Bio 367 - sensory systems, internal anatomy
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
dendrites
Attach in or on sensory neurons, under seta. Sensory input triggers action potential on neuron membrane
axon
Path following nerve cell from which signal travels to brain
mechanoreceptor
receptor that must be moved
tactile mechanoreceptor
detect touch or air current
proprioceptors
detect position of body components relative to one another
tactile receptors
must be touched
stretch receptors
on inside of the body
auditory receptors
detect sound-producing air waves
Types of tactile receptors
tactile seta, hair row/plate, campaniform sensillum
Traits of tactile receptors
Seta hollow w/no pores, most soft and flexible (stiff=bristles). Detect air, water, & solid vibrations
Traits of hair row or plate
Found on cuticle between two adjacent sclerites, when sclerites touch/deflect hairs proprioceptors are stimulated
Traits of campaniform sensillum
Seta modified into dome, proprioceptors on cuticle must be pushed to detect pressure. On insect wings too
Types of non-touch proprioceptors
stretch organs
Example of internal stretch organ
Ventriculus lining in the gut detects being full of food
Example of subdermal stretch organ
Inside body wall, detects growth
Traits of stretch organs
Composed of cells, neural dendrites spread out & terminate at epithelial or cuticle layer
Types of auditory receptors
Tympanum, Johnston’s organ
Traits of tympanum
Contain chamber in exoskeleton oftentimes covered w/tympanic membrane & lined w/sensory neurons. On tibia & abdomen
Traits of Johnston’s organ
Open or closed chamber in antennae containing thousands of radially arranged mechanosensory units. Used to pick up wing beats/determine sex or species in mosquitos.
infrared organs
Pit in cuticular surface containing several infrared sensilli
Example of thermoregulation in fire beetles
Have an especially large array of IR sensilli so they can detect distant fires to lay eggs in trees
Gustatory chemoreceptors
liquid chemicals, taste
Olfactory chemoreceptors
gas chemicals, smell
Traits of Gustatory chemoreceptors
Hollow seta with a single terminal pore that liquid enters. Chemicals picked up by sensory neuron receptors on dendrite.
Traits of Olfactory chemoreceptors
Hollow seta w/multiple pores that gas enters, then diffuses into ECM and is picked up by receptors on sensory neuron dendrites inside seta
photoreceptors
visual receptors that pick up light
Apposition eye
Typical compound eye. High resolution, low light sensitivity because small lenses are separated by pigments, panoramic view due to array of ommatidia
Role of ommatidia
Each resolves its own image and brain stitches them together to make a high resolution image. More ommatidia=better color, more 3D, clearer
Structure of Apposition eye
Each ommatidia has: 1 cuticular lens, 8 retinula cells, rhabdomeres
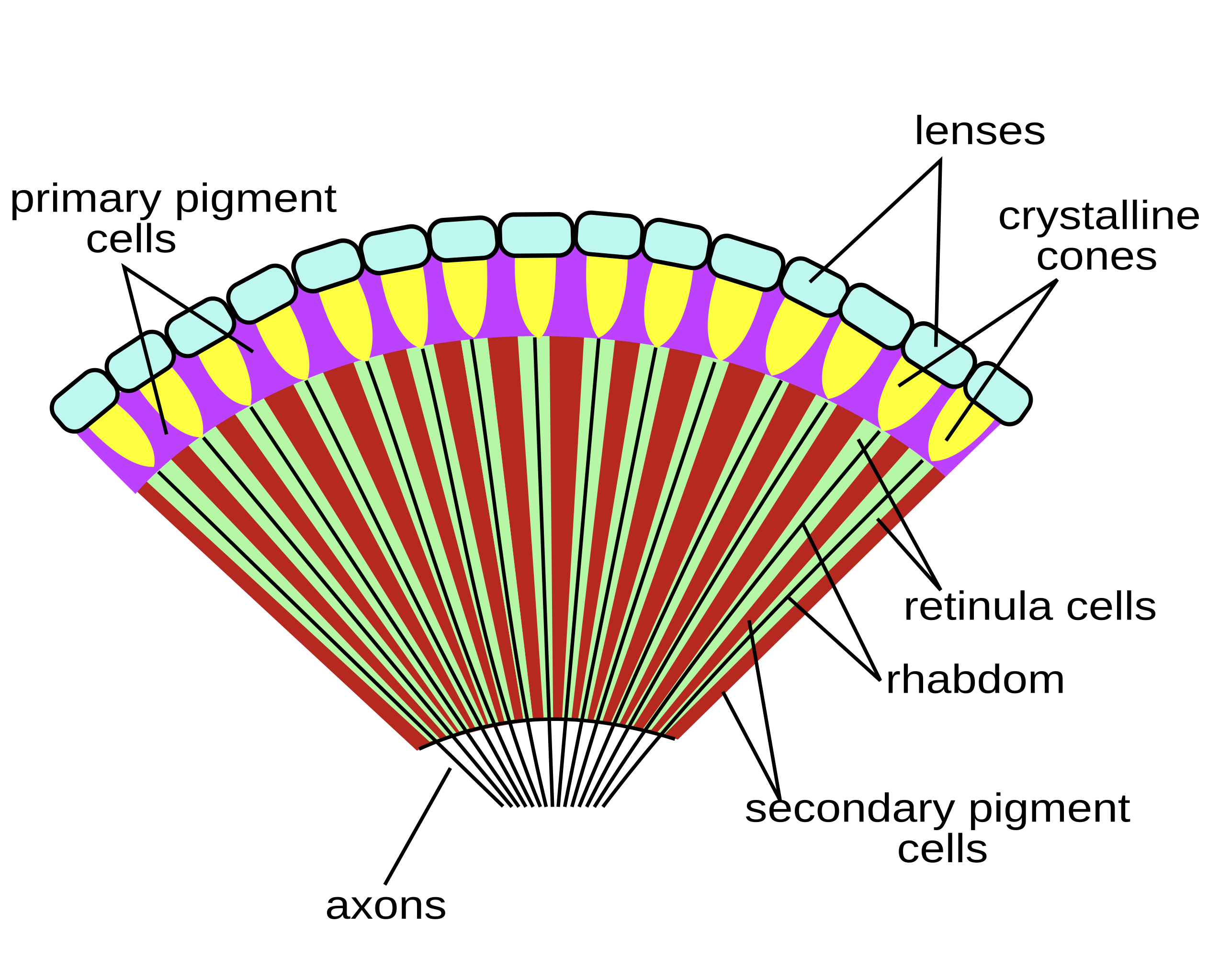
Apposition compound eye
cuticular lens
cornea, directs light into eye
retinula cells
light directed here, arranged like petals of a flower
rhabdomeres
8 rhabdomeres=rhabdom, microtubules on retinula cells w/rhodopsin.
What’s the difference of rhabdoms in a nocturnal vs diurnal bee?
Nocturnal bees have larger rhabdoms with more SA to better absorb light. Pigments surround retinula cells to cut of light between ommatidium and deters it from bouncing out, which helps with light absorption
Light into vision steps
Light enters lens, stimulates optical pigments in rhabdomeres, changes pigment shape from cis to trans, excitation in retinula cell membrane travels along axons of neurons of retinula cells
Color vision (most have rhodopsin)
Absorb a wide range of electromagnetic frequencies on UV spectrum, some are biochromatic & cannot see many colors
trichromatic
bees & butterflies, can see wider ranges of colors due to three visual pigments
Optical superposition eye
Modified compound eye for changing light conditions and lower resolution, in nocturnal insects
Sensing polarized light
Longitudinally twisted ommatidia descatter light waves. Rhabdoms rotate through length of ommatidium to catch scattered light coming at different angles
Structure of Optical Superposition Eye
Visual pigments missing from some pigment cell clusters so light can pass through ommatidium
Modified Optical Superposition eye
High light absorption and sensitivity when light is needed, or vice versa to change with insect needs. In insects active at crepuscular hours or ones that go into dark environments
Structure of Modified Optical Superposition eye
Mobile pigments of certain pigment cells can block light between ommatidium to increase resolution, OR migrate back to allow light between ommatidium increasing light capture
Stemma
Group of simple eyes that work collectively, on side of head of holometabolous larvae, structurally the same as one ommatidium. High light sensitivity w/low resolving power
Structure of Stemma
Lens (cornea), one rhabdom, pigment cells surrounding retinula cells

Stemma
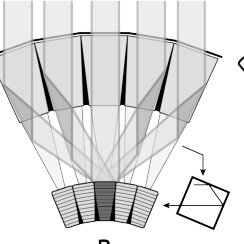
Optical Superposition eye
Structure of Ocellus
Lens (cornea), many rhabdoms, pigment cells surrounding 8 retinula cells, 1 lens for all rhabdoms
Ocellus
Group of simple eyes that work collectively in addition to compound eyes, sensitive in low-light & subtle changes, very low resolution. Horizon detectors & register changes in intensity that effect diurnal behavioral rhythms

ocellus
dermal photoreceptors
Respond to light only-not an optical system & may be present in those that lack eyes. Determine day/night, position relative to shade, circadian rhythms.
Insect circulatory system
Open with a series of hearts and open-ended blood vessels. When heart contracts blood is pushed toward vessel openings
hemocoel
body cavity containing bulk of hemolymph and few vessels, has muscles that push food in foregut but not for nutrient digestion in midgut
Coelomate
In humans, muscles surround all areas of body responsible for food intake, digestion, and excretion
Where does circulation start?
Hemolymph is pulled through ostia (openings) of dorsal blood vessels. Hearts push blood anterior from heart to heart, then out of vessel into head
What happens when hemolymph leaves the head?
Blood flows into antennae, eyes, & thorax. Diaphragm pushes blood posterior through wings, antennae, legs, and back into hemocoel, to re-enter ostia of hearts.
Hemolymph makeup
Water, ions, hormones, ventriculus digestive products, trehalose (blood sugar), hemocytes (blood cells)
prohemocytes
hemocyte stem cells, low abundance
granulocytes
initial detection of foreign invaders, encapsulation (proteins block invaders signals)
plasmatocytes
phagocytosis of invasive pathogens, parasitic eggs, multicellular organisms
adipohemocytes
store lipids
What is circulated?
Hormones, digestive nutrients, hemocytes, ions, water, not respiratory gasses
What is stored?
Water, ions, allelochemicals and other toxins
allelochemicals
Chemicals stored in plants for defense, example of reflexive bleeding in lady bugs
Tracheal system
for gas exchange (respiration)
Tracheal system organization
spiracle, atrium, tracheae, tracheoles, aeriferous tracheae
Spiracle
can close and open similar to stomata, may be able to filter
atrium
pocket for air to enter inside spiracle, filter and valve to prevent water loss, invasion, etc.
trachea(e)
tracheal tubes w/taenidia, molted
tracheoles
cellular, fluid filled, no taenidia, not molted
aeriferous tracheae
spirals into hemolymph around ovaries, is the exception to gas being transported to a part of the hemocoel
Pre-oral cavity consists of…
Buccal cavity (food mixes w/saliva), mouthparts (manipulation), saliva, pharynx
role of saliva
Has enzymes for carb breakdown, mucus, anesthetic in some
role of pharynx
swallowing organ, pushes food into esophagus
Foregut consists of…
esophagus, crop, proventriculus
Esophagus
transfers food from pharynx
crop
stores food, vestigial or absent in fluid feeders
proventriculus
grinding, vestigial or absent in fluid feeders
Midgut consists of…
gastric caecae, ventriculus, endoperitrophic space, ectoperitrophic space, endothelium, malpighian tubules
gastric caecae
produce & circulate digestive enzymes
ventriculus
absorption & digestion, lined by endothelium cells, much longer in fluid feeders
peritrophic membrane
divides endo & ectoperitrophic space to protect from invaders, slightly sclerotized
endoperitrophic space
enzyme digestion
ectoperitrophic space
digested nutrients enter this space
endothelium
absorb digested nutrients
malpighian tubules
osmoregulation while ions, water, and vitamins flow past
Hindgut consists of…
ileum, rectum, colon
ileum
contains beneficial microbes, final absorption of water, salts, vitamins & microbe produced fatty-acids
rectum
final compaction of frass and excretion
colon
where frass compaction starts
Cryptorephretic system for excretion
In insects with dry diets, very efficient water conservation and drying of feces. Distal ends of malpighian tubules attach to rectal pads
Filter chamber
Efficient water and sugar elimination in Hemiptera, midgut attaches to itself at junction of hindgut
Glowing malpighian tubules - glow worms
Produce light via chemical reaction to attract insects. Sticky, high protein saliva traps flying insects
Fat bodies
Organs composed of adipocytes (fat)
Fat bodies function
Carb, lipids, nitrogenous compound metabolism. Stores glycogen, lipids, proteins. Synthesis and regulation of blood sugar. Stores uric acid and sequesters allelochemicals for defense.
apophyses
flexible joint and striated muscle attachment sites that contain resilin
resilin
molecule that gives spring of wings and jump to insects
apodemes
rigid apophyses
tentorium
apophyses in head
visceral muscle
Surround tubes & ducts, dorsal & ventral diaphragm, peristalsis (moved food through digestive tract)
segmental muscle
Telescoping of body, molting and locomotion in larval insects