein [not at renal hilum]
.
a) respiratory phasicity + mild pulsatility
b) mild pulsatility w/no respiratory changes
c) respiratory phasicity w/no pulsatility
d) continuous flow
a. respiratory phasicity + mild pulsatility

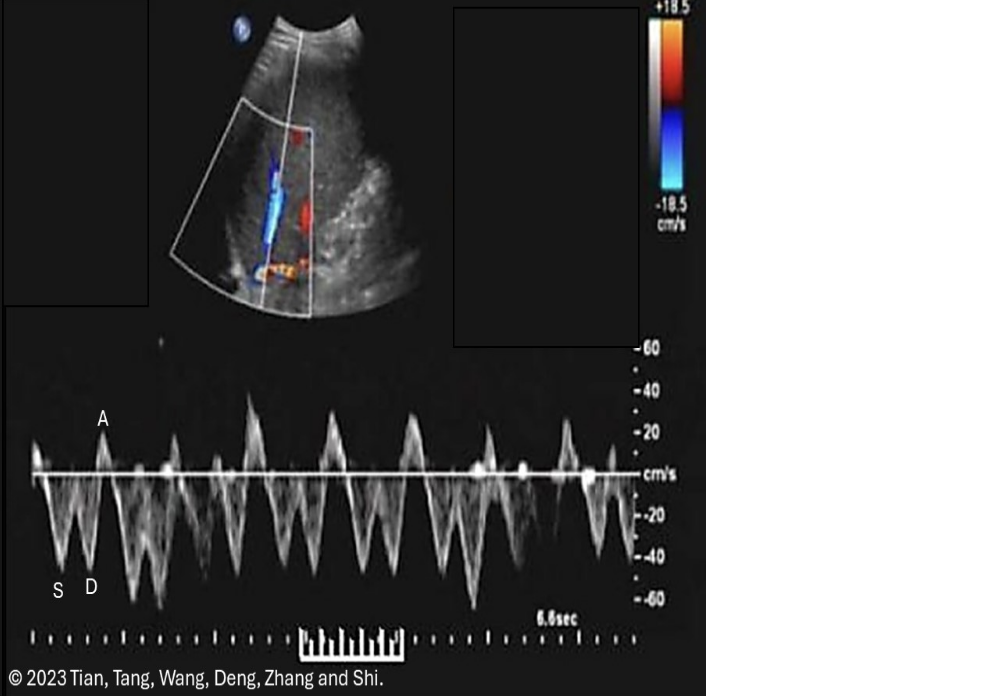
which flow characteristics is/are seen in a normal hepatic vein doppler
.
a) monophasic flow + respiratory phasicity
b) respiratory phasicity only
c) cardiac pulsatility only
d) cardiac pulsatility + respiratory phasicity
d. cardiac pulsatility + respiratory phasicity
normal splenic artery flow is
.
a) laminar
b) has Reynold’s number >2,000
c) high resistant
d) hepatopetal
b. has Reynold’s number >2,000

![<p>where is the superior mesenteric artery [SMA]</p><p>.</p><p>write [anterior to left renal vein]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a0ad8e36-963b-464b-809a-668896716acd.png)
where is the superior mesenteric artery [SMA]
.
write [anterior to left renal vein]
anterior to left renal vein
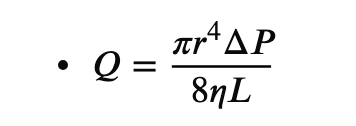
Poiseuille’s law states that the _____ has the most significant effect on blood flow in a vessel
.
a) fluid viscosity
b) vessel radius
c) pressure gradient
d) vessel length
.
Q = volume over time
n = fluid viscosity
b. vessel radius

which describes normal flow in the hepatic vessels
.
a) portal veins = hepatofugal
b) hepatic artery = hepatofugal
c) hepatic veins = hepatopetal
d) hepatic artery = hepatopetal
d. hepatic artery = hepatopetal

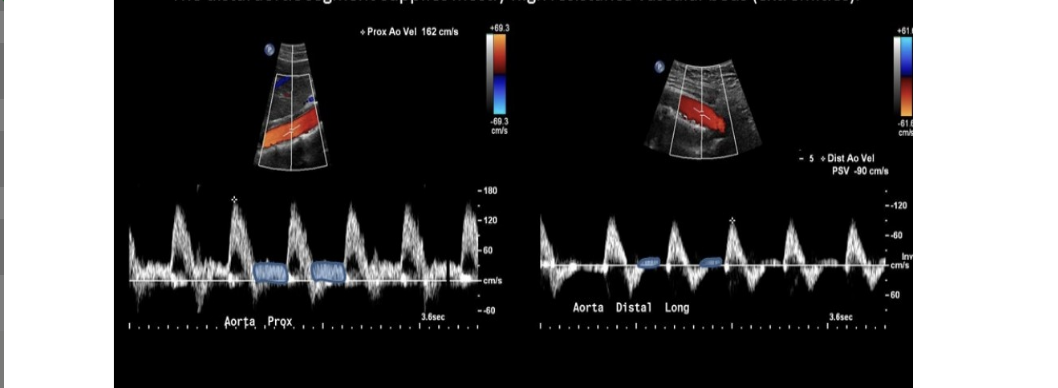
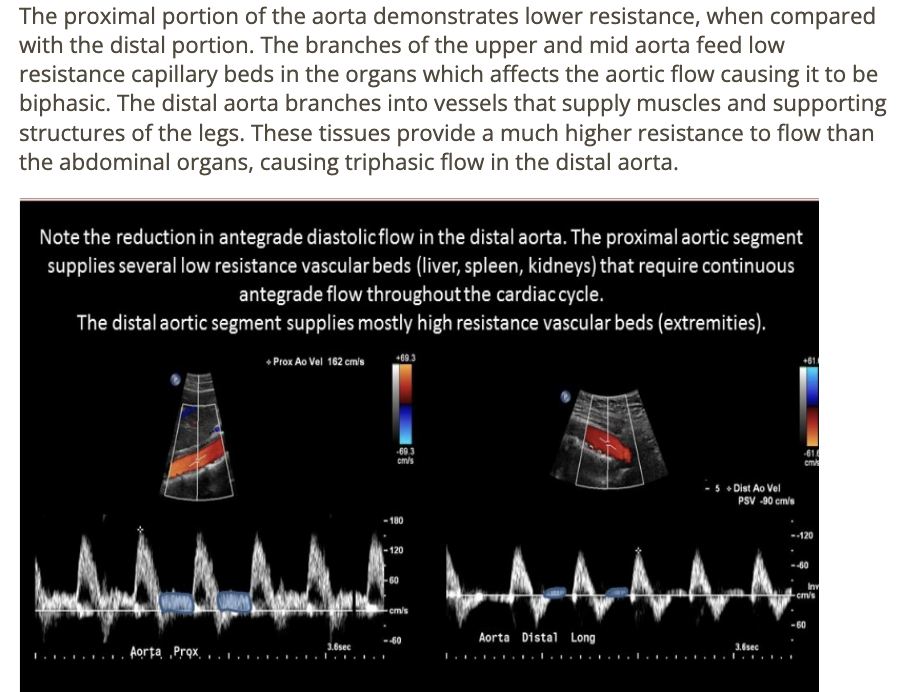
resistance to flow ___ as blood travels distally through the abdominal aorta
.
a) increases
b) decreases by 50%
c) decreases slightly
d) remains constant
a. increases
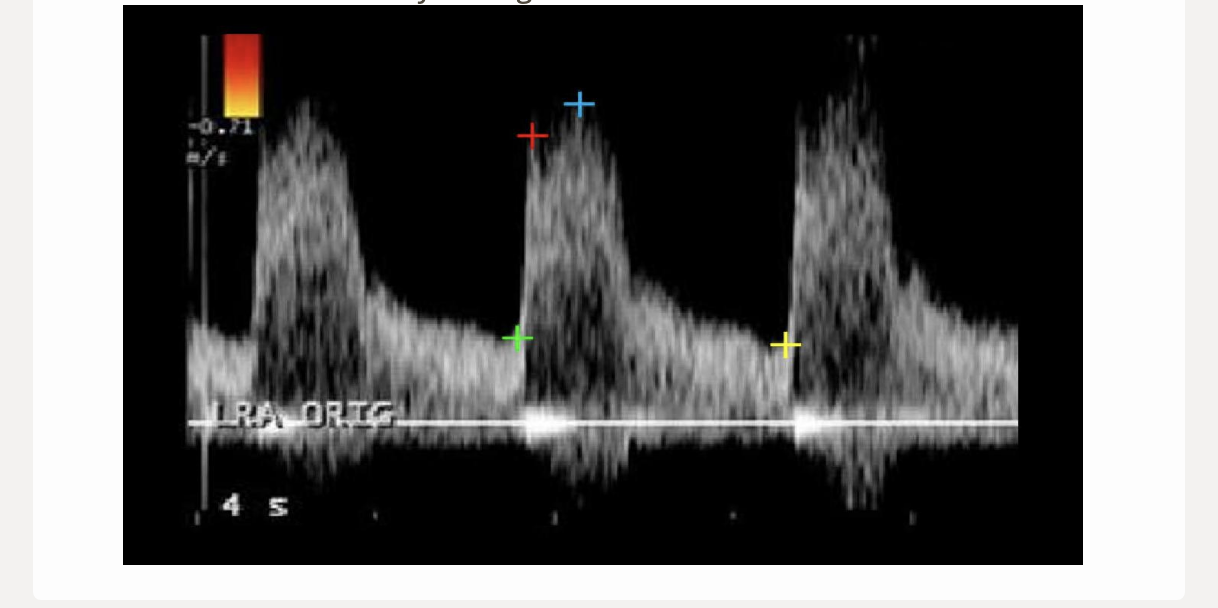
which 2 cursors would be used to measure the acceleration time for this renal artery flow
.
a) green + yellow
b) green + red
c) red + blue
d) blue + green
b. green + red

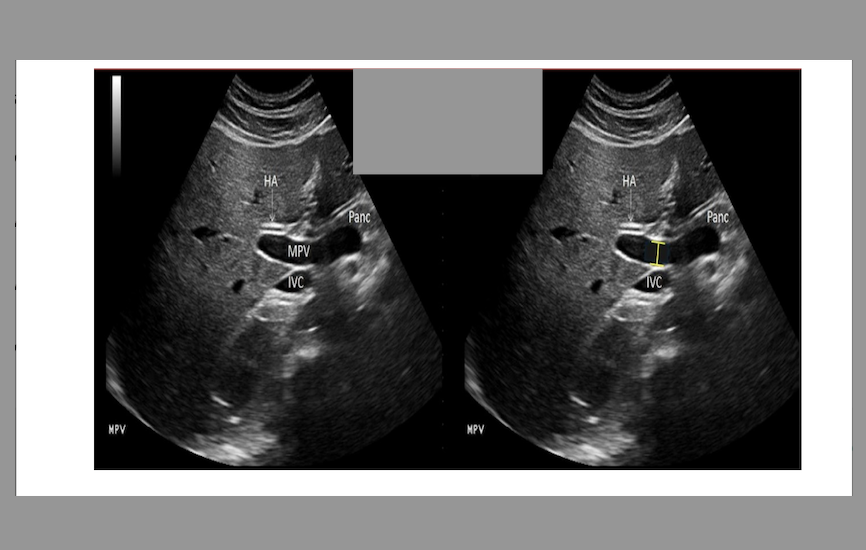
what is the proper caliper placement for assessing portal vein diameter
.
a) inner to inner wall at the junction of splenic vein + portal vein
b) outer to outer wall at the junction of splenic vein + portal vein
c) outer to outer wall where portal vein crosses IVC
d) inner to inner wall where portal vein crosses IVC
d. inner to inner wall where portal vein crosses IVC

which normally shows a low resistance doppler flow
.
a) ECA [external carotid artery]
b) hepatic + renal artery
c) renal + internal iliac artery
d) ECA + renal + hepatic arteries
b. hepatic + renal artery
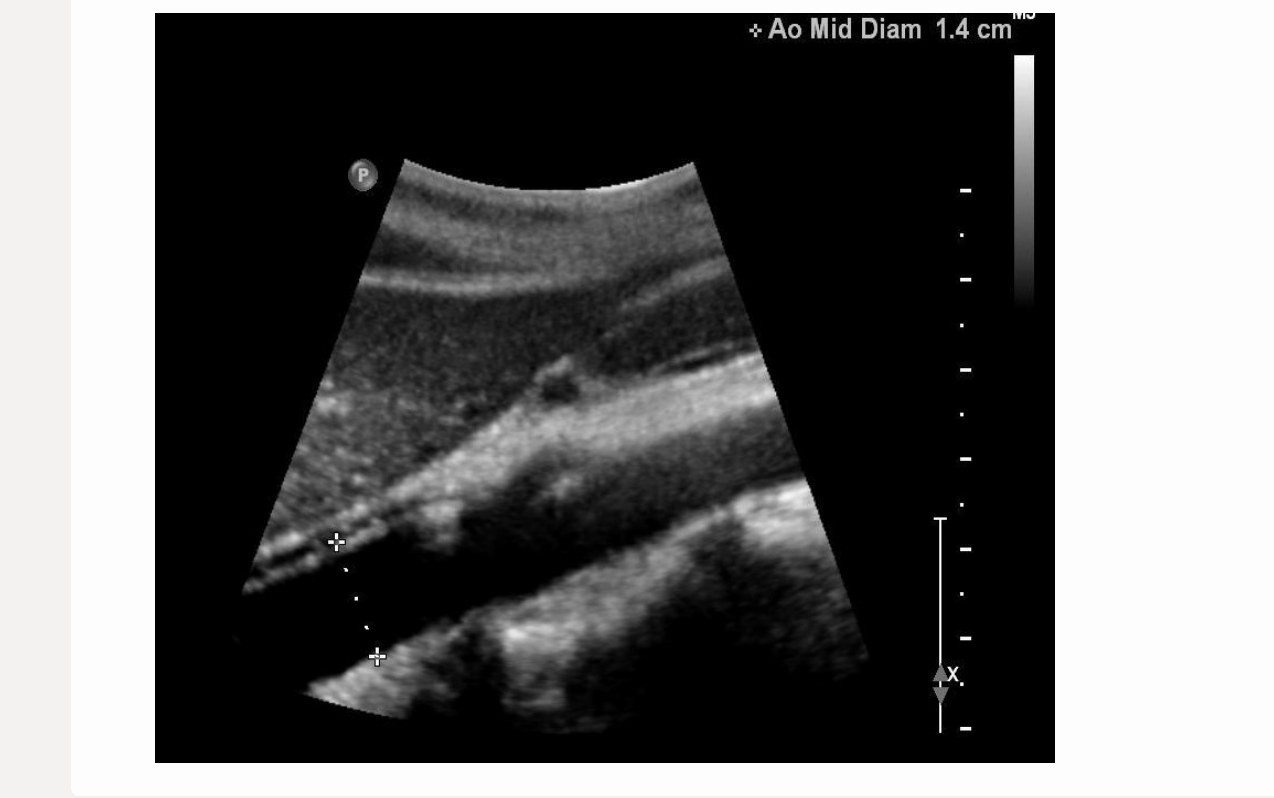
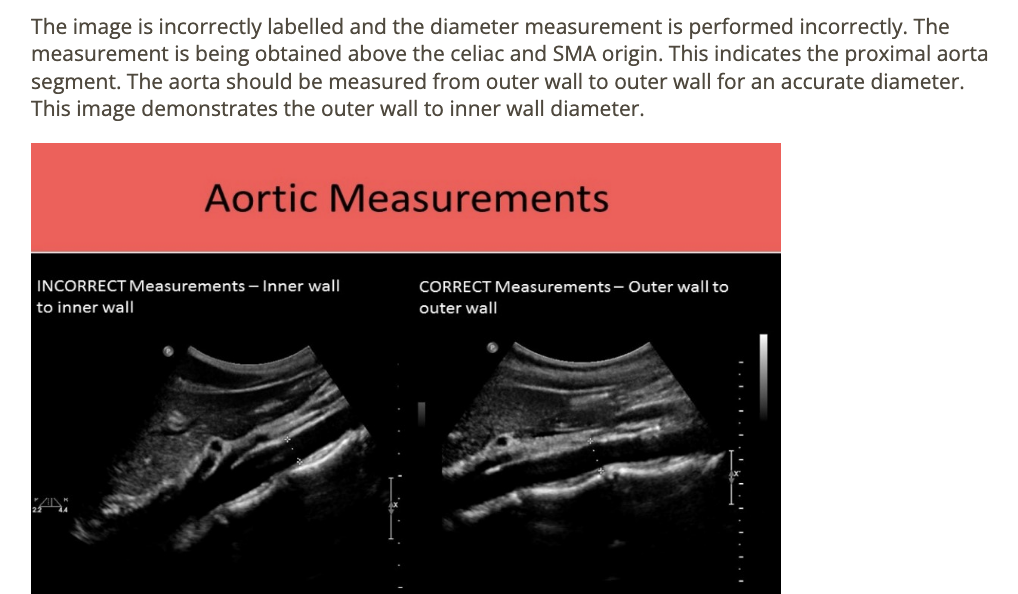
this image is
.
a) incorrect label + diameter
b) correct label; incorrect diameter
c) correct label; correct diameter
d) incorrect label; correct diameter
a. incorrect label + diameter
what describes thickness of blood
.
a) impedance
b) vasoconstriction
c) viscosity
d) resistance
c. viscosity
where is the marginal artery of Drummond
.
a) part of the cerebrovascular circulatory system
b) connects the dorsalis pedis artery to posterior tibial artery in foot
c) at splenic hilum
d) connects SMA + IMA through mesenteric
d. connects SMA + IMA through mesenteric

what is the best technique to visualized + locate the inferior mesenteric artery
.
a) sag; left of midline near umbilicus
b) coronal; left mid flank
c) sag; right of midline near umbilicus
d) trv; find renal arteries + slide inferiorly
d. trv; find renal arteries + slide ineriorly
![<p>[IVC = posterior to caudate lobe]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/37ddafef-a01e-4241-a6eb-4fd43401e918.png)
[IVC = posterior to caudate lobe]
IVC = posterior to caudate lobe
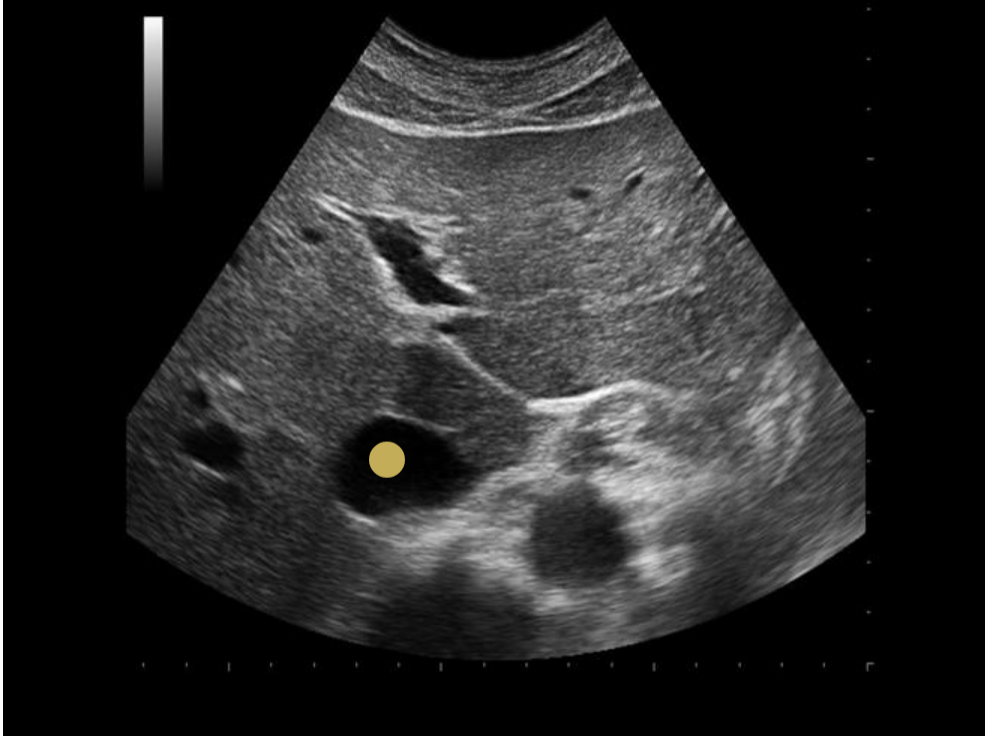
the diameter of a normal portal vein should not exceed
.
a) 10mm
b) 13mm
c) 12mm
d) 11mm
b. 13mm
![<p>find IVC </p><p>.</p><p>[IVC = posterior to panc head]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/61e93537-e382-4129-8353-88053b5a2e79.png)
find IVC
.
[IVC = posterior to panc head]
IVC = posterior to panc head
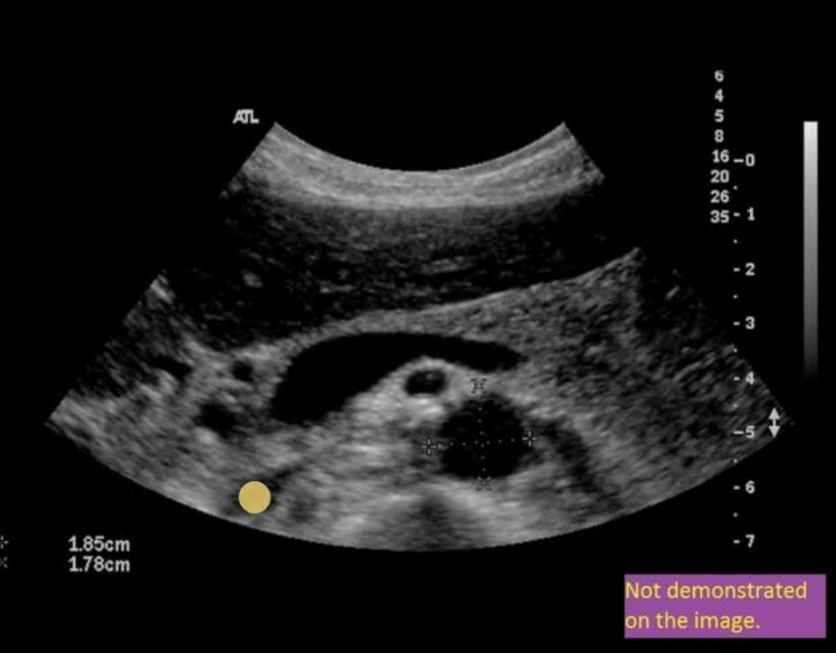
which vessel does not drain into IVC
. think confluence
.
a) right gonadal vein
b) right renal vein
c) left hepatic vein
d) splenic vein
d. splenic vein
blood in the pulmonary veins [coming from lungs] has
.
a) high O2; flows into right atrium
b) low O2; flows into left atrium
c) high O2; flows into left atrium
d) is normally high resistance
c. high O2; flows into left atrium

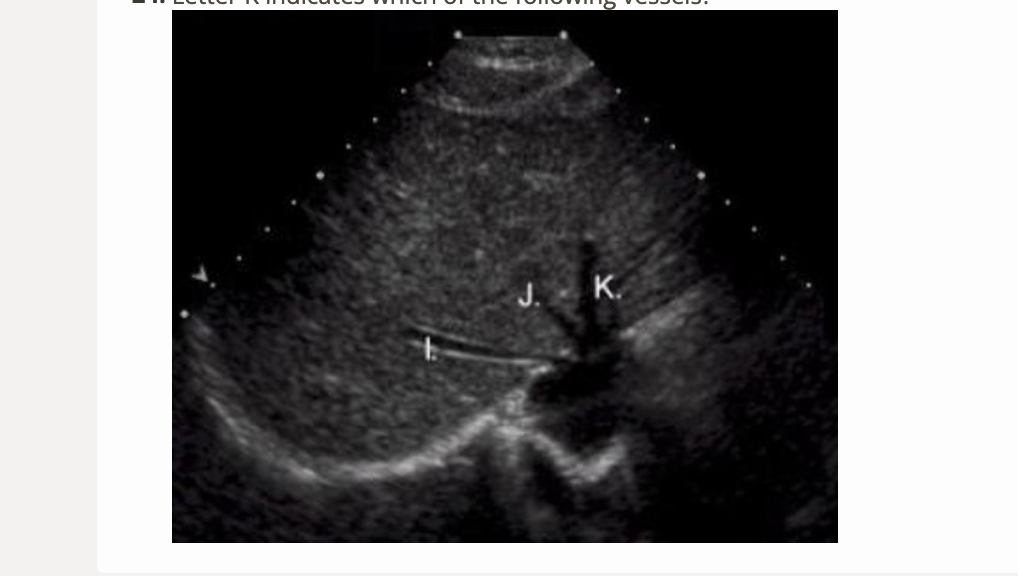
letter K is which vessel
.
a) left portal vein
b) right portal vein
c) middle hepatic vein
d) left hepatic vein
d. left hepatic vein
what is the best landmark for left renal artery
.
a) celiac axis origin
b) left renal vein
c) iliac bifurcation
d) portal confluence
b. left renal vein

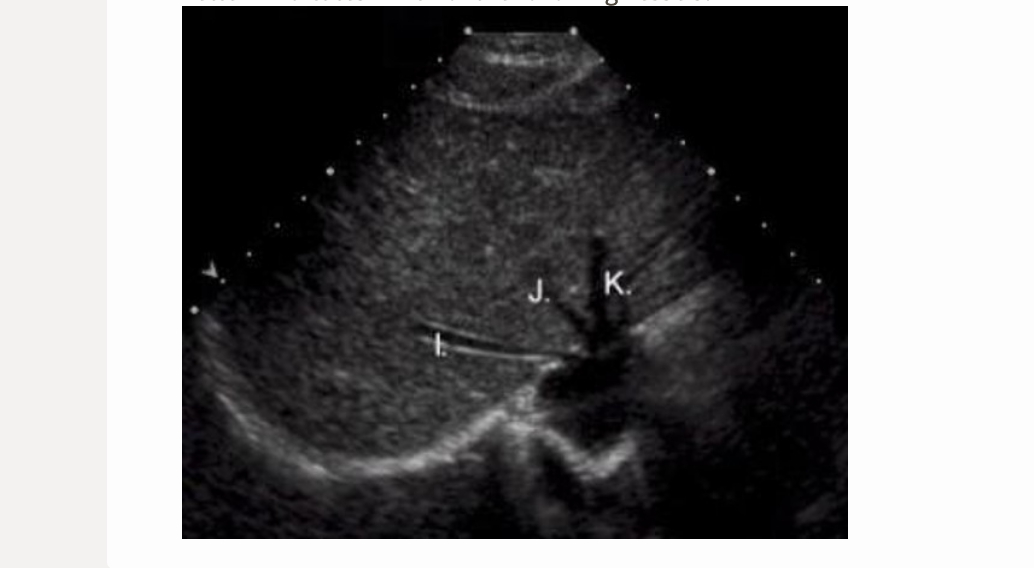
letter I is which vessel
.
a) left portal vein
b) right hepatic vein
c) middle hepatic vein
d) left hepatic vein
b. right hepatic vein
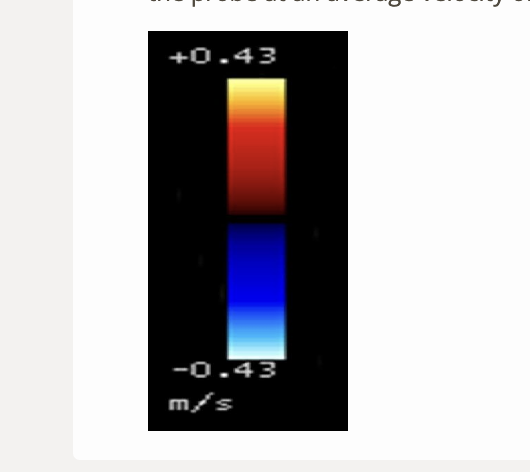
what color will blood be shown moving toward the probe at an average velocity of 100cm/s
.
a) yellow
b) red
c) white/light blue
d) blue
c. white/light blue

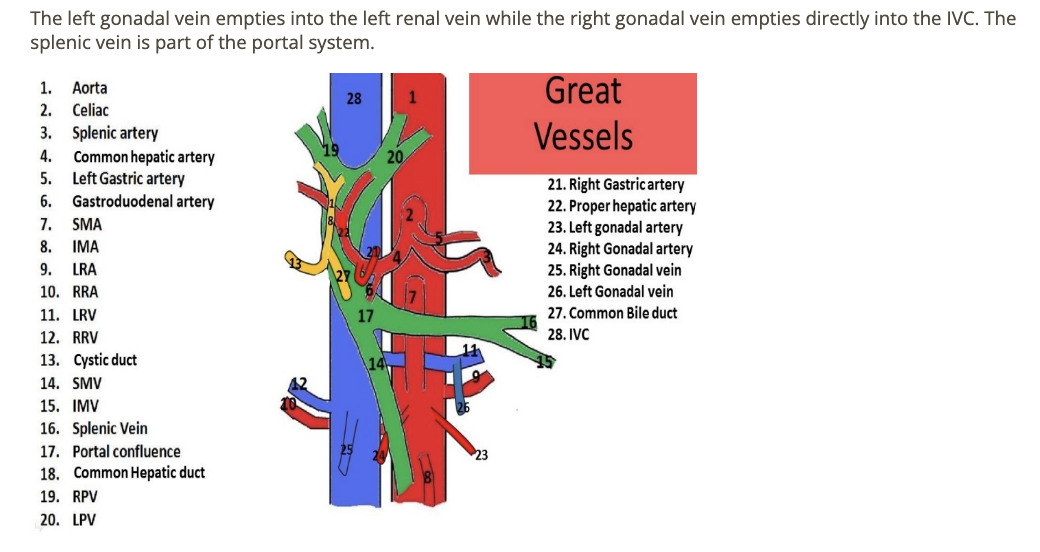
which gonadal vein empties directly into the IVC
.
a) right gonadal vein
b) left gonadal vein
c) right + left gonadal veins
d) neither gonadal veins drain directly into IVC
a. right gonadal vein
the ___ is formed by the junction of the splenic vein + superior mesenteric vein
.
a) left hepatic vein
b) right hepatic vein
c) inferior mesenteric vein
d) main portal vein
d. main portal vein
the primary mechanisms that control arterial flow volume changes during the cardiac cycle are
.
a) cardiac output; peripheral resistance
b) vessel length; peripheral resistance
c) cardiac output; viscosity
d) viscosity; vessel radius
a. cardiac output; peripheral resistance
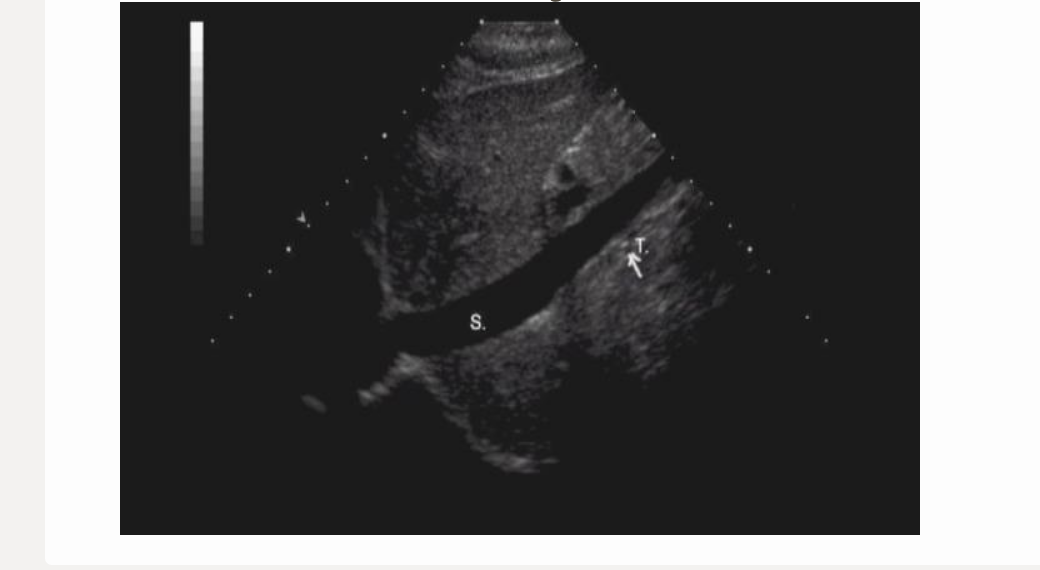
letter t is
.
a) left renal artery
b) right renal artery
c) IVC
d) superior mesenteric artery
b. right renal artery
![<p>where is the splenic artery </p><p>.</p><p>[not visible in this imaging plane] </p><p>.</p><p>splenic vein = posterior to panc body</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/badc4d96-787e-4944-8ec3-29ab19d20f83.png)
where is the splenic artery
.
[not visible in this imaging plane]
.
splenic vein = posterior to panc body
not visible in this imaging plane
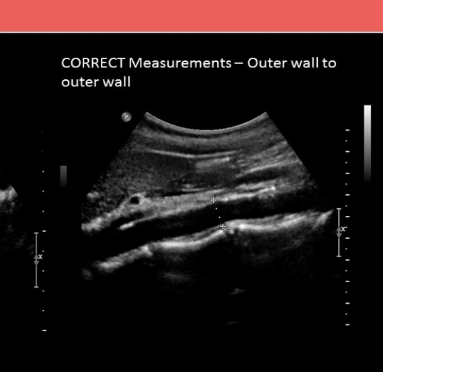
the preferred imaging plane to measure AO AP is
.
a) coronal
b) transverse
c) sagittal
d) radial
c. sagittal
the cardiovascular application of the Bernoulli Principle explains the [high velocity, low pressure]
.
a) relationship between pressure, resistance, and flow volume
b) relationship of vessel radius and flow volume
c) turbulence + layers of flow separation within carotid bulb
d) reason for aliasing of the doppler signal at high velocities
c. turbulence + layers of flow separation within carotid bulb

what is the proper pt position + respiration for assessing the portal vein diameter
.
a) supine w/inspiration + valsalva
b) RLD w/deep inspiration
c) LLD w/deep inspiration
d) supine w/quiet respiration
d. supine w/quiet respiration
![<p>the seagull sign refers to </p><p>.</p><p>a) common femoral bifurcation</p><p>b) celiac axis [CHA + SA]</p><p>c) 3 hepatic veins</p><p>d) bilateral renal origins</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1c412444-e075-4a25-8c1c-799777dfd76e.png)
the seagull sign refers to
.
a) common femoral bifurcation
b) celiac axis [CHA + SA]
c) 3 hepatic veins
d) bilateral renal origins
b. celiac axis
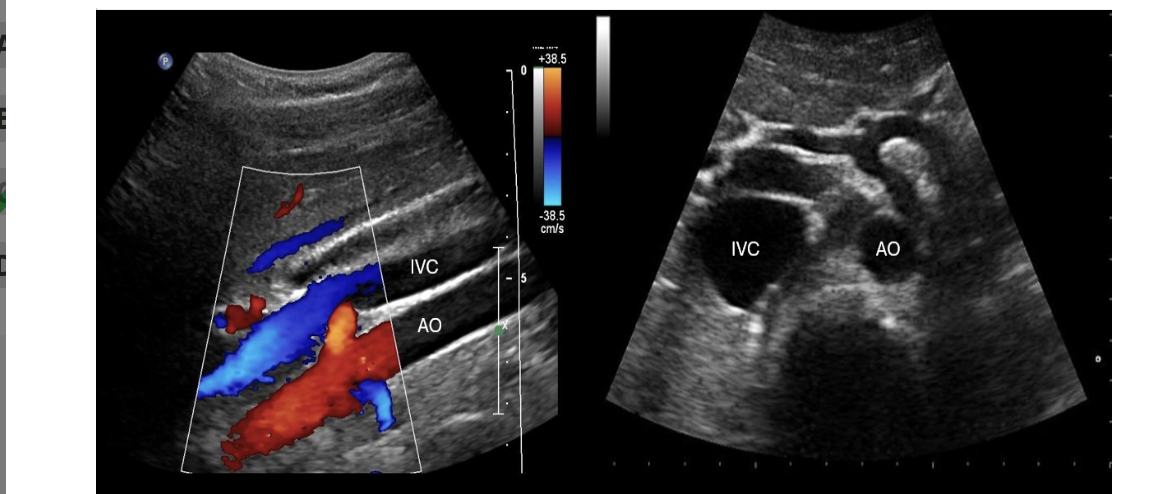
which imaging plane shows the IVC + AO on the same image in a normal pt
.
a) coronal
b) transverse
c) midsagittal
d) coronal + transverse
d. coronal + transverse
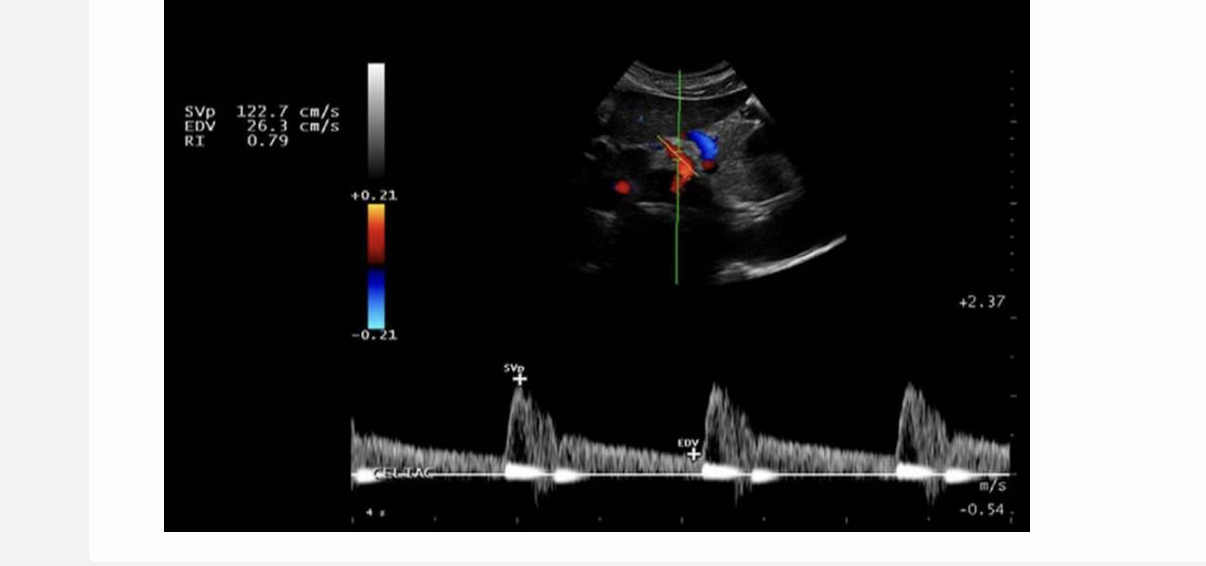
image is from the celiac axis. which is the likely finding when the vessel is re-evaluated after eating?
. is the SMA in the celiax axis?? hmmmm?
.
a) decreased resistance + increased peak velocity
b) decreased resistance w/no change in peak velocity
c) increased resistance + peak velocity
d) no change in flow
d. no change in flow

the most cephalic branch of the abdominal aorta is
.
a) celiac axis
b) common hepatic artery
c) splenic artery
d) SMA
a. celiac axis

a common anatomic variant of the mesenteric arterial anatomy is
.
a) celiac artery + SMA originate from posterior AO
b) celiac axis + SMA share a common trunk
c) SMA + IMA share a common trunk
d) celiac artery is absent; liver, stomach, spleen are supplied w/blood from the IMA
b. celiac axis + SMA share a common trunk

the normal flow profile within the aorta is
.
a) continuous flow
b) recoil flow
c) plug flow
d) phasic flow
c. plug flow

![<p>where is the hepatic artery</p><p>.</p><p>[not seen in this plane]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/504c9033-e7c6-4031-a0ae-7b265b279f47.png)
where is the hepatic artery
.
[not seen in this plane]
not seen in this plane

as pressure increases, resistance must ____ to maintain constant flow volume
.
ΔP = Q × R (Pressure = Flow × Resistance)
.
If resistance increases, either
pressure must increase to maintain flow
flow rate must reduce to maintain pressure
.
a) increase
b) resistance does not vary related to pressure + flow volume
c) stay constant
d) decrease
a. increase

![<p>find the right renal vein</p><p>.</p><p>[has to be on the IVC]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5adbc8e1-39b5-4de0-b0fe-537313dcc040.png)
find the right renal vein
.
[has to be on the IVC]
has to be on the IVC
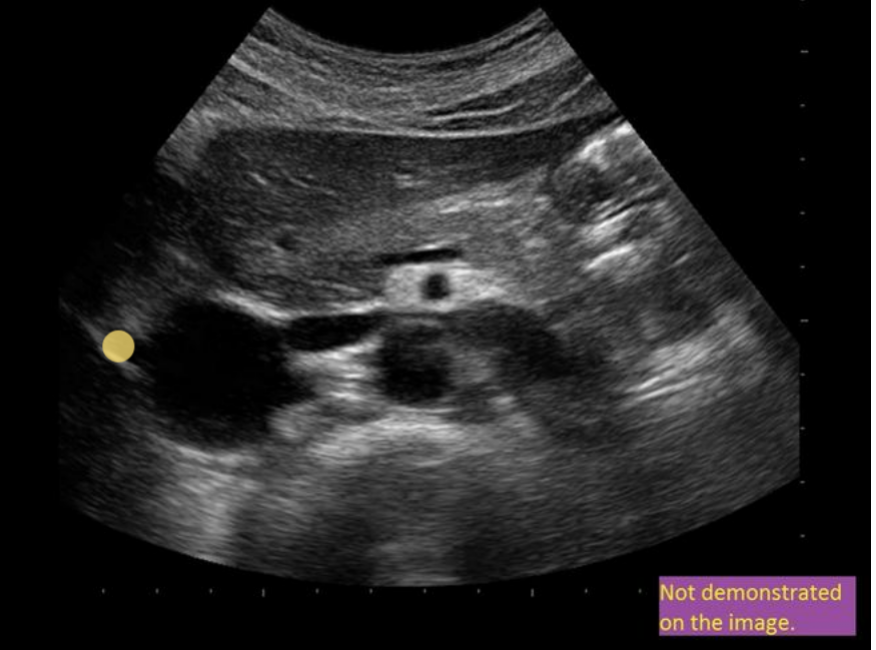
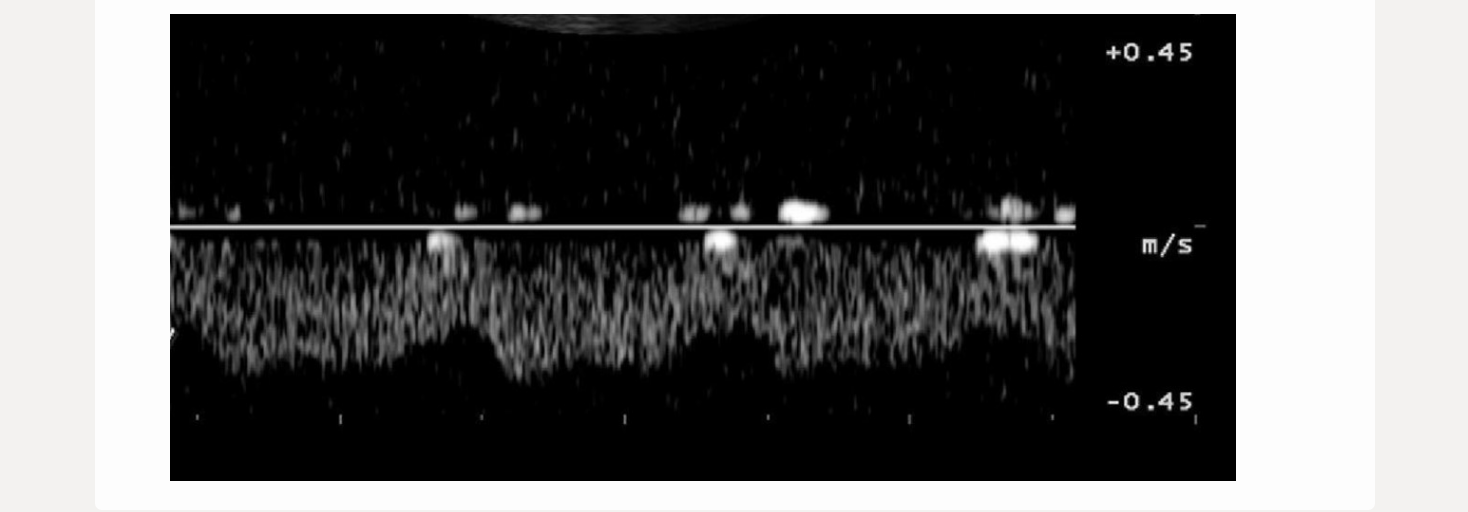
the waveform from an abdominal vessel displays what 2 characteristics
.
a) flow reversal during augmentation
b) flow reversal during diastole
c) mild phasicity + pulsatility
d) triphasic flow + no respiratory variation
c. mild phasicity + pulsatility

which factors are related to potential hemodynamic changes within a vessel
.
a) vessel length + blood viscosity, but not vessel radius
b) blood viscosity + vessel radius, but not vessel length
c) vessel length + radius, but not blood viscosity
d) vessel length, radius, and viscosity
d. vessel length, radius, and viscosity
which abdominal vessel arises from the anterior AO surface approximately 2cm distal to the celiac axis
.
a) common hepatic artery
b) superior mesenteric artery
c) gastroduodenal artery
d) inferior mesenteric artery
b. superior mesenteric artery
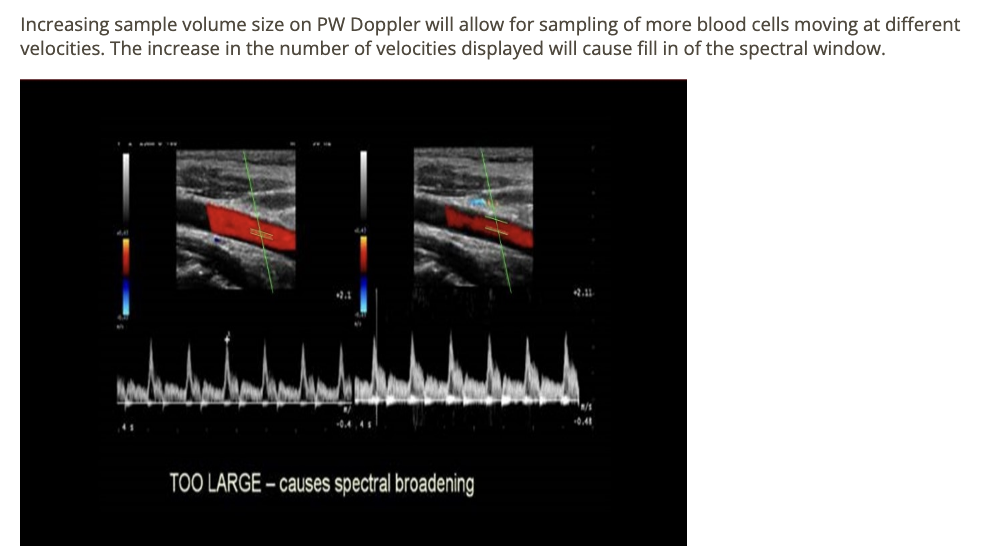
which increases spectral broadening [stronger PW signals]
.
a) increased wall filter
b) increased PRF
c) more laminar flow
d) increased sample volume size
d. increased sample volume size
the _____ suplies arterial blood to the small intestines + proximal colon
.
the _____ supplies blood to the distal colon
.
a) GDA; SMA
b) SMA; IMA
c) celiac axis; SMA
d) LGastricA; IMA
b. SMA; IMA
where should the doppler sample be placed to obtain the highest velocity when evaluating laminar flow
.
a) in vessel center
b) adjacent to anterior wall
c) varies w/type of vessel being evaluated
d) adjacent to posterior wll
a. in vessel center

![<p>which describes a normal renal artery waveform</p><p>.</p><p>a) low resistance w/increased diastolic flow</p><p>b) increased diastolic flow reversal</p><p>c) biphasic w/mild diastolic flow reversal</p><p>d) pulsus alternans [methodical variation in peak vel on every other beat]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8c8e8b11-eaa0-4474-8147-a50abca9736d.png)
which describes a normal renal artery waveform
.
a) low resistance w/increased diastolic flow
b) increased diastolic flow reversal
c) biphasic w/mild diastolic flow reversal
d) pulsus alternans [methodical variation in peak vel on every other beat]
a. low resistance w/increased diastolic flow

which is directly related to the calculated peak doppler velocity in an artery
.
a) doppler shift frequency
b) vessel radius
c) sin of cursor angle
d) flow volume
a. doppler shift frequency
bradycardia = heart rate <xxx BPM
.
a) 45
b) 50
c) 60
d) 65
. tachycardia = >100 BPM
c. 60
a mesenteric [SMA] to aortic ratio is normal when it is
.
a) >1.0
b) 1.0 or less
c) >3.0 [stenosis]
d) <3.0
b. 1.0 or less

![<p>find the left renal artery</p><p>.</p><p>[IVC is on the RIGHT side of AO]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a0616f87-f54d-442a-b437-2245e19cdc6b.png)
find the left renal artery
.
[IVC is on the RIGHT side of AO]
IVC is on the RIGHT side of AO
the release of norepinephrine has what effect on the arterioles
.
. I NEED TO INCREASE BLOOD PRESSURE
.
a) decreased flow resistance
b) stenosis
c) vasoconstriction
d) vasodilation
c. vasoconstriction

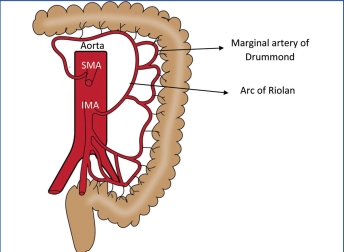
where is the arc of Riolan found
.
+ marginal artery of drummond connect x + x through the x as a collateral pathway
.
a) at popliteal fossa
b) in kidney
c) in brain
d) in mesentery
d. in mesentery

in cases of interrupted IVC, how does blood from the distal IVC and lower extremities get back to the right atrium
.
a) umbilical vein = collateral + empties into portal system
b) azygos vein = collateral + empties into SVC
c) pelvic AV malformation needs to be present at birth to survive
d) iliac veins empty directly into renal veins
b. azygous vein = collateral + empties into SVC
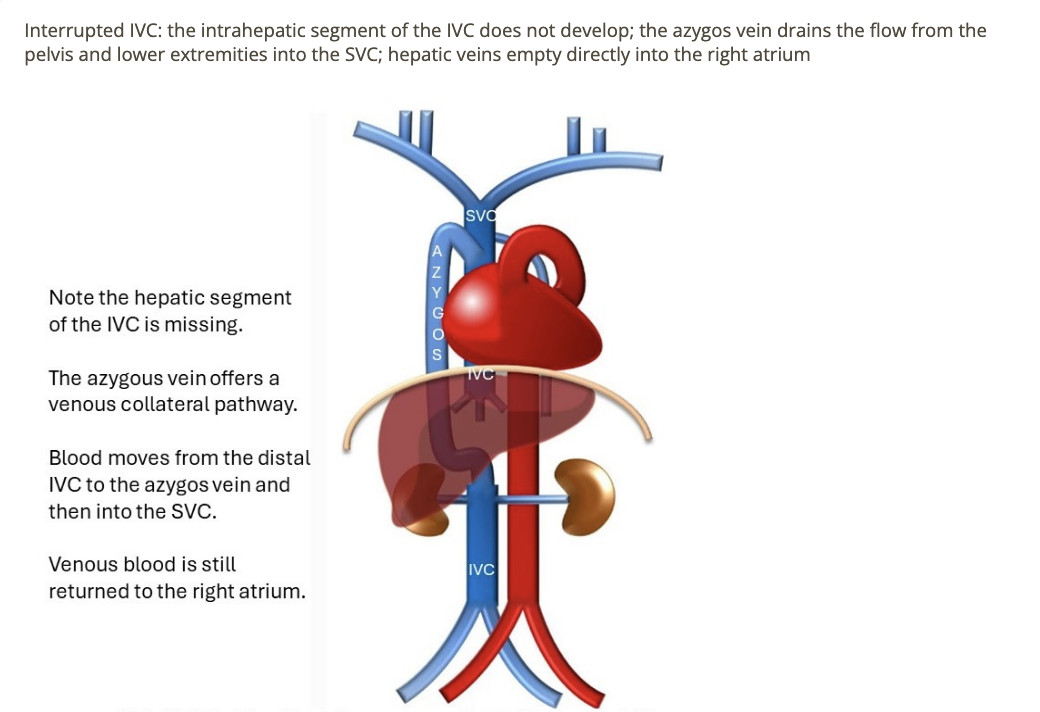
which is about IVC is correct
.
a) IVC normally maintains a relatively constant diameter w/respiration
b) IVC = most posterior vessel in abdomen
c) IVC empties blood into left atrium
d) congestive heart failure + pulmonary HTN can cause IVC dilation
d. congestive heart failure + pulmonary HTN can cause IVC dilation

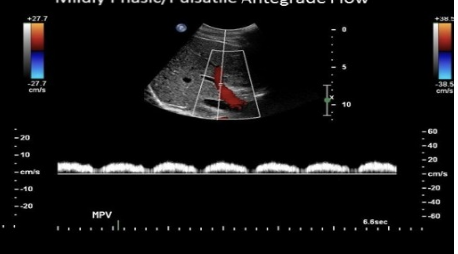
which describes normal doppler waveform in the portal vein
.
a) mild pulsatility w/respiratory variation
b) blunted w/respiratory variation
c) prominent respiratory variation + mild pulsatility
d) moderately pulsatile flow due to vessel proximity to heart
a. mild pulsatility w/respiratory variation
![<p>what is the most common [1/3] normal variant in renal artery anatomy </p><p>.</p><p>a) duplicated renal arteries</p><p>b) no left renal artery</p><p>c) right renal artery courses anterior into IVC</p><p>d) no right renal artery</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0effa5a3-9df3-47ed-935c-82b65e009898.png)
what is the most common [1/3] normal variant in renal artery anatomy
.
a) duplicated renal arteries
b) no left renal artery
c) right renal artery courses anterior into IVC
d) no right renal artery
d. duplicated renal arteries
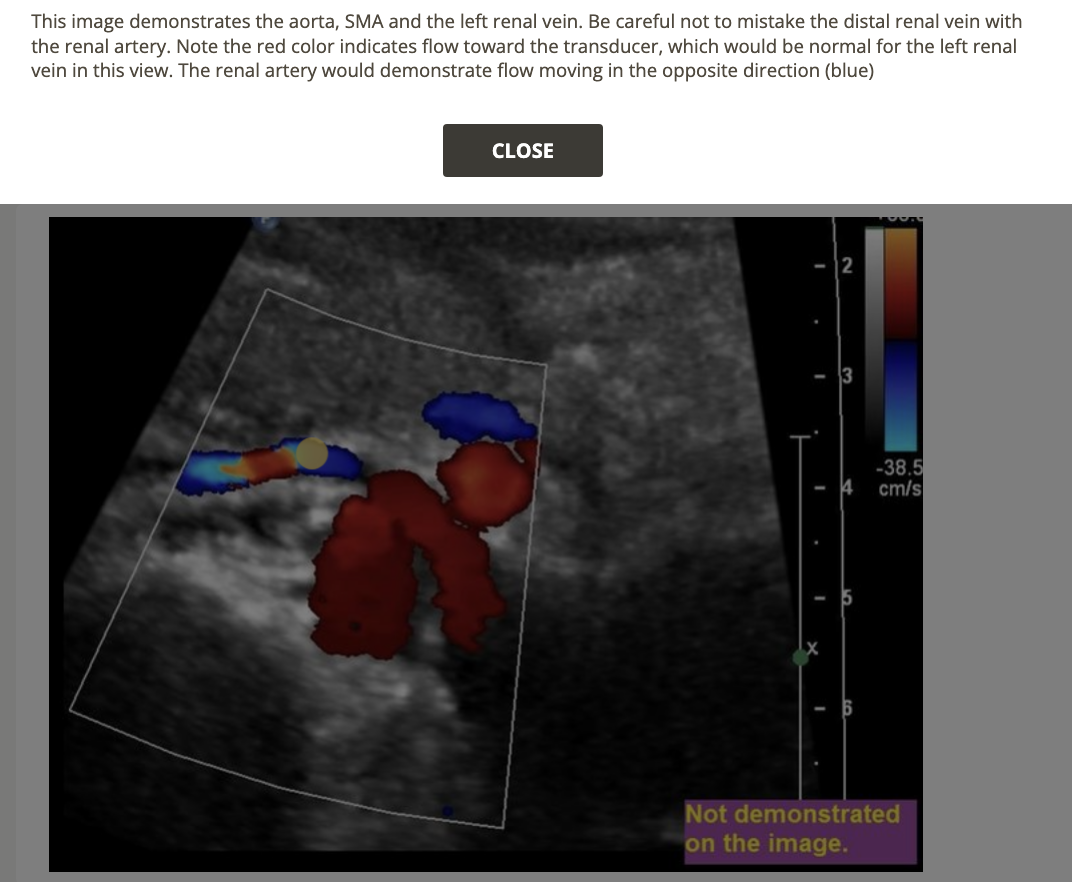
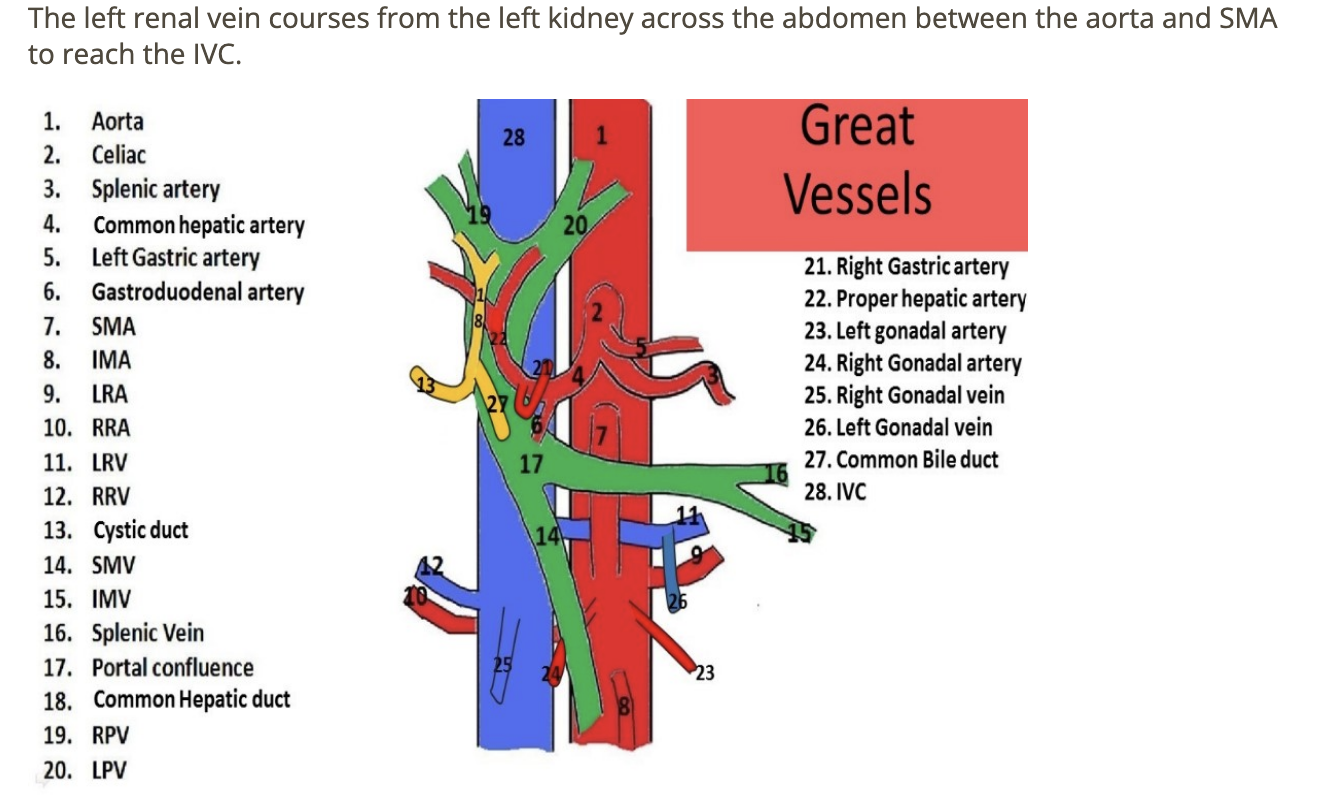
![<p>find the left renal vein</p><p>.</p><p>[left renal vein = between SMA + AO]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/522e32e3-0c34-4507-81e5-c8f625b0171c.png)
find the left renal vein
.
[left renal vein = between SMA + AO]
left renal vein = between SMA + AO