Lecture 9: Abdomen
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
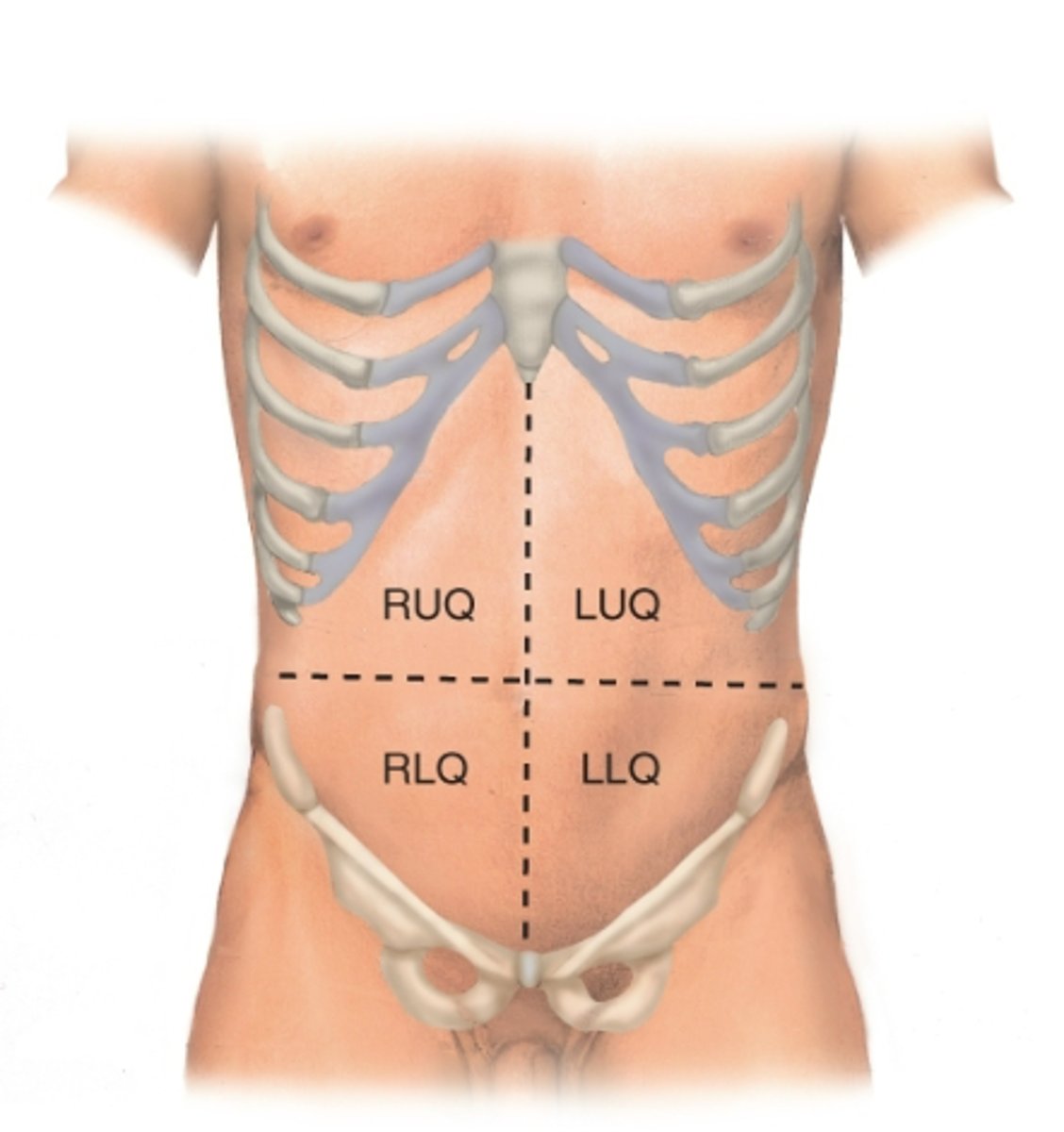
What are the four quadrants of the abdomen?
RUQ, LUQ, RLQ, LLQ
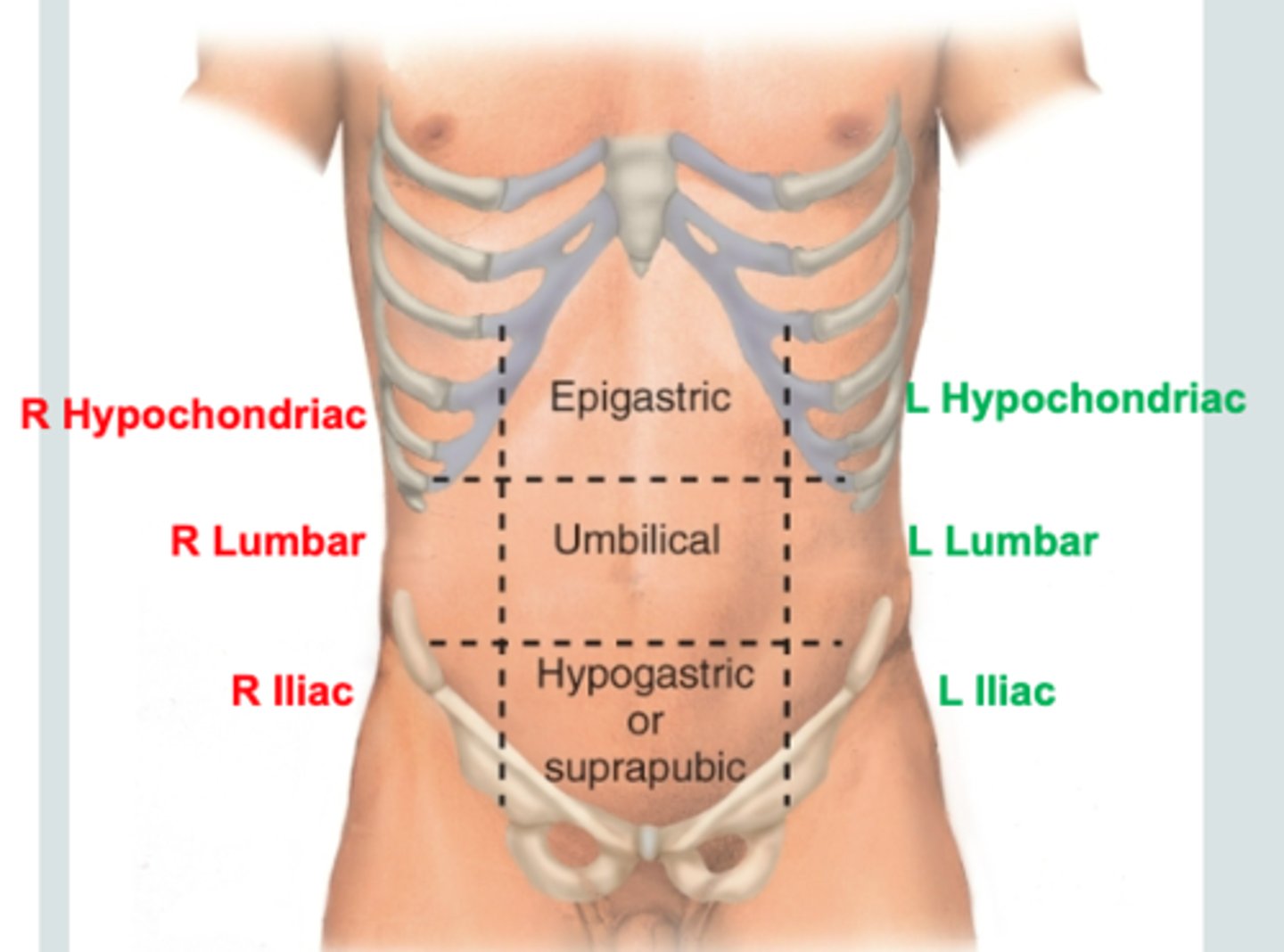
What are the nine regions of the abdomen?
- right hypochondriac
- epigastric
- left hypochondriac
- right lumbar
- umbilical
- left lumbar
- right inguinal
- hypogastric
- left inguinal
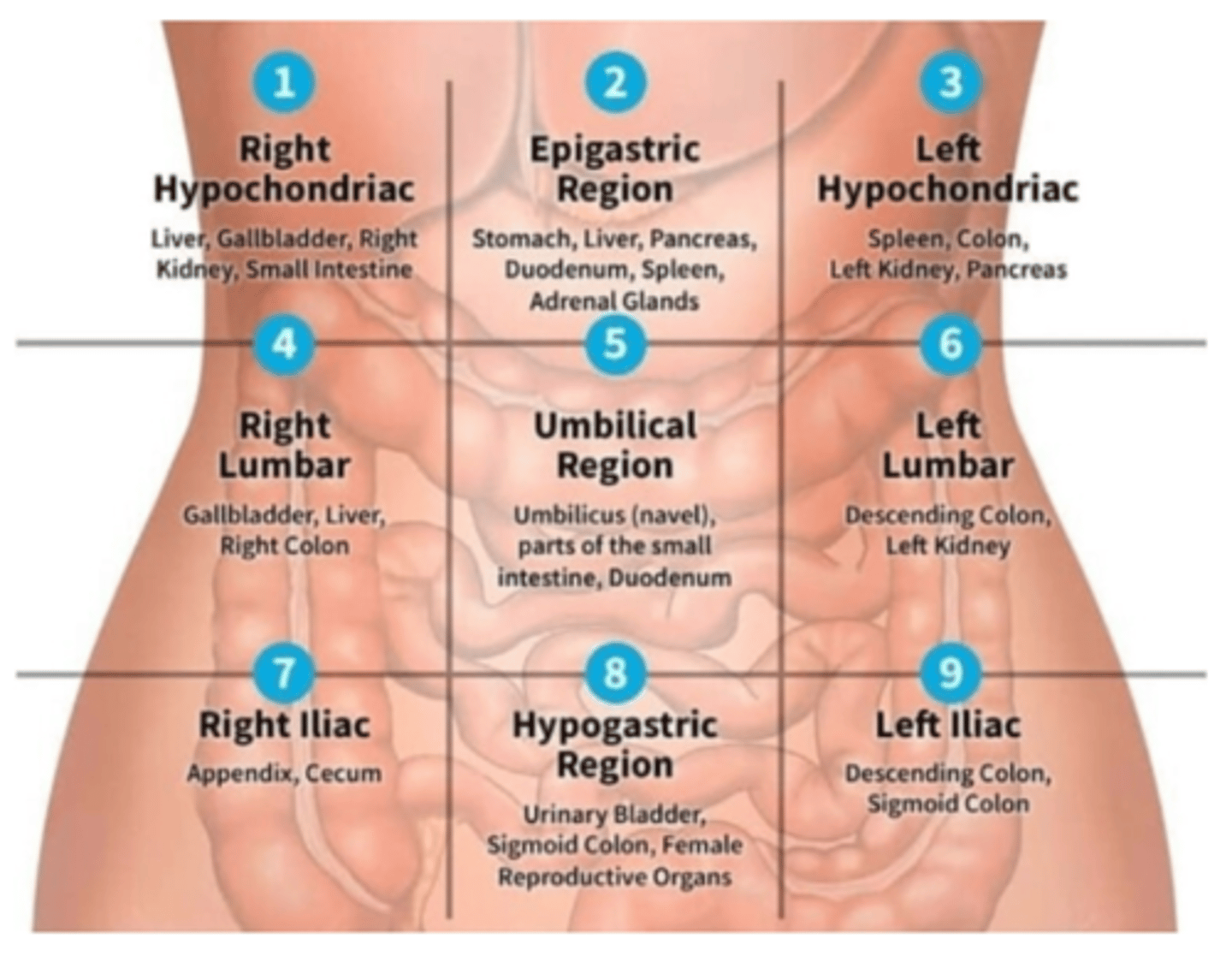
What are the structures within the right hypochondriac section? (4)
liver, gallbladder, right kidney, small intestine
What are the structures in the epigastric region? (6)
stomach, liver, pancreas, duodenum, spleen, and adrenal glands
What are the structures in the left hypochondriac region? (4)
spleen, colon, left kidney, pancreas
What are the structures in the right lumbar region? (3)
gallbladder, liver, and right colon
What are the structures sin the umbilical region? (3)
umbilicus (navel), parts of the small intestine, duodenum
What are the structures in the left lumbar? (2)
descending colon, left kidney
What are the structures in the right iliac? (2)
appendix, cecum
What are the structure in the hypogastric region? (3)
urinary bladder, sigmoid colon, female reproductive organs
What are the structures in the left iliac region? (2)
descending colon, sigmoid colon
OVERVIEW: What are all the structures in each abdominal section?
What are the structures in the Right Upper Quadrant of the abdomen? (6)
liver, gallbladder, pylorus, duodenum, hepatic flexure, head of pancreas
What are the structures in the Left Upper Quadrant of the abdomen? (4)
Spleen, splenic flexure, stomach, body and tail of pancreas
What are the structures in the Right Lower Quadrant of the abdomen? (5)
Cecum, appendix, ascending colon, terminal ileum, right ovary
What are the structures in the Left Lower Quadrant of the abdomen? (3)
Sigmoid colon, descending colon, left ovary
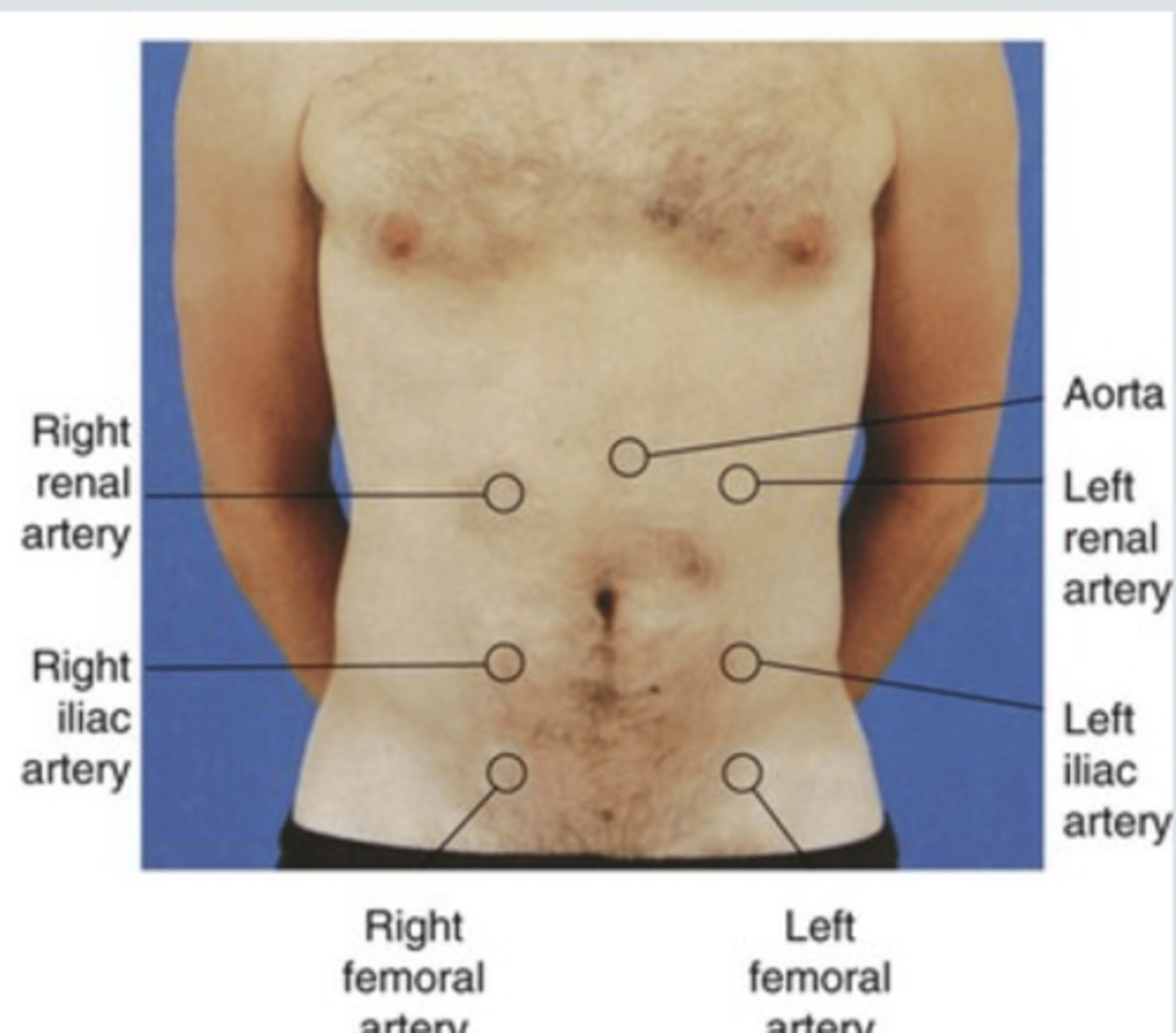
What are the major arteries of the abdomen? (4)
aorta, renal, iliac, and femoral
What are four types of abdominal pain?
- viceral
- parietal
- colicky
- referred
_____________: Pain that originates at different sites but shares innervation from the same spinal level
referred pain
What is the order of the abdominal exam? (6)
1. Inspection
2. Auscultation
3. Percussion
4. Light Palpation
5. Deep Palpation
6. Special tests
What is Cullen's sign?
periumbilical ecchymosis (brusing)
- abdominal wall hemorrhage
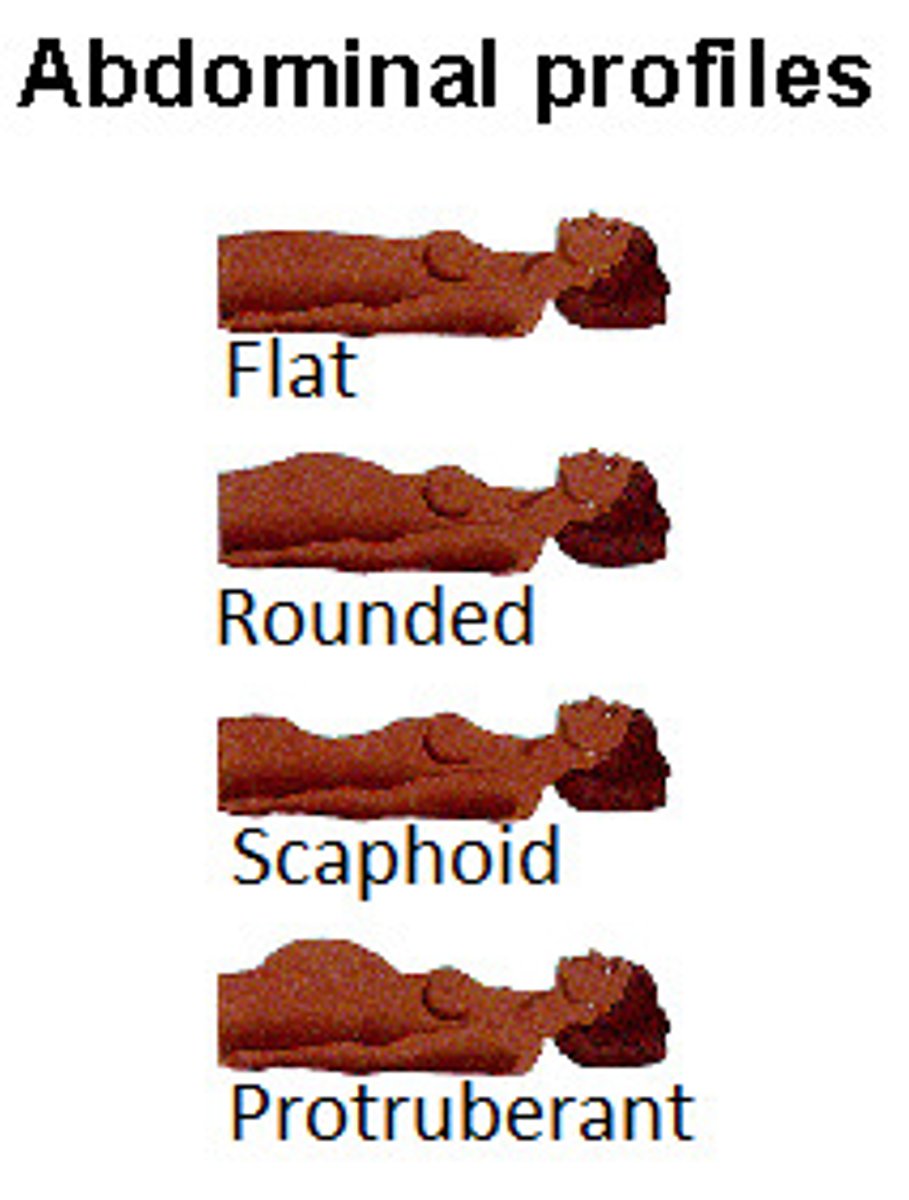
What are the four types of abdominal contour?
flat, rounded, scaphoid, protuberant
Always ___________ before palpating or percussing the abdomen.
auscultate
When auscultating the abdomen, Place the diaphragm over the abdomen to hear bowel sounds (borborygmi) which are long gurgles. Normal frequency of sound is ...
5 to 34 sounds per minute
Increased pulsations of the aorta or an increased pulse pressure may be a sign of an ...
abdominal aortic aneurysm
When percussing the abdomen, you should hear ________ over air-filled structures such as the stomach. You should hear ________ over solid organs, or you may hear ________ over an abdominal mass.
tympany, dullness, dullness
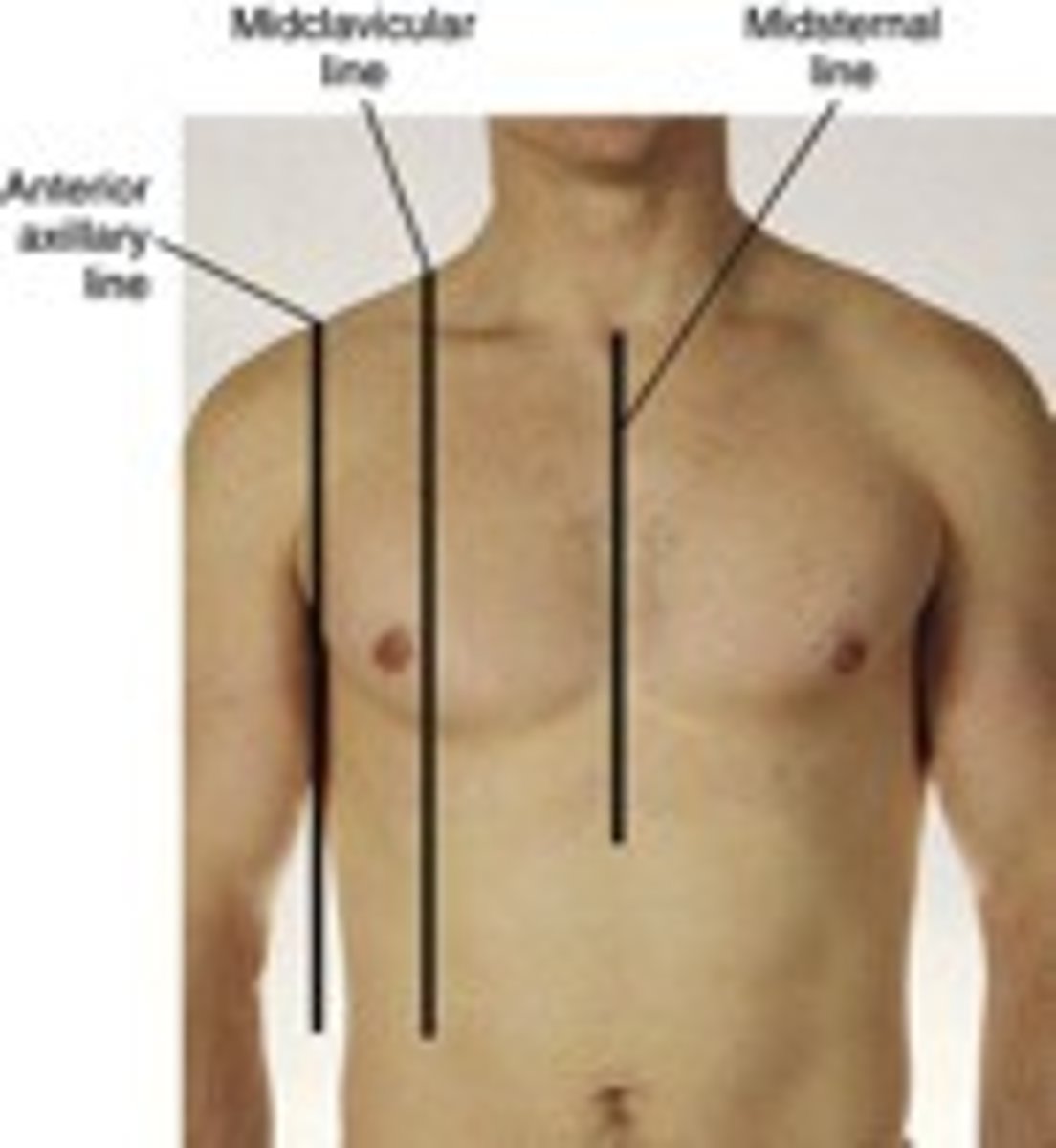
You percuss over the liver at the ____________________. How do you percuss the liver?
midclavicular line
- lightly percuss in the midclavicular line starting at the 3rd intercostal space (nipple line) from lung resonance until you hear dullness from the upper border of the liver (usually at the 5th intercostal space) - MARK THIS SPOT
- Percuss again starting from below the umbilicus on the midclavicular line until you hear dullness from the lower border of the liver- MARK THIS SPOT
- midclavicular percussion should be 6 -12 centimeters; longer than this indicates an enlarged liver (hepatomegaly)
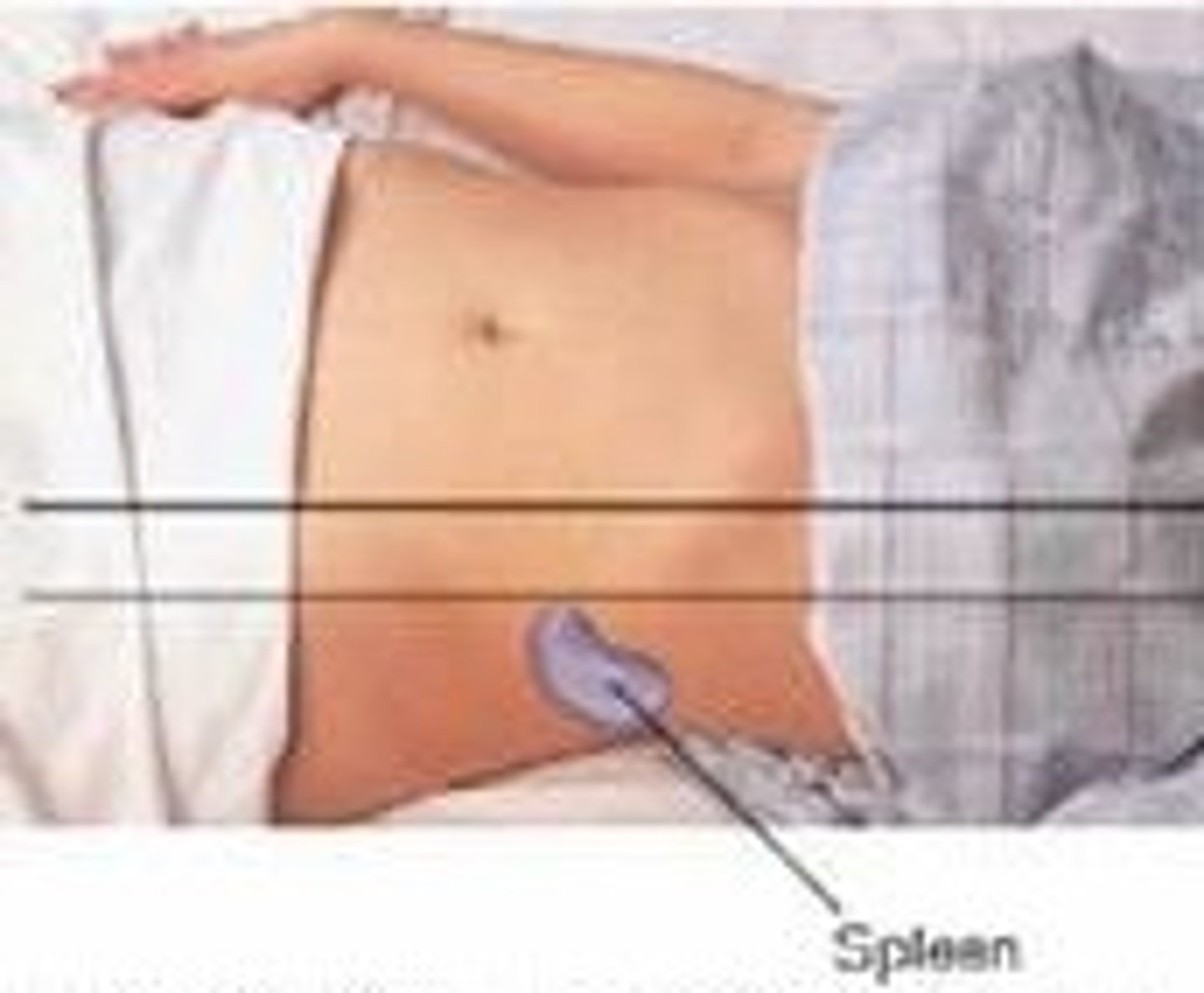
How do you percuss the spleen?
Percuss the lowest interspace in the left anterior axillary line. This area is usually tympanitic. Then have the patient take a deep breath and percuss again. IF the spleen is normal in size the percussion remains tympanitic. Shifting from tympany to dullness with inspiration suggest an enlarged spleen
When doing light palpations of the abdomen, what are you assessing for?
- identify any superficial organs or masses
- asses for voluntary guarding (patient consciously flinches when you touch) vs involuntary guarding (muscles spasm when you touch, but the patient cannot control the reaction)
When doing deep palpations of the abdomen, what are you assessing for?
asses for masses - note location, size, shape, consistency, tenderness, pulsations and any mobility with respiration or pressure
What is rebound tenderness?
occurs if pain increases when the examiner decreases the pressure against the abdomen
- apply firm pressure for several seconds to the abdomen with hand at right angles and fingers extended
- quickly release the pressure
What are some signs of peritonitis?
guarding
- patient voluntarily contracts the abdominal wall usually with a grimace. If the patient is distracted, the guarding may diminish
rigidity
- patient involuntarily contracts abdominal wall- persists over several examinations
rebound tenderness
- pain when examiner's hand is removed - "hurts more when you let go"
How do you palpate the liver?
using the left hand to support the back at the level of the 11th and 12th rib, the right-hand presses on the abdomen inferior to the border of the liver and continues to palpate superiorly until the liver border is palpated. Ask the patient to take a DEEP BREATH. This can illicit pain in liver or gallbladder disease and makes it easier to find the inferior border of the liver (the diaphragm lowering during deep inspiration forces the liver downward)
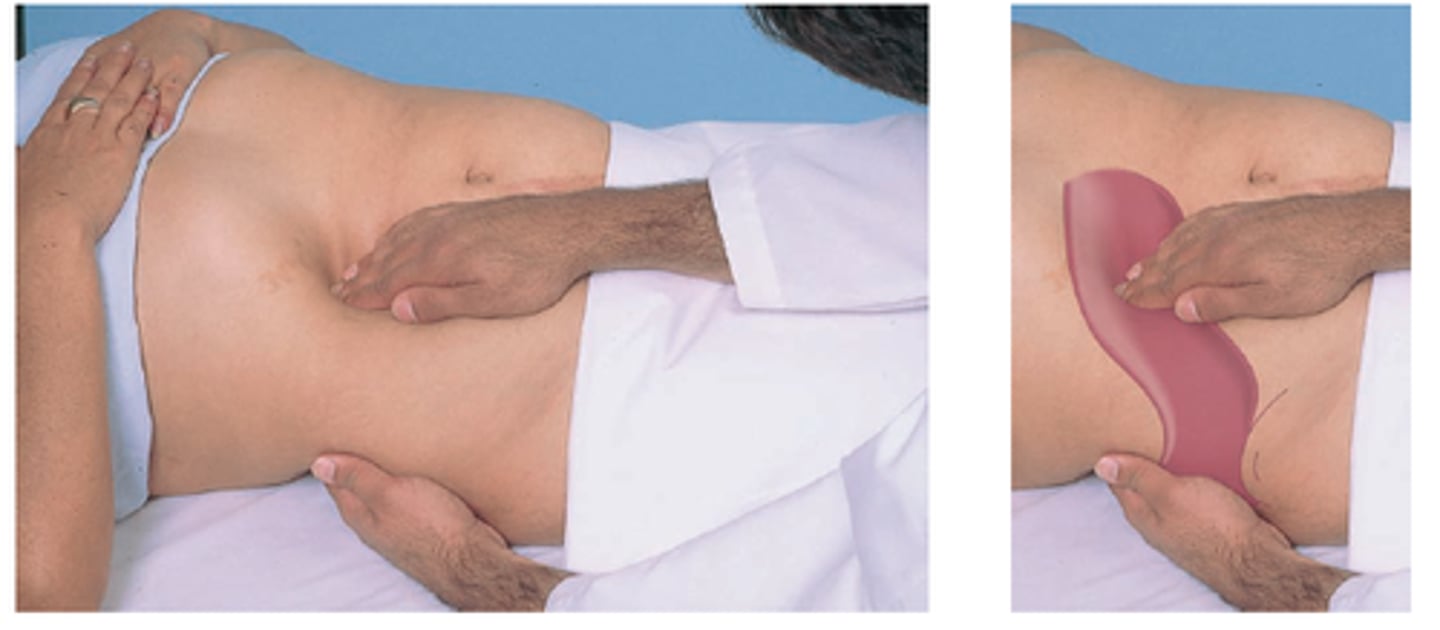
When it comes to palpating the liver, the _______________ is helpful if the patient is obese.
"hooking technique"
- place both hands side to side, on the right abdomen below the border of liver dullness
- press in with the fingers and go up toward the costal margin. Ask the patient to take a deep breath. The liver edge should be palpable under the finger pads of both hands
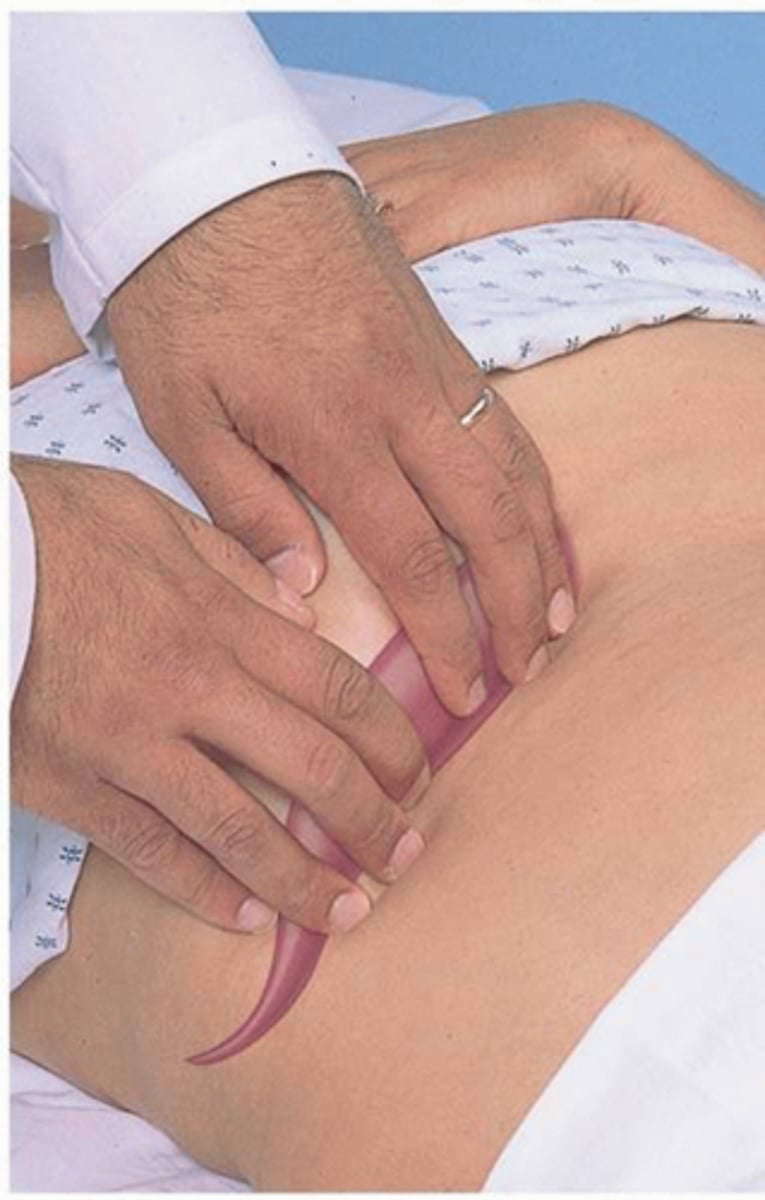
How do you palpate the spleen?
palpate the spleen with the left hand supporting the back and the right hand palpating the abdomen
- generally the spleen cannot be palpated this way even with deep inspiration. Palpating a splenic tip may indicate splenomegaly
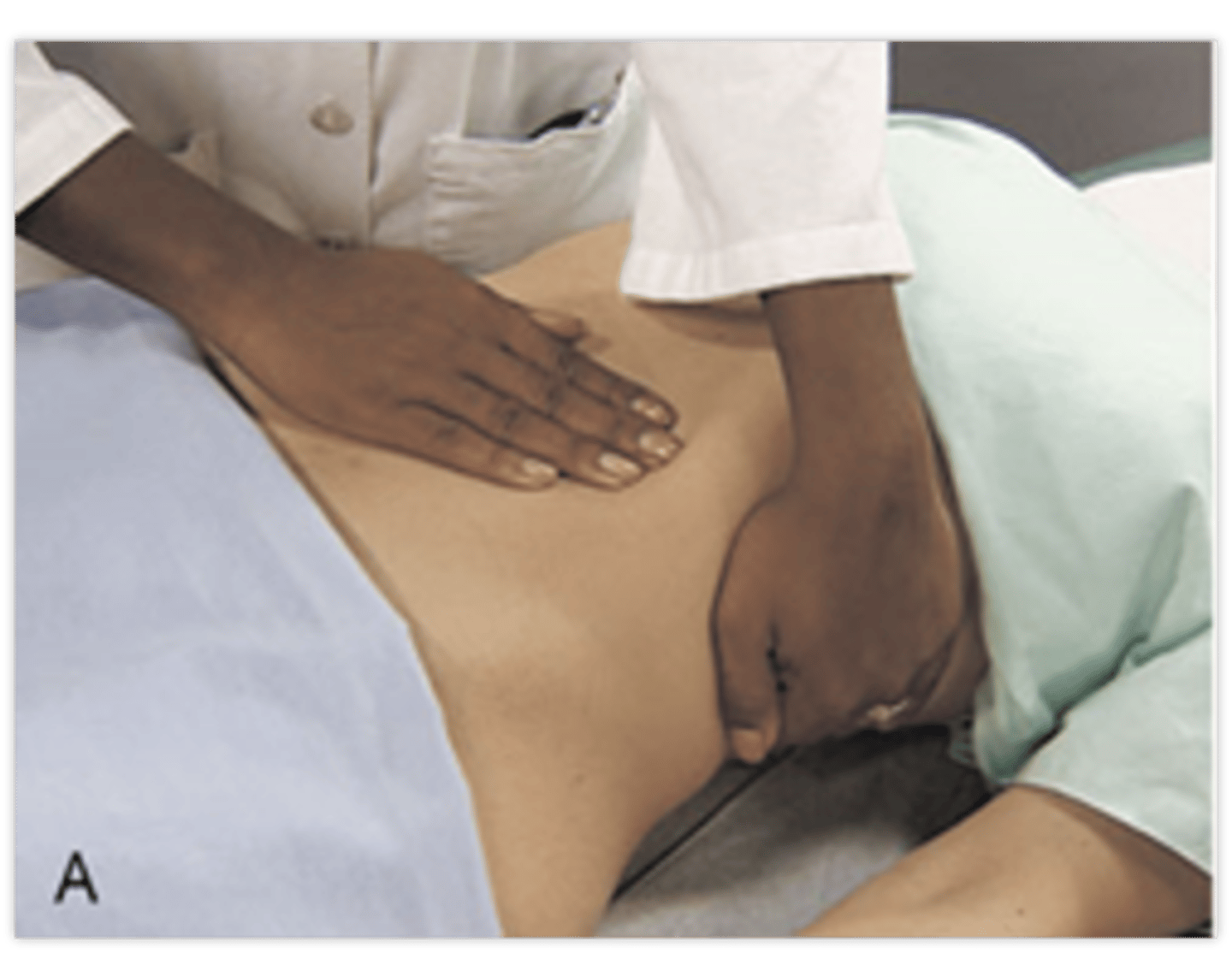
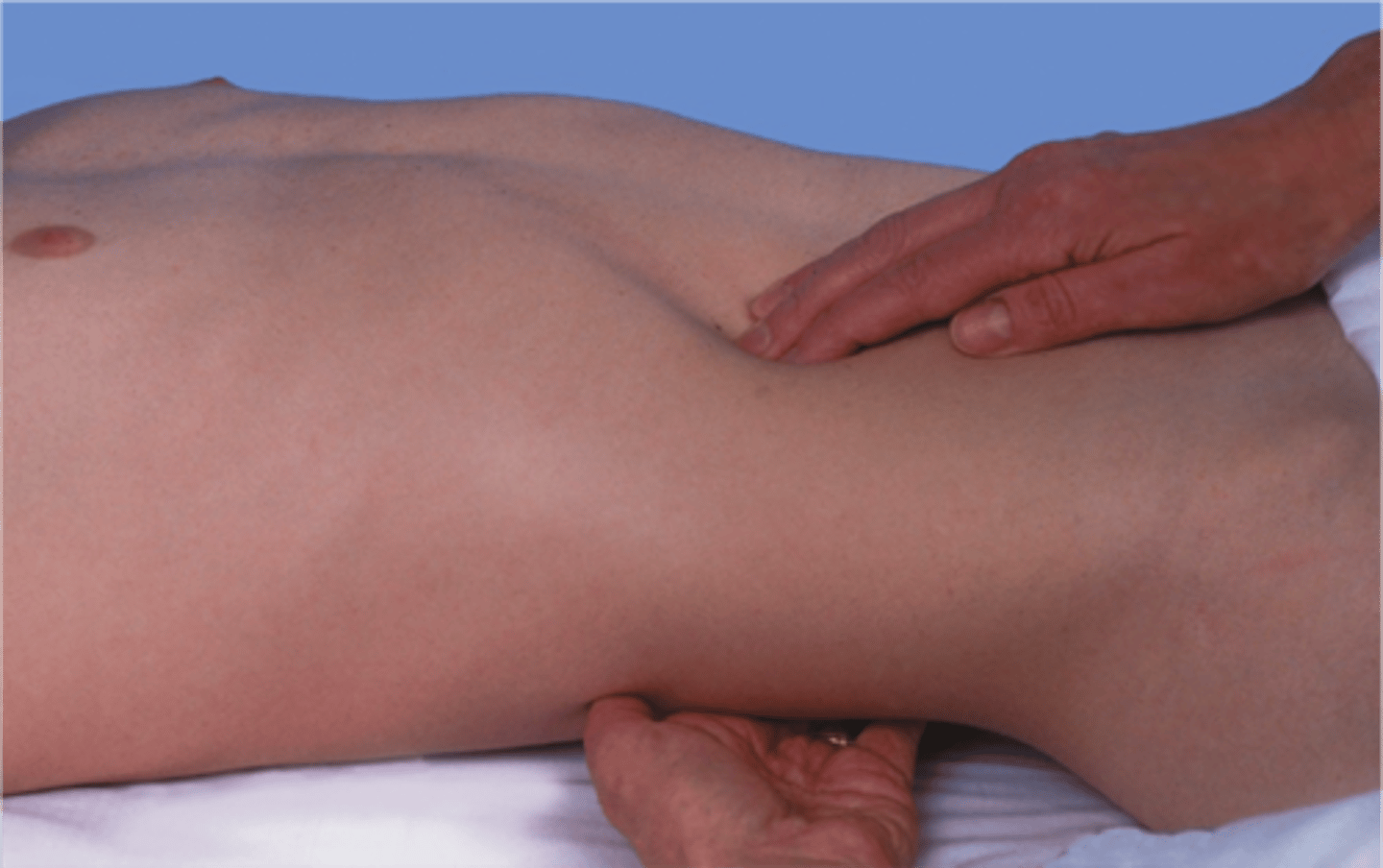
How do you palpate the kidneys?
Left kidney:
- move to the patient's left side. Place your right hand under the 12th rib. Lift up trying to displace the kidney anteriorly. Place your left hand in the left upper quadrant. Ask the patient to take a deep breath. At the peak of inspiration press your left hand deeply into the left upper quadrant trying to "capture" the kidney between your hands
Right kidney:
- return to the patient's right side. Use your left hand to lift the back while your right hand feels deeply into the right upper quadrant. Repeat the same steps as used for the left kidney
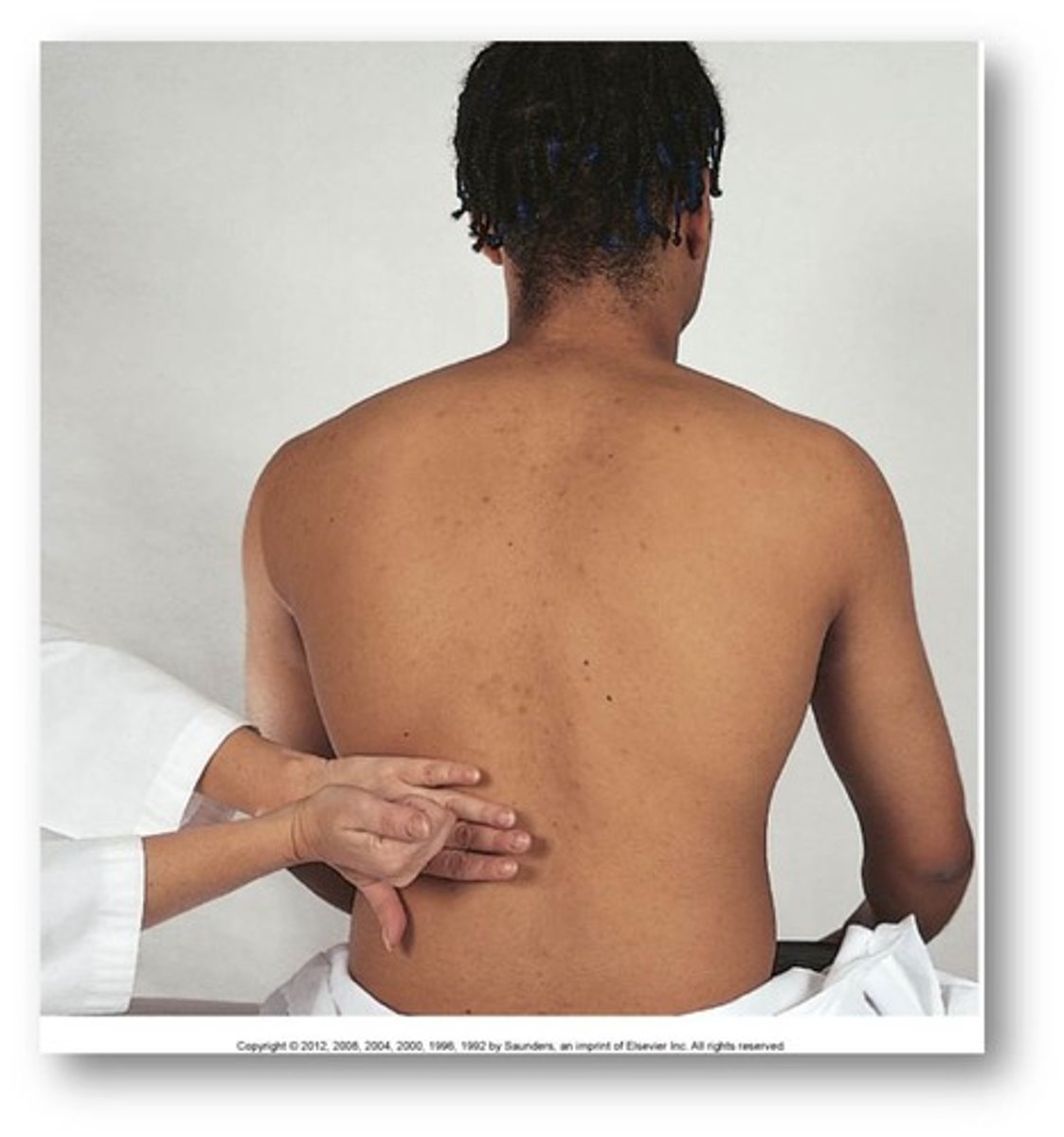
How do you test for kidney tenderness? (CVAT)
place a hand flat over the costovertebral angel (CVA) on each side of the back and use your other fist to hit your hand to assess for kidney tenderness
What is a normal width of an aorta?
< 3.5 cm
What is Murphy's sign? What is it indicative of?
halted inspiration with palpation under right costal margin
1. Ask the patient to exhale
2. Examiner places hand below costal margin on the right side at the mid-clavicular line
3. The patient is instructed to inspire
The patients stops breathing in and winces with a "catch" in breath is a positive Murphy's sign
A positive Murphy's sign is indicative for Acute cholecystitis
What is ascites? What is a suspicious sign?
fluid in the abdomen from diseases such as cancer
a protuberant abdomen with bulging flanks is suspicious for ascites
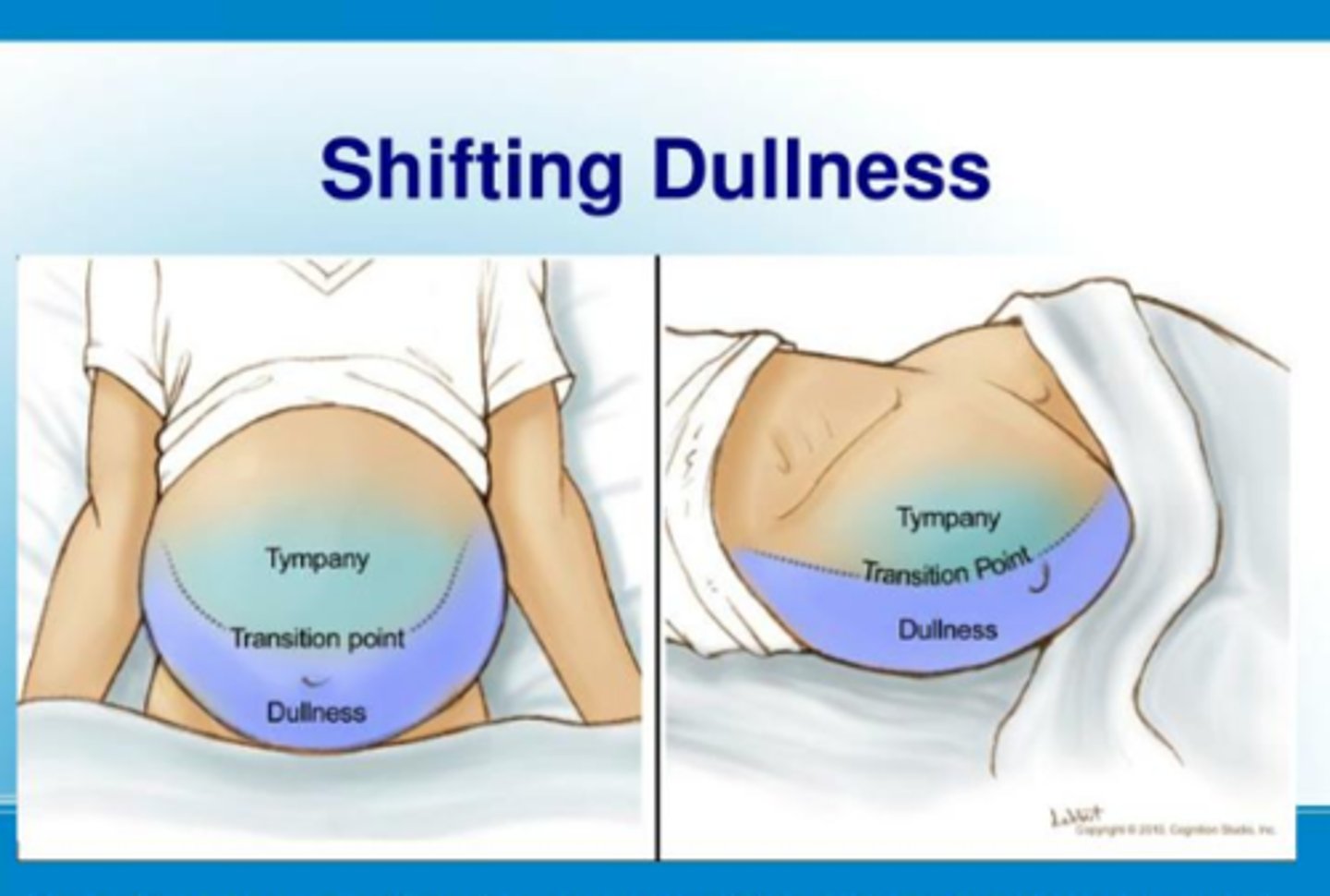
How do you test for ascites?
testing for shifting dullness
- after mapping out the areas of tympany and dullness, have the patient roll to one side. Remap the areas of tympany and dullness. In ascites there should be a shift due to free fluid moving with gravity
How do you test for a fluid wave?
Have the patient lay supine. Ask the patient or an assistant to press the edges of both hands firmly down the midline of the abdomen. This pressure helps to stop the transmission wave through fat. While you tap one flank sharply with your fingertips, feel on the opposite flank for an impulse transmitted through the fluid
How do you check for Rovsing's sign? What is a positive sign indicated of?
Check for involuntary guarding and rebound tenderness in the right lower quadrant. Perform a rectal examination ini both sexes and a pelvic examination in women
- if pain is elicited in the right lower quadrant, it is suggestive of appendicitis
What is the Psoas sign? What does a positive sign indicate?
pain elicited by extending the hip with the knee in full extension or by flexing the hip against resistance
A positive sign can indicate appendicitis
What is the Obturator sign?
Positive when there is pain on passive internal rotation of the hip with the right knee flexion
What is McBurney's point?
The RLQ location of the most tender area in the early stages of appendicitis