3.5: Population growth and resource availability
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Population distribution
A description of how individuals are distributed with respect to one another.
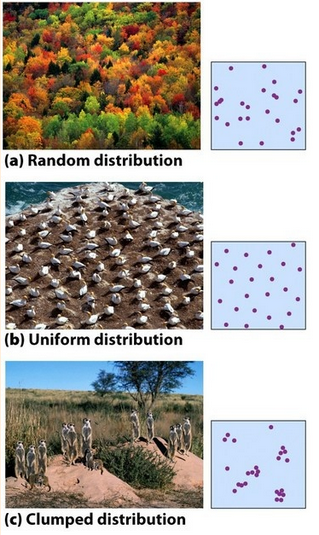
Random distribution
occurs with dandelion and other plants that have wind-dispersed seeds that germinate wherever they happen to fall in a favorable environment.

Uniform distribution
animals that maintain defined territories, such as nesting penguins, exhibit uniform dispersion.

Clumped distribution
Schools of fish or herds of elephants. May also result when favorable conditions are localized, organisms will tend to clump around those, such as lions around a watering hole.

Metapopulation
A group of spatially distinct populations that are connected by occasional movements of individuals between them.
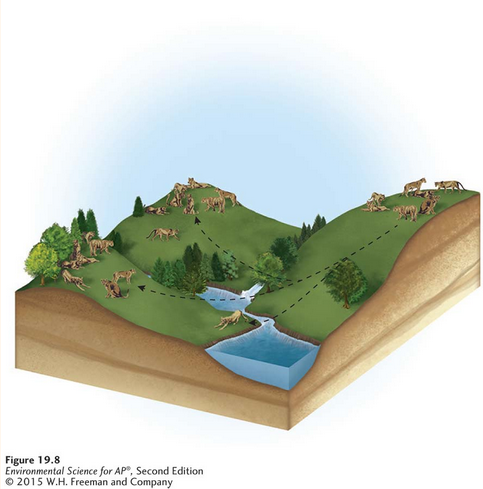
Corridor
Strips of natural habitat that connect populations.
Sampling Populations
Sampling - is the process of collecting a representative group of a population or area to estimate characteristics of the whole, such as population size, density, or environmental conditions.
Capture, Mark, Release, Recapture
(Mark and Recapture Method)
Procedure:
Capture a sample of animals from the population.
Mark each individual with a unique identifier (tags, bands, or safe dyes).
Release the marked animals back into their habitat.
After a set time, capture another sample of animals and record how many are marked.
Use the ratio of marked to unmarked individuals in the second sample to estimate the total population.
Advantages:
Allows scientists to estimate population sizes without needing to count every individual.
Effective for mobile or elusive species.
Limitations:
Assumes no significant migration, births, or deaths between samples.

Quadrat Sampling
Procedure:
Place a series of square frames (quadrats) randomly or systematically in the study area.
Count all the individuals of the target species within each quadrat.
Calculate the average number per quadrat and extrapolate to estimate total population.
Advantages:
Useful for studying species that are immobile or less likely to move (e.g., invertebrates).
Can provide data on density and distribution.
Limitations:
NOT effective for larger or mobile species.
Requires a large number of quadrats for accuracy. (sample size)

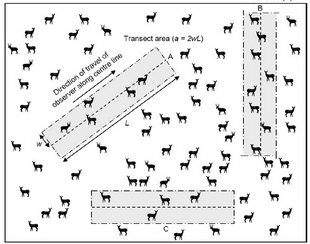
Transect Sampling
Procedure:
Set up a line or strip (transect) across the study area.
Record all individuals of the target species observed along the transect.
Often combined with quadrats placed at intervals along the transect.
Advantages:
Useful for studying population gradients or changes across a habitat.
Provides a snapshot of species distribution.
Limitations:
Accuracy may vary depending on the width of the transect and the density of the population.
Remote Sampling (Camera Traps and Acoustic Surveys)
Purpose: Monitor elusive or nocturnal species
Method: Using motion-activated cameras (camera traps) or sound-recording devices (acoustic surveys) to capture images or sounds of animals. Often used for species that are hard to observe directly.

Inbreeding depression
When individuals with similar genotypes—typically relatives—breed with each other and produce offspring that have an impaired ability to survive and reproduce. Low genetic diversity.