kaitlyn PHR 938 Block 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
diabetes mellitus
insulin is not secreted adequately or tissues are resistant to its effects
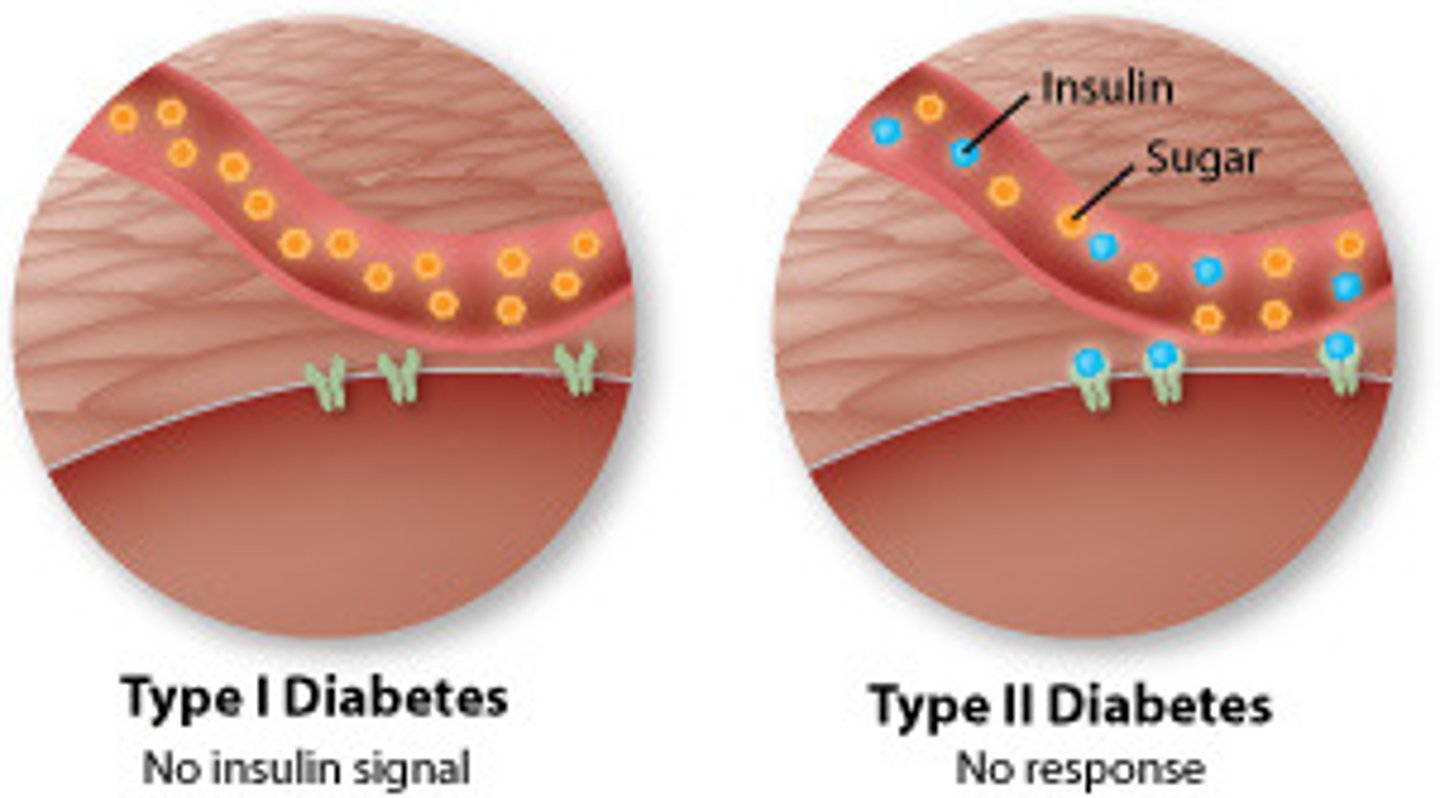
T2DM
type 2 diabetes mellitus
impaired insulin secretion and action
- genetic predisposition, overweight
hyperglycemia
excessive sugar in the blood
cause: excessive glucose production/ impaired glucose utilization
result: tissue injury
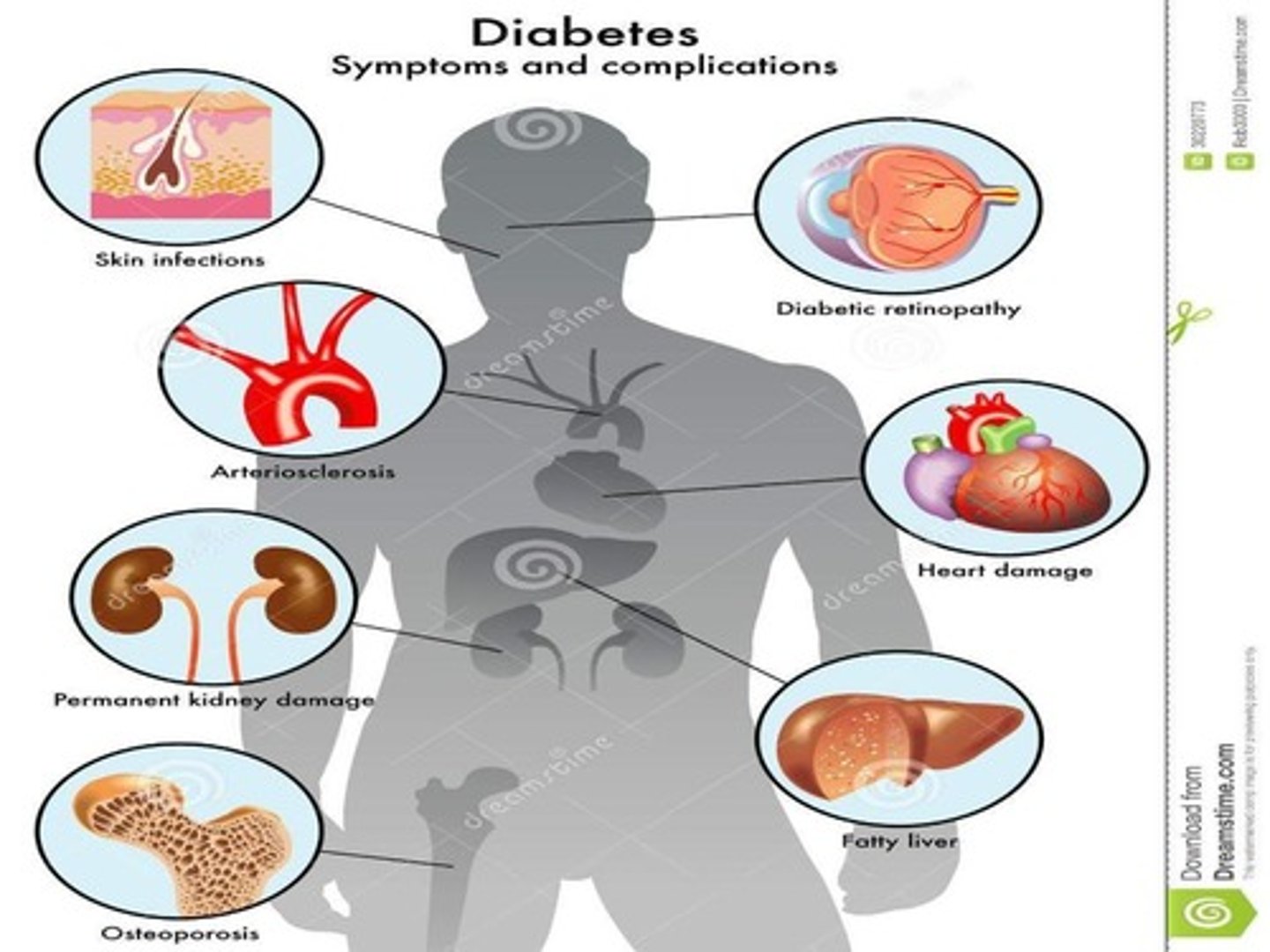
chronic complications of T2DM
retinopathy
neuropathy
nephropathy
cardiovascular disease
infections
what causes tissue changes in hyperglycemia?
there is:
- altered protein function and turnover -> cytokine activation
- osmotic and oxidative stress (too many free radials)
- reduced motor and sensory nerve (myelin sheath) conduction velocity
- altered glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
which ethnic groups are most affected by T2DM?
1. native americans
2. spanish descent
3. african descent
4. northern european descent
normal glucose range
70 - 130 mg/dL
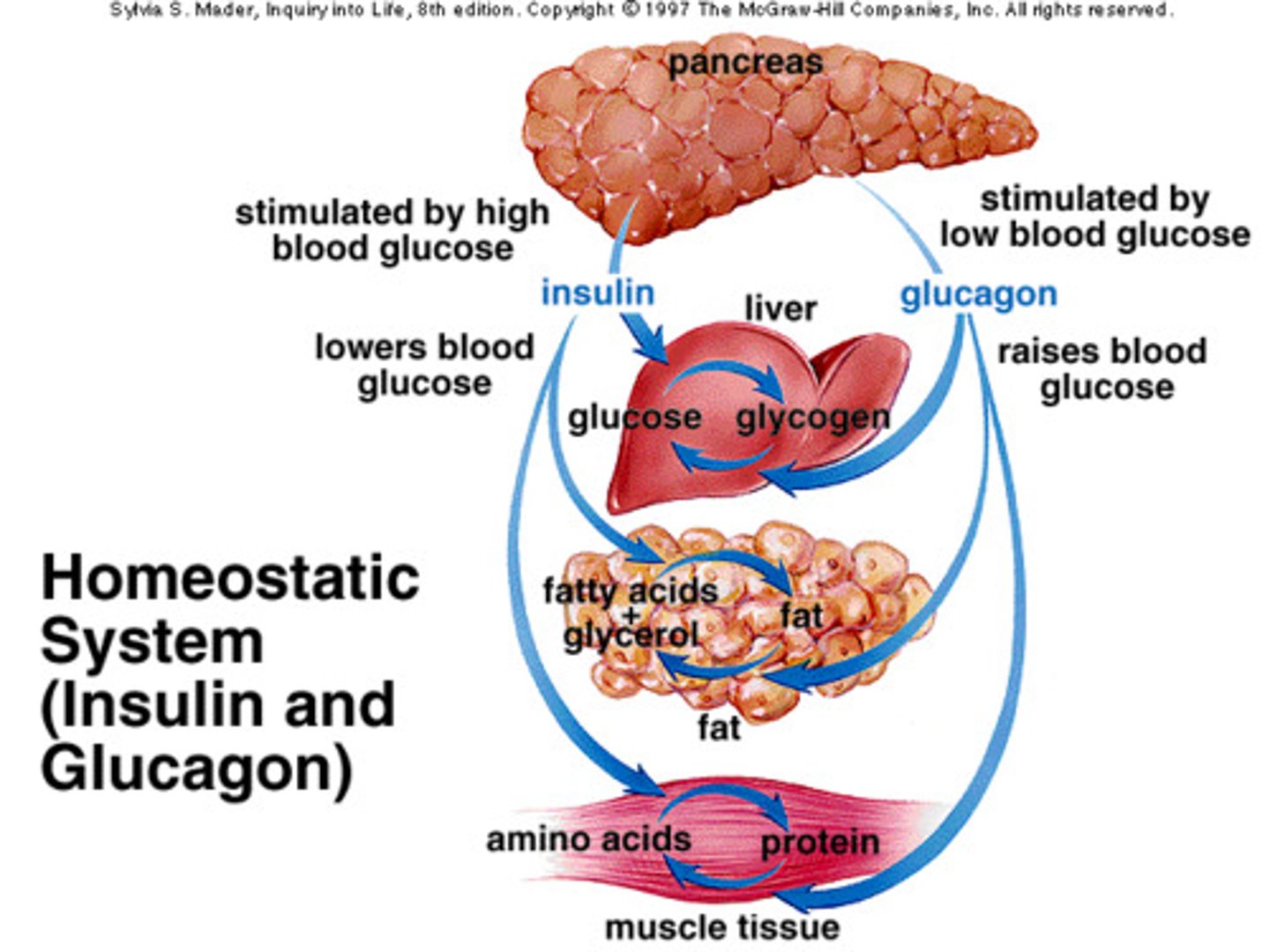
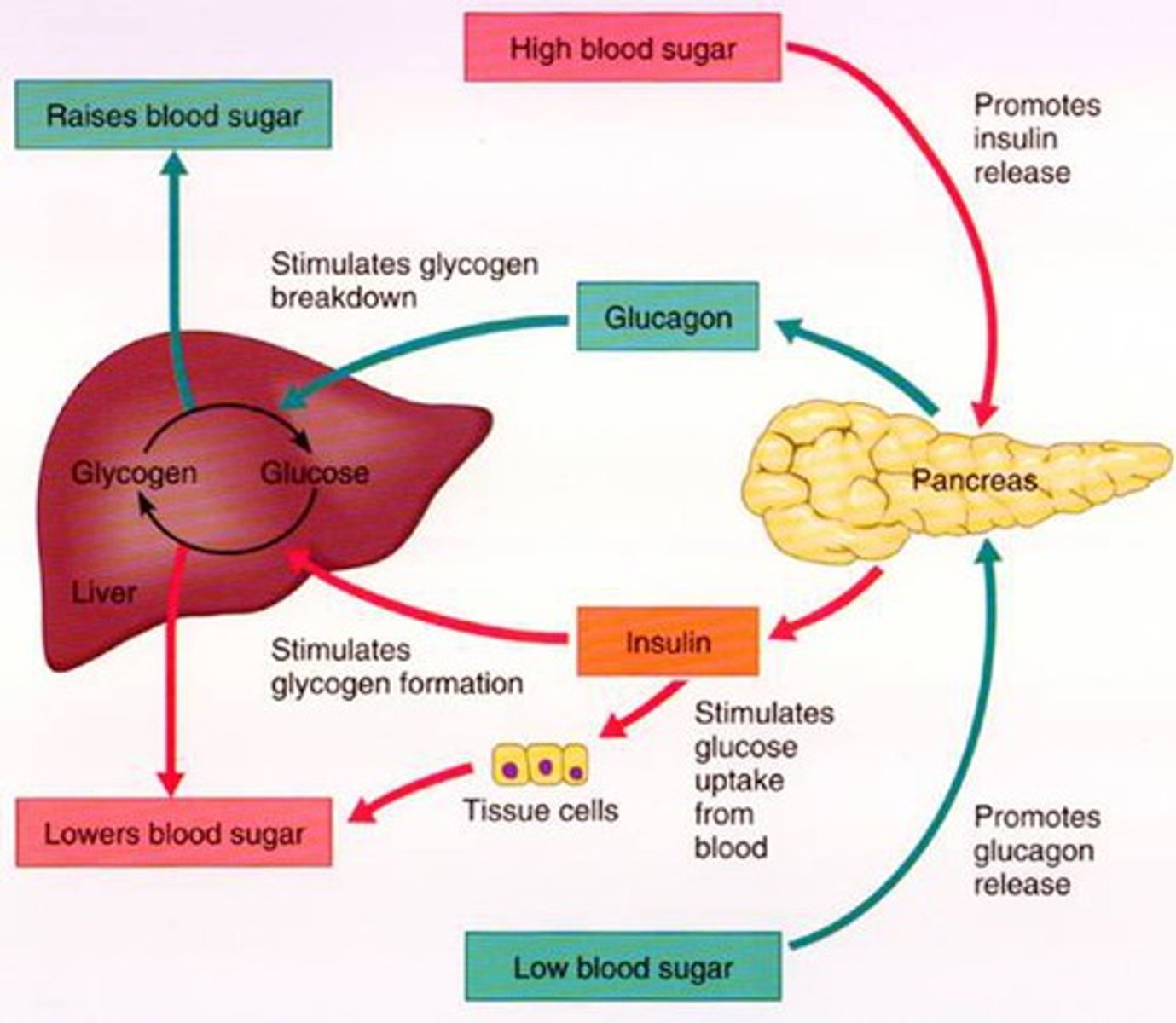
insulin
- produced from beta cells in the pancreas
- promotes glucose uptake into tissues
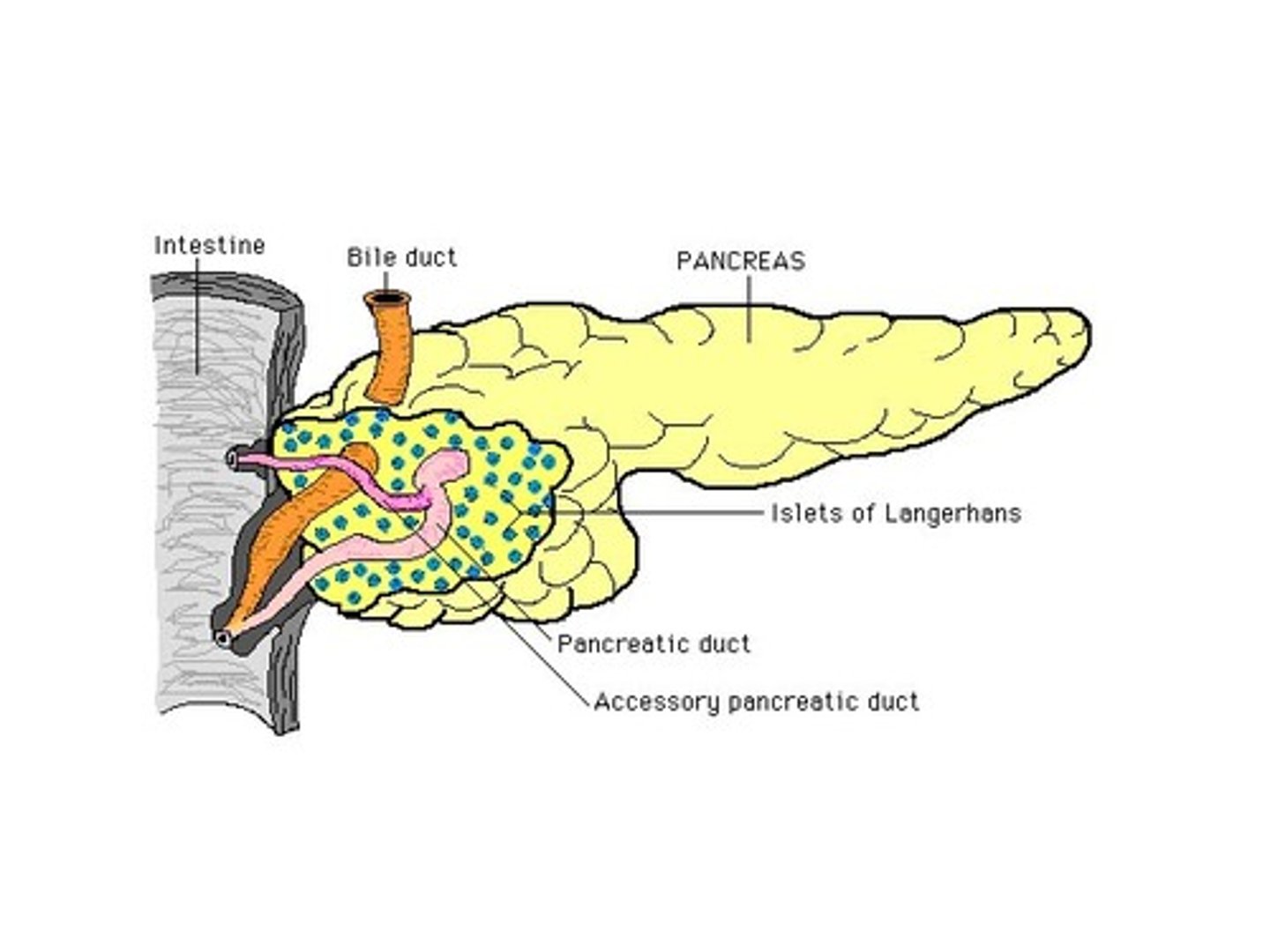
islets of Langerhans
areas of pancreatic cells that produce insulin and glucagon
- alpha cell: stimulates glucagon secretion (↓ BG)
- beta cell: stimulates insulin and amylin (↑ BG)
blood glucose trends in T2DM
- post-prandial hyperglycemia (~200 mh/dL)
- glucose remains high during fasting
- insulin secretion is delayed after a meal
- glucagon secretion is not suppressed after a meal
glycogen
storage form of glucose
T1DM
type 1 diabetes mellitus
autoimmune activation -> selective destruction of beta cells
- insulin is REQUIRED! body can no longer produce its own
3 main tissues responsive to insulin
1. skeletal muscle
2. adipose tissue
3. liver
adipocytes (T2DM)
fat cells - store triglycerides
- in insulin resistance (IR), lipolysis is increased + more fatty acids are released into circulation to use as an energy source
- contributes to IR in liver + muscle, fatty liver, dyslipidemia
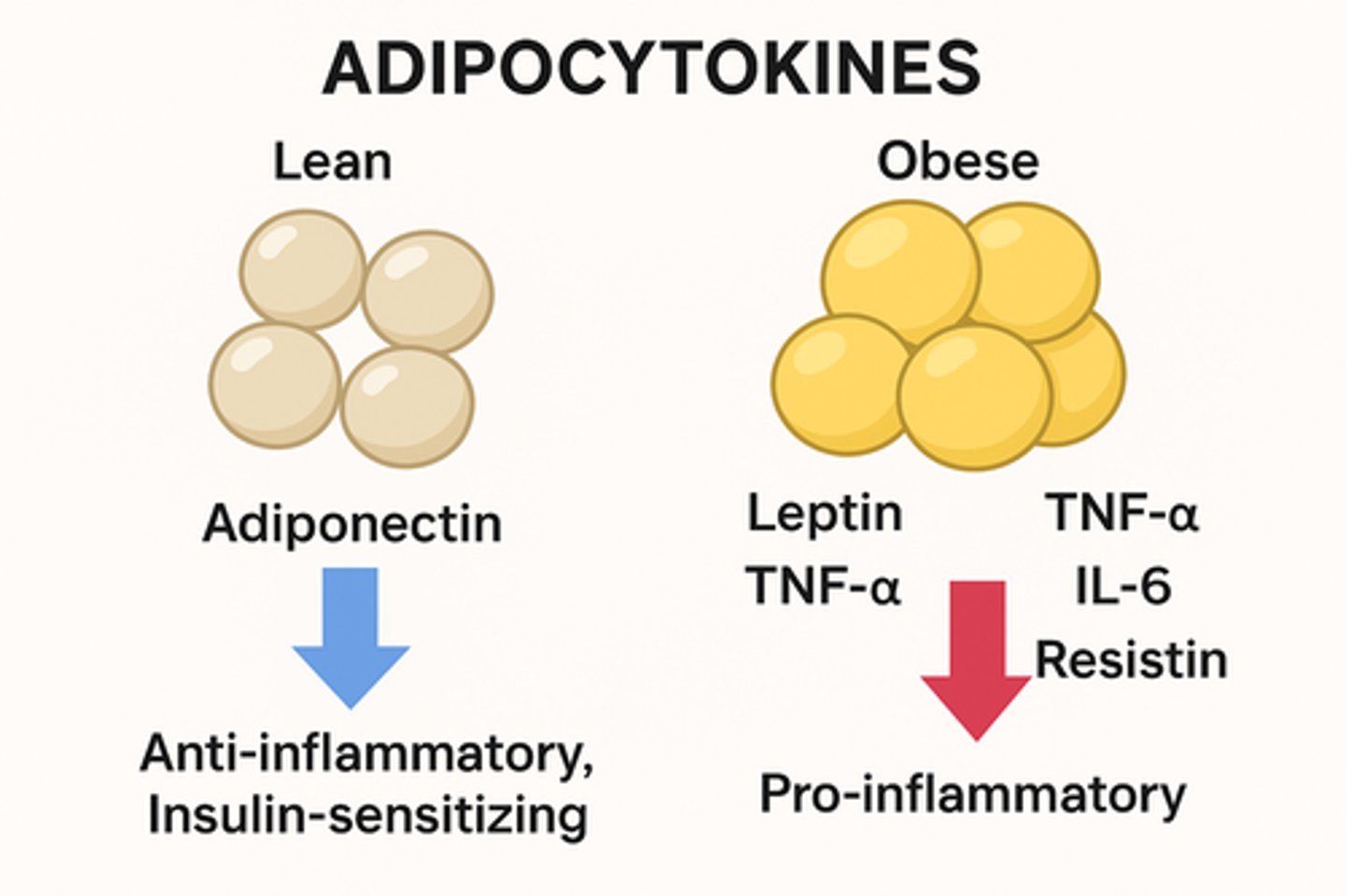
adipocytokines (T2DM)
chemical signals secreted by adipose tissue
- contribute to systemic insulin resistance
- (cytokines made by fat -> inflammation)
liver (T2DM)
- releases excessive glucose in the fasting state = hyperglycemia between meals
- glucose release from the liver is not suppressed after meals = excessive post-prandial BG rise
all caused by poorly regulated hepatic glucose metabolism
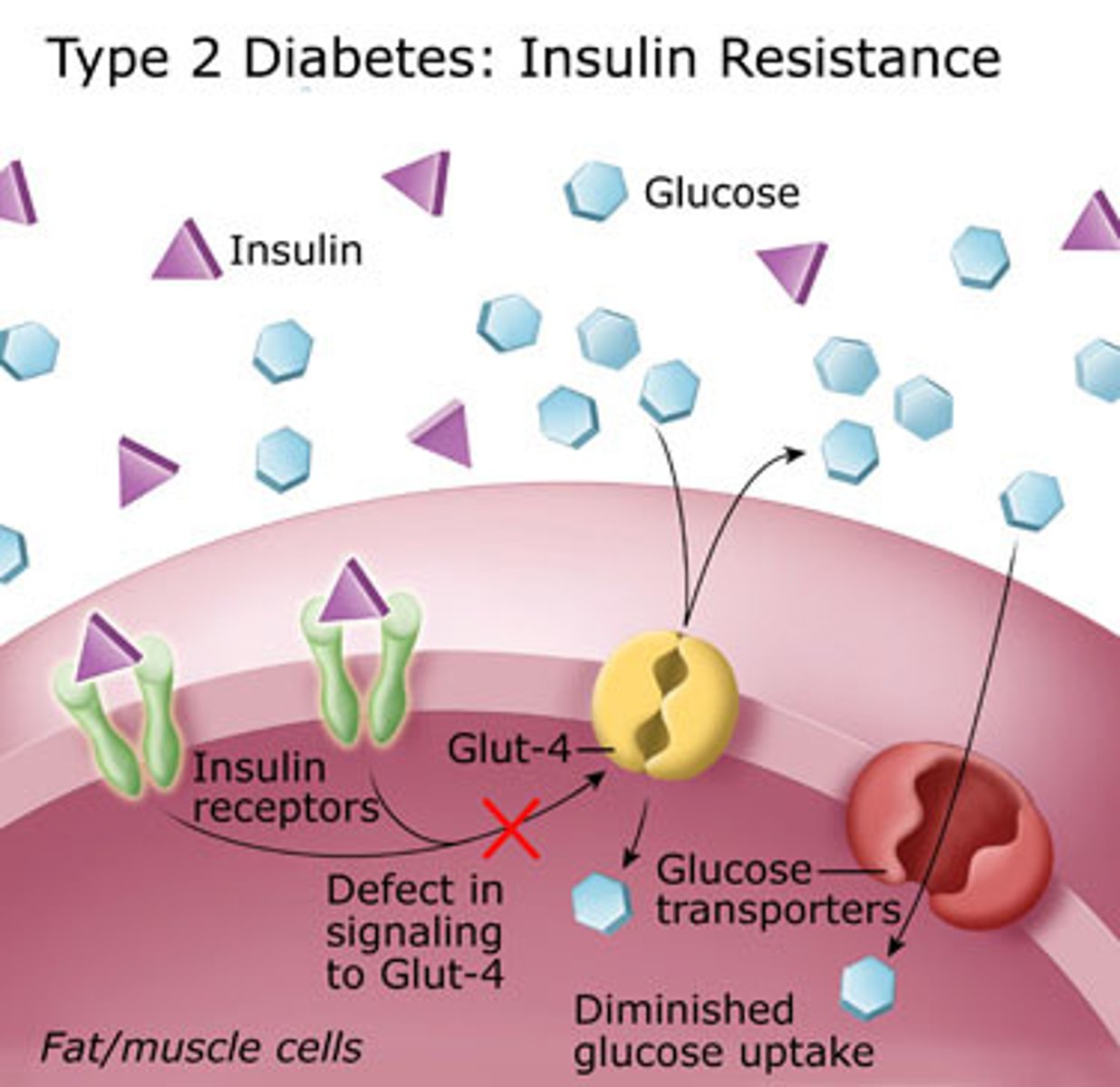
sedentary individuals are (more/ less) insulin resistant
more
exercise:
- improves insulin sensitivity
- decreases risk of developing diabetes
- improves glycemic control in those with diabetes
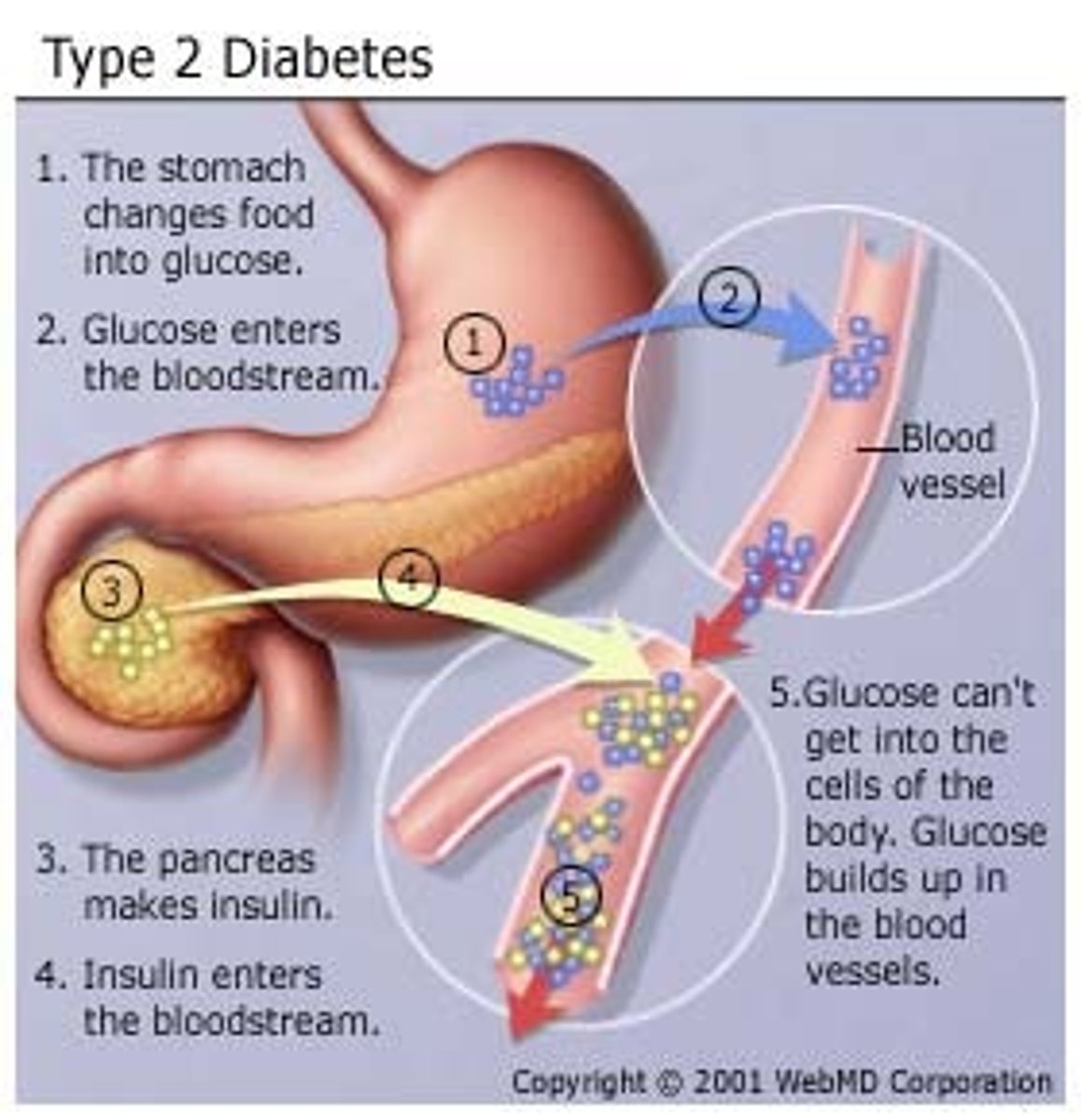
diagnosis of DM
any 1 of the following:
- symptoms of diabetes + random blood glucose concentration ≥ 200
- fasting plasma glucose ≥ 126 (most common)
- 2 hr plasma glucose test ≥ 200 during oral glucose tolerance test
- HbA1C ≥ 6.5%
goals of DM therapy
- treat hyperglycemia, alleviate symptoms
- prevent or reduce acute and chronic complications
- avoid hypoglycemia (deadly)
- regular blood glucose self-monitoring
metformin
Glucophage
biguanide
MOA: increases the activity of AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK)
- activated AMPK = reduced gluconeogenesis, increased peripheral glucose uptake
- does NOT affect insulin release
- most common, usually 1st line for T2DM
advantages:
- positive changes in plasma lipid profiles
- unlikely to cause weight gain
- unlikely to produce hypoglycemia
- persistant efficacy (2-5 yrs)
- delays diabetes progression / need for insulin
ADE:
- [black box]: lactic acidosis (very rare)
- GI (N/V/D, abdominal cramps)
![<p>Glucophage</p><p>biguanide</p><p>MOA: increases the activity of AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK)</p><p>- activated AMPK = reduced gluconeogenesis, increased peripheral glucose uptake</p><p>- does NOT affect insulin release</p><p>- most common, usually 1st line for T2DM</p><p>advantages:</p><p>- positive changes in plasma lipid profiles</p><p>- unlikely to cause weight gain</p><p>- unlikely to produce hypoglycemia</p><p>- persistant efficacy (2-5 yrs)</p><p>- delays diabetes progression / need for insulin</p><p>ADE: </p><p>- [black box]: lactic acidosis (very rare)</p><p>- GI (N/V/D, abdominal cramps)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/38c9153d-53e7-4e30-86a3-44c738ec8fa6.jpg)
GLUT4
glucose transporter type 4
- insulin-dependent glucose transporter in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue
- metformin reduces GLUT4 intracellular migration
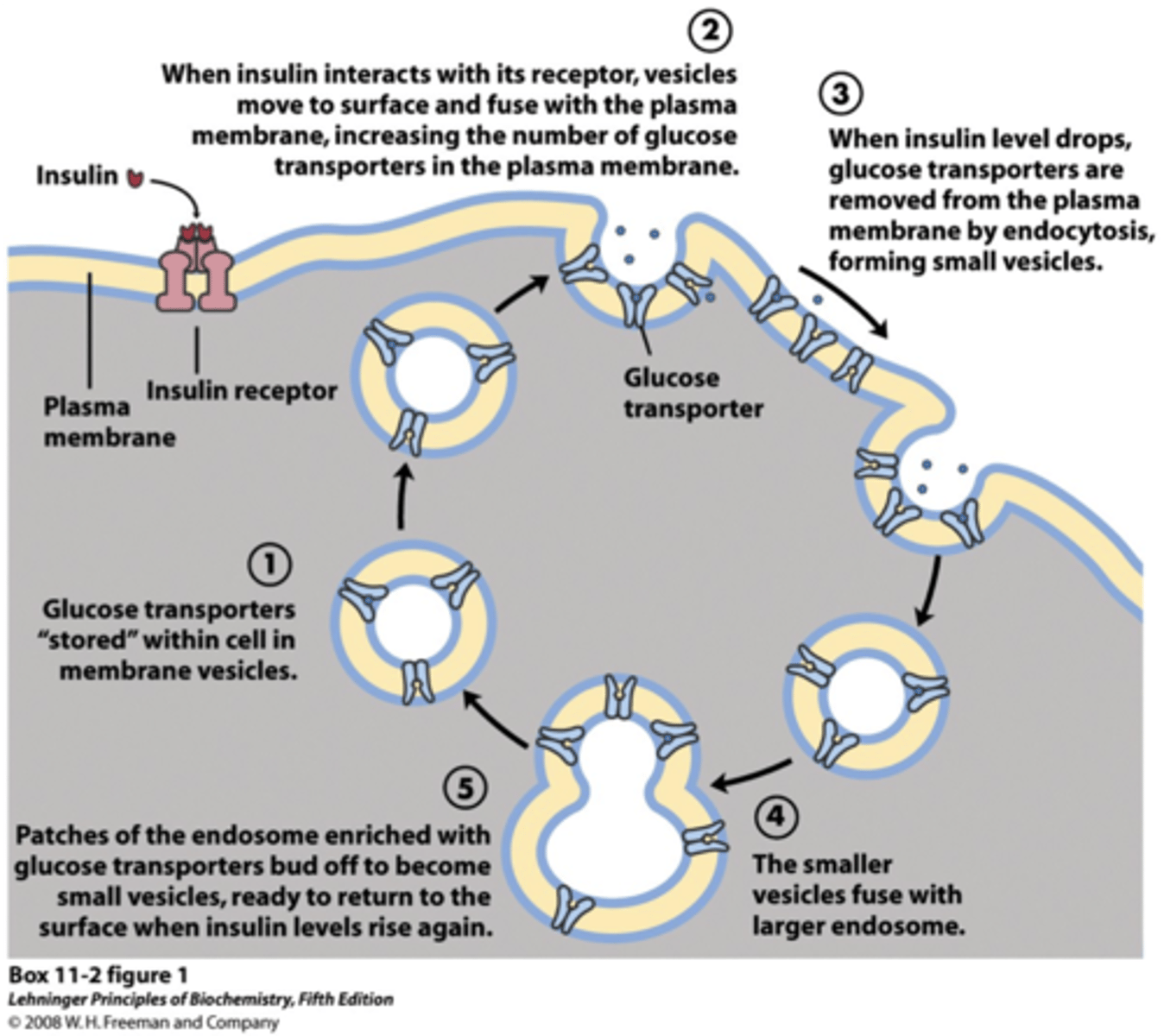
insulin secretion is stimulated by:
- glucose
- hormones (GLP-1, GIP)
- cholinergic nerves
- medications
mechanism of stimulated insulin release
1. glucose enters cell
2. glucose metabolized
3. increased ATP production
4. K+ channels close
5. cell depolarization + Ca2+ influx
6. influx stimulates release of insulin-containing vesicles into the blood steam
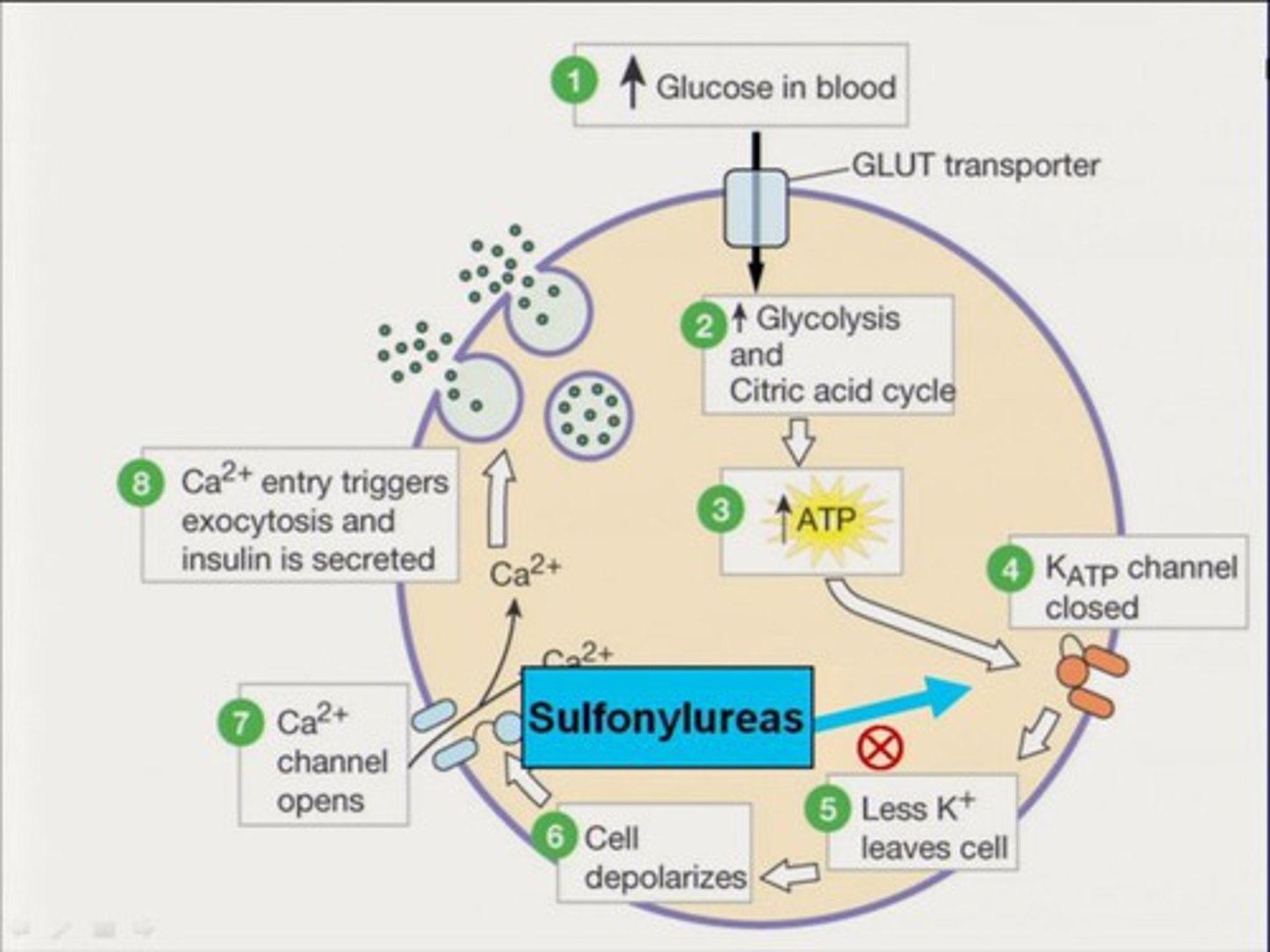
sulfonylureas
glipizide, glyburide, glimepiride (-ides)
MOA: stimulate insulin secretion by blocking ATP-sensitive potassium (K-ATP) channels in pancreatic beta cells, which depolarizes the cell membrane and opens voltage-gated calcium channels
- outward flow of K+ is inhibited
- preformed insulin is released, NO biosynthesis
- no 1st gens - t1/2 was too long
- 2nd gens - shorter t1/2, fewer ADEs
glyburide has longest t1/2 (10 hrs), glipizide has shortest (3 hrs)
- pts stop responding after ~1 year
ADE: does not correct initial post-prandial spike, hypoglycemia, weight gain
intx: ethanol, sulfonamides, beta-blockers
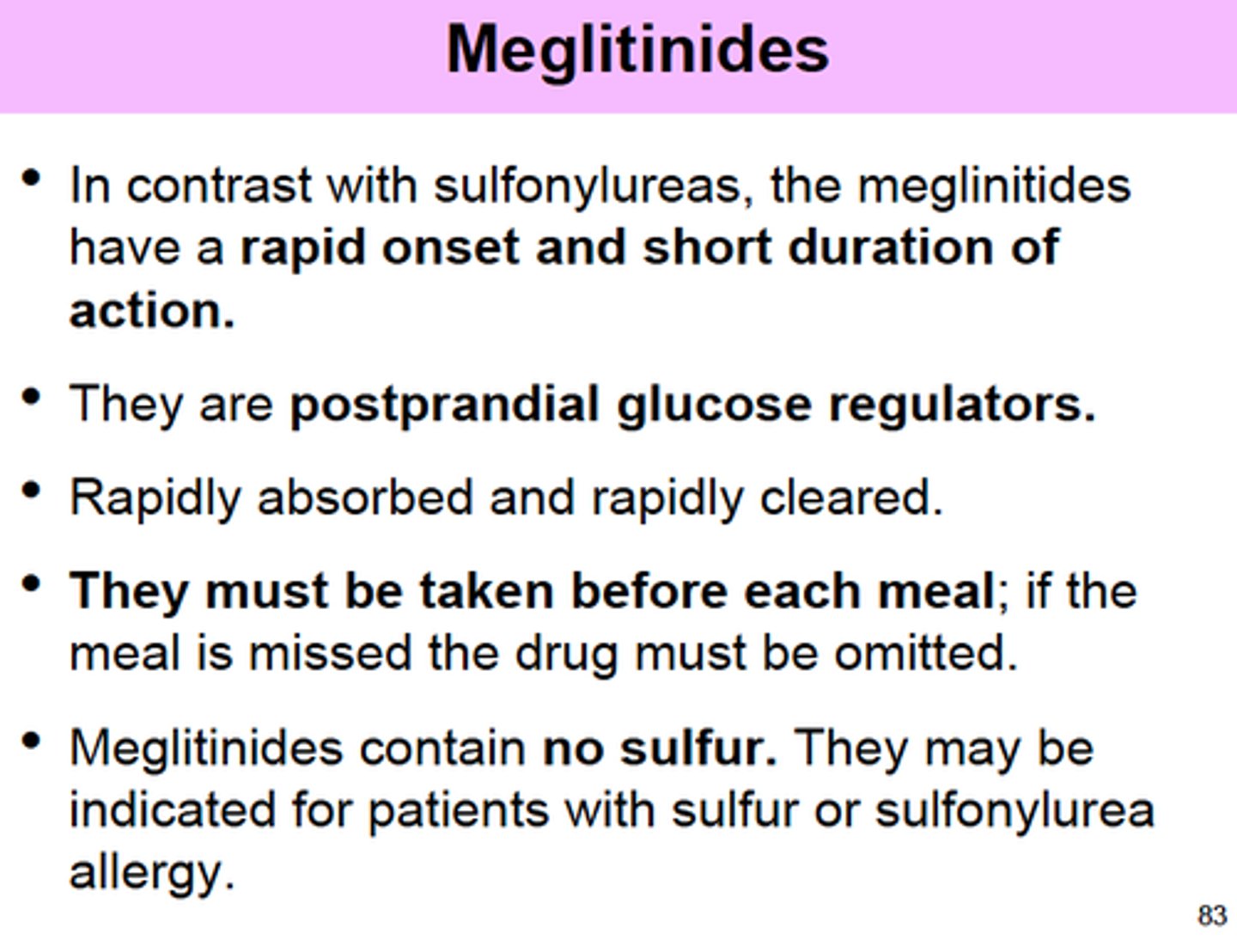
meglinitides
repaglinide, nateglinide
MOA: stimulates insulin release by closing K-ATP channels in beta cells
- t1/2 ~ 1 hr
thiazolidinediones
pioglitazone (Actos), rosiglitazone (Avandia)
MOA: act as PPAR-gamma agonists
- basically, allow more glucose to get into the tissues
- also reduce free fatty acid blood levels
ADE:
- [black box]: congestive heart failure (pioglitazone)
- fluid retention/ weight gain
- onset of action is slow (requires changes in gene transcription, which can take a few months)
![<p>pioglitazone (Actos), rosiglitazone (Avandia)</p><p>MOA: act as PPAR-gamma agonists</p><p>- basically, allow more glucose to get into the tissues</p><p>- also reduce free fatty acid blood levels</p><p>ADE: </p><p>- [black box]: congestive heart failure (pioglitazone)</p><p>- fluid retention/ weight gain</p><p>- onset of action is slow (requires changes in gene transcription, which can take a few months)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/44264c7d-0b45-4d27-9db8-b2122afa4061.jpg)
incretins
a group of hormones produced by the gastrointestinal system that stimulate the release of insulin from the pancreas and help preserve the beta cells
- secreted in proportion to the amount of glucose ingested
- allows insulin secretion to begin before the peak in BG
GLP-1
glucagon like peptide 1 (incretin)
regulate blood glucose levels, particularly after eating
(secreted from the small intestine after a meal)
functions:
- increases insulin secretion
- inhibits glucagon secretion
- signals satiety in the CNS
- delays gastric emptying
- stimulates beta cell proliferation
GIP
gastric inhibitory peptide (incretin)
regulate blood glucose levels, particularly after eating
(secreted from the small intestine after a meal)
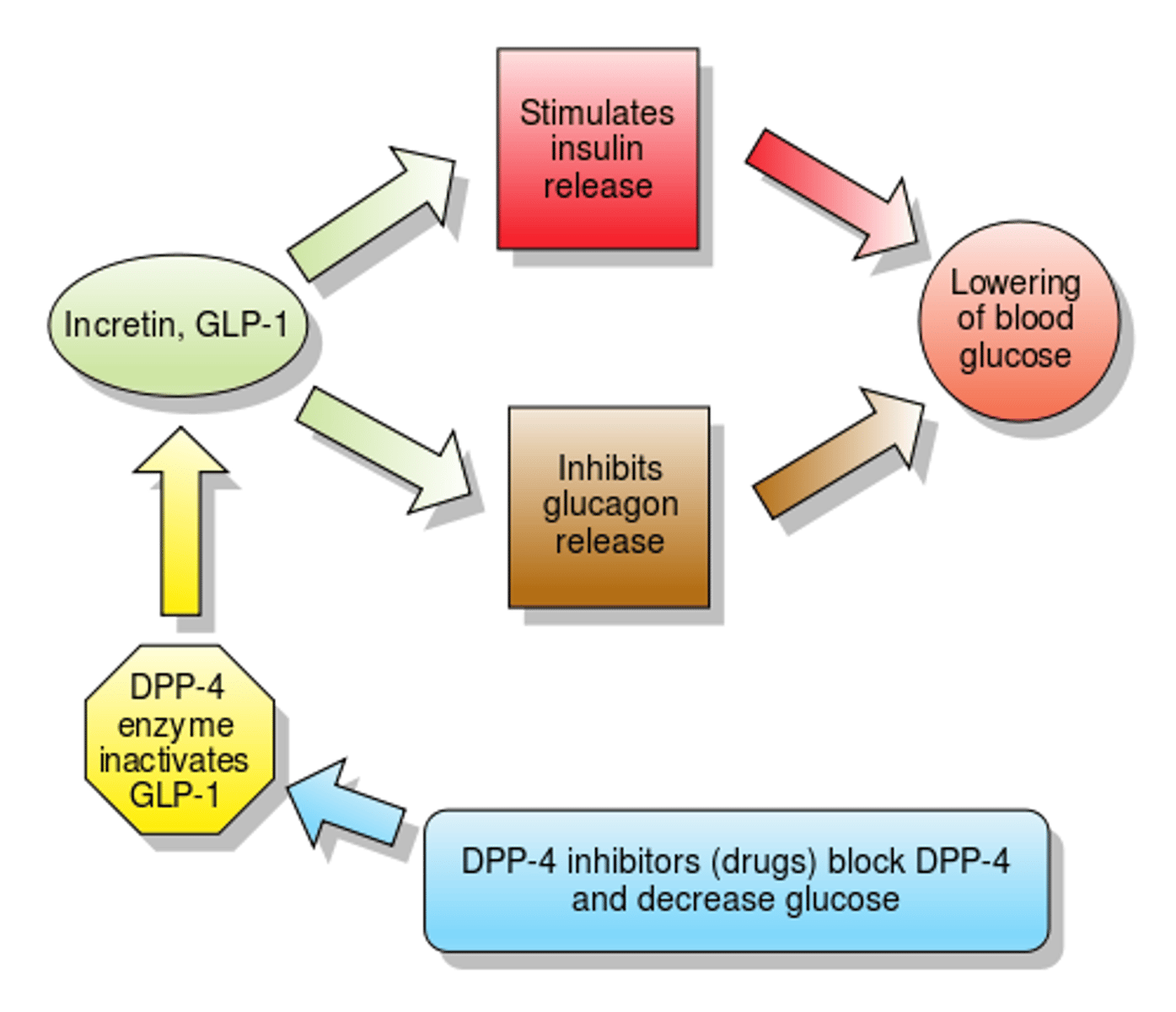
DPP-4 inhibitors
dipetpidylpetase-4 inhibitors
sitagliptin (Januvia), saxagliptin (Onglyza), alogliptin, linagliptin (Trradjenta)
MOA: inhibits degradation of GLP-1 and GIP -> increased plasma concentrations of GLP-1 and GIP
ADE: arthralgia
- can be combined with another therapy of a different mechanism
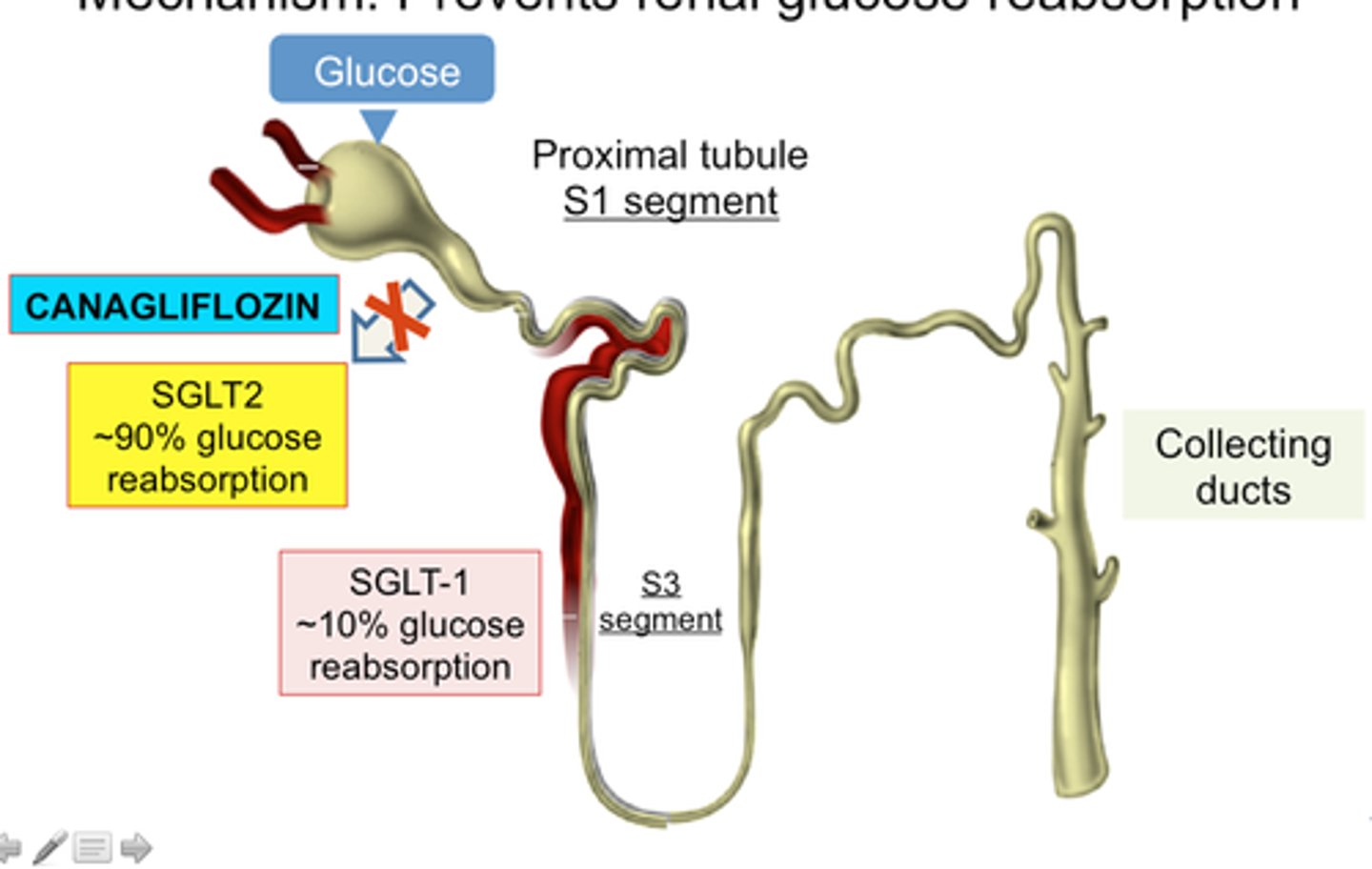
SGLT2 inhibitors
sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors
canagliflozin (Invokana), dapagliflozin (Farxiga), empagliflozin (Jardiance), ertugliflozin (Steglatro), bexagliflozin (Brenzavvy)
MOA: block reabsorption of filtered glucose by the kidneys -> lowered BG concentration
- also, risk reduction of major cardiovascular events and heart failure
ADE: UTIs (increased glucose excretion thru urine)
exenatide
Byetta
GLP-1 based therapy
- discovered from salivary glands of Gila monster
- glucose-dependent insulin secretion
- leads to delayed gastric emptying, reduced glucagon levels, reduced food intake
- SQ once weekly
caution: antibody development that limits effectiveness, due to being from an animal source

liraglutide
Victoza
GLP-1 based therapy
- amino acid substitution with a fatty acid group
- binding to albumin extends the half life
- SQ once daily
dulaglutide
Trulicity
GLP-1 based therapy
- recombinant fusion protein composed of 2 identical disulfide-linked chains of GLP-1 analog, covalently fused to human immunoglobulin to prolong t1/2
- amino acid substitution in human GLP-1
- SQ once weekly

semaglutide
Ozempic
GLP-1 based therapy
- analogues of GLP-1
- SQ once weekly
PO semaglutide
Rybelsus
GLP-1 based therapy (new)
- 1st oral GLP-1 receptor agonist
- take 30+ minutes before 1st food/ medications of the day with ≤ 4 oz PLAIN water (too much water = drug degradation)
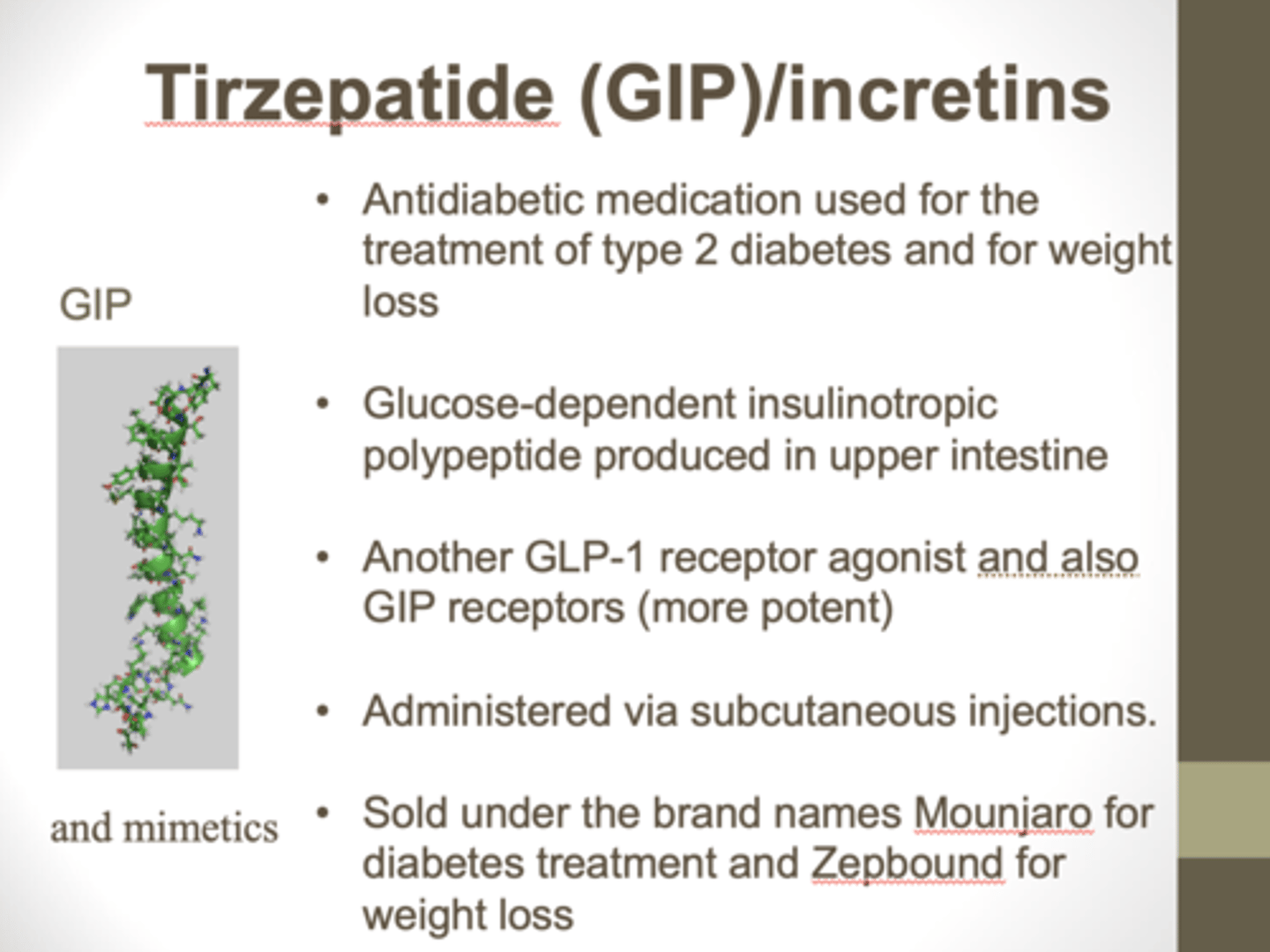
tirzepatide
Mounjaro
dual GLP-1 and GIP based therapy
- new peptide sequence
GLP-1 analogues overview
- all are approved for T2DM, adjunct to diet and exercise
- ADE (N/V) typically decrease w continued use
- box warnings for thyroid tumors in rodents
- also reduce major CV events
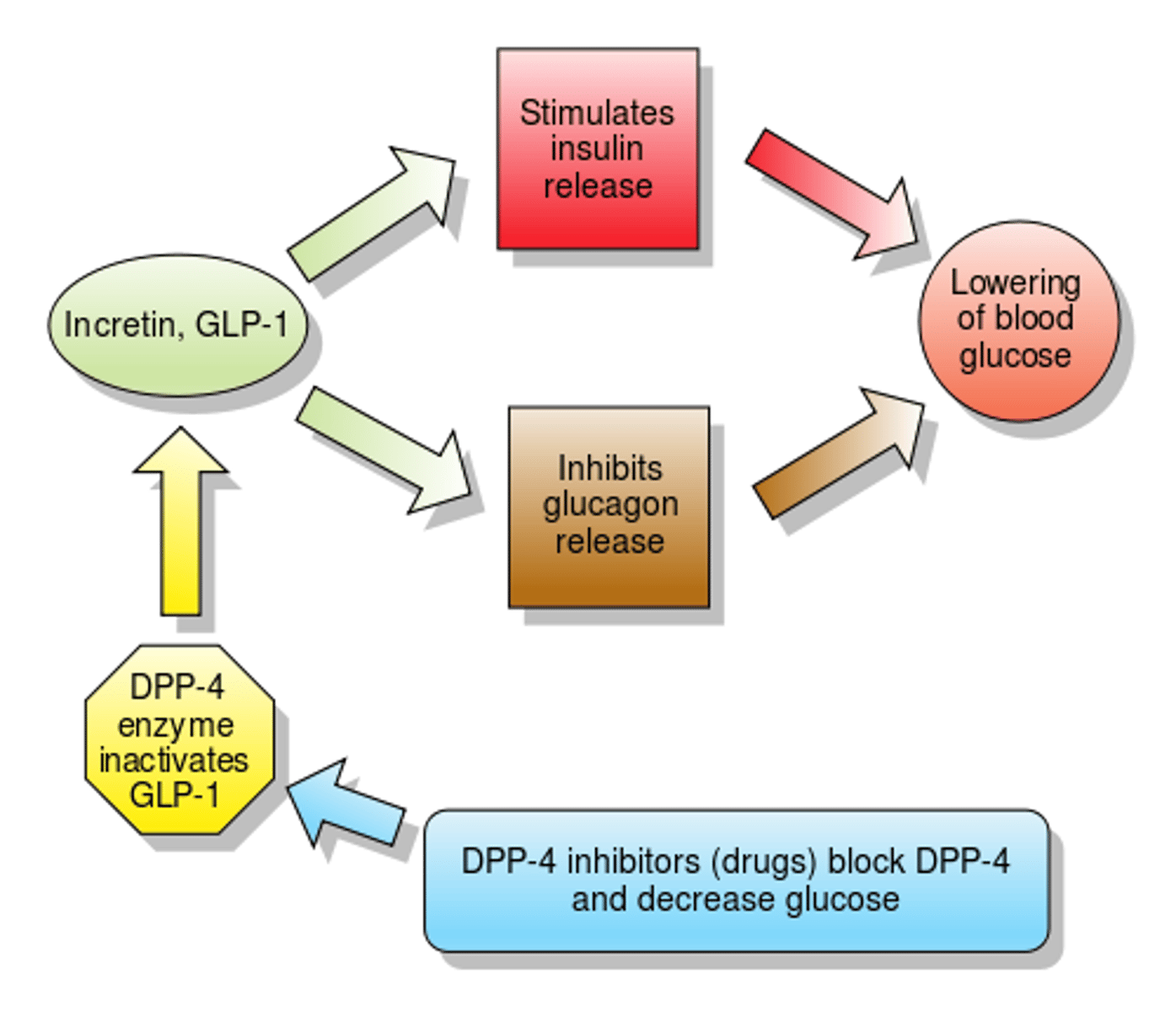
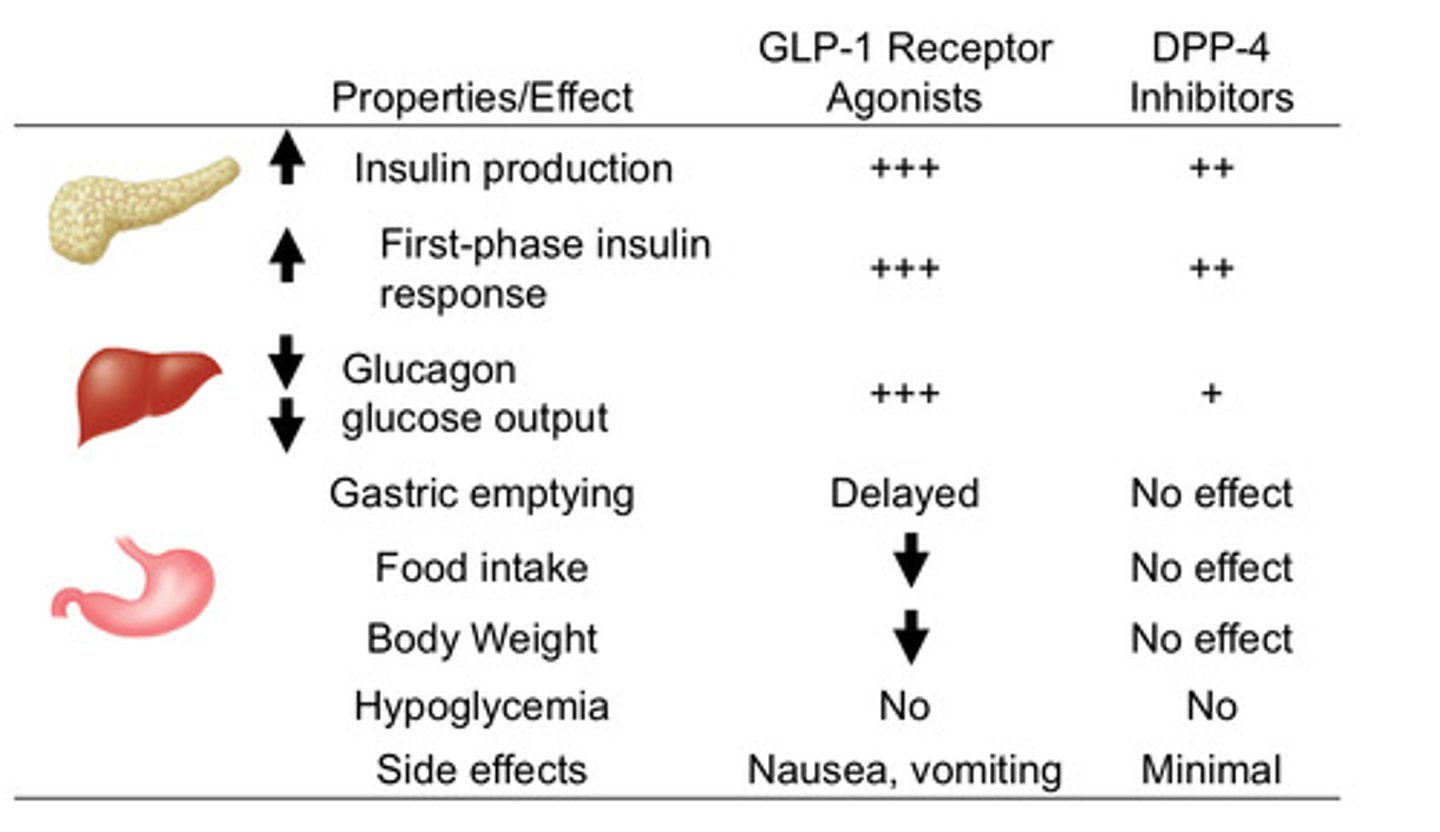
GLP-1 agonists vs DPP-4 inhibitors
pic
pramlinitide
SymlinPen
synthetic amylin analog
- amylin is secreted with insulin from beta cells
MOA: binds amylin receptors in the brain (area postrema), signaling alpha cells in pancreas
results:
- reduces post-prandial glucagon secretion/ liver glucose release
- delays gastric emptying
- produced satiety to suppress appetite
- adjunct for T1 and T2 with mealtime insulin when insulin therapy alone is insufficient
[box warning]: severe hypoglycemia, esp in T1
![<p>SymlinPen</p><p>synthetic amylin analog</p><p>- amylin is secreted with insulin from beta cells</p><p>MOA: binds amylin receptors in the brain (area postrema), signaling alpha cells in pancreas </p><p>results:</p><p>- reduces post-prandial glucagon secretion/ liver glucose release</p><p>- delays gastric emptying</p><p>- produced satiety to suppress appetite</p><p>- adjunct for T1 and T2 with mealtime insulin when insulin therapy alone is insufficient</p><p>[box warning]: severe hypoglycemia, esp in T1</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cefd65cc-82f2-4821-8527-7f9126deafc5.jpg)
diabetic glycemic goals
A1C: <7.0%
fasting glucose: 80-130
post prandial glucose: <180
why would you not start with healthy lifestyle behaviors alone before pharm therapy?
pharm therapy will take effect now, lifestyle will take a while to see physiological changes (if pt is compliant)
- we don't want the blood glucose to destroy the body while waiting to see lifestyle effects kick in
what is metformin's A1C lowering effect?
1-1.5%
when to choose something other than metformin monotherapy?
- if A1C is 1.5% or more above goal
- A1C is 10%+ or there is significant hyperglycemia symptoms (may require insulin)
- pt has ASCVD/high risk ASCVD, HF, or CKD
what are good pharm therapies for someone with ASCVD or indicators of high CVD risk?
SGLT2 inhibitor with proven CVD benefit (Jardiance, Invokana)
or
GLP-1 RA with proven CVD benefit (Victoza, Ozempic, Trulicity)
what are good pharm therapies for someone with CKD?
SGLT2 inhibitor (Invokana, Farxiga, Jardiance)
or
GLP-1 RA with proven CKD benefit (Victoza, Ozempic, Trulicity)
what are the best therapies for weight loss?
highest: Ozempic (semaglutide) and Mounjaro (tirzepatide)
high: Trulicity (dulaglutide) and Victoza (liraglutide)
intermediate: other GLP-1 RAs, SGLT2i
what are good pharm therapies for someone with heart failure?
SGLT2 inhibitors with proven HF benefit
(Jardiance, Farxiga, Invokana, Steglatro)
duplicate mechanisms to avoid in therapy
DPP-4 inhibitors + GLP-1 RAs
(Januvia + Ozempic)
sulfonylureas + meglitinides
sulfonylureas/ meglitinides + rapid insulin
which therapies have the potential for weight gain?
sulfonylureas
TZDs
insulin
hypoglycemia
BG < 70
symptoms: shaky, sweaty, dizzy, confusion, difficulty speaking, hunger, weak, tired, headache, nervous, upset
rule of 15
hypoglycemia treatment
1. eat/ drink 15 g of carbs
2. wait 15 minutes
3. check BG
4. still less than 70 = repeat
what does 15g of carbs look like?
3-4 glucose tablets
3-5 heard candies
4 oz od fruit juice
1/2 can of regular soda
1 tablespoon sugar, honey, or corn syrup
who is at highest hypoglycemic risk?
- pts who are asymptomatic with BG <70
- pts with cardiovascular disease
- older patients (severe consequences)
- pts with cognitive impairment
what are the best pharm options if a pt is at high risk for hypoglycemia?
DDP-4i
GLP-1 RA
SGLT2i
TZD