Portage A&P1 Module 6 Exam
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Explain two reasons why a woman with low levels of LH would not be able to become pregnant.
(1) LH acts on the ovary to cause ovulation to occur.
(2) LH causes progesterone release to facilitate potential fertilization of the egg and pregnancy.
Progesterone is a key hormone for the maintenance of pregnancy.
Would you expect a female to have testosterone in their bloodstream? Explain why or why not.
(1) Yes.
Both male and female bodies produce "all" the sex hormones. However, the ratios are different.
(2) The adrenal glands are largely responsible for producing this "opposite" hormone that the ovaries would not.
Explain the concept of positive feedback.
Give an example of a hormone that works through positive feedback.
1- Positive feedback is the action of a hormone increasing the production of that hormone. (This is the opposite of negative feedback).
2- One example is the action of oxytocin causing the uterus to contract during labor. Oxytocin enhances the effect of the uterus contractions, causing more oxytocin to be released.
The positive feedback loop is stopped once the baby is born and the uterus no longer needs to contract, stopping the production of oxytocin.
Explain the concept of negative feedback and how it helps to maintain homeostasis.
1- The effect or increased level of the hormone acts to shut down the continued release of the hormone.
2- The brain is constantly monitoring hormone levels to keep levels within a certain range or set-point (homeostasis). Negative feedback is a way of "turning off" hormone production when the desired level is achieved
Explain in detail how PTH and calcitonin work to maintain calcium balance.
Calcitonin: produced by the thyroid glands, deposits calcium into bone.
Calcitonin opposes the action of PTH. When the blood calcium level reaches the appropriate level through all these means, the parathyroid glands stop producing PTH through negative feedback.
PTH: produced by the parathyroid glands increase the amount of calcium in the blood.
PTH stimulates the increased absorption of calcium from the intestines. PTH retains calcium through excreting phosphate at the kidneys.
In the bones, PTH promotes the activity of osteoclasts to demineralize of the bone, increasing the amount of calcium in the blood.
Explain why it would be harmful to have an increased secretion of ACTH in someone who is diabetic.
ACTH controls the secretion of cortisol from the adrenal cortex. Increased levels of ACTH would cause increased levels of cortisol within the blood.
Cortisol increases blood glucose levels which will decrease the effectiveness of insulin treatments.
Aldosterone is involved in the regulation of sodium and potassium in the body. Explain how too much aldosterone could contribute to high blood pressure.
Aldosterone's primary target organ is the kidney, where it promotes renal absorption of sodium and renal excretion of potassium.
The blood sodium level is particularly important to the maintenance of blood pressure. Too much sodium causes retention of fluid and increases blood pressure. Therefore, too much aldosterone will cause increased and potentially high blood pressure.
Explain in detail why the thyroid becomes enlarged during an iodine deficiency
When there is a low level of thyroxin in the blood, the anterior pituitary continues to produce TSH. The thyroid responds by increasing in size and producing a goiter, but this increase in size is ineffective because active thyroxin cannot be produced without iodine
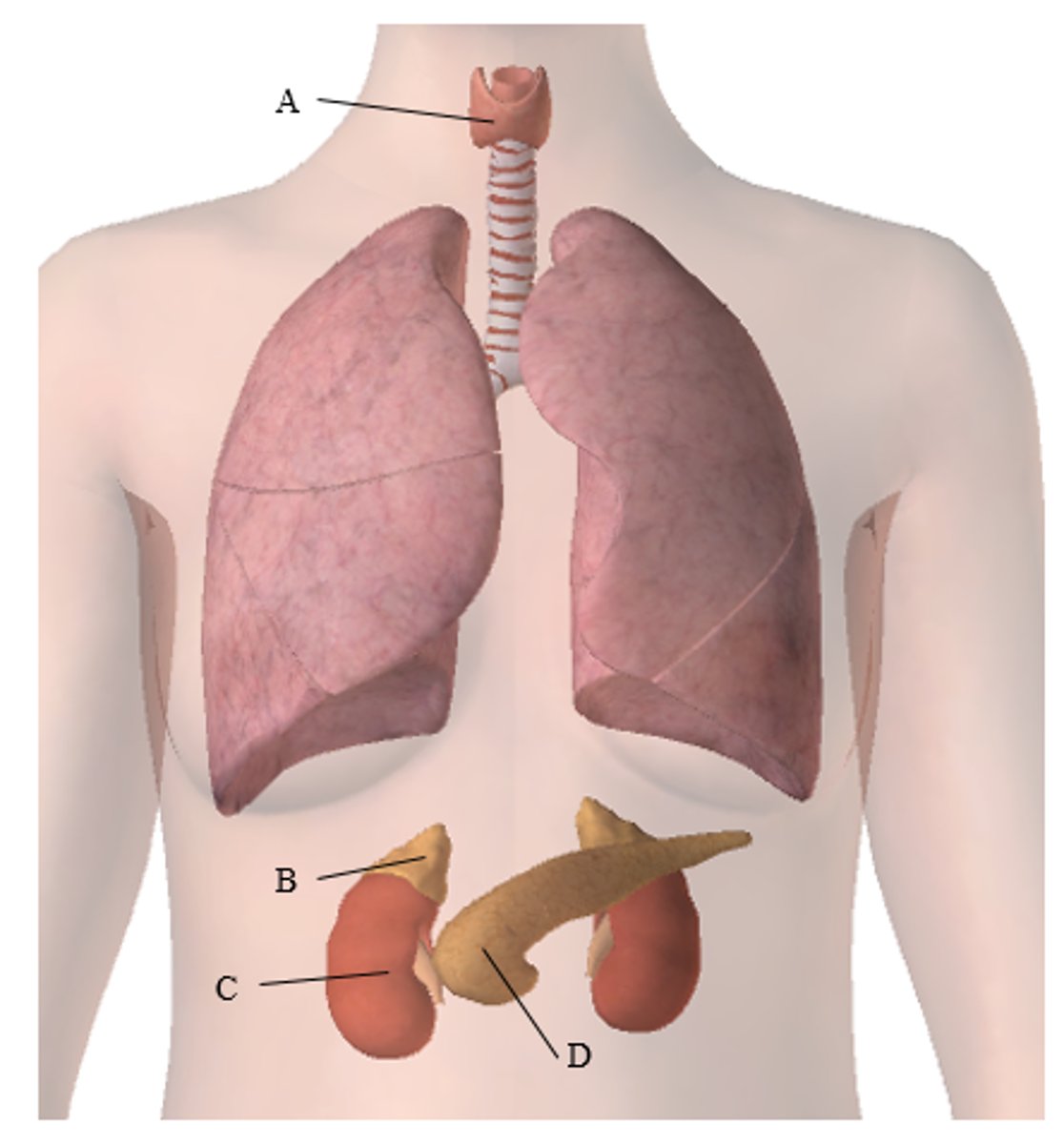
Label the endocrine glands (A-D)
A: ______________
B: ______________
C: ______________
D: ______________
A. thyroid gland
B. adrenal gland
c. kidney
d. pancreas
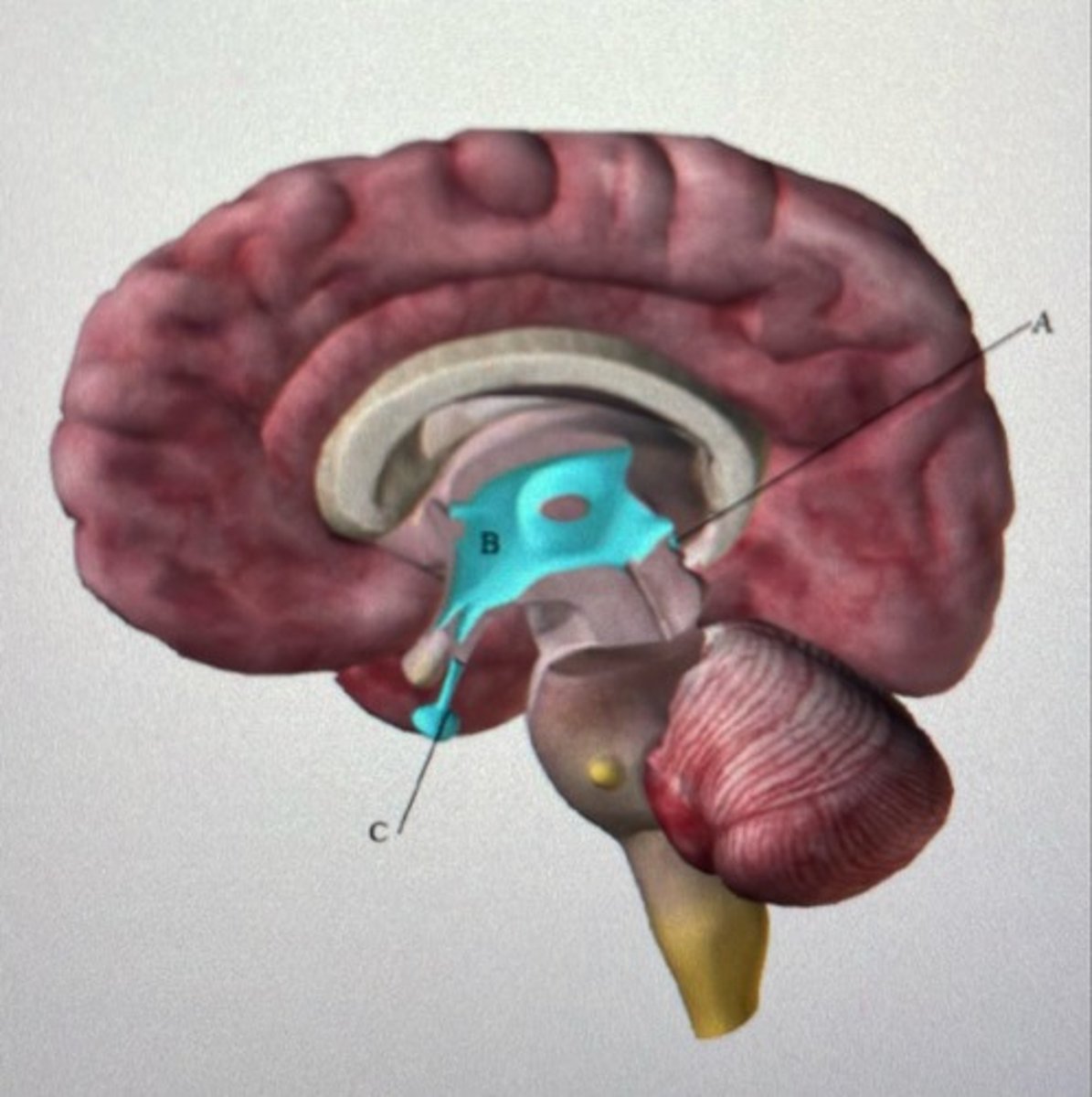
Label the endocrine glands (A-C)
A: Pineal gland
B: Hypothalamus
C: Pituitary gland
This type of hormone is derived from cholesterol:
Steroid hormones
This type of hormone is derived from proteins:
Peptide hormones
Growth hormone:
Is produced by the anterior pituitary gland
A. is most active during childhood/adolescence.
B. can cause disease if levels are not correct.
Neurosecretory cells are a part of what endocrine organ?
Hypothalamus
Which hormone production is increased with sunlight?
MSH (melanocyte stimulating hormone)
Neurons in the hypothalamus are called
neurosecretory
Which hormone production is decreased with sunlight?
melatonin
The posterior pituitary stores these two hormones:
ADH and Oxytocin
A. I lower the level of calcium in the blood by depositing calcium into bone.
Calcitonin
I am secreted by the pituitary and stimulate the gonads.
FSH & LH (gonadotropic hormones)
I promote reabsorption water at the collecting ducts of the kidneys.
ADH
I am secreted by the pituitary to stimulate the adrenal cortex.
ACTH
I am secreted by the pituitary to stimulate the thyroid.
TSH
I am secreted by the beta cells of the pancreas.
insulin
I am secreted by the alpha cells of the pancreas.
Glucagon
I cause blood glucose to rise and breakdown stored nutrients.
Glucagon
Which hormone/s are involved in milk production?
prolactin
Where is the thyroid stimulating hormone produced?
Anterior Pituitary gland
Which cells mature in the thymus?
T cells
Which gland decreases in size with age?
thymus
Iodine is needed to produce which hormone/s?
T3 and T4
Which of the following is NOT a function of oxytocin?
Growth of uterus and vagina
Bone growth
Which hormones are produced in the anterior pituitary?
ACTH, FSH, and GH
D. ACTH, GH, and prolactin
Matching each of the following conditions with the one best explanation (1-):
1. Congenital hypothyroidism --C. Low thyroxin production since birth
2. Pituitary giant --- A. Overproduction of GH as a child
3. Acromegaly --- H. Overproduction of GH as an adult
4. Tetany --- F. Results if PTH is not produced in response to low blood calcium
5. Anemia ---- E. Lack of erythropoietin to act on the bone marrow
Matching each of the following conditions with the one best explanation (1-5):
1. Jet Lag ---F. Melatonin production is produced according to body's normal rhythm
2. Pituitary dwarf ----A. Underproduction of GH as a child
3. Acromegaly---- C. Overproduction of GH as an adult
4. Inflammation---- E. Cortisol helps to counteract this condition
5. Tetany--- H. Results if calcitonin is not produced in response to low blood calcium
In addition to the endocrine system, the pancreas is also part of which system?
Digestive
Which part of the adrenal glands is vital to life?
Cortex
What hormone/s are produced by the adrenal medulla?
Epinephrine
Which of the following is false regarding aldosterone?
A. It is a regulated by the concentration of sodium.
B. It causes the kidneys to excrete potassium and retain sodium.
C. It causes the kidneys to retain potassium and excrete sodium.
D. It is a mineralocorticoid.
E. It increases blood pressure
It causes the kidneys to retain potassium and excrete sodium.
Which of the following is true regarding aldosterone?
A. It is regulated by the anterior pituitary.
B. It causes the kidneys to retain potassium and excrete sodium.
C. It causes the kidneys to excrete potassium and retain sodium.
D. It causes "fight or flight" responses in times of emergency.
E. It decreases blood pressure
It causes the kidneys to excrete potassium and retain sodium.
5. Which of the following is true regarding estrogen?
A. Production is highest in childhood.
B. It causes growth of the uterus and vagina.
C. It decreases fat storage.
D. It causes females to have a narrower pelvis (compared to males).
B. It causes growth of the uterus and vagina.
If you were calcium deficient, which condition would occur in your body if there was no hormonal compensation?
tetany
If you were calcium deficient which hormone would most likely be high in your body and that would occur?
B. Calcitonin, tetany
If you were calcium deficient, which hormone would most likely need to increase in your body in order to compensate?
A. PTH
If you were experiencing kidney disease, what hormone level would be low and what would occur?
Erythropoietin, anemia
Which of the following is false regarding testosterone?
It causes males to have a wider pelvis (compared to females).
In addition to the endocrine system, the hypothalamus is also part of which system?
Nervous