Class 2: Microscopy Slides
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Important characteristics of microscopy types
• Sample preparation
• Method of image generation
• Cellular features detectable
• Resolution
• Contrast
Selecting a type of microscopy
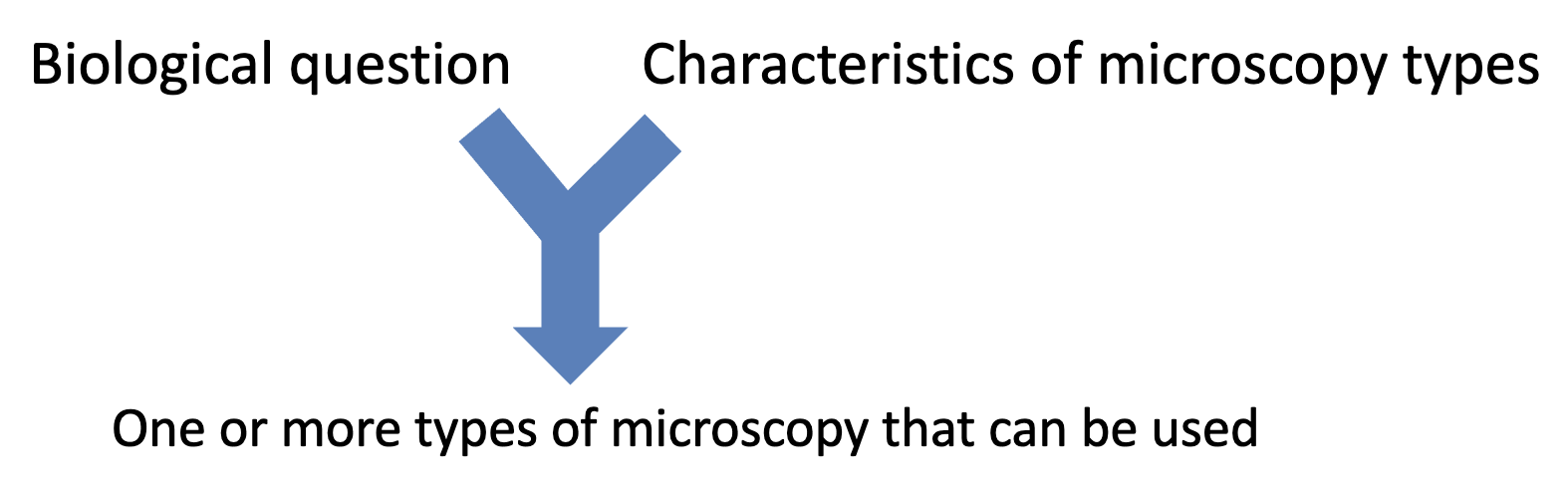
Considerations in choosing a type of microscopy simplified
detectable?
resolution required?
contrast sufficient?
Specimen properties, like sample thickness?
3D?
alive or dead?
time taken?
image analysis?
tools available?
microscope available?
cost?
simplest approach that will suffice?
Considerations in choosing a type of microscopy original
Is the object of interest detectable?
• What resolution is required to distinguish the relevant cellular parts?
• Is the contrast sufficient to detect the relevant cellular parts?
• What is the specimen like (sample thickness)?
• Is the object of interest detectable?
• Do you need 3-dimensional information?
• Do cells need to be alive?
• How fast/long is imaging needed?
• How will image be analyzed and quantitated?
• Are the necessary tools available?
• Is the type of microscope available?
• What is the cost and time required?
• What is the simplest approach that will be sufficient?
Some common microscopy techniques
• Hemotoxylin and eosin staining
• Immunohistochemistry
• Immunofluorescence microscopy
• Fluorescent fusion protein microscopy
• Immungold electron microscopy
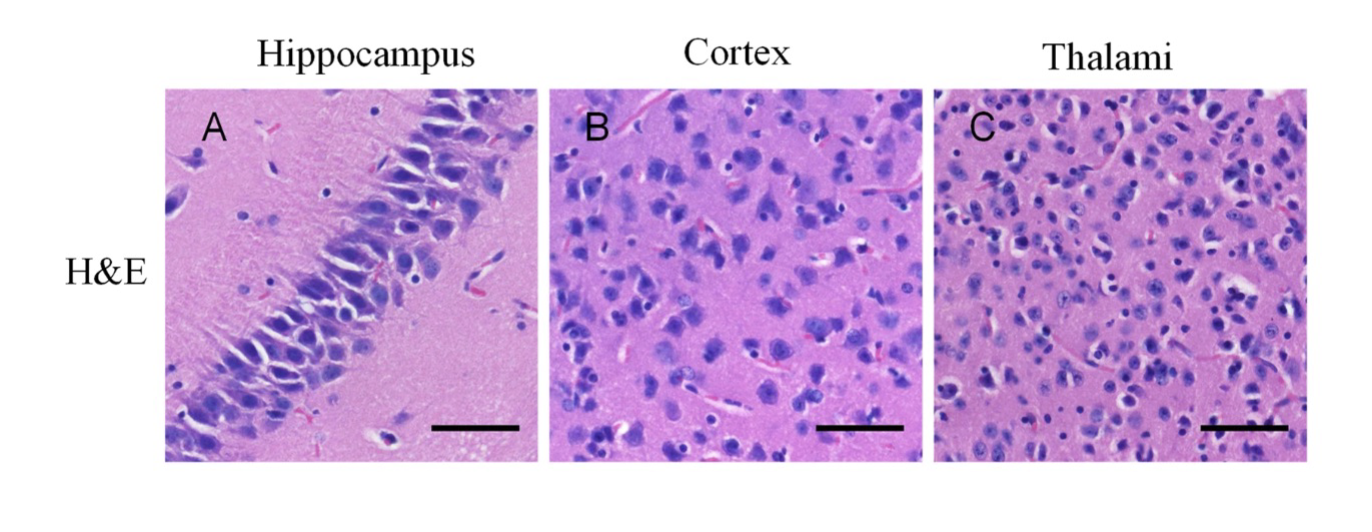
H & E staining
to visualize cells in tissues
• Hematoxylin (H) dye is blue and binds to nucleic acids
• Eosin (E) dye is red/pink binds to proteins
• Stained samples are visualized by white-light microscopy (Brightfield)
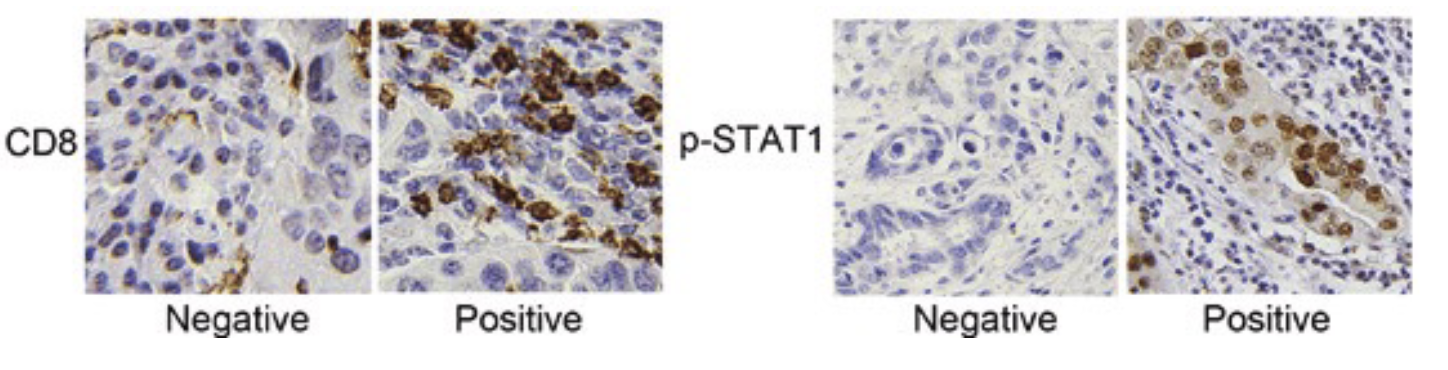
Immunohistochemistry to
detect proteins in tissues
• uses antibodies to detect antigens in a tissue sample
• antibodies usually linked to an enzyme or fluorescent dye for visualization
• enzyme substrate added or dye activated for detection by light microscopy
Detecting Proteins by Fluorescence Microscopy
• You do not need to know about secondary antibodies or other antibody details for the purposes of this class.
• All three approaches are used commonly
• In some cases, any of the three aproaches would be suitable.
• Sometimes differences are important and one of the approaches is advantageous.
• Using more than one approach can be useful to confirm the result.
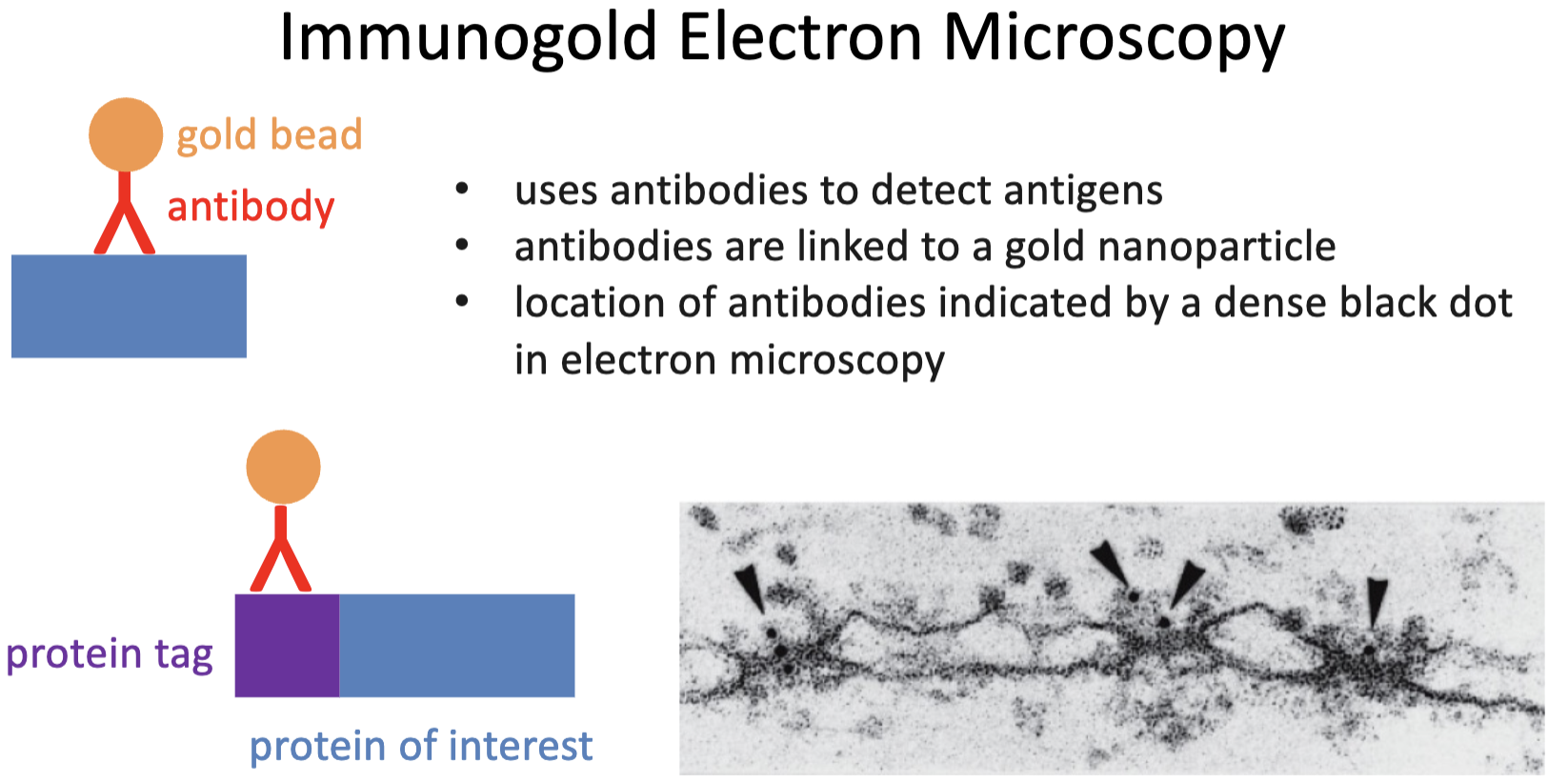
Immunogold Electron Microscopy text
• uses antibodies to detect antigens
• antibodies are linked to a gold nanoparticle
• location of antibodies indicated by a dense black dot in electron microscopy
Immunogold Electron Microscopy diagram
Cell Biology Course Goals for Microscopy
• Describe the important characteristics of different general types of microscopy.
• Justify the selection of a specific microscopy approach for addressing a specific cell biological question.
• Identify the type of microscopy used based on an image.
• Interpret microscopy images.